Carrying density of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations based on water balance
-
摘要:目的
研究冀北地区华北落叶松人工林水分平衡规律及其供求关系,准确计算区域不同降水条件下华北落叶松适宜经营密度。
方法依据水量平衡原理构建包含大气降水土壤入渗分量、林下蒸散发分量和不同胸径华北落叶松单株蒸腾耗水分量的水源承载密度计算公式。通过对小五台山自然保护区华北落叶松人工林树干液流、林下蒸散发、水量再分配特征的长期定位观测,以及胸径与木质部周长关系模型的构建,确定计算参数,计算不同降水条件下华北落叶松人工林各径级可承载密度。
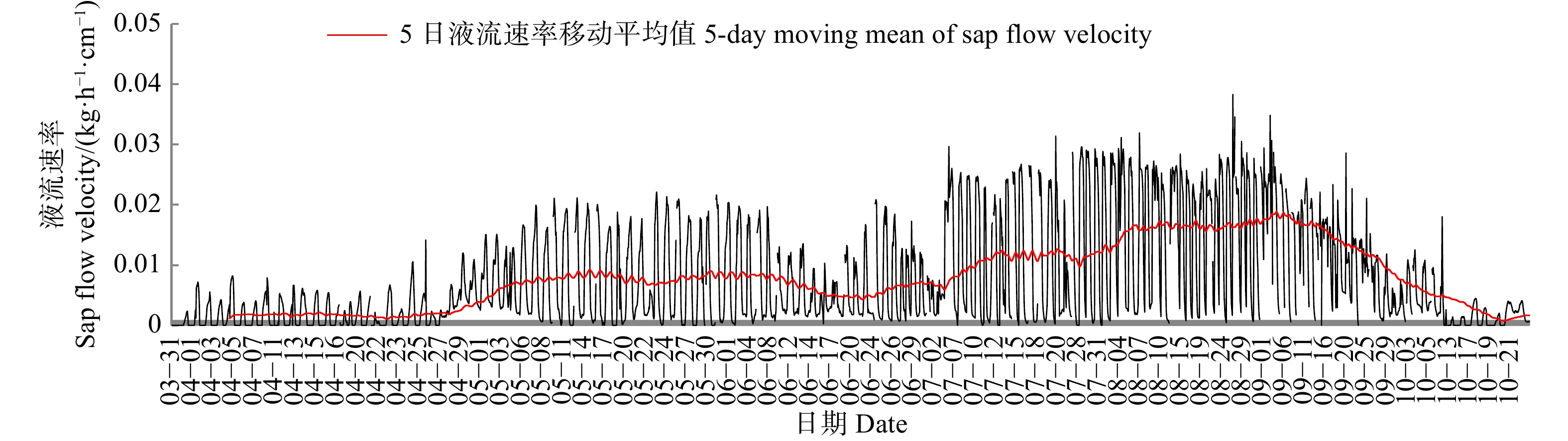
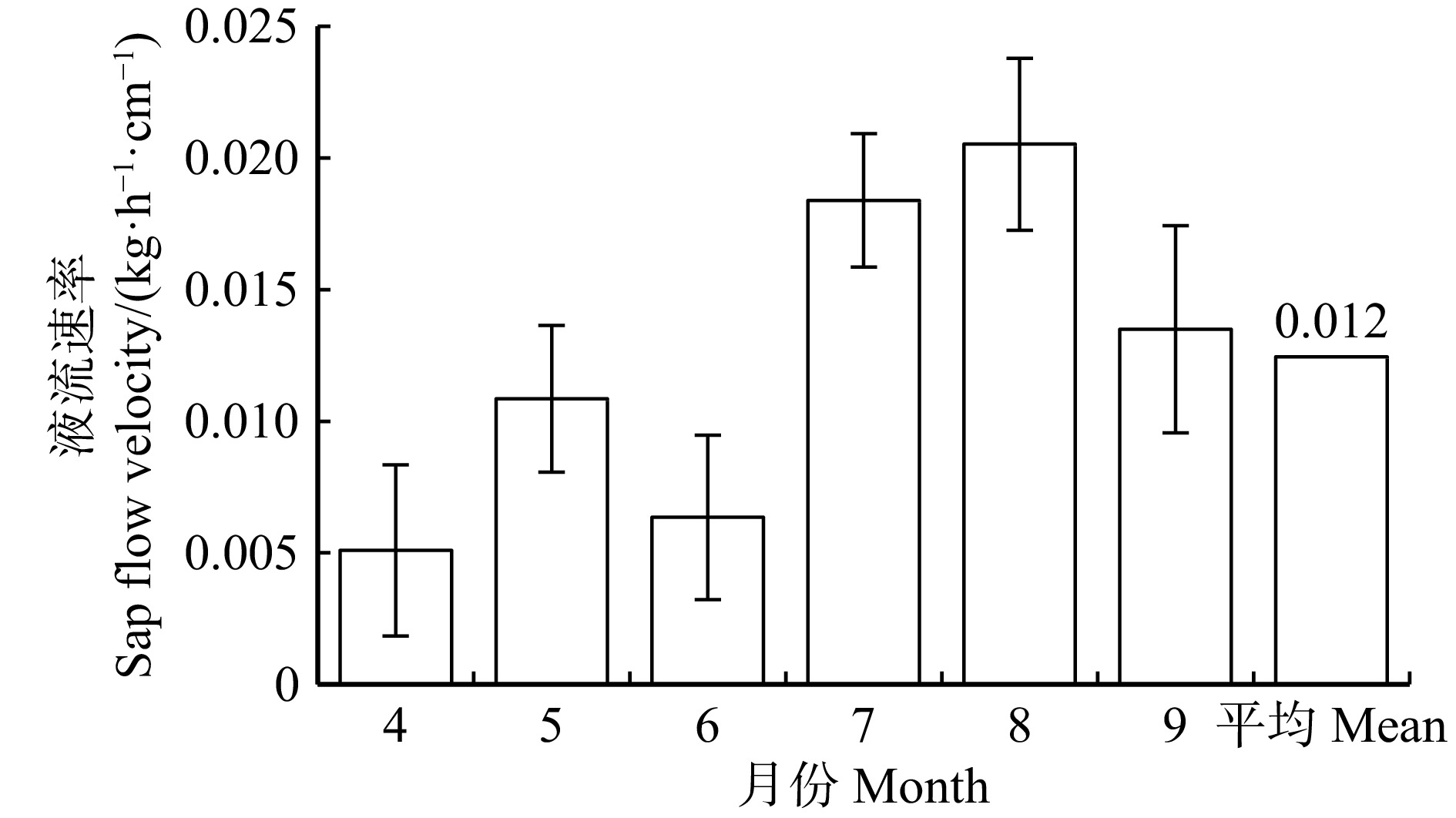
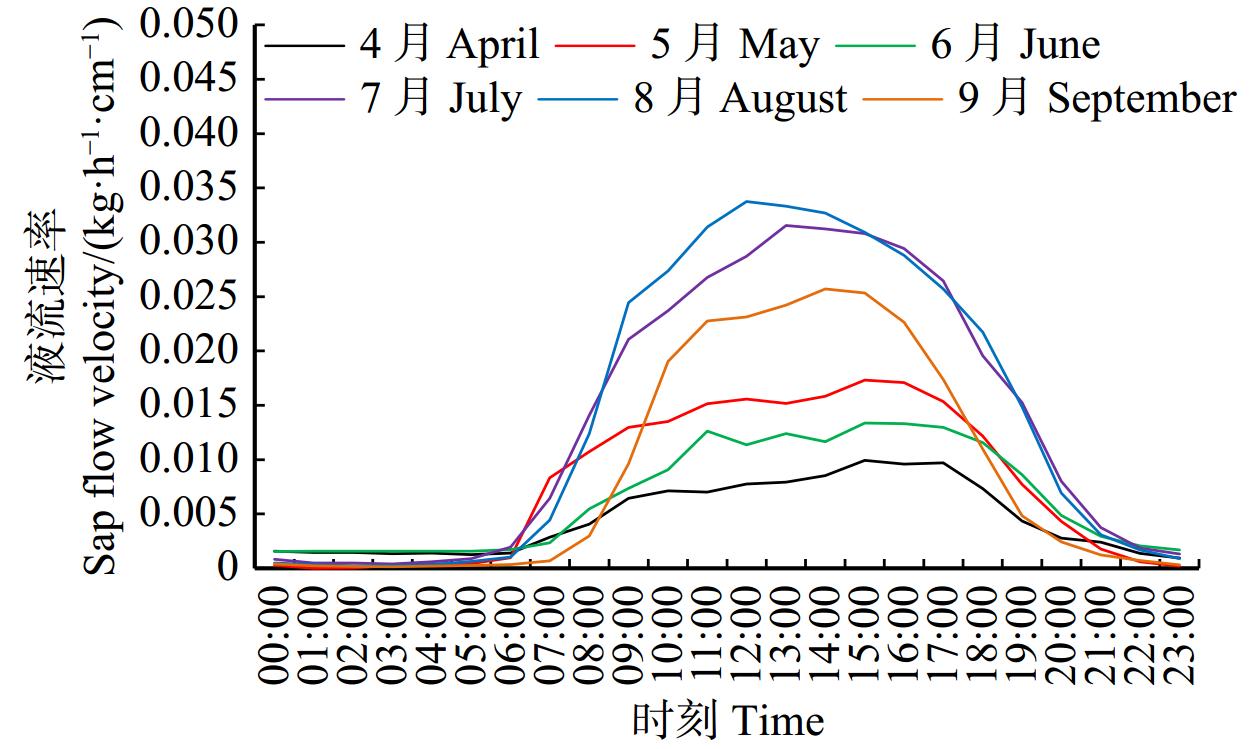
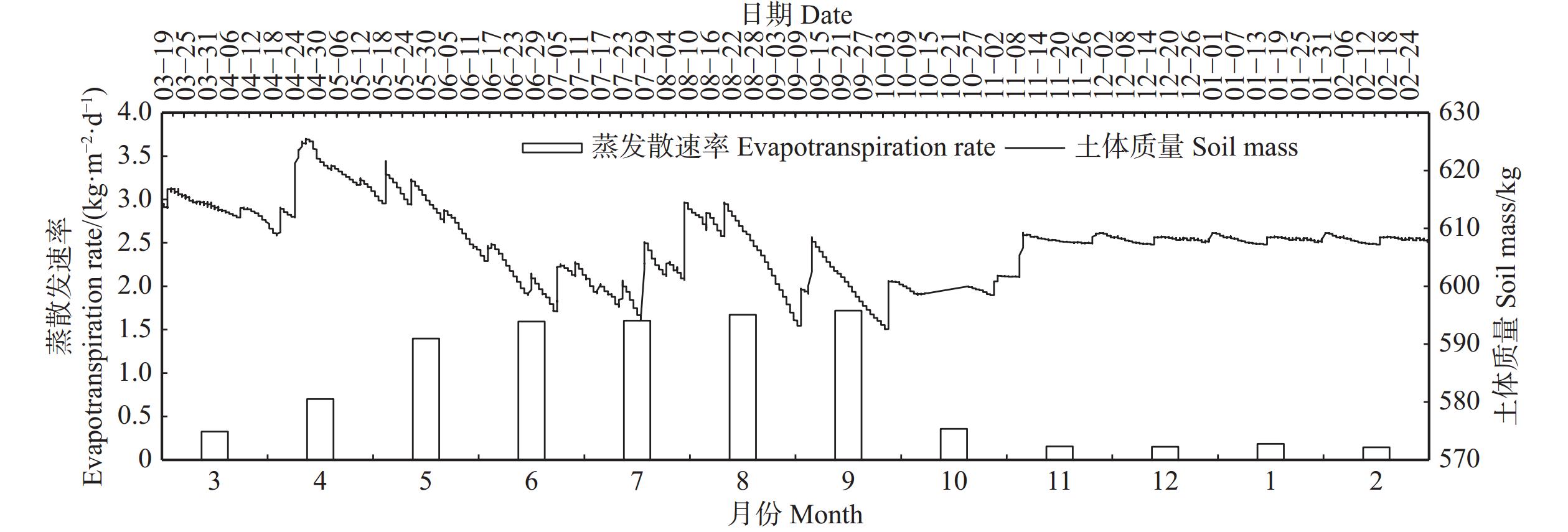
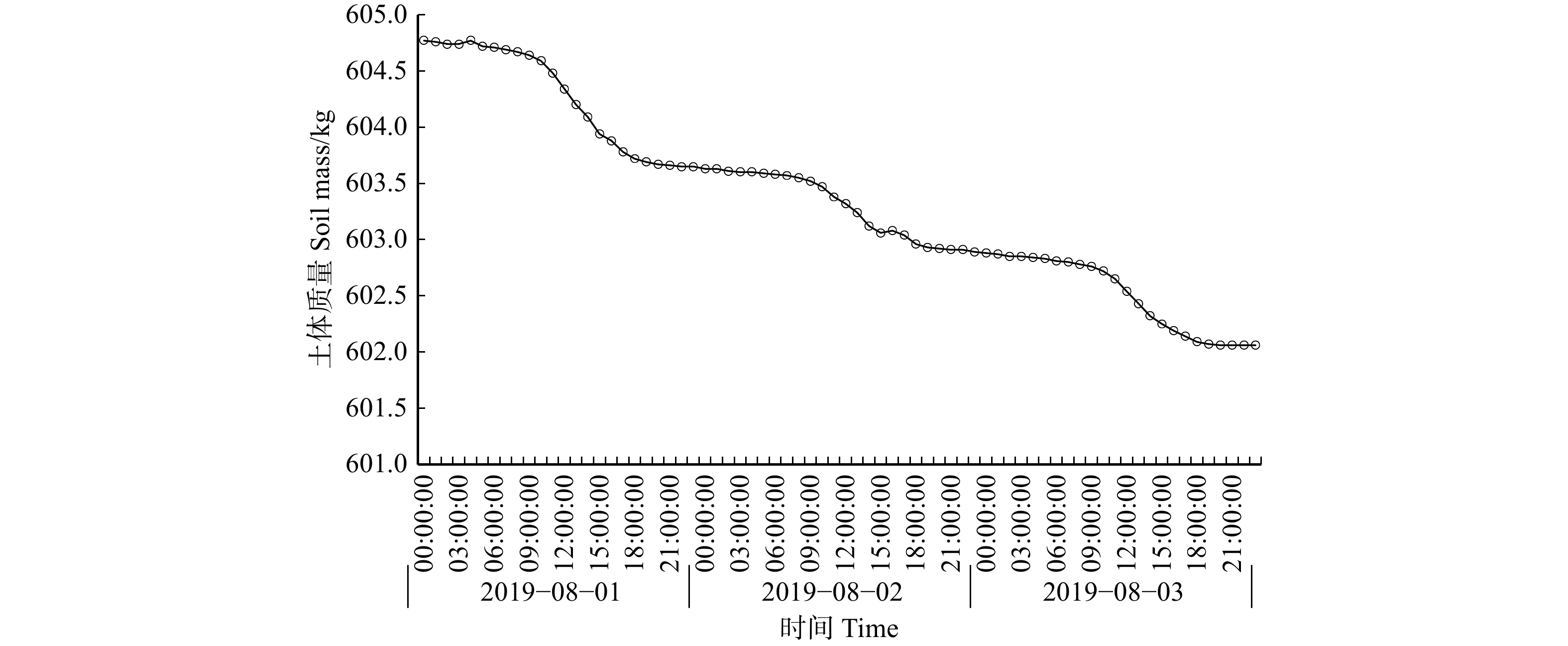
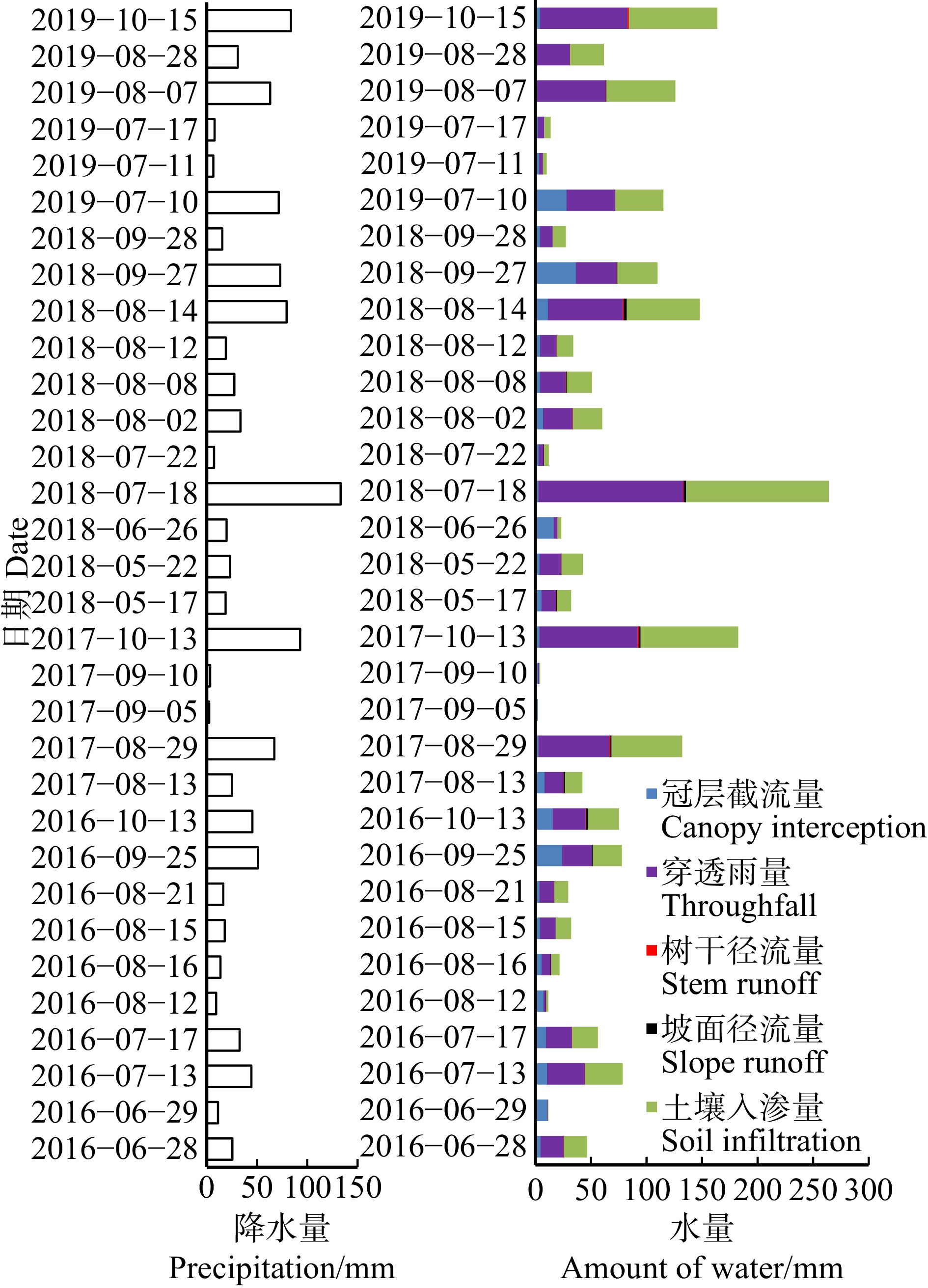
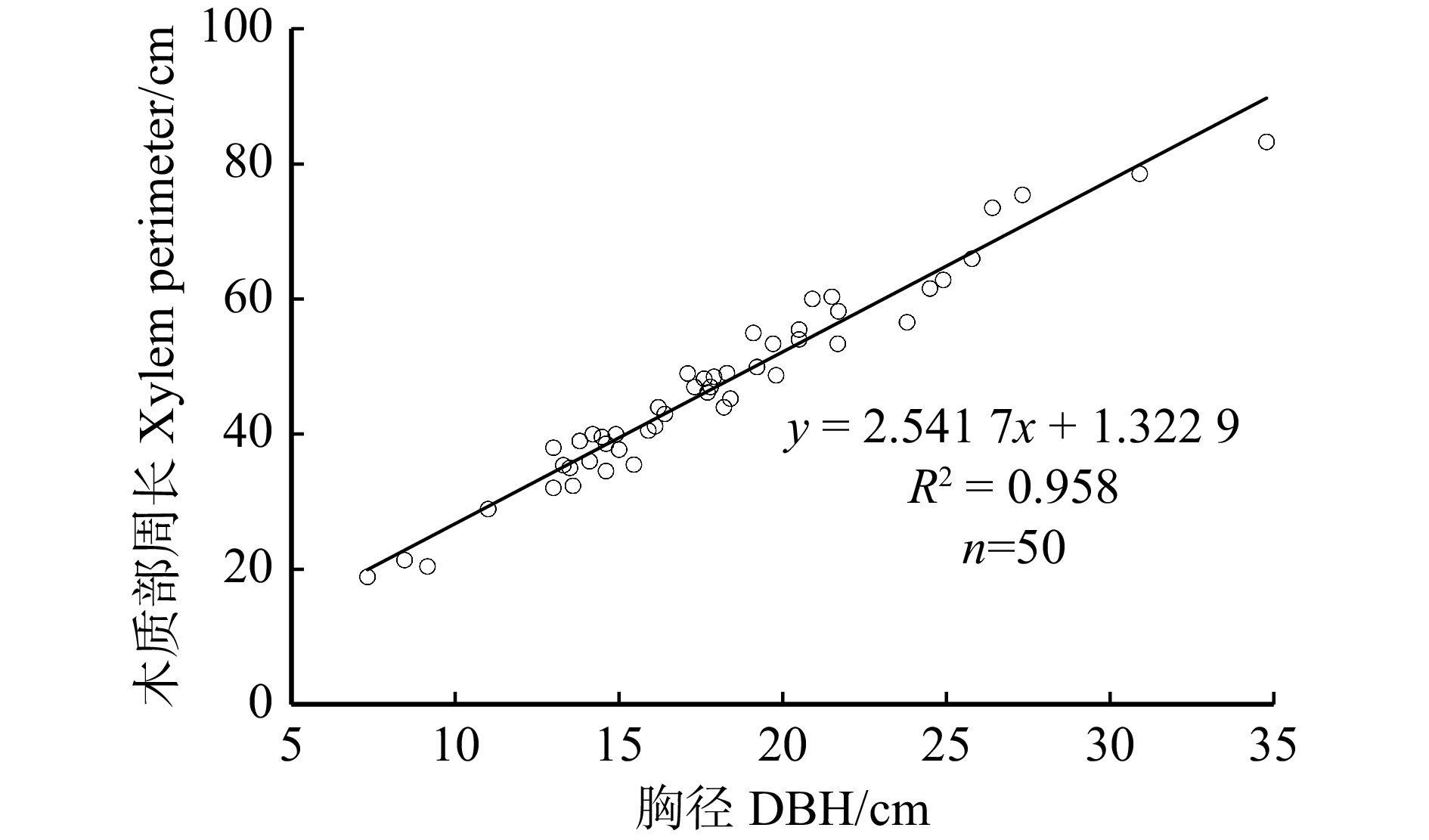
结果(1)小五台地区华北落叶松生长季6个月,生长季昼间蒸腾平均时长15 h;生长季平均液流速率0.012 kg/(h·cm),除4月、6月较低外,其余各月都达到0.011 kg/(h·cm)以上,尤其以8月最高,达到0.021 kg/(h·cm)。(2)生长季华北落叶松林下平均蒸散发速率1.448 kg/(m2·d),全年平均速率0.833 kg/(m2·d);蒸散发速率4—6月上升较快,6—9月上升缓慢,并在9月达到峰值,10月迅速下降,11月到来年2月处于较低水平。(3)华北落叶松林冠层截留量占降水量的21.22%,穿透雨量占78.10%,树干径流量占0.68%,坡面径流量占1.50%,土壤入渗量占77.28%。(4)华北落叶松胸径与木质部周长呈线性相关关系,R2为0.958。
结论依据水量平衡原理计算出小五台地区不同降水条件下华北落叶松林各径级可承载密度,对于冀北地区现有林分的科学经营具有重要指导意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to study the water balance law and supply-demand relationship of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations in the northern Hebei Province region of northern China, and accurately calculate the proper management density of L. principis-rupprechtii plantations under different precipitation conditions in the region.
MethodThe calculation parameters were determined through long-term location observation of sap flow, understory evapotranspiration, water redistribution characteristics of L. principis-rupprechtii plantations in Xiaowutai Mountain Nature Reserve, and the construction of relationship model between DBH and xylem perimeter, and the carrying density of each diameter class of L. principis-rupprechti plantation under different precipitation conditions was calculated.
Result(1) The growth season of Larix principis-rupprechtii in the Xiaowutai area was 6 months, with an average diurnal transpiration time of 15 h during the growth season. The average sap flow velocity of L. principis-rupprechtii during the growth season was 0.012 kg/(h·cm). Except for lower values in April and June, it reached above 0.011 kg/(h·cm) in all other months, with the highest value reaching 0.021 kg/(h·cm) in August. (2) The average evapotranspiration rate under L. principis-rupprechtii forest during the growth season was 1.448 kg/(m2·d), and the annual average rate was 0.833 kg/(m2·d). The evapotranspiration rate increased rapidly from April to June, slowly increased from June to September, and reached its peak in September, rapidly decreased in October, and remained at a relatively low value from November to February of the followed year. (3) The canopy interception of L. principis-rupprechtii forest accounted for 21.22% of the precipitation, the penetrating precipitation accounted for 78.10%, the trunk runoff accounted for 0.68%, the slope runoff accounted for 1.50%, and the soil infiltration accounted for 77.28%. (4) There was a linear correlation between DBH and xylem perimeter of L. principis-rupprechtii, R2 was 0.958.
ConclusionBased on the principle of water balance, the bearing density of different DBH of L. principis-rupprechtii forests under varied precipitation conditions in the Xiaowutai area is calculated, which has important guiding significance for the scientific management of existing forests in the northern Hebei region of northern China.
-
胡杨(Populus euphratica)是最古老的杨属植物,是唯一能够在极端干旱区自然成林的高大乔木种[1-2]。天然的胡杨林具有沿河岸呈条带状分布的特点[3],由于胡杨对于荒漠河岸林生态系统维持的重要性,前人对胡杨的适应性已经开展了很多研究。研究表明,水文因子是制约胡杨种群分布和发育的最关键因子[4-6],洪水漫溢后湿润低盐的河漫滩环境是胡杨通过种子更新的最理想场所[7]。水文条件改变带来的干旱区土壤盐渍化问题是影响胡杨种群分布的一个重要因素[8-9]。由于安全生境的缺失,目前胡杨无法通过有性繁殖的方式形成有效的更新[5, 10-12]。
根系的生长是胡杨幼苗能否定植和实现有效更新的关键,近年来越来越多的研究从根系角度对胡杨的生长策略进行分析。在环境条件改变的情况下,植物根系的空间分布、形态特征会表现出相应的适应策略,以更高效地获取资源[13-14]。吕爽等人[15]研究了胡杨幼苗根系对水分因子的响应特征,发现胡杨幼苗一定程度上可以通过地上地下生长权衡来适应干旱环境,良好的水分条件可以促进胡杨幼苗侧根的扩展。Ye等人[16]对干旱胁迫下胡杨实生苗根系特征的研究表明,深根系、大根冠比和鱼尾状根构型是胡杨当年实生苗适应河漫滩环境的重要特征,这与Wang等人[17]的观点类似,胡杨幼苗是通过根系性状和生物量分配的塑性响应来适应一定地下水位条件的。
以往的研究多采用单因素控制条件对胡杨根系进行研究,多因素交互作用,特别是将种间关系和根−土壤水分关系结合的研究更为缺乏。而植物种间关系及其对环境胁迫梯度响应的研究,对胁迫环境下植被的恢复有重要的指导意义[18]。有研究表明,比根面积除了受到土壤水分的影响,来自邻体植物的竞争也对比根面积有重要的影响[19]。除了土壤环境,在干旱区种内种间相互作用也是影响种群动态的重要因素[20-21]。在荒漠河岸林中,胡杨常常和多枝柽柳(Tamarix ramosissima)幼苗在河滩上聚集分布[22]。一些研究发现了胡杨幼苗与多枝柽柳竞争能力的差异[23],但是目前尚未引起足够重视。因此,本研究以胡杨作为研究对象,设置胡杨−胡杨和胡杨−柽柳两种伴生模式,研究胡杨当年生幼苗根系形态特征对多枝柽柳以及土壤水盐变化的响应,旨在为胡杨林的保护、更新和复壮提供理论依据。拟解决以下几个问题:(1)胡杨幼苗根系生长对水盐交互作用的响应;(2)异种伴生者存在条件下,胡杨当年生实生幼苗根系的竞争适应策略;(3)种间竞争存在条件下,胡杨幼苗根系对水盐条件的塑性响应变化。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 实验设计
实验在内蒙古自治区国营额济纳旗林场的日光温室内进行。使用的胡杨种子和多枝柽柳种子采自额济纳旗胡杨林国家自然保护区(41°30′ ~ 42°07′N、101°03′ ~ 101°17′E),均为上一年风干冷藏保存。土壤取自林场苗圃,筛除石子、植物根系等杂质后,经过暴晒,装入口径25 cm,深度达60 cm的塑料软花盆。将花盆里的土浇透之后,平整土面,播入经过清水浸泡的胡杨种子。实验设置了两种伴生模式,既胡杨−胡杨(P-P)组和胡杨−柽柳(P-T)组。后者在胡杨种子萌发、幼苗扎根后,播入多枝柽柳种子。在胡杨幼苗生长了40 d时进行间苗,去除长势不佳的弱苗、畸形苗,胡杨−胡杨组保留10株长势一致、在花盆中均匀分布的幼苗,胡杨−柽柳组各保留5株胡杨和5株柽柳幼苗。间苗后开始对水盐进行控制。
实验对两个伴生模式设置了相同的3个水分梯度(W)和3个盐分梯度(S),水分梯度为低水、中水、高水,分别以W1、W2、W3进行表示,实验控制期间对应的最低质量含水量约为5%、10%、15%,其中中水处理为胡杨人工育苗常用的水分管理模式。盐分处理以加入NaCl水溶液的形式进行,盐分梯度为低盐(0 g/盆)、中盐(1.8 g/盆)和高盐(3.6 g/盆),分别以S1、S2、S3表示。为避免幼苗因离子毒害致死,盐分分为5次施入。水盐两两进行交互,即所有实验处理为以下9种:低水低盐(W1S1)、低水中盐(W1S2)、低水高盐(W1S3)、中水低盐(W2S1)、中水中盐(W2S2)、中水高盐(W2S3)、高水低盐(W3S1)、高水中盐(W3S2)、高水高盐(W3S3)。每个处理4个重复。
1.2 根系性状测定方法
胡杨幼苗经过100 d(一个生长季)的生长后进行破坏性取样。用加压水柱冲洗附在根系上的土壤,以获取完整的根系,并在水中小心地进行单株苗的分离,去除根系上缠绕的杂质。随后将根系置于盛水的透明根盘中,用镊子小心将根系摊开至舒展状态,使其尽可能不重叠,用扫描仪(Epson Perfection V700)进行扫描后,用WinRhizo对扫描的图片进行分析,以获得根系各形态指标,根系分析的径级设置在0.5 mm级别。将扫描后的根系放在纸袋中,在80 ℃下烘干至恒质量,用万分之一天平称得生物量。
需要说明的是,生长的后期,胡杨−柽柳组陆续出现胡杨幼苗地上部分死亡的情形(以叶片全部脱落为准),但幼苗根系还具有活性,形态和生物量积累情况能够反映其生长过程,因此在本实验中,死亡的胡杨幼苗根系数据并入同一处理组进行分析。
1.3 指标计算
根据WinRhizo的分析结果,计算根系的比根长和比根面积及径级在0.5 mm以下的根系数量特征。
比根长 = 总根长(cm)/根生物量(g);
比根面积 = 总根表面积(cm2)/根生物量(g);
根长占比 = 0.5 mm以下根系长度/总根长;
根表面积占比 = 0.5 mm以下根系表面积/总根表面积;
根体积占比 = 0.5 mm以下根系体积/总根体积;
根尖占比 = 0.5 mm以下根尖数/总根尖数。
1.4 数据分析
用Spss 17.0对数据进行分析,对各指标进行水分、盐分和伴生类型进行多因素方差分析,对同一水分梯度下不同盐分梯度间,以及同一盐分梯度不同水分梯度间的幼苗根系特征进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),采用Duncan法来判定差异显著性。同一处理下,两个不同伴生组采用t检验判定显著性。用sigmaplot 12.5作图。
2. 结果和分析
2.1 水分、盐分和伴生模式对胡杨幼苗根系生长的影响
三因素方差分析(表1)结果表明,水分、盐分和伴生模式对胡杨幼苗根系有显著的影响(P < 0.05),其中水分和伴生模式对总根长、根表面积、基径等多个指标的影响达到极显著(P < 0.001),且水分和伴生模式的交互作用对总根长、总根体积、根表面积和分支数也有显著的影响(P < 0.05)。盐分对总根体积、根尖数和基径有显著的影响(P < 0.05),水盐的交互对幼苗基径、比根长、比根面积影响显著(P < 0.05),但对其他指标影响未达到显著。以上结果表明,当年生胡杨幼苗的根系生长受水分和种间竞争的影响较盐分大。
表 1 水分、盐分及伴生模式对胡杨幼苗根系的影响(三因素方差分析)Table 1. Effects of water, salinity conditions and neighbor patterns on seedling roots of Populus euphratica (three-way ANOVA)因子及因子间交互作用
Factor and interaction among factorsdf 总根长
Total root
length根表面积
Root surface
area总根体积
Total root
volume根尖数
Root tip number基径
Basal diameter比根长
Specific root
length比根面积
Specific root
areaW 2 38.078*** 40.891*** 38.977*** 27.309*** 65.906*** 2.097 4.116* S 2 1.532 2.128 3.438* 3.257* 3.527* 2.833 5.419** N 1 182.288*** 227.118*** 239.979*** 97.963*** 277.821*** 44.807*** 31.885*** W × S 4 0.782 0.709 0.751 0.844 3.255* 5.163*** 4.929*** W × N 2 4.693* 7.819*** 11.472*** 1.071 2.863 1.470 1.003 S × N 2 2.442 2.578 2.420 2.016 0.782 0.266 0.627 W × S × N 4 1.551 1.109 0.610 2.752* 1.878 2.860* 1.201 注:W为水分;S为盐分;N为伴生模式。表中数值为F检验值,“*”表示P < 0.05,“**”表示P < 0.01,“***”表示P < 0.001。下同。Notes: W, water condition; S, salinity condition; N, neighbor pattern. Data are F testing values. “*” means P < 0.05, “**” means P < 0.01 and “***” means P < 0.001. The same below. 进一步分析两种伴生模式下水盐对幼苗根系形态的影响(表2),结果表明水分对总根长、根表面积等各个指标的影响均达到极显著(P < 0.001)。单一盐分对胡杨−胡杨组幼苗根系形态指标没有显著影响(P > 0.05),但对胡杨−柽柳组的总根长、根表面积、总根体积和根尖数的影响均达到极显著(P < 0.001),该结果表明多枝柽柳伴生下,胡杨幼苗根系形态对盐分的响应更为敏感。水盐交互作用较弱,仅对胡杨−胡杨组幼苗基径和胡杨−柽柳组幼苗根尖数有显著的影响(P < 0.05)。
表 2 不同伴生模式下水盐条件对胡杨幼苗根系形态的影响Table 2. Effects of water and salinity conditions on root morphology of P. euphratica seedlings in group P-P and P-T因子及因子
间交互作用
Factor and interaction between factorsdf 总根长
Total root length根表面积
Root surface area总根体积
Total root volume根尖数
Root tip number基径
Basal diameterP-P P-T P-P P-T P-P P-T P-P P-T P-P P-T W 2 21.566*** 22.685*** 24.951*** 22.401*** 26.058*** 19.628*** 12.405*** 20.860*** 35.513*** 31.782*** S 2 0.392 9.185*** 1.03 10.154*** 1.987 11.240*** 0.063 10.540*** 1.113 2.547 W×S 4 1.095 1.533 0.822 1.43 0.631 1.177 1.468 2.931* 4.291** 1.43 注:P-P为胡杨−胡杨组;P-T为胡杨−柽柳组。Notes: P-P, Populus euphratica seedlings neighbored by P. euphratica seedlings; P-T, P. euphratica seedlings neighbored by T. ramosissima seedlings. 2.2 胡杨幼苗根系的径级分布特征
由表3可知,当年生胡杨幼苗的绝大部分根系直径在0.5 mm以下,除胡杨−柽柳组的个别处理,该径级根长占比达到90%以上,根表面积占比超过65%,所有处理中根尖径级低于0.5 mm的比例均超过99%。而根径在0.5 mm以下的根体积占总根体积的比例除个别处理外均低于30%,表明胡杨幼苗的主根体积在总根体积中占比较大。在胡杨−胡杨组,除中水中盐(W2S2)处理根体积占比显著小于低水中盐(W1S2)组,各个指标不同水分和盐分条件下没有显著差异。胡杨−柽柳组在W1和W3条件下,幼苗根系表现出随盐胁迫程度增加,0.5 mm以下根长、根表面积、根体积占比增加的趋势。
表 3 径级为0.5 mm以下的根系占比Table 3. Root proportion of P. euphratica with diameter under 0.5 mm% 指标 Index 胡杨-胡杨组
Group P. euphratica-P. euphratica (group P-P)胡杨-柽柳组
Group P. euphratica-Tamarix ramosissima (group P-T)W1 W2 W3 W1 W2 W3 根长占比
Proportion of root lengthS1 94.84 ± 0.45Aa 93.37 ± 1.12Aa 93.11 ± 1.16Aa 89.89 ± 1.95Bb 94.18 ± 1.08Aa 94.74 ± 0.34Aa S2 93.93 ± 0.98Aa 94.77 ± 0.59Aa 95.27 ± 0.14Aa 92.89 ± 0.73Bab 95.09 ± 0.85Aa 95.08 ± 0.45Aa S3 94.24 ± 0.57Aa 93.82 ± 0.43Aa 94.64 ± 0.62Aa 95.13 ± 0.82Aa 87.92 ± 2.83Bb 95.27 ± 0.62Aa 根表面积占比
Proportion of root surface areaS1 68.50 ± 1.97Aa 66.69 ± 3.40Aa 65.46 ± 3.40Aa 57.32 ± 5.01Ab 67.66 ± 4.07Aa 67.74 ± 1.20Ab S2 68.56 ± 3.03Aa 66.85 ± 2.50Aa 70.89 ± 1.37Aa 65.01 ± 2.29Ab 71.05 ± 3.99Aa 71.64 ± 1.58Aab S3 66.29 ± 2.03Aa 65.69 ± 1.77Aa 71.20 ± 1.88Aa 78.03 ± 2.63Aa 59.40 ± 4.81Ba 73.84 ± 2.40Aa 根体积占比
Proportion of root volumeS1 22.53 ± 1.60Aa 23.33 ± 2.88Aa 20.50 ± 2.51Aa 22.15 ± 3.72Ab 26.99 ± 5.03Aa 22.40 ± 1.19Ab S2 26.22 ± 2.74Aa 19.65 ± 1.67Ba 23.03 ± 1.71ABa 27.38 ± 2.76Ab 31.89 ± 5.57Aa 28.53 ± 1.60Aab S3 21.37 ± 2.38Aa 21.22 ± 1.92Aa 24.92 ± 1.88Aa 49.38 ± 4.39Aa 28.23 ± 3.36Ba 32.70 ± 3.28Ba 根尖占比
Proportion of root tipS1 99.91 ± 0.04Aa 99.83 ± 0.03Aa 99.83 ± 0.03Aa 99.84 ± 0.04Ba 99.91 ± 0.01ABa 99.94 ± 0.01Aa S2 99.83 ± 0.17Aa 99.87 ± 0.03Aa 99.90 ± 0.02Aa 99.89 ± 0.02Aa 99.92 ± 0.01Aa 99.93 ± 0.01Aa S3 99.88 ± 0.03Aa 99.84 ± 0.02Aa 99.83 ± 0.03Aa 99.89 ± 0.02Aa 99.84 ± 0.06Aa 99.92 ± 0.02Aa 注:W1、W2、W3分别为低水、中水、高水;S1、S2、S3分别为低盐、中盐、高盐。不同小写字母(a、b)代表同一水分梯度(W)下各盐分梯度(S1、S2、S3)间有显著性差异,不同大写字母(A、B)代表同一盐分梯度(S)下不同水分梯度(W1、W2、W3)间有显著性差异,P < 0.05。Notes: W1, W2, W3 represent water condition at low, medium and high level, respectively. S1, S2, S3 represent salinity condition at low, medium and high level, respectively. Different lowercase letters (a, b) indicate significant differences among salinity conditions under the same water condition. Different uppercase letters (A, B) indicate significant differences among water conditions under the same salinity condition. 2.3 胡杨幼苗根系的形态特征
在各个水盐梯度下,胡杨−柽柳组胡杨幼苗基径均显著小于相应处理的胡杨−胡杨组幼苗(P < 0.01)(图1)。盐分及水盐交互作用对胡杨−柽柳组幼苗的基径影响均不显著(P > 0.05);对胡杨−胡杨组,单一盐分影响不显著(P > 0.05),但水盐交互作用的影响达到极显著(P < 0.01)(表2、图1)。在各水分梯度下,胡杨−胡杨组幼苗基径对盐分变化的响应不同,低水条件下基径对盐分无响应;中水条件下,高盐处理显著增加幼苗基径(P < 0.05);高水条件下,随盐分梯度升高,幼苗基径降低。所有处理中,胡杨−胡杨组高水低盐的幼苗基径达到最大,为(3.84 ± 0.18)mm。高盐条件下,胡杨−胡杨组各水分梯度间幼苗基径无显著差异,胡杨−柽柳组高水梯度下幼苗基径显著大于低水梯度下的幼苗基径(P < 0.05)。两种伴生模式下幼苗基径在低盐、中盐条件下,高水处理均显著高于对应盐分处理低水、中水条件下的幼苗基径(P < 0.05)。
![]() 图 1 水盐条件对两种伴生模式下当年生胡杨幼苗基径的影响不同小写字母(a、b)代表同一水分梯度(W)下各盐分梯度(S)间有显著性差异,不同大写字母(A、B)代表同一盐分梯度(S)下不同水分梯度(W)间有显著性差异,P < 0.05。*代表胡杨−胡杨组和胡杨−柽柳组间有显著性差异,P < 0.05,“**”、“***”分别代表P < 0.01和P < 0.001。Different lowercase letters (a, b) indicate significant differences among salinity conditions (S) under the same water condition(W). Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among water conditions (W) under the same salinity condition (S). “*” means significant difference between group P-P and group P-T under the same water and salinity condition at P < 0.05 level, “**” means P < 0.01 and “***” means P < 0.001. The same below.Figure 1. Effects of water and salinity conditions on basal diameter of annual P. euphratica seedlings of group P-P and P-T
图 1 水盐条件对两种伴生模式下当年生胡杨幼苗基径的影响不同小写字母(a、b)代表同一水分梯度(W)下各盐分梯度(S)间有显著性差异,不同大写字母(A、B)代表同一盐分梯度(S)下不同水分梯度(W)间有显著性差异,P < 0.05。*代表胡杨−胡杨组和胡杨−柽柳组间有显著性差异,P < 0.05,“**”、“***”分别代表P < 0.01和P < 0.001。Different lowercase letters (a, b) indicate significant differences among salinity conditions (S) under the same water condition(W). Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among water conditions (W) under the same salinity condition (S). “*” means significant difference between group P-P and group P-T under the same water and salinity condition at P < 0.05 level, “**” means P < 0.01 and “***” means P < 0.001. The same below.Figure 1. Effects of water and salinity conditions on basal diameter of annual P. euphratica seedlings of group P-P and P-T胡杨−胡杨组幼苗的总根表面积对盐分变化无明显响应(P > 0.05),而胡杨−柽柳组随盐胁迫程度增加,总根表面积减小(P < 0.05)。同一盐分条件下,两种伴生模式低水和中水处理的幼苗总根表面积之间没有差异,高水条件下幼苗的总根表面积显著高于其他两个水分梯度(P < 0.05)(表2、图2)。
总根体积的变化趋势和总根表面积类似,盐分对胡杨−胡杨组幼苗总根体积无显著影响(P > 0.05),而对胡杨−柽柳组幼苗总根体积影响显著(P < 0.001)。胡杨−柽柳组总根体积表现出随盐胁迫程度升高而下降的趋势,但在各个水分条件下均未达到显著(P > 0.05)。相同盐分条件下,两个伴生模式下低水和中水处理间均无差异,高水处理显著高于低水、中水处理(P < 0.05)(表2、图3)。
2.4 胡杨幼苗根系的功能性状
比根长和比根面积可以作为表征植物根系吸收能力的形态指标。一些研究者认为,比根面积比根生物量更能表征植物资源获取能力[19]。和胡杨组相比,胡杨−柽柳组趋向于有更大的比根面积和比根长(图4、5)。在低水、中水分条件下,两个伴生模式下比根面积和比根长对盐分变化没表现出明显的变化趋势;高水条件下,随盐分增大,胡杨−胡杨组和胡杨−柽柳组比根面积和比根长均增大。低盐条件下,胡杨−胡杨组比根面积和比根长随水分增加而减小,但中盐、高盐条件下,中水、高水处理的幼苗比根长和比根面积与低水处理相比没有显著性差异。对胡杨−柽柳组,低盐、中盐条件下,水分升高对比根面积影响不明显,高盐条件下,中水梯度比根长和比根面积显著低于低水和高水梯度(P < 0.05)。
2.5 两种伴生模式下胡杨幼苗根性状间相关性
两种伴生模式下,胡杨幼苗根系性状之间相关性基本一致。比根长和根生物量、平均直径呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),总根长与根尖数、分支数、总根体积呈极显著相关(P < 0.01)。在胡杨−胡杨组,平均直径和总根长呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),与总根体积呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),而在胡杨−柽柳组,平均直径与总根长、总根体积关系较弱(P > 0.05)。比根长在胡杨−胡杨组,与根表面积、总根体积关系不显著(P > 0.05),但在胡杨−柽柳组,与根表面积、总根体积呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01)。此外,胡杨−柽柳组比根面积与除比根长之外的各个指标呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),而胡杨−胡杨组比根面积与总根长、根表面积、总根体积、根尖数、分支数关系不显著(P > 0.05)。
3. 讨论与结论
水分、盐分胁迫下胡杨幼苗的生长特性已经有较多的研究报道,受到干旱胁迫的条件下,胡杨幼苗株高、生物量积累、光合作用等受到抑制[24-26]。盐胁迫下胡杨幼苗的成活率和生长下降[27],光合作用受阻,根系生长和根尖数、根木质部的吸水效率显著受到抑制,幼苗株高、基径、各器官生物量和总生物量均显著降低[28-29]。但是水盐交互下当年生胡杨幼苗的生长特征研究得还比较少,种间关系对胡杨幼苗的影响也一直未受到重视。本研究采用了3个梯度的水分和盐分进行两两交互,研究两种伴生模式下胡杨幼苗根系生长对土壤水盐环境的响应,发现水分、盐分和伴生模式及其之间的交互作用对当年生胡杨实生幼苗根系的生长起到重要的影响。特别是水分和伴生模式对胡杨幼苗根系生长的影响更为关键。
3.1 水盐交互对胡杨−胡杨组幼苗根系生长的影响
水分对胡杨根系各个指标影响显著,而单一盐分对幼苗的总根长、根表面积、总根体积、基径影响均不显著,水盐交互仅对基径有显著的影响(表1、2),表明在水盐对根系生长的影响中,水分占据绝对的主导地位。这是由于胡杨幼苗对盐分有一定的耐受性[30],一些研究也表明了低盐环境能够刺激胡杨产生不定根[31]。在极端干旱区,水分才是胡杨根系生长的限制性因子。本研究中,随水分梯度升高,胡杨−胡杨组幼苗总根长、基径、根体积等指标增大,表明水分促进胡杨根系的生长,较好的水分利于当年生胡杨幼苗根系的扩展和增粗生长。
在不同水分梯度下,胡杨幼苗基径对盐分的响应有所不同(图1 ~ 3)。在低水的条件下各盐分梯度间的幼苗基径没有差异,中水的条件下,随盐胁迫程度增加而增大,在高水条件下随盐胁迫增加而降低(图1)。这种现象可能是由于低水条件下,幼苗根系生长主要受水分的限制,盐分不是限制幼苗的主要因素;中水条件下,水盐的交互对胡杨幼苗影响较大,主根增粗可能是幼苗增强抗逆性、提高适合度的形态策略;高水条件下,水分限制作用减弱,盐分成为影响胡杨幼苗根系生长的主要因素。
相关性分析表明,胡杨−胡杨组幼苗平均直径和总根长显著负相关,而和总根体积呈显著正相关(表4),结合幼苗径级分布,表明胡杨幼苗具有明显主根的特征(表3)。反映了在无异种竞争者存在的环境下,胡杨幼苗的根系扩展是通过产生大量吸收根来实现的。根系径级分布特征显示根径0.5 mm以下的根系长度占到总长的90%以上,根表面积占总根表面积65%以上,根尖占比超过99%,根体积仅占总根体积20%左右(表2),各指标不随水盐的变化而变化,表明了胡杨根系形态具有一定的保守性。在一定水盐条件范围内,生长状态不同的根系可以保持一定的根系径级数量分布特征,起固着作用的主根和主要发挥吸收功能的根系比例较为稳定,反映了胡杨幼苗对盐旱胁迫具有较强的适应性。这和Ye等人[16]的研究结果一致,根形态变化对干旱胁迫下幼苗根深增加的作用较小,幼苗根系对水分的响应可能更多反映在根系构型的变化上。
表 4 胡杨−胡杨组幼苗指标间相关性Table 4. Correlations between root traits of seedlings in group P-P指标 Index AD TRL RSA TRV Tips Forks BB SRL SRA AD 1 TRL − 0.246* 1 RSA 0.040 0.971** 1 TRV 0.208* 0.869** 0.961** 1 Tips − 0.434** 0.883** 0.789** 0.638** 1 Forks 0.194 0.954** 0.944** 0.859** 0.819** 1 BB 0.166 0.671** 0.736** 0.783** 0.552** 0.632** 1 SRL − 0.516** 0.139 0.034 0.104 0.181 0.136 − 0.472** 1 SRA − 0.247* 0.081 0.039 0.034 0.034 0.101 − 0.500** 0.939** 1 注:AD为平均直径;TRL为总根长;RSA为根表面积;TRV为总根体积;Tips为根尖数;Forks为分支数;BB为根生物量;SRL为比根长;SRA为比根面积。*代表显著相关,P < 0.05,**代表极显著相关,P < 0.01。下同。Notes: AD, average diameter; TRL, total root length; RSA, root surface area; TRV, total root volume; Tips, root tip number; Forks, fork number; BB, belowground biomass; SRL, specific root length; SRA, specific root area. * means correlation is significant at P < 0.05 level; ** means correlation is extremely significant at P < 0.01 level. The same below. 3.2 多枝柽柳对不同水盐条件下胡杨幼苗根系生长的影响
有研究表明,根系竞争在植物种间竞争中具有外显性,无论地上部分竞争存在与否,根系竞争的存在都具有明显的竞争效应[32]。本研究结果表明,胡杨根系的生长受到伴生多枝柽柳的强烈抑制,在任何一个水盐梯度上,两种伴生模式下胡杨幼苗在总根长、总根体积、总根表面积都有极显著的差异(P < 0.01)(图1 ~ 3),表明种间竞争对胡杨根系伸长生长、生物量积累有显著的负效应。
在多枝柽柳的伴生下,当年生胡杨幼苗根系对水盐的响应方式发生改变,表现为幼苗总根长、总根体积、根表面积和根尖数对盐的响应更敏感(表2)。径级分布特征也显示,胡杨−柽柳组幼苗根径低于0.5 mm的根系根长、根表面积和根体积占比对水盐变化响应敏感(表3、图2 ~ 3),仅基径对盐分变化无响应(表2、图1)。本研究结果表明,种间竞争对胡杨幼苗根系形态产生的影响比土壤水盐环境更为显著。多枝柽柳伴生的条件下,根系生长在获取资源和防御之间进行权衡,而造成根系形态调整[33],这可能是胡杨幼苗应对种间竞争提高适合度的策略。
然而幼苗对土壤盐分变化响应敏感,也表明了胡杨幼苗抗逆性减弱。胡杨幼苗在面对来自多枝柽柳的种间竞争时,比根长、比根面积增大。较大的比根长和比根面积表明,单位质量的根系有较大的总根长和根表面积,因此对应较高的水分和养分吸收效率。但结合本实验幼苗正常发育受阻的结果,多枝柽柳竞争下胡杨幼苗比根长、比根面积增大,也表明了幼苗木质化过程受到抑制。研究表明,根系营养状况对比根长有重要的影响,营养状况较好的幼苗倾向有更低的比根长[34]。胡杨−胡杨组的幼苗比根长与根表面积、总根体积无显著相关性,而胡杨−柽柳组的比根长和根表面积、总根体积呈极显著负相关(表4、5)。表明较大的比根长可能是柽柳的竞争导致胡杨幼苗根直径减小,根系强度降低的结果[35-36],即种间竞争使胡杨幼苗根系木质化程度降低,而木质化程度与胡杨当年生幼苗越冬存活息息相关[37]。根系的适应性是影响胡杨幼苗定居和生长的首要因素[7],本研究结果表明,种间竞争可能使野外的胡杨通过实生苗进行更新变得更加困难。
表 5 胡杨−柽柳组幼苗指标间相关性Table 5. Correlations between seedling root indices in group P-T指标 Index AD TRL RSA TRV Tips Forks BB SRL SRA AD 1 TRL 0.184 1 RSA 0.085 0.989** 1 TRV 0.031 0.953** 0.986** 1 Tips − 0.232* 0.974** 0.956** 0.912** 1 Forks 0.196 0.984** 0.965** 0.922** 0.959** 1 BB 0.000 0.895** 0.921** 0.930** 0.881** 0.897** 1 SRL − 0.710** − 0.194 − 0.281** − 0.369** − 0.172 − 0.177 − 0.401** 1 SRA − 0.512** − 0.298** − 0.363** − 0.431** − 0.302** − 0.289** − 0.503** 0.938** 1 目前对种间关系的研究普遍认为,干旱区植物趋向于通过根系生态位的分离来减少竞争,实现互惠共存[18, 38],即支持“环境梯度胁迫假说”[39]。但本研究发现,在不同的环境梯度下,多枝柽柳与胡杨当年生幼苗的种间竞争对胡杨根系的生长产生了强烈的负效应,表现出胡杨幼苗受到多枝柽柳幼苗的竞争排斥,但是种间竞争影响胡杨幼苗根系生长的机制目前还不清楚。很多研究都表明植物的根系具有识别同种和异种根系的能力,并会对此产生不同的响应[40],胡杨根系生长受限是由于种间竞争导致胡杨对限制性资源的获取减少(竞争性抑制),还是由于多枝柽柳根系的化感作用[41],本实验没有进行探究,两者互作的地下生态过程还需要进一步的研究。
-
表 1 树干液流监测样树主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters of sap flow monitoring sample trees
编号
No.树高
Tree height/m胸径
DBH/cm冠幅
Crown width1 16.4 25.1 4.5 m × 3.2 m 2 12.5 23.2 6.2 m × 5.0 m 3 10.8 20.8 5.3 m × 4.7 m 4 10.4 17.3 3.8 m × 3.3 m 5 9.8 17.1 4.3 m × 3.3 m 6 12.5 17.0 4.0 m × 3.4 m 7 9.5 15.5 3.9 m × 3.8 m 8 7.3 10.6 3.1 m × 2.6 m 9 6.1 8.5 2.3 m × 2.2 m 表 2 树干径流监测样树主要参数
Table 2 Main parameters of trunk runoff monitoring sample trees
编号
No.树高
Tree height/m胸径
DBH/cm冠幅
Crown width1 12.3 24.7 6.00 m × 5.00 m 2 12.6 23.5 6.50 m × 5.60 m 3 12.7 21.4 6.90 m × 5.90 m 4 14.6 19.7 4.60 m × 4.06 m 5 14.0 17.6 4.30 m × 4.00 m 6 12.6 16.8 4.90 m × 4.00 m 7 8.6 14.6 4.80 m × 3.00 m 8 8.9 13.8 3.90 m × 3.80 m 9 6.3 10.5 4.20 m × 3.00 m 表 3 不同降水条件下不同胸径华北落叶松林最大承载密度 株/hm2
Table 3 Max. carrying density of Larix principis-rupprechtii forests with different DBH under varied precipitation conditions tree/ha
胸径
DBH/cm降水量 Precipitation/mm 450 500 550 600 650 700 5 1 053 1 903 2 753 3 603 4 453 5 303 6 892 1 611 2 331 3 050 3 770 4 490 7 773 1 397 2 021 2 645 3 269 3 893 8 682 1 233 1 784 2 334 2 885 3 436 9 611 1 104 1 596 2 089 2 582 3 075 10 553 999 1 445 1 891 2 337 2 783 11 505 912 1 319 1 727 2 134 2 541 12 464 839 1 214 1 589 1 963 2 338 13 430 777 1 124 1 471 1 818 2 165 14 400 724 1 047 1 370 1 693 2 016 15 375 677 979 1 282 1 584 1 886 16 352 636 920 1 204 1 488 1 772 17 332 600 867 1 135 1 403 1 671 18 314 567 821 1 074 1 327 1 581 19 298 538 779 1 019 1 259 1 500 20 283 512 741 969 1 198 1 427 21 270 488 706 924 1 142 1 360 22 258 467 675 883 1 092 1 300 23 247 447 646 846 1 045 1 245 24 237 428 620 811 1 003 1 194 25 228 412 596 779 963 1 147 26 219 396 573 750 927 1 104 27 211 382 552 723 893 1 064 28 204 368 533 697 862 1 026 29 197 356 515 674 833 992 30 190 344 498 652 805 959 31 184 333 482 631 780 929 32 179 323 467 612 756 900 33 173 313 453 593 733 873 34 168 304 440 576 712 848 35 164 296 428 560 692 824 -
[1] Liang W J, Wei X. Factors promoting the natural regeneration of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in the Lüliang Mountains of central China[J/OL]. Peer J, 2020, 8: 107717[2022−02−12]. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9339.
[2] 任启文, 张树梓, 李联地, 等. 冀西北水源涵养林生态水文过程研究与应用技术[M]. 石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社, 2021: 158−170. Ren Q W, Zhang S Z, Li L D, et al. Research and application technology on ecological hydrological processes of water source conservation forests in northwest Hebei Province[M]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Science & Technology Press, 2021: 158−170.
[3] Barbeta A, Mejía-Chang M, Ogaya R, et al. The combined effects of a long-term experimental drought and an extreme drought on the use of plant-water sources in a Mediterranean forest[J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21: 1213−1225. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12785
[4] Leo M, Oberhuber W, Schuster R, et al. Evaluating the effect of plant water availability on inner alpine coniferous trees based on sap flow measurements[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2014, 133: 691−698. doi: 10.1007/s10342-013-0697-y
[5] 彭小梅, 车存伟, 苏靖茸, 等. 干旱区人工林稳定性与适宜性的树轮学评价体系构建与应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 1−10. Peng X M, Che C W, Su J R, et al. Construction and application of a dendrochronological evaluation method for the stability and suitability of artificial forests in arid areas[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 1−10.
[6] Zheng X, Zhu J J, Yan Q L, et al. Effects of land use changes on the groundwater table and the decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in southern Horqin Sandy Land, Northeast China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2012, 109: 94−106. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2012.02.010
[7] Song L N, Zhu J J, Zhang J X, et al. Divergent growth responses to warming and drying climates between native and non-native tree species in Northeast China[J]. Trees, 2019, 33: 1143−1155. doi: 10.1007/s00468-019-01848-z
[8] 孜尔蝶·巴合提, 贾国栋, 余新晓, 等. 基于稳定同位素分析不同退化程度小叶杨水分来源[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 1807−1816. Zierdie·Baheti, Jia G D, Yu X X, et al. Assessing water sources for Populus simonii with different degrees of degradation based on stable isotopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 1807−1816.
[9] Li M Y, Fang L D, Duan C Y, et al. Greater risk of hydraulic failure due to increased drought threatens pine plantations in Horqin Sandy Land of northern China[J/OL]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2020, 461: 117980[2023−02−21]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.117980.
[10] Grossiord C, Sevanto S, Dawson T E, et al. Warming combined with more extreme precipitation regimes modifies the water sources used by trees[J]. New Phytologist, 2017, 213: 584−596. doi: 10.1111/nph.14192
[11] Deng J F, Yao J Q, Zheng X, et al. Transpiration and canopy stomatal conductance dynamics of Mongolian pine plantations in semiarid deserts, Northern China[J/OL]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 249: 106806[2023−02−21]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106806.
[12] Song L N, Zhu J J, Zheng X, et al. Comparison of canopy transpiration between Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica and Pinus tabuliformis plantations in a semiarid sandy region of Northeast China[J/OL]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2022, 314: 108784[2023−02−21]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108784.
[13] 张凯, 孙艳丽, 隗骥超, 等. 北京山区大果榆树干液流的季节与昼夜环境调控[J]. 林业科学, 2023, 59(7): 24−34. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.LYKX20220868 Zhang K, Sun Y L, Wei J C, et al. Control of environmental factors on the sap flow at daily and seasonal scales in Ulmus macrocarpa in Beijing, China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2023, 59(7): 24−34. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.LYKX20220868
[14] Chang X X, Zhao W Z, He Z B. Radial pattern of sap flow and response to microclimate and soil moisture in Qinghai spruce (Picea crassifolia) in the upper Heihe River Basin of arid northwestern China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2014, 187: 14−21. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2013.11.004
[15] Chen L X, Zhang Z Q, Li Z D, et al. Biophysical control of whole tree transpiration under an urban environment in northern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 402(3): 388−400.
[16] Du S, Wang Y L, Kume T, et al. Sap flow characteristics and climatic responses in three forest species in the semiarid Loess Plateau region of China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2011, 151(1): 1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.08.011
[17] 孔喆, 陈胜楠, 律江, 等. 欧美杨单株液流昼夜组成及其影响因素分析[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(3): 8−20. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200302 Kong Z, Chen S N, Lü J, et al. Characteristics of Populus euramericana sap flow over day and night and its influencing factors[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 56(3): 8−20. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20200302
[18] 马菁, 郭建斌, 刘泽彬, 等. 六盘山华北落叶松林分蒸腾日内变化及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(5): 1−11. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190468 Ma J, Guo J B, Liu Z B, et al. Diurnal variations of stand transpiration of Larix principis-rupprechtii forest and its response to environmental factors in Liupan Mountains of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(5): 1−11. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190468
[19] 余新晓, 甘敬. 水源涵养林研究与示范[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2007: 258−270. Yu X X, Gan J. Research and demonstration of water conservation forests[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2007: 258−270.
[20] 王绪芳, 井赵斌, 程积民, 等. 华北落叶松人工林生长的合理经营密度探讨[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2013, 41(10): 168−171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2013.10.047 Wang X F, Jing Z B, Cheng J M, et al. Study on reasonable management density of Larix principis-rupprechtii artificial forest[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(10): 168−171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2013.10.047
[21] 张丽楠, 王得祥, 郝亚中, 等. 陕西宁东林业局华北落叶松人工林最适经营密度研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2013, 28(1): 146−150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2013.01.30 Zhang L N, Wang D X, Hao Y Z, et al. Optimal management density of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations of Ningdong Forestry Bureau in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2013, 28(1): 146−150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2013.01.30
[22] 刘慧敏, 韩海荣, 程小琴, 等. 不同密度调控强度对华北落叶松人工林土壤质量的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(6): 50−59. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200322 Liu H M, Han H R, Cheng X Q, et al. Effects of different density regulation intensities on soil quality in Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(6): 50−59. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200322
[23] 田平, 韩海荣, 康峰峰, 等. 密度调整对太岳山华北落叶松人工林冠层结构及林下植被的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(8): 45−53. Tian P, Han H R, Kang F F, et al. Influence of density adjustment on canopy structure and understory vegetation of the Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi, China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(8): 45−53.
[24] 卫舒平, 梁文俊, 魏曦, 等. 不同密度华北落叶松林天然更新及其影响因子[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(10): 2687−2694. Wei S P, Liang W J, Wei X, et al. Natural regeneration of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations with different densities and its influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(10): 2687−2694.
[25] 陈雪姣. 洛南县油松人工林生长模型及合理密度研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. Chen X J. Research on growth model and stand reasonable density of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Luonan Area[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2019.
[26] 王玲, 赵广亮, 周红娟, 等. 华北地区油松人工林林分密度对土壤化学性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(12): 9−16, 33. Wang L, Zhao G L, Zhou H J, et al. Effects of stand density on soil chemical properties and enzyme activity of Pinus tabulaeformis in north China[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(12): 9−16, 33.
[27] 刘宇, 郭建斌, 王彦辉, 等. 宁夏六盘山不同密度华北落叶松人工林枯落物水文效应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(8): 36−44. Liu Y, Guo J B, Wang Y H, et al. Hydrological effects of forest litter of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations with varying densities in Liupan Mountains of Ningxia, China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(8): 36−44.
[28] 韩辉, 张学利, 党宏忠, 等. 基于树干液流通量的沙地樟子松合理林分密度的确定[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(6): 797−803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2015.06.006 Han H, Zhang X L, Dang H Z, et al. Study on proper stand density of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in sandy land based on stem sap flow velocity[J]. Forest Research, 2015, 28(6): 797−803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2015.06.006
[29] 熊伟, 王彦辉, 于澎涛, 等. 华北落叶松树干液流的个体差异和林分蒸腾估计的尺度上推[J]. 林业科学, 2008, 44(1): 34−40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2008.01.006 Xiong W, Wang Y H, Yu P T, et al. Variation of sap flow among individual trees and scaling-up for estimation of transpiration of Larix principis-rupprechtii stand[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2008, 44(1): 34−40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2008.01.006
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 梅诗意,李瑜,李士帅,朱怡宁,何金春,孟鑫淼,高颖. 寒冷地区多层轻型木结构墙体热湿性能试验研究. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(06): 135-145 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 代倩,胡家航,姬晓迪,郭明辉. 建筑用集成材制造技术的环境效能影响. 林业工程学报. 2018(04): 46-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨俊霞,邹惠芬. 木结构建筑节能技术研究. 西部皮革. 2018(08): 48 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: