Effects of epoxy resin doping on properties of geopolymer wood adhesive
-
摘要:目的
为了解决地质聚合物木材胶黏剂的界面相容性差等问题,采用环氧树脂为有机掺杂剂构建有机–无机交联网络的方法,研究环氧树脂掺杂对地质聚合物木材胶黏剂综合性能的影响。
方法将地质聚合物与环氧树脂、聚醚胺、硅烷偶联剂KH550共混制备地质聚合物基木材胶黏剂,分析不同有机掺杂剂对胶黏剂性能的影响作用,结合FTIR、XPS、SEM-EDS和锥形量热仪等分析有机掺杂剂的作用机制。
结果不同有机物掺杂均会提高地质聚合物浆体的黏度,当环氧树脂和聚醚胺的质量分数分别为4.8%和1.2%(GECS6)时,地质聚合物浆体黏度较低,有利于均匀施胶。不同物质掺杂均会不同程度地提高地质聚合物基胶合板的胶合强度,GECS6的湿态胶合强度达到较优值0.87 MPa,相比于纯地质聚合物胶黏剂提高了248%。相较于纯地质聚合物,有机掺杂地质聚合物胶合板的热释放速率和总热释放量分别下降了7.01%和17.95%,阻燃性能得到一定程度的提高。
结论环氧树脂与硅烷偶联剂协同作用,构建了有机–无机交联网络,提高了地质聚合物胶黏剂与木材的相容性及浆体的致密性,解决了地质聚合物木材胶黏剂的界面相容性差的问题,从而增强了胶合板的胶合强度和阻燃性能。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to solve the problems of poor interfacial compatibility of geopolymer wood adhesive, epoxy resin was used as an organic dopant to construct organic-inorganic crosslinking network, so as to improve the comprehensive performance of epoxy resin doping on geopolymer wood adhesive.
MethodGeopolymer-based wood adhesive was prepared by blending geopolymer with epoxy resin, polyether amine, and silane coupling agent KH550. The effects of different organic dopants on performance of the adhesive were analyzed, and the mechanism of organic dopants was analyzed by combining FTIR, XPS, SEM-EDS, and conical calorimeter.
ResultDifferent organic doping improved the viscosity of geopolymer slurry. Given the mass fraction of epoxy resin of 4.8% and polyether amine of 1.2% (GECS6), the viscosity of geopolymer slurry was lower, which was conducive to the uniform application of adhesive. Different doping substances improved the bond strength of geopolymer-based plywood to varying degrees. The wet bond strength of GECS6 reached a better value of 0.87 MPa, which was higher than that of pure geopolymer adhesive by 248%. Compared with pure geopolymer adhesive, the heat release rate and total heat release of the organically doped geopolymer plywood decreased by 7.01% and 17.95%, respectively, and the fire resistance properties were improved to a certain extent.
ConclusionThe synergistic effect of epoxy resin and silane coupling agent constructs an organic-inorganic crosslinking network, which can improve the compatibility between geopolymer adhesive and wood, improve the densification of paste, and solve the problem of poor interfacial compatibility of geopolymer wood adhesive, thus enhance bond strength and fire resistance of plywoods.
-
Keywords:
- organic compounds /
- adhesives /
- geopolymers /
- doping /
- epoxy resins /
- crosslinking /
- fire resistance
-
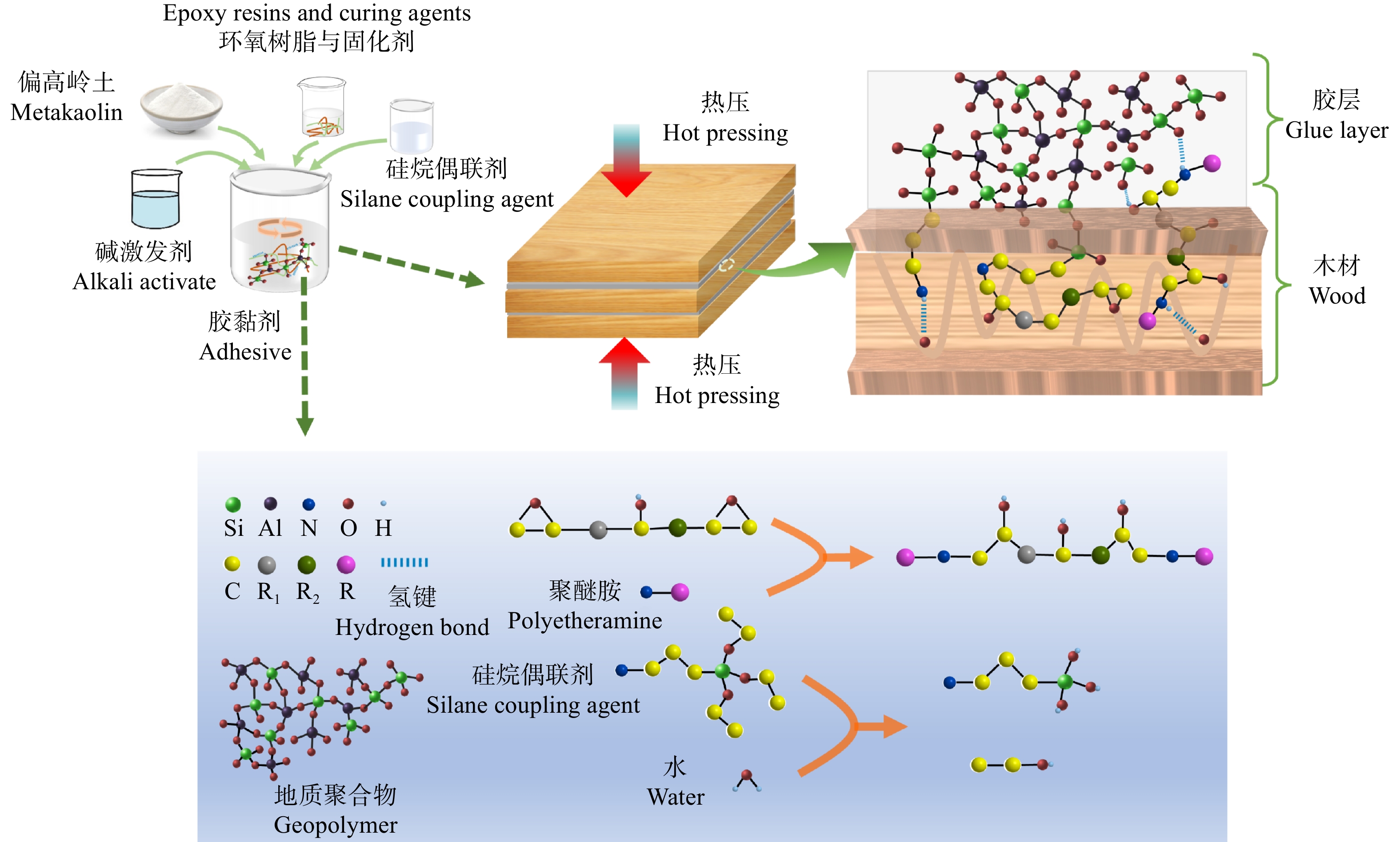
人造板用甲醛系胶黏剂在生产和使用过程中释放出游离甲醛,危害人体健康。聚氨酯类、大豆蛋白、木质素、淀粉等无醛胶黏剂可以有效解决人造板甲醛释放问题,但存在生产成本高、工艺复杂等问题,限制了其应用范围。地质聚合物作为一种新型的无机胶黏剂,有效地解决了甲醛释放的问题,并且具有低成本、高耐热、耐久性好、绿色环保等优势,有望替代甲醛系胶黏剂[1]。地质聚合物是由铝氧四面体和硅氧四面体组成的三维立体网状结构的无机聚合物,通常由高岭土、粉煤灰等工业固废物经碱激发制备而成,偏高岭土是由高岭土在高温(600 ~ 900 ℃)经脱水形成的无水硅酸铝,碱激发后的偏高岭土具有优异的力学性能与耐久性能等,可用于制备胶凝材料。有研究发现地质聚合物基胶黏剂在热压作用下会渗透到木材细胞壁和细胞腔中,通过机械互锁作用与木材相连以实现胶合作用[2],但作为木材胶黏剂,地质聚合物存在无机胶黏剂与木材界面相容性差等共性缺点,导致胶接强度较低,限制其进一步推广应用。有研究通过有机掺杂提高地质聚合物性能,聚氨酯掺杂对性能影响不大[3],酚醛树脂掺杂提高了胶黏剂强度,但存在甲醛释放问题[4]。
环氧树脂固化体系中有活性极大的环氧基、羟基等极性基团,具有胶接强度高、力学性能好、收缩率小、绿色环保等特点,常用于混凝土加固、木质素胶黏剂改性等[5−6]。有学者发现环氧树脂掺杂到地质聚合物中可以填充孔隙和优化孔隙结构,两者之间形成的氢键作用增强了基体的韧性[7]。因此,本研究以偏高岭土为地质聚合物原料,以环氧树脂作为有机掺杂剂,以聚醚胺为固化剂,以γ-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷为偶联剂,经碱激发、有机掺杂制备地质聚合物基胶黏剂,研究不同有机物质掺杂对地质聚合物胶黏剂性能的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
偏高岭土购于上海昊弗化工有限公司,采用X射线荧光光谱仪测试其氧化物组分(表1);液体硅酸钠(Na2SiO3)购于江苏省无锡市亚泰联合化工有限公司,模数为2.13;氢氧化钠(NaOH,纯度≥96%)颗粒购于天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;环氧树脂E51(环氧值0.5)购于北京科奥科技有限公司;聚醚胺固化剂购于中山金诚黏合剂有限公司;γ-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(KH550)购于上海迈瑞尔化学技术有限公司;杨木单板购于山东省菏泽市,幅面为400 mm × 400 mm,厚度为1.5 mm。
表 1 偏高岭土的氧化物成分Table 1. Oxide compositions of biotite kaolinite成分 Component SiO2 Al2O3 TiO2 Fe2O3 P2O5 Na2O CaO 其他 Others 质量分数 Mass fraction 50.778% 44.703% 2.641% 0.634% 0.491% 0.206% 0.169% 0.378% 1.2 胶黏剂与胶合板的制备
1.2.1 胶黏剂的制备
制备8 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液,根据式(1)计算所需碱激发剂模数对应的硅酸钠溶液和氢氧化物溶液的体积,将上述两种溶液混合均匀后,静置24 h待用。
n=w0w=aρwn0/62aρw/62+bc/2000 (1) 式中:n为碱激发剂模数1.7;w0为二氧化硅的质量分数,%;w为氧化钠的质量分数,%;ρ为硅酸钠溶液的密度,g/mL;n0为工业水玻璃模数;a为硅酸钠溶液的体积,mL;b为氢氧化物溶液的体积,mL;c为硅酸钠溶液的体积,mL。
将碱激发剂与偏高岭土混合,高速剪切搅拌120 s(纯地质聚合物G),依次加入环氧树脂(E)、聚醚胺固化剂(C)、硅烷偶联剂KH550(S)制备不同物料配比(质量比)的胶黏剂,具体参数见表2。
表 2 环氧树脂掺杂地质聚合物胶黏剂的物料配比(质量比)Table 2. Material ratios of epoxy resin doped geopolymer adhesive (mass ratio)编号 No. 物料配比 Material ratio G A∶B = 10∶15 GE A∶B∶E = 10∶15∶1.60 GC A∶B∶C = 10∶15∶0.32 GEC A∶B∶E∶C = 10∶15∶1.28∶0.32 GECS3 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶0.62∶0.16∶0.129 GECS6 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶1.28∶0.32∶0.134 GECS9 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶1.99∶0.50∶0.138 GECS12 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶2.74∶0.69∶0.143 注:A代表偏高岭土,B代表碱激发剂,C代表聚醚胺固化剂,E代表环氧树脂,S代表硅烷偶联剂KH550。Notes: A represents metakaolin, B represents alkali-activator, C represents polyether amine curing agent, E represents epoxy resin, and S represents silane coupling agent KH550. 1.2.2 地质聚合物胶合板的制备
将杨木单板裁切为幅面200 mm × 200 mm × 1.5 mm的规格,单板施胶为量300 g/m2,采用相邻层纹理垂直的方法将单板热压为三层胶合板,热压工艺为压力1.2 MPa、时间260 s、温度150 ℃。
1.3 胶黏剂性能表征
1.3.1 化学结构表征
将从胶合板胶层部分刮取的胶黏剂粉末使用玛瑙研钵粉碎至200目,使用X射线光电子能谱仪(Thermo Kalpha,美国 Thermo 公司)对样品进行分析,辐射源为Al-Kα,结合能相对于C1s峰在284.8 eV进行校正。
使用傅里叶变换衰减全反射红外光谱仪(Nicolet iS5,赛默飞世尔科技公司)对干燥后的样品粉末测试,分析不同物质掺杂导致的化学结构变化,光谱范围500 ~ 4 000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,采集次数为32次。
1.3.2 流变性、凝结时间与热稳定性测试
使用旋转流变仪(HAAKE Roto Viscol,德国)匀变速剪切模式在室温下测试现配胶黏剂的黏度,剪切速率为1 ~ 60 s−1,时间为1 min,取100个数据。使用恒速变温模式测试胶黏剂在升温过程中的流动性,剪切速率为30 s−1,温度范围为30 ~ 100 ℃,时间为8 min,取100个数据。
将现配的胶黏剂置于模具中,参照GB/T 1346—2011《水泥标准稠度、凝结时间、安定性检验方法》测试凝结时间,其中初凝针距底板(4 ± 1) mm时,记为初凝时间。
使用热重分析仪(STA200,日本日立HITACHI)对样品热稳定性进行表征,温度范围30 ~ 800 ℃,加热速率10 ℃/min,测试氛围使用氮气气流。
1.4 胶合板性能检测
1.4.1 胶合强度测试
根据GB/T 17657—2022《人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法》中Ⅱ类胶合板的要求进行测试,将放置3天的胶合板试件放入63 ℃恒温水浴中浸泡3 h,取出试件后在室温下放置10 min后,用微机控制人造板万能力学试验机(WDW-E,济南耐而试验机有限公司)测试湿态胶合强度和干态胶合强度,测试时均匀加载,加载速率5 mm/min,直至胶合试件发生剪切破坏,记录最大载荷数值,根据式(2)计算胶合强度。
X=PS (2) 式中:X为胶合强度,MPa;P为最大载荷数值,N;S为受剪切面的面积,S = 625 mm2。
1.4.2 胶合界面形貌和阻燃性能测试
采用扫描电子显微镜(Regulus 8100,日本日立公司)表征水热处理后胶合板的胶合界面结构形貌。
采用锥形量热仪(i-Cone,英国FTT公司)测试地质聚合物基杨木试件的阻燃性能,测试方法参考ISO 5660-1:2015《Reaction-to-fire tests—heat release,smoke production and mass loss rate—part 1:Heat release rate (cone calorimeter method) and smoke production rate (dynamic measurement)》。采用7层胶合板,并加工成100 mm × 100 mm × 10 mm规格尺寸,测试热辐射强度为50 kW/m2。
1.4.3 甲醛释放量测试
根据GB/T 17657—2022《人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法》中干燥器法测定胶合板的甲醛释放量,评价胶合板的环保性能。测试时,将9个胶合板样品(150 mm × 50 mm × 10 mm)放在装有300 mL蒸馏水玻璃结晶皿的密闭干燥器中24 h,用乙酰丙酮分光光度计法测定吸收液在波长412 nm处的吸光度。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 地质聚合物基胶黏剂的化学结构分析
图1a、b显示:在掺杂环氧树脂与聚醚胺胶黏剂浆体(GEC)的N1s分峰拟合图中位于398.0 eV的峰是C−N,浆体中N来源仅有聚醚胺,并且相较于未掺杂环氧树脂的浆体(GC),掺杂环氧树脂与聚醚胺浆体的C−N峰面积上升了78.57%。这表明聚醚胺中的氨基与环氧树脂的环氧键反应,形成了更多的C−N[8]。
图1c ~ f显示:环氧树脂、聚醚胺添加并不会对Si−OH的峰值及面积产生较大影响;GECS6的Si2p分峰拟合图中位于102.1和102.9 eV的峰分别是Si−O−T(T为Si或Al)和Si−OH,相比于未掺杂硅烷偶联剂的胶黏剂(GEC),GECS6中占据主导地位的Si−O−T峰面积从75.2%下降到50.4%,而Si−OH的相对含量从24.8%上升至49.6%,表明硅烷偶联剂水解后生成的硅醇基团与地质聚合物骨架结构成功结合,起到有机–无机之间的桥接作用[4]。
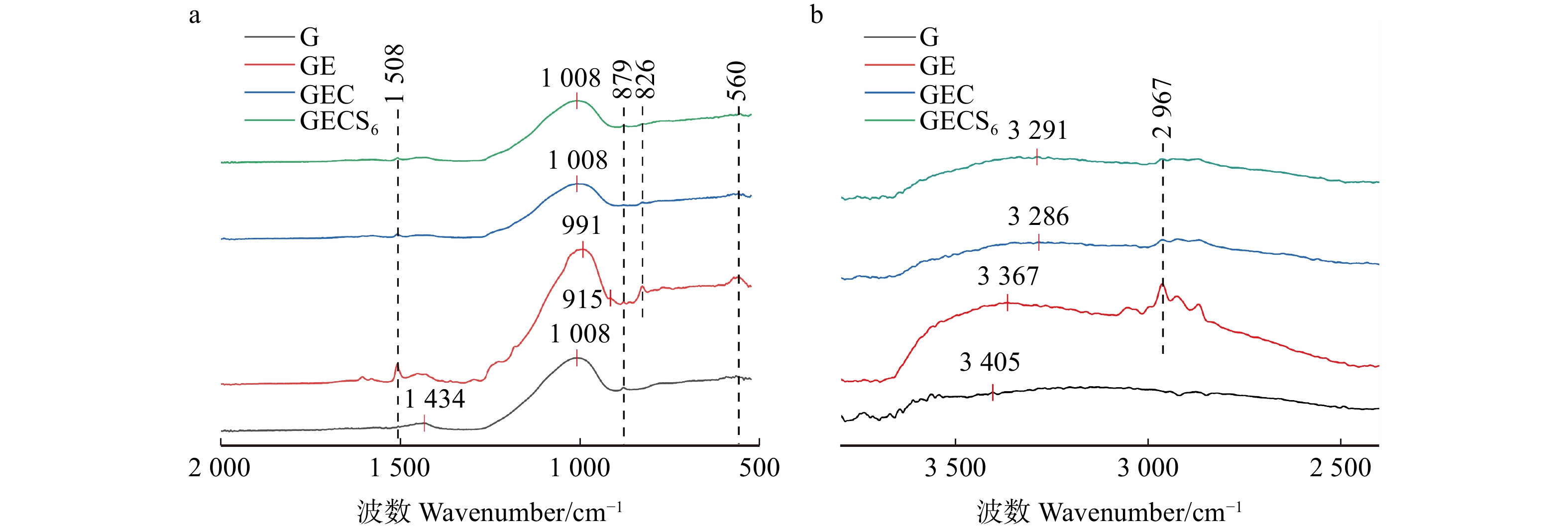
图2显示:在3 100 ~ 3 600 cm−1是−OH的特征峰,加入环氧树脂与聚醚胺后峰值向波数低的方向移动,表明生成了更多的Si−OH,验证了XPS的检测结果,并且说明了环氧树脂与地质聚合物末端羟基、KH550水解有机羟基存在较强的氢键结合[9];地质聚合物的主峰出现在1 008 cm−1处,由地质聚合物中的Si−O−T的不对称伸缩振动造成的[10],仅加入环氧树脂后峰值向波数低的方向移动,可能是端基环氧环的加入导致的[11];在915 cm−1处为环氧环的特征峰,加入固化剂和偶联剂后峰消失,表明环氧键与氨基发生反应,形成交联结构[12]。
2.2 地质聚合物基胶黏剂浆体的黏度与凝结时间
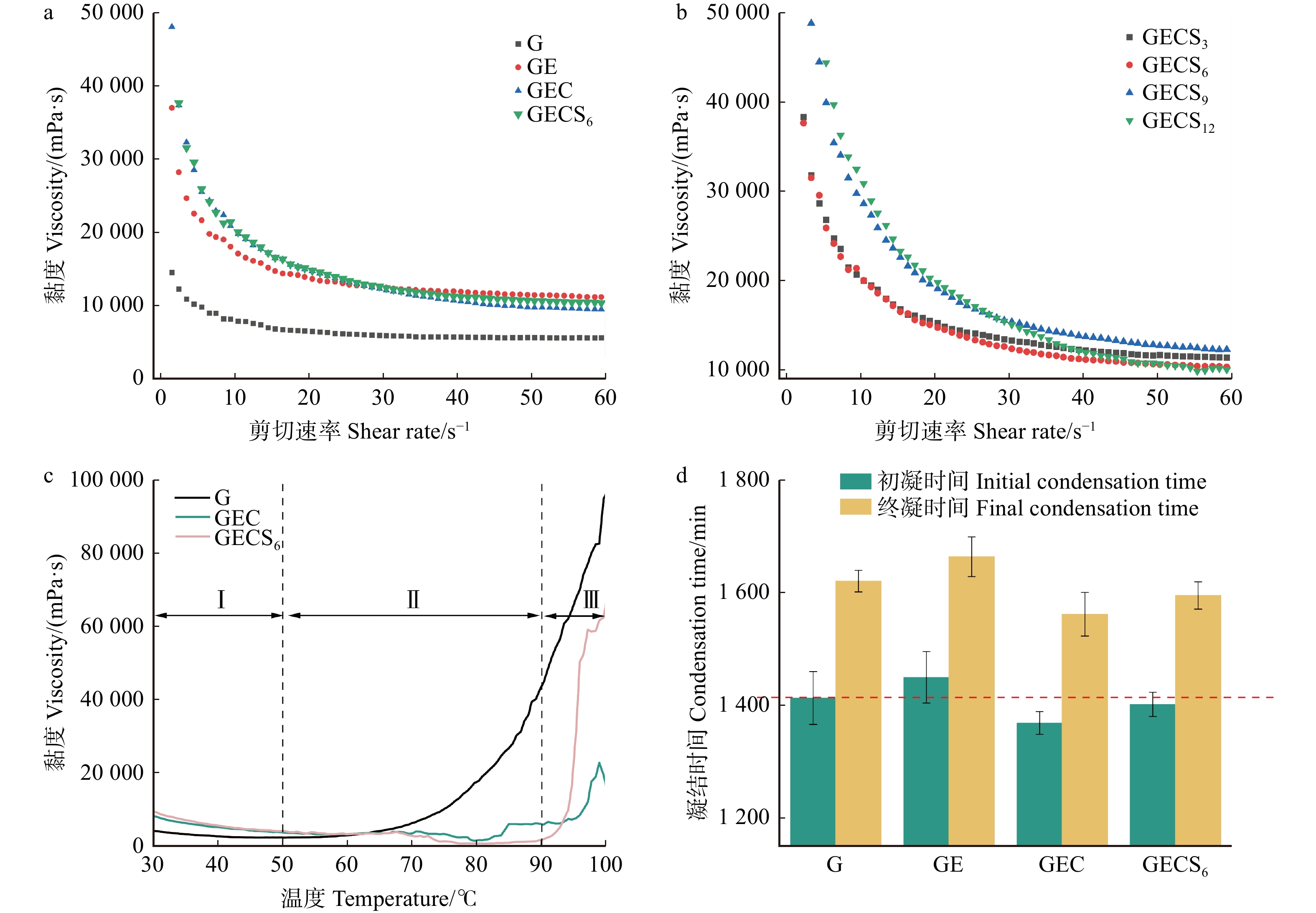
地质聚合物浆体是一种假塑性流体,在稳态的剪切作用下,流体黏度随剪切速率的升高而降低,保持“剪切变稀”的流体特性[13],环氧树脂的加入并不会改变这种特性(图3a);随着环氧树脂质量分数的增加,地质聚合物基浆体初始黏度会增大,但在高剪切速率下浆体黏度相差不大(图3b)。胶黏剂浆体的黏度会影响板材施胶的均匀性以及板材性能,因此制备的地质聚合物胶黏剂在施胶过程中需要不断地搅拌,确保浆体时刻处于低黏度状态。
![]() 图 3 不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂黏度的影响(a),不同环氧树脂浓度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(b),不同温度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(c),不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂凝结时间的影响(d)Figure 3. Effects of different substance doping on adhesive viscosity (a), effects of different epoxy resin concentrations on adhesive viscosity (b), effects of different temperatures on adhesive viscosity (c), and effects of different substance doping on condensation time (d)
图 3 不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂黏度的影响(a),不同环氧树脂浓度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(b),不同温度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(c),不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂凝结时间的影响(d)Figure 3. Effects of different substance doping on adhesive viscosity (a), effects of different epoxy resin concentrations on adhesive viscosity (b), effects of different temperatures on adhesive viscosity (c), and effects of different substance doping on condensation time (d)图3c显示:在第Ⅰ阶段30 ~ 50 ℃,浆体黏度逐渐变小,符合地质聚合物剪切变稀规律;在第Ⅱ阶段50 ~ 90 ℃,地质聚合物浆体黏度逐渐变大,并且变化速率加快,这是升温促成的三维网络结构形成,浆体聚合程度高[14],而环氧树脂、聚醚胺和硅烷偶联剂的掺杂导致黏度拐点从50 ℃延长至90 ℃,可能是有机物质掺杂阻隔了地质聚合物间反应,延缓了地质聚合物胶黏剂固化并导致黏度增加[15];在第Ⅲ阶段90 ~ 100 ℃,掺杂硅烷偶联剂的胶黏剂浆体黏度上升速率明显快于其他有机物,可能是因为高温加快了硅烷偶联剂与地质聚合物的反应,胶黏剂固化速率提高[16]。
图3d显示:环氧树脂的加入会增加浆体的凝结时间,这是由于环氧树脂阻碍了地质聚合物间的反应;在加入聚醚胺固化剂后,环氧树脂固化速度加快[17],交联网络开始形成,因此凝结时间减少;硅烷偶联剂加入后,硅烷与地质聚合物水化产物的耦合作用使得聚合物分子进一步吸附到水化产物上,使得反应延缓,因此凝结时间增大[9]。
2.3 地质聚合物基胶黏剂的热稳定性
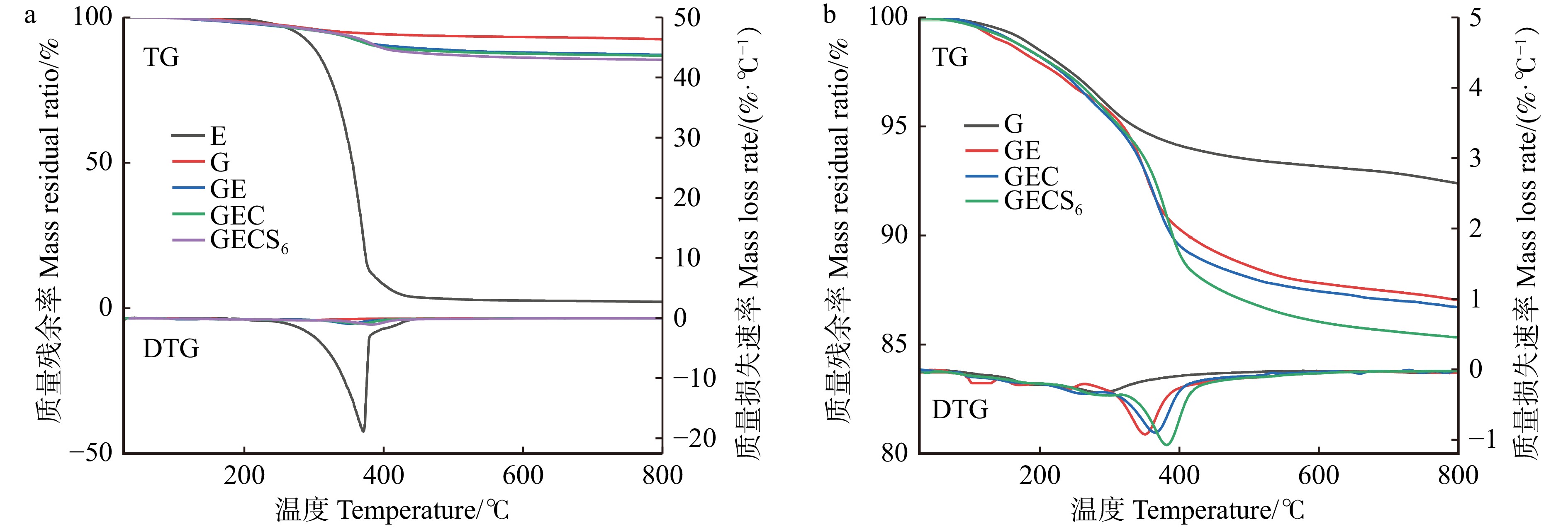
图4显示有机物质掺杂均会不同程度地降低胶黏剂的稳定性。第一个热降解阶段(100 ~ 200 ℃),环氧树脂和地质聚合物质量损失率相近,环氧树脂是由羟基的脱水引起的[18],并且此温度下胺类固化剂上的氮原子容易被热氧化破坏,地质聚合物是由于其孔隙中游离水、吸着水的去除引起的[19]。第二个热降解阶段(200 ~ 450 ℃),环氧树脂大量热解是由于290 ℃时其分子中的聚合物主链破裂引起的快速分解[18],聚醚胺和硅烷偶联剂的加入均使得DTG峰值向右偏移(图4b),表明两种物质均会与地质聚合物和环氧树脂形成更为致密的交联网络,抑制水分的散失[19];地质聚合物在280 ℃的峰值归因于C−S−H凝胶的脱水[20]。第三个热降解阶段(400 ~ 800 ℃),地质聚合物较稳定的降解归因于方解石中水分的散失[21]。
2.4 地质聚合物基胶合板胶合性能分析
2.4.1 胶合界面
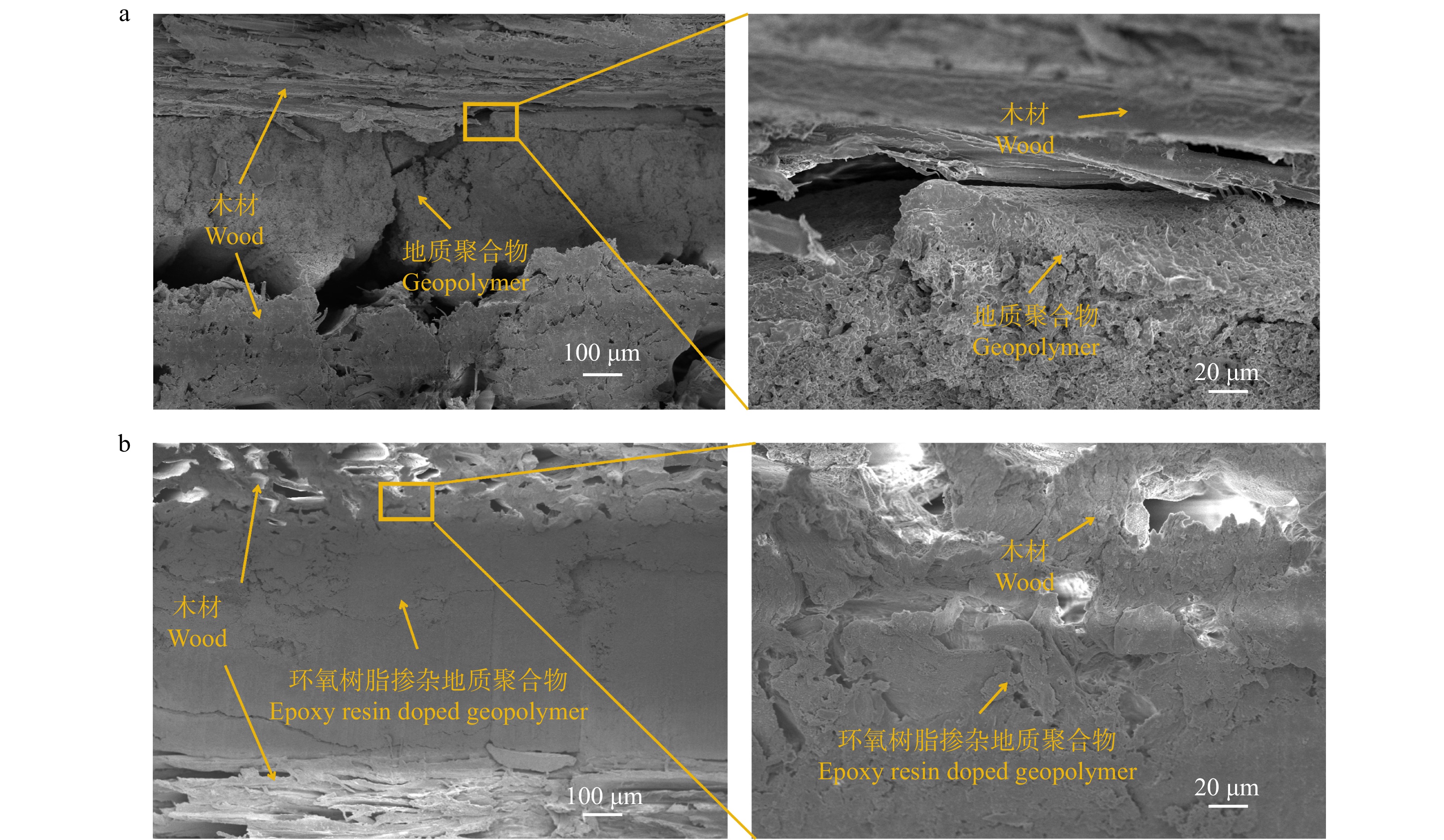
图5显示:水热处理后的纯地质聚合物胶合板中地质聚合物基体较为疏松,存在较大裂缝,地质聚合物和胶层之间存在明显开裂;而环氧树脂、聚醚胺与硅烷偶联剂掺杂后,地质聚合物基体结构致密,胶接界面连续且开裂较少。这是因为硅烷偶联剂水解产生Si−OH与地质聚合物形成化学结合,并与环氧树脂和木材形成致密的氢键,形成了多元复合和多键结合的“有机–无机”网络结构,增强了胶黏剂与木材间的界面附着力。
2.4.2 胶合强度
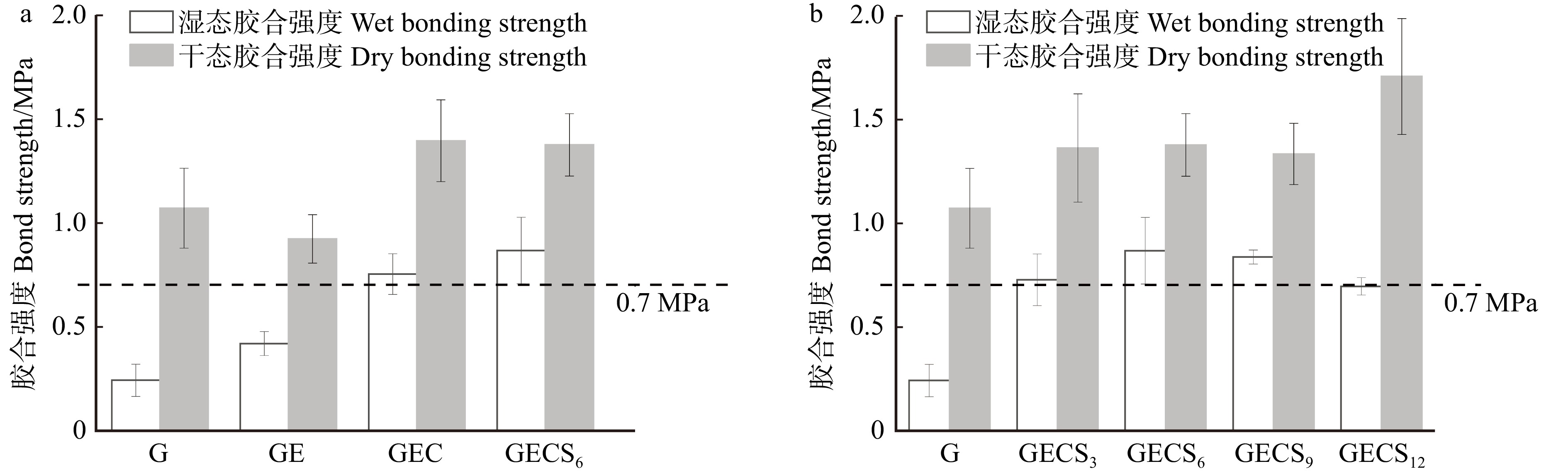
图6显示:纯地质聚合物(G)的湿态胶合强度最低值为0.25 MPa,有机物质掺杂均会不同程度地提高胶合板的胶合强度,环氧树脂(GE)、聚醚胺固化剂(GEC)和硅烷偶联剂(GECS6)掺杂后胶合强度较纯地质聚合物分别提高了64%、160%和248%;当环氧树脂和聚醚胺的质量分数分别为4.8%和1.2%(GECS6)时,胶合板的湿态胶合强度达到较优值0.87 MPa,因此该工艺参数较优。有机掺杂剂与地质聚合物通过化学键合,提高了胶合强度,但当环氧树脂质量分数超过4.8%时,过量树脂会阻碍地质聚合反应,影响地质聚合物的性能,导致板材强度下降[22]。
2.5 地质聚合物基胶合板阻燃性能分析
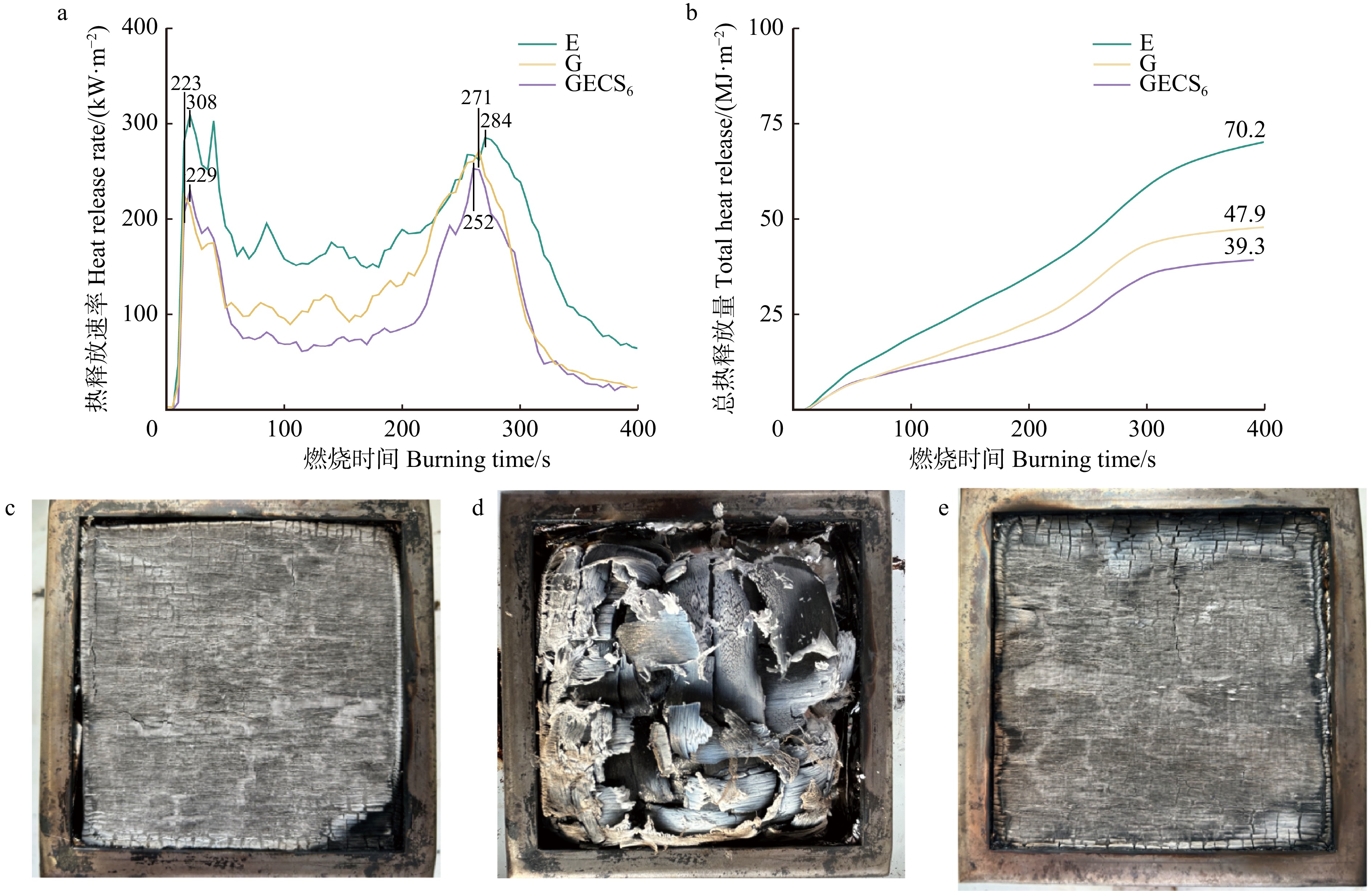
图7a,b显示:相较于纯地质聚合物,掺杂硅烷偶联剂GECS6胶合板的第二热释放速率峰值和总热释放量分别降低了7.01%和17.95%,阻燃性能得到一定程度的提高。图7c ~ e显示:纯地质聚合物胶合板和掺杂硅烷偶联剂组的胶合板均能保持较为完整的状态。这是由于地质聚合物渗透到木材内部,通过包裹部分纤维防止木材直接燃烧,地质聚合物结构中Al−O键和Si−O键热分解需要比C−C键更多的能量,氧化物(Al2O3)等的存在促进纤维素、半纤维素和木质素等有机物质在低温下的裂解,在燃烧初期更容易形成炭层,这些炭层有效地隔绝了氧气,并且胶合板中的含N固化剂和硅烷偶联剂在高温下会分解产生N2等不燃气体,稀释氧气浓度,在加热时形成保护层,进一步抑制燃烧[23−24]。
2.6 地质聚合物基胶合板甲醛释放量
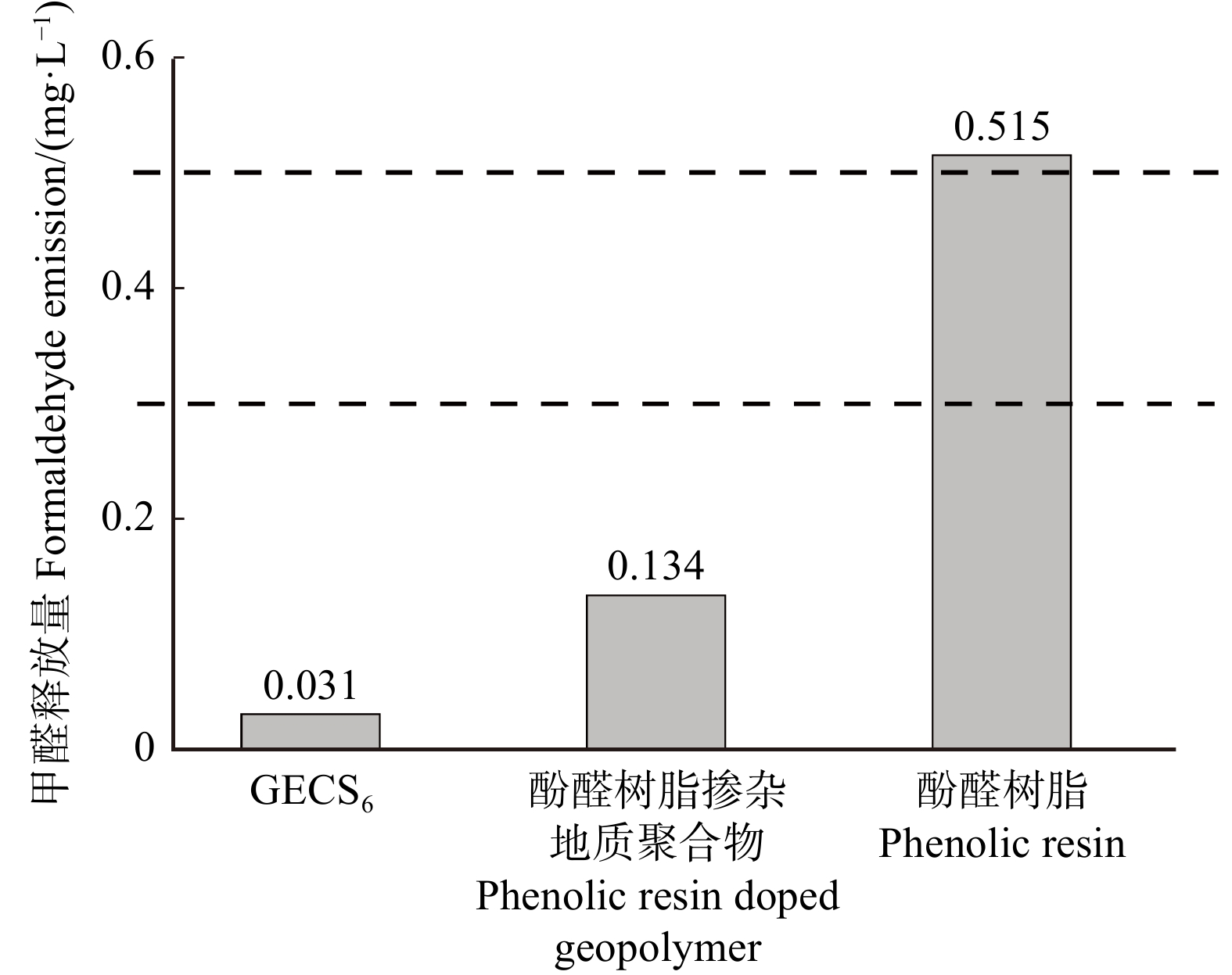
环氧树脂掺杂地质聚合物基胶合板的甲醛释放量为0.031 mg/L(图8),远低于酚醛树脂掺杂地质聚合物基胶合板(0.134 mg/L)和纯酚醛树脂基胶合板(0.515 mg/L)。参照日本人造板制品环保标准JIS A 5908:2015《Particleboards》,环氧树脂掺杂地质聚合物基胶合板的甲醛释放量满足最高环保标准F☆☆☆☆(甲醛释放量 ≤ 0.3 mg/L),环保性能优良。
2.7 环氧树脂掺杂地质聚合物木材胶黏剂增强机理
2.7.1 纯地质聚合物木材胶黏剂的胶接机理
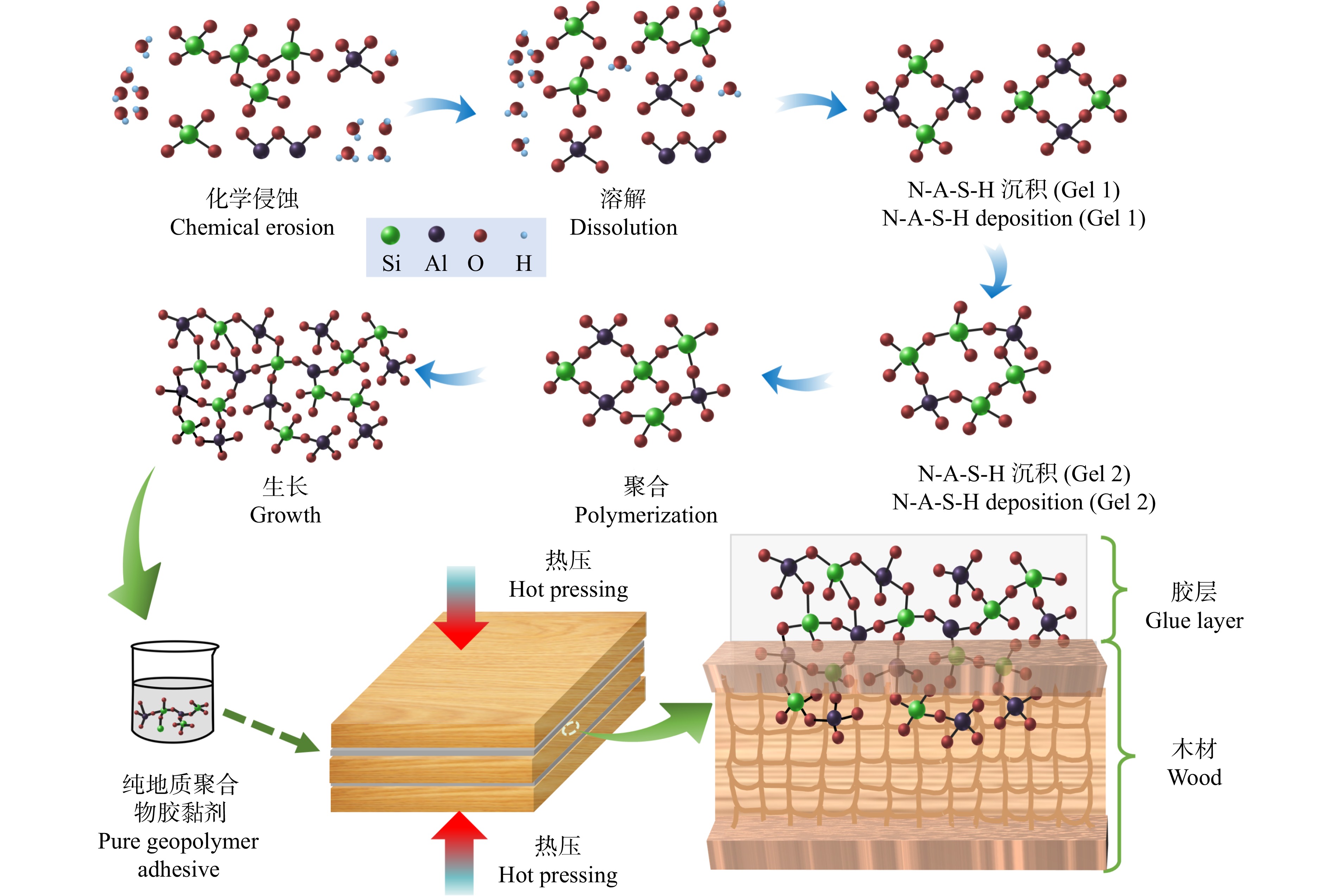
地质聚合物的形成以及与木材胶黏剂的胶接机理如图9所示。在高碱性的条件下,硅铝表面逐渐溶解,随着硅四面体和铝四面体单体的结合,形成硅铝交替的四面体的环结构(Gel 1和Gel 2),少量新生成的产物填充孔隙,最终形成无定形碱硅酸铝凝胶为主的地质聚合物[25−26]。由于碱的存在,地质聚合物会降解木材表面,并在压力作用下渗透到木材细胞壁和细胞腔中,形成类似“铆钉”结构的机械互锁连接以及较弱的氢键结合,从而在界面上加固木材[2]。
2.7.2 环氧树脂掺杂对地质聚合物木材胶黏剂的增强机理
综上分析,可以总结出如图10所示的环氧树脂掺杂对地质聚合物木材胶黏剂增强机理。第一阶段,铝硅酸盐前驱体与碱激发剂进行地质聚合反应,在热压条件下形成地质聚合物空间网络,同时硅烷偶联剂水解暴露出羟基[27],环氧树脂与聚醚胺和部分硅烷偶联剂KH550发生开环反应[16]。第二阶段,地质聚合物逐渐形成硅氧四面体和铝氧四面体,硅烷偶联剂中的Si−OH与地质聚合物中的Si相连形成Si−O−Si[9,27],硅烷偶联剂将有机环氧树脂与无机地质聚合物通过化学键相连,并且开环后的环氧树脂与地质聚合物、硅烷偶联剂形成密集的氢键连接,体系结构不断完善,形成致密的有机–无机网络结构[4]。第三阶段,在热压作用下,部分胶黏剂渗透到木材内部,胶层表面的环氧树脂、地质聚合物通过氢键与木材相连,在胶层体系不断完善的过程中,胶层与木材结合更为紧密,逐渐形成了多元复合与多键结合的“有机–无机”网络结构。
3. 结 论
本研究以环氧树脂为有机掺杂剂,以偏高岭土基地质聚合物为主体,通过FTIR、XPS、旋转流变仪分析有机物质掺杂对胶黏剂浆体性能的影响,通过SEM-EDS和锥形量热仪分析3种物质对板材胶合强度、阻燃性能的影响,具体结论如下。
(1)地质聚合物基胶黏剂黏度符合“剪切变稀”的变化规律,当环氧树脂和聚醚胺的质量分数分别为4.8%和1.2%(GECS6)时,浆体黏度较低,有利于均匀施胶;与纯地质聚合物相比,有机物质掺杂会不同程度地降低胶黏剂浆体的热稳定性。
(2)环氧树脂杂化地质聚合物胶黏剂具有优异的胶合性能、阻燃性能和环保性能。GECS6胶合板的胶合强度为较优值(0.87 MPa),相比于纯地质聚合物胶黏剂提高了248%;较纯地质聚合物GECS6胶合板的第二热释放速率峰值和总热释放量基胶合板分别降低了7.01%和17.95%,阻燃性能得到了一定的提升;GECS6胶合板的甲醛释放量为0.031 mg/L,满足F☆☆☆☆标准。
(3)硅烷偶联剂水解生成的Si−OH与地质聚合物末端羟基反应形成Si−O−Si键,环氧树脂在聚醚胺作用下环氧环打开,并通过氢键与地质聚合物形成致密结构,提高了地质聚合物胶黏剂的胶接性能。
本研究采用环氧树脂改性地质聚合物木材胶黏剂,有效地提高了胶黏剂地胶合性能和阻燃性能,为制备高性能的环保型胶黏剂和胶合板提供理论依据,产品可用于建筑、家具以及交通工具等领域。
-
图 3 不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂黏度的影响(a),不同环氧树脂浓度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(b),不同温度对胶黏剂黏度的影响(c),不同物质掺杂对胶黏剂凝结时间的影响(d)
Figure 3. Effects of different substance doping on adhesive viscosity (a), effects of different epoxy resin concentrations on adhesive viscosity (b), effects of different temperatures on adhesive viscosity (c), and effects of different substance doping on condensation time (d)
表 1 偏高岭土的氧化物成分
Table 1 Oxide compositions of biotite kaolinite
成分 Component SiO2 Al2O3 TiO2 Fe2O3 P2O5 Na2O CaO 其他 Others 质量分数 Mass fraction 50.778% 44.703% 2.641% 0.634% 0.491% 0.206% 0.169% 0.378% 表 2 环氧树脂掺杂地质聚合物胶黏剂的物料配比(质量比)
Table 2 Material ratios of epoxy resin doped geopolymer adhesive (mass ratio)
编号 No. 物料配比 Material ratio G A∶B = 10∶15 GE A∶B∶E = 10∶15∶1.60 GC A∶B∶C = 10∶15∶0.32 GEC A∶B∶E∶C = 10∶15∶1.28∶0.32 GECS3 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶0.62∶0.16∶0.129 GECS6 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶1.28∶0.32∶0.134 GECS9 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶1.99∶0.50∶0.138 GECS12 A∶B∶E∶C∶S = 10∶15∶2.74∶0.69∶0.143 注:A代表偏高岭土,B代表碱激发剂,C代表聚醚胺固化剂,E代表环氧树脂,S代表硅烷偶联剂KH550。Notes: A represents metakaolin, B represents alkali-activator, C represents polyether amine curing agent, E represents epoxy resin, and S represents silane coupling agent KH550. -
[1] 马苏, 甄晋, 汪珈羽, 等. 苯丙乳液掺杂对地质聚合物木材胶黏剂性能的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(7): 131−139. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200019 Ma S, Zhen J, Wang J Y, et al. Effects of styrene-acrylic emulsion doping on the properties of geopolymer wood adhesives[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(7): 131−139. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20200019
[2] Ye H Z, Pan D W, Tian Z, et al. Preparation and properties of geopolymer/soy protein isolate composites by in situ organic-inorganic hybridization: a potential green binder for the wood industry[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 276: 123363. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123363
[3] Pan D W, Ye H Z, Wang X Q, et al. Modified geopolymer-based wood adhesive using waterborne polyurethane[J]. BioResources, 2020, 15(4): 7573−7585. doi: 10.15376/biores.15.4.7573-7585
[4] Pan D W, Zhang N, Li S C, et al. Dual-crosslinking network and pre-anchorage effect enable high-performance, low-cost, and eco-friendly geopolymer adhesive for the wood industry[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 414: 137570. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137570
[5] 李佼蔓. 木质素改性环氧树脂的制备及性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2023. Li J M. Studies on preparation and properties of lignin modified epoxy resin[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2023.
[6] 胡智荣. 环氧树脂加固钢筋混凝土剪力墙耐火性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. Hu Z R. Study on the fire performance of reinforced concrete shear walls strengthened with epoxy resin[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012.
[7] 李明, 郭岑, 黄坤, 等. 环氧树脂改善固井用偏高岭土地质聚合物的力学性能与机理[J]. 功能材料, 2023, 54(2): 2224−2230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.02.030 Li M, Guo C, Huang K, et al. Mechanical properties and mechanism of metakaolin geopolymer for cementing improved by epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2023, 54(2): 2224−2230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.02.030
[8] Wang J S, Wang D Y, Liu Y, et al. Polyamide-enhanced flame retardancy of ammonium polyphosphate on epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2008, 108(4): 2644−2653. doi: 10.1002/app.27522
[9] Zhang C S, Hu Z C, Zhu H J, et al. Effects of silane on reaction process and microstructure of metakaolin-based geopolymer composites[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 32: 101695. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101695
[10] Ignazio B, Antonio D, Veronica V, et al. Metakaolin-based geopolymers filled with volcanic fly ashes: FT-IR, thermal characterization, and antibacterial property[J]. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2023, 30(1): 1−10.
[11] 王胜. 基于香草醛的高性能阻燃环氧树脂的研究[D]. 宁波: 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所, 中国科学院大学, 2017. Wang S. Study on high-performance flame retardant epoxy resins based on vanillin[D]. Ningbo: Ningbo Institute of Material Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017.
[12] Çam Ç, Bal A, Güçlü G. Synthesis and film properties of epoxy esters modified with amino resins from glycolysis products of postconsumer PET bottles[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2015, 55(11): 2519−2525.
[13] Aurélie F , Julie H , Guillaume H , et al. Flow properties of MK-based geopolymer pastes: a comparative study with standard Portland cement pastes[J]. Soft Matter, 2014, 10(8): 1134−1141.
[14] 张大旺. 地质聚合物新拌浆体流变性、微结构与界面研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2020. Zhang D W. Study on the rheology, microstructure, and interface of geopolymer fresh pastes[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology-Beijing, 2020.
[15] Chen X, Zhu G R, Zhou M K, et al. Effect of organic polymers on the properties of slag-based geopolymers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 167: 216−224. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.031
[16] Zhang M, Xu H Y, Phalé Z A L, et al. Coating performance, durability and anti-corrosion mechanism of organic modified geopolymer composite for marine concrete protection[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 129: 104495.
[17] 祁一信, 李玲. 高韧性及快速固化环氧树脂体系的研究进展[J]. 热固性树脂, 2023, 38(6): 48−56. Qi Y X, Li L. Research progress of high toughness and rapid curing epoxy resin systems[J]. Thermosetting Resin, 2023, 38(6): 48−56.
[18] Luo S J, Wei J X , Xu W T, et al. Design, preparation, and performance of a novel organic-inorganic composite coating with high adhesion and protection for concrete[J]. Composites Part B, 2022, 234: 109695.
[19] Xiong G Y, Gu X L, Zhang H M. Preparation of epoxy resin-geopolymer (ERG) for repairing and the microstructures of the new-to-old interface[J]. Composites Part B, 2023, 259: 110731.
[20] Djobo J N Y, Tchakouté H K, Ranjbar N, et al. Gel composition and strength properties of alkali-activated oyster shell-volcanic ash: effect of synthesis conditions[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(9): 3159−3166. doi: 10.1111/jace.14332
[21] Tognonvi T M, Petlitckaia S, Gharzouni A, et al. High-temperature, resistant, argillite-based, alkali-activated materials with improved post-thermal treatment mechanical strength[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2020, 68(3): 211−219. doi: 10.1007/s42860-020-00067-9
[22] Wang S F, Ma X, He L, et al. High strength inorganic-organic polymer composites (IOPC) manufactured by mold pressing of geopolymers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 198: 501−511. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.281
[23] Qian X D, Song L, Bihe Y, et al. Organic/inorganic flame retardants containing phosphorus, nitrogen and silicon: preparation and their performance on the flame retardancy of epoxy resins as a novel intumescent flame retardant system[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 143(3): 1243−1252. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.11.029
[24] Wei J, Long F J, Jin S P. Synthesis of a novel phosphorus-nitrogen-containing intumescent flame retardant and its application to fabrics[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 27(7): 40−43.
[25] Shi C J, Jiménez F A, Palomo A. New cements for the 21st century: the pursuit of an alternative to portland cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2011, 41(7): 750−763. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.03.016
[26] 叶翰舟. 云杉木材与地质聚合物复合界面的构造解析与调控[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2023. Ye H Z. Structure analysis and control of interface between spruce wood and geopolymer[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2023.
[27] Wang Y, Zhang H Y, Zheng C W, et al. Study of metakaolin geopolymer composites reinforced by clean broom-like bristle bamboo fibers[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 25(1): 3507−3521.



 下载:
下载: