Estimation of relative permittivity of tree root system based on ground penetrating radar
-
摘要:目的
本研究提出一种基于雷达波信号和树木根系参数的估算方法,以实现树木根系相对介电常数的定量估算。
方法首先,仿真模拟雷达波在不同半径、不同相对介电常数的树木根系下的传播路径,并通过正演分析获得探地雷达图像中双曲线顶点处的A-scan曲线;然后,提取A-scan曲线中与根系相对介电常数关联的目标振幅参数ΔF;最后,结合土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度,建立相对介电常数估算的数据集。分别基于偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)模型、反向传播(BP)神经网络模型和粒子群优化反向传播(PSO-BP)神经网络建立估算模型,并对比分析这3种模型的估算精度。
结果(1)在仿真实验中,PSO-BP神经网络估算模型的均方根误差、平均绝对误差分别为0.701、0.255,R2为0.990,各指标均优于PLSR和BP神经网络估算模型。(2)在实地预埋实验中,PSO-BP神经网络估算模型的估算精度均优于PLSR和BP神经网络估算模型,其最大绝对误差和整体平均相对误差分别为3.16和10.88%。
结论利用本研究提取的目标振幅参数ΔF、土壤相对介电常数、根系半径和根系深度建立的数据集,结合PSO-BP神经网络估算模型,能够实现对树木根系相对介电常数的准确估算。这对于评估树木根系的生长和健康状况具有重要意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to achieve the quantitative estimation of the relative permittivity of tree root system, an estimation method based on radar wave signals and tree root system parameters was proposed.
MethodFirstly, the propagation paths of radar waves in the root system of trees with different radii and relative permittivity were simulated, and the A-scan curves at the hyperbolic vertices in the ground-penetrating radar images were obtained through orthogonal analysis. Then, the target amplitude parameter ΔF, which was related to the relative permittivity of root system was extracted from A-scan curves. Finally, the dataset for relative permittivity estimation was established by combining the relative permittivity of soil, the radius of root system, and depth of root system. The estimation models were established based on partial least squares regression (PLSR), back propagation (BP) neural network, and particle swarm optimization-back propagation (PSO-BP) neural network, respectively, and the estimation accuracies of the three models were compared and analyzed.
Result(1) In the simulation experiment, the root mean square error and average absolute error of PSO-BP neural network estimation model were 0.701, 0.255, and the R2 was 0.990, and all indexes were better than PLSR and BP neural network estimation model. (2) In the field pre-embedding experiment, the estimation accuracies of PSO-BP neural network estimation model were all better than those of PLSR and BP neural network estimation models, with a maximum absolute error of 3.16 and the whole average relative error of 10.88%.
ConclusionUsing the dataset established by target amplitude parameter ΔF, soil relative permittivity, root radius and root depth extracted in this study, combined with PSO-BP neural network estimation model, an accurate estimation of the relative permittivity of root system of trees can be achieved, which is of great significance for assessing the growth status and health of tree root system.
-
Keywords:
- radar /
- model analysis /
- permittivity /
- nondestructive examination /
- estimation; neural networks
-
根系在生态系统中扮演着重要的角色,是森林碳–氮–水循环的重要驱动力,既可以帮助树木在生长发育过程中传输、贮存所需的水和营养物质,也是支撑和固定树干的重要器官[1]。为深入了解树木根系的生理特性及其在不同环境条件下的表现,树木根系的电学特性成为一个重要的研究方向。相对介电常数是表征材料介电性质或极化性质的物理参数,是介电常数与真空介电常数之比[2],主要受含水量、电磁波频率和温度等因素的影响[3]。相对介电常数反映了材料存储电能的能力,可以提供根系健康状态、含水量和生理功能等重要信息。在树木根系发生病害、干旱的情况下,及时采取措施,对于林业管理和水资源优化具有重要意义。
根系通常位于地表以下,受限于目前的根系观测和研究方法,根系的研究滞后于地上部分的研究[4]。挖掘法、土钻法等传统的植物根系探测方法复杂繁琐且具有破坏性,容易受到实验场地限制,上述原因使传统方法探测结果的准确性受到影响,因此根系相对介电常数等相关研究存在一定局限性[5]。探地雷达(ground penetrating rader,GPR)是一种用于探测地下物质结构与分布技术的工具,具有非侵入性、快速便捷、操作简单等优点[6]。近年来,探地雷达在根系方面的研究主要集中在生物量估测、直径预测、根系三维结构重建等方面,推动了根系生态学领域的研究。目前,关于树木根系相对介电常数的研究有限。Paz等[7]首次运用Power Law模型、Maxwell–Garnett模型和Polder van Santen模型进行根系介电常数的估测,实验结果证明:在稀疏的混合物质中,Maxwell–Garnett模型的预测结果更加准确,但计算较为复杂。Mihai等[8]首次使用矢量网络分析仪在50 MHz ~ 3 GHz频率范围内直接测量新鲜切割的树木根段的相对介电常数,将结果作为gprMax开源软件正演模拟的输入,但其仅将重点放在辅助解译GPR数据方面,并未建立雷达波图像与树木根系相对介电常数的关系。白雪等[9]采用衍射层析成像算法,通过引入并矢格林函数建立积分表示,将目标散射数据反演成电性参数剖面,但缺乏实测数据且反演精度不高。李怡娜等[10]使用探地雷达探究在不同含水率、温度、外电场频率下活立木介电常数的变化情况,结果表明:介电常数与含水率、环境温度成正相关,与外电场频率成负相关。肖夏阳等[11]采用900 MHz介质耦合树木雷达对柳木试件进行断层扫描,并采用层剥反演法对树木内部不同介质进行介电常数反演。树干介电常数的相关研究能为树根相对介电常数的估算提供一些方法和思路,但仍存在树木根系相对介电常数定量研究较少且精确度较低等问题。
针对以上问题,本研究提出一种基于探地雷达的树木根系相对介电常数无损估算方法。该方法首先利用gprMax设计仿真实验提取双曲线顶点处A-scan振幅参数并构建数据集;然后基于偏最小二乘回归(partial least squares regression,PLSR)模型、反向传播(back propagation,BP)神经网络模型和粒子群优化反向传播(particle swarm optimization-back propagation,PSO-BP)神经网络模型进行树木根系相对介电常数估算;最后通过仿真数据和实地预埋数据验证该估算方法的准确性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据集构建
为确保数据集的精确度和数量,本研究利用gprMax仿真软件模拟根系和土壤参数生成仿真数据集。许多研究者[12−13]已经通过理论和实践验证了利用gprMax进行仿真模拟的可行性和准确性。首先将根系和土壤的参数信息输入gprMax软件构建正演模型;然后选择影响根系相对介电常数估算的关键参数;最后提取关键参数的目标振幅,构建数据集。
1.1.1 仿真参数设置
在树木根系与土壤参数设置方面,郭立等[14]利用混合物理模型估算出部分根系相对介电常数为2.78 ~ 35.04。徐爱英等[15]测出风干的土壤相对介电常数为3 ~ 4,含水土壤的相对介电常数为3.5 ~ 35.5。Liang等[16]在利用gprMax仿真软件和BP神经网络估算根径中提出:当根系相对介电常数小于土壤相对介电常数时,gprMax模拟扫描的根系双曲线不清晰,所以只选取根系相对介电常数大于土壤相对介电常数的组合。Bi[17]和李光辉[18]等在使用探地雷达进行树根参数估算的研究中,均在gprMax软件中使用均质土壤简化土壤结构进行模拟,并通过实地实验证明了这种简化土壤模型的可行性。这些研究为仿真实验中根系和土壤相对介电常数的设置提供参考。
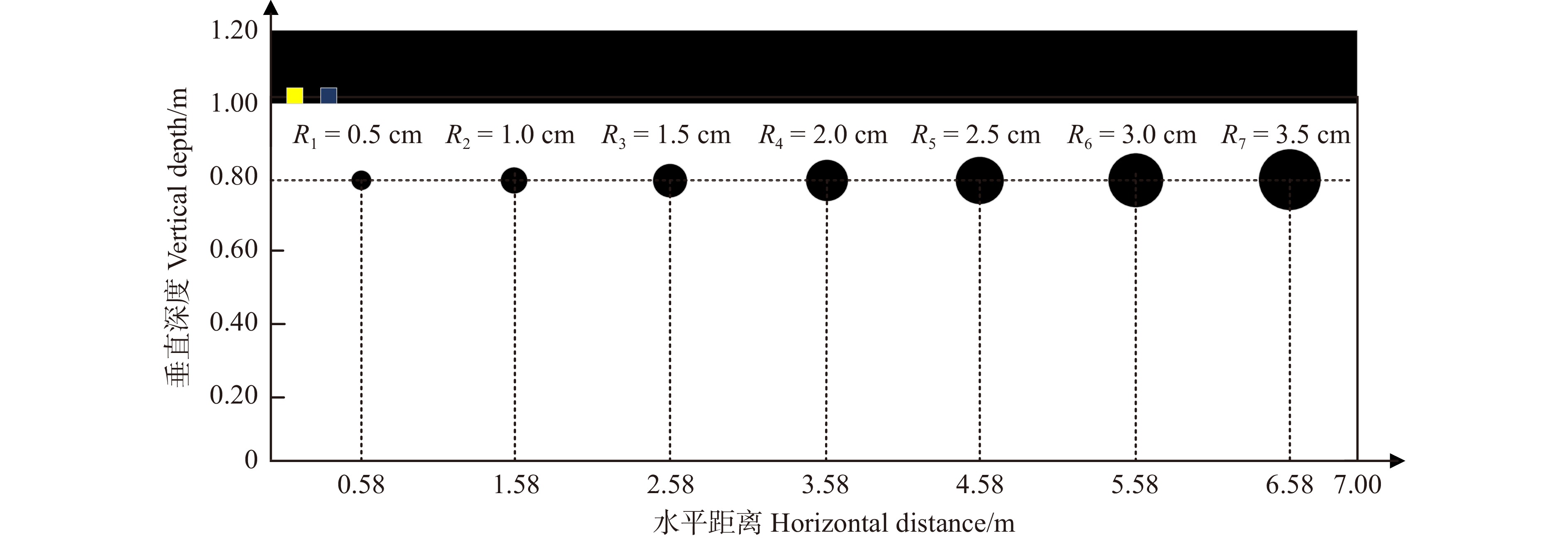
仿真模型的具体参数设置如下所述。选取中心频率为1.5 GHz的ricker波[19]为震源子波,探地雷达沿垂直根系方向进行扫描,每次移动0.02 m,移动340次。根系相对介电常数设置为5 ~ 35(以间隔2递增),土壤相对介电常数设置为3 ~ 33(以间隔2递增),使用不同相对介电常数的根系和土壤进行组合,共计136种根–土介电常数组合,每种组合方式下设置3种埋深(10、20、30 cm),每种埋深下设置7个半径为0.5 ~ 3.5 cm的根系(以间隔0.5 cm递增),得到408个仿真模型样本(图1)。
![]() 图 1 正演模型黑色矩形部分代表空气,白色矩形部分代表土壤,黑色圆圈代表根系(一共有7个根,其中R1,R2,···,R7表示根系的半径),一对黄色和蓝色矩形分别代表探地雷达的发射天线和接收天线,沿图中左侧向右移动完成模拟扫描。The black rectangle represents air, the white rectangle represents soil, the black circle represents root system (there are 7 roots in total, where R1, R2, ···, R7 denote the radius of roots), and a pair of yellow and blue rectangles represent the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna of ground-penetrating radar, respectively, and the simulated scanning is completed by moving along the left-hand side of the figure to the right-hand side.Figure 1. Orthotropic model
图 1 正演模型黑色矩形部分代表空气,白色矩形部分代表土壤,黑色圆圈代表根系(一共有7个根,其中R1,R2,···,R7表示根系的半径),一对黄色和蓝色矩形分别代表探地雷达的发射天线和接收天线,沿图中左侧向右移动完成模拟扫描。The black rectangle represents air, the white rectangle represents soil, the black circle represents root system (there are 7 roots in total, where R1, R2, ···, R7 denote the radius of roots), and a pair of yellow and blue rectangles represent the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna of ground-penetrating radar, respectively, and the simulated scanning is completed by moving along the left-hand side of the figure to the right-hand side.Figure 1. Orthotropic model1.1.2 数据集参数选择
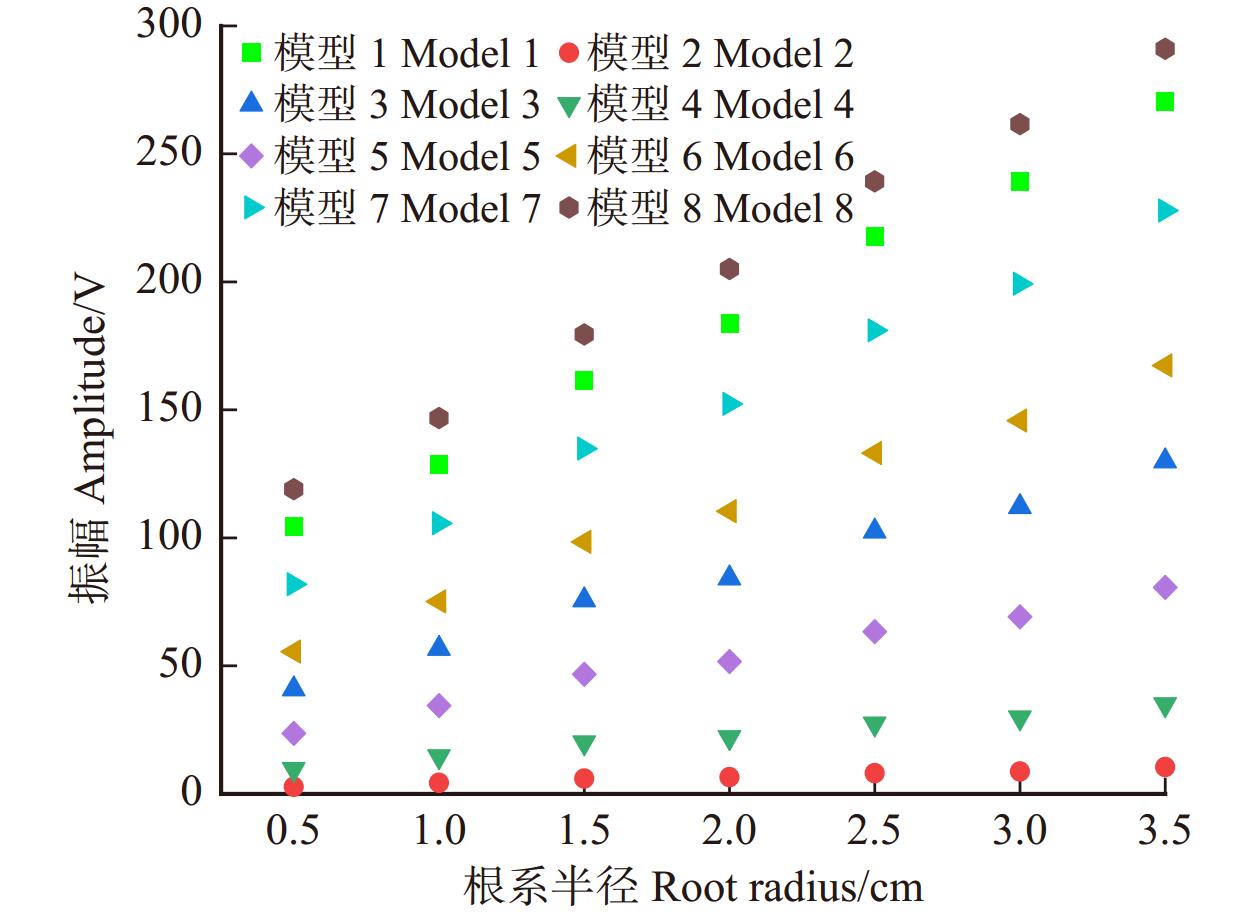
Wang等[20]利用物理机制说明回波信号中目标的振幅强度、埋藏深度和背景介质的相对介电常数是影响目标相对介电常数估算结果的主要参数,Zakarewicz等[21]研究表示根系相对介电常数会改变振幅强度从而影响根径的估算。然而我们在仿真实验中发现,目标振幅强度会随根系半径增大而增大(图2),这表明根系半径也会通过影响振幅强度影响目标相对介电常数的估算,所以半径也是影响相对介电常数估算的主要因素。因此,选用振幅强度与土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度作为输入参数,根系相对介电常数作为输出参数构建数据集。
1.1.3 目标振幅获取
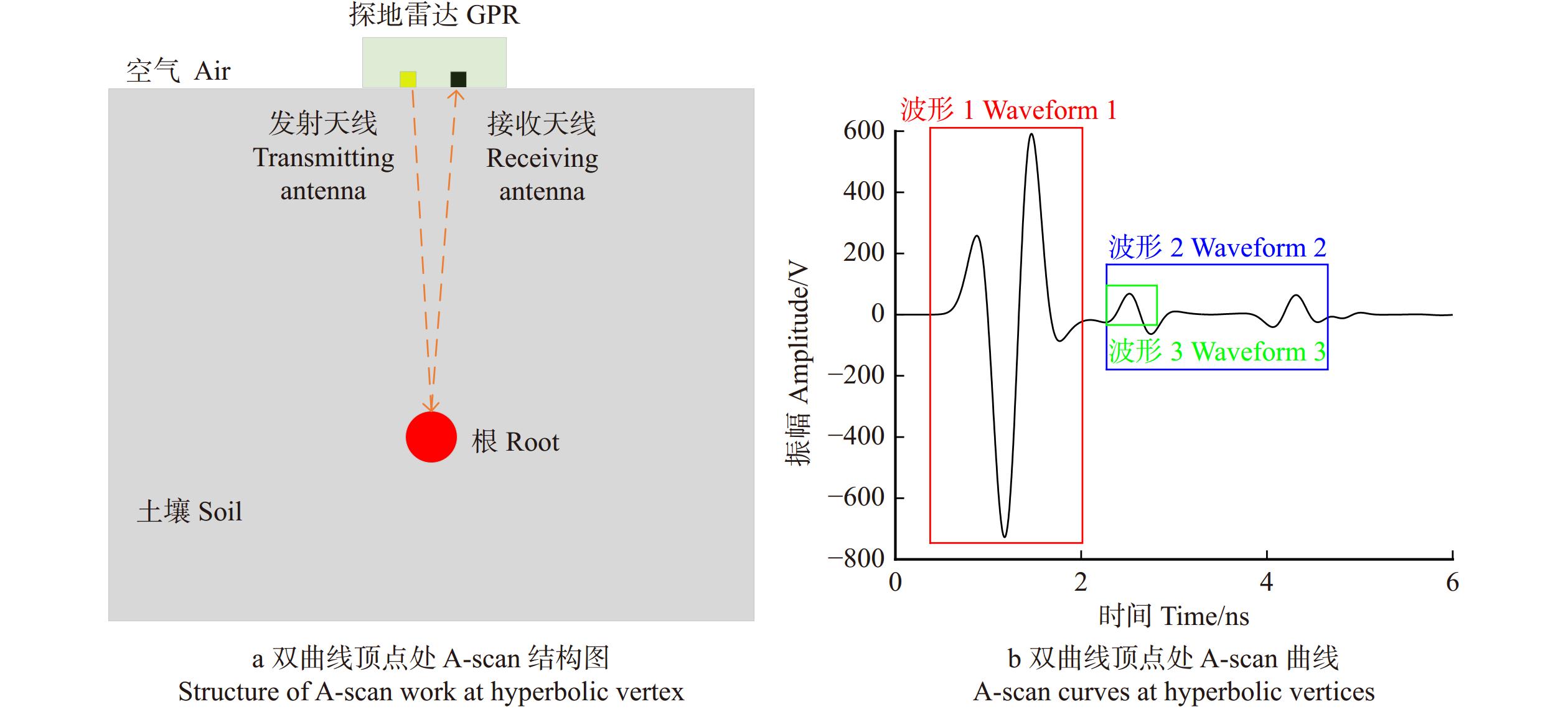
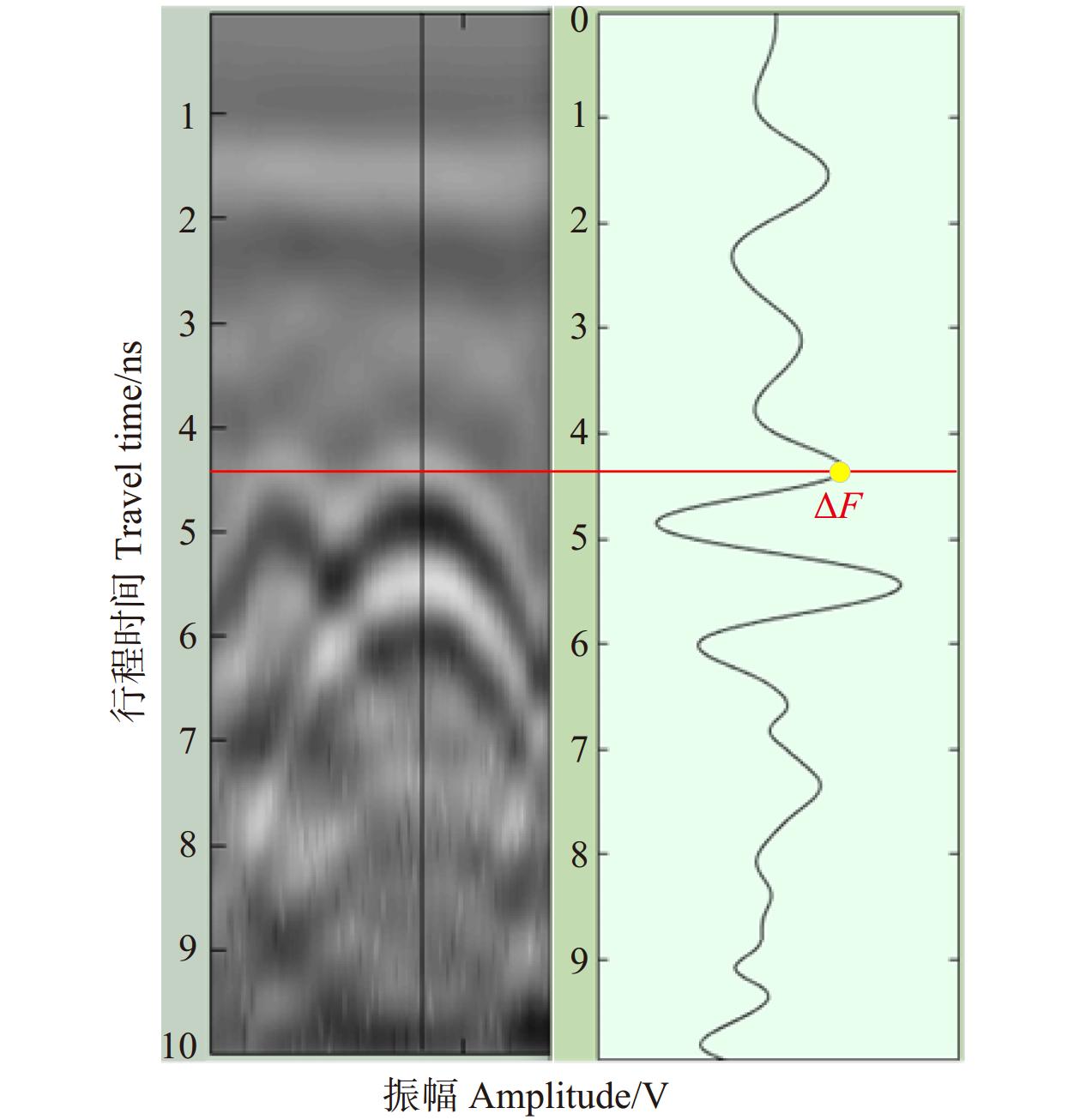
双曲线的顶点可以表示根系的位置[22],通过提取双曲线顶点处的A-scan曲线可以了解雷达波的传播情况,得到关于根系位置、深度、振幅强度等信息。双曲线顶点处的A-scan获取方式如图3a所示。按图3a所示结构在408个仿真模型样本中均生成7条A-scan曲线,总共获得2 856条A-scan曲线,生成的A-scan曲线如3b所示。在图3b中用矩形框标出几个主要的波形,这些波形初步反映了雷达波在根系和土壤中的传播情况。
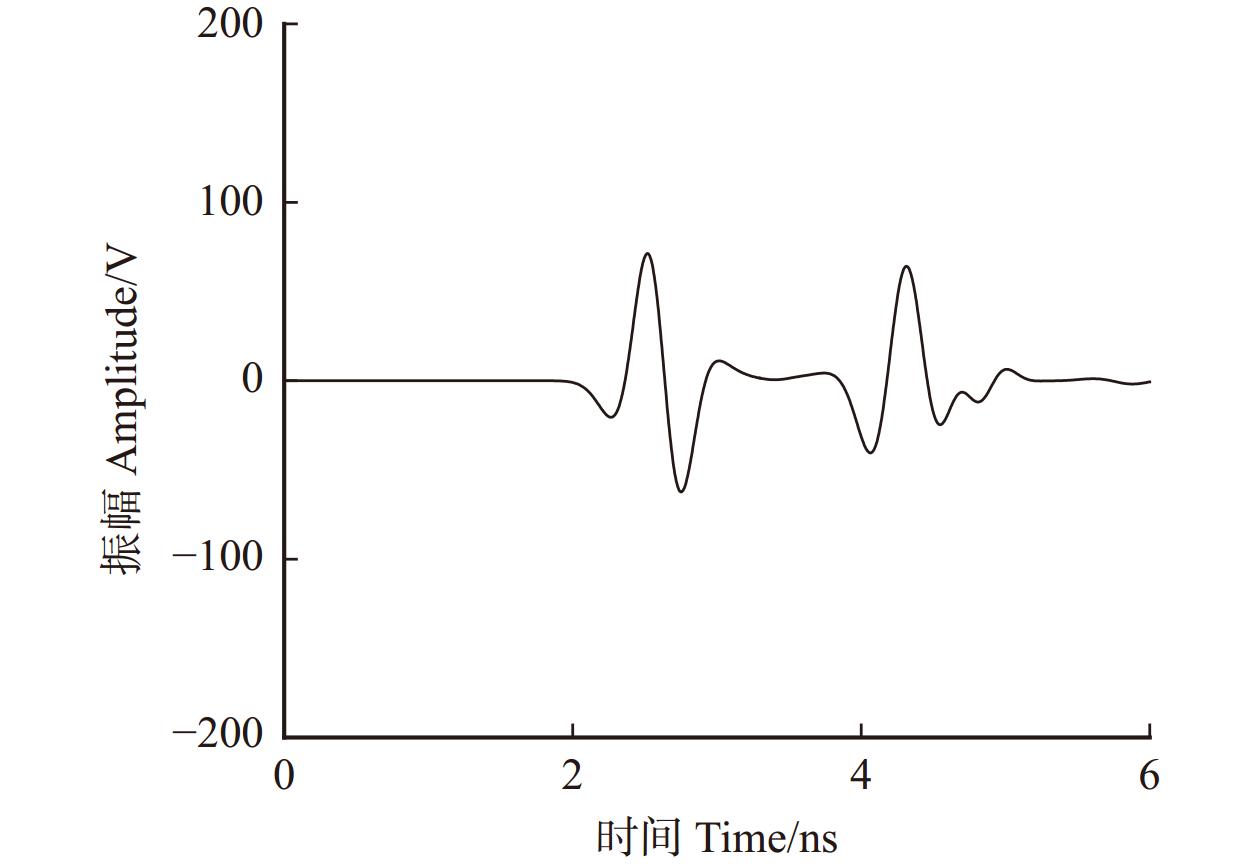
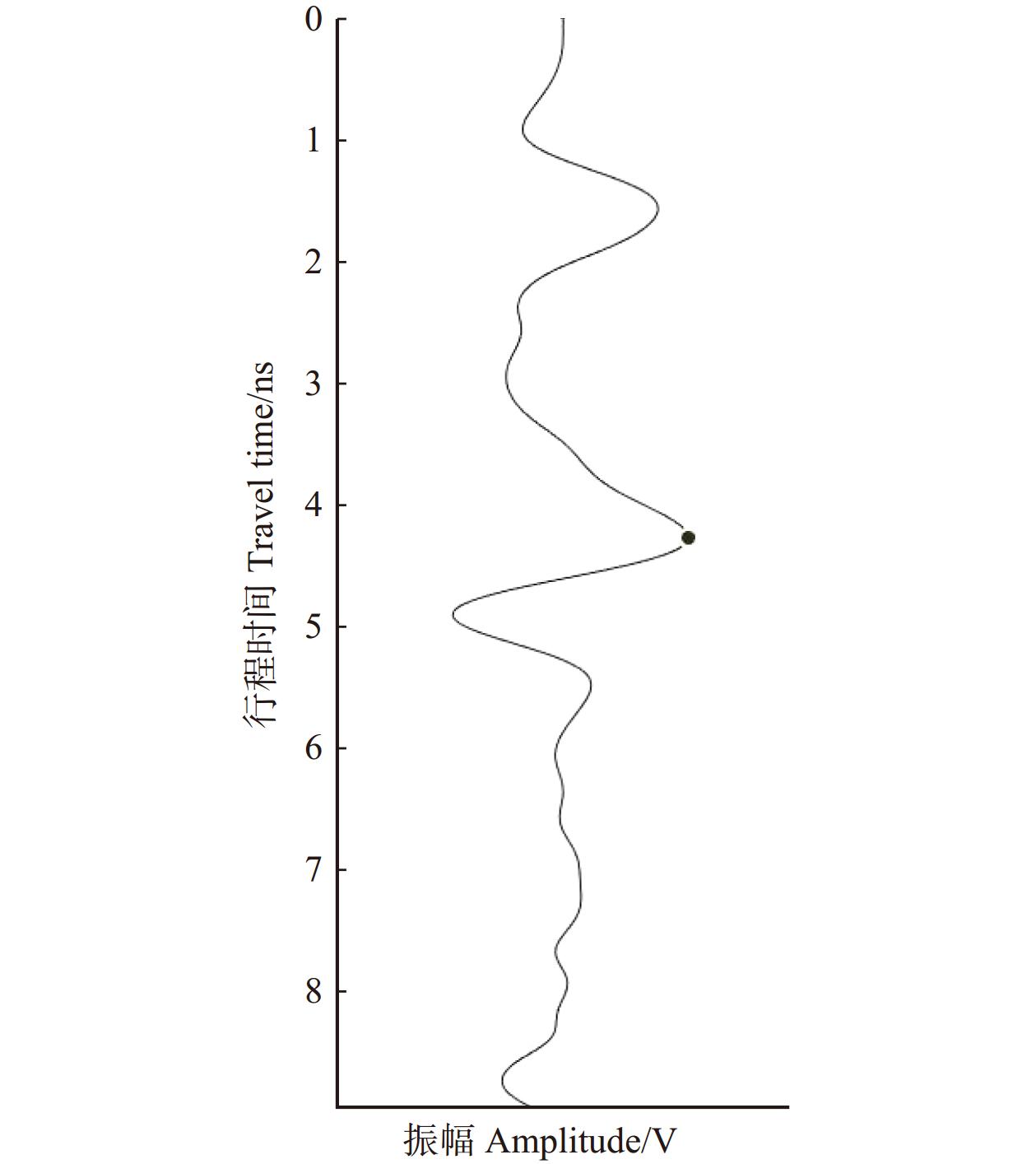
为了进一步了解波形的具体含义,在不改变雷达、模型参数的情况下,去除模型中树根进行扫描,得到雷达波对土壤的A-scan曲线。将含根A-scan曲线与不含根A-scan曲线相减,即为树根在雷达波扫描下的振幅波动曲线(图4)。将图4与图3b中的A-scan曲线进行对比,能够明确每个波形的具体代表意义。
对比图3b和图4,可以发现波形1是由地表反射引起的,波形2则是电磁波在穿过根系时由于根系和土壤相对介电常数差异引起的反射波强度的变化。将波形3波峰振幅值定义为目标振幅ΔF。所有双曲线顶点处A-scan数值导出并提取ΔF,除去异常值后得到2 842组数据,与土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度共同构建数据集。
1.2 模型建立与评估
1.2.1 偏最小二乘回归模型
PLSR是一种多元统计方法,主要研究一个因变量与多个独立变量之间的相关关系,可以用来解决多元回归分析中自变量之间的多重相关性问题,其主要目的是建立一个线性模型[23],将目标振幅、土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度等参数代入线性模型中,选取均方根误差最小的模型作为最终模型,具体见式(1)。
εroot=0.85ΔF+0.91εsoil+0.42r−0.22d (1) 式中:εroot代表根系相对介电常数,ΔF、εsoil、r、d分别代表目标振幅、土壤相对介电常数、根系半径和根系深度。
1.2.2 BP神经网络模型
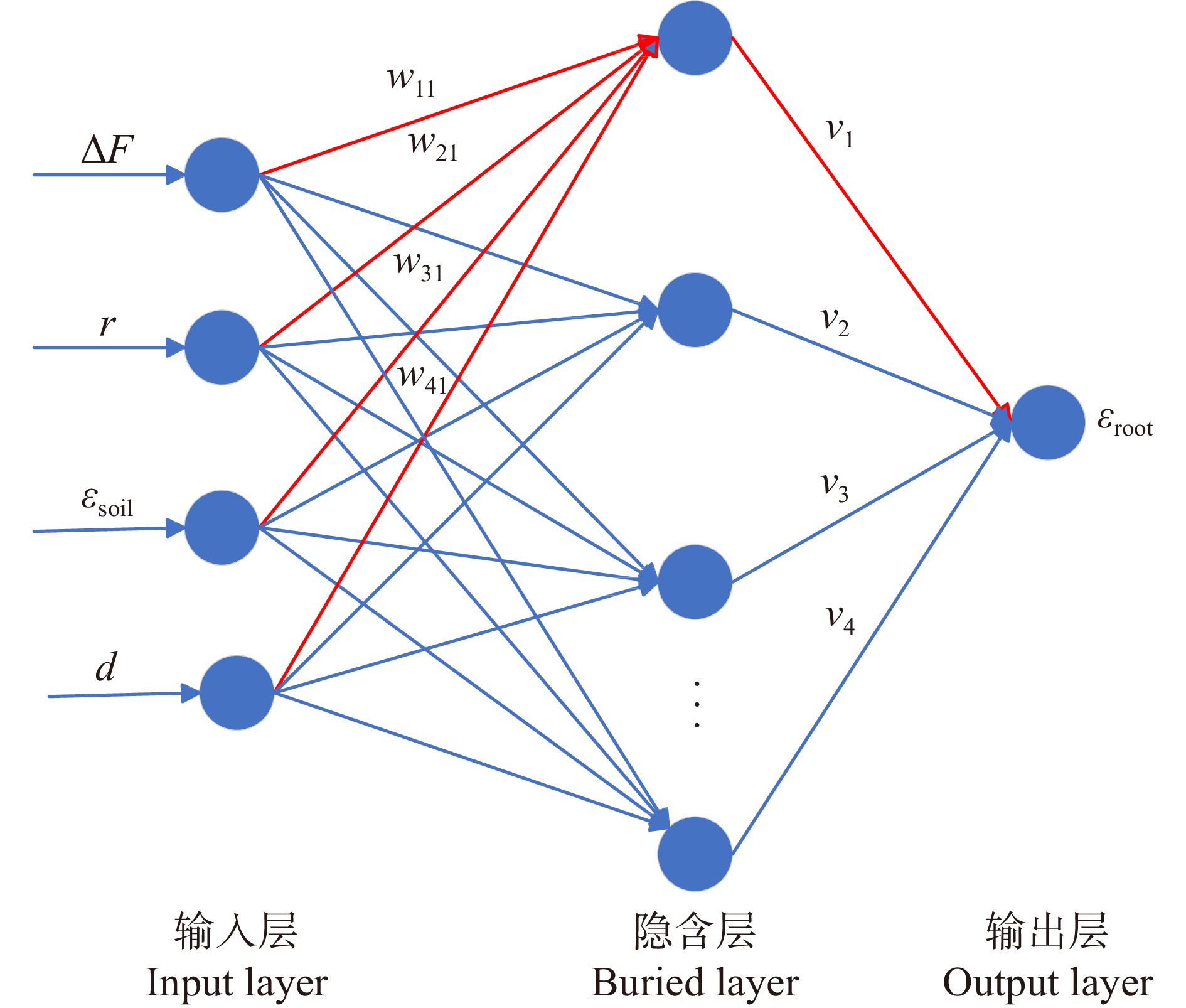
树木根系相对介电常数估算模型采用3层(输入层、隐含层、输出层)BP神经网络建立。将ΔF、εsoil、r和d这4个参数设置为输入参数,εroot设置为输出参数。数据集按7∶2∶1分为训练集、验证集和测试集。输入、输出层神经元数量为4和1,隐含层神经元数量为35。设置输入层到隐含层激活函数为logsig,隐含层到输出层激活函数为purelin。训练次数设为8 000,学习速率为0.1,当输出误差满足0.000 1时,停止训练,BP神经网络结构如图5所示。
![]() 图 5 BP神经网络结构ΔF、r、εsoil、d分别为目标振幅、根系半径、土壤相对介电常数、根系深度,εroot为根系相对介电常数,wij和vj为层间权重参数(i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4)。ΔF, r, εsoil and d are the target amplitude, root radius, soil relative permittivity, and root depth, respectively. εroot is root relative permittivity, and wij and vj are the interlayer weighting parameters (i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4).Figure 5. BP neural network structure
图 5 BP神经网络结构ΔF、r、εsoil、d分别为目标振幅、根系半径、土壤相对介电常数、根系深度,εroot为根系相对介电常数,wij和vj为层间权重参数(i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4)。ΔF, r, εsoil and d are the target amplitude, root radius, soil relative permittivity, and root depth, respectively. εroot is root relative permittivity, and wij and vj are the interlayer weighting parameters (i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4).Figure 5. BP neural network structure1.2.3 PSO-BP神经网络模型
在BP神经网络模型基础上,采用粒子群优化算法实现对BP神经网络权值阈值的优化。在粒子群优化算法中,粒子通过搜索空间来寻找最优解,其速度和位置的更新受到个体历史最佳位置和群体历史最佳位置的引导[24]。通过不断迭代更新,粒子群逐渐趋向于全局最优解,获得适应度值最优的初始权重和阈值,可以弥补BP神经网络收敛速度慢、易陷入局部极值等缺陷,从而得到满足精度要求的输出值[25]。
1.2.4 模型评估
在建立PLSR模型、BP神经网络模型、PSO-BP神经网络模型后,对模型在仿真数据上的估算效果进行对比分析。首先,通过绘制回归曲线,直观地比较各相对介电常数估算模型的估算性能。随后,使用均方根误差 (root mean square error,RMSE)、平均绝对误差(mean absolute error, MAE)、决定系数(R2)等参数作为模型评估指标,对模型精度进行量化比较,具体见式(2 ~ 4)。最后引入Bland-Altman图,以差异值(diff)为纵坐标,平均值(mean)为横坐标,平均差异值加减1.96个标准差(standard deviation,SD)为限值,进一步了解估算值与真实值之间的一致性和偏差情况。通过这一系列分析,能够更全面地评估并比较3种模型在仿真数据上的估算性能。
RMSE=√1nn∑i=1(yi−ˆyi)2 (2) MAE=1nn∑i=1|yi−ˆyi| (3) R2=1−n∑i=1(yi−ˆyi)2/n∑i=1(yi−yt)2 (4) 式中:yi表示样本i的实测值,ˆyi表示样本i的估算值,yt表示所有样本的平均值,n为样本数。
1.3 模型实地验证
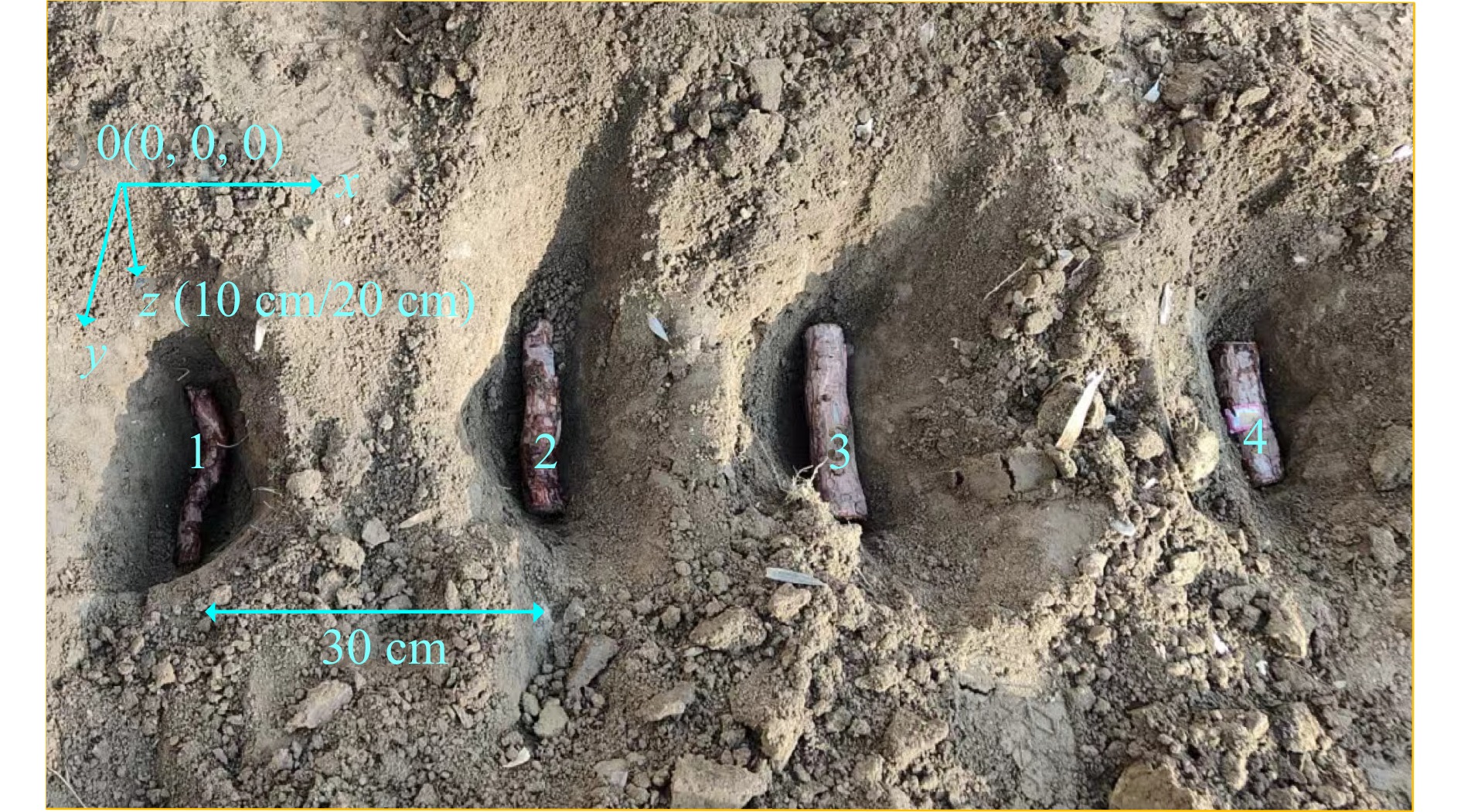
为进一步验证本文估算方法的有效性,采用人工预埋方式进行实地数据采集,预埋实验已经广泛应用于模型有效性的验证[18,26]。该实验使用的探地雷达为TRUTM(tree radar unit,Tree Radar Inc,Silver Spring,MD,USA),天线频率为1.5 GHz。实验场地位于北京市海淀区北京林业大学校外实验基地(40°00′58″N,116°21′15″E),属于温带大陆性季风气候。研究区土壤类型为粉砂壤土(粉粒粒径在0.002 ~ 0.250 mm之间),土壤密度为1.52 g/cm3,孔隙度为41.7%。实验前一周均未发生降雨,土壤含水量稳定且适用于探地雷达检测。
预埋实验选取新鲜的松树(Pinus sp.)根作为研究对象,使用游标卡尺多次测量树根半径,并计算平均值;根系相对介电常数在相同温度、相同频率下由基于驻波率原理的介电常数测量仪[27]获得。根参数如表1所示。
表 1 松树根系样本参数Table 1. Sample parameters of pine root system树根标号
Tree root No.树根长度
Tree root length/cm半径
Radius/cm相对介电常数
Relative permittivity1 15 1.27 12.65 2 15 1.83 13.03 3 15 2.07 17.40 4 15 2.64 16.45 根系预埋设置10和20 cm两组深度实验(图6),两根间隔30 cm。考虑到在预埋实验过程中改变了土壤的原有结构,其相对介电常数随深度增加的特性也随之改变。而且在实际情况下,地表20 cm以内的土壤相对介电常数相差不大,所以采用土壤相对介电常数平均值来表示预埋区域的土壤相对介电常数。在实验中首先使用体积为100 mL的采土器采集多个土壤样本,及时进行质量测试。随后,将土壤样本放入预热至150 ℃的烘箱中,直至质量恒定,记录土壤的干质量。然后计算出土壤体积含水率,通过土壤相对介电常数模型[28]估算土壤相对介电常数,具体见式(5)。
εsoil=3.03+9.3θv+146θ2v−76.7θ3v (5) 式中:εsoil为土壤相对介电常数,θv为土壤体积含水率。
预埋好后使用探地雷达沿垂直根系方向进行扫描,将实地预埋实验中雷达扫描图像进行目标振幅参数ΔF的提取,以图7为例详细讲述。首先用matgpr软件将探地雷达生成的dzt文件转化为图像,可以清晰地看到双曲波生成。然后使用matgpr软件中“Adjust Signal Position”功能将光标置于双曲波顶点处获得A-scan曲线,为进一步确定目标波峰的位置,将B-scan图像和A-scan曲线中雷达波传播时间对齐,然后在B-scan曲线中沿双曲线顶点绘制直线,找到直线与A-scan曲线的交点,判断其是否为波峰,若为波峰,则其交点横坐标为ΔF。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 仿真结果分析
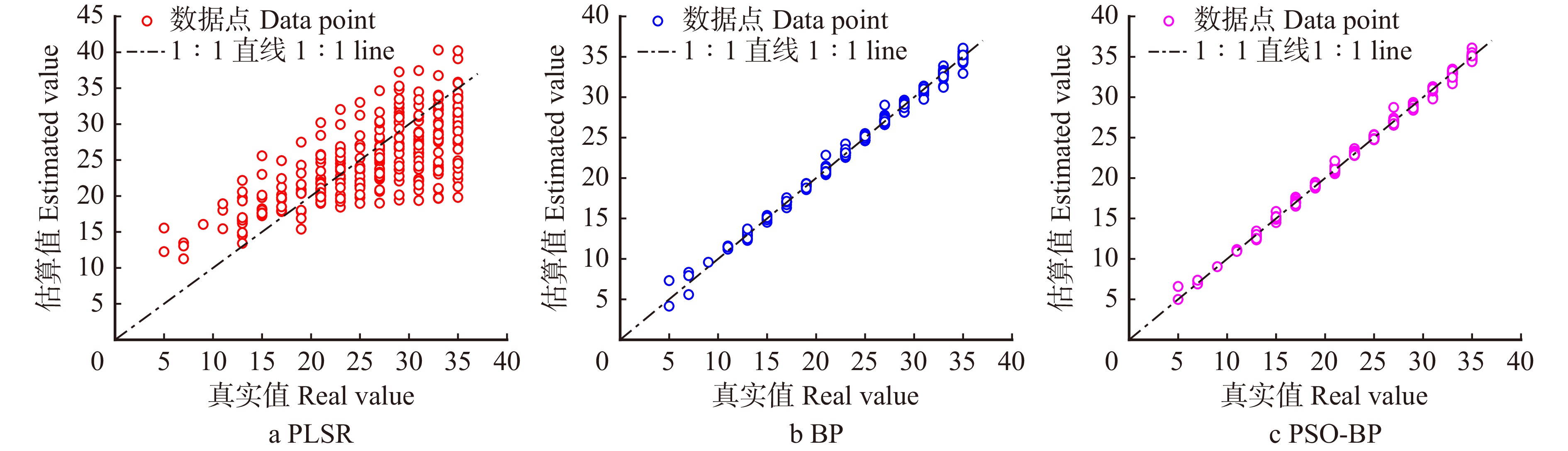
根系相对介电常数估算模型回归曲线(图8)显示:PLSR模型数据点在1∶1线周围最分散,尽管整体趋势与真实值一致,但存在明显的偏离。这表明PLSR模型估算能力不足。与之相比,BP神经网络模型和PSO-BP神经网络模型数据点集中在1∶1线周围,且PSO-BP模型数据点更贴合1∶1线。这表明PSO-BP神经网络模型的整体估算效果更好,其估算结果更接近真实值。
模型评估指标(表2)显示:PLSR模型R2为0.482,远小于BP神经网络模型和PSO-BP神经网络模型,且MAE最大,这表明PLSR模型的估算效果最差。相比之下,BP和PSO-BP神经网络模型具有不错的估算效果,其R2均大于0.95,但PSO-BP神经网络模型在各项指标上均略优于BP神经网络模型,这表明PSO-BP神经网络模型在估算精度和性能上更出色。
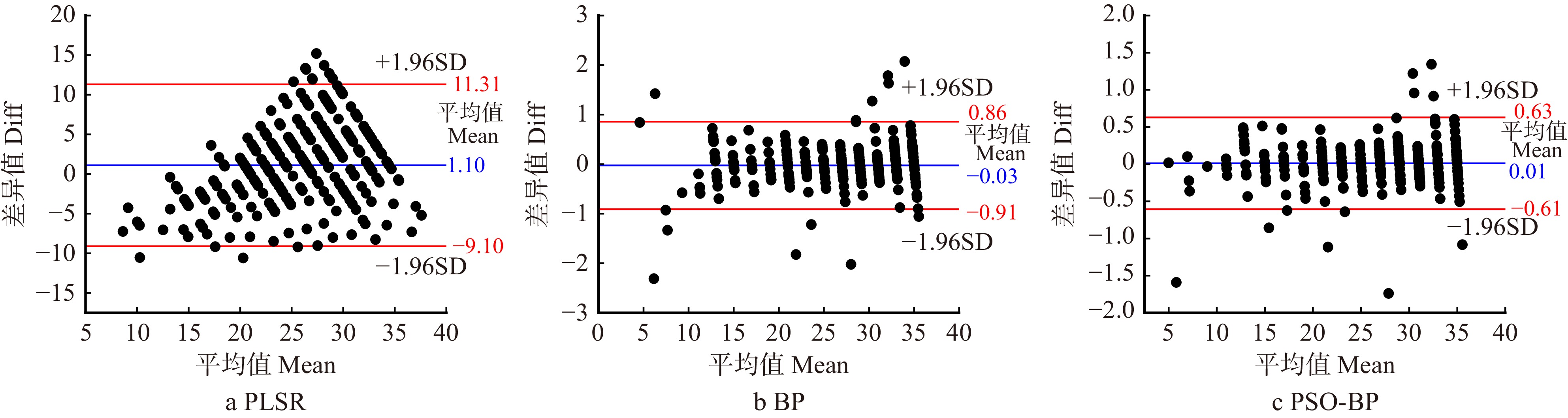
表 2 根系相对介电常数估算模型评估指标Table 2. Evaluation indicators for the estimation model of relative permittivity of root system模型 Model RMSE MAE R2 PLSR 0.719 4.240 0.482 BP 0.764 0.341 0.989 PSO-BP 0.701 0.255 0.990 PLSR模型的差异平均值为1.10,这表明该模型的估算存在系统性偏差;且限值范围为−9.10 ~ 11.31(图9a),进一步凸显了在多个条件下模型估算与真实值之间的差异。BP神经网络模型的差异平均值为−0.03,表明该模型整体上具有较小的系统性偏差;限值范围为−0.91 ~ 0.86,大部分数据集中在较小的差异范围内(图9b),这表明BP模型在整体上能够准确估算真实值,并且表现相对稳定。PSO-BP模型的差异平均值为0.01,且限值范围为−0.61 ~ 0.63(图9c),这说明PSO-BP模型在整体上表现出较好的一致性,其估算值与真实值之间的偏差相对较小;且大部分数据都集中在较小的差异范围内,证明PSO-BP模型性能相对稳定。
综合考虑,PSO-BP模型在多方面均表现出较好的性能,BP模型次之,PLSR模型需要进一步改进。
2.2 预埋结果分析
在目标振幅提取过程中,应用matgpr软件提取双曲波顶点处的A-scan曲线,发现实测图A-scan曲线(图10)和仿真A-scan曲线存在一定差异。差异的可能原因包括:预埋实验过程中土壤紧实度发生改变,造成地表反射波形变化;实地和仿真条件下地下土壤成分、水分等存在差异,导致了电磁波在传播过程中发生了反射、散射、吸收等不同的现象;在预埋实验中尽可能保持地形平整,但仍然存在坡度变化等因素,这些也会对雷达波的传播和反射产生影响。
依次对1~ 4号根进行ΔF参数提取,将从实地实验中提取出的ΔF、εsoil和测量得到的r、d、εroot参数导入PSO-BP神经网络训练好的模型,参数和根系相对介电常数估算结果如表3所示。表3显示目标振幅ΔF随深度增加整体呈下降趋势,这与雷达波在土壤传播过程中产生能量损耗的理论相一致。PLSR模型在10和20 cm深度处的平均相对误差则分别为34.77%和39.06%,最大绝对误差和整体平均相对误差分别为11.70和36.92%;BP神经网络模型在10和20 cm深度处的平均相对误差分别为14.60%和13.75%,最大绝对误差和整体平均相对误差分别为3.70和14.18%;PSO-BP神经网络模型在10和20 cm深度处的平均相对误差分别为10.84%和10.93%,最大绝对误差和整体平均相对误差为3.16和10.88%。
表 3 实地实验估算结果Table 3. Estimated results from field experiments模型
Model深度
Depth/cm树根标号
Tree root No.ΔF/V r/cm 真实值
Real value估算值
Estimated value绝对误差
Absolute error平均相对误差
Average relative error/%PLSR 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 23.13 10.48 34.77 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 22.06 9.03 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 23.27 5.87 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 22.72 6.27 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 24.35 11.70 39.06 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 23.13 10.10 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 24.95 7.55 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 25.03 8.58 BP 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 14.02 1.37 14.60 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 13.66 0.63 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 13.88 3.52 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 12.75 3.70 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 14.50 1.85 13.75 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 14.35 1.32 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 14.99 2.41 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 13.75 2.70 PSO-BP 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 14.06 1.41 10.84 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 12.95 0.08 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 14.24 3.16 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 14.24 2.11 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 14.80 2.15 10.93 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 14.16 1.13 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 15.66 1.74 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 14.71 1.74 注:土壤相对介电常数εsoil为12.76。Note: the relative permittivity of soil (εsoil) is 12.76. 实验结果表明:PSO-BP神经网络模型相比其他模型具有更高的准确性,而且在不同深度下的平均相对误差变化不显著,这表明此模型能够在不同深度下保持稳定的估算性能,具有较好的稳定性。尽管该方法存在一定的误差,但具有一定的可行性。
3. 讨 论
3.1 模型对比分析
PSO-BP神经网络模型在仿真和实地数据中相较于其他两种模型估算效果较好,其原因是PSO-BP模型结合了PSO算法的全局搜索能力和BP算法的局部搜索能力,能更好地拟合数据和优化模型参数,通过多层神经网络学习数据的非线性特征,从而更好地建模复杂的数据关系。而PLSR模型是一种基于线性回归的特征提取方法,如果数据之间存在非线性关系,PLSR可能无法充分捕捉这种关系。除此之外,PLSR模型对于多重共线性较为敏感。在存在高度相关自变量的情况下,PLSR可能会面临数值不稳定性和模型参数不确定性的问题,影响模型的可靠性和解释性。BP神经网络模型存在局部最优解问题,初始权重的选择对BP神经网络的性能影响较大,不恰当的初始权重可能导致模型收敛缓慢或者陷入局部最优解。
3.2 实验误差分析
实验误差将从仿真实验、输入参数以及实地实验等方面进行探讨。这些分析有助于深入理解根系相对介电常数估算过程中的误差来源和影响因素。
3.2.1 仿真实验方面
在仿真实验方面,模型训练建立在大量仿真数据基础上,有效排除环境、地形等干扰因素的影响。在这种理想环境下进行训练能够获得不错的估算结果,但仍然存在一定的局限性。具体而言,现实中土壤是非均质的,而在仿真实验中将土壤介质看作均质,这与实际情况存在一定的偏差。此外,根系的形状在真实情况下并非均匀的圆柱体,而且根系的生长方向也是多样化的。因此,需要进一步改进仿真实验中的土壤介质、根系方向等参数,以便更准确地模拟实际场景中的情况。
3.2.2 输入参数方面
在输入参数方面,根系相对介电常数的估算精度受土壤相对介电常数、根系半径和根系深度影响。目前对根系深度和半径估算已有较好的研究成果,李光辉等[18]提出一种基于探地雷达和深度学习的果树根径估算方法,其将A-scan波形送入神经网络进行训练,在实测数据上对根系半径估算的最大误差为1.56 mm,深度估算的最大误差为9.90 mm,总平均相对误差为5.83%。Liang等[16]提出一种基于BP神经网络估算根系直径的方法,其平均预测误差仅为3.62%。
土壤相对介电常数可直接利用专用传感器测量,或者通过钻孔GPR、平均包络振幅法、频移法和图像反演等方法来确定[29−30],如:徐兴倩等[31]提出红黏土多变量介电常数经验模型,均方根误差为0.026,拟合精度较高;王学等[32]按照Oh模型进行土壤介电常数反推计算,其模拟与实测数据的决定系数R2为0.821,具有较高的精度。
现有的研究已经尽可能减小根系半径、根系深度和土壤相对介电常数的估算误差,但误差仍然存在,且多个误差参数代入模型会导致估算结果误差叠加增大。因此,降低土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度的测量误差是准确估算根系相对介电常数的前提。
3.2.3 实地实验方面
在实地实验方面,虽然采用土壤相对介电常数平均值能更好地反映预埋区域的整体土壤特性,但这种方法存在误差。而且土壤相对介电常数由公式推测,也存在一定的不准确性。在预埋实验中,预埋区域深度的测量也存在误差。以10 cm的深度举例,虽然在预埋实验中设置深度为10 cm,但当根系被掩埋后,地面到根系中心的实际深度并非10 cm,而是10 cm减去根系的半径,因此根系的实际深度偏小。此外,在实验过程中发现,根系相对介电常数越大,根与土壤相对介电常数差值也越大,雷达波图像会更清晰,双曲线顶点处A-scan曲线更易识别,从而减小ΔF误差。因此,在实地预埋实验中选择新鲜的根系作为实验对象也将有助于减小估算误差。
4. 结 论
本研究提出一种基于探地雷达的树木根系相对介电常数无损估算方法。首先在仿真探地雷达图像中确定双曲线顶点处的A-scan曲线,提取A-scan曲线中与根系相对介电常数关联的目标振幅参数ΔF,并结合土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度构建数据集;然后建立基于PLSR、BP和PSO-BP神经网络的根系相对介电常数估算模型;最后通过实地预埋实验对模型进行验证。研究得出以下结论。
(1)提出了一种通过提取A-scan目标振幅参数ΔF,结合土壤相对介电常数、根系半径、根系深度建立估算根系相对介电常数的数据集方法。
(2)在仿真和实地预埋实验中,PSO-BP神经网络模型的估算精度最高,优于PLSR和BP神经网络估算模型。
(3)基于本研究提取的数据集和PSO-BP神经网络的估算模型,在仿真和预埋实验中表现出良好的预测效果,可以有效实现根系相对介电常数的估算,为树木根系相对介电常数的无损预测提供了一种可靠的方法。
本研究还存在一些不足之处,例如:简化土壤结构、忽略根方向的多样性造成数据集较为单一;根系半径、根系深度、土壤相对介电常数等输入参数的误差限制了根系相对介电常数的估算精度。后续研究将侧重于:增加非均质土壤、多方向根系的仿真模型扩充数据集;改进根系半径、根系深度、土壤相对介电常数等输入参数的估算方法,减小误差。
-
图 1 正演模型
黑色矩形部分代表空气,白色矩形部分代表土壤,黑色圆圈代表根系(一共有7个根,其中R1,R2,···,R7表示根系的半径),一对黄色和蓝色矩形分别代表探地雷达的发射天线和接收天线,沿图中左侧向右移动完成模拟扫描。The black rectangle represents air, the white rectangle represents soil, the black circle represents root system (there are 7 roots in total, where R1, R2, ···, R7 denote the radius of roots), and a pair of yellow and blue rectangles represent the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna of ground-penetrating radar, respectively, and the simulated scanning is completed by moving along the left-hand side of the figure to the right-hand side.
Figure 1. Orthotropic model
图 5 BP神经网络结构
ΔF、r、εsoil、d分别为目标振幅、根系半径、土壤相对介电常数、根系深度,εroot为根系相对介电常数,wij和vj为层间权重参数(i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4)。ΔF, r, εsoil and d are the target amplitude, root radius, soil relative permittivity, and root depth, respectively. εroot is root relative permittivity, and wij and vj are the interlayer weighting parameters (i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3, 4).
Figure 5. BP neural network structure
表 1 松树根系样本参数
Table 1 Sample parameters of pine root system
树根标号
Tree root No.树根长度
Tree root length/cm半径
Radius/cm相对介电常数
Relative permittivity1 15 1.27 12.65 2 15 1.83 13.03 3 15 2.07 17.40 4 15 2.64 16.45 表 2 根系相对介电常数估算模型评估指标
Table 2 Evaluation indicators for the estimation model of relative permittivity of root system
模型 Model RMSE MAE R2 PLSR 0.719 4.240 0.482 BP 0.764 0.341 0.989 PSO-BP 0.701 0.255 0.990 表 3 实地实验估算结果
Table 3 Estimated results from field experiments
模型
Model深度
Depth/cm树根标号
Tree root No.ΔF/V r/cm 真实值
Real value估算值
Estimated value绝对误差
Absolute error平均相对误差
Average relative error/%PLSR 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 23.13 10.48 34.77 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 22.06 9.03 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 23.27 5.87 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 22.72 6.27 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 24.35 11.70 39.06 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 23.13 10.10 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 24.95 7.55 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 25.03 8.58 BP 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 14.02 1.37 14.60 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 13.66 0.63 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 13.88 3.52 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 12.75 3.70 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 14.50 1.85 13.75 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 14.35 1.32 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 14.99 2.41 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 13.75 2.70 PSO-BP 10 1 8.984 1.27 12.65 14.06 1.41 10.84 10 2 7.849 1.83 13.03 12.95 0.08 10 3 9.434 2.07 17.40 14.24 3.16 10 4 8.851 2.64 16.45 14.24 2.11 20 1 5.464 1.27 12.65 14.80 2.15 10.93 20 2 4.171 1.83 13.03 14.16 1.13 20 3 6.387 2.07 17.40 15.66 1.74 20 4 6.627 2.64 16.45 14.71 1.74 注:土壤相对介电常数εsoil为12.76。Note: the relative permittivity of soil (εsoil) is 12.76. -
[1] Ma Z, Guo D, Xu X, et al. Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits[J]. Nature, 2018, 555: 94−97. doi: 10.1038/nature25783
[2] 秦瑞霞, 徐华东, 陈能志, 等. 基于介电谱的介电常数与木材含水率的相关性[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 162−169. Qin R X, Xu H D, Chen N Z, et al. The correlation between wood moisture content and dielectric constant based on dielectric spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2022, 42(3): 162−169.
[3] 叶文郁, 朱孟兆, 陈玉峰, 等. 温度对植物绝缘油纸介电响应特性的影响[J]. 绝缘材料, 2020, 53(4): 82−88. Ye W Y, Zhu M Z, Chen Y F, et al. Effect of temperature on dielectric response of vegetable insulating oil-paper[J]. Insulating Materials, 2020, 53(4): 82−88.
[4] 孙佳慧, 史海兰, 陈科宇, 等. 植物细根功能性状的权衡关系研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(8): 1055−1070. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2022.0456 Sun J H, Shi H L, Chen K Y, et al. Research advances on trade-off relationships of plant fine root functional traits[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(8): 1055−1070. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2022.0456
[5] 崔喜红, 陈晋, 关琳琳. 探地雷达技术在植物根系探测研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(6): 606−611. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.06.005 Cui X H, Chen J, Guan L L. The application of ground penetrating radar to plant root system detection[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2009, 24(6): 606−611. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.06.005
[6] Zhang X, Derival M, Albrecht U, et al. Evaluation of a ground penetrating radar to map the root architecture of HLB-infected citrus trees[J]. Agronomy-Basel, 2019, 9(7): 354. doi: 10.3390/agronomy9070354
[7] Paz A, Thorin E, Topp C. Dielectric mixing models for water content determination in woody biomass[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2011, 45(2): 249−259. doi: 10.1007/s00226-010-0316-8
[8] Mihai E A, Gerea G A, Curioni G, et al. Direct measurements of tree root relative permittivity for the aid of GPR forward models and site surveys[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2019, 17(3): 299−310. doi: 10.1002/nsg.12043
[9] 白雪, 纪奕才, 方广有. 探地雷达用于树木单根成像的模拟技术研究[J]. 中国农业科技导, 2011, 13(1): 129−136. Bai X, Ji Y C, Fang G Y. Studies on simulation technique of trees single root imaging by ground penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011, 13(1): 129−136.
[10] 李怡娜, 徐国祺, 王立海, 等. 面向探地雷达应用的活立木木材介电常数受主要应用条件的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(4): 152−161. Li Y N, Xu G Q, Wang L H, et al. Influence of main application conditions on the permittivity of standing trees for GPR applications[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2022, 42(4): 152−161.
[11] 肖夏阳, 文剑, 肖中亮, 等. 基于雷达波的树木躯干内部缺陷探测识别[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(5): 127−134. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180514 Xiao X Y, Wen J, Xiao Z L, et al. Detection and recognition of tree trunk internal structure based on radar[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2018, 54(5): 127−134. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180514
[12] Özkap K, Peksen E, Kalanvural İ, et al. 3D scanner technology implementation to numerical modeling of GPR[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020, 179: 1−8.
[13] Wang S, Zhao S, Al-Qadi L I. Real-time density and thickness estimation of thin asphalt pavement overlay during compaction using ground penetrating radar data[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2019, 41(3): 1−15.
[14] 郭立, 崔喜红, 陈晋. 基于GprMax正演模拟的探地雷达根系探测敏感因素分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(4): 1754−1763. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.04.057 Guo L, Cui X H, Chen J. Sensitive factors analysis in using GPR for detecting plant roots based on forward modeling[J]. Progress in Geophys, 2012, 27(4): 1754−1763. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.04.057
[15] 徐爱英, 马少辉, 牛旭, 等. 频率与含水率对残膜–土壤介电常数的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(7): 269−271. Xu A Y, Ma S H, Niu X, et al. Effect of frequency and moisture content on residual film-soil dielectric constant[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(7): 269−271.
[16] Liang H, Fan G Q, Li Y H, et al. Theoretical development of plant root diameter estimation based on GprMax data and neural network modelling[J]. Forests, 2021, 12(5): 615. doi: 10.3390/f12050615
[17] Bi L Y, Xing L Y, Liang H, et al. Estimation of coarse root system diameter based on ground-penetrating radar forward modeling[J]. Forests, 2023, 14(7): 1−10.
[18] 李光辉, 王哲旭, 徐汇, 等. 基于探地雷达和深度学习的果树根径预测方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(11): 306−313, 348. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2022.11.031 Li G H, Wang Z X, Xu H, et al. Root diameter prediction method of fruit trees based on ground penetrating radar and deep learning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(11): 306−313, 348. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2022.11.031
[19] 罗诗光, 任强, 王成浩, 等. 基于深度学习的GPR时频域联合电磁反演方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2022, 37(4): 555−567. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2021347 Luo S G, Ren Q, Wang C H, et al. GPR time-frequency domain joint electromagnetic inversion method based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2022, 37(4): 555−567. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2021347
[20] Wang H, Ouyang S, Liu Q, et al. Deep-learning-based method for estimating permittivity of ground-penetrating radar targets[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(17): 4293. doi: 10.3390/rs14174293
[21] Zakarewicz G A D, Luísa L, Figueredo M P D, et al. Dielectric permittivity effects in the detection of tree roots using ground-penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2021, 193: 1−10.
[22] Jone B, Frank D, John B. Experimental evaluation of several key factors affecting root biomass estimation by 1500 MHz ground-penetrating radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(12): 1337. doi: 10.3390/rs9121337
[23] Li C C, Huang H P. Model building by merging submodels using PLSR[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2003, 36(9): 1023−1033. doi: 10.1252/jcej.36.1023
[24] 张芳, 邓照龙, 田有文, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术的南果梨酸度无损检测方法[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2024, 55(2): 231−239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2024.02.011 Zhang F, Deng Z L, Tian Y W, et al. Non-destructive testing method for acidity of nanguo pear based on hyper-spectral imaging technology[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2024, 55(2): 231−239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2024.02.011
[25] 陈远玲, 侯怡, 李尚平, 等. 基于PSO-BP的甘蔗施肥监控系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(22): 23−31. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.22.003 Chen Y L, Hou Y, Li S P, et al. Design and experiments of the fertilization monitoring system based on the PSO-BP for sugarcane[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(22): 23−31. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.22.003
[26] 王泽鹏, 张潇巍, 薛芳秀, 等. 探地雷达树木根系定位与直径估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(8): 160−168. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.08.018 Wang Z P, Zhang X W, Xue F X, et al. Estimating the location and diameter of tree roots using ground penetrating radar[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(8): 160−168. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.08.018
[27] 赵燕东, 高超, 张新, 等. 基于驻波率原理的植物茎体水分无损检测方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(1): 310−316. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.01.042 Zhao Y D, Gao C, Zhang X, et al. Non-destructive measurement of plant stem water content based on standing wave ratio[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(1): 310−316. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.01.042
[28] 胡梦蛟, 武珂, 田云露, 等. 探地雷达在植物根系探测中的应用进展[J]. 河南科技, 2019(5): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2019.05.009 Hu M J, Wu K, Tian Y L, et al. Progress in application of ground penetrating radar in root detection of plants[J]. Henan Science and Technology, 2019(5): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2019.05.009
[29] Liu X, Chen J, Cui X, et al. Measurement of soil water content using ground-penetrating radar: a review of current methods[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2019, 12(1): 95−118. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2017.1412520
[30] 李春堂, 李旭. 基于改进注意力机制的探地雷达图像反演[J]. 电波科学学报, 2023, 38(5): 825−834. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2022175 Li C T, Li X. Attention mechanism based inversions for ground penetrating radar image[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2023, 38(5): 825−834. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2022175
[31] 徐兴倩, 王海军, 赵熹, 等. 红黏土介电常数模型试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56(11): 165−173, 183. Xu X Q, Wang H J, Zhao X, et al. Experimental study on dielectric constant model of laterite[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56(11): 165−173, 183.
[32] 王学, 刘全明, 屈忠义, 等. 盐渍化土壤水分微波雷达反演与验证[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(11): 108−114. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.014 Wang X, Liu Q M, Qu Z Y, et al. Inversion and verification of salinity soil moisture using microwave radar[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(11): 108−114. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.014



 下载:
下载: