Fabrication of lignin containing nanocellulose and films from wheat straw pretreated by deep eutectic solvent
-
摘要:目的
为了麦草秸秆原料的高效利用,开发新型低共熔溶剂(DES),以实现含木质素纳米纤维素的制备,以及后续功能材料的构建。
方法以麦草为原料,通过不同DES预处理(苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES、苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES)结合高压均质机械处理,制备含木质素纳米纤维素,利用溶液浇筑法制备聚乙烯醇/含木质素纳米纤维素复合薄膜,研究含木质素纳米纤维素微观形貌、化学基团、热稳定性、分散性,以及复合薄膜的光学性能、微观结构和力学性能。
结果苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES预处理后,麦草残渣尺寸更加细小且热稳定性更强,获得的含木质素纳米纤维素带有更强的负电性(−8.62 mV),制备的复合薄膜具有更高的雾度(36.82%)。苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理制备的含木质素纳米纤维素保持了复合薄膜较高透明度(> 67%),并实现了最高的薄膜拉伸强度(57.16 MPa)。
结论苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES在增强含木质素纳米纤维素负电性和提高复合薄膜雾度方面更有优势,苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES在提高复合薄膜透明度和力学强度方面效果更佳,两者可满足不同光管理应用场景的需求。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to efficiently utilize wheat straw raw materials, a new type of deep eutectic solvent (DES) was developed to achieve the preparation of lignin containing nanocellulose and the subsequent construction of functional materials.
MethodWheat straw was used as the raw material. Lignin containing nanocellulose was prepared by different DES pretreatments (benzyltrimethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES and benzyltriethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES) combined with high-pressure homogenization. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/lignin containing nanocellulose composite films were prepared using the solution casting method. The study comparatively examined the microstructure, chemical groups, thermal stability, dispersibility lignin containing nanocellulose, as well as the optical properties, microstructure, and mechanical properties of composite films.
ResultThe residues of wheat straw pretreated by benzyltrimethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES showed smaller residue sizes and enhanced thermal stability. The obtained lignin containing nanocellulose exhibited stronger negative charge (−8.62 mV) and the composite films demonstrated higher haze (36.82%). In contrast, lignin containing nanocellulose prepared with benzyltriethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES maintained higher transparency of composite films (> 67%) and achieved a maximum film tensile strength of 57.16 MPa.
ConclusionBenzyltrimethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES is more advantageous in enhancing the negative charge of lignin-containing nanocellulose and increasing haze of composite films. Benzyltriethylammonium chloride-oxalic acid DES is more effective in improving the transparency and mechanical strength of composite films, meeting the needs of different light management applications.
-
中国是农业大国,农业生产过程中会产生大量的秸秆资源,然而农作物秸秆的潜在价值长期被忽略,大量秸秆不能得到有效利用,这种情况造成了资源的浪费并加剧了环境污染[1]。因此,发展秸秆相关产业,提高秸秆利用率,实现秸秆高值绿色转化具有重要的现实意义。麦草是最常见的农业秸秆之一,具有来源广泛、价格低廉和可再生的特点,其高值化应用前景广阔[2]。
通过物理、化学、生物或多种方法结合的方式,可以从秸秆等木质纤维原料中分离出纳米纤维素(即至少在一个维度上的尺寸为纳米级(< 100 nm)的纤维素材料[3])。纳米纤维素具有高活性、高强度、高模量、大比表面积和低热膨胀系数等优点,广泛应用于生命科学[4]、食品和药物工业[5]以及复合材料[6]等领域。通常,来源于木质纤维生物质原料的纳米纤维素可分为两类:短棒状高结晶的纤维素纳米晶体(cellulose nanocrystal,CNC)[7]和高长径比的纤维素纳米纤丝(cellulose nanofibril,CNF)[8]。纳米纤维素的生产主要包括两个步骤:首先从木质纤维原料中化学提取纤维素,然后利用强酸水解[9]、TEMPO氧化[10]、机械处理[11]和静电纺丝[12]等技术对纤维素进行纳米加工。目前,通常采用制浆、漂白和精制等化学处理方法,以去除木质纤维原料中的木质素和半纤维素,得到高纯度的纤维素材料(如化学木浆、溶解木浆)用于后续生产纳米纤维素。然而,这些过程复杂且需要大量环境不友好的化学品,污染负荷较重。
含木质素纳米纤维素(lignin-containing cellulose nanofiber,LCNF)可以直接从木质纤维原料或未漂白木浆中获得,除了具有纳米纤维素的基本特性外,由于木质素的存在,还具有高热稳定性[13]、疏水性[14]、抗氧化性[15]和紫外线屏蔽特性[16]。在LCNF的生产过程中,部分半纤维素和木质素被保留下来,这不仅增加了纳米材料的产量,还减少了能源和化学品的消耗,为木质纤维原料的充分利用提供了新的途径。目前,LCNF的制备方法与CNF相似,需要结合化学预处理和机械处理,如酸碱处理结合高压均质。然而,这些方法存在局限性,如生产成本高,制备效率低,制备流程复杂,对环境影响大。因此,开发一种环境友好、简单高效的LCNF制备工艺对于实现木质纤维原料的高值转化具有重要意义。
低共熔溶剂(deep eutectic solvent,DES)是一类新型绿色溶剂,通过将氢键受体和氢键供体按一定比例混合得到,其熔点明显低于原始成分[17−18]。目前的相关研究已经表明:DES可以很好地去除半纤维素和木质素,并且可以通过减压蒸馏回收并在下游工艺中重新使用;DES可以实现木质纤维原料的组分分离或结构拆解,是一种环境友好且绿色可持续的方法[19]。DES作为一种廉价、低毒或无毒的绿色溶剂,已被用于纸浆[20]、丝瓜络[21]、杨木[22]、玉米芯[23]等生物质原料的预处理,以实现主要组分的分离或后续纳米纤维素的制备。目前,针对麦草等农业秸秆原料,开发一种新型DES溶剂体系以实现含木质素纳米纤维素的制备,后续构建功能材料并进行性能研究,具有重要的现实意义。
为了实现麦草的高值转化利用,本研究探索了绿色溶剂体系下含木质素纳米纤维素的制备方法。本研究采用DES对麦草进行预处理,并结合高压均质机械处理制备含木质素纳米纤维素,进而制备透明复合薄膜并进行系统表征。分别合成基于苄基三甲基氯化铵、苄基三乙基氯化铵的DES体系,探究不同DES体系对麦草微观结构、纤维素结晶度和化学结构的影响;探讨DES预处理对含木质素纳米纤维素表面特性、结晶度、分散性和热稳定性的影响规律;研究含木质素纳米纤维素种类及质量分数对复合薄膜光学性能、微观形貌和力学强度的影响。研究结果将有助于促进木质纤维原料功能转化与含木质素纳米纤维素材料的发展。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
麦草(wheat straw,WS)原料取自河北省邢台市,经过粉碎并过筛,取尺寸为40 ~ 60目之间的麦草颗粒,置于塑封袋中备用。苄基三甲基氯化铵、苄基三乙基氯化铵、草酸二水合物均购自安徽泽升科技股份有限公司,聚乙烯醇购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司,所有试剂均未经过再提纯。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 含木质素纳米纤维素的制备
将苄基三甲基氯化铵、苄基三乙基氯化铵分别与草酸二水合物以摩尔比1∶1混合,在圆底烧瓶80 ℃下油浴搅拌4 h后,室温静置冷却分别得到澄清透明的DES溶液。苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸和苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES分别记为DES-1和DES-2。将制好的两组DES分别加热至120 ℃,向两组DES中分别加入10 g麦草,持续搅拌4 h。反应结束后,使用去离子水对DES处理后的麦草进行过滤洗涤,将滤渣置于真空干燥箱中烘干,得到两组麦草残渣(分别记为WS-1和WS-2)。将WS-1和WS-2分别配制为一定浓度的水分散液,使用高压均质机(SPX FLOW,APV 2000)进行机械后处理,在130 MPa压强下循环处理10次得到含木质素纳米纤维素悬浮液,分别记为LCNF-1和LCNF-2。
1.2.2 复合薄膜的制备
将聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohol,PVA)与去离子水混合,在80 ℃下加热搅拌3 h,制得质量分数为5%的PVA溶液,室温下冷却,放置备用。称取一定质量的PVA溶液与含木质素纳米纤维素溶液,机械搅拌混合均匀,后续置于塑料培养皿中进行干燥处理,制备得到含木质素纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合薄膜(PN)。
1.2.3 性能表征
利用纳米粒度和Zeta电位分析仪(Zetasizer Nano ZS90)测定麦草分散液的Zeta电位。将麦草样品置于氧化铝坩埚中,利用热重分析仪(TG 209)测定麦草样品的热重曲线,测试过程中保持流速为20 mL/min的N2氛围,升温速率10 ℃/min,测试温度范围25 ~ 800 ℃。
将制备的含木质素纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合薄膜裁剪成固定形状,利用万能材料试验机(Zwick Z2005)测定其应变–应力曲线。利用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker AXS)获得麦草样品的结晶结构。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,SU8010)观察麦草处理前后样品以及复合薄膜的微观形貌。通过配备积分球附件的紫外–可见分光光度计(Shimadzu UV2550)测定薄膜的透明度和雾度,透明度和雾度均取值550 nm波长可见光处的数值。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 预处理麦草微观形貌
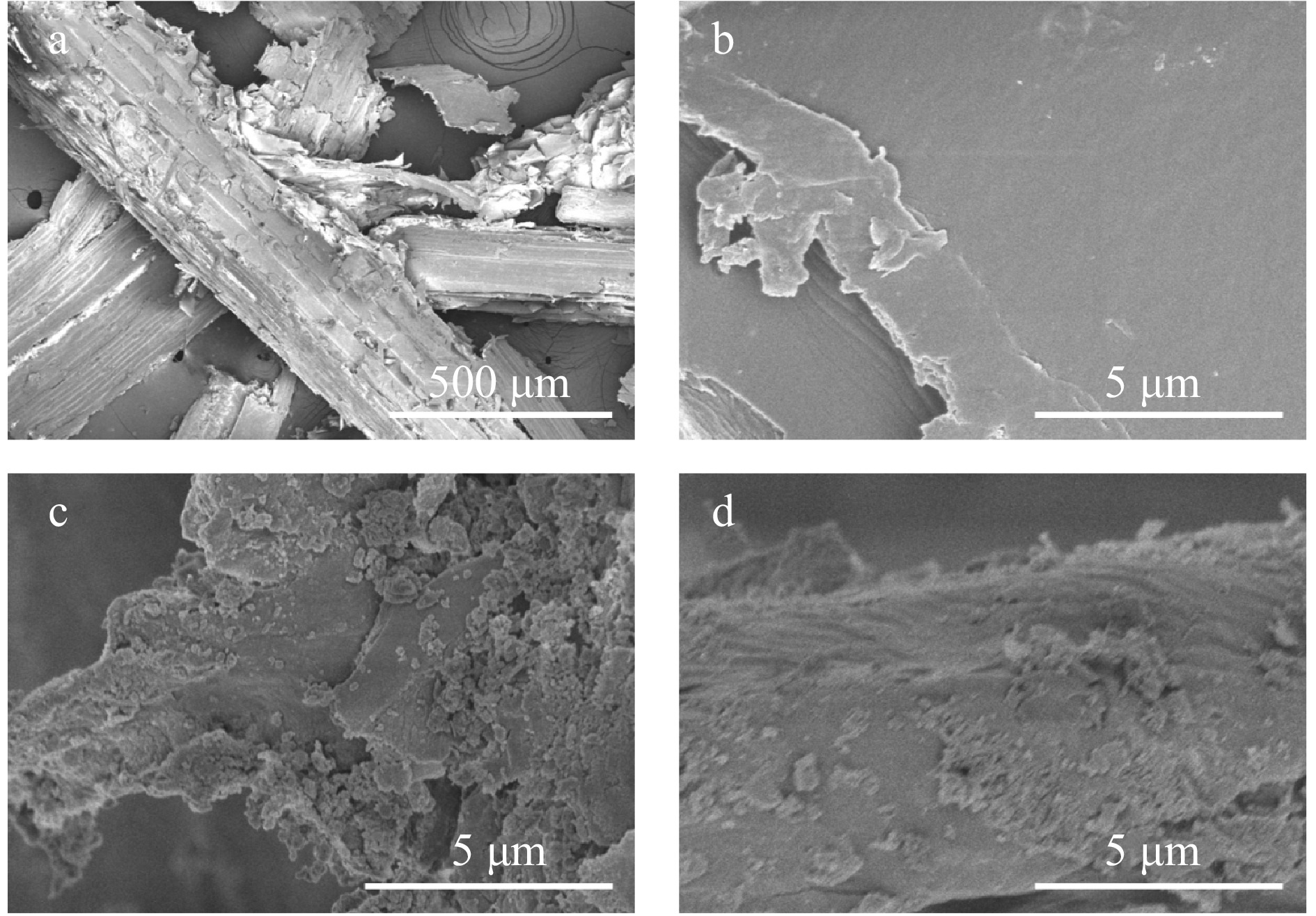
未处理的麦草表面形态完整、光滑,纤维之间结合紧密(图1a,b);与此相比,DES预处理后的麦草残渣表面出现了更多的孔洞,麦草原有的致密结构被严重破坏(图1c,d)。这些显著的结构变化可归因于DES预处理后麦草中的半纤维素和木质素被协同去除。此外,相比苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣(图1d),苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣(图1c)表面更加粗糙,这表明该DES实现了更优异的预处理效果。
2.2 含木质素纳米纤维素性能
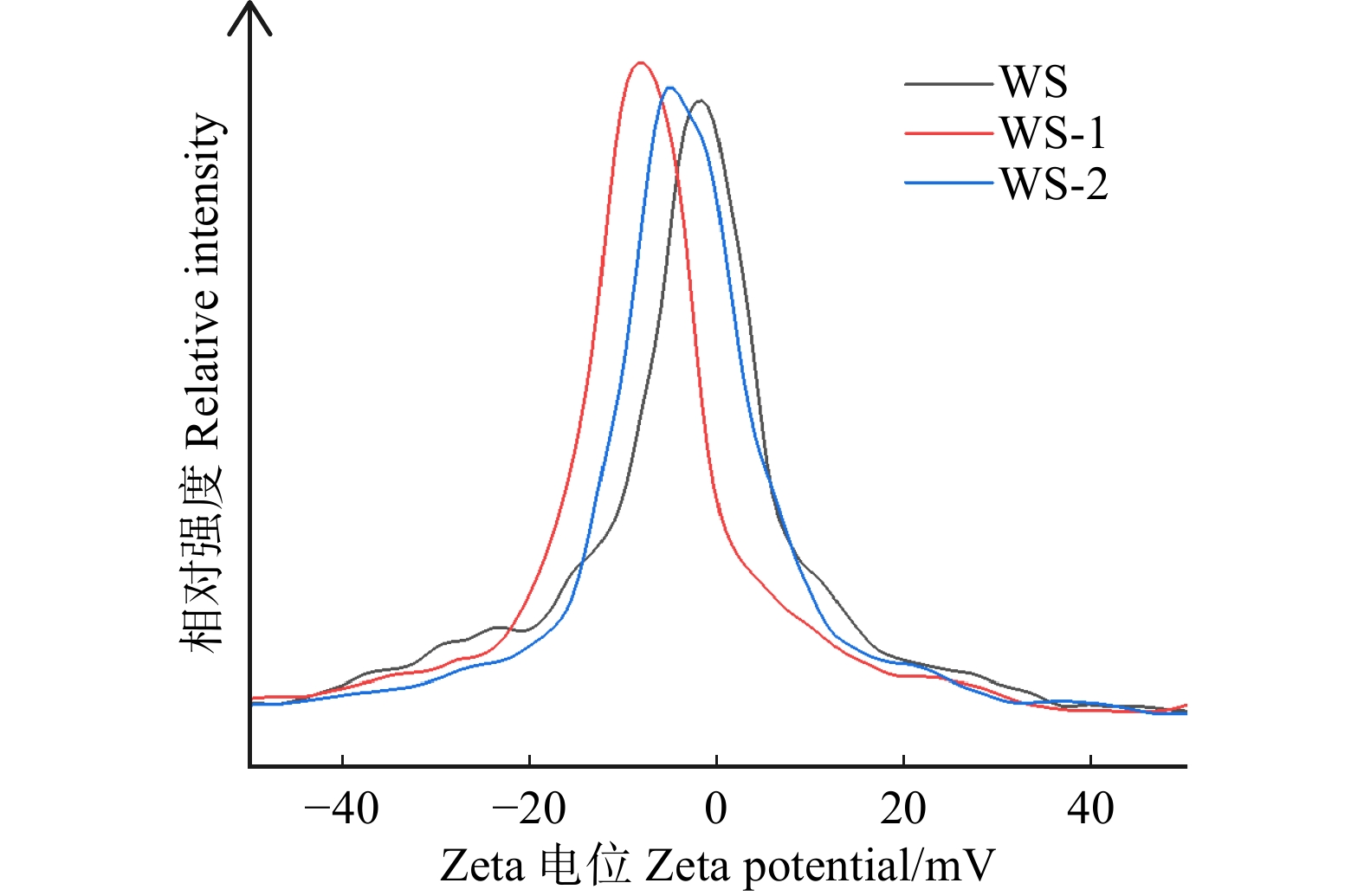
Zeta电位与材料胶态分散的稳定性密切相关,度量颗粒之间的相互排斥或吸引力强度。Zeta电位的绝对值(正或负)越高,体系越稳定,即在溶解或分散时抵抗聚集的能力越强。未处理麦草分散液测得的Zeta电位为−1.86 mV,DES处理麦草残渣分散液的Zeta电位展现出更强的负电位:WS-1样品的Zeta电位为−8.62 mV,WS-2样品的Zeta电位为−4.98 mV(图2)。上述结果表明:经过DES预处理后,纤维样品相比于未处理样品的负电性显著增强,且苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES相比于苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES,在增加样品表面电荷方面展现出更优异的性能,这更有利于后续含木质素纳米纤维素样品的体系稳定和功能应用。
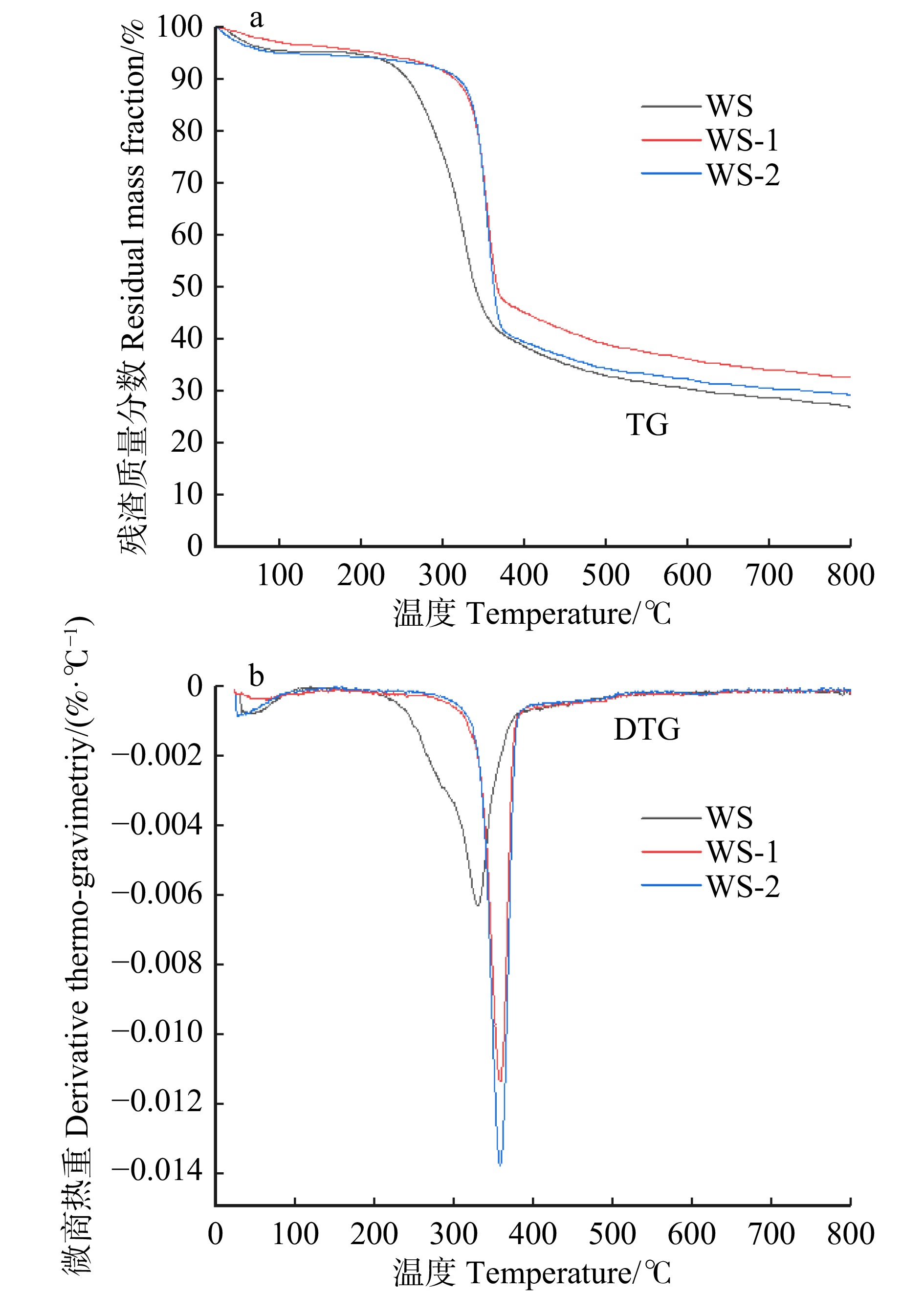
含木质素纳米纤维素的热稳定性对于后续功能利用十分重要,本研究通过测定样品的热重曲线研究麦草样品的热稳定特性。麦草样品的降解可分为3个阶段:30 ~ 220 ℃为初始分解阶段,220 ~ 410 ℃为主要热解阶段,410 ~ 800 ℃为炭化阶段(图3a)。在主要降解阶段,随着温度的升高,样品质量损失呈稳定下降趋势。在800 ℃时,未处理麦草残余质量分数为27.0%,苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣残余质量分数为32.7%,苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣残余质量分数为29.5%。结果表明:预处理后麦草的热稳定性有所提升;相比于苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES,苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES对于热稳定性的提升更为显著。
DTG曲线显示:样品的主要质量损失发生在220 ~ 410 ℃内;对比未处理与预处理的麦草残渣,未处理麦草的最大热解速率出现在330 ℃(图3b),这部分质量损失与木质素和纤维素的降解有关;两组不同麦草残渣的最大热解速率出现在358 ℃时,这表明DES处理后麦草残渣的热稳定性升高;苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣的峰位要高于苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理的麦草残渣(图3b),后者的热稳定性要更加优异。
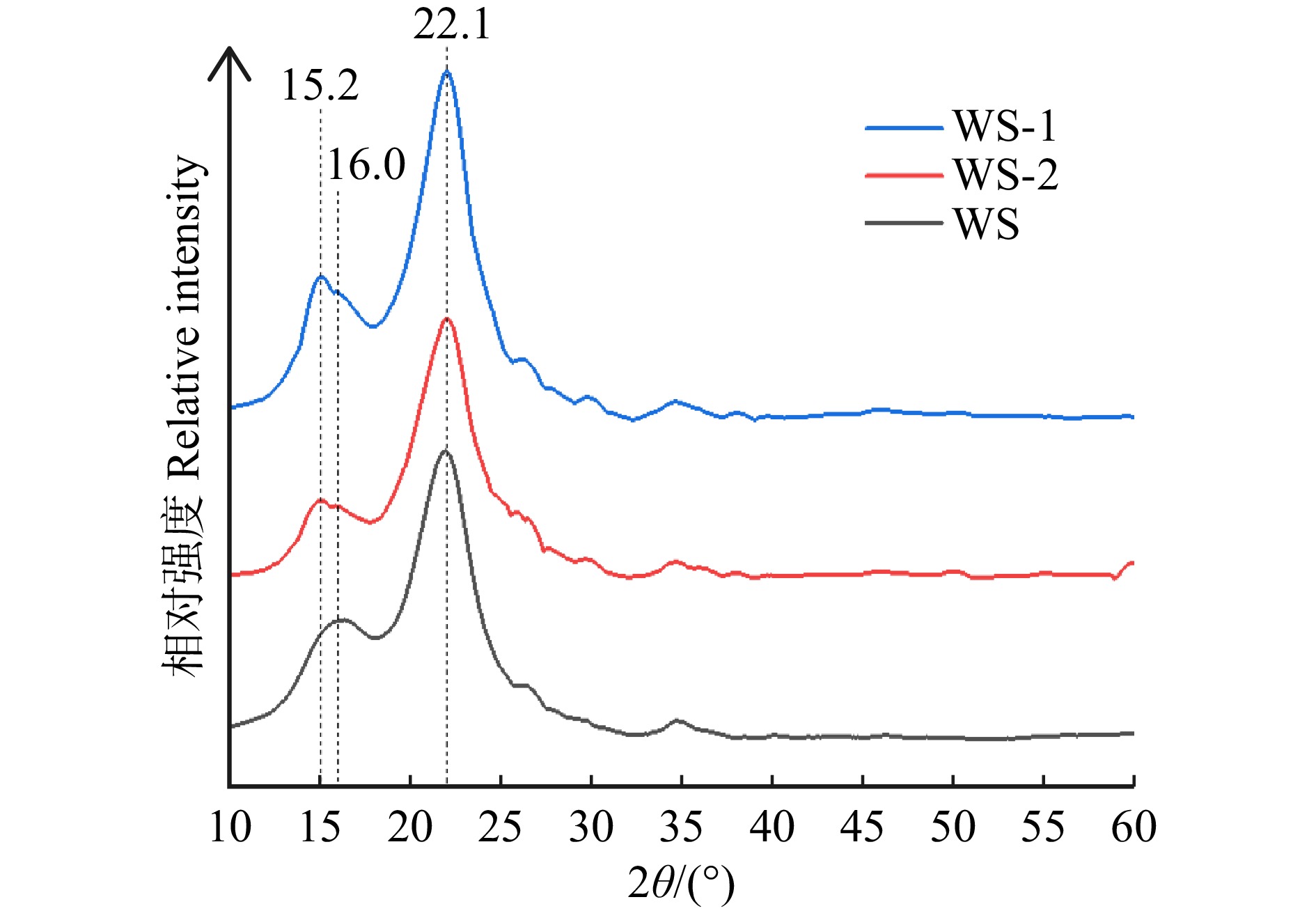
3种样品的XRD谱线的峰均位于2θ为15.2°、16.0°、22.1°处,分别对应纤维素的(−110)、(110)和(200)晶面,属于纤维素I的特征峰(图4)。结果表明:苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES和苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理均没有改变样品的结晶结构,麦草残渣中的纤维素仍旧为纤维素I晶型。
2.3 复合薄膜性能
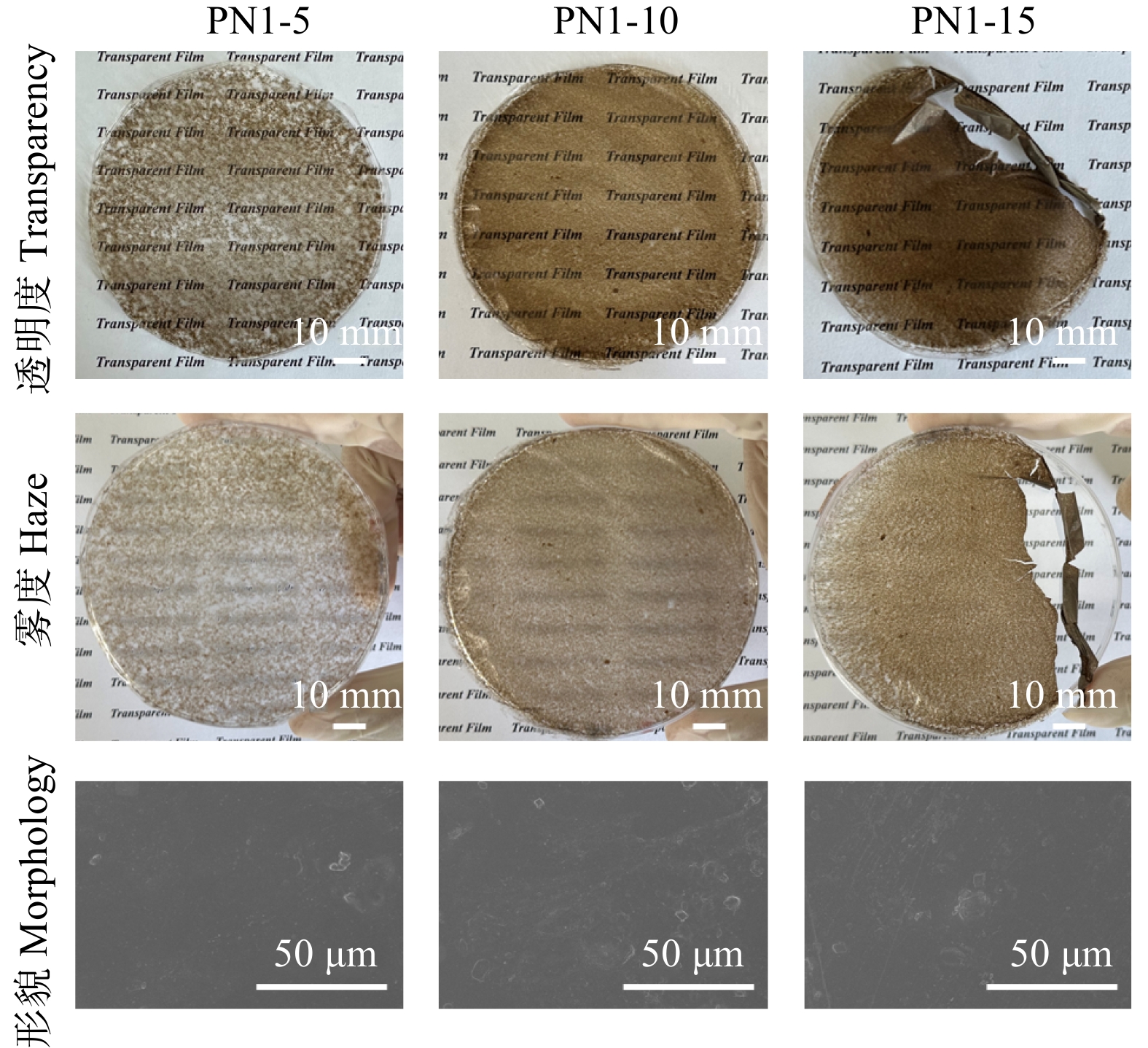
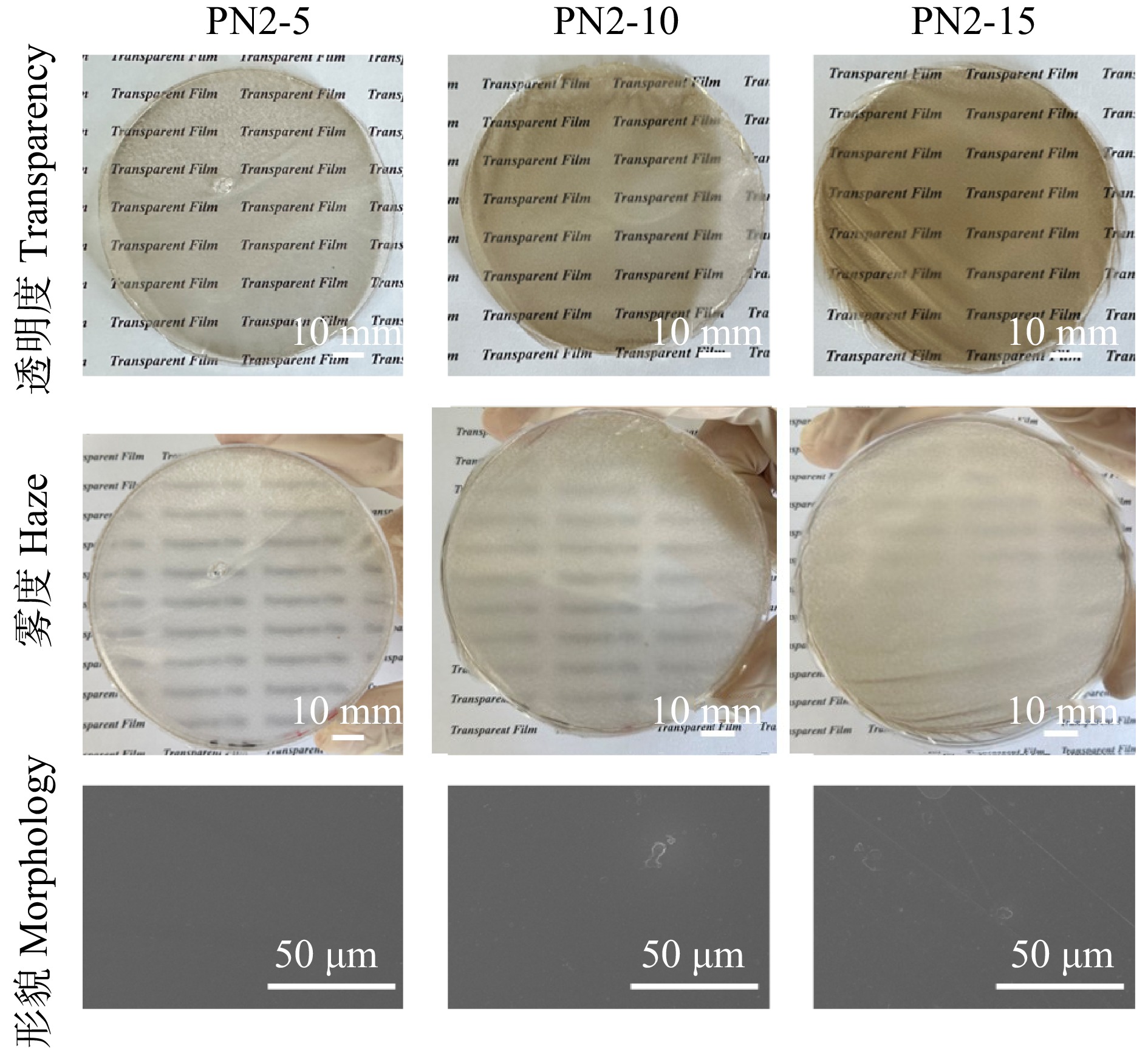
制备的复合薄膜中PVA和LCNF的质量百分数如表1所示。通过观察复合薄膜的照片分析其透明度与雾度。复合薄膜中含木质素纳米纤维素的质量分数提高,其透明度呈现出下降趋势,而雾度会上升(图5、6),这主要是因为含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的提高促进了光的散射。对于LCNF-1复合薄膜,当含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数提高到15%时(PN1-15),无法得到完整的薄膜材料。通过SEM图观察复合薄膜的表面微观形貌,随着复合薄膜中含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的升高,薄膜表面更加粗糙。对比两种复合薄膜,LCNF-1在PVA薄膜基体中有着更加显著的聚集现象,而LCNF-2在PVA薄膜基体中实现了更均一的分散,这可能是由于苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES在促进含木质素纳米纤维素在复合薄膜中的分散性方面要优于苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES。
表 1 复合薄膜中聚乙烯醇(PVA)和含木质素纳米纤维素(LCNF)的质量百分数Table 1. Mass percentage of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and lignin containing cellulosenanofiber (LCNF) in composite film% 复合薄膜编号
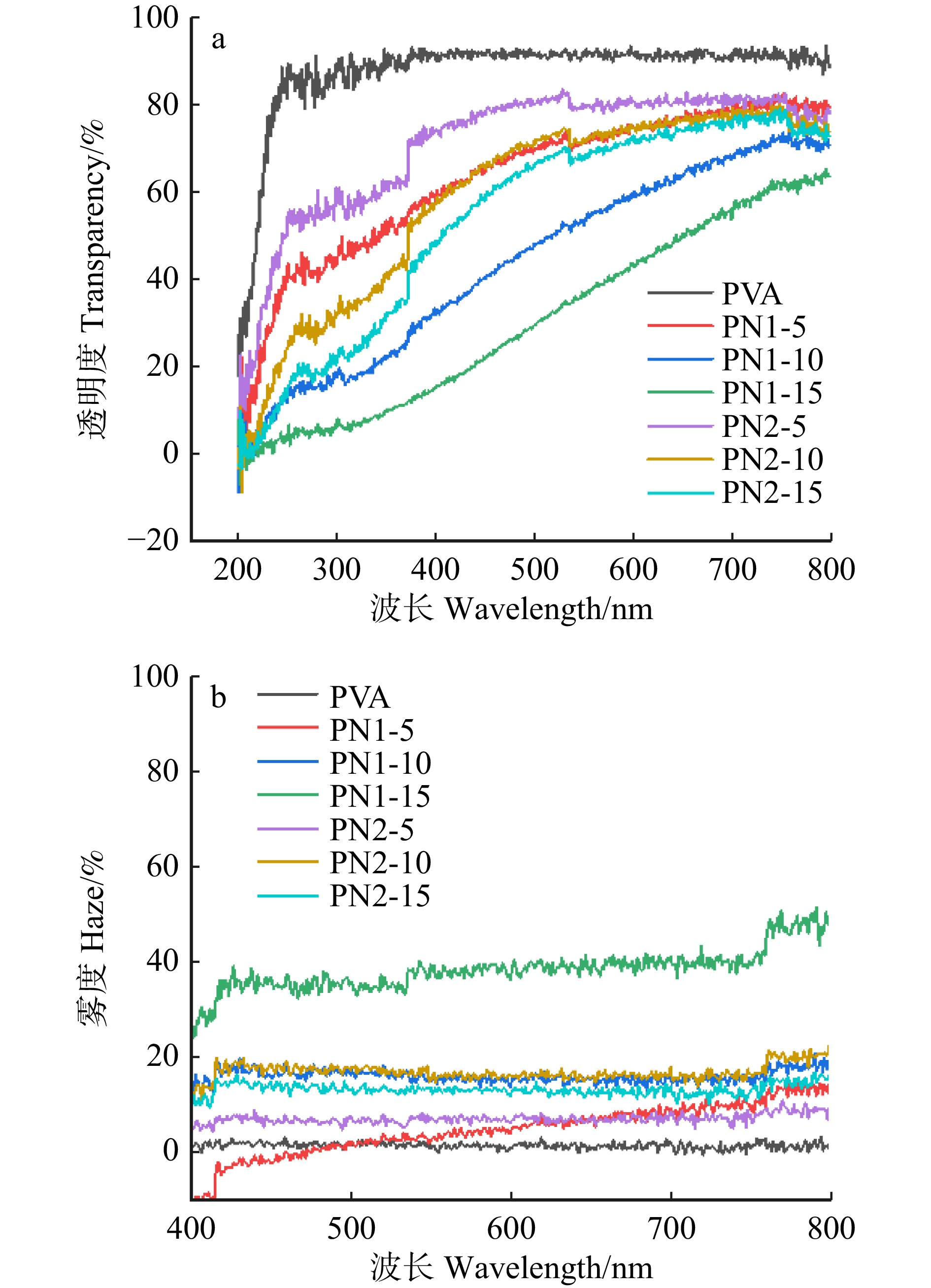
No. of composite filmPVA LCNF-1 LCNF-2 PN1-5 95 5 0 PN1-10 90 10 0 PN1-15 85 15 0 PN2-5 95 0 5 PN2-10 90 0 10 PN2-15 85 0 15 注:LCNF-1和LCNF-2分别为基于苄基三甲基氯化铵、苄基三乙基氯化铵制备的含木质素纳米纤维素。Notes: LCNF-1 and LCNF-2 are lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers prepared by benzyltrimethylammonium chloride and benzyltriethylammonium chloride, respectively. 纯PVA薄膜的透明度为92.1%(图7a)。添加含木质素纳米纤维素后,复合薄膜的透明度下降,并且随含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的增加而降低,其中LCNF-1复合薄膜的透明度从72.2%(PN1-5)下降到36.8%(PN1-15)。相比之下,LCNF-2复合薄膜透明度的下降幅度并不显著。相比于PN1-15薄膜的低透明度,PN2-15薄膜的透明度高达67.9%,PN2-5薄膜的透明度更是达到80.3%,这可能是因为由苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理得到的含木质素纳米纤维素在复合薄膜中更容易聚集。此外,随着复合薄膜中含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的增加,其对紫外线的阻隔性能得到了显著提升(图7a),这对于复合薄膜在智能建筑等光管理领域的应用具有重要意义。
雾度是光学薄膜重要的性能指标,它反映了透明薄膜对光线的散射能力。图7b显示:纯PVA薄膜的雾度仅为1.01%;添加含木质素纳米纤维素后,复合薄膜的雾度随含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的增加而升高;对于LCNF-1复合薄膜,雾度从2.2%(PN1-5)上升到36.8%(PN1-15)。复合薄膜中含木质素纳米纤维素的质量分数较低时,LCNF-1复合薄膜的雾度低于LCNF-2复合薄膜,如PN1-5薄膜的雾度为2.2%,而PN2-5薄膜的雾度为6.8%;在含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数较高时,LCNF-1复合薄膜的雾度则高于LCNF-2复合薄膜,如PN1-15复合薄膜的雾度为36.8%,而PN2-15薄膜的雾度为13.7%。在实际应用过程中,可以根据不同应用场景的需求调控复合薄膜中的组分配比,构建符合雾度要求的复合薄膜材料。
在复合薄膜中添加两种不同的含木质素纳米纤维素,对薄膜力学性能的影响有一定差异(图8)。相比于PVA薄膜,LCNF-1复合薄膜的断裂伸长率降低;随着含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的升高,复合薄膜强度相比于PVA薄膜呈现出先降低后升高的趋势;含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的质量分数从5%(PN1-5)提高到10%(PN1-10)后,复合薄膜的强度从14.3 MPa提高到了51.2 MPa。然而,对于LCNF-2复合薄膜,添加含木质素纳米纤维素之后,复合薄膜的强度相比于PVA薄膜得到提高,但含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的进一步增加导致复合薄膜的强度有一定的下降:PN2-5薄膜强度为57.2 MPa,而PN2-15的强度下降到45.2 MPa。
3. 结 论
本研究针对麦草的高值化利用,开发了苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸和苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸两种DES预处理新体系,建立了DES预处理麦草制备含木质素纳米纤维素的方法,研究了含木质素纳米纤维素以及复合薄膜材料的理化特性。具体结论有以下3点。
(1)苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES和苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES预处理结合高压均质机械处理,均能够实现以麦草为原料制备含木质素纳米纤维素,苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES预处理对麦草的结构破坏更为显著,得到的含木质素纳米纤维素具有更强负电性(Zeta电位为−8.62 mV)。
(2)随着复合薄膜中含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数的升高,薄膜的透明度下降,紫外线阻隔性能和雾度得到提升。其中,苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理得到的含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数为15%的复合薄膜具有最高的雾度(36.8%),苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理得到的含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数为5%的复合薄膜具有最高的透明度(80.3%)。
(3)苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸DES处理得到的含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数为10%时,复合薄膜具有最高强度(51.2 MPa);苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES处理得到的含木质素纳米纤维素质量分数为5%时,复合薄膜具有最高强度(57.2 MPa)。
综上所述,苄基三甲基氯化铵–草酸和苄基三乙基氯化铵–草酸DES预处理结合高压均质处理,能够实现麦草含木质素纳米纤维素的制备,通过改变PVA和含木质素纳米纤维素的配比可以调控复合薄膜材料的透明度与雾度、紫外线阻隔和力学性能,为其在光管理及更广阔领域的应用奠定了一定基础。
-
表 1 复合薄膜中聚乙烯醇(PVA)和含木质素纳米纤维素(LCNF)的质量百分数
Table 1 Mass percentage of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and lignin containing cellulosenanofiber (LCNF) in composite film
% 复合薄膜编号
No. of composite filmPVA LCNF-1 LCNF-2 PN1-5 95 5 0 PN1-10 90 10 0 PN1-15 85 15 0 PN2-5 95 0 5 PN2-10 90 0 10 PN2-15 85 0 15 注:LCNF-1和LCNF-2分别为基于苄基三甲基氯化铵、苄基三乙基氯化铵制备的含木质素纳米纤维素。Notes: LCNF-1 and LCNF-2 are lignin-containing cellulose nanofibers prepared by benzyltrimethylammonium chloride and benzyltriethylammonium chloride, respectively. -
[1] 王付云, 朱元芳, 张建胜, 等. 农业废弃物资源化利用现状研究进展[J]. 现代畜牧科技, 2024, 52(10): 98−101. Wang F Y, Zhu Y F, Zhang J S, et al. Research progress on the utilization of agricultural waste resources[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2024, 52(10): 98−101.
[2] 薛蓝馨, 林兆云, 陈嘉川, 等. 基于制浆废液和麦草废渣的生物质颗粒燃料预测模型的建立及分析[J]. 林产工业, 2024, 61(3): 8−14. Xue L X, Lin Z Y, Chen J C, et al. Establishment and analysis of biomass granular fuel prediction model based on pulping waste liquid and wheat straw residue[J]. China Forest Products Industry, 2024, 61(3): 8−14.
[3] Dufresne A. Nanocellulose: a new ageless bionanomaterial[J]. Materials Today, 2013, 16(6): 220−227. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2013.06.004
[4] Trache D, Tarchoun A F, Derradji M, et al. Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 8: 392.
[5] Thakur V, Guleria A, Kumar S, et al. Recent advances in nanocellulose processing, functionalization and applications: a review[J]. Materials Advances, 2021, 2(6): 1872−1895. doi: 10.1039/D1MA00049G
[6] Qi Y, Guo Y, Liza A A, et al. Nanocellulose: a review on preparation routes and applications in functional materials[J]. Cellulose, 2023, 30(7): 4115−4147. doi: 10.1007/s10570-023-05169-w
[7] 贾丽佳, 王汉琛, 黄彪, 等. 纳米纤维素的制备及功能应用[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2024, 58(4): 43−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2024.04.007 Jia L J, Wang H C, Huang B, et al. Preparation and functional application of nanocellulose[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2024, 58(4): 43−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2024.04.007
[8] Zhang F, Shen R, Li N, et al. Nanocellulose: an amazing nanomaterial with diverse applications in food science[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2023, 304: 120497. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120497
[9] Habibi Y, Lucia L A, Rojas O J. Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(6): 3479−3500.
[10] Koga H, Saito T, Kitaoka T, et al. Transparent, conductive, and printable composites consisting of TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose and carbon nanotube[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(4): 1160−1165. doi: 10.1021/bm400075f
[11] Wu C, McClements D J, He M, et al. Okara nanocellulose fabricated using combined chemical and mechanical treatments: Structure and properties[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 335: 116231. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116231
[12] Frey M W. Electrospinning cellulose and cellulose derivatives[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2008, 48(2): 378−391.
[13] 高佳, 王攀攀, 王丽君, 等. 含木质素的纤维素纳米纤丝的预处理工艺及研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2024, 43(2): 31−38. doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2024.02.005 Gao J, Wang P P, Wang L J, et al. Pretreatment technology and progress research for lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2024, 43(2): 31−38. doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2024.02.005
[14] Kumar A, Sood A, Maiti P, et al. Lignin-containing nanocelluloses (LNCs) as renewable and sustainable alternatives: prospects, and challenges[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2023, 41: 100830.
[15] Gu W, Zeng S, Dauletbek A, et al. Study on preparation of lignin-containing nanocellulose from bamboo parenchyma[J]. Journal of Renewable Materials, 2022, 10(2): 385. doi: 10.32604/jrm.2022.016457
[16] Kim D, Jeong J, Ryu J A, et al. In vitro evaluation of lignin-containing nanocellulose[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(15): 3365. doi: 10.3390/ma13153365
[17] Smith E L, Abbott A P, Ryder K S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(21): 11060−11082. doi: 10.1021/cr300162p
[18] Loow Y L, New E K, Yang G H, et al. Potential use of deep eutectic solvents to facilitate lignocellulosic biomass utilization and conversion[J]. Cellulose, 2017, 24: 3591−3618.
[19] Satlewal A, Agrawal R, Bhagia S, et al. Natural deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment: recent developments, challenges and novel opportunities[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(8): 2032−2050. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.08.009
[20] Jiang J, Carrillo-Enríquez N C, Oguzlu H, et al. Acidic deep eutectic solvent assisted isolation of lignin containing nanocellulose from thermomechanical pulp[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 247: 116727. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116727
[21] Hong S, Song Y, Yuan Y, et al. Production and characterization of lignin containing nanocellulose from luffa through an acidic deep eutectic solvent treatment and systematic fractionation[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 143: 111913. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111913
[22] Shu F, Guo Y, Huang L, et al. Production of lignin-containing nanocellulose from poplar using ternary deep eutectic solvents pretreatment[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 177: 114404.
[23] Li X, Ning C, Li L, et al. Fabricating lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils with unique properties from agricultural residues with assistance of deep eutectic solvents[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 274: 118650. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118650
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 梅诗意,李瑜,李士帅,朱怡宁,何金春,孟鑫淼,高颖. 寒冷地区多层轻型木结构墙体热湿性能试验研究. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(06): 135-145 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 代倩,胡家航,姬晓迪,郭明辉. 建筑用集成材制造技术的环境效能影响. 林业工程学报. 2018(04): 46-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨俊霞,邹惠芬. 木结构建筑节能技术研究. 西部皮革. 2018(08): 48 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: