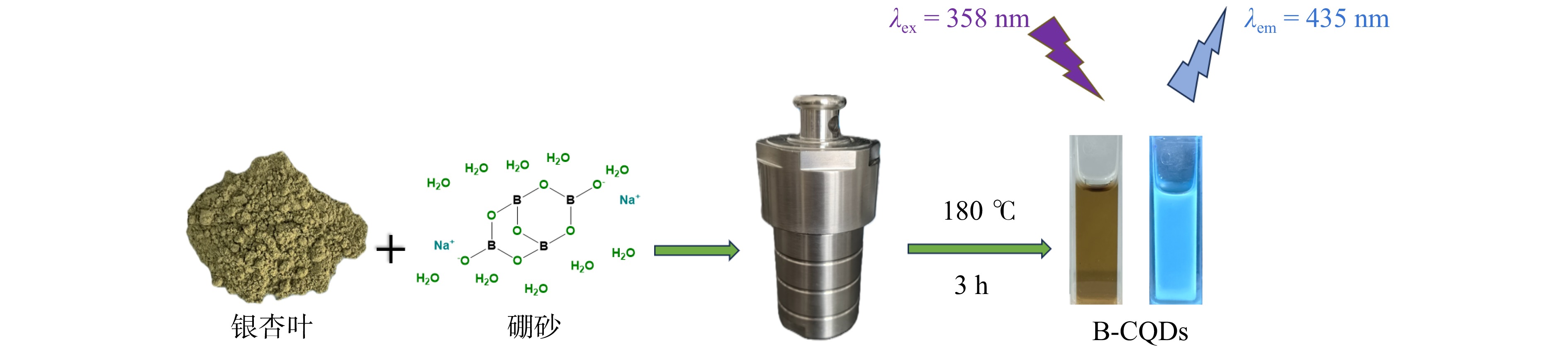
Developing a wood preservative based on boron doping Ginkgo biloba leaf carbon quantum dots with fluorescent tracer function
-
摘要:目的
环境友好型木材防腐剂的开发中,示踪功能对于木材防腐效果的评价研究具有重要意义。为充分发挥银杏叶的抗菌性能、硼砂的阻燃性能以及碳量子点的荧光示踪功能,制备一种新型硼掺杂银杏叶碳量子点(B-CQDs)木材防腐剂,以丰富环境友好型木材防腐剂体系,拓宽碳量子点抗菌性和荧光示踪应用。
方法以绿色生物质银杏叶为碳源,硼砂为硼元素掺杂剂,通过水热法一步合成B-CQDs木材防腐剂,进行单因素实验探究最优制备工艺。采用荧光光谱、紫外可见光光谱、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)、X-射线光电子能谱(XPS)等测试方法对其性能进行表征。以白腐菌彩绒革盖菌和褐腐菌密黏褶菌作为供试菌种,通过抑菌圈试验对不同质量分数的B-CQDs木材防腐剂抑菌效果进行综合评价。
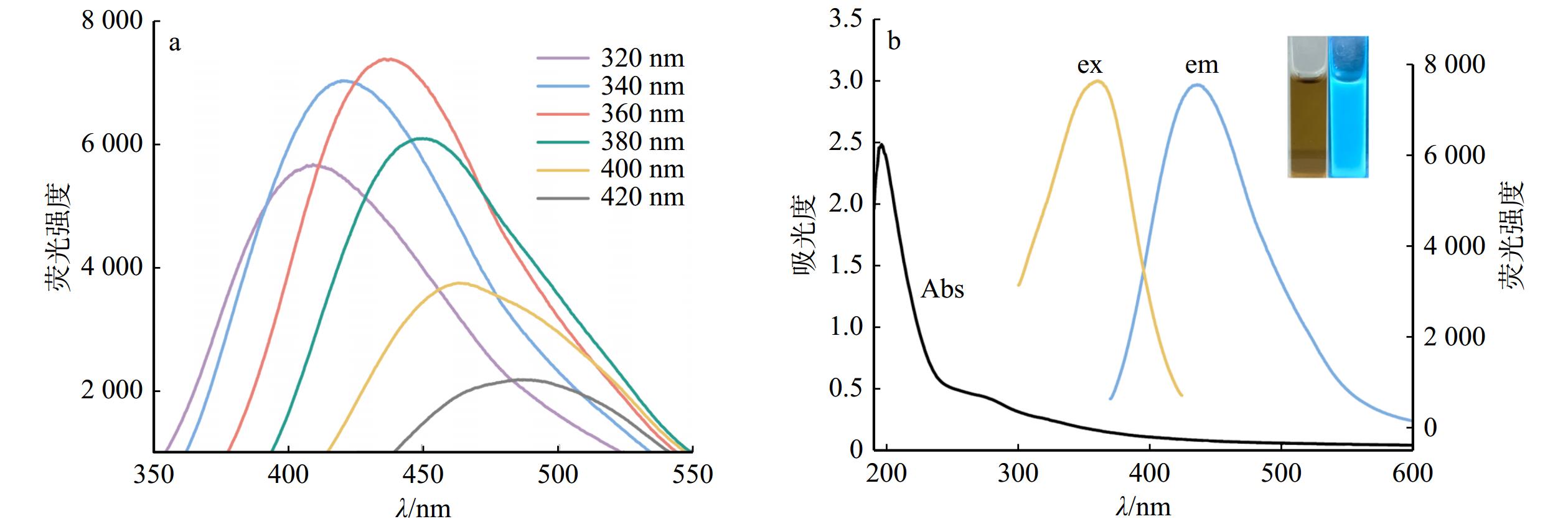
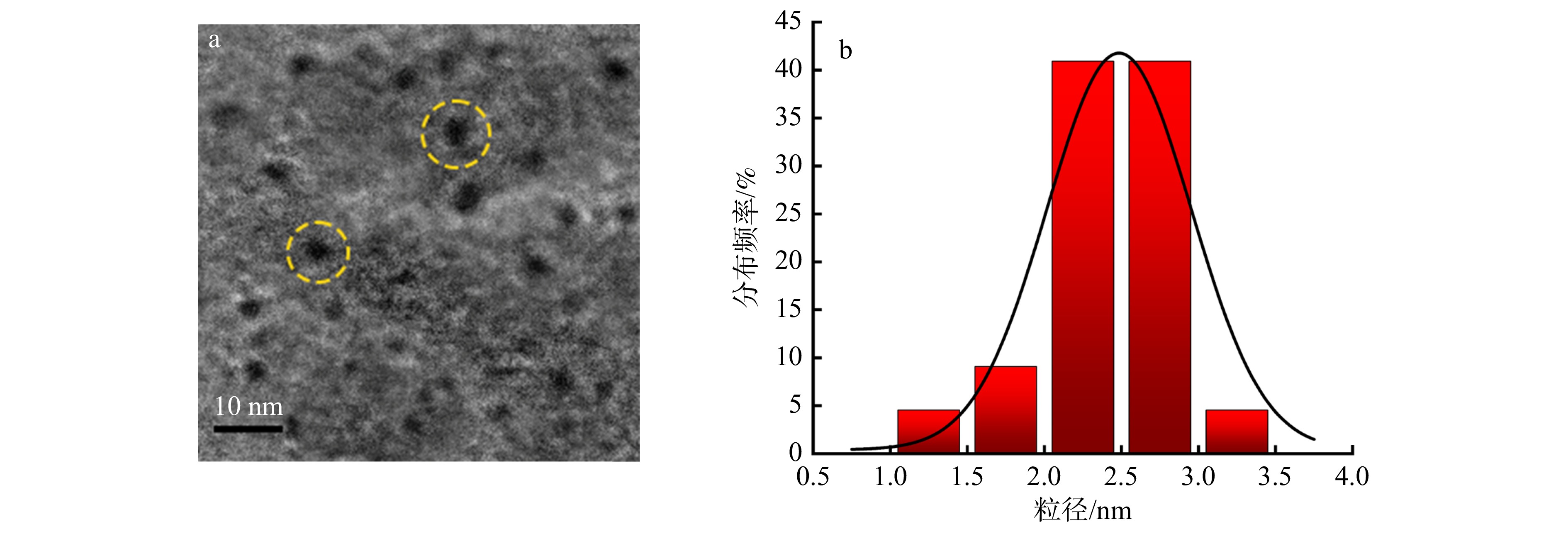
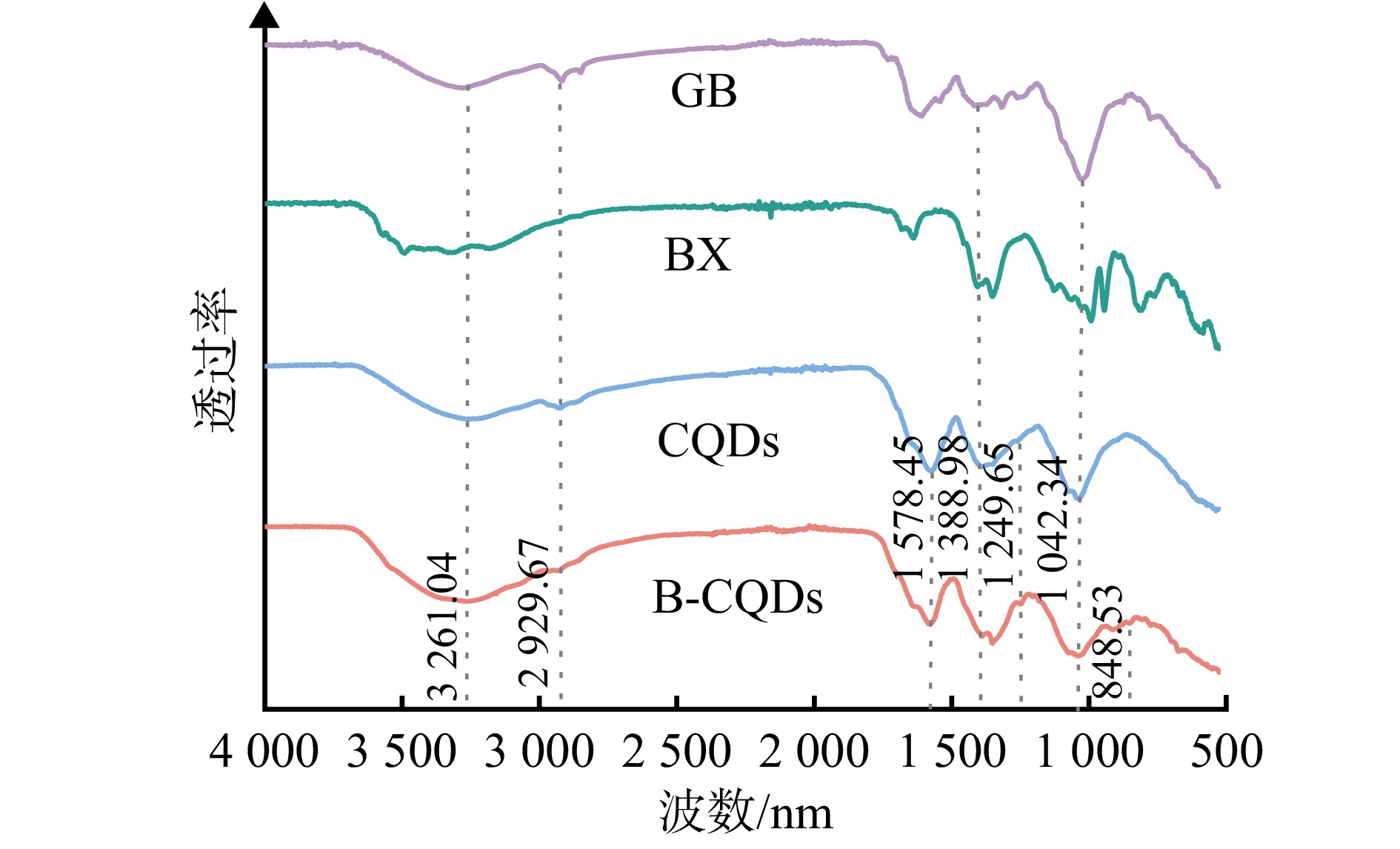
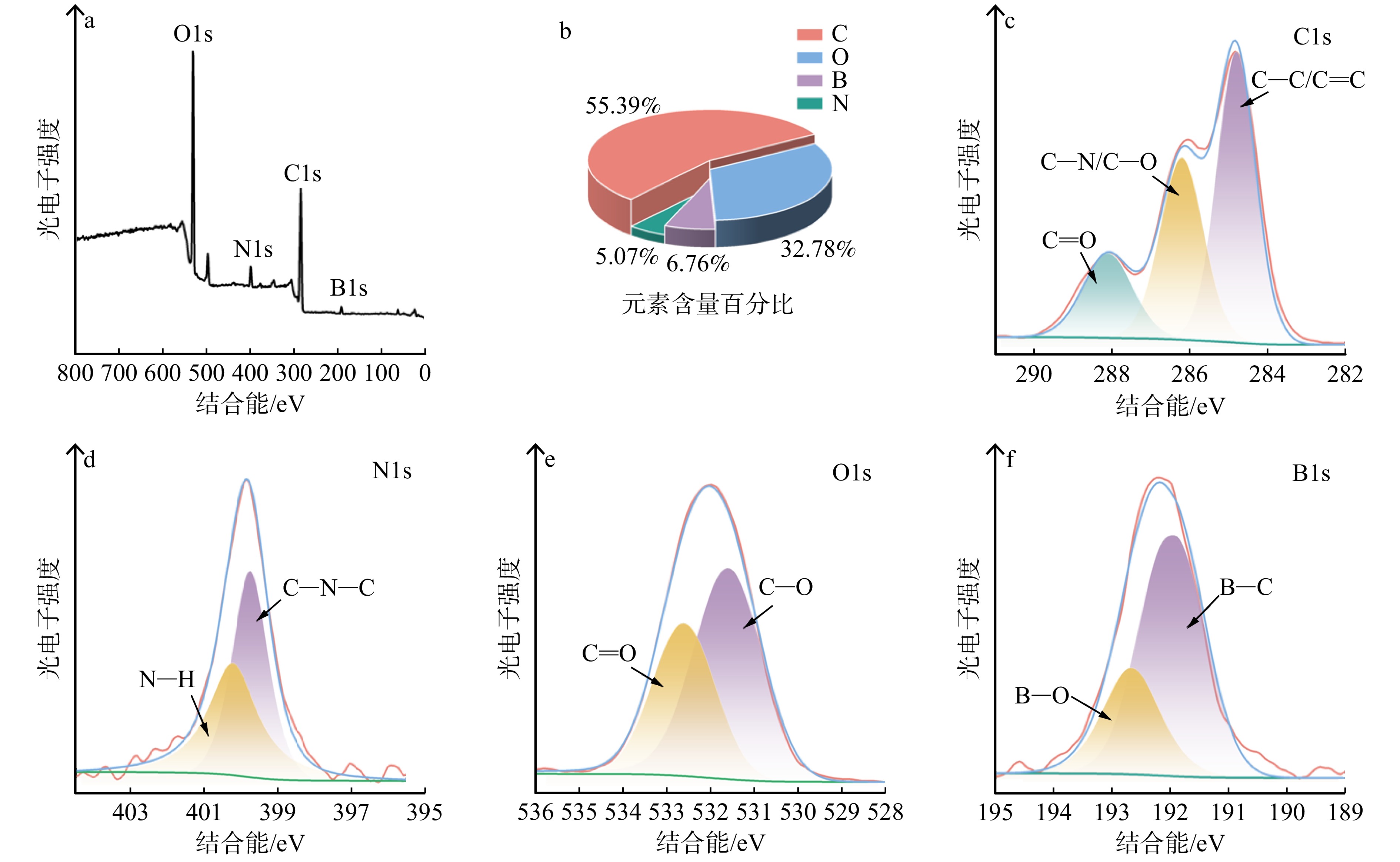
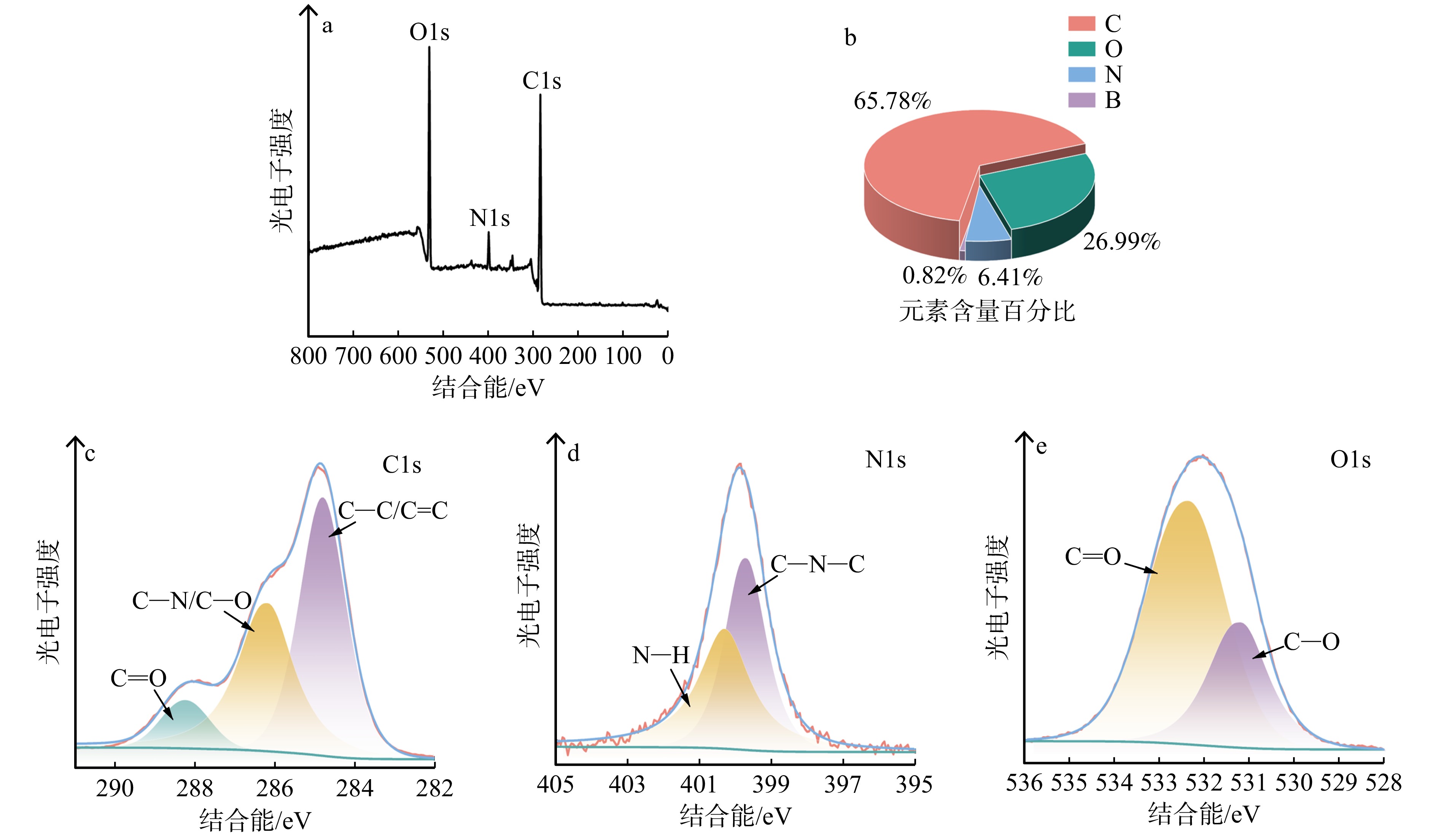
结果以荧光强度为参考指标,B-CQDs木材防腐剂最佳制备条件:水热反应时间3.0 h,水热反应温度180 ℃,银杏叶用量0.5 g,银杏叶与硼砂质量比5∶1。B-CQDs呈类球状,平均粒径为2.41 nm,分散性较好。B-CQDs木材防腐剂具有激发波长依赖性和荧光稳定性,在365 nm紫外光照射下发出明亮蓝色荧光。FTIR与XPS分析的元素组成和官能团信息一致,表明硼元素成功掺入碳量子点。木材腐朽真菌抑菌圈试验结果表明:随着B-CQDs木材防腐剂质量分数的增加,其对2种木材腐朽真菌的抑制效果逐渐增强,B-CQDs木材防腐剂抑制效果优于未掺杂的碳量子点木材防腐剂。当B-CQDs木材防腐剂的质量分数为0.80%时,彩绒革盖菌和密黏褶菌的抑菌圈直径均达到最大值,分别为54.15和63.59 mm。
结论本研究成功制备了B-CQDs木材防腐剂。该防腐剂具有光致发光特性和荧光示踪功能,且对彩绒革盖菌和密黏褶菌2种常见的木腐真菌均有较好的抑制作用,具备作为环境友好型荧光示踪木材防腐剂的潜力。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn the development of environment-friendly wood preservatives, its tracer function is of great significance to the evaluation of wood preservative effect. A new type of wood preservative based on boron doping Ginkgo biloba leaf carbon quantum dots (B-CQDs) was prepared, aiming to make full use of antifungal properties of Ginkgo biloba leaves, flame retardant properties of borax and fluorescent tracer function of carbon quantum dots. B-CQDs will enrich the environment-friendly wood preservative system, and broaden the antifungal properties and fluorescent tracer applications of carbon quantum dots.
MethodThe wood preservative of B-CQDs was one-step hydrothermal synthesized by green biomass Ginkgo biloba leaves as carbon source and borax as boron dopant. The optimum preparation process was investigated by single factor experiment. It was characterized by fluorescence spectrum, UV-visible spectrum, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The antifungal effects with different mass fractions of B-CQDs were evaluated by antifungal zone test with white rot fungi Trametes versicolor and brown rot fungi Gloeophyllum trabeum as the tested fungi.
ResultTaking the fluorescence intensity as test index, the optimum preparation conditions of B-CQDs were hydrothermal reaction time 3.0 h, hydrothermal reaction temperature 180 ℃, dosage of Ginkgo biloba 0.5 g, and mass ratio of Ginkgo biloba leaves to borax 5∶1. B-CQDs were semispherical with better dispersion. The average particle size was 2.41 nm. B-CQDs wood preservatives had excitation wavelength dependence and fluorescence stability, emitting bright blue fluorescence under ultraviolet light at 365 nm. The element composition and functional group information analyzed by FTIR and XPS were consistent, which indicated that boron elements were successfully incorporated into carbon quantum dots. The results of antifungal zone test of wood rot fungi showed that with the increase of mass fraction of B-CQDs, the control effect against two kinds of wood rot fungi had gradually improved. Among them, the antifungal effect of B-CQDs wood preservatives was better than non-doped carbon quantum dot wood preservatives. When the mass fraction of B-CQDs increased to 0.80%, the diameter of antifungal zone of the two groups reached the maximum, which were 54.15 and 63.59 mm, respectively.
ConclusionThe preparation of B-CQDs wood preservative is studied successfully. It has photoluminescence characteristics and fluorescent tracer function. The preservative has good antifungal effect on two kinds of common wood rot fungi (Trametes versicolor and Gloeophyllum trabeum). It has the potential to be used as environment-friendly wood preservative with the function of fluorescent tracer.
-
Keywords:
- wood preservation /
- fluorescence /
- tracer /
- carbon quantum dots /
- Ginkgo biloba leaves /
- boron doping /
- wood rot fungi
-
随着全球气候变暖,极端气候频现,干旱、盐害等非生物胁迫已成为威胁全球农林业生产和发展的一个重大挑战[1]。植物为了适应逆境环境并得以生存,进化出相关基因来维持细胞内结构和功能机制的稳定[2]。迄今为止,已发现许多与干旱和盐胁迫防御相关的功能基因,其中包括膜联蛋白基因。膜联蛋白是一个超级基因家族的多功能脂结合蛋白,到目前已从超过65个物种中分离和克隆了编码基因,包括真菌、原生生物、植物、高等脊椎动物和原核生物 [3]。Creutz等人[4]1978年首次从牛肾上腺髓质嗜铬细胞中分离纯化出一种蛋白质Annexin A7(synexin),这种蛋白促使嗜铬颗粒通过依赖Ca2+来结合一些膜或者内膜成分。而国内学者对植物膜联蛋白的研究较晚,第1个植物膜联蛋白是从悬浮培养的番茄 (Solanum lycopersicum) 细胞中发现和分离的[5],且与动物膜联蛋白在序列上有较高的同源性[6]。随着对植物膜联蛋白的进一步了解,发现膜联蛋白广泛分布于各种植物中,如棉花(Gossypium spp.)[7]、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)[8]、玉米(Zea mays)[9]、拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)[10]、水稻(Oryza sativa)[11]等。不同植物中的膜联蛋白以基因家族的形式存在,其家族成员各自具有不同的功能和时空表达模式,表达具有组织特异性。据报道膜联蛋白参与重要的生物过程,如膜运输、细胞骨架组织、细胞内稳态和离子运输,具有Ca2+结合、离子通道和过氧化物酶活性等不同的生物学功能,在植物生长发育、信号转导、适应环境和响应非生物逆境胁迫中发挥着重要作用[12]。在渗透胁迫、脱落酸(ABA)或干旱等非生物胁迫时紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)中的膜联蛋白被激活上调表达[13]。拟南芥中膜联蛋白的表达能响应各种非生物胁迫(如盐胁迫、渗透胁迫和低温胁迫)而发生变化[14]。Cantero等人[15]评估了拟南芥中的8种膜联蛋白基因表达模式,并建立了它们在盐、干旱和其他非生物胁迫下的差异调控机制。拟南芥t-dna突变体表明,AtAnn1和AtAnn4在萌发过程中能应答渗透胁迫[16]。拟南芥AtAnn1基因是植物中研究较多的一个膜联蛋白,过表达AtAnn1导致耐旱性增强,而AtAnn1缺失突变株抗旱能力降低,对干旱更敏感[17]。印度芥菜(Brassica juncea)中,过表达AnnBj1分别增强了转基因烟草和棉花的耐旱性和耐盐性[18]。小麦 经低温胁迫可诱导膜联蛋白p39和p22.5的表达,嵌插在质膜上感受或转导钙信号的同时还调节胞质中的钙离子浓度适应胁迫环境[19]。虽然膜联蛋白在植物胁迫反应中发挥重要作用,但不同植物膜联蛋白的分子性能、生理和生物学功能是否有所不同,还属未知。
胡杨(Populus euphratica)适应非生物胁迫环境能力极强,其抗逆机制受到国内外广泛关注。胡杨耐旱性的生理及分子机制虽有较多的研究,但目前未有胡杨膜联蛋白与水分胁迫相关性的报道。本研究通过对比胡杨Annexin1转基因拟南芥、野生型、突变体(atann1)在渗透胁迫、干旱胁迫及复水后的表型及生理生化反应,明确PeAnn1在植物耐受水分胁迫中的作用,研究结果有助于揭示树木的抗旱性机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
将来自新疆的胡杨1年生实生苗栽植在北京林业大学苗圃的温室,培养3个月后,利用250 mmol/L甘露醇处理12 h,在渗透胁迫处理0、4、8、12 h后采集叶片,进行RT-qPCR分析。
将野生型拟南芥(WT)、突变体(atann1)和2个过表达胡杨PeAnn1拟南芥(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)种子在超净台中用质量分数为1%的次氯酸钠消毒10 min后,无菌水冲洗5次,播种于1/2 MS固体培养基(含有10 g/L蔗糖和质量分数为0.3%的植物凝胶,pH 5.8)上,4 ℃低温暗培养春化2 d,取出置于22 ℃、16 h光照/8 h黑暗的人工气候培养箱中生长。生长7 d的幼苗移栽于草炭土和蛭石的混合比例为 2∶1(w∶w)的土壤中,转入22 ℃、16 h光照/8 h黑暗,55% ~ 65%相对湿度的温室中生长。
胡杨苗木培养,PeAnn1基因克隆,RT-qPCR分析,以及转基因植物的培育及分子检测参见文献[20]。RNA提取试剂盒购自康为世纪生物科技有限公司;cDNA反转录试剂盒购自普洛麦格生物技术有限公司;其余试剂由北京拜尔迪生物科技有限公司提供。引物合成由北京睿博兴科生物技术有限公司完成。RNA提取、纯化、RT-qPCR参见文献[21]。
1.2 PeAnn1序列与进化树分析
通过NCBI(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)在线获取不同植物Annexin同源基因序列。利用Mega 6软件(http://www.megasoftware.net/index.php)对胡杨PeAnn1、毛白杨(Populus tomentosa)PtAnn1、拟南芥AtAnn1、野生大豆(Glycine soja)GsANN和水稻OsAnn8等基因序列进行多重序列比对分析,并对不同物种同源Annexins构建系统进化树。
1.3 渗透胁迫下拟南芥耐旱性检测
1.3.1 种子萌发率
在1/2 MS固体培养基中添加不同浓度的甘露醇模拟渗透胁迫,甘露醇浓度梯度设为150、200、250、300 mmol/L 4个梯度,以不加甘露醇的培养基作为对照。拟南芥种子在超净台中用质量分数为1%的次氯酸钠消毒10 min后,无菌水冲洗5次,依次点播在各个培养基上,每个株系点播50粒种子,每种处理做3次重复。4 ℃低温暗培养2 d后置于22 ℃、16 h光照/8 h黑暗的恒温培养箱中培养,10 d后记录萌发率。
1.3.2 根 长
选取在1/2MS固体培养基中萌发5 d,长势相似的拟南芥幼苗,移栽到正常对照培养基和甘露醇浓度梯度150、200、250、300 mmol/L的固体培养基上,观察拍照并测量记录拟南芥竖直生长7 d后的根长。
1.4 渗透胁迫下转基因拟南芥H2O2含量的测定
采用荧光探针H2DCF-DA(molecular probe)染色测定H2O2含量[22]。将在1/2MS固体培养基上萌发、生长7 d的各株系拟南芥幼苗(WT、atann1、PeAnn1-OE1
和PeAnn1-OE2)移到含有250 mmol/L甘露醇的LMS培养基中,12 h后取出幼苗,将幼苗浸入10 μmol/L H2DCF-DA的探针溶液,室温避光孵育15 min。取出幼苗,用蒸馏水冲洗3 ~ 4次,去除表面残留探针染料。利用Leica SP5激光共聚焦显微镜(Wetzlar, 德国)测定H2DCF-DA绿色荧光,激发光波长488 nm,发射光波长510 ~ 530 nm,相对荧光强度由Image-Pro Plus version 4.5软件计算。 1.5 渗透胁迫下转基因拟南芥抗氧化酶活性的测定
采用紫外吸收法[23]测定过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性,以1 min内ΔA240减少0.01的酶量为1个过氧化氢酶活性单位(U)。采用NBT(氮蓝四唑)光化还原法[24]测定超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,以抑制NBT光还原50%的酶量为1个酶活力单位(U)。采用愈创木酚法[25]测定过氧化物酶(POD)活性,以每分钟OD值变化(升高)0.01为1个酶活性单位(U)。按照考马斯亮蓝G250法进行蛋白含量的测定。
1.6 转基因拟南芥中抗逆相关基因表达水平的检测
将野生型拟南芥和转基因拟南芥播种于1/2MS培养基上进行培养,萌发5 d后长势相似的拟南芥移至250 mmol/L甘露醇的1/2MS培养基上进行处理。处理10 d后取样,利用TRIzon试剂(康为世纪)提取总RNA并反转录合成第1条cDNA,通过荧光定量PCR检测抗逆相关基因SOD(超氧化物歧化酶基因)、CAT(过氧化氢酶基因)、POD(过氧化物酶基因)的转录水平表达情况,以拟南芥AtACTIN2(At3g18780)为内参,各抗氧化酶基因荧光定量引物见表1。
表 1 本文实验中所用到的引物序列Table 1. Gene-specific primer sequences used in this study引物名称 Primer name 上游引物 Forward primer (5′−3′) 下游引物 Reverse primer (5′−3′) AtACTIN2 GGTAACATTGTGCTCAGTGGTGG AACGACCTTAATCTTCATGCTGC AtSOD AGGAAACATCACTGTTGGAGAT GAGTTTGGTCCAGTAAGAGGAA AtCAT AGGATCAAACTTTGAGGGGTAG CTTGTGGTTCCTGGAATCTACT AtPOD CGTGCCCTTCATATTGTTGG GACGCCATCAACAACGAGTC 1.7 自然干旱条件下拟南芥叶绿素荧光参数的测定
选取生长20 d,状况良好且一致的野生型、突变体和转基因株系通过控制浇水模拟土壤干旱,浇足水后当天作为干旱的第1天,设置5个重复。分别在正常浇水、干旱处理8 d和复水3 d后采样进行相关指标的测定。
1.7.1 叶绿素荧光参数
每次早上10:00开始测定,选取暗适应30 min后的拟南芥叶片。利用Junior PAM便携式荧光仪(WALZ,德国)测定叶片正常浇水,干旱处理8 d和复水3 d后的荧光参数,包括PSⅡ最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)、实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)和相对电子传递速率(ETR)。各个参数直接从仪器导出,每个株系重复3 ~ 5次,取平均值。
1.7.2 叶绿素相对含量
利用日本Minolta公司生产的便携式叶绿素计(SPAD-502 Plus)原位测定叶绿素相对含量,以SPAD值表示[26]。测定时选取长势一致的叶片、叶缘和叶脉中间的部位。要注意避开叶脉集中的部位,同时适当遮挡直射阳光,以保证测量的准确性。每个株系重复3 ~ 5次,取平均值。
1.8 数据分析
实验数据采用Excel和SPSS 19.0软件进行数据统计、分析并绘图。用SPSS 19.0软件中的最小显著性差异法(LSD)进行单因素方差分析,用Duncan法进行多重比较分析,显著性水平设定为α = 0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 渗透胁迫诱导胡杨PeAnn1基因表达
胡杨苗木经250 mmol/L甘露醇处理后,PeAnn1基因表达发生明显变化,PeAnn1基因相对表达量在渗透胁迫处理4 h后显著提高,之后下降,在渗透胁迫处理12 h后降至对照水平(图1)。
![]() 图 1 甘露醇处理对胡杨PeAnn1基因表达的影响胡杨1年生苗木经250 mmol/L甘露醇处理12 h,渗透胁迫处理0、4、8、12 h后采集叶片进行RT-qPCR分析,每个数值均为3次生物样本重复,*表示差异显著,P < 0.05。One-year-old seedlings of P. euphratica were subjected to 250 mmol/L mannitol and stressed for 12 hours. Then leaves were sampled after being treated for 0, 4, 8, 12 hours under osmotic stress and used for RT-qPCR analysis. Each column is the mean of three biological repeats. Asterisk represents significant differences at P < 0.05 level.Figure 1. Effects of mannitol stress on expression of PeAnn1 in Populus euphratica leaves
图 1 甘露醇处理对胡杨PeAnn1基因表达的影响胡杨1年生苗木经250 mmol/L甘露醇处理12 h,渗透胁迫处理0、4、8、12 h后采集叶片进行RT-qPCR分析,每个数值均为3次生物样本重复,*表示差异显著,P < 0.05。One-year-old seedlings of P. euphratica were subjected to 250 mmol/L mannitol and stressed for 12 hours. Then leaves were sampled after being treated for 0, 4, 8, 12 hours under osmotic stress and used for RT-qPCR analysis. Each column is the mean of three biological repeats. Asterisk represents significant differences at P < 0.05 level.Figure 1. Effects of mannitol stress on expression of PeAnn1 in Populus euphratica leaves2.2 胡杨PeAnn1序列与进化树分析
胡杨PeAnn1与毛白杨PtAnn1、拟南芥AtAnn1、大豆GsANN和水稻OsAnn8同源基因的相似度分别为85%、72.56%、56%、29.51%,胡杨PeAnn1与毛白杨PtAnn1的相似性最高(图2A)。系统进化树分析结果表明,PeAnn1与毛白杨PtAnn1的亲缘关系最为接近(图2B)。
![]() 图 2 胡杨PeAnn1基因序列比对与系统进化树分析A. 胡杨 PeAnn1基因与其他植物Annexin同源基因多重序列比对。B. 不同植物Annexin蛋白的系统进化树分析。胡杨PeAnn1(XM_011018027.1)、毛白杨PtAnn1(JX986594.1)、拟南芥AtAnn1(NM_103274.4)、野生大豆GsANN(GU474544.1)、水稻OsAnn8(LOC_Os09g20330.1)。A, multiple alignment of the deduced gene sequences of PeAnn1 with other Annexins from different plant species. B, phylogenetic tree analysis of Annexin proteins. P. euphratica Anneixn1(XM_011018027.1), P. tomentosa PtAnn1(JX986594.1), Arabidopsis thaliana AtAnn1(NM_103274.4), Glycine soja GsANN(GU474544.1), and Oryza sative OsAnn8(LOC_Os09g20330.1).Figure 2. Multiple alignment of PeAnn1 gene sequences with other Annexins from different plant species and phylogenetic tree analysis of Annexin proteins
图 2 胡杨PeAnn1基因序列比对与系统进化树分析A. 胡杨 PeAnn1基因与其他植物Annexin同源基因多重序列比对。B. 不同植物Annexin蛋白的系统进化树分析。胡杨PeAnn1(XM_011018027.1)、毛白杨PtAnn1(JX986594.1)、拟南芥AtAnn1(NM_103274.4)、野生大豆GsANN(GU474544.1)、水稻OsAnn8(LOC_Os09g20330.1)。A, multiple alignment of the deduced gene sequences of PeAnn1 with other Annexins from different plant species. B, phylogenetic tree analysis of Annexin proteins. P. euphratica Anneixn1(XM_011018027.1), P. tomentosa PtAnn1(JX986594.1), Arabidopsis thaliana AtAnn1(NM_103274.4), Glycine soja GsANN(GU474544.1), and Oryza sative OsAnn8(LOC_Os09g20330.1).Figure 2. Multiple alignment of PeAnn1 gene sequences with other Annexins from different plant species and phylogenetic tree analysis of Annexin proteins2.3 渗透胁迫下拟南芥的萌发率
将各株系拟南芥种子播种于含有不同浓度甘露醇的1/2 MS培养基中培养,观察萌发率和生长状态。从图3A中可以看出,未经甘露醇处理时,各个基因型的拟南芥均正常生长,长势一致,无显著差异。但在含有甘露醇的培养基上,各株系的拟南芥的生长均受到抑制,且随着甘露醇浓度的升高,生长抑制作用逐渐加强。当甘露醇浓度达到250 mmol/L时,野生型、突变体种子萌发率急剧降低,降至75.8%、78.7%,转基因拟南芥OE1和OE2的种子受到的抑制作用更严重,萌发率降至69.0%、71.6%(图3B)。当甘露醇浓度达到300 mmol/L时,转基因株系OE1和OE2的种子萌发率分别为46.9%、48.9%,仅是对照组的47.8%、49.1%,与野生型和突变体间差异显著(P < 0.05, 图3B)。结果表明,过表达PeAnn1拟南芥株系OE1和OE2在甘露醇培养基上的长势弱于野生型和突变体,对渗透胁迫更敏感。
![]() 图 3 不同浓度甘露醇对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1
图 3 不同浓度甘露醇对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2 )拟南芥萌发率的影响 A. 甘露醇对种子萌发生长的影响(拟南芥播种在含有不同浓度甘露醇的1/2MS培养基上,生长10 d后的照片);B. 种子萌发率分析。不同字母表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著,下同。A, effects of mannitol stress on seed germination rate (seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana are allowed to germinate on 1/2 MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of mannitol. Representative photographs are taken after 10 days of treatment); B, analysis on seed germination rate. Different letters denote significant differences at P < 0.05 level, the same below.Figure 3. Effects of different concentrations mannitol on seed germination rate of WT, atann1 and PeAnn1-transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana (PeAnn1-OE1 , PeAnn1-OE2) 2.4 渗透胁迫下拟南根长的变化
根长结果显示,在无甘露醇的对照培养基上,转基因拟南芥OE2根长生长低于其他株系(图4A、4B)。在含有不同浓度梯度(150、200、250、300 mmol/L)的甘露醇培养基上,各拟南芥的根长生长均受到抑制,且随着处理浓度的增加抑制作用逐渐加强,其长度逐渐缩短(图4A)。250 mmol/L浓度的甘露醇处理后,野生型和突变体株系根长分别降低了42.5%和46.3%,转基因株系OE1和OE2根的长度下降更显著,达到58.8%和57.7%(图4B)。当甘露醇的浓度达到300 mmol/L时,转基因OE1和OE2的根长分别降低了72.4%和70.7%(图4B),说明高浓度的甘露醇对拟南芥根生长产生极大的抑制作用。而渗透胁迫下野生型与突变体根长显著高于转基因拟南芥OE1和OE2,说明过表达PeAnn1影响了转基因株系的根长生长。根据甘露醇梯度实验结果,确定250 mmol/L甘露醇为拟南芥渗透胁迫处理的最适浓度,并进行H2O2含量、抗氧化酶活性和基因表达等指标的测定。
![]() 图 4 不同浓度甘露醇对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥根长生长的影响A. 甘露醇对根长生长的影响(拟南芥播种在1/2MS培养基萌发5 d后,移植到含有不同浓度甘露醇的1/2MS培养基垂直生长7 d后的照片), 标尺为1 cm;B. 根系生长分析。A, effects of mannitol stress on root growth (seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana are allowed to germinate on 1/2 MS medium for 5 days, then transplanted to 1/2 MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of mannitol. Representative photographs are taken after 7 days of treatment). Scale bar = 1 cm; B, root growth analysis.Figure 4. Effects of different concentrations mannitol on root growth of WT, atann1 and PeAnn1-transgenicArabidopsis thaliana (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)
图 4 不同浓度甘露醇对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥根长生长的影响A. 甘露醇对根长生长的影响(拟南芥播种在1/2MS培养基萌发5 d后,移植到含有不同浓度甘露醇的1/2MS培养基垂直生长7 d后的照片), 标尺为1 cm;B. 根系生长分析。A, effects of mannitol stress on root growth (seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana are allowed to germinate on 1/2 MS medium for 5 days, then transplanted to 1/2 MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of mannitol. Representative photographs are taken after 7 days of treatment). Scale bar = 1 cm; B, root growth analysis.Figure 4. Effects of different concentrations mannitol on root growth of WT, atann1 and PeAnn1-transgenicArabidopsis thaliana (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)2.5 渗透胁迫下拟南芥H2O2含量的变化
H2DCFDA是一种脂溶性荧光探针,具有细胞渗透性且自身无荧光的氧化反应指示剂。进入细胞后被细胞酯酶水解成非脂溶性的DCFH且不被质膜排出,之后在过氧化物酶的催化下可被H2O2氧化转变成为强荧光性的DCF,细胞内DCF的荧光强度与胞内H2O2水平呈显著正相关,因此被广泛用来检测细胞内活性氧(ROS)的含量和监测细胞氧化还原反应过程[27]。H2DCFDA的测定结果显示,在正常条件下,转基因株系OE1和OE2根细胞H2O2水平较高,与野生型、突变体拟南芥有显著差异。经250 mmol/L甘露醇渗透胁迫后,除转基因株系OE2外,各拟南芥株系的H2O2水平均有显著增加(图5),说明渗透胁迫下,植物体内积累了大量的活性氧,而且250 mmol/L甘露醇对转基因株系的作用更加明显:OE1和OE2 H2O2的水平分别是野生型拟南芥、突变体的1.19 ~ 1.36倍和1.37 ~ 1.55倍(图5),说明转基因拟南芥在渗透逆境下难以清除体内过多的H2O2,抗氧化防御系统能力弱于野生型拟南芥和突变体。
![]() 图 5 甘露醇胁迫下野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1
图 5 甘露醇胁迫下野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥根细胞H2O2荧光强度的变化 甘露醇(250 mmol/L)胁迫下拟南芥根细胞H2O2荧光强度的变化。H2O2 fluorescence intensity variation of Arabidopsis thaliana under mannitol stress (250 mmol/L).Figure 5. Effects of mannitol stress on H2O2 fluorescence intensity in root cells of wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic lines(PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)2.6 渗透胁迫下拟南芥抗氧化物酶活性的变化
当植物处于不利于自身生长的条件时,活性氧增多,SOD、CAT、POD等抗氧化酶清除超氧阴离子和H2O2,从而保持活性氧的动态平衡,减轻ROS对植物的危害[28]。通过对250 mmol/L甘露醇胁迫处理后各株系中SOD活性的检测,发现甘露醇处理后各拟南芥体内的SOD活性均显著增加,野生型和突变体的SOD值变化幅度较大,分别较对照组上升了33.1%和52.8%,说明拟南芥幼苗的SOD对其在干旱胁迫下自由基的清除具有重要作用。转基因株系OE1和OE2的SOD活性增幅较低,且在渗透胁迫后,SOD活性显著低于野生型和突变体(图6A)。POD能清除对植物体有毒害作用的氧自由基,防止细胞衰老,提高植物的抗逆能力。由图6B可知,渗透胁迫后,各拟南芥的POD活性均呈不同程度的下降,其中野生型、转基因株系OE1和OE2与对照组间差异显著,分别下降了15.2%、33.4%、35.7%;突变体拟南芥无显著差异。CAT作为植物体内分解、清除H2O2的重要保护酶类之一。在250 mmol/L甘露醇胁迫条件下,水分的缺失诱导植物体内CAT活性提高,从而加速H2O2的分解,避免羟基、自由基的产生,对植物细胞膜的过氧化有一定减缓作用。图6C中结果显示,正常条件下各个拟南芥株系的CAT活性差异显著。胁迫处理后,野生型和突变体的CAT活性显著增加,而转基因株系OE1的CAT活性升高幅度较小,OE2的CAT活性显著降低,较处理前下降了29.3%。
![]() 图 6 甘露醇胁迫下野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥中SOD酶活性、POD酶活性和CAT酶活性的变化A. 甘露醇胁迫下SOD活性;B. 甘露醇胁迫下POD活性;C. 甘露醇胁迫下CAT活性。A, SOD activity under mannitol stress; B, POD activity under mannitol stress; C, CAT activity under mannitol stress.Figure 6. Effects of mannitol stress on the activities of SOD, POD and CAT in wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic lines (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)
图 6 甘露醇胁迫下野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥中SOD酶活性、POD酶活性和CAT酶活性的变化A. 甘露醇胁迫下SOD活性;B. 甘露醇胁迫下POD活性;C. 甘露醇胁迫下CAT活性。A, SOD activity under mannitol stress; B, POD activity under mannitol stress; C, CAT activity under mannitol stress.Figure 6. Effects of mannitol stress on the activities of SOD, POD and CAT in wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic lines (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)2.7 渗透胁迫下抗氧化酶基因表达量的变化
为了探究PeAnn1转基因株系在渗透胁迫下抗氧化酶活性下降的原因,本文检测了渗透胁迫后各基因型抗氧化酶基因的表达。图7A结果表明,渗透胁迫处理后,AtSOD基因的表达水平在野生型和突变体拟南芥中显著升高,与对照组相比分别上升了50%、38.5%;而在转基因株系OE1和OE2中显著下降。图7B中显示,渗透胁迫处理的野生型和突变体拟南芥AtPOD基因表达水平几乎没有变化,而转基因株系OE1和OE2与对照组间差异显著,AtPOD表达量分别下降了33.4%、35.7%。同样,在渗透胁迫后,各个拟南芥的AtCAT表达水平也均显著降低,转基因株系OE1和OE2的AtCAT基因表达水平下降幅度最大,分别较对照组下降了58.2%、66.1%(图7C)。综上可知,250 mmol/L甘露醇处理条件下转基因株系OE1和OE2体内AtSOD、AtPOD和AtCAT基因的表达水平显著均低于野生型和突变体(图7A~7C),说明过表达胡杨PeAnn1降低了拟南芥ROS清除酶基因的表达,导致不能清除体内过量的H2O2,抗旱性较弱。
![]() 图 7 甘露醇胁迫对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1
图 7 甘露醇胁迫对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2 )拟南芥抗氧化酶基因AtSOD、AtPOD和AtCAT表达的影响 A. 甘露醇胁迫下AtSOD基因表达;B. 甘露醇胁迫下AtPOD基因表达;C. 甘露醇胁迫下AtCAT基因表达;内参基因为AtACTIN2,n = 3。A, AtSOD expression under mannitol stress; B, AtPOD expression under mannitol stress; C, AtCAT expression under mannitol stress; reference gene: AtACTIN2, n = 3.Figure 7. Effects of mannitol stress on relative expression of antioxidant-enzyme genes (AtSOD, AtPOD and AtCAT) in wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic lines (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2)![]() 图 8 干旱和复水后野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥的光合参数变化A. 干旱及复水后拟南芥的生长状况;B~D. 正常浇水、干旱8 d、复水3 d拟南芥的PSⅡ最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)、相对电子传递效率(ETR)、实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)的变化。A, plant performance of Arabidopsis thaliana after drought stress and rewatering; B−D, maximum photon efficiency of PSⅡ(Fv/Fm), relative electron transfer efficiency(ETR), and actual photosynthetic quantum yield(ΦPSⅡ) of Arabidopsis thaliana under normal watering, 8 days of drought stress and 3 days of rewatering.Figure 8. Changes of photosynthetic parameters in wild-type (WT), atann1, and transgenic lines (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2) under drought stress and rewatering
图 8 干旱和复水后野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥的光合参数变化A. 干旱及复水后拟南芥的生长状况;B~D. 正常浇水、干旱8 d、复水3 d拟南芥的PSⅡ最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)、相对电子传递效率(ETR)、实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)的变化。A, plant performance of Arabidopsis thaliana after drought stress and rewatering; B−D, maximum photon efficiency of PSⅡ(Fv/Fm), relative electron transfer efficiency(ETR), and actual photosynthetic quantum yield(ΦPSⅡ) of Arabidopsis thaliana under normal watering, 8 days of drought stress and 3 days of rewatering.Figure 8. Changes of photosynthetic parameters in wild-type (WT), atann1, and transgenic lines (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2) under drought stress and rewatering2.8 干旱胁迫下拟南芥叶绿素荧光参数的变化
对各株系拟南芥进行土壤干旱处理,并测定叶绿素含量及荧光参数。干旱处理前,拟南芥生长状况没有明显差异,干旱胁迫8 d后植株失水枯黄,野生型和突变体拟南芥长势较好。复水3 d后,转基因株系死亡率较高(图8A)。
叶绿素荧光参数反映植物光反应中心活性和光合生理状况。胁迫条件下PSⅡ的最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)的变化可反映PSⅡ的光抑制程度[29]。如图8B所示,在干旱胁迫前,野生型、突变体和转基因株系OE1和OE2的Fv/Fm为0.706 ~ 0.747,其中转基因株系OE2的Fv/Fm最低,与其他拟南芥株系有显著差异(P < 0.05)。干旱胁迫8 d后,各株系的Fv/Fm有不同程度的降低,转基因株系的Fv/Fm下降更为显著;复水3 d后,PSⅡ最大光化学效率均迅速恢复,但转基因株系的恢复幅度不及野生型和突变体(图8B)。说明PeAnn1转基因株系的光反应中心在干旱胁迫条件下受到逆境的伤害较大。
干旱处理前,转基因株系和突变体的相对电子传递效率(ETR)、实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)均低于野生型(图8C、8D)。干旱8 d后,转基因株系的ETR和ΦPSⅡ值均大幅度降低,明显高于野生型、突变体株系的下降幅度(图8C、8D)。复水3 d后,各个拟南芥株系的相对电子传递效率(ETR)和实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)均快速恢复,但转基因株系的恢复程度远低于野生型、突变体拟南芥(图8C、8D)。这说明,与光反应中心相似,PeAnn1转基因株系的捕光蛋白复合体在干旱胁迫下被严重破坏,电子传递受阻,光能转化效率降低。
2.9 干旱胁迫下拟南芥叶绿素含量的变化
叶绿素相对含量采用叶绿素仪(SPAD 仪)原位测定[22]。由图9可以看出,在干旱前,突变体atann1的SPAD值显著高于野生型和转基因株系OE1和OE2(P < 0.05)。干旱8 d后,SPAD值均显著降低,其中转基因株系下降幅度最大。复水后第3天,各株系拟南芥的SPAD值均有所增加,但仍远低于干旱前的水平,特别是转基因株系。这表明干旱胁迫使转基因拟南芥叶绿素含量显著下降。与转基因株系相比,突变体atann1能在干旱和复水期间维持较高的叶绿素含量。
![]() 图 9 干旱和复水后野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥的叶绿素相对含量拟南芥正常浇水、干旱8 d、复水3 d叶绿素SPAD值的变化。Chlorophyll SPAD values of Arabidopsis thaliana under normal watering, 8 days of drought stress and 3 days of rewatering.Figure 9. Changes of relative chlorophyll content in wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic plant (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2) under drought stress and rewatering
图 9 干旱和复水后野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和过表达PeAnn1(PeAnn1-OE1和PeAnn1-OE2)拟南芥的叶绿素相对含量拟南芥正常浇水、干旱8 d、复水3 d叶绿素SPAD值的变化。Chlorophyll SPAD values of Arabidopsis thaliana under normal watering, 8 days of drought stress and 3 days of rewatering.Figure 9. Changes of relative chlorophyll content in wild-type (WT), atann1 and transgenic plant (PeAnn1-OE1, PeAnn1-OE2) under drought stress and rewatering3. 讨 论
渗透胁迫处理诱导了胡杨叶片PeAnn1基因瞬时的上调表达(图1),表明PeAnn1参与了胡杨对水分胁迫的响应。为了明确胡杨PeAnn1在植物耐受水分胁迫中的作用,本文对野生型(WT)、Annexin1突变体(atann1)和PeAnn1转基因株系OE1和OE2进行渗透胁迫和干旱胁迫处理,研究各株系的表型差异。结果表明,甘露醇处理后,WT、atann1和转基因株系OE1和OE2的种子萌发率和根长均受到抑制,且抑制作用随甘露醇浓度提高而增强(图3、4)。在高渗透胁迫(250 ~ 300 mmol/L甘露醇)条件下,转基因植株的萌发率、根长显著低于野生型和突变体。干旱胁迫下,转基因株系的光合参数下降幅度高于野生型和突变体(图8、9),这些表型结果说明,过表达胡杨PeAnn1使转基因植株对水分胁迫的敏感性提高。
PeAnn1转基因株系对水分胁迫耐受性的下降与光合参数的下降有关。叶绿素含量、PSⅡ最大光量子效率(Fv/Fm)、相对电子传递效率(ETR)和实际光合量子产量(ΦPSⅡ)的高低反映植物的光合能力和生长状况[30]。SPAD 值是一项表征叶片光合活性的指标,它与单位叶面积的叶绿素含量及叶绿素的密度显著正相关[31],因此,常用SPAD 值的大小来衡量叶片中叶绿素含量。干旱胁迫下SPAD显著降低(图9),说明在干旱条件下叶绿素蛋白质的合成受到抑制,叶绿素逐渐分解,光合色素含量下降。干旱还会破坏捕光蛋白复合体,使电子传递受阻,光能转化效率降低,导致Fv/Fm、ETR、ΦPSⅡ显著下降(图8)。复水后,光合参数有所回升,说明光系统并未完全受到损伤。但与野生型和突变体相比,转基因株系修复损伤能力最弱,这与其干旱期间光系统受损的程度有关(图8、9)。
在逆境胁迫下,植株体内会生成大量的超氧自由基和过氧化氢,SOD作为植物抗氧化系统的第一道防线,通过歧化超氧阴离子生成H2O2,生成的H2O2进一步被CAT、POD等分解消除,保护细胞免受氧化伤害[32]。渗透胁迫下各株系H2O2水平提高(图5),野生型和突变体维持较高抗氧化酶活性,有助于活性氧的清除(图6)。但转基因株系中SOD、CAT、POD酶活较低(图6),不能有效清除活性氧(图5),减轻氧化胁迫对细胞膜的伤害,难以保持光合系统的相对稳定。这与在印度芥菜[18]和小麦[19]中的研究结果不完全一致,表明不同物种膜联蛋白在抗氧化防御中的作用有所差异。众多研究表明,抗氧化酶活性与编码基因表达的表达量相关[33-34]。在渗透胁迫后PeAnn1转基因株系OE1和OE2抗氧化酶SOD、POD和CAT的活性和基因表达量均显著低于野生型和突变体(图6、7),表明过表达PeAnn1株系在干旱胁迫下不能及时清除体内大量的活性氧,破坏了细胞内蛋白质的结构和功能。
关于膜联蛋白在植物耐受水分逆境中的作用有不同的研究报道。Lee等人[16]用甘露醇模拟渗透胁迫,发现过表达AtAnn1表现强耐旱性。这与Konopka-Postupolska等人[17]报道的结果类似,但不同于Huh等人[35]研究的结果。PeAnn1基因序列与拟南芥AtAnn1有较大差别(图2),因此,PeAnn1在调控植物抗旱性中作用可能有所不同。王希等人[36]通过超表达GsANN发现转基因拟南芥提高了对盐胁迫和干旱胁迫的敏感性,却志群等人[37]研究水稻OsAnn8基因可能通过负调控方式参与水稻对干旱胁迫的响应。这些研究与本文结论类似。另外,Liao等[38]发现拟南芥MYB30转录因子调控植物胁迫响应的信号转导机制。拟南芥MYB30通过结合ANN1和ANN4基因的启动子,抑制ANN1和ANN4基因表达,从而影响ANNs介导的特异胞内钙信号的产生,以此调控植物的氧化胁迫和热胁迫响应过程。胡杨PeAnn1是否也与相关转录因子互作,通过调控胞内钙信号影响抗氧化酶基因的表达,有待深入研究。
综上所述,本文从生理和分子转录水平上揭示了胡杨PeAnn1基因对植物抗旱性的影响,研究结果有助于阐明胡杨的抗旱机制。
-
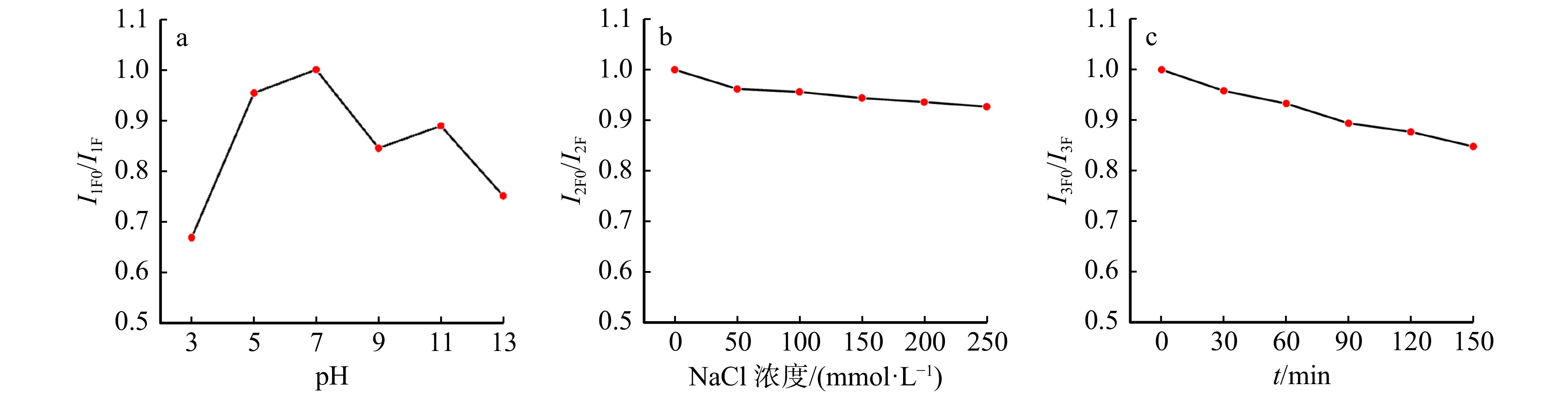
图 3 pH(a)、NaCl浓度(b)、紫外激发时间(c)对B-CQDs相对荧光强度的影响(λex = 358 nm)
I1F0、I2F0、I3F0分别为不同条件下的溶液荧光强度,I1F为pH值为7的溶液荧光强度,I2F为含有0 mmol/L NaCl混合液的荧光强度,I3F为紫外光激发照射时间为0 min的溶液荧光强度。
Figure 3. Effects of pH (a), concentration of NaCl (b), ultraviolet excitation time (c) on relative fluorescence intensity of B-CQDs (λex = 358 nm)
表 1 不同质量分数试剂的木腐菌抑菌圈平均直径
Table 1 Average diameter of inhibition zone of different mass fractions of reagents against wood rot fungi
试剂 抑菌圈平均直径/mm 彩绒革盖菌 密黏褶菌 无菌水 0 0 0.50%GB 0 0 0.10%BX 0 0 0.10%CQDs 20.64 ± 0.19 21.80 ± 0.32 0.20%CQDs 28.56 ± 0.37 28.11 ± 0.48 0.40%CQDs 34.45 ± 0.46 32.06 ± 0.46 0.60%CQDs 37.83 ± 0.76 39.79 ± 0.59 0.80%CQDs 41.41 ± 0.51 51.18 ± 0.68 0.10%B-CQDs 30.93 ± 0.24 31.51 ± 0.08 0.20%B-CQDs 38.71 ± 0.48 39.98 ± 0.32 0.40%B-CQDs 41.51 ± 0.45 54.59 ± 0.40 0.60%B-CQDs 47.03 ± 0.45 56.91 ± 0.73 0.80%B-CQDs 54.15 ± 0.90 63.59 ± 0.62 -
[1] 葛晓雯, 王立海, 侯捷建, 等. 褐腐杨木微观结构、力学性能与化学成分的关系研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(10): 112−122. Ge X W, Wang L H, Hou J J, et al. Relationship among microstructure, mechanical properties and chemical compositions in Populus cathayana sapwood during brown-rot decay[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(10): 112−122.
[2] 张继东, 候丹, 陈汉. 碳量子点荧光材料在金属离子检测中的应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 2022, 50(11): 5−10. Zhang J D, Hou D, Chen H. Application of carbon quantum dots fluorescent materials in metal ions detection[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2022, 50(11): 5−10.
[3] Xu X, Ray R, Gu Y, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(40): 12736−12737. doi: 10.1021/ja040082h
[4] 杨磊, 杨志, 连锋. 碳量子点作为生物相容性发光材料在再生医学方面的应用[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(增刊2): 1−9. Yang L, Yang Z, Lian F. Application of carbon quantum dots as biocompatible luminous materials in regenerative medicine[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(Suppl. 2): 1−9.
[5] Shen C L, Lou Q, Zang J H, et al. Near-infrared chemiluminescent carbon nanodots and their application in reactive oxygen species bioimaging[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(8): 1903525. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903525
[6] 黄国杰. 硫硒掺杂碳量子点的合成及其应用的探究[D]. 广州:广东药科大学, 2020. Huang G J. Study on synthesis and application of sulfur-selenium doped carbon quantum dots[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2020.
[7] 成诗琦, 杨锦, 覃上英, 等. 碳量子点增敏的葡萄糖分子印迹电化学传感器[J]. 分析化学, 2023, 51(4): 549−558. Cheng S Q, Yang J, Qin S Y, et al. Molecularly imprinted glucose electrochemical sensor sensitized by carbon quantum dots[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(4): 549−558.
[8] Rasal A S, Yadav S, Yadav A, et al. Carbon quantum dots for energy applications: a review[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(7): 6515−6541. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c01372
[9] 何静, 陈佳, 邱洪灯. 中药碳点的合成及其在生物成像和医学治疗方面的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2023, 35(5): 655−682. He J, Chen J, Qiu H D. Synthesis of traditional Chinese medicines-derived carbon dots for bioimaging and therapeutics[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2023, 35(5): 655−682.
[10] 李琼洋. 艾叶碳量子点的制备及其抗菌和抗氧化活性研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2022. Li Q Y. Study on the synthesis of carbon dots from mugwort leaves (Artemisia argyi Levl. et Van) and their antibacterial and antioxidant activities[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2022.
[11] 孙笑槐. 银杏叶中有效成分的研究进展[J]. 中国科技信息, 2011(4): 111−116. Sun X H. Research progress of effective components in Ginkgo biloba leaves[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2011(4): 111−116.
[12] Liu Y, Jiang L, Li B, et al. Nitrogen doped carbon dots: mechanism investigation and their application for label free CA125 analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2019, 7: 3053−3058. doi: 10.1039/C9TB00021F
[13] Percin O, Sofuoglu S D, Uzun O. Effects of boron impregnation and heat treatment on some mechanical properties of oak (Quercus petraea Liebl.) wood[J]. Bioresources, 2015, 10: 3963−3978.
[14] 蒋明銜, 陈奶荣, 林巧佳. 木材防腐的研究进展[J]. 福建林业科技, 2013, 40(1): 207−213. Jiang M X, Chen N R, Lin Q J. Research progress in preservative-treated wood[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2013, 40(1): 207−213.
[15] Sürdem S, Eseroglu C, Yildiz S, et al. Combustion and decay resistance performance of scots pine treated with boron and copper based wood preservatives[J]. Drvna Industrija, 2022, 73(4): 397−404. doi: 10.5552/drvind.2022.2125
[16] 张宇, 母军, 李思锦, 等. 阻燃剂硼酸–硼砂对杨木定向刨花板热解特性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(1): 127−133. Zhang Y, Mu J, Li S J, et al. The effect of boric acid-borax on the pyrolysis characteristics of poplar oriented strand board[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(1): 127−133.
[17] 邓祥, 黄小梅, 邓子禾, 等. 碳量子点荧光探针的制备及其在苦味酸检测中的应用[J]. 分析测试学报, 2023, 42(6): 736−742. Deng X, Huang X M, Deng Z H, et al. Preparation of a carbon quantum dots fluorescent probe and its application in detection of picric acid[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2023, 42(6): 736−742.
[18] 胡妙言, 刘凯, 高诗雨, 等. 淡竹叶碳量子点的微波法制备及在细胞成像中的应用探究[J]. 发光学报, 2022, 43(12): 2001−2013. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20220256 Hu M Y, Liu K, Gao S Y, et al. Microwave preparation of common lophatherum herb carbon quantum dots and application in cell imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2022, 43(12): 2001−2013. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20220256
[19] 董蕾, 何利, 钱玟, 等. 氮掺杂鸡毛碳点荧光关开探针用于测定百草枯[J]. 分析试验室, 2021, 40(1): 1−6. Dong L, He L, Qian W, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from chicken feathers as off-on fluorescence probe for detection of paraquat[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2021, 40(1): 1−6.
[20] 刘凯, 张培培, 胡妙言, 等. 双氮源共掺杂木素碳量子点/有机溶剂水份探针的构建及性能[J]. 光子学报, 2024, 53(9): 0916001. Liu K, Zhang P P, Hu M Y, et al. Construction and performance of dual-nitrogen source Co-doped lignin carbon quantum dots/organic solvent moisture probes[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2024, 53(9): 0916001.
[21] 刘冬梅, 李理, 杨晓泉, 等. 用牛津杯法测定益生菌的抑菌活力[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2006(3): 110−111. Liu D M, Li L, Yang X Q, et al. Determination of the antibacterial activity of probiotic by oxford plate assay system[J]. Food Research and Development, 2006(3): 110−111.
[22] 常璐璐, 孙墨珑, 徐国祺, 等. 樟树叶提取物对木材霉菌的防治效果及防霉机理研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(1): 99−106. Chang L L, Sun M L, Xu G Q, et al. Control efficiency and action mechanisms of camphor leaf extractives on mold resistance of wood[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(1): 99−106.
[23] 魏建斐, 马国聪, 张安莹, 等. 明胶基碳点的热解法制备及其阻燃与防伪应用[J]. 纺织学报, 2023, 44(12): 106−114. Wei J F, Ma G C, Zhang A Y, et al. Preparation of gelatin-based carbon dots by pyrolysis and its applications in flame retardant and anti-counterfeiting[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2023, 44(12): 106−114.
[24] Parya E, Whan J R, Rahim M, et al. Preparation and characterization of B, S, and N-doped glucose carbon dots: antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activity[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022, 32: e00397. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00397
[25] 湛志华, 陈茺而, 莫大幸, 等. 单激发双发射近红外荧光碳量子点制备、荧光性能与细胞成像[J]. 发光学报, 2021, 42(8): 1307−1313. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210157 Zhan Z H, Chen C E, Mo D X, et al. Preparation, fluorescent properties and cell imaging of near infrared fluorescent carbon quantum dots with single excited double emission[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 42(8): 1307−1313. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210157
[26] 钱玟, 何利, 潘无双, 等. 猪骨氮掺杂碳量子点制备及其用于检测Co2+[J]. 发光学报, 2021, 42(11): 1818−1827. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210260 Qian W, He L, Pan W S, et al. Preparation of pig bone nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots and application in detection of Co2+[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 42(11): 1818−1827. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210260
[27] 张文博, 石建丽, 马建中, 等. 荧光碳量子点及其在防伪中的应用[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(7): 145−155. Zhang W B, Shi J L, Ma J Z, et al. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots and their applications in anti-counterfeiting[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(7): 145−155.
[28] Yuan F, Li S, Fan Z, et al. Shining carbon dots: synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications[J]. Nano Today, 2016, 11(5): 565−586. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.08.006
[29] Zheng H, Wang Q, Long Y, et al. Enhancing the luminescence of carbon dots with a reduction pathway[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(38): 10650−10652. doi: 10.1039/c1cc14741b
[30] 王子儒, 张光华, 郭明媛. N掺杂碳量子点光稳定剂的制备及光学性能[J]. 发光学报, 2016, 37(6): 655−661. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163706.0655 Wang Z R, Zhang G H, Guo M Y. Preparation and optical properties of N-doped carbon quantum dots light stabilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 37(6): 655−661. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163706.0655
[31] Hu Y, Yang J, Tian J, et al. Waste frying oil as a precursor for one-step synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon dots with pH-sensitive photoluminescence[J]. Carbon, 2014, 77: 775−782. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.081
[32] 李宏, 田浩, 于丽娟, 等. 铽掺杂碳点的制备及其抑菌性能[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(2): 291−298. Li H, Tian H, Yu L J, et al. Preparation of terbium doped carbon dots and their antibacterial capacity against Escherichia coli[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32(2): 291−298.
[33] Sun D, Ban R, Zhang P H, et al. Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties[J]. Carbon, 2013, 64: 424−434. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.095
[34] Kumar A, Lee Y, Kim D, et al. Effect of crosslinking functionality on microstructure, mechanical properties, and in vitro cytocompatibility of cellulose nanocrystals reinforced poly (vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hybrid scaffolds[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 95: 962−973. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.085
[35] Zhai X, Zhang P, Liu C, et al. Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(64): 7955−7957. doi: 10.1039/c2cc33869f
[36] Liu W, Diao H, Chang H, et al. Green synthesis of carbon dots from rose-heart radish and application for Fe3+ detection and cell imaging[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 241: 190−198.
[37] Lu F, Song Y, Huang H, et al. Fluorescent carbon dots with tunable negative charges for bioimaging in bacterial viability assessment[J]. Carbon, 2017, 120: 95−102. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.05.039
[38] Salman B I, Hassan A I, Hassan Y F, et al. Ultra-sensitive and selective fluorescence approach for estimation of elagolix in real human plasma and content uniformity using boron-doped carbon quantum dots[J]. BMC Chemistry, 2022, 16(1): 58. doi: 10.1186/s13065-022-00849-3
[39] 李玉栋, 王建军, 周勤. 橡胶木的防变色试验[J]. 木材工业, 2002(4): 15−17. Li Y D, Wang J J, Zhou Q. Experiment on protection of rubberwood from blue stain and mould[J]. China Wood Industry, 2002(4): 15−17.
[40] Baysal E, Altinok M, Colak M, et al. Fire resistance of Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menzieesi) treated with borates and natural extractives[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(5): 1101−1105. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.04.023
[41] 张景朋, 蒋明亮, 马星霞, 等. 甲氧基丙烯酸酯类制剂的木材防腐性能研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(3): 131−137. Zhang J P, Jiang M L, Ma X X, et al. Wood decay performance of strobilurins preservatives[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(3): 131−137.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张欢欢,范挺秀,高双成,范丙友,史国安. 2个牡丹切花品种核型、花药形态与花粉特性的比较. 浙江农业学报. 2025(02): 329-337 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙榕泽,宋焕芝,蒋珈琦,于晓南. 三倍体芍药品种染色体制片优化和核型分析. 河北农业大学学报. 2024(03): 46-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 段英姿,客绍英,王晓英,张胜珍,马艳芝. 15个油用紫斑牡丹品种核型及亲缘关系分析. 种子. 2023(07): 96-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: