Internal-standard quantitative determination of chlorogenic acid in Eucommia ulmoides plant by CE-MS
-
摘要: 杜仲作为一种传统的中药材,其药用成分主要为次级代谢产物绿原酸,是很多种中草药的重要活性成分,广泛存在于杜仲叶片和忍冬科植物的干燥花蕾或初开的花朵中。本研究提供了一种高效准确的从植物样本中检测绿原酸的方法。该方法使用萘乙酸作为内标物提高定量的精确性,减少系统误差,并通过毛细管电泳联用质谱定性提高检测的灵敏度。毛细管电泳联用质谱仪建立萘乙酸标准品与绿原酸标准品的标准曲线,其中萘乙酸与绿原酸的标准曲线相关性系数分别为0.999 4和0.999 1,均大于0.999 0,说明仪器方法及毛细管电泳参数与质谱参数可靠。绿原酸标准品分别以杜仲与金银花植物粉末作为基质,其添加回收率分别为93.61%和97.43%,说明提取方法的提取效率较高。为验证方法的适用性,运用本方法检测分析得出杜仲植物粉末中绿原酸含量为0.92%,金银花植物粉末中绿原酸含量为1.31%。
-
关键词:
- 毛细管电泳-质谱联用 /
- 萘乙酸 /
- 绿原酸 /
- 杜仲 /
- 金银花
Abstract: Eucommia ulmoides is a traditional Chinese herb medicine plant and its pharmaceutical component is a secondary metabolite chemical chlorogenic acid. And it is also an important active component in many kinds of Chinese traditional medicine. Chlorogenic acid widely exists in the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides and dried buds or open flowers of Caprifoliaceae plant. The high sensitivity detection method and precise quantification pretreatment program of chlorogenic acid are important for exploring the role of the Chinese traditional medicine in curing disease, and could provide the more detection method for the study of accumulation of plant secondary metabolites. This work establishes an effective analytical method to accurately determine the chlorogenic acid content in plant samples. This method introduces the 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) into the analysis procedure function as the internal standard to improve the determination analysis quality and use the electrophoresis-mass spectrometry to enhance the specificity and sensitivity of the detection. The standard curves of standard chemicals of NAA andchlorogenic acid were established and the R2 of two curves was greater than 0.999 0. The spiked recovery of chlorogenic acid in plant samples was 93.61% and 97.43%. The method has been used to analyze the chlorogenic acid of E. ulmoides and Lonicera japonica. The content of chlorogenic acid extracted from E. ulmoides was 0.92%, and Lonicera japonica was 1.31%.-
Keywords:
- CE-MS /
- NAA /
- chlorogenic acid /
- Eucommia ulmoides /
- Lonicera japonica
-
杜仲(Eucommia ulmoides)是杜仲科(Euco-mmiaceae),杜仲属的一种落叶乔木,在我国各地广泛栽种。杜仲在我国中医药领域的使用上已有上千年的历史,是一种价值很高的药用植物。目前已经从杜仲中提取出十几种简单酚类与苯丙素类物质,其中研究较多的就是绿原酸。金银花(Lonicera japonica)作为忍冬科(Caprifoliaceae)忍冬属的植物,同样含有绿原酸。
绿原酸(Chlorogenic acid)是由咖啡酸(Caffeic acid)与奎尼酸(Quinic acid)组成的缩酚酸,分子式为C16H18O9。绿原酸具有广泛的生物活性,如茵陈(Artemisa capillaris)的利胆作用,金银花的抗菌作用,苎麻(Boehmeria nivea)的止血和升高白细胞作用等都与绿原酸有密切关系[1]。临床上用于治疗各种急性细菌性感染疾病及放射治疗、化学治疗所致的白细胞减少症。目前测定杜仲中绿原酸常用的方法有分光光度法[2],液相色谱-串联质谱联用法[3]与高效毛细管电泳法[4]等,这些方法分别有准确度低,分离速度缓慢,以及无法良好定性的缺点。毛细管电泳-质谱联用技术(CE-MS)是近年来发展起来的一种新的检测技术[5]。这种方法结合了毛细管电泳分离速度快和分离度高,样品用量少,自动化程度高与质谱检测灵敏度高,分析准确的优点,弥补了上面几种方法的不足。同时,该技术也被越来越多的应用于中草药分析中[6-9],尤其适合水溶性或醇溶性成分的分析,适合对杜仲中的绿原酸进行测定。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
试剂:绿原酸标准品(5 μg/μL,色谱纯)与萘乙酸标准品(5 μg/μL,色谱纯)购自Sigma公司;甲醇(色谱纯)、氢氧化钠(色谱纯)与醋酸铵(色谱纯)购自新西兰Mallinckrodt Baker公司,试验用水为去离子超纯水。
仪器:Agilent 3D-CE 1100 LC/MSD离子阱质谱(美国Agilent公司),75 μm内径未涂层熔融石英毛细管90 cm;数据分析软件为Chemstation(美国Agilent公司);精密电子天平(美国Mettler Toledo公司);高速冷冻离心机(日本日立公司);KQ-250F型超声波清洗仪(中国舒美仪器公司);FD-1型冷冻干燥仪(北京德天佑科技发展有限公司);恒温水浴锅(中国国华电器有限公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品的制备
将杜仲样品与金银花样品用研钵磨碎成粉末,分别称取冷冻干燥后的杜仲粉末,金银花粉末25、50、100 mg于试管中,用40%甲醇1.4 mL提取,超声30 min,收集上层清液,上层清液60 ℃水浴30 min。用10 000 r/min离心10 min后再取上清用直径0.45 μm的滤膜过滤作为样品。
1.2.2 CE-MS条件
毛细管在每次进样前使用20 mmol醋酸铵缓冲液冲洗5 min,以保证其重现性,进样采用30 mbar进样1 s,在8 kV条件下进行电泳,紫外波长选择214 nm,柱温为25 ℃。质谱条件为阴离子模式,二级质谱全扫描,氮气流速15 psi,氦气7 psi,气体温度为300 ℃,分离电压3.5 kV,鞘流液使用50%的甲醇溶液(含0.01%醋酸铵),流量为100 nL/min, 泵流速为0.4 L/min,分流比为100:1。
1.2.3 标准曲线与最低检测限
毛细管电泳由于其高分辨率的特性,能够对非常微量的样品进行测定。在绘制标准曲线时,我们同时对其最低检测限进行了测定。萘乙酸和绿原酸的标准曲线质量浓度200、100、50、25 mg/L用于制作标准曲线,每个质量浓度重复上样3次,用Chemstation软件进行峰面积积分计算。根据3倍信噪比原则,测得该仪器对萘乙酸和绿原酸的最低检测限。
1.2.4 加标回收率
分别取2 mg绿原酸标准品1份,配制好的25、50、100 mg杜仲样品和金银花样品各1份,再取添加2 mg绿原酸标准品的上述杜仲样品与金银花样品各1份进行检测,使用Chemstation计算峰面积以得出进样量,用标准曲线公式计算这些峰面积所对应的进样量,分别记为S0、S1、S2,由于毛细管电泳的进样为固定体积,回收率=(2S2-S1)/S0×100%。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 萘乙酸和绿原酸的ESI质谱裂解行为
在1.2.1的条件下,萘乙酸标准样品的母离子的质荷比(m/z)为186,在二级质谱中发生断裂生成m/z为141的子离子;绿原酸标准样品的母离子为353,子离子为191。裂解产生的子离子均为各自母离子的特征离子。本次试验均采用特征子离子作为检测分析离子,随着电压的增大,碰撞强度上升,特征子离子随之增加,母离子逐渐减少。
2.2 CE-MS的绿原酸与萘乙酸分析结果
Agilent 1100离子阱可检测到的m/z范围从15~2 200,能满足植物小分子的分析。经测定,萘乙酸与绿原酸的色谱图见图 1,其中萘乙酸母离子为186,子离子为141,绿原酸母离子为353,子离子为191。图 1a~1c分别为萘乙酸标准品、绿原酸标准品和杜仲植物样品的色谱图,图 1d~1f为其对应的质谱图和化学结构裂解图。由图 1可知,杜仲样品中绿原酸的质谱图与标准样品的质谱图一致,并且色谱保留时间一致,说明该色谱峰是绿原酸组分,说明本方法可以用来检测杜仲植物品中的绿原酸含量。
2.3 标准曲线的绘制和最低检测限
分别配制200、100、50、25 mg/L质量浓度的萘乙酸和绿原酸系列标准溶液,每个质量浓度重复上样3次,用Chemstation软件进行峰面积积分计算。根据3倍信噪比原则,测得该仪器对萘乙酸和绿原酸的最低检测限得到表 1,二者的最低检测限分别为1.40 pmol(258.38 pg)与0.73 pmol(260.04 pg)。根据得到的峰面积,绘制标准曲线(图 2),回归方程分别为y=11 538x-10 925(R2=0.999 4,萘乙酸NAA), y=19 809x-793.29(R2=0.999 1,绿原酸CGA),决定系数均大于0.999 0,可以依据该曲线进行定量分析。
表 1 萘乙酸和绿原酸的标准曲线公式与最低检测限Table 1. Standard curve formula and lowest detectable limit of NAA and CGA组分
Component标准曲线公式
STD curve equation决定系数
R2 value最低检测限
Lowest limit of detection/pmol萘乙酸NAA y=11 538x-10 925 0.999 4 1.40 绿原酸CGA y=19 809x-793.29 0.999 1 0.73 2.4 加标回收率
标准样品,植物样品和植物样品中添加标准样品分别测量后计算出色谱峰面积,用标准曲线公式计算这些峰面积所对应的进样量,根据1.2.3的公式计算出加标回收率见表 2。由表 2可知,杜仲基质中绿原酸标准品的回收率是93.61%,金银花基质中绿原酸标准品的回收率是97.43%,回收率较高,表示本试验所用的提取方法可以用于提取2种基质中绿原酸。
表 2 杜仲与金银花样品的加标回收率Table 2. Recovery of standard addition of E. ulmoides sample and L. japonica sample植物样品
Plant sample样品编号
Sample No.加标回收率
Spiked recovery/%平均回收率
Average recovery/%RSD/% 杜仲
Eucommia ulmoides1 92.51 93.61 2.88 2 98.12 3 90.50 金银花
Lonicera japonica1 94.20 97.43 2.53 2 99.47 3 98.63 2.5 杜仲样品与金银花样品中的绿原酸检测
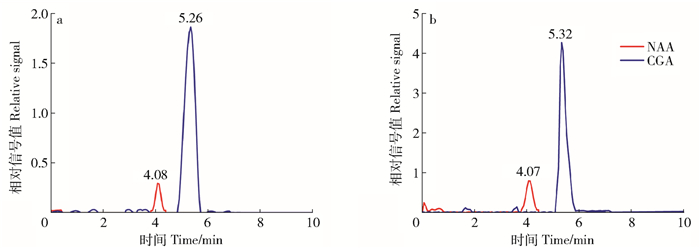
将配制好的杜仲样品与金银花样品提取液上机检测分析,将得到的样品峰(图 3)通过Chemstation软件积分,代入2.3的标准曲线方程,结合加入的萘乙酸内标可分别通过外标法和内标法计算出绿原酸的含量,结果见表 3。图 3a、3b分别为杜仲和金银花基质中添加的萘乙酸标准品、检测到的绿原酸的色谱峰,红色曲线表示添加的萘乙酸标准品,蓝色曲线表示检测到的绿原酸组分。表 3为分别用外标法和内标法计算得到的绿原酸含量,由于内标法的RSD较小,而且更为准确,本试验采用内标法数据作为标准数据,得到杜仲中绿原酸的含量为0.92%,金银花中绿原酸的含量为1.31%。
表 3 杜仲样品与金银花样品内标与外标结果分析Table 3. Results of internal and external standard method of Eucommia ulmoides and Lonicera japonica samples植物样品
Plant sample样品编号
Sample No.外标法External standard method 内标法Internal standard method 含量
Content/%平均值
Average content/%RSD/% 含量
Content/%平均值
Average content/%RSD/% 杜仲Eucommia ulmoides 1 0.70 0.68 1.41 0.92 0.92 1.15 2 0.69 0.94 3 0.66 0.90 金银花Lonicera japonica 1 0.94 1.03 3.27 1.22 1.31 2.94 2 1.18 1.45 3 0.98 1.27 3. 结论
本试验建立了添加萘乙酸内标CE-MS定性定量测定杜仲与金银花中绿原酸的方法,可计算出杜仲样品中绿原酸的含量为0.92%,金银花中绿原酸含量为1.31%。产率并不是很高,这可能与提取方法有很大关系,也可能与植物样品的取样时间在秋冬季有关[10]。由于添加了萘乙酸为内标,使得该方法较外标曲线法具有更好的适用性,结果更为准确。该方法与分光光度法相比,灵敏度和准确度更高,与单纯的高效毛细管电泳法相比,该方法能够精确测量分子质量数,试验结果更加精准,与液相色谱-串联质谱法相比,毛细管电泳分离所用的时间短,分离效率更高。同时,这种方法还适用于大多数生物样品以及小分子的分析[11]。然而,CE-MS联用技术由于硬件接口问题等仍旧有一定的缺陷[12],随着接口技术的不断改进,与质谱相容性更好的等电聚焦用两性电解质的发展[13],CE-MS会在更多的领域成为研究者的重要分析手段。
-
表 1 萘乙酸和绿原酸的标准曲线公式与最低检测限
Table 1 Standard curve formula and lowest detectable limit of NAA and CGA
组分
Component标准曲线公式
STD curve equation决定系数
R2 value最低检测限
Lowest limit of detection/pmol萘乙酸NAA y=11 538x-10 925 0.999 4 1.40 绿原酸CGA y=19 809x-793.29 0.999 1 0.73 表 2 杜仲与金银花样品的加标回收率
Table 2 Recovery of standard addition of E. ulmoides sample and L. japonica sample
植物样品
Plant sample样品编号
Sample No.加标回收率
Spiked recovery/%平均回收率
Average recovery/%RSD/% 杜仲
Eucommia ulmoides1 92.51 93.61 2.88 2 98.12 3 90.50 金银花
Lonicera japonica1 94.20 97.43 2.53 2 99.47 3 98.63 表 3 杜仲样品与金银花样品内标与外标结果分析
Table 3 Results of internal and external standard method of Eucommia ulmoides and Lonicera japonica samples
植物样品
Plant sample样品编号
Sample No.外标法External standard method 内标法Internal standard method 含量
Content/%平均值
Average content/%RSD/% 含量
Content/%平均值
Average content/%RSD/% 杜仲Eucommia ulmoides 1 0.70 0.68 1.41 0.92 0.92 1.15 2 0.69 0.94 3 0.66 0.90 金银花Lonicera japonica 1 0.94 1.03 3.27 1.22 1.31 2.94 2 1.18 1.45 3 0.98 1.27 -
[1] 陈绍华, 王亚琴, 罗立新.天然产物绿原酸的研究进展[J].食品科技, 2008(2): 195-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2008.02.057 CHEN S H, WANG Y Q, LUO L X. Advances in research on chlorogenic acid[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2008(2): 195-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2008.02.057
[2] 陈乃炽, 汪洪武, 刘艳清, 等.杜仲叶中绿原酸的提取与含量测定[J].经济林研究, 2001(2): 59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2001.02.021 CHEN N Z, WANG H W, LIU Y Q, et al. Isolation and determination of chlorogenic acid in the leaf of Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Economic Forest Researches, 2001(2): 59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2001.02.021
[3] 田晨煦, 徐小平, 廖丽云, 等.高效液相色谱-串联质谱法分离鉴定绿原酸及其相关杂质[J].色谱, 2007(4): 496-500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2007.04.010 TIAN C X, XU X P, LIAO L Y, et al. Separation and identification of chlorogenic acid and related impurities by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2007(4): 496-500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2007.04.010
[4] 何新荣, 张琼, 刘萍.毛细管区带电泳法测定杜仲药材中绿原酸的含量[J].中国药物应用与监测, 2008, 5(6): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8157.2008.06.012 HE X R, ZHANG Q, LIU P. Determination of chlorogenic acid in cortex eucommia by capillary zone electrophoresis[J]. Chinese Journal of Drug Application and Monitoring, 2008, 5(6): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8157.2008.06.012
[5] 王宁, 刘佳, 李书文, 等.毛细管电泳-质谱联用技术研究进展[J].氨基酸和生物资源, 2015(2): 1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ajshswzy201502002 WANG N, LIU J, LI S W, et al. Progress of capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry[J]. Amino Acids and Biotic Resources, 2015(2): 1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ajshswzy201502002
[6] 高玲.毛细管电泳在中药分析中的应用进展[J].赤峰学院学报(自然科学版), 2009(9): 102-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-260X.2009.09.044 GAO L. Application of capillary electrophoresis in the analysis of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Chifeng University(Natural Science Edition), 2009(9): 102-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-260X.2009.09.044
[7] 孙毓庆, 孙国祥, 金郁.毛细管电泳指纹图谱及毛细管电泳-质谱联用在中药质量控制中的作用[J].色谱, 2008(2): 160-165. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.02.006 SUN Y Q, SUN G X, JIN Y. Quality control of traditional Chinese medicines by the capillary electrophoresis finger print and capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2008(2): 160-165. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.02.006
[8] 刘一, 白玉, 庞楠楠, 等. LC-MS及CE-MS技术在中药分析中的应用[J].中国科技论文在线, 2009(3): 179-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2009.03.004 LIU Y, BAI Y, PANG N N, et al. Applications of LC-MS and CE-MS in the analysis of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Sciencepaper Online, 2009(3): 179-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2009.03.004
[9] 陈琴华.中药活性成分的LC/CE-IT-MS分析新方法研究[D].武汉: 武汉大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10486-1015026749.htm CHEN Q H. New methods for analysis of active compounds in tradition Chinese medicine by LC/CE-IT-MS[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10486-1015026749.htm
[10] 冯彬彬, 王小翠, 张建海, 等.不同产地金银花与山银花中绿原酸含量的比较研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(2): 729-730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.02.039 FENG B B, WANG X C, ZHANG J H, et al. Comparative study on the content of chlorogenic acid in Lonicerae japonica flos and Lonicerae flos from different producing areas[J]. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 2012, 40(2): 729-730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.02.039
[11] 李媛, 陈媛梅, 郑彩霞.高效毛细管电泳法测定毛白杨雄花芽中的IAA与GA3[J].分析测试学报, 2011(10): 1128-1132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2011.10.009 LI Y, CHEN Y M, ZHENG C X. Determination of IAA and GA3 in the male floral buds of Populus tomentosa Carr. by high performance capillary electrophoresis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2011(10): 1128-1132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2011.10.009
[12] 张政祥, 薄涛, 米健秋, 等.毛细管电泳-质谱联用中的若干关键技术问题及解决方案[J].现代科学仪器, 2011(5): 45-47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkxyq201105008 ZHANG Z X, BO T, MI J Q, et al. CE-MS key technical issues and corresponding solutions[J]. Modern Scientific Instruments, 2011(5): 45-47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkxyq201105008
[13] 许崇峰, 申华莉, 宋浩威, 等.毛细管电泳-电喷雾质谱联用技术及其在蛋白质分析领域中的应用[J].分析测试学报, 2002(4): 95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2002.04.030 XU C F, SHEN H L, SONG H W, et al. Capillary electrophoresis-electrospray mass spectrometry and its application in proteomics[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2002(4): 95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2002.04.030
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 鹿林,张程凯,张慧. 自橡子壳中提取橡子壳棕色素的实验研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(10): 179-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 靳子旋,张岩岩,杜黔运,徐静,赵余庆. 橡子化学成分及药理作用的研究进展. 中草药. 2023(24): 8301-8308 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 翟淑红,曹洪坤,余诗琴,朱斯豪. 红菜苔多酚超声提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究. 农产品加工. 2023(22): 49-52+56 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张博,李德海,王泽童,王楚雅,王怡雪. 橡子壳主要成分的生理功能及开发利用研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(07): 393-399 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王荣芳,张子言,李德海. 酶解法对蒙古栎实壳提取物活性成分及抗氧化活性的影响. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(05): 150-160 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 豆佳媛,何志鹏,梁馨月,逯莉. 橡子中挥发油的提取及抗氧化性质研究进展. 广东化工. 2021(24): 55-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 黄艳,傅新征,吴琳珊,李烨. 锥栗壳色素抗氧化活性研究. 食品科技. 2019(02): 274-280 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 魏园园,侯盼盼,梁宗瑶,任维维,李珉梦,高鹏程,张建新,段旭昌. 栓皮栎橡子壳多酚的体外抗氧化与抑菌活性研究. 现代食品科技. 2019(09): 190-197+73 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: