Rust pathogen identification and mechanism of disease-resistance research on Kentucky bluegrass dwarf mutant
-
摘要: 锈病是草坪草的重要病害,且病原菌种类多,鉴定困难。本研究以草地早熟禾野生型和矮化突变材料中的感病株系为对象,通过观察锈菌的形态特征,并结合ITS和β-tubulin基因序列分析,其中ITS序列的同源比对分析和β-tubulin基因的分子进化分析结果表明,该菌种与小麦禾柄锈菌的同源关系接近,所以初步认定该菌株属于禾柄锈菌,这是国内对禾柄锈菌引起草地早熟禾锈病的首次报道。同时,我们对病原菌诱导后草地早熟禾PR1L、NPR1L基因的表达变化和PRs蛋白表达进行了研究,发现PR1L、NPR1L基因在病菌诱导12 h时的表达量达到了峰值,且在矮化突变植株(A16)中的相对表达量分别达到了8.8-fold、4.5-fold,均大于在对照植株(WT)中的表达量。另外植物的PRs蛋白在禾柄锈菌侵染植物第8天后的表达量明显高于未侵染的植株。初步对草地早熟禾锈病的防御机制进行了探讨,为今后开展草地早熟禾锈病的预防及抗病育种研究奠定基础。Abstract: Rust is one of the destructive diseases on turfgrass. The species of rust pathogens are multiple and difficult to identify. In order to determine the rust pathogen species on Kentucky bluegrass wild type and dwarf mutant plant, pathogen morphology, along with ITS and β-tubulin gene sequence analysis were carried out. The analysis of ITS by BLAST and phylogenetic analysis of β-tubulin showed that the strains were related to Puccinia graminis of wheat, so we identified it as Puccinia graminis, which is the first report on Kentucky bluegrass in China. Moreover, transcriptional level of PR1L and NPR1L genes in Kentucky bluegrass inoculated with Puccinia graminis, as well as the expression of PRs protein, were investigated. The results presented that the expression of PR1L and NPR1L genes reached peak at 12 hours induced by Puccinia graminis, and the fold changes in dwarf mutant (A16) were 8.8 and 4.5, respectively, greater than in control wild type (WT). Besides, the expression of PRs in P. graminis infected plants 8 days later was higher than in non-infected plants. Defense mechanism of Kentucky bluegrass to rust was preliminary investigated and it presented the related disease-resistant gene and protein induced by rust pathogen. The research provides foundation for rust prevention and disease resistance breeding on Kentucky bluegrass in future.
-
Keywords:
- turfgrass /
- Kentucky bluegrass /
- dwarf mutant /
- rust pathogen identification /
- disease resistance
-
-
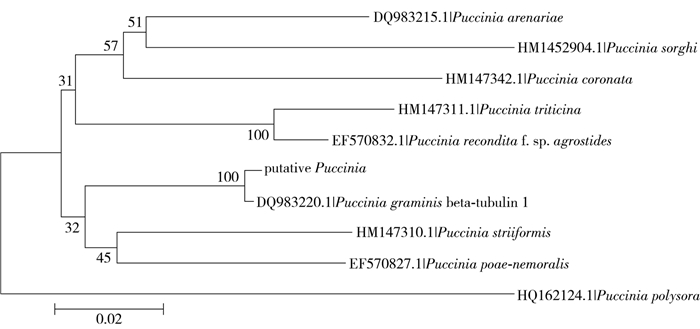
图 2 供试菌株及Puccinia相关菌株β-tubulin基因的系统发育树
候选锈菌菌株为供试材料的锈病病原菌。进化树右端的字母和数字代表GenBank中的序列号,分支上的数字代表自举的可信度,0.02为序列分歧度。
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree of isolate strain and their relatives in Puccinia
Putative Puccinia is the isolate rust strain. Numbers in parentheses represent the sequences' accession number in Gen Bank. The number at each branch points is the percentage supported by bootstrap. Bar, 2% sequence divergence.
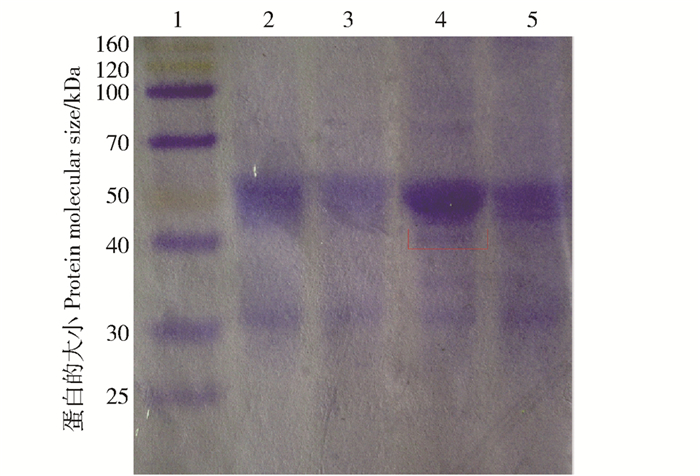
图 4 草地早熟禾野生型(WT)及其矮化突变(A16)植株接种禾柄锈菌前后的病程相关蛋白电泳分析
1.蛋白marker;2.未接种的WT样品;3.未接种的A16样品;4.接种后的A16样品;5.接种后的WT样品。
Figure 4. 12% SDS-PAGE analysis of pathogenesis-related proteins extracted from leaves of WT and A16 inoculated with/without Puccinia graminis
1, protein marker; 2, the A16 sample inoculated without Puccinia graminis; 3, the WT sample inoculated without Puccinia graminis; 4, the A16 sample inoculated with Puccinia graminis; 5, the WT sample inoculated with Puccinia graminis.
表 1 实验所需引物的序列
Table 1 List of primer sequences used in this study
引物名称
Primer name引物序列
Primer sequence(5′—3′)ITS1 TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG ITS4 TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC Tubulin-F ATGGAYTCGGTYCGATCTGGCG Tubulin-R CYTCTCCRGTGTACCAATGCAGG PR1L-qF CGCTACGCCCGCTCCC PR1L-qR GCCCCTCGTCCACCCA NPR1L-qF CAAGGAAGGGCAGACTAA NPR1L-qR GCAGCGATGTGAAGAACA Actin-qF TTGACTGAGAGGGGCT Actin-qR TCATACGGTCTGCGAT 表 2 草地早熟禾的抗病相关的候选基因筛选
Table 2 List of candidate disease-resistant gene studied in Kentucky bluegrass clones
基因名称
Gene ID候选基因注释
Candidate gene annotation开放阅读框序列长度
ORF length/bp同源基因编号
GenBank accession of homologs同源物种
Allied speciesPR1L pathogenesis-related protein 1A-like 552 XM_004975168 栗Setaria italica NPR1L NPR1-like 1 protein 1 758 JX424315 硬粒小麦Triticum durum -
[1] BEARD J B, TOSHIKAZU T. Color atlas of turfgrass diseases[M]. Chelsea: Ann Arbor Press, 1997.
[2] CPUCH H B. Diseases of turfgrasses[M]. New York: Reinhold Pub. Corp., 1962.
[3] 陈吉虎, 赵永军, 高旭彪, 等.北京地区冷季型草坪草病害调查及防治[J].草业科学, 2007, 24(12): 103-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2007.12.025 CHEN J H, ZHAO Y J, GAO X B, et al. Investigation and control of cold-season turfgrass diseases in Beijing areas[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2007, 24(12): 103-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2007.12.025
[4] 李春杰, 南志标.甘肃草坪草真菌病害初报[J].草业科学, 1998, 15(1): 49-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKX801.011.htm LI C J, NAN Z B. Primary report on fungal diseases of turfgrass in Gansu Province, China[J]. Pratacultural Science, 1998, 15(1): 49-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CYKX801.011.htm
[5] 薛福祥, 姚拓, 席琳乔.成都高尔夫球场草坪草主要病害病原鉴定及防治对策初报[J].草原与草坪, 2003(2): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2003.02.006 XUE F X, YAO T, XI L Q. Preliminary study on identification and control of turfgrass diseases in Chengdu golf course[J]. Grassland and Turf, 2003(2): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2003.02.006
[6] 薛福祥.兰州地区冷季型草坪真菌病害研究[J].草业科学, 2003, 20(3): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2003.03.019 XUE F X. Study on cold-season turfgrass diseases in Lanzhou rejoin[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2003, 20(3): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2003.03.019
[7] 文克俭, 尚以顺.贵州优良冷季型草坪主要病虫害防治技术[J].贵州畜牧兽医, 2003, 27(4): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1474.2003.04.038 WEN K J, SHAN Y S. Study on pests and disease management control technology of cold-season turf in Guizhou rejoin[J]. Guizhou Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2003, 27(4): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1474.2003.04.038
[8] 刘金荣, 谢晓蓉.河西走廊草坪草病害调查[J].植物保护, 2002, 28(5): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2002.05.013 LIU J R, XIE X R. Investigation of turfgrass diseases in the Hexi Corridor[J]. Plant Protection, 2002, 28(5): 39-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2002.05.013
[9] 侯玉霞, 石建宁.宁夏草坪草病害调查及防治[J].植物保护, 1999, 25(6): 28-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.1999.06.013 HOU Y X, SHI J N. Identification and control of turfgrass diseases in Ningxia[J]. Plant Protection, 1999, 25(6): 28-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.1999.06.013
[10] 张庆峰, 林树燕, 张强.南京市观赏型草坪草主要病害发生的特点及防治[J].江苏林业科技, 2005, 32(3): 26-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2005.03.010 ZHANG Q F, LIN S Y, ZHANG Q. Prevention and control measures of main turfgrass diseases in Nanjing City[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 2005, 32(3): 26-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2005.03.010
[11] 侯丽冰, 贺伟, 刘小勇, 等.我国几种松干锈菌亲缘关系的ITS序列分析[J].北京林业大学学报, 2002, 24(5/6): 179-186. http://bjly.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=87A21F4E-16FC-4BEE-90B9-3658AC3458C9 HOU L B, HE W, LIU X Y, et al. Sequence analysis of ITS region in relationships of Chinese isolates of Cronartium [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2002, 24(5/6): 179-186. http://bjly.chinajournal.net.cn/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=87A21F4E-16FC-4BEE-90B9-3658AC3458C9
[12] 郑素娇.红小豆锈病菌鉴定和越冬及侵染过程的研究[D].大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10223-1015593026.htm ZHENG S J. Identification, overwintering and infection process of the pathogen causing adzuki bean rust[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10223-1015593026.htm
[13] 代君丽, 于思勤, 韩帅, 等.一种从感病叶片中高效提取条锈菌基因组DNA的方法[J].西北农业学报, 2009, 18(2): 304-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1389.2009.02.068 DAI J L, YU S Q, HAN S, et al. An efficient protocol for isolatiing genomic DNA of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici from infected leaves[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2009, 18(2): 304-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1389.2009.02.068
[14] SOHPAL V K, DEY A, SINGH A. MEGA biocentric software for sequence and phylogenetic analysis: a review[J]. International Journal of Bioinformatics Research and Applications, 2010, 6(3): 230-240. doi: 10.1504/IJBRA.2010.034072
[15] TIAN B, HARRISON R, MORTON J, et al. Proteomic analysis of sauvignon blanc grape skin, pulp and seed and relative quantification of pathogenesis-related proteins[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e130132[2016-05-04]. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130132.
[16] CARUSO C, CHILOSI G, CAPORALE C, et al. Induction of pathogenesis-related proteins in germinating wheat seeds infected with Fusarium culmorum [J]. Plant Science, 1999, 140(1): 87-97. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00199-X
[17] ZAMBINO P J, SZABO L J. Phylogenetic relationships of selected cereal and grass rusts based on rDNA sequence analysis[J]. Mycologia, 1993, 85(3): 401-414. doi: 10.1080/00275514.1993.12026292
[18] MA G B. Functional analysis of plant disease resistance genes and their downstream effectors.[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 1999, 2(4): 273-279. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(99)80049-1
[19] DURRANT W E, DONG X. Systemic acquired resistance[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2004, 42(1): 185-209. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.42.040803.140421
[20] CAO H, GLAZEBROOK J, CLARKE J D, et al. The arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats[J]. Cell, 1997, 88(1): 57-63. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81858-9
[21] KINKEMA M, FAN W, DONG X. Nuclear localization of NPR1 is required for activation of PR gene expression[J]. The Plant Cell, 2000, 12(12): 2339-2350. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.12.2339
-
期刊类型引用(24)
1. 张秀芸,伍文慧,梁英梅. 落叶松枯梢病在中国的适生性. 生态学报. 2024(07): 3027-3037 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 葛婉婷,刘莹,赵智佳,张珅,李洁,杨桂娟,曲冠证,王军辉,麻文俊. 不同气候情景下黄心梓木在我国的潜在适生区预测. 林业科学. 2024(11): 63-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汤思琦,武扬,梁定东,郭恺. 未来气候变化下栎树猝死病菌在中国的适生性分析. 生态学报. 2023(01): 388-397 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘璐璐,赵亮,蔺诗颖,冯建龙. 基于MaxEnt和GARP的阿蒙森海域南极磷虾(EUPHAUSIA SUPERBA)的分布区预测. 海洋与湖沼. 2023(02): 399-411 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 唐雨薇,张晓龙,张雪云,吕佩锋,罗乐. 基于GIS与AHP分析法的单叶蔷薇生态适宜性评价. 绿色科技. 2023(13): 205-208+213 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王广平,李成,王书砚,刘超,杨君珑. 宁夏罗山青海云杉林空间分布特征研究. 农业科学研究. 2023(03): 10-15+23 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张惠惠,孟祥霄,林余霖,陈士林,黄林芳. 基于GMPGIS系统和MaxEnt模型预测人参全球潜在生长区域. 中国中药杂志. 2023(18): 4959-4966 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李盼畔,何旭诺,吴海荣,陈萍,刘明航,武目涛,王亚锋. 多年生豚草在中国的潜在分布预测. 植物检疫. 2022(04): 57-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李盼畔,何旭诺,左然玲,吕文刚,吴海荣. 4种蒺藜草属杂草在中国的潜在适生性预测. 杂草学报. 2022(02): 15-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 林姗,陆兴利,王茹琳,李庆,王明田,郭翔,文刚. RCP8.5情景下气候变化对四川省猕猴桃溃疡病病菌地理分布的影响. 江苏农业科学. 2020(03): 124-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王华辰,朱弘,李涌福,伊贤贵,李蒙,南程慧,王贤荣. 中国特有植物雪落樱桃潜在分布及其生态特征. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2020(02): 136-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 赵金鹏,王茹琳,刘原,陆兴利,王庆,郭翔,文刚,李庆. RCP4.5情景下四川省猕猴桃溃疡病菌适生性分析. 沙漠与绿洲气象. 2020(02): 137-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 段义忠,王佳豪,王驰,王海涛,杜忠毓. 未来气候变化下西北干旱区4种扁桃亚属植物潜在适生区分析. 生态学杂志. 2020(07): 2193-2204 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 陈爱莉,赵志华,龚伟,孔芬,张克亮. 气候变化背景下紫楠在中国的适宜分布区模拟. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2020(05): 435-444 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 文雪梅,艾科拜尔·木哈塔尔,木巴来克·阿布都许科尔,阿不都拉·阿巴斯. 基于MaxEnt模型的新疆微孢衣属地衣生境适宜性评价. 武汉大学学报(理学版). 2019(01): 77-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 常红,刘彤,王大伟,纪孝儒. 气候变化下中国西北干旱区梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)潜在分布. 中国沙漠. 2019(01): 110-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 吕汝丹,何健,刘慧杰,姚敏,程瑾,谢磊. 羽叶铁线莲的分布区与生态位模型分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2019(02): 70-79 .  本站查看
本站查看
18. 陆兴利,罗伟,李庆,林姗,王茹琳,游超,郭翔,王明田. RCP2.6情景下四川省猕猴桃溃疡病菌潜在分布预测. 湖北农业科学. 2019(18): 49-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 王蕾,罗磊,刘平,侯晓臣,邱琴,高亚琪,李曦光. 基于MaxEnt模型分析新疆特色林果区春尺蠖发生风险. 新疆农业科学. 2019(09): 1691-1700 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 王茹琳,郭翔,李庆,王明田,游超. 四川省猕猴桃溃疡病潜在分布预测及适生区域划分. 应用生态学报. 2019(12): 4222-4230 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 赵健,李志鹏,张华纬,陈宏,翁启勇. 基于MaxEnt模型和GIS技术的烟粉虱适生区预测. 植物保护学报. 2019(06): 1292-1300 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 王奕晨,郑鹏,潘文斌. 运用GARP生态位模型预测福寿螺在中国的潜在适生区. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版). 2018(01): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 邱靖,朱弘,陈昕,汤庚国. 基于DIVA-GIS的水榆花楸适生区模拟及生态特征. 北京林业大学学报. 2018(09): 25-32 .  本站查看
本站查看
24. 王野,陈磊,白云,张俊娥,刘红霞,田呈明. 云杉矮槲寄生遗传多样性的ISSR分析. 西北植物学报. 2017(11): 2153-2162 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(20)




 下载:
下载: