Comprehensive selection of growth and stem form of superior paulownia clones in the hilly region of southern China
-
摘要: 针对南方低山丘陵区缺乏适宜栽培的泡桐优良无性系的现状,本研究以湖北省赤壁市泡桐无性系测定林为对象,对5年生24个泡桐无性系的4个生长性状(胸径、主干高、总材积、接干高/苗干高)和2个干形性状(主干削度、形数)进行了遗传参数估算及性状间的相关性分析,并利用多性状指数法对其进行了评价和选择。结果表明:各性状在无性系间的差异达到显著或极显著水平。胸径和总材积的重复力较大,分别达到0.727 3和0.726 9,其余4个性状的重复力稍小,为0.201 8~0.383 7。4个生长性状间呈极显著的表型和遗传正相关关系,2个干形性状间呈极显著的表型和遗传负相关关系。形数与4个生长性状间均呈极显著的遗传和表型负相关关系。削度与胸径、主干高、接干高/苗干高的遗传正相关关系均达到极显著水平,与胸径、总材积的表型正相关关系分别达到极显著和显著水平。依据建立的多性状指数方程选择出适宜在南方丘陵区栽培的4个优良无性系,分别为609、204、302和207,入选率17%。与CK相比,入选群体的胸径、主干高、总材积、接干高/苗干高、削度和形数的遗传增益分别为3.93%、5.75%、21.84%、13.18%、5.72%和-0.45%,实际增益分别为5.40%、16.75%、30.04%、34.35%、28.34%和-1.62%。Abstract: To address the problem of lacking superior Paulownia spp. clones in the hilly region of southern China, the study was carried out with 5-years-old clonal test plantation contained 24 Paulownia spp. clones. The genetic parameter estimations of 4 growth traits including DBH(D1.3), height of the trunk(Ht), total volume(Vt) and ratio of height of extened trunk to original trunk (H1/H0), and 2 stem form traits including taper of the trunk (β) and form factor(f) of clones were conducted, and correlations among these traits were analyzed. Furthermore, evaluation and selection of Paulownia spp. clones were conducted by comprehensive selection index method. Results indicated that: significant differences existed in each of the 6 traits among these 24 clones. The repeatability of D1.3 and Vt were 0.727 3 and 0.726 9, respectively. The repeatability of other four traits was smaller ranging from 0.201 8 to 0.383 7. There were very significantly positive phenotypic and genetic correlations among 4 growth traits, and there were negative phenotypic and genetic correlations between the two form traits (β and f). There were very significantly negative correlations between form factor and 4 growth traits. Genetic correlations between β and D1.3, Ht, H1/H0 were significantly positive. Phenotypic correlations between β and D1.3, Vt were significantly positive and positive, respectively. With a selection rate of 17%, clones 609, 204, 302 and 207 were selected as the superior clones by the method of comprehensive selection index. Compared with control, genetic and actual gains through these 4 clones were 3.93% and 5.40% for D1.3, 5.75% and 16.75% for Ht, 21.84% and 30.04% for Vt, 13.18% and 34.35% for H1/H0, 5.72% and 28.34% for β, -0.45% and -1.62% for f, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- Paulownia spp. /
- clone /
- growth /
- stem form /
- comprehensive selection index
-
泡桐(Paulownia spp.)是我国特有的重要的优质速生用材树种之一,在我国25个省(市、区)均有自然分布,传统的人工栽培集中在黄淮海平原区[1]。系统的泡桐良种选育工作开始于20世纪70年代初期[2],经过我国几代泡桐研究专家的共同努力,重点面向黄淮海平原地区选育出40多个泡桐优良无性系,这些无性系的推广应用对该地区泡桐产业的发展发挥了极为重要的作用,但也存在一些不足。例如,过去多采用单性状直接选择方法对泡桐无性系进行选择,或者利用单项排列选择法逐步实现多个性状的改良,而缺乏利用多个目标性状对泡桐无性系进行综合改良的研究[3-6],而对多个性状同时进行选择和改良已经成为林木遗传育种的研究主题。
近年来,随着林权制度改革,受桐材利用途径逐渐拓展、供需矛盾不断加大和发展泡桐人工林带来的较高经济、生态效益回报等因素的影响,南方低山丘陵区因其良好的土壤、水热状况和丰富的土地资源,泡桐种植业发展日益得到重视,正在成为我国重要的泡桐速生用材林基地。但是针对该区域泡桐工业用材林的新品种选育工作一直没有开展,也没有经研究证明适于该区域大规模发展的泡桐新品系,导致目前在鄂、湘、赣3省大面积发展的泡桐人工林已暴露出较为严重的盲目引种、品系混杂等问题,对该区域泡桐种植业的健康发展带来重大隐患。因此,本研究以湖北省赤壁市5年生的泡桐无性系测定林为对象,以生长和干形的综合改良为目标,进行无性系生长和干形性状的遗传参数估算及性状间的相关性分析,在此基础上采用多性状选择指数法选择出适合在南方低山丘陵区栽培的泡桐优良无性系,为该区域泡桐种植业的发展提供速生、优质的良种。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 试验区概况和试验材料
试验区域位于湖北省赤壁市中伙铺镇董家岭村(112°52′21″E、31°12′49″N),海拔200 m,坡度10°~15°,为典型的低山丘陵区。年平均气温16.8 ℃,日平均气温≥10 ℃的活动积温达5 470 ℃。年降雨量1 690 mm。年平均日照时数1 880 h。土壤为黄红壤,质地中壤,pH 4.50~5.95。
2012年2月对试验区进行穴状整地,规格为60 cm×60 cm,密度为4 m×5 m。每穴内施3 kg有机肥作为底肥。按照完全随机区组试验设计,每个无性系设置6株小区,4次重复,共24个无性系参试,其中P6为CK(当地主栽的白花泡桐(P.fortunei))(见表 1)。采用1年生泡桐苗木造林,平均苗高和胸径分别为2.89 m、4.23 cm。测定林采用统一的抚育管理措施。
表 1 参试无性系及其来源Table 1. Origin of Paulownia spp. clones tested in this study无性系
Clone来源
Origin204 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 601 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 602 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 604 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 302 兰考泡桐、优树P. elongata, plus tree 209 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 606 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 201 白花泡桐、优树P. fortunei, plus tree 501 川泡桐P. fargesii 609 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 301 兰考泡桐、优树P. elongata, plus tree 612 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 102 毛泡桐、实生选择P. tomentosa, seeding selection 610 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 611 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 801 毛泡桐×兰考泡桐P. tomentosa×P. elongata 207 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 202 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 205 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 607 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 608 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 401 楸叶泡桐、实生选择P. catalpifolia, seeding selection 毛四Maosi 毛泡桐、四倍体P. tomentosa, autotetraploid P6(CK) 白花泡桐、优树P. fortunei, plus tree 1.2 试验林生长、干形性状的测算
2011年3月造林后调查测定林的初始胸径和苗高,此后每年落叶后对测定林进行每木检尺,调查6项生长指标,分别为胸径(D1.3)、2.6 m直径(D2.6)、接干+0.5 m直径(De0.5)、接干+1.5 m直径(De1.5)、苗干高(H0)和接干高(H1)。以接干高/苗干高(H1/H0)代表接干能力,以主干削度(β)和形数(r)代表干形。选择已达到早期选择年龄[7]的5年生泡桐的调查数据参与分析。采用公式(1)~(10)分别计算主干高(Ht)、主干削度(β)、形数(f)和总材积(Vt)[8]。为了减少初始苗高和胸径对试验结果的影响,采用协方差分析对高、径生长指标进行调整[9]。
Ht=H0+H1 (1) Vt=V0+V1 (2) β1=11.3(D2.6−D1.3) (3) β2=(De0.5−De1.5) (4) β=12(β1+β2) (5) {v_0} = \frac{{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }}}{{40\;000}}\left\{ {\left. {2.6D_{1.3}^2 + {{\left[ {{D_{2.6}} - \frac{1}{2}{\beta _1}\left( {{H_0} - 2.6} \right)} \right]}^2}\left( {{H_0} - 2.6} \right)} \right\}} \right. (6) {v_1} = \frac{{\rm{ \mathsf{ π} }}}{{40\;000}}D_{{\rm{ec}}}^2{H_1} (7) {D_{{\rm{ec}}}} = {D_{{\rm{e}}1.5}} - {\beta _2}\left( {\frac{{{H_1}}}{2} - 1.5} \right) (8) A = \frac{{\rm{ \mathsf{ π} }}}{{40\;000}}D_{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.3}}}^2 (9) f = {V_{\text{t}}}/(A{H_{\text{t}}}) (10) 1.3 分析方法
1.3.1 方差分析模型
a个无性系参试,b次重复,n株小区,以单株观测值为统计单元,方差分析线性模型如下[10]:
{x_{ijk}} = \mu + {\alpha _i} + {\beta _i} + \alpha {\beta _{ij}} + {e_{ijk}} (11) 式中:xijk为第i个无性系在第j个区组的平均值,μ为总体平均值,αi为无性系效应,βj为区组效应,αβij为无性系与区组的交互效应,eijk为随机误差。
1.3.2 遗传参数估算
无性系重复力(H2)计算公式如下[11]:
{H^2} = \frac{{\sigma _a^2}}{{\sigma _a^2 + \sigma _{ab}^2/b + \sigma _e^2/nb}} (12) 式中:σa2为无性系方差分量,σab2为无性系和区组交互效应方差分量,σe2为随机误差的方差分量,n为区组内各无性系样本数,b为区组(重复)数。
表型变异系数(CV)、遗传变异系数(GCV)计算公式如下[12]:
{\rm{CV = }}\frac{S}{{\overline x }} \times 100\% (13) {\rm{GCV = }}\frac{{\sqrt {\sigma _a^2} }}{{\overline x }} \times 100\% (14) 式中:S为某一性状的表型标准差,x为某一性状的平均值。
表型相关系数(rp12)及遗传相关系数(rg12)的计算公式如下[11]:
\;{\mathit{r}_{{\rm{p}}12}} = \frac{{{\rm{Co}}{{\rm{v}}_{{\rm{p}}12}}}}{{\sqrt {\sigma _{{\rm{p1}}}^2\sigma _{{\rm{p2}}}^2} }};{\mathit{r}_{{\rm{g}}12}} = \frac{{{\rm{Co}}{{\rm{v}}_{{\rm{g}}12}}}}{{\sqrt {\sigma _{{\rm{g1}}}^2\sigma _{{\rm{g2}}}^2} }} (15) 式中:σp12和σp22分别为2个性状的表型方差,σg12和σg22分别为2个性状的遗传方差。Covp12和Covg12分别为2个性状的表型协方差和遗传协方差。
1.3.3 多性状综合选择
采用Smith-Hazel选择指数进行多性状综合评价[13]。其关键是依据选择目标确定合理的经济权重。本研究采用等权重法确定各性状的经济权重,假设各性状表型标准差的单位变化具有同等的重要性,经济权重w的计算公式为wi=1/σi[14],并依据不同的育种目标进行适宜的倍数调整[15]。选择指数的计算公式如下[16]:
\begin{array}{c} I = {b_1}{x_1} + {b_2}{x_2} + \cdots {b_n}{x_n}\\ b = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{P}}^{ - 1}}\mathit{\boldsymbol{GW}} \end{array} (16) 式中:b为各性状的指数系数,xi为各性状的平均值,σi为各性状的表型标准差,P为表型方差协方差矩阵,G为遗传方差协方差矩阵,W为各性状的经济权重向量。
遗传增益(ΔG)和实际增益(G)的计算参考赵承开等[17]并做了适当调整,计算公式如下:
\Delta G = \frac{{{H^2}M}}{X} \times 100\% (17) \mathit{G = }\frac{M}{X} \times 100\% (18) 式中:X为λ选无性系群体某一性状的平均值,M为X与对照无性系相应性状的平均值之差。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 无性系各性状差异性分析和遗传参数估算
对无性系测定林各性状进行方差分析和遗传参数估算,结果显示:D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0、β和f各性状在无性系间的差异性F值为1.836 8~4.090 4,均达到显著或极显著水平(表 2)。说明这些性状受环境的影响较小,无性系间的遗传基础存在真实差异,开展无性系的选择可以获得较大的增益[18]。各性状在无性系间的Duncan’s多重比较结果见表 3。可以看出,D1.3显著高于CK的有604和609,Ht显著高于CK的有207,Vt显著高于CK的有609、604和302,H1/H0显著高于CK的有207和609,β显著低于CK的有201、205、毛四、207、602、302和204,f显著高于CK的是801。
表 2 方差分析及遗传参数估算Table 2. Variance analysis and genetic parameter estimation性状Trait D1.3 Ht Vt H1/ H0 β f 平均值Mean 16.116 8 cm 6.295 8 m 0.097 5 m3 1.243 9 0.992 1 0.757 4 无性系间F值F value of clones 4.004 4** 2.649 5* 4.090 4** 2.838 0* 2.549 9* 1.836 8* 无性系间方差分量Variance analysis among clones 12.855 0 6.826 0 0.004 4 0.963 2 0.349 0 0.020 7 互作方差分量Interaction variance component 3.506 2 4.481 3 0.001 2 0.593 6 0.245 6 0.015 0 误差Error 3.210 3 2.576 4 0.001 1 0.339 4 0.136 9 0.011 3 无性系重复力Repeatability of clone 0.727 3 0.343 5 0.726 9 0.383 7 0.201 8 0.278 3 表型变异系数CV/% 13.096 3 28.909 6 40.218 7 53.645 8 39.945 6 14.733 9 遗传变异系数GCV/% 22.246 3 41.498 5 68.033 3 78.899 2 59.546 6 18.995 9 注:D1.3为胸径,Ht为主干高,Vt为总材积,H1/H0为接干高/苗干高,β为主干削度,f为形数,*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。下同。Notes: D1.3, Ht, Vt, H1/H0, β and f stand for trunk diameter at breast height, trunk height, total volume growth of the trunk, ratio of extened height to trunk height before pruning, taper of the trunk, trunk form, respectively, * means significant difference at P<0.05 level, ** means extremely significant difference at P<0.01 level. The same below. 表 3 泡桐无性系各性状的Duncan’s多重比较结果Table 3. Duncan's test of the Paulownias spp. clone performance无性系Clone D1.3/cm Ht/m Vt/m3 H1/H0 β f 204 16.853 0±1.609 7abc 6.786 6±2.029 7abcd 0.116 7±0.036 8ab 1.413 2±0.684 2abcd 0.848 3±0.325 3def 0.776 5±0.101 7abcde 601 16.665 2±1.681 7abcde 6.843 5±1.872 5ab 0.110 5±0.034 9abc 1.370 2±0.671 7abcde 1.000 2±0.348 9abcdef 0.749 1±0.111 7bcde 602 15.254 6±1.466 1hi 5.387 2±1.743 2e 0.078 9±0.023 9gh 0.882 4±0.637 4h 0.816 3±0.374 5ef 0.821 3±0.121 4ab 604 17.281 4±2.219 0a 6.596 8±1.817 2abcde 0.113 6±0.044 4ab 1.405 4±0.655 4abcd 1.150 6±0.448 4abc 0.728 7±0.101 4cde 209 15.629 3±1.691 9defgh 6.111 8±1.476 2bcde 0.084 9±0.030 6defgh 1.173 1±0.561 1bcdefgh 1.094 8±0.472 4abcd 0.723 5±0.134 9cde 302 16.767 7±2.016 3abcd 6.774 3±2.079 9abcd 0.110 6±0.043 5ab 1.399 3±0.757 2abcd 0.810 2±0.261 7f 0.738 3±0.103 8bcde 102 16.444 0±2.210 3abcdefgh 6.507 4±1.582 9abcde 0.104 1±0.037 1abcd 1.367 2±0.736 1abcde 0.942 6±0.338 0bcdef 0.748 8±0.091 8bcde 610 15.371 5±3.224 1ghi 6.375 8±2.360 1abcde 0.099 7±0.064 2abcdefg 1.279 9±0.869 8abcdefg 0.955 2±0.347 3bcdef 0.778 5±0.115 3abcd 611 15.627 9±2.467 6defghi 6.245 7±1.798 2bcde 0.093 7±0.048 4bcdefgh 1.234 2±0.629 9bcdefgh 0.981 6±0.282 2abcdef 0.738 6±0.105 2bcde 801 16.540 8±1.918 7abcdefg 5.331 7±1.401 7e 0.095 3±0.026 2bcdefgh 0.900 2±0.544 3gh 1.075 2±0.285abcdef 0.841 3±0.093 2a 301 15.454 3±2.119 5fghi 5.339 0±1.970 2e 0.080 1±0.038 9fgh 0.888 3±0.720 7gh 0.997 9±0.32abcdef 0.800 7±0.12abcd 612 15.534 0±2.380 5efghi 5.786 7±1.671 7bcde 0.083 1±0.029 8efgh 0.946 3±0.475 7fgh 1.070 8±0.494 6abcdef 0.767 2±0.131 4abcde 207 16.211 7±1.720 7abcdefgh 7.325 9±1.554 5a 0.110 5±0.036 5abc 1.642 6±0.566a 0.843 8±0.327 3ef 0.720 3±0.110 7de 202 15.309 3±1.219 0hi 5.579 6±1.544 2cde 0.077 6±0.016 6gh 1.040 2±0.601 3defgh 1.086 7±0.416 5abcde 0.777 9±0.117 1abcd 606 16.371 1±2.203 0abcdefgh 6.806 4±1.819 4abc 0.099 9±0.033 2abcdef 1.339 4±0.631abcdef 1.206±0.362 1ab 0.698 4±0.120 9e 201 16.561 0±2.487 3abcdef 6.669 2±2.192 3abcd 0.107 3±0.049 3abcd 1.391 8±0.783 2abcd 0.901 0±0.349 2cdef 0.742 4±0.129 7bcde 501 16.201 0±1.682 9bcdefgh 6.947 4±1.671 1ab 0.105 0±0.033 1abcd 1.493 5±0.617 2abc 0.945 7±0.279 6bcdef 0.733 7±0.113 3cde 609 17.105 1±1.433 0ab 6.955 3±1.822 1ab 0.119 0±0.036 7a 1.568 3±0.694 3ab 0.904 6±0.590 2bcdef 0.747 1±0.107 2bcde 205 15.764 6±1.930 1cdefgh 6.318 6±1.546 5abcde 0.092 0±0.035 5bcdefgh 1.301 9±0.582 1abcdef 0.884 6±0.371 4cdef 0.730 3±0.088 8cde 607 16.539 8±2.557 2abcdefgh 6.262 9±1.708abcde 0.100 1±0.039 5abcde 1.281 2±0.621 8abcdefg 0.917 0±0.510 7bcdef 0.754 0±0.100 9bcde 608 16.508 5±2.602 8abcdefgh 5.937 1±1.851 7bcde 0.098 2±0.051 1abcdefgh 1.123 5±0.663 7cdefgh 1.086 9±0.322 2abcd 0.763 9±0.1114bcde 401 16.547 1±1.324 3abcdefg 6.432 6±1.634 3abcde 0.100 8±0.024 1abcde 1.219 2±0.610 4bcdefgh 1.259 0±0.416 8a 0.746 9±0.115bcde 毛四Maosi 14.599 3±2.293 9i 5.526 2±1.981 8de 0.075 8±0.036h 0.983 4±0.695 3efgh 0.859 8±0.244 7cdef 0.802 6±0.120 4abc P6(CK) 15.876 3±1.313 3cdefgh 5.961 8±1.654 6bcde 0.087 8±0.026 8cdefgh 1.120 7±0.549 1cdefgh 1.188 5±0.458 1ab 0.757 8±0.112 6bcde 注:表中同列数字后不同字母表示P<0.05水平上差异显著。Note: Data with different letters within the same column are significantly different at P<0.05 level according to ANOVA analysis and Ducan’s multiple comparisons. 由表 2可以看出,H1/H0和Vt的遗传变异系数较大,分别达到78.899 2%和68.033 3%。β和Ht的遗传变异系数处于中等水平,分别达到59.546 6%和41.498 5%。D1.3和f的遗传变异系数稍小,分别为22.246 3%和18.995 9%。表明在参试的24个无性系中选出Vt大和接干能力强的无性系的可能性较大,而对Ht、β、D1.3和f选择改良的可能性次之。
重复力分析结果显示D1.3和Vt的无性系重复力较大,分别达到0.727 3和0.726 9,表明其受遗传控制较强,受随机环境影响较弱,对其进行表型选择可以选出遗传优良无性系的概率大[19]。Ht、H1/H0、β和f的重复力稍小,为0.201 8~0.383 7。
2.2 泡桐无性系各性状间相关性分析
由表 4可知,泡桐的D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/ H0间均呈极显著水平的表型和遗传正相关关系,且遗传相关系数接近于1,说明这种相关关系主要受遗传因素控制[20]。这4个生长性状均与干形性状中的f呈现出极显著的表型和遗传负相关关系。D1.3、Ht、H1/H0与β呈极显著的遗传正相关关系,D1.3、Vt与β分别呈显著和显著的表型正相关关系。β与f呈极显著的表型和遗传负相关关系,与Vt的遗传相关关系、与Ht的表型相关关系均未达到显著水平。
表 4 泡桐无性系各性状间的相关系数Table 4. Correlation coefficients among traits of Paulownia spp. clones性状Trait D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f D1.3 0.330 3** 0.860 5** 0.318 5** 0.169 1** -0.162 3** Ht 1.085 2** 0.659 7** 0.959 2** 0.003 0 -0.844 7** Vt 0.996 0** 1.042 2** 0.636 6** 0.008 3* -0.348 3** H1/H0 1.143 9** 0.987 0** 1.084 5** -0.002 2 -0.818 5** β 0.335 2** 0.245 8** 0.070 7 0.182 4** -0.244 8** f -0.741 8** -0.794 6** -0.709 2** -0.678 3** -0.778 7** 注:左下角为遗传相关系数,右上角为表型相关系数。*表示相关关系达到显著水平(P<0.05),**表示相关关系达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。Notes: phenotypic correlation coefficients in the upper triangle, and genetic correlation coefficients in the below triangle. * and ** represent significant correlations at P<0.05 level and P<0.01 level, respectively. 2.3 泡桐无性系多性状指数选择
无性系各性状间的相关关系复杂,如果从多性状角度来评价参试的无性系,就需要建立一个考虑到各性状的表型、遗传参数和性状间相关性的综合指标。理想的泡桐优良无性系应该是D1.3、Ht和Vt的生长量大、接干能力强、f大、β小。分别按照等权重、强调生长改良和强调干形改良确定6个性状的经济权重(表 5)。根据性状间的相关性,选择不同的性状配合,采用无约束、等权重方法分别构建了等权重的指数方程(I1~I3)、强调生长的指数方程(I4~I6)和强调干形的指数方程(I7~I9),并计算了各指数方程的综合选择进展及各性状的遗传进展(表 6、7)。可以看出,在等权重的各指数方程中,以D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0和β这5个性状配合的指数方程I2的综合选择进展最大,此时Ht和H1/H0的遗传进展也最大,但是D1.3和Vt的进展却较小。I1和I2方程的主干削度均为负向进展,I1和I3的形数均为负向进展。比较强调生长改良的3个指数方程发现,D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0和β 5个性状配合的指数方程I5虽然D1.3和Vt的遗传进展小于I4和I6,但是其综合选择进展在这3个指数方程中居于最高,而且该指数方程所包含的5性状均得到了改良。比较强调干形性状改良的3个指数方程发现,D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0和β 5个性状配合的指数方程I8的综合选择进展最大,但是主干削度为负向进展。与指数方程I8相比,虽然I9的D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0 4个性状的遗传进展略小,但也均高于由6个性状配合的指数方程I7中这4个性状的遗传进展,而且3个指数式中只有I9的干形性状(f)为正向遗传进展。
表 5 各性状经济权重及估算方法Table 5. Economic weight and estimation method of 6 traits方法
Method指数方程
Selection index经济权重Economic weight D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f 等权重Equal weight I1 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -2.523 7 8.851 6 I2 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -2.523 7 I3 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 8.851 6 强调生长Strengthening growth I4 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 -2.523 7 8.851 6 I5 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 -2.523 7 I6 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 8.851 6 强调干形Strengthening stem form I7 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -7.571 0 26.554 8 I8 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -7.571 0 I9 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 26.554 8 表 6 生长和干形性状配合的指数方程和综合选择进展Table 6. Combined selection progress and selection index equation with growth and stem form序号No. 性状配合及指数方程式Selection index equation with various traits 综合选择进展ΔI
Comprehensive selection progressI1 1.666 9x1+0.220 0x2-77.282 7x3+6.666 8x4+0.110 8x5+25.282 2x6 2.333 2 I2 0.972 1x1-1.633 9x2+3.564 0x3+5.968 1x4-0.423 9x5 2.477 6 I3 1.898 2x1+0.835 8x2-89.799 2x3+4.841 5x4+21.837 8x6 2.296 6 I4 5.189 0x1+0.547 3x2-205.816 4x3+16.672 8x4+1.318 1x5+52.189 0x6 7.350 3 I5 3.470 2x1-3.298 7x2-28.279 0x3+14.718 9x4-0.279 5x5 7.475 8 I6 5.460 0x1+1.023 6x2-216.140 0x3+14.502 1x4+44.776 0x6 7.362 3 I7 1.478 5x1+0.332 9x2-103.314 4x3+9.994 2x4-0.875 0x5+48.939 8x6 2.813 8 I8 0.418 0x1-3.237 0x2+42.534 8x3+9.153 5x4-1.416 1x5 2.646 1 I9 2.133 0x1+2.319 4x2-143.057 0x3+4.864 0x4+42.575 2x6 2.176 2 表 7 指数方程中各性状的遗传进展Table 7. Genetic progress on the traits of all selection indices序号No. D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f I1 1.567 8 0.816 3 0.028 2 0.329 1 -0.029 2 -0.016 1 I2 1.551 0 0.883 9 0.027 5 0.368 3 -0.002 2 I3 1.602 7 0.871 2 0.028 7 0.350 0 -0.022 4 I4 1.625 2 0.902 4 0.028 9 0.360 9 0.007 9 -0.029 0 I5 1.564 4 0.913 0 0.027 6 0.374 9 0.019 2 I6 1.615 4 0.906 3 0.028 8 0.366 1 -0.030 8 I7 0.954 7 0.350 1 0.017 9 0.148 7 -0.117 6 0.022 5 I8 1.389 2 0.731 3 0.024 8 0.320 3 -0.062 5 I9 1.300 3 0.611 5 0.024 0 0.238 6 0.009 6 综合以上结果,强调生长改良的指数方程I5和强调干形改良的指数方程I9是比较理想的多性状指数方程。按照30%的选择强度依据指数方程I5从参试无性系中选择出排在前7位的无性系依次是609、604、204、302、207、201和102,依据指数方程I9从参试无性系中选择出排在前7位的无性系依次是609、204、207、801、601、501和302。可以看出,分别选出的7个无性系都包含609、204、302和207。因此,这4个无性系可作为入选的生长和干形兼优的无性系,入选率17%。由表 8可知,入选无性系生长性状均有不同程度的提高。其中,D1.3、Ht、Vt和H1/H0与CK相比分别增加了2.11%~7.74%、13.63%~22.88%、25.85%~35.54%和24.85%~46.56%。干形性状中β与CK相比降低了23.95%~31.91%。除204的f与CK相比增加了2.47%之外,其余3个无性系的f与CK相比稍有减小(1.41%~4.95%)。
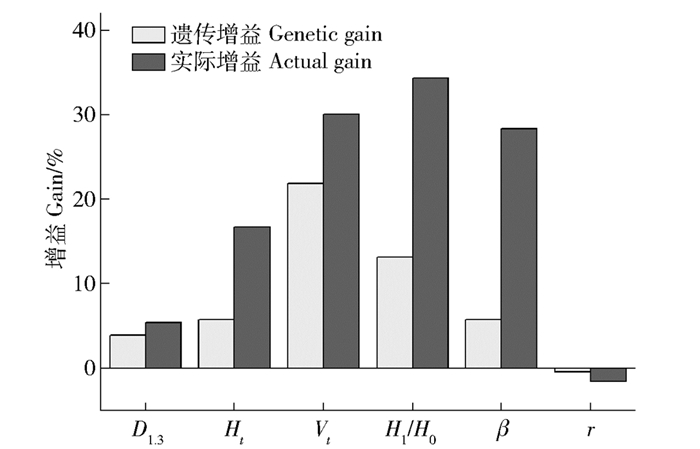
表 8 泡桐无性系各性状的均值Table 8. Means of 6 traits of Paulownia spp. clones and its value of index formula系号Clone No. D1.3 /cm Ht/m Vt/m3 H1/H0 β f 609 17.105 1 6.955 3 0.119 0 1.568 3 0.904 6 0.747 1 204 16.853 0 6.786 6 0.116 7 1.413 1 0.848 3 0.776 5 302 16.767 7 6.774 3 0.110 6 1.399 3 0.810 2 0.738 3 207 16.211 7 7.325 9 0.110 5 1.642 6 0.843 7 0.720 3 P6(CK) 15.876 3 5.961 8 0.087 8 1.120 8 1.188 5 0.757 8 将入选群体各性状的平均值与CK相比计算入选群体的遗传增益和实际增益。结果如图 1所示:在所有性状中,H1/H0的实际增益最高,达到34.35%,其次是Vt,达到30.04%。二者的遗传增益也较高,分别达到13.18%和21.84%。这说明入选群体的H1/H0和Vt在获得较大实际增益的基础上,也显著提高了遗传增益。β的实际增益达到28.34%,但由于其重复力偏小,导致其遗传增益与实际增益相差稍大[21]。入选群体的D1.3和Ht的遗传和实际增益稍小,f呈现出负的遗传和实际增益。
3. 结论与讨论
无性系间的变异是进行无性系育种的基础,变异系数的大小反映了群体的变异程度,决定了选择空间[22-23]。遗传变异系数是用来反映遗传因素导致性状观测值变异的程度,遗传变异系数大,说明各无性系在该性状中可利用的改良潜力比较大,即对其进行改良能够带来较大的选择响应[16]。本研究中参试无性系各性状变异丰富,在无性系间差异显著,各性状的表型变异系数的变化范围为13.096 3%~53.645 8%,遗传变异系数的变化范围为18.995 9%~78.899 2%。其中Ht、Vt、β和f的遗传变异系数均高于施士争等[24]对11个4年生泡桐无性系的研究结果,D1.3、Ht和Vt的遗传变异系数均高于杨途熙等[25]对12个10年生泡桐无性系的研究结果。其原因可能是本研究中参试无性系的数量较二者多[22]。本研究中相应性状较高的变异系数为无性系选择提供了较大的空间。
数量性状的表型值可以分解为基因型值和环境差值两部分,重复力是基因型方差与一般环境方差之和在表型方差中所占的比例[10],其大小直接影响选择效果[26]。D1.3和Vt的重复力较高,表明二者受较强的遗传控制,根据表型值对其选择的可靠性很大,这与杨途熙等[25]的研究结果一致。本研究在生长性状中首次采用H1/H0作为代表无性系接干能力的性状,其重复力为0.383 7,居于中等偏下水平,Ht、β和f的重复力较低[22]。其原因可能是本研究中的24个参试无性系都是经过逐步筛选出的无性系,接干能力都有所提高,干形性状也有所改善,导致这4个性状在无性系间的方差分量偏小[27]。同时也说明重复力不是一个常数,它因研究时间、研究环境和研究群体的不同而异。
林木性状间相关系数的高低反映了性状间的相关程度,可为林木的遗传改良策略提供理论参考,对林木育种工作具有重要意义[28-29]。本研究中各性状间的相关关系复杂,6个性状的表型和遗传相关系数不仅在数值上相差较大,且正负方向也有所不同,既存在着有利相关,也存在相互制约。生长性状中,D1.3、Ht、Vt和H1/H0间呈极显著的表型和遗传正相关关系,这与何贵平等[28]的研究结果一致。在林龄较大时,根据胸径进行选择,材积会相应得到改良,可以减少测量树高的工作[30]。干形指标中,β和f呈极显著的遗传和表型负相关关系。形数与4个生长性状均呈极显著的遗传和表型负相关关系,可能是由于参试无性系普遍具有自然接干能力,接干对f产生了影响所致[24],这也是泡桐与其他树种的不同之处。上述结果也说明,对泡桐某一个性状进行选择改良,可能会对其他性状产生显著的影响。比如,如果过分强调生长性状的改良,则有导致干形性状下降的的趋势,反之亦然。值的注意的是,本研究中D1.3与Ht、H1/H0,Ht与Vt,Vt与H1/H0之间的遗传相关系数出现了大于1的情况,而且前期也有过类似的报道[31],而相关系数的绝对值是不应大于1的。导致出现这一结果的原因有待于进一步探讨。
一个完善和成功的育种方案应该涉及综合性状,开展多性状选择时,应根据选育目标进行统筹考虑和取舍,达到综合性状最优的目的[32]。本研究通过建立多性状指数方程对参试的泡桐无性系进行评价。以D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0和β这5个性状配合构建的强调生长的指数方程I5和以D1.3、Ht、Vt、H1/H0和f这5个性状配合构建的强调干形的指数方程I9中各性状的遗传进展均较为合理。依此选出了609、204、302和207这4个无性系。入选无性系群体Vt的遗传增益最高,为21.84%,Ht、H1/H0和β的遗传增益为5.72%~13.18%,D1.3的遗传增益较低,为3.93%。f的遗传增益为-0.45%,可能是f与D1.3、Ht、Vt和H1/H0呈极显著水平的遗传和表型负相关关系导致了这一结果。在实际品种选择中若尤其注重干形的改良,则可选择β和f均得到改良的204作为入选无性系;若无此要求,则609、204、302和207这4个无性系由于4个生长性状和1个干形性状(β)均得到改良,皆可作为适宜在南方低山丘陵区栽培的生长和干形综合改良的泡桐无性系。
-
表 1 参试无性系及其来源
Table 1 Origin of Paulownia spp. clones tested in this study
无性系
Clone来源
Origin204 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 601 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 602 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 604 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 302 兰考泡桐、优树P. elongata, plus tree 209 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 606 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 201 白花泡桐、优树P. fortunei, plus tree 501 川泡桐P. fargesii 609 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 301 兰考泡桐、优树P. elongata, plus tree 612 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 102 毛泡桐、实生选择P. tomentosa, seeding selection 610 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 611 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 801 毛泡桐×兰考泡桐P. tomentosa×P. elongata 207 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 202 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 205 白花泡桐、实生选择P. fortunei, seeding selection 607 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 608 毛泡桐×白花泡桐P. tomentosa×P. fortunei 401 楸叶泡桐、实生选择P. catalpifolia, seeding selection 毛四Maosi 毛泡桐、四倍体P. tomentosa, autotetraploid P6(CK) 白花泡桐、优树P. fortunei, plus tree 表 2 方差分析及遗传参数估算
Table 2 Variance analysis and genetic parameter estimation
性状Trait D1.3 Ht Vt H1/ H0 β f 平均值Mean 16.116 8 cm 6.295 8 m 0.097 5 m3 1.243 9 0.992 1 0.757 4 无性系间F值F value of clones 4.004 4** 2.649 5* 4.090 4** 2.838 0* 2.549 9* 1.836 8* 无性系间方差分量Variance analysis among clones 12.855 0 6.826 0 0.004 4 0.963 2 0.349 0 0.020 7 互作方差分量Interaction variance component 3.506 2 4.481 3 0.001 2 0.593 6 0.245 6 0.015 0 误差Error 3.210 3 2.576 4 0.001 1 0.339 4 0.136 9 0.011 3 无性系重复力Repeatability of clone 0.727 3 0.343 5 0.726 9 0.383 7 0.201 8 0.278 3 表型变异系数CV/% 13.096 3 28.909 6 40.218 7 53.645 8 39.945 6 14.733 9 遗传变异系数GCV/% 22.246 3 41.498 5 68.033 3 78.899 2 59.546 6 18.995 9 注:D1.3为胸径,Ht为主干高,Vt为总材积,H1/H0为接干高/苗干高,β为主干削度,f为形数,*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。下同。Notes: D1.3, Ht, Vt, H1/H0, β and f stand for trunk diameter at breast height, trunk height, total volume growth of the trunk, ratio of extened height to trunk height before pruning, taper of the trunk, trunk form, respectively, * means significant difference at P<0.05 level, ** means extremely significant difference at P<0.01 level. The same below. 表 3 泡桐无性系各性状的Duncan’s多重比较结果
Table 3 Duncan's test of the Paulownias spp. clone performance
无性系Clone D1.3/cm Ht/m Vt/m3 H1/H0 β f 204 16.853 0±1.609 7abc 6.786 6±2.029 7abcd 0.116 7±0.036 8ab 1.413 2±0.684 2abcd 0.848 3±0.325 3def 0.776 5±0.101 7abcde 601 16.665 2±1.681 7abcde 6.843 5±1.872 5ab 0.110 5±0.034 9abc 1.370 2±0.671 7abcde 1.000 2±0.348 9abcdef 0.749 1±0.111 7bcde 602 15.254 6±1.466 1hi 5.387 2±1.743 2e 0.078 9±0.023 9gh 0.882 4±0.637 4h 0.816 3±0.374 5ef 0.821 3±0.121 4ab 604 17.281 4±2.219 0a 6.596 8±1.817 2abcde 0.113 6±0.044 4ab 1.405 4±0.655 4abcd 1.150 6±0.448 4abc 0.728 7±0.101 4cde 209 15.629 3±1.691 9defgh 6.111 8±1.476 2bcde 0.084 9±0.030 6defgh 1.173 1±0.561 1bcdefgh 1.094 8±0.472 4abcd 0.723 5±0.134 9cde 302 16.767 7±2.016 3abcd 6.774 3±2.079 9abcd 0.110 6±0.043 5ab 1.399 3±0.757 2abcd 0.810 2±0.261 7f 0.738 3±0.103 8bcde 102 16.444 0±2.210 3abcdefgh 6.507 4±1.582 9abcde 0.104 1±0.037 1abcd 1.367 2±0.736 1abcde 0.942 6±0.338 0bcdef 0.748 8±0.091 8bcde 610 15.371 5±3.224 1ghi 6.375 8±2.360 1abcde 0.099 7±0.064 2abcdefg 1.279 9±0.869 8abcdefg 0.955 2±0.347 3bcdef 0.778 5±0.115 3abcd 611 15.627 9±2.467 6defghi 6.245 7±1.798 2bcde 0.093 7±0.048 4bcdefgh 1.234 2±0.629 9bcdefgh 0.981 6±0.282 2abcdef 0.738 6±0.105 2bcde 801 16.540 8±1.918 7abcdefg 5.331 7±1.401 7e 0.095 3±0.026 2bcdefgh 0.900 2±0.544 3gh 1.075 2±0.285abcdef 0.841 3±0.093 2a 301 15.454 3±2.119 5fghi 5.339 0±1.970 2e 0.080 1±0.038 9fgh 0.888 3±0.720 7gh 0.997 9±0.32abcdef 0.800 7±0.12abcd 612 15.534 0±2.380 5efghi 5.786 7±1.671 7bcde 0.083 1±0.029 8efgh 0.946 3±0.475 7fgh 1.070 8±0.494 6abcdef 0.767 2±0.131 4abcde 207 16.211 7±1.720 7abcdefgh 7.325 9±1.554 5a 0.110 5±0.036 5abc 1.642 6±0.566a 0.843 8±0.327 3ef 0.720 3±0.110 7de 202 15.309 3±1.219 0hi 5.579 6±1.544 2cde 0.077 6±0.016 6gh 1.040 2±0.601 3defgh 1.086 7±0.416 5abcde 0.777 9±0.117 1abcd 606 16.371 1±2.203 0abcdefgh 6.806 4±1.819 4abc 0.099 9±0.033 2abcdef 1.339 4±0.631abcdef 1.206±0.362 1ab 0.698 4±0.120 9e 201 16.561 0±2.487 3abcdef 6.669 2±2.192 3abcd 0.107 3±0.049 3abcd 1.391 8±0.783 2abcd 0.901 0±0.349 2cdef 0.742 4±0.129 7bcde 501 16.201 0±1.682 9bcdefgh 6.947 4±1.671 1ab 0.105 0±0.033 1abcd 1.493 5±0.617 2abc 0.945 7±0.279 6bcdef 0.733 7±0.113 3cde 609 17.105 1±1.433 0ab 6.955 3±1.822 1ab 0.119 0±0.036 7a 1.568 3±0.694 3ab 0.904 6±0.590 2bcdef 0.747 1±0.107 2bcde 205 15.764 6±1.930 1cdefgh 6.318 6±1.546 5abcde 0.092 0±0.035 5bcdefgh 1.301 9±0.582 1abcdef 0.884 6±0.371 4cdef 0.730 3±0.088 8cde 607 16.539 8±2.557 2abcdefgh 6.262 9±1.708abcde 0.100 1±0.039 5abcde 1.281 2±0.621 8abcdefg 0.917 0±0.510 7bcdef 0.754 0±0.100 9bcde 608 16.508 5±2.602 8abcdefgh 5.937 1±1.851 7bcde 0.098 2±0.051 1abcdefgh 1.123 5±0.663 7cdefgh 1.086 9±0.322 2abcd 0.763 9±0.1114bcde 401 16.547 1±1.324 3abcdefg 6.432 6±1.634 3abcde 0.100 8±0.024 1abcde 1.219 2±0.610 4bcdefgh 1.259 0±0.416 8a 0.746 9±0.115bcde 毛四Maosi 14.599 3±2.293 9i 5.526 2±1.981 8de 0.075 8±0.036h 0.983 4±0.695 3efgh 0.859 8±0.244 7cdef 0.802 6±0.120 4abc P6(CK) 15.876 3±1.313 3cdefgh 5.961 8±1.654 6bcde 0.087 8±0.026 8cdefgh 1.120 7±0.549 1cdefgh 1.188 5±0.458 1ab 0.757 8±0.112 6bcde 注:表中同列数字后不同字母表示P<0.05水平上差异显著。Note: Data with different letters within the same column are significantly different at P<0.05 level according to ANOVA analysis and Ducan’s multiple comparisons. 表 4 泡桐无性系各性状间的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficients among traits of Paulownia spp. clones
性状Trait D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f D1.3 0.330 3** 0.860 5** 0.318 5** 0.169 1** -0.162 3** Ht 1.085 2** 0.659 7** 0.959 2** 0.003 0 -0.844 7** Vt 0.996 0** 1.042 2** 0.636 6** 0.008 3* -0.348 3** H1/H0 1.143 9** 0.987 0** 1.084 5** -0.002 2 -0.818 5** β 0.335 2** 0.245 8** 0.070 7 0.182 4** -0.244 8** f -0.741 8** -0.794 6** -0.709 2** -0.678 3** -0.778 7** 注:左下角为遗传相关系数,右上角为表型相关系数。*表示相关关系达到显著水平(P<0.05),**表示相关关系达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。Notes: phenotypic correlation coefficients in the upper triangle, and genetic correlation coefficients in the below triangle. * and ** represent significant correlations at P<0.05 level and P<0.01 level, respectively. 表 5 各性状经济权重及估算方法
Table 5 Economic weight and estimation method of 6 traits
方法
Method指数方程
Selection index经济权重Economic weight D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f 等权重Equal weight I1 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -2.523 7 8.851 6 I2 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -2.523 7 I3 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 8.851 6 强调生长Strengthening growth I4 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 -2.523 7 8.851 6 I5 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 -2.523 7 I6 1.421 3 1.638 6 76.687 0 4.495 8 8.851 6 强调干形Strengthening stem form I7 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -7.571 0 26.554 8 I8 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 -7.571 0 I9 0.473 8 0.546 2 25.562 3 1.498 6 26.554 8 表 6 生长和干形性状配合的指数方程和综合选择进展
Table 6 Combined selection progress and selection index equation with growth and stem form
序号No. 性状配合及指数方程式Selection index equation with various traits 综合选择进展ΔI
Comprehensive selection progressI1 1.666 9x1+0.220 0x2-77.282 7x3+6.666 8x4+0.110 8x5+25.282 2x6 2.333 2 I2 0.972 1x1-1.633 9x2+3.564 0x3+5.968 1x4-0.423 9x5 2.477 6 I3 1.898 2x1+0.835 8x2-89.799 2x3+4.841 5x4+21.837 8x6 2.296 6 I4 5.189 0x1+0.547 3x2-205.816 4x3+16.672 8x4+1.318 1x5+52.189 0x6 7.350 3 I5 3.470 2x1-3.298 7x2-28.279 0x3+14.718 9x4-0.279 5x5 7.475 8 I6 5.460 0x1+1.023 6x2-216.140 0x3+14.502 1x4+44.776 0x6 7.362 3 I7 1.478 5x1+0.332 9x2-103.314 4x3+9.994 2x4-0.875 0x5+48.939 8x6 2.813 8 I8 0.418 0x1-3.237 0x2+42.534 8x3+9.153 5x4-1.416 1x5 2.646 1 I9 2.133 0x1+2.319 4x2-143.057 0x3+4.864 0x4+42.575 2x6 2.176 2 表 7 指数方程中各性状的遗传进展
Table 7 Genetic progress on the traits of all selection indices
序号No. D1.3 Ht Vt H1/H0 β f I1 1.567 8 0.816 3 0.028 2 0.329 1 -0.029 2 -0.016 1 I2 1.551 0 0.883 9 0.027 5 0.368 3 -0.002 2 I3 1.602 7 0.871 2 0.028 7 0.350 0 -0.022 4 I4 1.625 2 0.902 4 0.028 9 0.360 9 0.007 9 -0.029 0 I5 1.564 4 0.913 0 0.027 6 0.374 9 0.019 2 I6 1.615 4 0.906 3 0.028 8 0.366 1 -0.030 8 I7 0.954 7 0.350 1 0.017 9 0.148 7 -0.117 6 0.022 5 I8 1.389 2 0.731 3 0.024 8 0.320 3 -0.062 5 I9 1.300 3 0.611 5 0.024 0 0.238 6 0.009 6 表 8 泡桐无性系各性状的均值
Table 8 Means of 6 traits of Paulownia spp. clones and its value of index formula
系号Clone No. D1.3 /cm Ht/m Vt/m3 H1/H0 β f 609 17.105 1 6.955 3 0.119 0 1.568 3 0.904 6 0.747 1 204 16.853 0 6.786 6 0.116 7 1.413 1 0.848 3 0.776 5 302 16.767 7 6.774 3 0.110 6 1.399 3 0.810 2 0.738 3 207 16.211 7 7.325 9 0.110 5 1.642 6 0.843 7 0.720 3 P6(CK) 15.876 3 5.961 8 0.087 8 1.120 8 1.188 5 0.757 8 -
[1] 蒋建平.泡桐栽培学[M].北京:中国林业出版社, 1990. JIANG J P. Paulownia cultivation[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1990.
[2] 李芳东, 乔杰, 王保平, 等.中国泡桐属种质资源图谱[M].北京:中国林业出版社, 2013. LI F D, QIAO J, WANG B P, et al. Chinese paulownia genus germplasm resources[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2013.
[3] 魏安智, 杨途熙, 杨焕叶, 等.泡桐优良无性系相关选择的研究[J].西北植物学报, 1998, 18(1): 39-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800052678 WEI A Z, YANG T X, YANG H Y, et al. Study on correlate selection of superion Paulownia clones[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1998, 18(1): 39-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800052678
[4] 叶金山, 胡伟华, 谢青, 等.白花泡桐×兰考泡桐和毛泡桐×白花泡桐F1无性系自然接干性状遗传变异的比较研究[J].东北林业大学学报, 2008, 36(10): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.10.001 YE J S, HU W H, XIE Q, et al. Genetic variation of natural stem-join characters of Paulownia fortunei×P. elonagta and P. tomentosa×P. fortunei hybrid F1 clones[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2008, 36(10): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.10.001
[5] 邱乾栋, 莫文娟, 王楠, 等.白花泡桐材色优良单株的选择[J].林业科学研究, 2014, 27(2): 277-283. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201402022 QIU Q D, MO W J, WANG N, et al. Selection of excellent wood color Paulownia fortunei indiciduals[J]. Forest Research, 2014, 27(2): 277-283. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201402022
[6] 杨俊秀, 张刚龙, 王培新, 等.抗丛枝病泡桐表型单株选择及其育种技术[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(9): 90-96. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2007.09.019 YANG J X, ZHANG G L, WANG P X, et al. Single trunk of a tree selecting for resistance to witches'- broom disease of Paulownia and breeding technique[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2007, 35(9): 90-96. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2007.09.019
[7] 魏安智, 杨途熙.泡桐优良无性系早期选择的研究[J].林业科学研究, 1993, 6(2): 136-140. http://www.lykxyj.com/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19930204&flag=1 WEI A Z, YANG T X. A study on the early selection of superior Paulownia clones[J]. Forest Research, 1993, 6(2): 136-140. http://www.lykxyj.com/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19930204&flag=1
[8] WU L C, WANG B P, QIAO J, et al. Effects of trunk-extension pruning at different intensities on the growth and trunk form of Paulownia fortunei[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2014, 327: 128-135. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2014.05.008
[9] 汪东华.多元统计分析与SPSS应用[M].上海:华东理工大学出版社, 2010. WANG D H. Multivariate statistical analysis and application of SPSS[M]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology Press, 2010.
[10] PÂQUES L E, CARMEN G C, CHARPENTIER J P. Distribution of heartwood extractives in hybrid larches and in their related European and Japanese larch parents: relationship with wood colour parameters[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 2013, 132(1): 61-69. doi: 10.1007/s10342-012-0654-1
[11] 续九如.林木数量遗传学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2006. XU J R. Quantitative genetics in forestry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006.
[12] LAI M, SUN X M, CHEN D, et al. Age-related trends in genetic parameters for Larix kaempferi and their implications for early selection[J]. BMC Genetics, 2014, 15(Suppl.): 10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-S1-S10
[13] COTTERILL P P, DEAN C A. Successful tree breeding with index selection[M]. Collingwood, Victoria: Center for Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO), 1990.
[14] COTTERILL P P, JACKSON N. On index selection Ⅰ: methods of determining economic weight[J]. Silvae Genetica, 1985, 34: 56-63. doi: 10.1097-EDE.0b013e3181e08eb3/
[15] 赵曼茜, 闫翠起, 王炜, 等.马尾松家系筛选与药材松针的相关性研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(9): 1698-1704. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgzyzz201509013 ZHAO M Q, YAN C Q, WANG W, et al. Relationship between selection of Pinus massoniana families and folium pini[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2015, 40(9): 1698-1704. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgzyzz201509013
[16] 王润辉, 胡德活, 郑会全, 等.杉木无性系生长和材性变异及多性状指数选择[J].林业科学, 2012, 48(3): 45-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201203008 WANG R H, HU D H, ZHENG H Q, et al. Clonal variation in growth and wood quality and the multi-trait index selection of Chinese fir[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2012, 48(3): 45-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201203008
[17] 赵承开.杉木优良无性系早期选择年龄和增益[J].林业科学, 2002, 38(4): 53-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.04.009 ZHAO C K. A study on optimum age and gain for early selection of superior clone in Cunninghamia lanceolata Hook[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2002, 38(4): 53-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2002.04.009
[18] 黄寿先, 施季森, 李力, 等.杉木纤维用材优良无性系的选择[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 29 (5): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2005.05.005 HUANG S X, SHI J S, LI L, et al. Seletion of superior clones of Chinese fir for fibre wood[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2005, 29 (5): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2005.05.005
[19] 李善文, 姜岳忠, 王桂岩, 等.黑杨派无性系多性状遗传分析及综合评选研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2004, 26(3): 36-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2004.03.007 LI S W, JIANG Y Z, WANG G Y, et al. Genetic analysis and comprehensive evaluation for multi-traits in Section Aigeiros clones[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2004, 26(3): 36-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2004.03.007
[20] 孙晓梅, 张守攻, 齐力旺, 等.日本落叶松自由授粉家系纸浆材材性遗传变异的研究[J].林业科学研究, 2003, 16(5): 515-522. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2003.05.001 SUN X M, ZHANG S G, QI L W, et al. Genetic variations in pulpwood qualities of open-pollinated Japanese larch families[J]. Forest Research, 2003, 16(5): 515-522. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2003.05.001
[21] 方乐金, 施季森, 张运斌, 等.杉木优良家系及单株综合选择研究[J].南京林业大学学报, 1998, 22(1): 20-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njlydxxb199801006 FANG L J, SHI J S, ZHANG Y B, et al. Study on comprehensive selection for superior familly and clone of Chinese fir[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 1998, 22(1): 20-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njlydxxb199801006
[22] 杜超群, 许业洲, 孙晓梅, 等.鄂西亚高山区日本落叶松无性系生长性状变异分析与早期选择[J].华中农业大学学报, 2015, 34(3): 19-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hznydx201503004 DU C Q, XU Y Z, SUN X M, et al. Variation of growth and early selection of Larix kaempferi clones in sub-alpine area of western Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015, 34(3): 19-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hznydx201503004
[23] 赵曦阳, 马开峰, 沈应柏, 等.白杨派杂种无性系植株早期性状变异与选择研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(2): 45-51. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9725 ZHAO X Y, MA K F, SHEN Y B, et al. Characteristic variation and selection of forepart hybrid clones of Sect. Populus[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(2): 45-51. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9725
[24] 施士争, 倪善庆, 朱超, 等.泡桐胶合板材栽培性状的综合选择[J].南京林业大学学报, 1996, 20(3): 27-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NJLY603.006.htm SHI S Z, NI S Q, ZHU C, et al. Comprehensive selection in cultural traits of polywood timber of Paulownia[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 1996, 20(3): 27-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NJLY603.006.htm
[25] 杨途熙, 魏安智, 杨焕叶, 等.泡桐无性系数量性状的遗传分析和指数选择研究[J].西北植物学报, 1997, 17(3): 374-381. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.1997.03.019 YANG T X, WEI A Z, YANG H Y, et al. Genetic analyses and index selection of the quantitative characters of Paulownia clones[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1997, 17(3): 374-381. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.1997.03.019
[26] 朱积余, 申文辉, 蒋燚, 等.红锥家系遗传变异与优良家系选择[J].热带亚热带植物学报, 2014, 22(3): 270-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2014.03.009 ZHU J Y, SHEN W H, JIANG Y, et al. Genetic variation and superior family selection of Castanopsis hystrix families[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2014, 22(3): 270-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2014.03.009
[27] 李火根, 黄敏仁, 潘惠新, 等.美洲黑杨新无性系生长动态遗传分析及早期选择[J].南京林业大学学报, 1996, 20(4): 2-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njlydxxb199604001 LI H G, HUANG M R, PAN H X, et al. A dynamic genetic analysis of geowth pattern and early selection for new cotton wood clones[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 1996, 20(4): 2-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njlydxxb199604001
[28] 何贵平, 陈益泰, 张国武.杉木主要生长、材质性状遗传分析及家系选择[J].林业科学研究, 2002, 15(5): 559-563. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2002.05.009 HE G P, CHEN Y T, ZHANG G W. Genetic analysis and family selection for main traits of growth and wood quality of Chinese fir[J]. Forest Research, 2002, 15(5): 559-563. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2002.05.009
[29] 周志春, 金国庆, 周世水.马尾松自由授粉家系生长和材质的遗传分析及联合选择[J].林业科学研究, 1994, 7(3): 263-268. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.1994.03.003 ZHOU Z C, JIN G Q, ZHOU S S. Genetic analysis and combined selection for growth and wood quality open-pollinated families of Masson pine[J]. Forest Research, 1994, 7(3): 263-268. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.1994.03.003
[30] 曾志光, 肖复明, 沈彩周, 等.江西省优质速生杉木无性系选育研究[J].林业科学研究, 2006, 19(5): 561-566. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2006.05.004 ZENG Z G, XIAO F M, SHEN C Z, et al. Clone selection of Chinese fir with fast growth and superior timber property[J]. Forest Research, 2006, 19(5): 561-566. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2006.05.004
[31] 符建明, 沈熙环, 朱少彬. 14年生油松测定林树高生长分析[J].林业科学, 1990, 26(5): 457-460. http://www.linyekexue.net/CN/Y1990/V26/I5/457 FU J M, SHEN X H, ZHU S B. The height analysis in 14-year-old Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. stands[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1990, 26(5): 457-460. http://www.linyekexue.net/CN/Y1990/V26/I5/457
[32] 孙晓梅, 张守攻, 李时元, 等.日本落叶松纸浆材优良家系多性状联合选择[J].林业科学, 2005, 41(4): 48-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.04.009 SUN X M, ZHANG S G, LI S Y, et al. Multi-traits selection of open-pollinated Larix kaempferi families for pulpwood purpose[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(4): 48-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2005.04.009



 下载:
下载: