Effects of seasonal freeze and thaw cycles on the micro-aggregate characteristics of the mechanically compacted black soil
-
摘要: 采用田间模拟机械压实的方法,通过对连续两季季节性冻融后不同深度(表层0~20 cm、亚表层20~40 cm和下层40~80 cm)不同压实次数(0、3和12次)土壤水稳性微团聚体组成(≥0.25 mm、0.25~0.05 mm、0.05~0.02 mm、0.02~0.002 mm、<0.002 mm粒级)、分形维数(D)和分散系数等特征指标的测定、计算与分析,研究了两季季节性冻融对黑土区0~80 cm土层范围内土壤微团聚体特征的影响,讨论了季节性冻融与机械压实的交互作用。结果表明:季节性冻融对不同深度黑土微团聚体组成及稳定性的影响不同,主要表现为增加表层土壤微团聚体的稳定性,降低亚表层和下层土壤微团聚体的稳定性,且连续两季冻融对黑土微团聚体组成及稳定性的影响也存在差异,1季冻融主要显著增加无压实土壤微团聚体的稳定性,而2季冻融却显著降低无压实土壤微团聚体的稳定性;两季冻融结束后,3次压实土壤微团聚体D值和分散系数均高于对照(P<0.05),尽管12次压实土壤分散系数同样高于对照(P<0.05),但土壤微团聚体D值与对照相比无显著差异,季节性冻融与机械压实的交互作用主要表现为季节性冻融加剧少次压实土壤微团聚体的破坏、降低其稳定性,而对多次压实土壤微团聚体的组成及稳定性有一定的恢复作用。Abstract: Based on the simulation of mechanical compaction in the field, the impacts of seasonal freeze and thaw cycles on soil micro-aggregates composition and stability were revealed in the vertical range by measuring and analyzing the soil micro-aggregates distribution(≥0.25 mm, 0.25-0.05 mm, 0.05-0.02 mm, 0.02-0.002 mm, < 0.002 mm), fractal dimension (D) and dispersion coefficient in two consecutive years at different soil depths (0-20 cm, 20-40 cm, 40-80 cm) of different compaction passes (no compaction, 3 passes, 12 passes), and the interaction effects between seasonal freezing-thawing cycles and mechanical compaction were discussed emphatically. The results showed that the effects of seasonal freeze and thaw cycles on the composition and stability of micro-aggregates in black soil were different at varied soil depths, the stability of soil micro-aggregates mainly increased in the surface soil layer (0-20 cm) after seasonal freeze and thaw cycles, while decreased in other soil layers. Simultaneously, the effects of seasonal freeze and thaw cycles were also different from year to year. The first seasonal freezing-thawing process mainly increased the micro-aggregates stability of the uncompacted soil, but the second seasonal freezing-thawing processes reduced the stability of the soil micro-aggregates significantly. However, it is worth noting that the interaction effects between seasonal freezing-thawing cycles and mechanical compaction on the soil micro-aggregates characteristics were more complicated. After two seasonal freezing-thawing processes, the D value of soil micro-aggregates and dispersion coefficient were significantly higher than control condition (P < 0.05) when the mechanical compaction treatment was only 3 compaction passes, although the soil dispersion coefficient was also higher than control (P < 0.05) when the mechanical compaction passes increased to 12 times, the D value of soil micro-aggregates was no significant difference compared with the control. In general, the seasonal freeze and thaw cycles generally exacerbated the damage of micro-aggregates and reduced the stability when the soil was compacted only a few times, but displayed a certain recovery characteristic when the mechanical compaction passes were extremely increased.
-
-
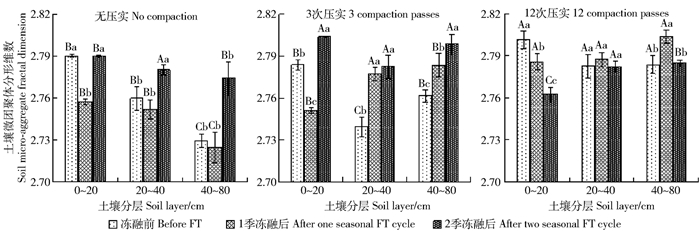
图 2 季节性冻融前后不同压实土壤微团聚体分形维数
大写字母不同表示相同土层内不同压实处理间差异显著,小写字母不同表示相同压实次数,相同土层内,季节性冻融前后差异显著,P<0.05。下同。
Figure 2. Fractal dimension of soil micro-aggregate from different depths under varied compaction passes before and after seasonal freezing and thawing
Different uppercase letters indicate significant difference between compaction passes of the same soil depth, while different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level before and after the seasonal freezing and thawing of the same compaction passes and the same soil depth. The same below.
表 1 不同深度土壤基本理化性状
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of soil under different soil layers
土层
Soil layer/cm有机质含量
Organic matter content/(g·kg-1)pH 总孔隙度
Total porosity/%土壤密度Bulk density/(g·cm-3) 土壤颗粒组成
Soil particle size/%砂粒Sand 粉粒Silt 黏粒Clay 0~20 63.52 5.54 55.72 1.15 23.32 30.21 46.48 20~40 49.67 5.83 54.19 1.14 23.01 30.84 46.15 40~80 35.90 5.45 39.40 1.23 20.50 29.67 49.83 表 2 不同处理间的GLM检验P值
Table 2 P-values from the GLM text of different treatment effects
指标Indicator 处理Treatment FT SL CT FT×SL FT×CT FT×SL×CT 分形维数Fractal dimension <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 分散系数Dispersion coefficient 0.354 0.422 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:FT.冻融作用;SL.土层深度;CT.压实次数;×.交互作用;n=324。Notes: FT, freezing and thawing; SL, soil layer; CT, compaction treatment; ×, interaction effect; n=324. -
[1] FLOWERS M D, LAL R. Axle load and tillage effects on soil physical properties and soybean grain yield on a mollic ochraqualf in northwest Ohio[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 1998, 48(1-2): 21-35. doi: 10.1016/S0167-1987(98)00095-6
[2] SHAHGHOLI G, ABUALI M. Measuring soil compaction and soil behavior under the tractor tire using strain transducer[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2015, 59: 19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2015.02.007
[3] HAMZA M A, ANDERSON W K. Soil compaction in cropping systems: a review of the nature, causes and possible solutions[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2005, 82(2): 121-145. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2004.08.009
[4] MCDONALD A J, RIHA S J, DUXBURY J M, et al. Soil physical responses to novel rice cultural practices in the rice-wheat system: comparative evidence from a swelling soil in Nepal[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2006, 86(2): 163-175. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2005.02.005
[5] 秦红灵, 高旺盛, 马月存, 等.两年免耕后深松对土壤水分的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2008, 41(1): 78-85. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.01.010 QIN H L, GAO W S, MA Y C, et al. Effects of subsoiling on soil moisture under no-tillage 2 years later[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(1): 78-85. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.01.010
[6] HE J, LI H W, WANG X Y, et al. The adoption of annual subsoiling as conservation tillage in dryland maize and wheat cultivation in northern China[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2007, 94(2): 493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2006.10.005
[7] KVARNO S H, OYGARDEN L. The influence of freeze-thaw cycles and soil moisture on aggregate stability of three soils in Norway[J]. Catena, 2006, 67(3): 175-182. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2006.03.011
[8] OZTAS T, FAYETORBAY F. Effect of freezing and thawing processes on soil aggregate stability[J]. Catena, 2003, 52(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(02)00177-7
[9] MATZNER E, BORKEN W. Do freeze-thaw events enhance C and N losses from soils of different ecosystems? A review[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 59(2): 274-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.00992.x
[10] 王恩姮, 赵雨森, 陈祥伟.季节性冻融后机械压实黑土自然恢复特征[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(6): 1137-1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2010.06.034 WANG E H, ZHAO Y S, CHEN X W. Natural recovery of black soil compacted by machinery after seasonal freeze and thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science), 2010, 29(6): 1137-1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2010.06.034
[11] 王展, 张玉龙, 虞娜, 等.冻融作用对土壤微团聚体特征及分形维数的影响[J].土壤学报, 2013, 50(1): 83-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201301010 WANG Z, ZHANG Y L, YU N, et al. Effects of freezing-thawing on characteristics and fractal dimension of soil microaggregates[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(1): 83-88. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201301010
[12] 蒲玉琳, 谢德体, 林超文, 等.植物篱-农作坡耕地土壤微团聚体组成及分形特征[J].土壤学报, 2012, 49(6): 1069-1077. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201206001 PU Y L, XIE D T, LIN C W, et al. Composition and fractal features of soil micro-aggregates in sloping farmland with hedgerow[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(6): 1069-1077. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201206001
[13] DU Z, REN T, HU C, et al. Transition from intensive tillage to no-till enhances carbon sequestration in microaggregates of surface soil in the North China Plain[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2014, 146(1): 26-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=866d70548b96d32f411b67e500174cf4
[14] 卢倩倩, 王恩姮, 陈祥伟.模拟机械压实对黑土微团聚体组成及稳定性的影响[J].农业工程学报, 2015, 31(11): 54-59. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.11.008 LU Q Q, WANG E H, CHEN X W. Effect of mechanical compaction on soil micro-aggregate composition and stability of black soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(11): 54-59. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.11.008
[15] 刘宁, 李新举, 郭斌, 等.机械压实过程中复垦土壤紧实度影响因素的模拟分析[J].农业工程学报, 2014, 30(1): 183-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.01.024 LIU N, LI X J, GUO B, et al. Simulation analysis on influencing factors of reclamation soil compaction in mechanical compaction process[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(1): 183-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.01.024
[16] 王恩姮, 赵雨森, 陈祥伟.前期含水量对机械压实土壤结构特征的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2009, 23(1): 159-163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.01.034 WANG E H, ZHAO Y S, CHEN X W. Effect of antecedent moisture content on soil structure compacted by machinery[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(1): 159-163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2009.01.034
[17] 龚伟, 颜晓元, 蔡祖聪, 等.长期施肥对小麦-玉米轮作土壤微团聚体组成和分形特征的影响[J].土壤学报, 2011, 48(6): 1141-1148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201106005 GONG W, YAN X Y, CAI Z C, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on composition and fractal feature of soil micro-aggregates under a wheat-maize cropping system[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(6): 1141-1148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201106005
[18] LEHRSCH G A, SOJKA R E, CARTER D L, et al. Freezing effects on aggregate stability affected by texture, mineralogy, and organic matter[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1991, 55: 1401-1406. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500050033x
[19] HENRY H A L. Soil freeze-thaw cycle experiments: trends, methodological weaknesses and suggested improvements[J]. Soil Biologyand Biochemistry, 2007, 39(5): 977-986. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.11.017
[20] MUSA A, LIU Y, WANG A, et al. Characteristics of soil freeze-thaw cycles and their effects on water enrichment in the rhizosphere[J]. Geoderma, 2016, 264(11): 132-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a9b56a46f8e38879f241e0e8d7116f12
[21] SIX J, BOSSUYT H, DEGRYZE S, et al. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2004, 79(1): 7-31. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2004.03.008
[22] KUNCORO P H, KOGA K, SATTA N, et al. A study on the effect of compaction on transport properties of soil gas and water. Ⅱ: soil pore structure indices[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2014, 143(12): 180-187. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167198714000154
[23] MENON M, JIA X, LAIR G J, et al. Analysing the impact of compaction of soil aggregates using X-ray microtomography and water flow simulations[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2015, 150(3): 147-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6e2c589471d1741d5ac3bdc3207aba9e
[24] TARAWALLY M A, MEDINA H, FRÓMETA M E, et al. Field compaction at different soil-water status: effects on pore size distribution and soil water characteristics of a Rhodic Ferralsol in Western Cuba[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2004, 76(2): 95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2003.09.003
[25] 娄鑫, 谷岩, 张军辉, 等.冬季积雪与冻融对土壤团聚体稳定性的影响[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(4): 63-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201604007 LOU X, GU Y, ZHANG J H, et al. Effects of snow cover and freeze-thaw cycles on stability of surface soil aggregates in forest[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(4): 63-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201604007
[26] MOSSADEGHI-BJÖRKLUND M, ARVIDSSON J, KELLER T, et al. Effects of subsoil compaction on hydraulic properties and preferential flow in a Swedish clay soil[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2016, 156: 91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2015.09.013
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 苏岫,王祥,宋德瑞,李飞,杨正先,张浩. 基于改进光谱角法的红树林高分遥感分类方法研究. 海洋环境科学. 2021(04): 639-646 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈冀岱,牛树奎. 多时相高分辨率遥感影像的森林可燃物分类和变化分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2018(12): 38-48 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: