Construction of ecological security patterns based on ecological red line in Erhai Lake Basin of southwestern China
-
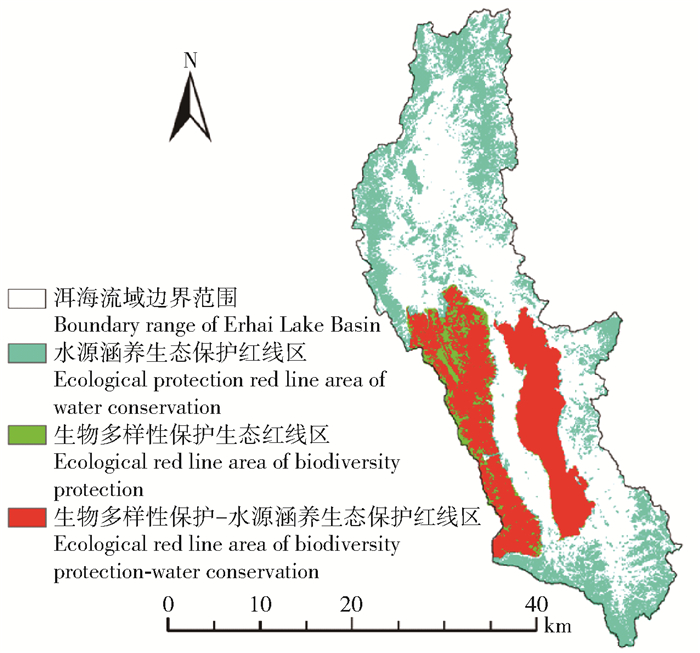
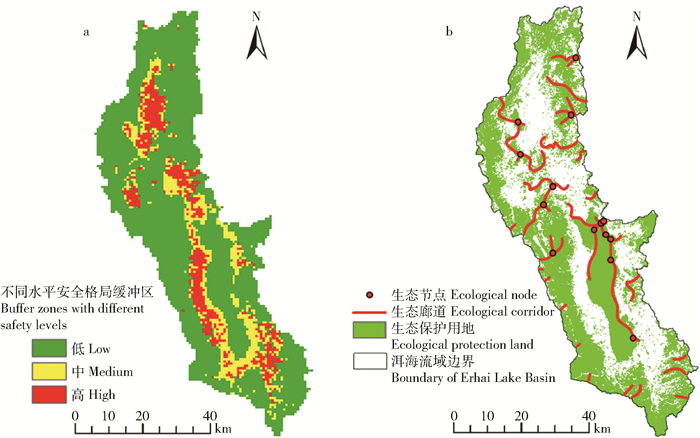
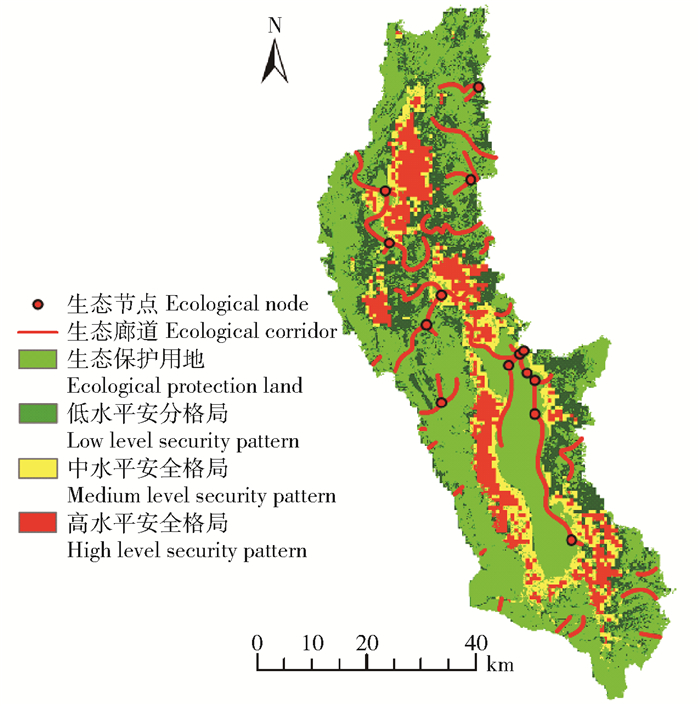
摘要:目的构建区域生态安全格局解决生态环境问题,是实现区域可持续发展的重要途径。生态红线是国家和区域生态安全的底线,对维护区域生态安全具有重要作用。通过构建生态安全格局,为洱海流域土地资源和生态系统管理提供科学依据。方法本研究以洱海流域为对象,通过生物多样性保护和水源涵养重要性评价的方法划定红线区;基于土地适宜性评价,将生态红线区作为生态源地,建立最小阻力模型,构建生态安全格局。结果根据生态红线具有的生态系统服务功能,将其划分成“生物多样性保护生态红线区”“生物多样性保护—水源涵养生态红线区”和“水源涵养生态红线区”3类,面积分别为81.92、656.37和536.06 km2,占研究区总面积的3.15%、25.24%和20.62%。洱海流域生态安全格局由生态源地,高、中、低3种水平缓冲区,47条生态廊道和14个生态节点构成。其中,高、中、低3种生态安全格局缓冲区,面积分别为359.88、294.9和1 945.42 km2,分别占总面积的13.84%、11.34%和74.82%。结论本研究根据土地利用/覆盖类型与生物多样性保护、水源涵养功能之间的空间对应关系,选取参评因子划定生态红线,为区域生态红线的划分提供了实践参考。根据生态红线区识别生态源地构建生态安全格局,不仅具有全面性和准确性,也为区域生态红线的划定及应用于生态安全格局的构建提供实践参考。Abstract:ObjectiveBuilding comprehensive ecological security pattern to solve ecological problems is an important way to achieve regional sustainable development. Ecological red line is the base line of national and regional ecological security, and it also plays an important role in maintaining regional ecological security. Building an ecological security pattern also provides a scientific basis for the management of land resource and ecosystem in Erhai Lake Basin of southwestern China.MethodTaking Erhai Lake Basin as object in this study, we designed the ecological red line by means of evaluating the biodiversity protection and water conservation. Based on land suitability evaluation, we took the ecological red line area as the ecological source and established the minimum resistance model to construct the ecological security pattern.ResultAccording to the ecosystem service function of the ecological red line area, Erhai Lake Basin was divided into "biodiversity protection ecological red line area", "biodiversity protection-water conservation ecological red line area" and "water conservation ecological red line area", which were 81.92, 656.37 and 536.06 km2, occupied 3.15%, 25.24% and 20.62% of the total area of the study area, respectively. The comprehensive ecological security pattern of Erhai Lake Babin was composed of ecological sources, three kinds of buffer zones with high, medium and low level, 47 ecological corridors and 14 ecological nodes. The area of high, medium and low level buffer zones was 359.88, 294.9 and 1 945.42 km2, accounted for 13.84%, 11.34% and 74.82% of the total area, respectively.ConclusionAccording to the spatial correspondence between land use types and biodiversity, water conservation function, selecting assessment factors to define the ecological red line provides practical reference for the division of regional ecological red line. Selecting ecological sources based on ecological red line is not only accurate and comprehensive, but also provides practical reference to design ecological red line and application to build ecological security patterns.
-
-
表 1 生物多样性保护重要性评价分级标准
Table 1 Classification standard of importance evaluation of biodiversity protection
重要性分级
Importance level评价因子
Evaluation factor分级赋值
Grading assignment极重要
Most important自然生态系统类保护区、国家级和省级保护的物种分布区域Distribution area of natural ecosystem reserve, national and provincial protected species 7 重要
Important常绿针叶林、常绿阔叶林、常绿阔叶灌木林、草甸、水库/坑塘、湖泊、河流
Evergreen coniferous forest, evergreen broadleaved forest, evergreen broadleaved shrub forest, meadow, reservoir/swag, lake, river5 比较重要
Quite important草丛
Grass3 一般重要
General important水田、旱地、裸地、居住地、工业用地、交通用地
Paddy filed, dry farm, bare land, residence area, industrial land, transportation land1 表 2 生态系统水源涵养重要性评价分级标准
Table 2 Classification standard of importance evaluation of source of river conservation
重要性分级
Importance level评价因子
Evaluation factor分级赋值
Grading assignment极重要
Most important水库/坑塘、湖泊、河流、常绿针叶林、常绿阔叶林
Reservoir/swag, lake, river, evergreen coniferous forest, evergreen broadleaved forest7 重要
Important常绿阔叶灌木林
Evergreen broadleaved shrub forest5 比较重要
Quite important草甸、草丛、水田、旱地
Meadow, grass, paddy filed, dry farm3 一般重要
General important裸地、居住地、工业用地、交通用地
Bare land, residence area, industrial land, transportation land1 表 3 景观过程阻力赋值体系
Table 3 Resistance assigning system of landscape process
生态保护用地扩张阻力值
Expansion resistance value of ecological protection land建设用地扩张阻力值
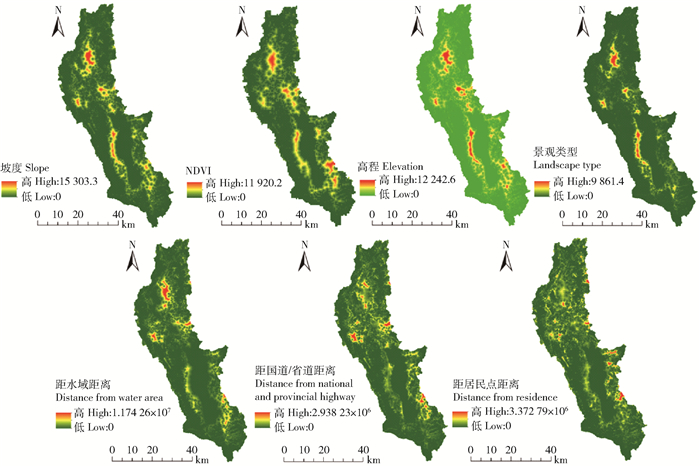
Expansion resistance value of construction land自然因素Natural factor 社会经济因素Social economic factor 坡度
Slope degree/(°)归一化植被指数
Normalized difference vegetation index, NDVI海拔
Altitude/m景观类型
Landscape type距水域距离
Distance from water area/m距国道/省道距离
Distance from national and provincial highway/m距居民点距离
Distance from residence area/m1 5 >35 0.8~1 >3 500 常绿针叶林、常绿阔叶林、常绿阔叶灌木林、水库/坑塘、河流、湖泊
Evergreen coniferous forest, evergreen broadleaved forest, evergreen broadleaved shrub forest, reservoir/swag, river, lake0~500 >1 200 >1 500 2 4 25~35 0.6~0.8 3 000~3 500 水田、旱地
Paddy filed, dry farm500~1 000 800~1 200 1 000~1 500 3 3 15~25 0.4~0.6 2 500~3 000 草丛、草甸
Grass, meadow1 000~2 000 400~800 500~1 000 4 2 8~15 0.2~0.4 2 000~2 500 裸地、工业用地
Bare land, industrial land2 000~3 000 200~400 200~500 5 1 0~8 0~0.2 0~2 000 居住地、交通用地
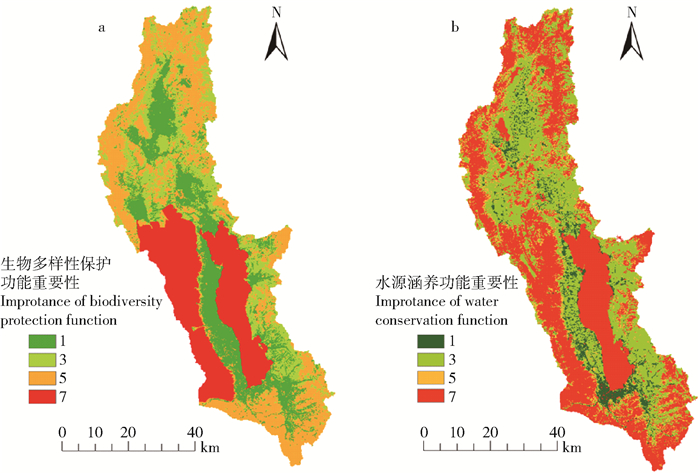
Residence area, transportation land>3 000 0~200 0~200 表 4 生物多样性保护和水源涵养重要性评价结果
Table 4 Importance evaluating results of biodiversity protection and water conservation
重要性评价
Importance evaluation生物多样性保护
Biodiversity conservation/km2比例
Proportion/%水源涵养
Water conservation/km2比例
Proportion/%1 555.750 21.373 4 153.765 5.911 6 3 537.480 20.670 8 988.335 37.997 3 5 888.975 34.188 8 265.680 10.214 3 7 617.985 23.766 9 1 193.288 45.876 8 表 5 不同水平安全格局缓冲区分区区间
Table 5 Threshold range for buffer zone with different safety levels
不同水平安全格局缓冲区
Buffer zone with different safety scale levels阻力值断点区间
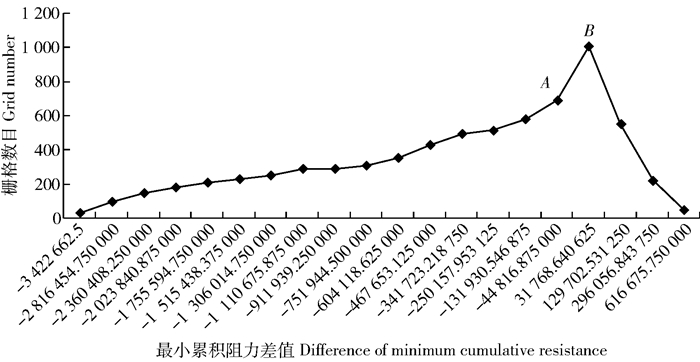
Resistance breakpoint interval高High -4 122 103.500 00~-44 816.875 00 中Medium -44 816.875 000~31 768.640 625 低Low 31 768.640 625~616 675.750 00 -
[1] 李谦, 戴靓, 朱青, 等.基于最小阻力模型的土地整治中生态连通性变化及其优化研究[J].地理科学, 2014, 34(6):733-739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkx201406013 Li Q, Dai J, Zhu Q, et al. Ecological connectivity changes and its pattern optimization during land consolidation based on minimal accumulative resistance model[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(6):733-739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkx201406013
[2] 徐德琳, 邹长新, 徐梦佳, 等.基于生态保护红线的生态安全格局构建[J].生物多样性, 2015, 23(6):740-746. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdyx201506006 Xu D L, Zou C X, Xu M J, et al. Ecological security pattern construction based on ecological protection redlines[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2015, 23(6):740-746. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdyx201506006
[3] 史培军, 王静爱, 冯文利, 等.中国土地利用/覆盖变化的生态环境安全响应与调控[J].地球科学进展, 2006, 21(2):111-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.02.001 Shi P J, Wang J A, Feng W L, et al.Response of eco environmental security to land use/cover changes and adjustment of land use policy and pattern in China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(2):111-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.02.001
[4] 徐卫华, 栾雪菲, 欧阳志云, 等.对我国国土生态安全格局与空间管理策略的思考[J].国土资源情报, 2014, 1(5):27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2014.05.006 Xu W H, Luan X F, Ouyang Z Y, et al. Ecological security pattern and spatial management strategy in China[J]. Land and Resource Information, 2014, 1(5):27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3709.2014.05.006
[5] 崔胜辉, 洪华生, 黄云凤, 等.生态安全研究进展[J].生态学报, 2005, 25(4):861-868. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.04.031 Cui S H, Hong H S, Huang Y F, et al. Progress of the ecological security research[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(4):861-868. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.04.031
[6] 蒙吉军, 朱利凯, 杨倩, 等.鄂尔多斯市土地利用生态安全格局构建[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(21):6755-6766. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201221018 Meng J J, Zhu L K, Yang Q, et al. Building ecological security pattern based on land use: a case study of Ordos, northern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(21):6755-6766. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201221018
[7] 苏泳娴, 张虹鸥, 陈修治, 等.佛山市高明区生态安全格局和建设用地扩展预案[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(5):1524-1534. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201305020 Su Y X, Zhang H O, Chen X Z, et al. The ecological security patterns and construction land expansion simulation in Gaoming[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5):1524-1534. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201305020
[8] 俞孔坚.生物保护的景观生态安全格局[J].生态学报, 1999, 19(1):8-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb199901002 Yu K J. Landscape ecological security patterns in biological conservation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1999, 19(1):8-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb199901002
[9] 李晖, 易娜, 姚文璟, 等.基于景观安全格局的香格里拉县生态用地规划[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(20):5928-5936. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201120008 Li H, Yi N, Yao W J, et al. Shangri-La County ecological land use planning based on landscape security pattern[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(20): 5928-5936. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201120008
[10] 潘竟虎, 刘晓.基于空间主成分和最小累积阻力模型的内陆河景观生态安全评价与格局优化:以张掖市甘州区为例[J].应用生态学报, 2015, 26(10):3126-3136. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_yystxb201510026 Pan J H, Liu X. Assessment of landscape ecological security and optimization of landscape pattern based on spatial principal component analysis and resistance model in arid inland area: a case study of Ganzhou District, Zhangye City, Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(10):3126-3136. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_yystxb201510026
[11] 蒙吉军, 王雅, 王晓东, 等.基于最小累积阻力模型的贵阳市景观生态安全格局构建[J].长江流域资源与环境, 2016, 25(7):1052-1061. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201607006 Meng J J, Wang Y, Wang X D, et al. Construction of landscape ecological security pattern in Guiyang based on MCR model[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2016, 25(7):1052-1061. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201607006
[12] 彭建, 郭小楠, 胡熠娜, 等.基于地质灾害敏感性的山地生态安全格局构建:以云南省玉溪市为例[J].应用生态学报, 2017, 28(2):627-635. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201702031 Peng J, Guo X N, Hu Y N, et al. Constructing ecological security patterns in mountain areas based on geological disaster sensitivity: a case study in Yuxi City, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(2):627-635. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201702031
[13] 吴健生, 张理卿, 彭建, 等.深圳市景观生态安全格局源地综合识别[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(13):4125-4133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201313026 Wu J S, Zhang L Q, Peng J, et al. The integrated recognition of the source area of the urban ecological security pattern in Shenzhen[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(13):4125-4133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201313026
[14] 岳德鹏, 王计平, 刘永兵, 等. GIS与RS技术支持下的北京西北地区景观格局优化[J].地理学报, 2007, 62(11):1223-1231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb200711011 Yue D P, Wang J P, Liu Y B, et al. Landscape pattern optimization based on RS and GIS in Northwest of Beijing[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 62(11):1223-1231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb200711011
[15] 刘杰, 叶晶, 杨婉, 等.基于GIS的滇池流域景观格局优化[J].自然资源学报, 2012, 27(5):801-808. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-2009161796.htm Liu J, Ye J, Yang W, et al. A GIS-Based landscape pattern optimization approach for Lake Dianchi Watershed[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2012, 27(5):801-808. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-2009161796.htm
[16] 赵筱青, 王海波, 杨树华, 等.基于GIS支持下的土地资源空间格局生态优化[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(9):4892-4901. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.036 Zhao X Q, Wang H B, Yang S H, et al. GIS-based ecological optimization of spatial patterns of land resources[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(9):4892-4901. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.036
[17] 刘吉平, 吕宪国, 杨青, 等.三江平原东北部湿地生态安全格局设计[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(3):1083-1090. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.004 Liu J P, Lü X G, Yang Q, et al. Wetland landscape ecological security patterns analysis and plan in Northeast of Sanjiang Plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(3):1083-1090. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.004
[18] 杨姗姗, 邹长新, 沈渭寿, 等.基于生态红线划分的生态安全格局构建:以江西省为例[J].生态学杂志, 2016, 35(1):250-258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201601034.htm Yang S S, Zou C X, Shen W S, et al. Construction of ecological security patterns based on ecological red line: a case study of Jiangxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(1):250-258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201601034.htm
[19] 杨姗姗.江西省生态安全格局构建[D].南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10300-1015639664.htm Yang S S. Ecological security pattern construction of Jiangxi Province[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10300-1015639664.htm
[20] 李锦胜.洱海流域土地利用格局研究[J].环境科学导刊, 2011, 30(4):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2011.04.010 Li J S, Research on structures and patterns of land use of Erhai Watershed[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2011, 30(4):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2011.04.010
[21] 胡婷.洱海流域土地利用变化及驱动力分析[D].武汉: 华中师范大学, 2012. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2078723 Hu T. Land-use change and driving forces analysis of Erhai Lake Basin[D].Wuhan: Central China Normal University, 2012. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2078723
[22] 郦建锋, 杨树华, 谭志卫, 等.洱海流域土地利用格局变化研究[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 30(增刊1):396-402. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ2008S1087.htm Li J F, Yang S H, Tan Z W, et al. Study on dynamic changes of land use in Erhai Watershed[J]. Journal of Yunnan University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2008, 30(Suppl.1):396-402. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ2008S1087.htm
[23] 张馨方.洱海流域土地利用与生态系统服务价值变化研究[D].昆明: 云南财经大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10689-1014035723.htm Zhang X F. Study on the change of land use and ecosystem service value in Erhai Lake Basin[D].Kunming: Yunnan University of Finance Economics, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10689-1014035723.htm
[24] 左志莉, 周兴, 吴壮金.广西贵港市生态环境敏感性评价及其空间分布[J].江西农业大学学报, 2009, 31(6):1172-1177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2009.06.038 Zuo Z L, Zhou X, Wu Z J. A study on the assessment of eco-environmental sensitivity and its spatial distribution in Guigang City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxisis, 2009, 31(6):1172-1177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2009.06.038
[25] 杨世凡, 安裕伦, 王培彬, 等.贵州赤水河流域生态红线区划分研究[J].长江流域资源与环境, 2015, 24(8):1405-1411. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201508020 Yang S F, An Y L, Wang P B, et al. Study of ecological redline zones in Guizhou Chishui River Basin[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2015, 24(8):1405-1411. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201508020
[26] 左志莉.基于生态红线区划分的土地利用布局研究: 以广西贵港市为例[D].南宁: 广西师范学院, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10603-1011014618.htm Zuo Z L. The study on land-use layout based on ecological red-line areas: a case study of Guigang City in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Teachers Education University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10603-1011014618.htm
[27] 张艳艳, 孔范龙, 郗敏, 等.青岛市湿地保护红线划定研究[J].湿地科学, 2016, 14(1):129-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shidkx201601021 Zhang Y Y, Kong F L, Xi M, et al. Delimitation of red line of wetland conservation in Qingdao City[J]. Wetland Science, 2016, 14(1):129-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shidkx201601021
[28] 俞龙生, 李志琴, 梁志斌, 等.广州南沙新区生态保护红线划分与管理体系[J].环境工程技术学报, 2014, 4(5):421-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2014.05.067 Yu L S, Li Z Q, Liang Z B, et al. Division and management framework of urban ecological protection red line: a case study in Nansha new district of Guangzhou City[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2014, 4(5):421-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2014.05.067
[29] 燕守广, 林乃峰, 沈渭寿.江苏省生态红线区域划分与保护[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(3):294-299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.03.004 Yan S G, Lin N F, Shen W S. Delineation and protection of ecological red lines in Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(3):294-299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.03.004
[30] Knaapen J P, Scheffer M, Harms B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning[J]. Landscape & Urban Planning, 1992, 23(1):1-16.
[31] 赵筱青, 和春兰.外来树种桉树引种的景观生态安全格局[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(6):1860-1871. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201306020 Zhao X Q, He C L. Landscape ecological security pattern associated with the introduction of exotic tree species Eucalyptus[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(6):1860-1871. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxb201306020
[32] 匡丽花, 叶英聪, 赵小敏.基于最小累积阻力模型的土地生态适宜性评价:以鄱阳县为例[J].江西农业大学学报, 2014, 36(4):903-910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2014.04.032 Kuang L H, Ye Y C, Zhao X M. Evaluation of land ecological suitability based on minimum cumulative resistance model:a case study of Poyang County[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2014, 36(4):903-910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2014.04.032
[33] 刘孝富, 舒俭民, 张林波.最小累积阻力模型在城市土地生态适宜性评价中的应用研究:以厦门为例[J].生态学报, 2010, 20(2):421-428. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STXB201002019.htm Liu X F, Shu J M, Zhang L B. Research on applying minimal cumulative resistance model in urban land ecological suitability assessment: as an example of Xiamen City[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 20(2):421-428. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STXB201002019.htm
[34] 李平星, 陈东, 樊杰.基于最小费用距离模型的生态可占用性分析:以广西西江经济带为例[J].自然资源学报, 2011, 26(2):227-236. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZRZX201102005.htm Li P X, Chen D, Fan J. Research of ecological occupiability based on least-cost distance model: a case study on Xijiang River Economic Belt in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Nature Resources, 2011, 26(2):227-236. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZRZX201102005.htm
[35] 郭宏斌.最小耗费生态功能网络规划研究:以厦门岛内为例[J].环境与发展, 2009, 21(6):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0370.2009.06.005 Guo H B. A study on the planning of least-cost ecological function network: a case study of Xiamen Downtown[J]. Environment and Development, 2009, 21(6):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0370.2009.06.005
[36] Xu W, Li X, Pimm S L, et al. The effectiveness of the zoning of China s protected areas[J]. Biological Conservation, 2016, 204:231-236. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2016.10.028
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 苏岫,王祥,宋德瑞,李飞,杨正先,张浩. 基于改进光谱角法的红树林高分遥感分类方法研究. 海洋环境科学. 2021(04): 639-646 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈冀岱,牛树奎. 多时相高分辨率遥感影像的森林可燃物分类和变化分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2018(12): 38-48 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: