Influence on antioxidants and alkaloid content of Phellodendron amurense seedlings grown under supplementary UV-B radiation
-
摘要:目的本文以东北重要药用植物黄檗幼苗为对象, 研究黄檗幼苗中抗氧化物质以及主要药用活性成分含量变化对增补不同的UV-B辐射强度的响应。方法通过在温室内控制实验, 设置了3个UV-B辐射强度梯度的处理, 分别是对照组(CK, 自然光照)、低辐射组(T1, UV-B辐射强度为3.26 μW/cm2)和高辐射组(T2, UV-B辐射强度为9.78 μW/cm2), 研究黄檗幼苗中的抗氧化物质及主要有效活性成分, 即3种生物碱(小檗碱、药根碱和掌叶防已碱)含量对不同UV-B辐射强度的响应。结果增补UV-B辐射会使黄檗幼苗中的羟基自由基、丙二醛、单宁、可溶性蛋白含量明显增加并随辐射强度升高而增加; 除第40天处理外, 不同处理间黄檗幼苗根中总黄酮含量随紫外辐射强度呈下降趋势, 而茎中总黄酮含量随辐射强度增强而升高, 叶中总黄酮含量随辐射强度升高和处理时间延长而升高; 在辐射处理40 d时, 黄檗幼苗茎中3种生物碱含量都高于对照, 低强度辐射的T1组含量高于高强度辐射的T2组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。根和叶中3种生物碱在辐射处理40 d时虽随辐射时间增长含量有所升高但仍低于对照且差异显著(P < 0.05)。结论UV-B辐射增强会导致药用植物黄檗不同器官中的抗氧化物质和药用活性成分含量发生不同的变化, 这对以后黄檗不同利用模式的大规模种植有着重要意义, 同时也对今后的药用植物中生物碱的利用有着深远影响。Abstract:ObjectiveThe rapid development of the global industry has led to the enhancement of UV-B radiation in the atmosphere, which directly affects the growth and development of plants and their physiological activities. All kinds of secondary metabolites in plants are greatly influenced by the environment, how to respond to the enhancement of UV-B radiation is also increasingly emphasized by the planting industry. In this paper, Phellodendron amurense, the important medicinal plant in the Northeast China was taken as the object of research to study the responses of the contents of antioxidant substances and main medicinal active components in the seedlings of P. amurense to different intensities of UV-B radiation.MethodExperiments were carried out in greenhouse with controlled environment. Three levels of UV-B radiation intensity treatments were set as control (CK, natural light), low radiation (T1, supplement UV-B radiation intensity 3.26 μW/cm2, and high radiation(T2, supplement UV-B radiation intensity 9.78 μW/cm2, to study the responses of antioxidants and the main active ingredients (three alkaloids of bererine, jatrorrhizine and palmatine) contents in P. amurense seedlings to different UV-B radiation intensity.ResultThe results showed that the content of malondialdehyde (MDA), hydroxyl radical, tannin and soluble protein in P. amurense seedlings significantly increased along with the radiation intensity. The total flavonoid contents in the root of P. amurense seedlings declined with UV-B radiation intensity, except those in treatments of 40 days. On the contrary, the total flavonoid contents in the stem rose with radiation intensity. At the time of radiation treatment for 40 days, the contents of three alkaloids in the stem of P. amurense seedlings were higher than in the CK group, and the T1 group with low intensity radiation was higher than the T2 group with high intensity radiation (P < 0.05).The content of three alkaloids in the root and leaf increased with the 40 days of radiation treatment, but it was still lower than the CK group and the difference was significant (P < 0.05).ConclusionUV-B radiation enhancement will lead to different changes in the content of antioxidants and medicinal active ingredients in different organs of P. amurense seedling, which is of great significance for the large-scale cultivation of different utilization patterns of P. amurense as the traditional Chinese medicinal plant.
-
Keywords:
- Phellodendron amurense seedling /
- UV-B radiation /
- antioxidant component /
- bererine /
- jatrorrhizine /
- palmatine
-
近年来,全球工业经济迅猛发展,使得大气平流层中臭氧层减薄,最终导致到达地球表面的紫外线B不断增强,这已成为全球性环境问题,对此的研究也成为诸多学者研究的热点[1]。大量研究表明,在增强UV-B辐射条件下,许多植物的光合作用能力下降,蛋白质合成速度减缓,叶绿体功能受损,DNA片段受损以及膜脂发生过氧化现象[2],植株生长和其生长量都明显降低[3]。产生这一现象的原因可能是与植物体内活性氧代谢的失衡有关[4],活性氧的积累会抑制CO2固定、降解叶绿素、加速叶片的衰老和膜脂过氧化。目前,清除活性氧作为高等植物抗氧化体系的重要防御系统已经普遍被接受,植物对逆境胁迫抗性的大小与植物的抗氧化系统的有效性密切相关[5]。有研究表明,植物叶片在长期UV-B辐射下类黄酮(紫外吸收物)的含量能够提高[6]。也有文献研究指出,在UV-B辐射增强条件下,能够加重植物细胞膜脂的过氧化程度,从而提高植物体内羟基自由基的含量,因此一部分维生素C和番茄红素等物质被消耗用于清除植物体内过多的自由基[7]。由此可见,紫外辐射会对植物的抗氧化物质造成影响,从而影响植物生长发育过程。同时植物的生长状况又与人类息息相关,所以控制紫外辐射对植物生长及利用的影响意义重大。
黄檗(Phellodendron amurense)是芸香科(Rutaceae)黄檗属高大落叶阔叶乔木,渐危物种。是中国的珍贵的用材树种[8]。主要分布在我国东北地区,是东北阔叶红松(Pinus koraiensis)林的重要伴生树种,我国东北“三大硬阔(另两种为水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)和核桃楸(Juglans mandshurica))之一”。黄檗系第三纪古热带植物区系的孑遗植物,对研究古植物区系、古代地理及第四纪冰期气候有重要的科学价值[9]。黄檗材质坚韧,纹理美观,不但是我国珍贵的用材树种,还是我国传统大宗中药材关黄柏唯一来源植物。黄檗外皮具较厚的木栓层并且有不规则网状或深沟状开裂,其内皮为黄色或鲜黄色,其内皮(韧皮部)可入药,称为关黄柏。从黄檗中提取的生物碱主要含有小檗碱(Berberine),掌叶防已碱(Palmatine),药根碱(Jatrorrhizine)等。黄檗中含有的生物碱具有很高的药用价值。中医通常将其炮制后制成中药饮片为关黄柏,具有较好的清热解毒和泻火燥湿的作用[10]。本研究以黄檗幼苗为对象,研究黄檗幼苗中抗氧化物质以及主要次生代谢产物(药用活性成分)含量变化对增补不同的UV-B辐射强度的响应,以期为深入研究药用木本植物环境适应及对药用植物的开发利用提参考与依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料及实验设计
本实验于2014年5—9月在东北林业大学森林植物与生态学教育部重点实验室温室中进行。黄檗种子采于长白山区并于2013年12月进行沙藏3个月打破其休眠,次年3月中下旬在温室内播种,5月份将黄檗幼苗移入到直径为10 cm的花盆中,每盆1株。选取生长一致黄檗苗330盆,共设置3个实验组:对照组(CK组),在自然光照情况下生长;T1组为在相同条件下增补UV-B辐射,辐射强度为3.26 μW/cm2,T2组为增补UV-B辐射强度为9.78 μW/cm2。每组处理100盆,放置在2 m×1 m的矩形架内,四周均用不透光黑布遮挡,每组之间用黑布隔开,以防相互干扰。在植株上方悬挂UV-B(波长为280~310 nm)的紫外灯管(40 W,北京电光源研究所),灯管外部包被0.08 mm的醋酸纤维膜,用来消除UV-C辐射对本研究的影响,实验期间每天UV-B辐射处理12 h(6:00—18:00),阴雨天除外。UV-B辐射强度用辐照计(UV-B型,北京师范大学光电仪器厂)进行测定。在实验处理期间,为减少人为因素影响,通过调整灯管与植株冠层高度,以保证植株所接受的UV-B辐射剂量基本一致。为保证各实验组接受到的自然光照一致,在对照组上方只悬挂灯架,不设置UV-B辐射。实验处理期间,为排除其他条件干扰,3组统一管理,并定期除草、浇水等。处理10、25和40 d后,分别取样,进行各项指标检测。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 黄檗叶片·OH自由基含量的测定
·OH自由基含量的测定方法见文献[11]。取黄檗叶片0.5 g,浸泡在5%的二甲基亚砜中3~5 min,取出后用滤纸吸干,放置于已在-20 ℃中预冷的研钵内,加入液氮研磨,用5 mL蒸馏水提取,10 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液于5 mL容量瓶中定容,从容量瓶中取1 mL溶液(参比组取1 mL蒸馏水),加入1 mL的正丁醇-甲苯(体积比为1:3)混合物,小心吸取下层水相并置于试管中,加入浓度为1.5 mmol/L的固蓝BB盐溶液2 mL,室温下暗反应10 min,加入上述正丁醇-甲苯混合液3 mL,震荡30 s混合均匀。弃去未反应的重氮盐,加入5 mL水饱和的正丁醇以除去残留的重氮盐,在3 000 r/min下离心5 min,将上层液相转移置另一试管,加入吡啶1 mL使颜色稳定。在波长为420 nm下测定吸光值,样品中的羟基自由基含量用每克鲜质量表示。
1.2.2 黄檗叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量测定
MDA含量的测定方法见文献[11]。取黄檗叶片0.5 g,剪碎后置于研钵中,加入少量石英砂和10%三氯乙酸(TCA)2 mL,研磨至匀浆,再加入TCA 3 mL进一步研磨,所得的匀浆转入离心管中,在5 000 r/min离心15 min,所得上清液即为样品提取液。取2 mL样品提取液于具塞试管,加入2 mL的0.5%硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)后混匀。混合液于沸水浴反应20 min,迅速冷却,在8 000 r/min离心15 min。取上清液于600 nm、532 nm和450 nm波长下测定吸光值。
根据双组分分光光度法,MDA浓度为6.452×(OD532-OD600)-0.559OD450。其中OD450、OD532和OD600,分别代表 450、532和600 nm波长下的吸光值。根据MDA的浓度再计算出单位鲜质量MDA含量(mmol/g)。
1.2.3 可溶性蛋白测定
可溶性蛋白的测定方法,参照考马斯亮兰G-250染色法[11]。黄檗叶片中可溶性蛋白含量单位为mg/g。
1.2.4 总黄酮含量的测定
采用铝离子显色-分光光度法见文献[12]。精密称取过20目的黄檗叶粉片1 g左右,加60%甲醇80 mL,加热回流提取60 min,倒出提取液,加少量60%甲醇洗残渣3次,洗液与提取液合并,过滤后置于100 mL容量瓶中,冷却后以60%甲醇定容至刻度。吸取提取液10 mL置于25 mL容量瓶中,加5%亚硝酸钠溶液1 mL,混匀后静置6 min,加1 mL 10%硝酸铝溶液,混匀静置6 min后加10 mL 4.3%氢氧化钠试液,以蒸馏水定容至刻度,摇匀静置15~20 min后,在500 nm波长下测定吸光度。以芦丁为标准品,根据芦丁浓度和吸光度值建立回归方程,计算总黄酮含量(mg/g)。
1.2.5 单宁含量的测定
称取0.5 g黄檗叶片于60 mL水中,沸水浴中煮1 h,冷却至室温过滤,将滤液稀释至100 mL。取0.5 mL置于25 mL容量瓶中,加入0.01 mol/L铁(Ⅲ)溶液1.5 mL,在80 ℃下水浴25 min,冷却至室温。加入pH为4.4的缓冲溶液2.0 mL,浓度为0.015 mol/L的邻二氮菲溶液3 mL,0.05 mol/L的EDTA溶液0.5 mL,蒸馏水定容至刻度后摇匀,静置10 min后,在波长510 nm处测定吸光度值。以单宁标准溶液浓度和吸光度值建立回归方程,计算黄檗叶片中单宁含量(mg/g)。
1.2.6 生物碱提取及含量的测定
生物碱提取:精确称取过40目筛的黄檗样品粉末0.1 g,置于10 mL容量瓶中,加入5 mL甲醇冰醋酸溶液(甲醇+1%冰醋酸),浸提5 h,再用超声波仪超声提取1 h,定容至刻度。取1.0 mL以12 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清待质谱分析检测。
质谱条件:色谱柱:KYA HIQsil C18柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相:50%甲醇+50%水+2%甲酸;流速:1 mL/min;进样量:10 μL。以上方法详见文献[13]。
1.3 统计分析
采用Excel 2007软件对数据进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析法和LSD法进行方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗抗氧化胁迫相关物质的影响
2.1.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗羟基自由基含量影响
增补UV-B辐射处理10、25和40 d后,各处理黄檗幼苗·OH自由基含量如图 1所示。由图 1可见,增补UV-B辐射,T1和T2两个处理组在3个取样时间羟基自由基含量均明显高于对照组,并且高辐射强度的T2组高于低辐射强度的T1组。整个辐射处理过程中,黄檗羟基自由基含量呈随处理时间先升高后降低,在每个取样时间点,羟基自由基含量随辐射强度增加而增大并且差异显著(P < 0.05)。由此可以看出增强的UV-B辐射可以增加黄檗幼苗羟基自由基含量,并且与辐射强度呈线性关系;同一辐射强度下,随辐射处理时间增长,叶片中的羟基自由基含量呈现先增加后下降趋势。
![]() 图 1 不同UV-B处理下黄檗幼苗羟基自由基的含量变化不同小写字母表示差异显著,相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Variation in hydroxyl radical content of P. amurense seedlings under different UV-B treatmentsDifferent lowercase letters mean significant difference, same lowercase letters mean no significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below.
图 1 不同UV-B处理下黄檗幼苗羟基自由基的含量变化不同小写字母表示差异显著,相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Variation in hydroxyl radical content of P. amurense seedlings under different UV-B treatmentsDifferent lowercase letters mean significant difference, same lowercase letters mean no significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below.2.1.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗叶片丙二醛含量影响
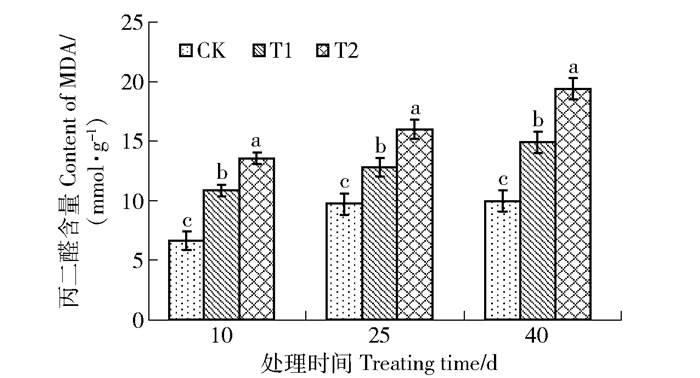
从图 2可以看出,增补UV-B辐射同一取样时间的不同强度的辐射处理间呈显著差异(P < 0.05)。与对照相比,两个处理组在UV-B辐射处理期间丙二醛的含量均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),并且同一辐射强度处理下,随着辐射处理时间的延长,丙二醛的含量逐渐升高。丙二醛是膜质过氧化的产物之一,其含量高低表示脂质过氧化和膜系统受到伤害的程度。丙二醛含量越高说明植物组织自身的保护能力越弱,这种情况下植物的整个细胞膜功能将会受到破坏,出现功能上的紊乱[14]。
2.1.3 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗叶片单宁含量影响
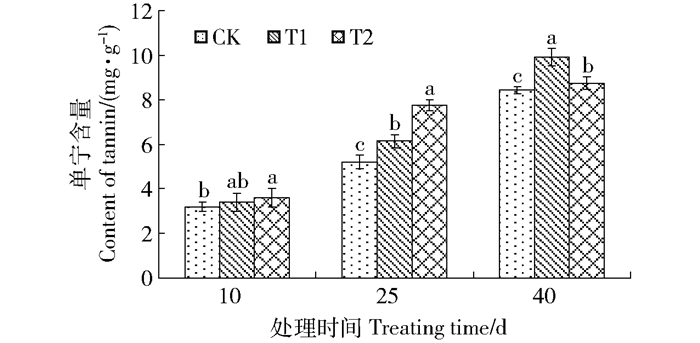
从图 3中可以看出,在增补UV-B辐射处理前期(10 d),T1组和T2组黄檗叶片中单宁的含量与对照组相比有小幅度升高但差异不显著(P < 0.05)。在UV-B辐射处理中期(25 d)时,T1组和T2组单宁的含量均明显高于对照,T1组与T2组分别比对照组增加了17.24%、49.29%并且差异显著(P < 0.05);在处理末期(40 d)时,T1组与T2组的单宁含量较对照组分别增加了18.69%、3.92%。出现上述情况可能是实验处理前期,UV-B辐射剂量小,时间短,植物可以通过调节自身代谢途径来增加单宁的合成,以快速吸收过多的UV-B辐射,形成一种功能性防御机制,使植物适应变化的外部环境,保持正常的生理功能。但随着UV-B辐射时间的延长和辐射剂量的增加,植物合成单宁达到了一定阈值,高辐射剂量T2组中单宁增加不显著(P < 0.05),而低剂量辐射T1组黄檗的单宁含量增加显著(P < 0.05)。
2.1.4 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗叶片可溶性蛋白含量影响
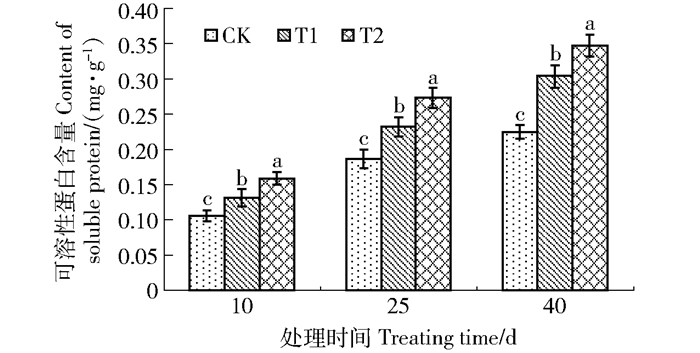
从图 4可以看出,增补UV-B辐射后,T1组、T2组均比CK组叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量高,且随辐射强度升高均呈上升趋势。在同一取样时间下辐射强度越大,叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量就越高并且差异显著(P < 0.05),并随辐射处理时间越长增长的趋势越明显。
2.1.5 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗不同器官总黄酮含量影响
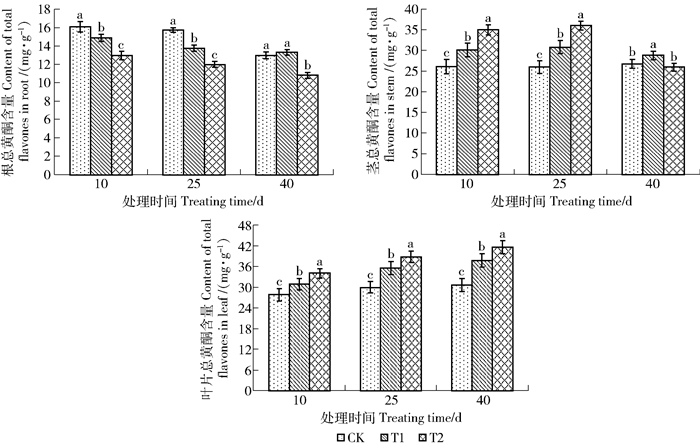
本文对增补UV-B辐射处理的黄檗幼苗的根、茎、叶分别进行了总黄酮含量测定,结果见图 5。从图 5可以看出,不同处理间黄檗幼苗根中总黄酮含量随紫外辐射强度呈下降趋势,并且差异显著(P < 0.05)(处理40 d的T1组与CK组除外,二者差异不显著P < 0.05)。相同辐射强度下随处理时间延长黄檗根中总黄酮含量呈下降趋势。UV-B辐射处理第10天和25天,两个辐射处理组中的总黄酮含量均低于对照组,直到辐射处理的第40天,低辐射强度的T1组和对照组总黄酮含量基本持平,差异不显著(P < 0.05),而高辐射强度的T2组中的总黄酮含量仍低于对照组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗不同器官生物碱含量影响
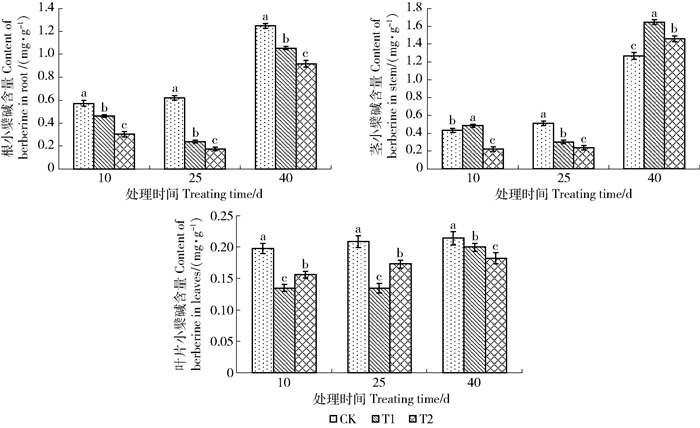
2.2.1 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中小檗碱含量影响
从图 6可以看出,增补UV-B紫外辐射后,在同一采样时间,根中小檗碱的含量随辐射强度增加而降低。而对同一处理组,随处理时间延长,小檗碱含量先降低而后升高,但都低于对照,且低强度辐射T1组的小檗碱含量高于高辐射强度T2组。
黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量,同一采样时间不同处理组间无明显变化规律。但同一处理组,CK与T2组的黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量随处理时间的延长而升高,T1组茎中小檗碱含量是先下降而又升高。与对照相比,在辐射处理第10天,T2组黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量低于CK组,是CK组的51.40%,而T1组则高于CK组,是CK组的112.15%。辐射处理第25天,T1组和T2组黄檗幼苗茎中小檗碱含量低于CK组,分别为CK组的59.21%和46.73%;UV-B辐射处理第40天,T1组和T2组茎中小檗碱含量明显升高。
黄檗幼苗叶的小檗碱含量,相同处理组随处理时间的延长含量升高,但T1和T2组的小檗碱含量都低于CK组。在处理10和25 d,叶中小檗碱含量,高辐射强度的T2组高于T1组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。处理40 d时,茎中小檗碱含量随辐射强度升高而降低且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
2.2.2 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中药根碱含量影响
增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗根、茎和叶中药根碱的含量变化如图 7所示。在处理第10天和第25天,T1和T2组根中药根碱含量均没有变化且都低于CK组,并且随辐射强度越高,药根碱含量越低,3组处理差异极显著(P < 0.01)。辐射处理第40天,3组处理根中药根碱含量均明显升高,但T1和T2组中的药根碱含量仍低于CK组。
对于茎中药根碱的含量,辐射处理第10天时,T1组高于CK组和T2组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。在处理第25天时,T1组和T2组药根碱含量又低于CK组。在处理40 d时,3组处理茎中药根碱均明显升高,并且T1和T2组茎中药根碱含量高于CK组。
与茎中药根碱含量变化不同,在处理的第10天和第25天时,T1和T2组叶中药根碱含量几乎没有变化。而CK组叶中药根碱含量随处理时间持续升高,在处理第40天时,T1和T2组叶中药根碱含量有明显升高但仍低于CK组并且差异显著(P < 0.05)。
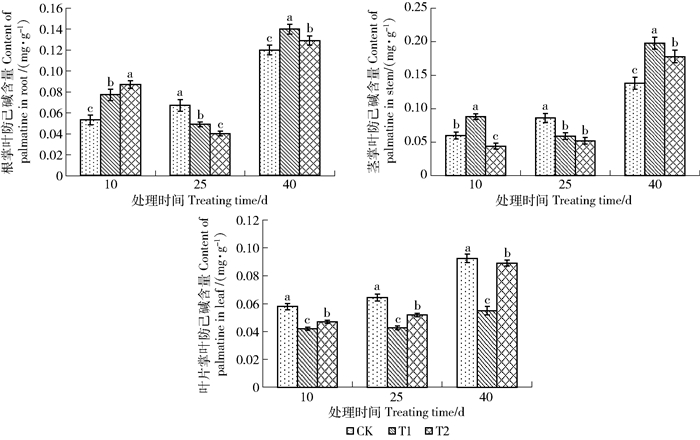
2.2.3 增补UV-B辐射对黄檗幼苗中掌叶防已碱含量影响
如图 8所示,黄檗幼苗根中掌叶防已碱的含量在辐射处理第10天,T1组与T2组掌叶防已碱的含量均高于CK组,并随辐射强度升高面升高。辐射处理第25天时,黄檗根中掌叶防已碱的含量有所下降,两个辐射处理组中掌叶防已碱的含量均比CK组低且随辐射强度升高而降低。辐射处理第40天,T1组和T2组的掌叶防已碱含量较CK组有所增加,并随辐射强度先升高后降低。
茎中掌叶防已碱含量变化如图 8所示,UV-B辐射处理第10天,T1组茎中掌叶防已碱含量高于CK组,而T2组则低于CK组。处理第25天时,T1组与T2组中掌叶防已含量均明显低于CK组,且T1组与T2组差异不显著(P < 0.05)。处理第40天时,T1组与T2组均高于CK组,且T1组中掌叶防已碱含量高于T2组,差异显著(P < 0.05)。
而黄檗幼苗叶中掌叶防已碱含量,相同处理时间随辐射强度增加,掌叶防已碱的含量先降低而后升高,但都低于CK组且差异显著(P < 0.05)。同一辐射强度下随处理时间延长,黄檗幼苗叶中掌叶防已碱含量都呈升高的趋势。
3. 讨论
植物中的次生代谢产物主要包括生物碱、黄酮类和酚类等几大类。大量研究结果都表明,UV-B辐射可明显增加植物次生代谢产物的含量,多数情况下,植物在受到UV-B辐射等逆境胁迫时,会产生一系列多角度、多层面、多标准的保护机制,以此来不断的减少不利环境对植物本身造成的伤害。
丙二醛(MDA)的含量高低在某种程度上能够体现出植物细胞膜的过氧化水平和伤害程度,它是植物膜质过氧化的产物之一[15-17],一般认为植物适应不良外部环境的特性可通过植物膜质的过氧化程度来体现。在一定胁迫强度范围内,植物细胞内的保护机制能够使丙二醛维持在一定水平,植物本身能够进行正常的生理活动,一旦胁迫强度超过植物所能承受的水平(阈值)后,植物细胞膜质过氧化作用加剧,引起细胞代谢功能失调,导致丙二醛含量增加。增补UV-B辐射可激发植物产生大量的活性氧自由基,引起植物内部特别是膜系统蛋白质的变化,产生大量的丙二醛。有文献研究表明,UV-B辐射可以显著增加南极冰藻(Chlamydomonas sp.)中的MDA含量,并且随着辐射剂量的增加而增加[18],这可能因为UV-B辐射能促使植物细胞质的酶系统和质膜的结构发生改变[19-21]。本实验研究发现,在增补UV-B辐射下对黄檗幼苗叶片中的丙二醛含量和羟基自由基含量有较大影响。增补UV-B处理后,黄檗叶片中的丙二醛和羟基自由基的含量均显著增加(P<0.05),并随增补UV-B辐射剂量增大而增加越明显,但随处理时间的延长,黄檗幼苗叶片中的羟基自由基的含量处理末期有所下降。这说明在增补UV-B辐射处理下,辐射剂量较小,黄檗幼苗通过增加相应抗氧化成分和自身调节系统维持其正常生理功能,随辐射时间延长和辐射剂量的增加,超过了黄檗叶片正常生理活动所能忍受的最大阈值,从而刺激了丙二醛和羟基自由基的大量产生。但随着处理时间的延长,黄檗幼苗逐渐适应了增强的UV-B辐射的胁迫环境,这可能与其自身的防御机制有关。
可溶性蛋白在植物发挥生理功能中起着重要作用,它不仅是植物本身的重要组成部分同时也是植物发挥生理功能重要的催化剂。可溶性蛋白在UV-B辐射植物可承受范围内有较大的吸收作用,因此,增强的UV-B辐射可以使植物产生大量的可溶性蛋白。植物体内蛋白质含量的增加,直接影响植物本身的色氨酸的光降解作用和膜蛋白的溶解度。相关研究认为,紫外辐射可增加植物蛋白质的含量,但也有部分研究认为这种增加机制与辐射剂量有关,一旦辐射剂量超过植物生理所承受的范围,可溶性蛋白的含量则有下降的趋势。此外,也有研究认为植物在UV-B辐射处理后增加了叶片中可溶性蛋白的含量,这可能是因为一些有关植物抗性的基因在辐射处理后得以表达或变异,从而产生一些新的与UV-B辐射抗性相关的蛋白质[22]。本研究认为,增补UV-B辐射增加了黄檗幼苗可溶性蛋白的含量,并且随着处理时间的延长,可溶性蛋白的含量增加的越显著,这与牛传坡等[23]的研究结果一致。
UV-B辐射可促使植物中大量的紫外吸收物质产生,Strid等[24]和Petropoulou等[25]认为UV-B辐射可使豌豆(Pisum sativm)、意大利松(Pinus pinea)和地中海松(P. halepensis)中单宁含量的增加,本文与其研究结果一致。本研究认为黄檗幼苗在受到UV-B辐射后其叶片中的单宁含量显著增加,单宁含量随辐射剂量增大而增多。单宁在植物生长发育过程中起着很重要的保护作用,单宁含量的增加不仅能有效地吸收UV-B辐射,还能提高植物的抗性和适应性。植物叶片中紫外吸收物质含量可以直接反映植物对UV-B辐射的抵抗能力[26]。
许多研究认为,植物在受到UV-B辐射时,植物叶片中的每种特定黄酮类物质对紫外光的不同波段具有特定的吸收波长,这导致在UV-B辐条件下,不同总黄酮类物质的积累在含量和速度上呈现出差异性[27]。植物通常通过增加目标产物的含量或通过改变黄酮类化合物的合成途径和合成种类来对过多的UV-B辐射作出响应。有研究表明,UV-B辐射增强可增加植物叶片中总黄酮含量的积累,Warren等[28]对3个树种(Pinus ponderosa、Quercus rubra、Pseudotsuga menziesii)的研究认为,经UV-B辐射处理后,3种树种总黄酮含量明显增加,且总黄酮的组成成分也发生了明显变化。本文对黄檗幼苗的总黄酮含量的测定也证实了这一点。增补UV-B辐射处理后,黄檗幼苗叶、根、茎中的总黄酮含量都不同程度的有所增加。此外,也有些学者认为UV-B辐射并非总是促进总黄酮类含量增加,有时也表现为抑制作用。Petropoulou等[23]认为长期的UV-B辐射可减少豌豆中总酚、总黄酮的含量,这可能是因为UV-B辐射增强引起植物细胞不可逆的伤害,导致植物细胞中总黄酮的含量下降[29]。另外UV-B辐射增强可降低植物的光合作用,减少同化产物的积累,引起有机合成中碳素的流速和流向发生改变,从而导致植物次生代谢产物合成的减少。
生物碱作为药用植物重要的一类次生代谢产物,在植物生长发育过程充当着重要的角色,其合成受到植物种类、所处的生长发育阶段和生存的环境等多方面因素的影响。植物生长过程中生物碱含量的变化体现出植物与其所处环境之间的相互关系,其合成和代谢的每一个环节都会受到所处环境的影响和调控。本文研究结果表明,黄檗幼苗在经过UV-B辐射处理后第40天时,茎中3种生物碱的含量都明显高于未经辐射处理的对照组,且差异显著(P < 0.05)。而且低辐射强度处理的T1组茎中3种生物碱含量都显著高于高辐射强度处理T2组的黄檗幼苗,根和叶中的3种生物碱的含量在辐射处理40 d时都低于对照组。这可能是UV-B辐射刺激了黄檗幼苗紫外吸收物质的合成,如总黄酮和单宁等,激活了保护酶的活性,而植物为应对辐射对自身造成的伤害,首先在最先感受到这种胁迫伤害的叶中体现,使得体内的代谢向有利于吸收紫外辐射的产物合成,从而维持植物正常的生理功能。另外,黄檗幼苗在受到UV-B辐射处理后,其次生代谢产物在黄檗各个器官内会进行重新分配,这也使得辐射处理末期的黄檗幼苗茎中的生物碱含量都高于对照,这也与王海霞等[30]的研究结果一致。另外,植物应对UV-B辐射的响应机制还体现在处理时间上,由于黄檗是高大乔木药用植物,可能其抗UV-B辐射的能力相对较强,但本文仅做了40 d的短期辐射处理,已表现出光合能力下降、生长生理的抑制(另文发表)和多种次生代谢产物含量的升高(如黄酮、单宁和茎中生物碱)。黄檗幼苗如何响应和适应更为长期的UV-B辐射的生理特征和机制以及次生代谢产物体内合成机理,是下一步研究关注的重点。目前关于UV-B辐射对植物次生代谢产物的积累作用机理还不完全清楚,仍需进一步深入研究。
-
图 1 不同UV-B处理下黄檗幼苗羟基自由基的含量变化
不同小写字母表示差异显著,相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Figure 1. Variation in hydroxyl radical content of P. amurense seedlings under different UV-B treatments
Different lowercase letters mean significant difference, same lowercase letters mean no significant difference (P < 0.05). The same below.
-
[1] Krupa S V, Kichert R N. The greenhouse effect: impacts of ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation, carbon dioxide (CO2), and ozone (O3) on vegetation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 1989, 61(4): 263-393. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/097152319400100208
[2] Callow J A. Advances in botanical research:volume 22 [M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1996, 22: 97-162.
[3] Teramura A H. UV-B Effects on terrestrial plants [J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 1989, 50(4): 479-487. doi: 10.1111/php.1989.50.issue-4
[4] 晏斌, 戴秋杰.紫外线B对水稻叶组织中活性氧代谢及膜系统的影响[J].植物生理学报, 1996, 22(4): 373-378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-3877.1996.04.001 Yan B, Dai Q J. Effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on active oxygen metabolism and membrane system of rice leaves [J]. Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1996, 22(4): 373-378. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-3877.1996.04.001
[5] Krause G H. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis: an evaluation of damaging and protective mechanisms [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 1988, 74(3): 566-574. doi: 10.1111/ppl.1988.74.issue-3
[6] 薛慧君, 岳明.UV-B辐射增强对陆地植物次生代谢的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2004, 24(6): 1131-1137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2004.06.033 Xue H J, Yue M. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on terrestrial plant secondary metabolite [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2004, 24(6): 1131-1137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2004.06.033
[7] 李方民, 陈怡平, 王勋陵, 等. UV-B辐射增强和CO2浓度倍增的复合作用对番茄生长和果实品质的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2006, 17(1): 71-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.01.015 Li F M, Chen Y P, Wang X L, et al. Combined effects of enhanced UV-B radiation and doubled CO2 on tomato growth and its fruit quality [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(1): 71-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.01.015
[8] 傅立国.中国植物红皮书:稀有濒危植物[M].北京:科学出版社, 1991. Fu L G. China plant redbook: rare and endangered plant [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991.
[9] 国家林业局.中国重点保护野生植物资源调查[M].北京:中国林业出版社, 2009: 156-157. State Forestry Administration. Investigation on the key protection of wild plant resources in China [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2009: 156-157.
[10] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典:1部[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2010: 137. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China: Volume 1[M]. Beijing: China Medicine Press, 2010: 137.
[11] 高俊凤.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2006. Gao J F. Experimental guidance for plant physiology [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006.
[12] 李兰芳, 张魁, 吴树勋, 等.不同生长期白羊草中总黄酮的含量测定[J].中国野生植物资源, 1996, 23(4): 37-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600890363 Li L F, Zhang K, Wu S X, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in different grown period of Bothriochloa ischaemum [J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 1996, 23(4): 37-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600890363
[13] 彭英丽.磷钾营养对黄檗幼苗生长及主要生物碱含量的影响[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2015: 8. Peng Y L. Influence of phosphorus and potassium nutrition on growth and alkaloid content of Phellodendren amurense seedlings[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2015: 8.
[14] Hilal M, Parrado M F, Rosa M, et al. Epidermal lignin deposition in quinoa cotyledons in response to UV-B radiation[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2004, 79(2): 205-210. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2004)079<0205:ELDIQC>2.0.CO;2
[15] 许大全, 张玉忠, 张荣铣.植物光合作用的光抑制[J].植物生理学通报, 1992, 28(4): 237-243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwxtb200003004 Xu D Q, Zhang Y Z, Zhang R X. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in plants [J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1992, 28(4): 237-243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwxtb200003004
[16] 张书娜, 王庆成, 郝龙飞, 等.光照和施肥对白桦林冠下水曲柳、胡桃楸苗木生长的影响[J].森林工程, 2015, 31(2): 51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.02.011 Zhang S N, Wang Q C, Hao L F, et al. Effects of light and fertilization on the growth of Fraxinus mandshurica and Juglans mandshurica seedlings under the canopy of Betula platyphylla secondary forest [J]. Forest Engineering, 2015, 31(2): 51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.02.011
[17] He J, Huang L K, Chow W S, et al. Effects of supplementary untraviolet-B radiation on rice and pea plants [J]. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 1993, 20(2): 129-142.
[18] 阚光锋, 史翠娟, 缪锦来, 等.南极冰藻Chlamydomonas sp. L4的UV-B辐射效应研究[J].高技术通讯, 2008, 18(9): 966-970. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2008.09.016 Kan G F, Shi C J, Miu J L, et al. Effect of UV-B radiation on Antarctic ice microalga Chlamydomonas sp. L4 [J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2008, 18(9): 966-970. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2008.09.016
[19] 吴杏春, 林文雄, 黄忠良. UV-B辐射增强对两种不同抗性水稻叶片光合生理及超显微结构的影响[J].生态学报, 2007, 27(2): 554-564. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.02.017 Wu X C, Lin W X, Huang Z L. Influence of enhanced ultraviolet-B radiation on photosynthetic physiologies and ultrastructure of leaves in two different resistivity rice cultivars [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(2): 554-564. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.02.017
[20] 雷晓强, 王竞红, 杨成武, 等.干旱胁迫下三种护坡植物种子萌发特性研究[J].森林工程, 2015, 31(3): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.03.002 Lei X Q, Wang J H, Yang C W, et al. Study on drought resistance of three woody plants during the seed germination [J]. Forest Engineering, 2015, 31(3): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.03.002
[21] 雷珍, 戴海英, 叶和军, 等.轮叶蒲桃对干旱胁迫的生理响应影响研究[J].森林工程, 2015, 31(5): 4-6, 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.05.002 Lei Z, Dai H Y, Ye H J, et al. Study on the physiological response of Syzygium grijsii to drought stress [J]. Forest Engineering, 2015, 31(5): 4-6, 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-005X.2015.05.002
[22] 刘敏, 李荣贵, 范海, 等.UV-B辐射对烟草光合色素和几种酶的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2007, 27(2): 291-296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2007.02.014 Liu M, Li R G, Fan H, et al. Effects of enhanced uv-b radiation on photosynthetic pigments and some enzymes in tobacco [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2007, 27(2): 291-296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2007.02.014
[23] 牛传坡, 蒋静艳, 黄耀. UV-B辐射对土壤-冬小麦系统碳氮转化的影响[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2007, 26(S14): 470-471. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb2007z1221 Niu C P, Jiang J Y, Huang Y. Effects of UV-B radiation on the carbon nitrogen conversion of soil- winter wheat system [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and geochemistry, 2007, 26(S14): 470-471. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb2007z1221
[24] Strid A·, Porra R J. Alterations in pigment content in leaves of Pisum sativum after exposure to supplementary UV-B [J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1992, 33(7):1015-1023. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HighWire000002647016
[25] Petropoulou Y, Kyparissis A, Nikolopoulos D, et al. Enhanced UV-B radiation alleviates the adverse effects of summer drought in two Mediterranean pines under field conditions[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 1995, 94(1): 37-44. doi: 10.1111/ppl.1995.94.issue-1
[26] Lud D, Moerdijk T C W, Van De Poll W H, et al. DNA damage and photosynthesis in Antarctic and Arctic Sanionia uncinata (Hedw.) Loeske under ambient and enhanced levels of UV-B radiation [J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 2002, 25(12): 1579-1589.
[27] 梁滨, 周青. UV-B辐射对植物总黄酮影响的研究进展[J].作物学报, 2001, 27(5): 319-323. Liang B, Zhou Q. Research progress on the influence of UV-B radiation on total flavonoids in plants [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(5): 319-323.
[28] Warren J M, Bassman J H, Mattinson D S, et al. Alteration of foliar flavonoid chemistry induced by enhanced UV-B radiation in field-grown Pinus ponderosa, Quercus rubra and Pseudotsuga menziesii [J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 2002, 66(2): 125-133. doi: 10.1016/S1011-1344(02)00230-0
[29] 董新纯, 赵世杰, 郭珊珊, 等.增强UV-B条件下类黄酮与苦荞逆境伤害和抗氧化酶的关系[J].山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 37(2): 157-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2006.02.001 Dong X C, Zhao S J, Guo S S, et al. Role of flavonoids on stress injury and antioxydative enzymes in Fagopyrum tataricum seedlings under enhanced UV-bradiation [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 37(2): 157-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2006.02.001
[30] 王海霞, 刘文哲.增强UV-B辐射对喜树幼苗生物量和两种生物碱含量的影响[J].植物科学学报, 2011, 29(6): 712-717. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whzwxyj201106009 Wang H X, Liu W Z. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on biomass and contents of camptothecin and 10-hydroxy-camptothecin in Camptotheca acuminata [J]. Plant Science Journal, 2011, 29(6): 712-717. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whzwxyj201106009
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 赵杰,赵秋玲,沙红,张晶. 基质理化性质对黄檗幼苗生物量及生理指标的影响. 温带林业研究. 2024(01): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何会流. UV-B胁迫下外源NO对辣椒叶绿素及光合特性的影响. 内江师范学院学报. 2020(10): 71-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 夏梅梅,钟宛凌,张子龙,秦梦圆. 论气候变化对中药资源的影响及应对策略. 中华中医药杂志. 2019(02): 677-680 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 及利,李绍臣,王君,王芳,杨雨春,陆志民,孙伟. 不同土壤基质下水分胁迫对黄檗幼苗形态和物质分配的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2019(08): 26-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周开兵,李世军,袁孟玲,岳堃. 杧果成年树在增强UV-B辐射处理下的损伤与抗氧化响应. 园艺学报. 2019(07): 1279-1289 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: