Dynamic changes of multi-form nitrogen in typical Pinus koraiensis forest of Xiaoxing'an Mountains of northeastern China
-
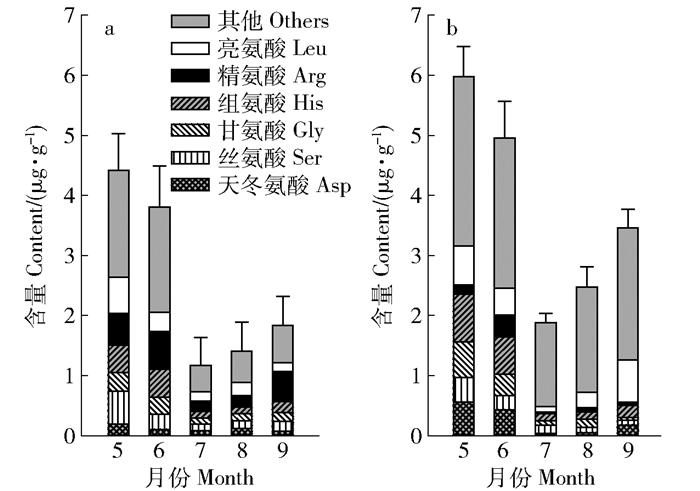
摘要: 以小兴安岭地区典型人工红松林和原始阔叶红松林为研究对象,于2016年对红松林下的土壤进行了连续5个月的分层次采样,测量了0~5 cm、5~15 cm和15~30 cm 3个层次土壤中的游离氨基酸态氮、硝态氮、铵态氮和可溶性有机氮的含量,以及0~5 cm层土壤中的含水量、pH、有机碳、全氮、微生物碳和微生物氮等因素的水平。通过对不同形态氮动态变化规律进行探讨,并整合土壤中所测量的生物化学因子,以揭示小兴安岭地区典型林型下不同形态氮库的大小及有效氮循环的季节性变化规律,并通过主成分分析探讨季节性变化规律潜在的驱动因素。结果表明,在小兴安岭地区的典型人工红松林和原始阔叶红松林下,氨基酸的组成是相似的,天冬氨酸、丝氨酸、甘氨酸、组氨酸、精氨酸和亮氨酸的含量较高,但不同月份中的优势氨基酸略有不同。3种有效氮库中,氨基酸态氮库同样是土壤可溶性氮库中的重要组成部分,铵态氮库>硝态氮库>游离氨基酸态氮库。在0~30 cm范围内,不同形态氮的含量随着土层的加深而下降,且这种规律不随时间的变化而波动。在温度和水文因子大环境的驱动下,冻融交替、微生物因子、pH以及复杂的生物化学过程随着时间在改变,从而导致土壤有效氮的动态变化;但由于土壤中潜在的物理、生物和化学因子的多变性及其综合作用的结果,导致有效氮动态变化趋势的差异性。Abstract: Nitrogen(N) is the nutrient regulating net plant primary production in most ecosystems, and N nutrient plays a significant role in N cycling. This study selects typical forest types in Xiaoxing'an Mountains of northeastern China in 2016, namely Pinus koraiensis plantation and pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest, and sampled continuously in 0-5 cm, 5-15 cm and 15-30 cm soil horizons for five months, measuring the contents of free amino acids-, nitrate-, ammonium-N and soluble organic N in the three soil horizons, and moisture content, pH, organic carbon, total N, microbial carbon and N levels in the 0-5 cm soil horizon. By exploring and discussing the dynamics of multi-form N and by incorporating some soil biochemical factors we measured, this study aims to discover the pool size of multi-form N and seasonal dynamics of available N in typical forests of Xiaoxing'an Mountains, with principal component analysis (PCA) analyzing the underlying driver factors of N seasonal dynamics. The final results showed that the composition of amino acids was similar in the two Pinus koraiensis forests of Xiaoxing'an Mountains, with aspartic acid, serine, glycine, histidine, arginine and leucine owning higher contents, but dominant amino acids varied in different months. The three forms of available N pool size followed ammonium>nitrate>free amino acids, and amino acids-N comprised a significant part of soil soluble N pool. The content of multi-form N decreased with soil depth in 0-30 cm soil horizon, with consistent relationship with time.With the temperature and hydrologic circumstances as drivers, free-thaw event, microbial factor, pH and complex biochemical processes changed over time leading to soil available N dynamics; as the variation in potential physical, chemical and biological factors and their combined effects in soils, however, tendency in available N dynamics appeared to be different.
-
Keywords:
- nitrogen /
- amino acid /
- production and consumption /
- principal component analysis /
- dynamic change
-
坡面薄层流是降雨在扣除截留、填洼、下渗等损失后沿坡面形成的浅层明流[1],是一种特殊而复杂的水流形态。研究表明,坡面薄层流不同于一般的明渠水流,水深一般只有几毫米甚至零点几毫米,薄层水流流向不稳定,沿程有质量源和动量源汇入,产生能量紊动,且受地表状况、雨强等诸多因素的影响,所以对坡面薄层水流的研究难度较大[2-4]。而坡面流是径流初始阶段和侵蚀演变的初始动力,其水动学特性对阐明土壤侵蚀和坡面产沙机理具有重要理论意义[5-8]。
目前,对于薄层水流特性的研究热点聚焦于坡面流流态及坡面流阻力特性,关于其流态归属问题,Horton等[9]认为坡面薄层水流是紊流中点缀层流的一种混合流区;Emmett[10]认为坡面流虽有紊流特性,但仍展现出较多层流性质,故定义为“扰动流”;Selby[11]认为坡面流是紊流和层流的混合流区。但仍然缺少公认的薄层流流态的界定方法。关于薄层水流阻力规律的研究,已有的研究成果多应用二元流雷诺数判别准则进行流区划分[4-5, 12]。关于降雨对坡面流阻力的影响,大部分的研究都表明,降雨对水流阻力的影响程度与水流流态有关,雨滴的打击作用和动能输入使其阻力增大,降雨在伪层流[4]情况下对水流阻力的影响最为显著,而有的学者认为降雨影响可以忽略[13]。而对于薄层水流特性的研究方法聚焦于人工模拟降雨或者水槽放水冲刷,两者共同作用下的水动力学特性研究十分少见。潘成忠等[13]通过上方来水和模拟降雨试验,研究了不同流量和坡度条件下坡面薄层水流水力学参数和滚波特性,初步探明了降雨和坡度对它们的影响。目前,对于坡面水流特性的探讨虽有不少研究成果,但由于坡度较小、床面光滑、缺少试验资料等因素,其结论的实际应用性也受到很大程度的限制,尤其在山地陡坡、雨量急、大的情况下。坡面流其底坡较天然明渠陡峭得多,重力作用更为突出。自然中,在山地陡坡、大雨条件下会发生超渗产流现象,坡面流冲刷和降雨同时作用于坡面,二者综合作用力对坡面的影响目前尚未明确。在国外,坡面流水动力学特性研究多侧重于缓坡,而国内多侧重于细沟水流,有研究表明,20°~ 25°是坡地土壤侵蚀的临界坡度[14]。目前针对陡坡和降雨对坡面流水流特性的研究尚显不足。与缓坡相比,陡坡条件下的水流动力特性和侵蚀特征具有其特殊性[15-16]。所以研究坡面流冲刷和降雨共同作用下的陡坡坡面流水动力学特性对防治水土流失有重要意义。
本文采用陡坡坡面定床阻力试验,通过人工模拟降雨和放水冲刷试验相结合的方法,定量研究5种流量和4个典型降雨强度(含无降雨)条件下,受4种不同粗糙度影响的水力要素关系及阻力的变化特征。研究陡坡降雨条件下的薄层水流水动力学特性对于揭示坡面薄层水流阻力的内在规律具有重要理论意义。
1. 研究区概况
缙云山位于三峡库区内,是国家级自然保护区,地理坐标为106°17′~106°24′ E、29°41′~29°52′ N,属于典型的亚热带季风湿润气候,植被资源丰富,森林覆盖率达96.6%。占地面积76 km2,海拔350.0~951.5 m,年平均降水量1 611.8 mm,最高年降水量1 683.8 mm。降雨主要发生在4—9月,降水量1 243.8 mm,占全年的77.2%。相对湿度年平均值为87%,年平均气温13.6 ℃。缙云山多雾,日照时数少,年平均雾日数高达89.8 d,年平均日照时数则低于1 293 h。缙云山地形平缓,土层深厚,土壤肥力高,以三叠纪须家河组厚层石英砂岩、灰质页岩和泥质页岩为木质风化而成的酸性黄壤土为主。试验研究林总面积约为33.5 hm2。保护区主要树种为四川大头茶(Gordonia acuminata)、杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata)、马尾松(Pinus massoniana)、四川山矾(Symplocos setchuensis)、川杨桐(Adinandra bockiana)、广东山胡椒(Lindera kwangtungensis)、毛竹(Phyllostachys heterocycla)、细齿叶柃(Eurya nitida)等。
2. 试验方法
试验时间为2016年7—9月。具有固定的不透水下垫面和一定粗糙度的坡面称为定床阻力坡面,为了便于测量和控制浅层水流的边界条件,本试验采用坡面定床阻力试验,在模拟天然地表粗糙度的同时也消除了床面形态变化对水流紊动的影响[17-22]。试验对降雨和坡面流共同作用下的坡面薄层流水动力学特性进行研究。
试验水槽结构示意图如图 1所示,试验水槽结构尺度为长4.0 m,宽0.4 m,深0.1 m,在进水口管道安装精度为0.001 m3/h的流量计用于测量流量,每次试验开始前进行流量率定,保证在设计流量允许误差范围内。为模拟缙云山陡坡条件下的坡面流,坡度恒定设置为20°。为保证水流波动仅由水砂纸糙度引起,同时减小水槽边壁对水流的影响,故在水槽侧壁刷清漆,在水槽底部黏贴有机玻璃板,有机玻璃板与水槽侧壁的黏合使用玻璃胶,用刀片将边缘刮平,水砂布黏贴在有机玻璃板上。
通过黏贴水砂布设置4种不同下垫面,其中3种分别为40、60、80目水砂布床面,另外一种为光滑坡面。按照尼库拉兹提出的床面粗糙度(ks)表示方法,试验粗糙度(ks)分别为0.009(光滑坡面)、0.180、0.250、0.425 mm,分别对应缙云山不同土壤粒径的裸土表面。根据重庆缙云山的坡面径流小区监测的产流情况,同时也考虑到尽可能使水深取值范围较大,设计进口放水流量为0.486×10-3、0.694×10-3、1.042×10-3、1.389×10-3和1.736×10-3 m3/(s·m)共5个试验处理。根据重庆缙云山典型降雨强度,设计降雨强度分别为30、60和100 mm/h和无降雨。本试验采用侧喷式降雨机模拟天然降雨。天然降雨的主要特性包括降雨分布的均匀性、降雨强度、雨滴直径大小、雨滴的终点速度等。目前大多数科学试验都是以上述降雨特征作为人工模拟降雨的评价标准[23]。在试验区域内用烧杯收集降雨并采用体积法测量雨量,计算降雨均匀度在85%以上,一般要求0.8以上[24],部分能达到90%。实际降雨强度与设计降雨强度之差与设计降雨强度的比值为降雨强度误差,其值在5%以内。真实降雨雨滴直径通常为0.1~6.5 mm,本试验降雨强度为30~100 mm/h时,雨滴中数直径为1.32~2.05 mm[25]。天然降雨雨滴的终点速度为2.0~2.9 mm/s,研究表明降雨高度为7~8 m时,95%雨滴达到相应的终点速度[26];高度大于4.3 m时,大雨滴达到终点速度的80%[27];具有初速度的下喷式喷头,降雨高度达2 m时,不同直径的雨滴可以获得终点速度[25]。本装置采用喷嘴式喷头(具有初速度),有效降雨高度为6 m,可以满足2.0~2.9 mm/s的终点速度。降雨试验场次设计采用雨强、粗糙度与放水流量的完全组合试验并重复试验一次,共4×4×5×2=160场降雨。
沿水槽自上而下设纵向水深观测断面3个,分别距槽顶1.0、2.0和3.0 m,每个观测断面横向设3个间距等分观测点(图 1),即每个工况下测量9次水深,求平均值获得该工况下的平均水深。水深采用水位测针仪测定,精度为0.1 mm。断面表层流速采用KMnO4染色示踪法测定,选择水槽中部实验段3 m测量流速[28],在水流表面滴入染色剂并记录时间与试验段距离,以此反映坡面流的表层流速,6次重复,求平均值获得该工况下的平均表层流速。
水动力学参数计算公式如表 1。
表 1 水力参数计算Table 1. Calculation of hydraulic parameters公式序号
Formula order No.公式Formula 符号及其意义Symbol and its meaning (1) u=qh u为断面平均流速,m/s;q为单宽流量,m3/(m·s);h为实测断面平均水深,cm
u is mean velocity, m/s; q is unit discharge, m3/(m·s); h is measured flow depth, cm(2) α=uus α为流速修正系数;us为表层流速,m/s
α is velocity correction factor; us is velocity, m/s(3) u=ηq1−mJn m为流态指数; J为水流坡降,可近似取sin θ; θ为水槽坡度;η和n为拟合函数中的系数
m is flow-state indicator; J is hydraulic slope which closes to sin θ; θ is slope of flume; η and n are coefficient of the fitting function(4) Re=uRv Re为雷诺数;R为水力半径,m,薄层水流可视为二元流,水力半径近似等于断面平均水深h;υ为运动黏滞系数,cm2/s;υ=0.017 75/(1+0.033 7t+0.000 22t2),t为水温,℃
Re is Reynolds number; R is hydraulic radius, m, overland flow is regarded as binary stream so R closes to h; υ is coefficient of kinematic viscosity, cm2/s. υ=0.017 75/(1+0.033 7t+0.000 22t2). t is water temperature, ℃(5) Fr=u√gh Fr为弗劳德数;g为重力加速度Fr is froude number and g is gravitational acceleration (6) f=8gRJu2 f为阻力系数f is resistance coefficient 3. 结果与分析
3.1 平均流速及流速修正系数
由流量计测得的流量与水槽宽度之比为单宽流量,不同工况下坡面流的平均流速可以通过公式(1)u=qh计算得到,即单宽流量与实测断面平均水深之比,平均流速精度为0.01 m/s,误差为5%。图 2为不同降雨强度下平均流速随单宽流量的变化规律,由图可知降雨时,水流的平均流速随着单宽流量的增大呈幂函数增加趋势,随粗糙度的增加而减小。一般认为,由于雨滴击溅作用产生的附加阻力会使流速减小,而在本试验坡度条件下,降雨对平均流速有增加作用,但是不同降雨强度影响间差异不明显,这可能与陡坡条件下雨滴动量沿坡面分量较大有关[13]。粗糙度和降雨强度相同时,单宽流量增大一倍时平均流速增加68.7%,说明单宽流量对平均流速影响显著。在无降雨条件下,平均流速增幅较为稳定,水流的平均流速随单宽流量的增加呈幂函数增加,随粗糙度的增加而减小。无降雨时水流平均流速与单宽流量和与粗糙度的定性关系与以往结果一致[15, 19-20]。
在本试验给定的降雨和坡面流条件下,流量和粗糙度对平均流速影响显著,降雨主要起到扰动坡面流的作用,有增大坡面平均流速的趋势。
流速修正系数表示坡面流平均流速(u)与表层流速(us)的比值,坡面薄层流的水深较薄,难以直接观测水流垂线流速分布,只能通过探究流速修正系数的变化规律间接研究流速的垂线分布。图 3为不同降雨条件下流速修正系数随平均流速的变化规律,由图可知,无降雨时,流速系数随着平均流速的增加而增加,流速修正系数范围为0.04~0.37,数值偏小,且粗糙度间的流速系数差异较小。说明无降雨时坡面流的流速梯度较大,流速分布不均匀,粗糙坡面对底层流速的阻碍作用明显。降雨时,流速修正系数取值范围为0.42~0.98,随着粗糙度的增大而增大,随着平均流速的增加而增加。降雨条件下的流速修正系数数值相对较大且分布较为分散,最大值接近1。
表 2为收集和整理的以往试验数据,由表 2可知,降雨时流速修正系数数值偏大,最大值将近1。降雨对坡面流表层水流产生击溅作用,薄层水流内部产生扰动。当降雨强度增大时,薄层流内部扰动越来越大,水流上下层的流速差异越来越小,流速梯度越小。所以,降雨时流速修正系数整体比无降雨条件下的大。
表 2 收集数据及试验数据概况Table 2. Overview of literature datasets and experimental data资料来源
Source of date中值粒径
Median size
(d50)/mm坡度
Slope degree
(J)/(°)降雨强度
Rainfall intensity
P/(mm·h-1)单宽流量
Unit discharges×
10-3(q)/(m2·s-1)水深
Depth of water
(h)/mm雷诺数
Reynolds
number (Re)流速修正系数
Velocity correction
factor (α)文献[13] Literature [13] 1.5~15 0 0.08、0.25 0.27~1.37 320~998 0.40~0.70 文献[13] Literature [13] 1.5~15 30 0.08、0.25 0.31~1.48 409~1 097 0.41~0.67 文献[29] Literature [29] 0.4、0.67 1.2 0 0.01~0.06 0.84~1.33 26~102 0.56~0.61 文献[30] Literature [30] 0.74 3.5、5.5 0 0.13~1.46 2.37~5.79 295~3 188 0.33~0.86 本文This paper 0.009~0.425 20 0 0.49~1.74 0.7~5.9 142~842 0.04~0.37 本文This paper 0.009~0.425 20 30、60、100 0.49~1.74 2.0~6.0 514~1 862 0.42~0.98 从流速修正系数角度同样可以得到粗糙度对流速影响显著,降雨主要起到扰动坡面流的作用。
3.2 流态指数
张宽地等[31]提出流态指数概念,m被认为是与流态相关的指数,流态指数反应了单宽流量对坡面水流流速的影响程度,即水流耗能的主要形式。m值范围在0到1之间,m值越大,水流能留转化为动能较少,此时以阻力做功为主,反之,则以水流转化为动能为主。
由表 3可知,本实验条件下,流态多数在过渡流区,少数处于层流区,流态指数范围为0.291~0.538,平均值为0.418。由表 3和图 4可知,无降雨时,流态指数随着粗糙度的增加而明显减小,随着粗糙度的增大其减小程度分别为21%、28%和39%;中小雨强时,流态指数无明显规律,雨强为30 mm/h时,变化程度分别为18%、-29%和12%,雨强为60 mm/h时,变化程度分别为12%、-17%和-16%;大雨强时,流态指数呈现出较为明显下降的趋势,随着粗糙度的增大其变化程度分别为-6%、1%和-11%。降雨扰动造成了流态的复杂性。坡面水流流态指数m值的影响因素比较复杂[1],无降雨时,影响水流状态的主要因素为粗糙度,粗糙度较小时,水流水面失稳产生滚波,阻力作功耗能居主要地位,粗糙度较大时,坡面凹凸影响滚波发育,水流紊动强度较低,增加水流流速耗能居主要地位。中小雨强时,流态指数无明显规律,说明降雨是造成流态指数不稳定的关键因素(F=4.55>F0.05=3.86)(见表 4),降雨对水面的击溅作用扰动水面,增加水流的紊动强度。大雨强时,流态指数呈现出较为明显下降的趋势。说明随着粗糙度的增加,水流从阻力做功耗能居主要地位发展到能量转化动能居主要地位,侧面反应出流速梯度逐渐增大,可能是由于陡坡条件下雨强的击溅对流速有促进作用。
表 3 各实验组次流态指数m的实测值Table 3. Measured m value of different experimental groups粗糙度Surface
roughness/mm降雨强度Rainfall intensity/(mm·h-1) 0 30 60 100 0.009 0.477 0.412 0.398 0.532 0.180 0.378 0.486 0.446 0.501 0.425 0.343 0.291 0.331 0.537 0.380 0.290 0.463 0.334 0.473 表 4 各实验组次流态指数m方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of m of different experimental groups变异来源Source of variation SS df MS F F0.05 F0.01 粗糙度间Among surface roughness 0.021 3 0.006 9 1.895 3.86 6.99 雨强间Among rainfall intensities 0.050 3 0.016 5 4.549* 3.86 6.99 误差Error 0.033 9 0.003 6 总变异Total variation 0.104 15 注:SS表示平方和;MS表示平均平方和;F表示平方和之比;F0.05和F0.01表示显著水平。Notes: SS represents sum of square; MS represents average sum of square; F is ratio of SS; F0.05 and F0.01 represent significant levels. 无降雨时,在试验粗糙度范围内,较大试验坡度的流态指数随着粗糙度的增加而明显减小,这与张宽地等[1]研究中的变化趋势相同,粗糙度继续增大时流态指数是否增加有待进一步研究。分析本试验的流态指数变化趋势,降雨引起水面失稳并产生滚波,其可能会影响水流流态。潘成忠等[13]认为降雨对断面滚波数具有增加效应,而对波高和波长影响不显著。在坡面薄层水流试验中,滚波可能是进一步的研究重点。
3.3 水流流型流态
水流流区是指坡面内的紊动水能,分为层流区、过渡区和紊流区,根据雷诺数Re判断,水流流型是指坡面流是缓流、临界流还是急流,根据弗劳德数Fr判断[22]。张宽地等[31]综合考虑雷诺数和弗劳德数对水流流态的判断标准,Re=500、Re=2 000和Fr=1将水流分为6区流态(图 5),分别是缓层流、缓过渡流、缓紊流、急层流、急过渡流和急紊流。将判断流态的雷诺数和判断流型的弗劳德数综合体现于一张图中,能够更为清晰地说明降雨、粗糙度和流量对坡面流状态的综合影响。
![]() 图 5 不同降雨条件下水流流态分区A.缓紊流区; B.缓过渡流区;C.急紊流区;D.缓层流区;E.急过渡流区;F.急层流区。Figure 5. Flow state zoning under different rainfall conditionsA, subcritical turbutent flow; B, subcritical transition flow; C, supercritical turbulent flow; D, subcritical laminar flow; E, supercritical transition flow; F, supercritical laminar flow.
图 5 不同降雨条件下水流流态分区A.缓紊流区; B.缓过渡流区;C.急紊流区;D.缓层流区;E.急过渡流区;F.急层流区。Figure 5. Flow state zoning under different rainfall conditionsA, subcritical turbutent flow; B, subcritical transition flow; C, supercritical turbulent flow; D, subcritical laminar flow; E, supercritical transition flow; F, supercritical laminar flow.陡坡时,在降雨和坡面流胁迫下,水流雷诺数为500~2 000,水流流态均属于层紊流过渡区,且多数属于急流区,少数属于缓流区。说明较大坡度增大了重力方向的分力,水流耗能主要以增加流速为主[13]。图 5a中,ks=0.425 mm时,雷诺数数值上是层流,然而实际中存在滚波现象,不符合“层层不混搀”的层流特性,因而属于“伪层流”[4]。模拟降雨条件下的薄层水流流态与流量密切相关,随着流量的增加,水流流态由层流区向过渡流区延伸[31]。
由图 5可知,粗糙度对坡面薄层流流态起重要作用。无雨时,坡面颗粒越大水流越趋近缓流,这与敬向锋等[22]得到的“床面越粗糙坡面流流态越倾向于向层流区延伸”结果一致。在水流运动过程中,遇到颗粒产生绕流,绕流过程中流速方向改变,流速大小减小,动能减少而阻力作功增加,粗糙程度越大,坡面对水流流动形成的阻力越大,流速减缓越显著。降雨时,粗糙度与流态不再具有相关关系。说明降雨对坡面流的击溅作用使薄层流产生扰动,所以水流流态均不处于层流区,多数处于急过渡流区,扰动程度相对削弱粗糙度对流态的影响。
与无降雨的坡面流相比,有降雨水流更趋向急流,说明降雨起到增加流速的作用。一般认为,由于雨滴击溅作用产生的附加阻力会使流速减小,张宽地等[1]通过试验认为在坡度较大(大于10.5%)条件下,基本上降雨均不同程度地增大表层流速,这与本试验结果一致,可能主要是因为陡坡条件下雨滴动量沿坡面的分量较大有关,能量更多地转化为动能。雨强越大,能够转化为动能的能量越多。
3.4 阻力特征
本试验在降雨条件下通过砂纸模拟下垫面,阻力规律只考虑颗粒阻力和降雨阻力的综合体现。
由图 6可知,坡面薄层流阻力系数与雷诺数呈负相关关系,随着雷诺数的增加阻力系数逐渐减小,且减小的幅度越来越小,最后趋于稳定。说明随着流量的增大,水流克服阻力所消耗的能量增加,而用于坡面侵蚀的能量减小。随着流量的增大,水深增加到一定程度后,坡面水砂纸处于完全淹没状态,由于水砂纸引起的坡面粗糙无法影响到主流区,该工况下阻力系数与雷诺数无关,而是趋近于一个常数。
降雨对坡面水流阻力系数的影响目前并无定论,吴普特等[32]认为降雨减少水流摩阻系数,但潘成忠等[13]认为降雨对坡面阻力系数无显著影响。本实验中与有降雨相比,无降雨时的阻力系数相对稳定,无明显波动。说明本实验条件下,降雨对坡面阻力系数的影响不显著,降雨主要起到扰动坡面流的作用。进一步地,采用逐步回归分析,定量研究糙度(ks)、单宽流量(q)和降雨强度(P) 3个影响因子对坡面流的阻力贡献率,计算结果见表 5。其中,降雨强度被排除,表明其对阻力系数无显著影响;由自变量系数可知,坡面流阻力系数与粗糙度呈正相关,与单宽流量呈负相关,这与上述的讨论相符合。
表 5 达西阻力系数影响因子的逐步回归分析Table 5. Stepwise regression of impact factors of resistance coefficient模型Model 相关变量Related variable 标准系数
Standardized coefficient自变量系数
Independent variable coefficient标准误差Standard error 常量Constant value 3.022 0.611 粗糙度Surface roughness 10.772 1.454 0.533 单宽流量Unit discharge -3 122.434 488.542 -0.460 已有研究成果表明,当颗粒阻力起主要作用时,阻力系数与雷诺数的幂函数关系 f=aRbe 才成立[10],为进一步研究降雨强度对坡面流阻力的影响,将本试验模拟降雨条件下裸坡薄层流数据进行拟合,得到阻力计算公式。
f′=2108.19R−1.227eP0.257,R2=0.3977 (7) 将降雨强度的因式去除,拟合得到阻力计算公式。
f′=5938.16R−1.227eP0.257,R2=0.3976 (8) 式中:f′为阻力系数;P为降雨强度(mm/h)。
对比式(7)和式(8),剔除雨强后,相关系数下降0.01%,说明降雨对坡面阻力系数的影响不显著,降雨主要起到扰动坡面流的作用。王俊杰在模拟降雨条件下得到相关系数下降了7.76%,雨强对于阻力系数的影响不能忽视[21]。这可能是由于下垫面因素不同,与降雨强度大小可能也有关系,降雨对坡面流的作用有待进一步研究。
4. 结论
本实验通过开展陡坡不透水下垫面条件下的模拟人工降雨和水槽放水冲刷试验,基于流态指数和紊动能量耗散规律,定性分析了降雨和坡面流共同作用下的坡面薄层流水动力学特性,得到以下结论。
1) 水流的平均流速随着单宽流量的增大呈幂函数增加,随粗糙度的增加而减小。粗糙度和单宽流量相同时,降雨强度增大一倍引起平均流速的变化程度为15.6%。粗糙度和降雨强度相同时,单宽流量增大一倍引起平均流速的变化程度为68.7%。无降雨时,流速系数随着平均流速的增加而增加,流速系数范围为0.04~0.37,粗糙度间的流速系数差异较小。降雨时,流速系数取值范围为0.42~0.98,随着粗糙度的增大而增大,随着平均流速的增加而增加。降雨条件下的流速修正系数数值相对较大且分布较为分散,最大值接近1。试验降雨下对坡面流起到扰动作用,有增大坡面平均流速的趋势。
2) 流态指数范围为0.291~0.538,无降雨时,流态指数随着粗糙度的增加而明显减小,其减小程度分别为21%、28%和39%;中小雨强时,流态指数无明显规律,雨强为30 mm/h时,变化程度分别为18%、-29%和12%,雨强为60 mm/h时,变化程度分别为12%、-17%和-16%;大雨强时,流态指数呈现出较为明显下降的趋势,其变化程度分别为-6%、1%和-11%。粗糙度继续增大时流态指数是否增加有待进一步研究。降雨引起水面失稳并产生滚波会影响水流流态,所以进一步的坡面薄层水流试验中滚波研究是不可忽略的一部分。
3) 水流雷诺数为500~2 000,所有实验工况下水流流型均属于层紊流过渡区;水流流态整体趋于急流状态;无雨时,粗糙度与流态关系明显,其值越小水流越趋近急流,而降雨时,由于降雨的扰动作用二者不再具有相关关系。
4) 定量研究糙度(ks)、单宽流量(q)和降雨强度(P)3个影响因子对坡面流的阻力贡献率,表明降雨对阻力系数无显著影响,坡面流阻力系数与粗糙度呈正相关关系,与单宽流量呈负相关关系,裸坡条件下考虑雨强影响的坡面流阻力计算公式与剔除雨强的公式相比,相关系数下降0.01%,说明降雨对阻力系数无显著影响,主要起到扰动坡面流的作用。另有研究表明模拟降雨条件下的相关系数下降了7.76%,雨强对于阻力系数的影响不能忽视。所以降雨对坡面流的作用有待进一步研究。
坡面薄层流是坡面径流的初始阶段和侵蚀演变的初始动力,本试验为深入研究降雨和坡面流共同作用下的坡面薄层流水动力学特性提供科学依据,对土壤侵蚀预报模型、水土流失治理方法、泥沙灾害及环境工程等问题均有重要的科学及实践意义。
-
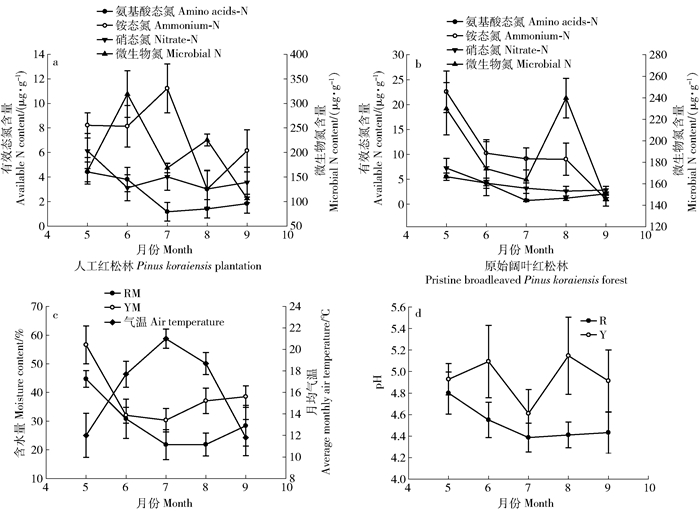
图 1 0 ~ 5 cm土层中有效氮含量、微生物氮含量、含水量、pH及该区域月均气温变化
RM.人工红松林含水量Moisture content of Pinus koraiensis plantation;YM.原始阔叶红松林含水量Moisture content of pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest
Figure 1. Available N content, microbial N content, moisture content, pH in 0-5 cm soil horizon and average monthly air temperature variation of study sites
图 2 红松人工林(a)与原始阔叶红松林(b)下不同土层间的氮含量
A.游离氨基酸态氮;B.铵态氮;C.硝态氮; D.可溶性有机氮;E.可溶性全氮;*表示土层间显著性差异(P<0.05)。
Figure 2. N contents in different soil horizons in Pinus koraiensis plantation (a) and pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest (b)
A, free amino acids-N; B, ammonium-N; C, nitrate-N; D, soluble organic N; E, total soluble N; * means significant difference among soil horizons at P < 0.05 level.
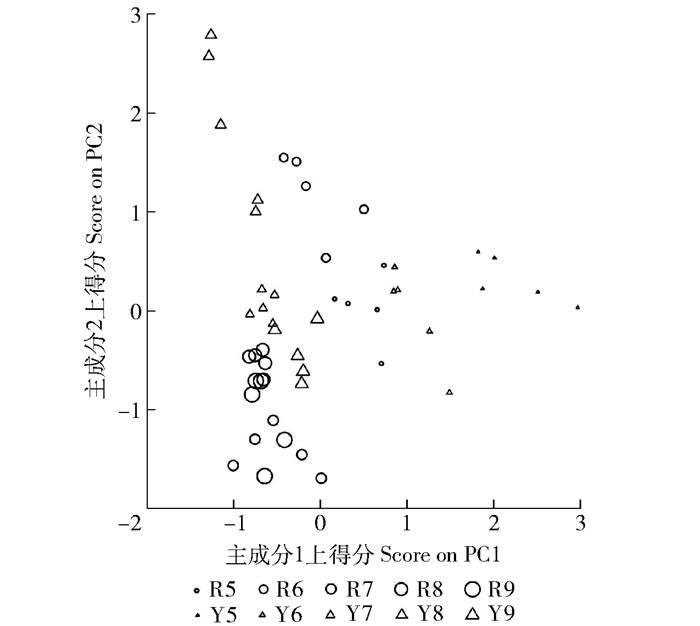
图 5 人工红松林(R)与原始阔叶红松林(Y)各个月份取样样本在主成分1和2上得分
R5、R6、R7、R8、R9分别表示5、6、7、8、9月的人工红松林;Y5、Y6、Y7、Y8、Y9分别表示5、6、7、8、9月的原始红松林。
Figure 5. Scores on PC1 and PC2 of monthly measurement of variables in soils of Pinus koraiensis plantation (R) and pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest (Y)
R5, R6, R7, R8, R9 mean May, June, July, August and September of Pinus koraiensis plantation, respectively; Y5, Y6, Y7, Y8, Y9 mean May, June, June, July, August and September of pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest, respectively.
表 1 不同林型下0~5 cm层次土壤理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical characteristics of 0~5 cm soil horizon in different forests
林型Forest type 有机碳Organic carbon 全氮Total N pH 微生物碳Microbial carbon 微生物氮Microbial N 可溶性有机氮Soluble organic N 硝态氮Nitrate-N 铵态氮Ammonium-N 游离氨基酸态氮
Free amino acids-NR 109.8(24.4) 5.0(1.8) 4.5(0.3) 0.9(0.3) 0.2(0.08) 92.1(28.8) 4.0(1.6) 7.3(3.1) 2.5(1.5) Y 112.0(22.8) 6.3(1.6) 4.9(0.3) 1.0(0.2) 0.2(0.04) 77.4(21.3) 4.0 (2.1) 10.4(7.5) 2.8(1.9) 注:R代表人工红松林, Y代表原始阔叶红松林, 括号外数字代表平均值, 括号内数字代表标准差(n = 25)。有机碳、全氮、微生物碳和微生物氮含量单位为mg/g, 可溶性有机氮、游离氨基酸态氮、硝态氮和铵态氮单位为滋g / g。下同。Notes: R represents Pinus koraiensis plantation, and Y represents pristine broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest. Data outside bracket is the mean of samples, and the inside is standard deviation (n=25). The unit of organic carbon, total N, microbial C and N contents is mg/g, and the unit of soluble organic N, free amino acids-, nitrate- and ammonium-N contents is μg/g. The same below. 表 2 主成分分析方案
Table 2 Solution of principal component (PC) analysis
变量
Variable公因子方差
Communality主成
分1
PC1主成
分2
PC2主成
分3
PC3组氨酸His (HI) 0.844 0.901 游离氨基酸
Free amino acid (FA)0.874 0.885 甘氨酸Gly (GL) 0.792 0.857 天冬氨酸Asp (AS) 0.726 0.848 含水量Moisture content (MC) 0.634 0.707 硝酸根Nitrate (NI) 0.531 0.675 铵离子Ammonium (AM) 0.483 0.667 丝氨酸Ser (SE) 0.630 0.624 亮氨酸Leu (LE) 0.423 0.612 全氮Total N (TN) 0.294 0.518 微生物碳
Microbial carbon (MI)0.827 0.872 微生物氮Microbial N (MN) 0.501 0.681 pH 0.511 0.660 可溶性有机氮
Soluble organic N (SN)0.652 0.794 有机碳Organic carbon (OC) 0.798 -0.728 精氨酸Arg (AR) 0.329 0.556 解释的变异
Variance explained/%35 19 13 -
[1] LEBAUER D S, TRESEDER K K. Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed[J]. Ecology, 2008, 89(2): 371-379. doi: 10.1890/06-2057.1
[2] NÄSHOLM T, EKBLAD A, NORDIN A, et al. Boreal forest plants take up organic nitrogen[J]. Nature, 1998, 392: 914-916. doi: 10.1038/31921
[3] HILL P W, FARRAR J, ROBERTS P, et al. Vascular plant success in a warming Antarctic may be due to efficient nitrogen acquisition[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2011, 1(1): 50-53. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3f0c81c19f75177ce0c7579fd2607fbc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] PAUNGFOO-LONHIENNE C, LONHIENNE T G A, RENTSCH D, et al. Plants can use protein as a nitrogen source without assistance from other organisms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(11): 4524-4529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712078105
[5] MCFARLAND J W, RUESS R W, KIELLAND K, et al. Cross-ecosystem comparisons of in situ plant uptake of amino acid-N and NH4+[J]. Ecosystems, 2010, 13(2): 177-193. doi: 10.1007/s10021-009-9309-6
[6] WILD B, SCHNECKER J, KNOLTSCH A, et al. Microbial nitrogen dynamics in organic and mineral soil horizons along a latitudinal transect in western Siberia[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2015, 29(5): 567-582. doi: 10.1002/2015GB005084
[7] WEINTRAUB M N, SCHIMEL J P. The seasonal dynamics of amino acids and other nutrients in Alaskan arctic tundra soils[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2005, 73(2): 359-380. doi: 10.1007/s10533-004-0363-z
[8] MCFARLAND J W, RUESS R W, KIELLAND K, et al. Cycling dynamics of NH4+ and amino acid nitrogen in soils of a deciduous boreal forest ecosystem[J]. Ecosystems, 2002, 5(8): 775-788. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e93fe55e2356adc7ce1bd088d66dec7a
[9] KIELLAND K, MCFARLAND J W, RUESS R W, et al. Rapidcycling of organic nitrogen in taiga forest ecosystems[J]. Ecosystems, 2007, 10(3): 360-368. doi: 10.1007/s10021-007-9037-8
[10] FARRELL M, HILL P W, FARRAR J, et al. Seasonal variation in soluble soil carbon and nitrogen across a grassland productivity gradient[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(4): 835-844. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.12.022
[11] JAN M T, ROBERTS P, TONHEIM S K, et al. Protein breakdown represents a major bottleneck in nitrogen cycling in grassland soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 41(11): 2272-2282. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.08.013
[12] JONES D L, KIELLAND K, SINCLAIR F L, et al. Soil organic nitrogen mineralization across a global latitudinal gradient[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2009, 23(1): 150-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2008GB003250
[13] O'DOWD R W, BARRACLOUGH D, HOPKINS D W. Nitrogen and carbon mineralization in soil amended with D- and L-leucine[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1999, 31(11): 1573-1578. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00083-8
[14] JONES D L, SHANNON D, MURPHY D V, et al. Role of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in soil N cycling in grassland soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2004, 36(5): 749-756. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.01.003
[15] OWEN A G, JONES D L. Competition for amino acids between wheat roots and rhizosphere microorganisms and the role of amino acids in plant N acquisition[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2001, 33(4/5): 651-657. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8269fc2a9a6f3da5ca30c113c29b9921&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] PERSSON J, NÄSHOLM T. Amino acid uptake: a widespread ability among boreal forest plants[J]. Ecology Letters, 2001, 4(5): 434-438. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00260.x
[17] 郝敬梅, 张韫, 崔晓阳, 等.原始阔叶红松林、次生林土壤矿质氮特征及树种吸收反应[J].北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(1): 21-25. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201401004 HAO J M, ZHANG Y, CUI X Y, et al. Soil mineral N characteristics in original broadleaved Pinus koraiensis forest and secondary forest and N absorption of some tree species[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(1): 21-25. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201401004
[18] JONES D L, SHANNON D, JUNVEEFORTUNE T, et al. Plant capture of free amino acids is maximized under high soil amino acid concentrations[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(1): 179-181. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.021
[19] RUESS R W, HENDRICK R L, VOGEL J G, et al. The role of fine roots in the functioning of Alaskan boreal forests[M]//CHAPIN Ⅲ F S, OSWOOD M W, VAN CLEVE K, et al. Alaska's changing boreal forest. New York: Oxford University Press, 2006.
[20] ABUARGHUB S M, READ D J. The biology of mycorrhiza in the Ericaceae (Ⅻ): quantitative analysis of individual 'free' amino acids in relation to time and depth in the soil profile[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 108(4): 433-441.
[21] WEINTRAUB M N, SCHIMEL J P. Seasonal protein dynamics in Alaskan arctic tundra soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(8): 1469-1475. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.01.005
[22] FARRELL M, MACDONALD L M, HILL P W, et al. Amino acid dynamics across a grassland altitudinal gradient[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 76(1): 179-182. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=551890eb1e72a7f1f56e4831efa0fbe8
[23] 侯松嵋, 孙敬, 何红波, 等. AQC柱前衍生反相高效液相色谱法测定土壤中氨基酸[J].分析化学, 2006, 34(10): 1395-1400. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2006.10.008 HOU S M, SUN J, HE H B, et al. Simultaneous determination of amino acids in soil by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography by using 6-Aminoquinoly-N-hydroxy succinmiidyl carbamate as a precolumn derivatization reagent[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2006, 34(10): 1395-1400. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2006.10.008
[24] 中国土壤学会农业化学专业委员会.土壤农业化学常规分析方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 1983. Professional Agriculture-Chemistry Committee of Soil Science Society of China. Common analytical methods of soil agriculture-chemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1983.
[25] BROOKES P C, LANDMAN A, PRUDEN G, et al. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1985, 17(6): 837-842. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0
[26] WU J, JOERGENSEN R G, POMMERENING B, et al. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction: an automated procedure[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1990, 22(8): 1167-1169. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(90)90046-3
[27] WERDIN-PFISTERER N R, KIELLAND K, BOONE R D. Soil amino acid composition across a boreal forest successional sequence[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 41(6): 1210-1220. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.03.001
[28] ROTHSTEIN D E. Soil amino-acid availability across a temperate-forest fertility gradient[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2009, 92(3): 201-215. doi: 10.1007/s10533-009-9284-1
[29] 王星, 崔晓阳, 郭亚芬.寒温带林区不同林型土壤中游离氨基酸的研究[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 2016, 40(4): 43-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201401004 WANG X, CUI X Y, GUO Y F. A study on free amino acid in different forest types soil of cold-temperate forest region[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2016, 40(4): 43-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjlydxxb201401004
[30] MOPPER K, ZIKA R G. Free amino acids in marine rains: evidence for oxidation and potential role in nitrogen cycling[J]. Nature, 1987, 325: 246-249. doi: 10.1038/325246a0
[31] MICHALZIK B, MATZNER E. Dynamics of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in a Central European Norway spruce ecosystem[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 1999, 50(4): 579-590. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.1999.00267.x
[32] JONES D L, DARRAH P R. Amino-acid influx at the soil-root interface of Zea mays L. and its implications in the rhizosphere[J]. Plant and Soil, 1994, 163(1): 1-12.
[33] JONES D L, HEALEY J R, WILLETT V B, et al. Dissolved organic nitrogen uptake by plants: an important N uptake pathway?[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(3): 413-423. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.08.008
[34] CHAPIN F S, MOILANEN L, KIELLAND K. Preferential use of organic nitrogen for growth by a non-mycorrhizal arctic sedge[J]. Nature, 1993, 361: 150-153. doi: 10.1038/361150a0
[35] NORDIN A, HÖGBERG P, NÄSHOLM T. Soil nitrogen form and plant nitrogen uptake along a boreal forest productivity gradient[J]. Oecologia, 2001, 129(1): 125-132. doi: 10.1007/s004420100698
[36] LIPSON D A, SCHMIDT S K, MONSON R K. Links between microbial population dynamics and nitrogen availability in an Alpine ecosystem[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80(5): 1623-1631. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080
[37] JONES D L, OWEN A G, FARRAR J F. Simple method to enable the high resolution determination of total free amino acids in soil solutions and soil extracts[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(12): 1893-1902. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00203-1
[38] COMERFORD N B. Soil factors affecting nutrient bioavailability[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2005.
[39] QUALLS R G, RICHARDSON C J. Factors controlling concentration, export, and decomposition of dissolved organic nutrients in the Everglades of Florida[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2003, 62(2): 197-229. doi: 10.1023/A:1021150503664
[40] CHRISTOU M, AVRAMIDES E J, JONES D L. Dissolved organic nitrogen dynamics in a Mediterranean vineyard soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(8): 2265-2277. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.01.025
[41] PRENDERGAST-MILLER M T, DE MENEZES A B, FARRELL M, et al. Soil nitrogen pools and turnover in native woodland and managed pasture soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 85:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.02.036
[42] JONES D L, KIELLAND K. Amino acid, peptide and protein mineralization dynamics in a taiga forest soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 55(2): 60-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5a9b26ff8cb23b6c188a1180fc4f6298
[43] WARREN C R, TARANTO M T. Temporal variation in pools of amino acids, inorganic and microbial N in a temperate grassland soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(2): 353-359. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.017
[44] CLEAVITT N L, FAHEY T J, GROFFMAN P M, et al. Effects of soil freezing on fine roots in a northern hardwood forest[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2008, 38(1): 82-91. doi: 10.1139/X07-133
[45] YANAI Y, TOYOTA K, OKAZAKI M. Effects of successive soil freeze-thaw cycles on soil microbial biomass and organic matter decomposition potential of soils[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2004, 50(6): 821-829. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2004.10408542
[46] GLANVILLE H C, HILL P W, MACCARONE L D, et al. Temperature and water controls on vegetation emergence, microbial dynamics, and soil carbon and nitrogen fluxes in a high arctic tundra ecosystem[J]. Functional Ecology, 2012, 26(6): 1366-1380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2012.02056.x
[47] ENDRES L, MERCIER H. Amino acid uptake and profile in bromeliads with different habits cultivated in vitro[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2003, 41(2): 181-187. doi: 10.1016/S0981-9428(02)00025-6
[48] STOELKEN G, SIMON J, EHLTING B, et al. The presence of amino acids affects inorganic N uptake in non-mycorrhizal seedlings of European beech (Fagus sylvatica)[J]. Tree Physiology, 2010, 30(9): 1118-1128. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpq050
[49] MCKANE R B, JOHNSON L C, SHAVER G R, et al. Resource-based niches provide a basis for plant species diversity and dominance in arctic tundra[J]. Nature, 2002, 415: 68-71. doi: 10.1038/415068a
[50] BERTHRONG S T, FINZI A C. Amino acid cycling in three cold-temperate forests of the northeastern USA[J]. Soil Biologyand Biochemistry, 2006, 38(5): 861-869. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.08.002
[51] KRANABETTER J M, DAWSON C R, DUNN D E. Indices of dissolved organic nitrogen, ammonium and nitrate across productivity gradients of boreal forests[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 39(12): 3147-3158. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1a7d96a5417b199f85bda538d3a2b42f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李辉,林沂,孟祥爽,史振伟,蔡万园. 基于地基激光雷达的栾树分形特征分析. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 475-483 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何东健,熊虹婷,芦忠忠,刘建敏. 基于多视角立体视觉的拔节期玉米水分胁迫预测模型. 农业机械学报. 2020(06): 248-257 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭彩玲,刘刚. 基于颜色取样的苹果树枝干点云数据提取方法. 农业机械学报. 2019(10): 189-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: