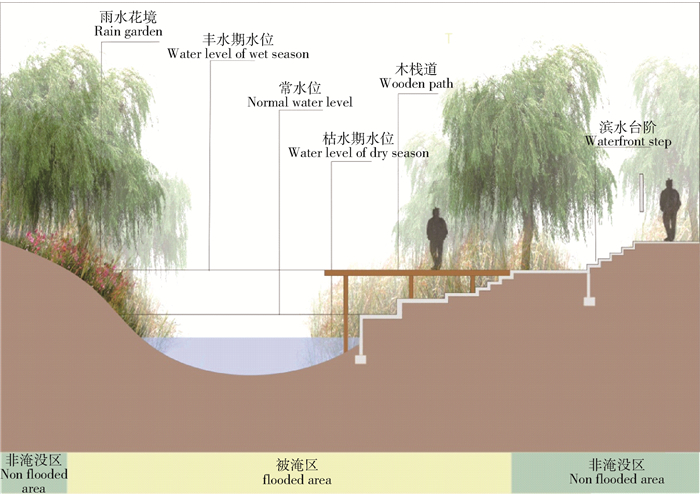
Design methods of sponge greenway in urban shallow mountainous area in northern China: taking the greenway of Luquan District in Shijiazhuang as an example
-
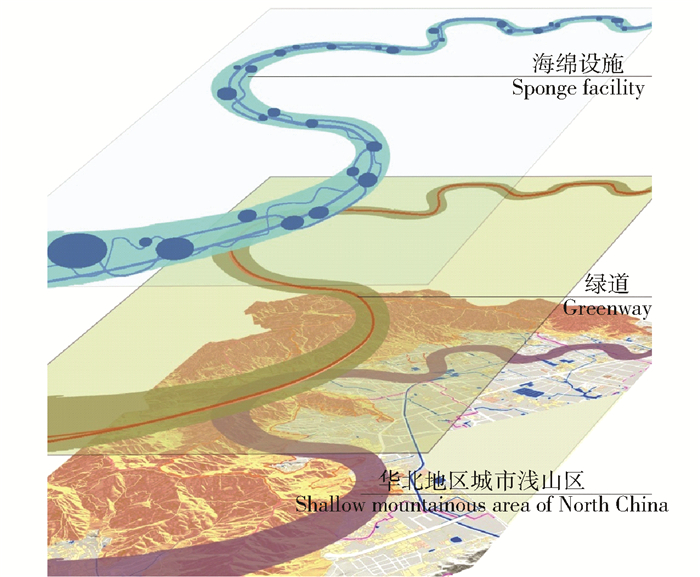
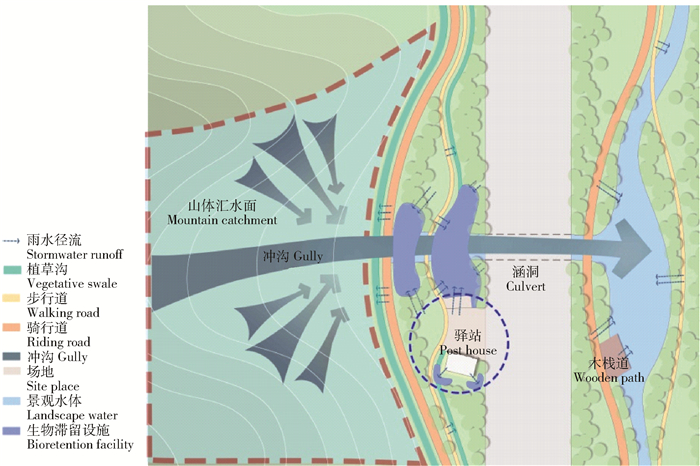
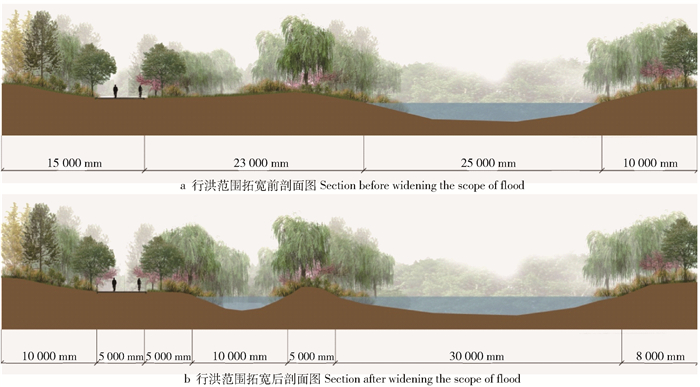
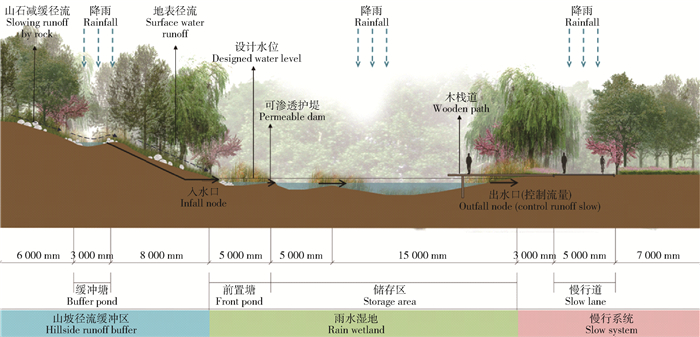
摘要: 华北地区年降雨量偏少,降水集中、多暴雨且年蒸发量大,导致严重的雨洪问题与水资源短缺问题。山麓迎风区多暴雨的气候特征对平原地区构成了雨洪灾害的威胁,在城市浅山区建设海绵绿道作为径流缓冲区,对于缓解雨洪灾害有着重要意义。为解决华北地区城市浅山区雨洪管理问题与水资源短缺问题,本研究通过分析华北地区的气候特征、城市浅山区的雨洪灾害情况及其特点,首先探讨了在华北地区城市浅山区建设海绵绿道的必要性。在此基础上,结合河北省石家庄市鹿泉区山前大道项目,提出了适用于华北地区浅山区的海绵绿道设计方法。该海绵绿道的设计策略综合考虑到3个维度:1)华北城市浅山区作为自然基底;2)绿道作为雨水径流缓冲带;3)低影响开发措施作为绿道设计内容之一。本研究基于雨水安全与利用两个视角综合考虑设计策略。最后,本文利用暴雨洪水管理模型(SWMM)量化模拟LID设施对雨水径流的控制效果,将海绵绿道与传统绿道的调蓄效能进行对比。结果显示,海绵绿道在控制径流总量、峰值流量以及推迟峰现时间方面具有更好的效能,能有效解决场地的雨水调蓄问题。Abstract: The annual rainfall in North China is less than normal and the rainfall is concentrated. Rainstorms frequently occurs and the annual evaporation is large, which cause serious flood and water shortage problems. The rainstorms in the windward area of the piedmont area constitute a threat of flood to the plain area. Building greenway in urban shallow mountainous area is of great significance to alleviate flood and rain disasters. With the aim of solving the problems of the water resource shortage in northern China and rainwater management problems in urban shallow mountainous areas, firstly, this paper discusses the necessity of sponge greenway's construction by analyzing the climatic characteristics of northern China and characteristics of rain and flood disasters in urban shallow mountainous area. On this basis, combined with the greenway project of Luquan District in Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province of northern China, the paper proposes design methods for spongy greenway. The design strategies of sponge greenway consider three following dimensions: 1) taking urban mountainous areas of northern China as the natural substrates; 2) taking greenway as the runoff buffer; 3) integrating the LID facilities into greenway design. This study considers the design strategies based on two perspectives of rainwater safety and utilization. Finally, this paper uses the storm water management model (SWMM) to quantify the control effect of LID facilities on stormwater runoff, and compares the storage efficiency of sponge greenway with the traditional one. The results show that the sponge greenway has better efficiency in controlling total runoff, peak flow and delaying peak time. Spongy greenway can effectively solve the problems of rainwater regulation.
-
森林是主要的陆地生态系统,也是最大的陆地生态系统碳库。森林在应对气候变化中具有独特的作用,是经济可行、成本较低的降低温室气体浓度的重要资源[1]。相关监测结果表明:我国森林碳汇供给能力稳步提升[2],对温室气体减排作用的贡献越来越大,但随着我国重点林业生态工程的持续开展,森林固碳不仅成为抵减工业温室气体排放的重要途径,也成为我国发展绿色低碳经济的最佳选择[3]。因此,开展中国森林碳汇与林业经济发展的耦合及长期变化特征分析,把握森林碳汇与林业经济发展的变化趋势,可为相关管理决策、生态治理和资源环境管理等提供参考,推动我国绿色低碳经济的发展。
1. 问题的提出
森林碳汇与经济发展的耦合关系反映的是碳汇与经济发展之间相互依赖、相互影响的关系和程度。伴随着我国经济发展由注重速度向注重质量的转变,绿色低碳经济发展越来越成为关注的焦点[3]。这其中,增加森林固碳能力,加强森林碳汇管理,提高经济系统、社会系统和自然系统之间的耦合协调性也成为研究的重点[4]。森林具有生态、经济、社会等多重效益,不仅具有生物多样性保护、涵养水源、固碳释氧等生态效益,也具有提供林副产品、森林旅游、就业机会等经济和社会效益。目前,对于森林单一效益的研究较多,对于多重效益的研究较少,尤其对于森林碳汇多重效益的计量和耦合研究较少[5]。对于森林碳汇经济效益评价的方法归纳起来主要有市场价值法、造林成本法、碳税法、人工固定CO2成本法、均值法、支付意愿法和成本效益法等[6-7]。森林生态效益和森林碳汇的大小不仅与森林结构、降雨量、平均气温等气候因素和生物多样性有关,也与森林火灾、病虫鼠害等风险因素和经营管理水平等有关。森林社会效益主要指森林提供就业机会、文化价值和维持原住民生计等[8],社会效益也与生物多样性、森林健康水平等有关。在这些多重效益中,林业碳中和与碳主要受生物多样性的影响较大[9],它不仅影响森林的结构,还影响森林碳汇的稳定性、大小等。因此,森林碳汇与经济、社会效益的耦合关系才是碳汇效益评估中不能忽视的科学问题。
国外对于森林碳汇与经济、社会效益的耦合关系和多重效益的计量研究也主要从其单一效益扩展开始的。如Sierra等[10]在研究森林碳汇中,除考虑森林生物量、地下生物量、枯落物、枯死木、土壤有机质碳库的碳汇外,还关注森林经营后木质林产品收获引起的经济收益和碳库的变化。Fernández-Manjarrés等[11]在考虑关于森林经营活动下的固碳增汇计量的同时,还考虑了出于对减少毁林和林地退化造成的减排量的森林碳汇的泄漏问题和非持久性的问题。Roces-Díaz等[12]建议在投资项目寿命期内对碳汇项目的经济效益进行计量,并建议采用B-S期权模型对碳汇投资的期权价值进行定量评估。政府间气候变化专门委员会(IPCC)也建议对森林碳汇的多重效益进行动态核算[13]。Ratcliffe等[14]认为:森林具有多重效益,碳汇不是唯一目标,在进行森林碳汇效益计量时,应考虑其他多重效益,尤其要考虑碳汇效益的耦合优化研究等。近年来,国内学者也关注到森林碳汇的多重效益计量和耦合优化的研究问题,如:牛玲[15]从宏观经济角度对森林碳汇的其他效益进行了研究;华志芹[16]在研究碳汇多效益计量时,从制度安排上探讨了林业碳汇市场与经济绩效的关系,并提出了优化林业碳汇产权制度安排的建议等。胡原等[17]则从耦合效益的角度探讨了碳汇造林项目促进当地经济发展的情况。因此,开展森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合研究,开发一些新的森林多重效应下固碳增汇效益及多重效益评估方法和模型,不仅是一个科学问题,也符合生态文明建设的需要,更是实施国家“双碳”目标的战略要求,对提高碳汇科学管理水平和促进碳汇市场管理的发展,加强生态系统服务管理和生态文明建设、绿色发展等具有重要价值和意义[18]。
2. 研究方法及数据来源
2.1 研究方法
对于中国森林碳汇与林业经济发展的耦合及长期变化特征研究,主要采用森林碳汇与林业经济发展综合评价模型、耦合度模型和耦合协调度模型3种方法进行研究[19]。参考相关资料,森林碳汇的主要指标为森林单位面积蓄积量(m3/hm2)、森林碳储量(108 t)、森林碳汇量(108 t/a);林业经济发展的主要指标有GDP(亿元)、林业产业总产值(亿元)、林业生态建设与保护投资完成额(亿元)、林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额(亿元)、林产品进口额(亿元)、林产品出口额(亿元)、林业产品生产者价格指数(上年 = 100)和林业产值年增长速度,共11项指标[20]。具体研究方法为:
(1)森林碳汇与林业经济发展综合评价模型:
N=∑nj=1λjN′ijt (1) E=n∑j=1λjE′ijt (2) 式中:N和E分别为森林碳汇与林业经济发展系统综合评价值,
N′ijt 为第t期i地区第j个森林碳汇指标值,E′ijt 为第t期i地区第j个林业经济发展指标值;λj 为评价指标的权重,研究中一般选择较为客观的主成分分析法确定指标的权重,并求其权重的均值得到综合权重,以缩小差异性[21]。(2)森林碳汇与林业经济发展耦合度模型
耦合度反映森林碳汇与林业经济之间相互依赖、相互影响的程度。森林碳汇与林业经济发展的耦合度模型为:
C=[NE(N+E2)2]k (3) 式中:C为森林碳汇—林业经济发展耦合度,
C∈[0,1] ,C越大,系统间关联程度越高,C越小,系统间关联程度越低,系统处于无序状态。K为调节系数,研究中只涉及森林碳汇和林业经济发展2个子系统,因此,K值取2[22]。(3)森林碳汇与林业经济发展耦合协调度模型
森林碳汇和林业经济发展耦合度能较好反映二者间的关联程度。但是,耦合度尚不能对系统自身协同发展的“整功效”进行度量。因此,为了有效地度量二者的综合发展水平,特引入耦合协调度以反映二者的整合功效[23],具体模型为:
{D=√C√TT=aN+bE (4) 式中:D为耦合协调度,C为耦合度,T为森林碳汇—林业经济发展综合评价指数,a、b取值均为0.5,即认为森林碳汇、林业经济发展具有相同的重要程度。
另外,根据有关参考文献[24],森林碳汇—林业经济发展耦合协调度的10个等级划分标准如表1所示。
表 1 森林碳汇与林业经济发展耦合协调度分类Table 1. Classification of coupling coordination degree between forest carbon sink and forestry economic development耦合协调等级
Coupling coordination level耦合协调度区间
Coupling coordination degree interval耦合协调程度
Degree of coupling coordination1 0.000 0 < D ≤ 0.100 0 极度失调
Extreme imbalance2 0.100 1 < D ≤ 0.200 0 严重失调
Serious imbalance3 0.200 1 < D ≤ 0.300 0 中度失调
Moderate imbalance4 0.300 1 < D ≤ 0.400 0 轻度失调
Mild imbalance5 0.400 1 < D ≤ 0.500 0 濒临失调
On the verge of imbalance6 0.500 1 < D ≤ 0.600 0 勉强协调
Barely coordination7 0.600 1 < D ≤ 0.700 0 初级协调
Primary coordination8 0.700 1 < D ≤ 0.800 0 中级协调
Intermediate coordination9 0.800 1 < D ≤ 0.900 0 良好协调
Good coordination10 0.900 1 < D ≤ 1.000 0 优质协调
High quality coordination注:D为耦合协调度。资料来源为参考文献[24]。Notes: D is coupling coordination degree. Data source is cited from reference [24]. 对于森林碳汇的测算方法主要采用蓄积量扩展法的计算公式测算,具体公式为:
TCF=SiCi+αSiCi+βSiCi (5) Ci=Viδργ (6) 式中:
TCF 为森林碳储量,具体包括林木固碳量、林下植被固碳量和林地固碳量;Si 为第i 类森林的面积;Ci 为第i 类森林的碳密度;Vi 为第i 类森林单位面积蓄积量;α 为林下植被碳转换系数;β 为林地碳转换系数;δ 为生物量扩大系数;ρ 为生物量蓄积转换成生物干质量系数,即容积密度;γ 为生物干质量转换成固碳量的系数,即含碳率[25]。在实际核算中,各种换算系数一般按照IPCC要求的默认参数取值。δ 一般取值为1.90;ρ 一般取0.45 ~ 0.50 t/m3,本研究取0.50 t/m3;γ 一般取0.5;α 取0.195;β 取值为1.244[26]。2.2 数据来源
本研究采用的数据主要来源于《中国森林资源清查》《中国林业统计年鉴》《中国统计年鉴(2021)》[27-29],以及已公开发表的相关文献资料和数据[25-26]。具体数据包括森林面积、蓄积量,不同林分的面积、生长量、蓄积量等,主要数据如表2所示。
表 2 1992―2018年中国森林碳汇与林业经济发展耦合及长期变化特征分析主要数据Table 2. Coupling and long-term change characteristics of forest carbon sink and forestry economic development in China from 1992 to 2018年份
Year森林碳储量
Forest carbon storage/108 t森林碳汇量/
(108 t·a−1)Forest carbon sink/ (108 t·year−1)林业产业
总产值/亿元
Total output value of forestry industry/108 CNY生态建设与
保护投资完
成额/亿元
Amount of investment
completed in ecological
construction and protection/108 CNY林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额/亿元
Investment in
key forestry ecological
projects actually
been completed/108 CNYGDP/亿元 GDP/108
CNY林产品
出口额/亿元
Export value of forest products/108 CNY林产品
进口额/亿元
Import value of forest products/108 CNY林业产品生产者价格指数(上年 = 100)
Producer price index for forestry products (last year = 100)1992 140.286 0.186 62 198.43 13.24 4.46 27 194.5 107.30 1993 140.710 0.173 90 994.56 15.88 11.89 35 673.2 38.861 96 37.938 27 111.10 1994 141.504 0.177 02 1 337.55 18.95 14.46 48 637.5 49.554 61 47.610 68 111.80 1995 142.298 0.180 14 1 577.24 20.85 16.26 61 339.9 60.585 00 54.200 50 105.10 1996 143.092 0.183 26 1 707.76 27.87 21.15 71 813.6 56.837 62 57.535 08 104.40 1997 143.886 0.186 38 1 918.24 38.47 25.51 79 715.0 61.216 67 66.413 40 98.90 1998 144.680 0.189 50 2 727.85 60.61 23.36 85 195.5 55.958 13 69.153 87 101.10 1999 147.298 0.366 40 3 187.73 91.55 81.58 90 564.4 61.247 30 95.884 74 101.40 2000 149.916 0.543 30 3 555.47 150.66 113.19 100 280.1 72.951 25 114.494 62 90.00 2001 152.534 0.720 20 4 090.48 191.62 166.44 110 863.1 78.550 79 109.825 86 94.15 2002 155.152 0.897 10 4 634.24 296.14 255.80 121 717.4 95.796 66 128.972 94 98.31 2003 157.770 1.074 00 5 860.33 388.47 333.92 137 422.0 122.359 84 166.419 87 107.01 2004 159.938 1.036 80 6 892.21 398.45 351.02 161 840.2 163.008 54 199.399 12 104.62 2005 162.106 0.999 60 8 458.74 439.78 361.63 187 318.9 205.741 72 221.021 07 104.79 2006 164.274 0.962 40 10 652.22 470.77 353.34 219 438.5 263.770 42 257.986 89 112.78 2007 166.442 0.925 20 12 533.42 615.11 348.04 270 092.3 319.309 93 323.601 69 104.37 2008 168.610 0.888 00 14 406.41 827.72 420.24 319 244.6 334.883 10 384.394 66 108.47 2009 172.132 0.999 20 17 493.43 1 109.52 508.73 348 517.7 363.163 17 339.024 86 94.88 2010 175.654 1.110 40 22 779.02 1 170.96 472.00 412 119.3 463.166 86 475.065 54 122.78 2011 179.176 1.221 60 30 596.73 1 302.49 532.51 487 940.2 550.337 14 652.991 00 114.92 2012 182.698 1.332 80 39 450.91 1 604.12 528.38 538 580.0 586.907 87 619.480 82 101.23 2013 186.220 1.444 00 47 315.44 1 870.57 536.15 592 963.2 644.546 14 640.883 32 99.09 2014 191.854 1.617 20 54 032.94 1 947.97 665.95 643 563.1 714.120 07 676.052 23 99.44 2015 197.488 1.790 40 59 362.71 2 110.00 705.65 688 858.2 742.625 43 636.037 10 97.88 2016 203.122 1.963 60 64 886.04 2 016.29 675.41 746 395.1 726.766 70 624.257 44 96.11 2017 208.756 2.136 80 71 267.07 2 016.29 718.01 832 035.9 734.059 06 749.839 84 104.86 2018 214.390 2.310 00 76 272.76 2 125.75 717.20 919 281.1 784.913 52 818.729 84 98.90 注:资料来源为参考文献[25]。 Note: data source is cited from reference [25]. 另外,在碳汇测算中,由于所得到的森林碳储量、森林碳汇量的数据主要为每个森林资源清查期末,即每个清查期最后一年的数据,为了便于与林业经济发展的统计数据相比较[30],研究采用插值法将1992年后不同清查期的森林碳储量、碳汇数据转换成年度数据。第4 ~ 9次森林资源清查期为1989—1993年、1994—1998年、1999—2003年、2004—2008年、2009—2013年和2013—2018年。插值法的计算公式为:
y=y1+(y2−y1)(x−x1)(x2−x1) (7) 式中:
y1 、y2 、x1 、x2 为已知统计数据;x 为x1 、x2 之间的任何数;y 为与x 所对应的插值数据。至于“森林单位面积蓄积量”“林业产值年增长速度”2项指标,主要依靠“森林面积”“林业产值”等指标计算获得,因此,在数据收集中没有直接列出。3. 森林碳汇与林业经济发展的耦合度分析
首先,对变量进行命名,具体为:year,时期(年);frcs,森林碳储量(108 t);fcs,森林碳汇量(108 t/a);topf,林业产业总产值(亿元);ince,生态建设与保护投资完成额(亿元);fkein,林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额(亿元);gdp,GDP(亿元);efp,林产品出口额(亿元);ifp,林产品进口额(亿元);ppi,林业产品生产者价格指数(上年 = 100)。这些变量分别从碳储量、碳汇量、林业经济发展、林产品贸易和生产价格等方面反映森林碳汇与林业经济发展的耦合变化情况。
其次,采用SPSSAU软件进行森林碳汇影响因素和耦合协调度分析。
3.1 森林碳储量、森林碳汇的影响因素分析
对森林碳储量、森林碳汇的影响因素和滞后性,分别采用逐步回归和ARIMA模型进行分析。
3.1.1 森林碳储量影响因素及滞后性
以森林碳储量为因变量,其他林业经济发展指标为自变量进行逐步回归分析,具体回归结果如表3所示。
表 3 森林碳储量(frcs)与林业经济发展变化指标逐步回归分析结果Table 3. Results of stepwise regression analysis between forest carbon stocks (frcs) and indicators of forestry economic development and change项目
Item非标准化系数
Unstandardized coefficient标准化系数
Standardized coefficientt P VIF B 标准误
Standard errorBeta 常数
Constant138.292 0.428 323.297 0.000** ince −0.008 0.002 −0.300 −5.134 0.000** 42.873 fkein 0.042 0.003 0.469 15.703 0.000** 11.197 gdp 0 0 1.026 19.045 0.000** 36.490 ifp −0.015 0.004 −0.183 −3.752 0.001** 29.758 注:ince为生态建设与保护投资完成额,fkein为林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额,gdp为GDP,ifp为林产品进口额,**代表显著性水平为0.01。下同。Notes: ince is the amount of investment completed in ecological construction and protection. fkein is the investment in key forestry ecological projects actually been completed. gdp is GDP. ifp is the import value of forest products. ** represents the significance level of 0.01. The same below. 由表3可以看出:将topf、ince、fkein、gdp、efp、ifp、ppi作为自变量,将frcs作为因变量进行逐步回归分析,经过模型自动识别,最终余下ince、fkein、gdp、ifp共4项指标在模型中。模型的R2为0.998,F = 3137.812,P = 0.000 < 0.05,杜宾-瓦特森值(D-W) = 1.603,接近2,表明ince、fkein、gdp、ifp可以解释frcs的99.8%变化原因,且模型通过F检验,说明模型有效。另外,对模型的多重共线性进行检验发现,模型中方差膨胀因子(VIF)大于10,表明模型存在多重共线性问题。最后,消除多重共性问题,得到最终逐步回归模型为:frcs = 138.292 − 0.008·ince + 0.042·fkein + 0.000 084·gdp − 0.015·ifp。
因此,ince的回归系数值为−0.008(t = −5.134,P = 0.000 < 0.01),ifp的回归系数值为−0.015(t = −3.752,P = 0.001 < 0.01),表明ince、ifp会对frcs产生显著的负向影响关系;fkein的回归系数值为0.042(t = 15.703,P = 0.000 < 0.01),gdp的回归系数值为0.000 084(t = 19.045,P = 0.000 < 0.01),表明fkein、gdp会对frcs产生显著的正向影响关系。
另外,针对各因素的滞后性影响问题,采用ARIMA模型和ADF检验分别进行分析,具体结果如表4所示。
表 4 frcs的ARIMA(0,2,0)模型参数Table 4. Parameters of ARIMA(0,2,0) model of frcs项目
Item符号
Symbol系数
Coefficient标准误
Standard errorz p 95% CI 常数
Constantc 0.091 0.082 1.109 0.267 −0.070 ~ 0.252 注:AIC值为67.767,BIC值为71.194。Notes: AIC value is 67.767, BIC value is 71.194. 针对frcs,结合赤池信息准则值(AIC)越低越好的信息准则,SPSSAU自动对多个潜在备选模型进行建模和对比选择,最终找出最优模型为:ARMA(0,2,0),说明自回归阶数p为0,差分阶数d为2,移动平均阶数q为0;模型公式为:y(t)=0.091,说明各因素对森林碳储量的影响滞后期为2。据此,对frcs进行ADF检验,二阶差分后数据ADF检验结果显示P = 0.000 < 0.01,有高于99%的把握拒绝原假设,此时序列平稳,也进一步说明frcs的滞后期为2。
3.1.2 森林碳汇影响因素及滞后性
同样,以森林碳汇为因变量,其他林业经济发展指标为自变量进行逐步回归分析,具体回归结果如表5所示。
表 5 森林碳汇量(fcs)与林业经济发展变化指标逐步回归分析结果Table 5. Stepwise regression analysis results of forest carbon sink (fcs) and forestry economic development and change indicators项目
Item非标准化系数
Unstandardized coefficient标准化系数
Standardized coefficientt P VIF B 标准误
Standard errorBeta 常数
Constant0.249 000 0.034 7.402 0.000** topf 0.000 026 0 0.871 7.996 0.000** 14.901 fkein 0.003 000 0 1.092 11.991 0.000** 10.403 efp −0.002 000 0 −0.951 −6.119 0.000** 30.337 注:topf为林业产业总产值,efp为林产品出口额。Notes:topf is the total output value of forestry industry, efp is the export value of forest products. 在逐步回归分析中,回归模型的R2 = 0.982,调整后的R2 = 0.980,模型F = 410.945,P = 0.000,D-W值为 1.609。回归中,将topf、ince、fkein、gdp、efp、ppi作为自变量,将fcs作为因变量进行逐步回归分析。经过模型自动识别,最终余下topf、fkein、efp共3项在模型中,表明topf、fkein、efp可以解释fcs的98.2%变化原因。而且模型通过F检验,D-W值接近2,说明模型有效。另外,对模型的多重共线性进行检验发现,模型中VIF值大于10,表明模型存在着共线性问题。最后,剔除掉相关关系紧密的自变量后,重新进行回归分析,得到最终模型为:fcs = 0.249 + 0.000 026·topf + 0.003·fkein − 0.002·efp。因此,topf的回归系数值为0.000 026(t = 7.996,P = 0.000 < 0.01),表明topf会对fcs产生显著的正向影响关系;fkein的回归系数值为0.003(t = 11.991,P = 0.000 < 0.01),表明fkein会对fcs产生显著的正向影响关系;efp的回归系数值为−0.002(t = −6.119,P = 0.000 < 0.01)。
同样,采用ARIMA模型对fcs各因素影响的滞后性进行分析,具体结果见表6。
表 6 fcs的ARIMA(1,1,0)模型参数Table 6. Parameters of ARIMA(1,1,0) model of fcs项目
Item符号
Symbol系数
Coefficient标准误
Standard errorz p 95% CI 常数
Constantc 0.071 0.044 1.618 0.106 −0.015 ~ 0.157 AR参数
AR parameterα1 0.800 0.092 8.681 0 0.619 ~ 0.981 在分析中,AIC值 = −107.335,贝叶斯信息准则值(BIC) = −102.194。针对fcs,结合AIC值越低越好的信息准则,通过SPSSAU自动对多个潜在备选模型进行建模和对比选择,最终找出最优模型为:ARMA(1,1,0),其模型公式为:y(t) = 0.071 + 0.800·y(t − 1)。因此,自回归阶数p为1,差分阶数d为1,移动平均阶数q为0,也说明各因素对森林碳汇的影响滞后期为1。
另外,针对fcs,进行一阶差分后数据ADF检验(单位根检验),结果显示P = 0.020 < 0.05,有高于95%的把握拒绝原假设,此时序列平稳。也进一步说明fcs的滞后期为1。
3.2 森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合度分析
耦合协调度更好的反映了森林碳汇和林业经济发展变化的整合功效。在耦合协调度模型和所收集数据的基础上,计算森林碳汇和林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度。
3.2.1 frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度
采用SPSSAU软件计算的frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度如表7所示。
表 7 frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度计算结果Table 7. Calculation results of coupling coordination degree between frcs and forestry economic development and change年份
Year耦合度
Coupling degree (C)协调指数
Coordination index (T)耦合协调度
Coupling coordination
degree (D)协调等级
Coordination level耦合协调程度
Degree of coupling
coordination1992 1.000 0.010 0.100 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1993 0.975 0.017 0.127 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1994 0.943 0.024 0.150 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1995 0.905 0.031 0.167 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1996 0.904 0.039 0.188 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1997 0.917 0.046 0.206 3 中度失调 Moderate imbalance 1998 0.935 0.052 0.221 3 中度失调 Moderate imbalance 1999 0.945 0.086 0.285 3 中度失调 Moderate imbalance 2000 0.954 0.115 0.331 4 轻度失调 Mild imbalance 2001 0.931 0.150 0.373 4 轻度失调 Mild imbalance 2002 0.908 0.204 0.431 5 濒临失调 On the verge of imbalance 2003 0.894 0.255 0.477 5 濒临失调 On the verge of imbalance 2004 0.907 0.276 0.500 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2005 0.924 0.298 0.525 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2006 0.946 0.315 0.546 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2007 0.975 0.351 0.585 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2008 0.977 0.421 0.641 7 初级协调 Primary coordination 2009 0.970 0.504 0.699 7 初级协调 Primary coordination 2010 0.988 0.527 0.722 8 中级协调 Intermediate coordination 2011 0.990 0.596 0.768 8 中级协调 Intermediate coordination 2012 0.992 0.655 0.806 9 良好协调 Good coordination 2013 0.990 0.715 0.842 9 良好协调 Good coordination 2014 0.990 0.801 0.891 9 良好协调 Good coordination 2015 0.991 0.865 0.926 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2016 0.998 0.878 0.936 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2017 0.999 0.935 0.966 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2018 1.000 0.990 0.995 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 在frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度计算中,针对不同年份耦合协调度进行区间化处理,区间化处理后数据全部介于0 ~ 1之间,然后进行耦合协调度计算。
由表7的计算结果可以看出:frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度由1992年的“严重失调”,上升到2018年的“优质协调”,虽然中间有所波动,但整体上处于上升趋势。耦合协调度D值和协调等级也由1992年的0.1和协调等级2,分别上升到2018年的0.995和协调等级10。因此,从计算结果可以看出:从1992—2018年,我国的森林碳储量与林业经济发展是耦合协调的,耦合协调度也是不断上升的,年均增长约9.24%,协调等级也由2上升到10。
3.2.2 fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度
同样,计算1992—2018年的森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度如表8所示。
表 8 fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度计算结果Table 8. Calculation results of coupling coordination degree between fcs and forestry economic development and change年份
Year耦合度
Coupling degree (C)协调指数
Coordination index
(T )耦合协调度
Coupling coordination
degree (D)协调等级
Coordination level耦合协调程度
Degree of coupling
coordination1993 1.000 0.010 0.100 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1994 0.960 0.016 0.123 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1995 0.910 0.021 0.139 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1996 0.953 0.023 0.146 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1997 0.945 0.027 0.158 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1998 0.969 0.027 0.162 2 严重失调 Serious imbalance 1999 0.893 0.071 0.251 3 中度失调 Moderate imbalance 2000 0.836 0.107 0.299 3 中度失调 Moderate imbalance 2001 0.778 0.149 0.341 4 轻度失调 Mild imbalanc 2002 0.746 0.208 0.394 4 轻度失调 Mild imbalanc 2003 0.757 0.268 0.450 5 濒临失调 On the verge of imbalance 2004 0.812 0.287 0.482 5 濒临失调 On the verge of imbalance 2005 0.859 0.305 0.512 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2006 0.906 0.324 0.542 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2007 0.929 0.342 0.564 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2008 0.924 0.374 0.588 6 勉强协调 Barely coordination 2009 0.924 0.437 0.636 7 初级协调 Primary coordination 2010 0.958 0.487 0.683 7 初级协调 Primary coordination 2011 0.970 0.575 0.747 8 中级协调 Intermediate coordination 2012 0.987 0.627 0.787 8 中级协调 Intermediate coordination 2013 0.992 0.687 0.826 9 良好协调 Good coordination 2014 0.990 0.797 0.888 9 良好协调 Good coordination 2015 0.994 0.857 0.923 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2016 0.999 0.879 0.937 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2017 0.999 0.937 0.968 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 2018 1.000 0.990 0.995 10 优质协调 High quality coordination 计算中,由于森林碳汇是森林碳储量的变化量,因此起始年份为1993年,终止年份为2018年。根据耦合协调度的计算公式,耦合度C值越大,说明系统间的相互作用越大;耦合协调度D值越大,说明系统间协调程度越高。耦合协调度D值一般介于0 ~ 1之间。
同样,由表8的计算结果可以看出:fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度由1993年的“严重失调”,上升到2018年的“优质协调”,虽然中间经历了“中度失调”“轻度失调”“勉强协调”“初级协调”等过程,但整体趋势是上升的。耦合协调度D值和协调等级也由1993年的0.1、协调等级2,分别上升到2018年的0.995、协调等级10级。因此,从计算结果可以看出:从1993—2018年,我国的森林碳汇与林业经济发展是耦合协调的,耦合协调度也是稳步上升的,年均增长9.63%。
4. 森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度预测
碳达峰碳中和已成为我国未来的发展战略,因此,森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度直接关系到我国“双碳”目标的实现。
本研究采用指数平滑法预测森林碳储量(frcs)与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度。指数平滑法适用于数据中短期预测,分为一次平滑法、二次平滑法和三次平滑法(Holt-Winters)。预测中,当序列个数小于20时,一般采用最初多期数据的平均值作为初始值;序列个数大于20时,一般采用第1期数据作为初始值;另外,平滑系数α值一般介于0 ~ 1之间,如果数据波动大,则α值在0.6 ~ 0.8之间,反之数据波动较小时,α值一般选取0.1 ~ 0.5的较小值。本研究更多的考虑森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度的趋势性,采用二次平滑法进行预测。具体到本研究,针对数据序列大于20个和初始值S0,特设置第1期数据作为初始值,寻找的最佳的模型参数分别是:初始值为0.100,α值为0.800,平滑类型为二次平滑,此时RMSE值为0.017。并以此参数进行模型构建从而得到数据预测值。指数平滑预测的frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度如表9所示。
表 9 frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度预测值Table 9. Predicted values of coupling coordination degree between frcs and forestry economic development and change年份
Year原始值
Original value预测值
Predicted value绝对误差
Absolute error1992 0.100 0.100 0.000 1993 0.127 0.100 0.027 1994 0.150 0.143 0.007 1995 0.167 0.171 0.004 1996 0.188 0.186 0.002 1997 0.206 0.208 0.002 1998 0.221 0.225 0.004 1999 0.285 0.237 0.048 2000 0.331 0.330 0.001 2001 0.373 0.378 0.005 2002 0.431 0.417 0.014 2003 0.477 0.483 0.006 2004 0.500 0.526 0.026 2005 0.525 0.533 0.008 2006 0.546 0.552 0.006 2007 0.585 0.569 0.016 2008 0.641 0.617 0.024 2009 0.699 0.688 0.011 2010 0.722 0.754 0.032 2011 0.768 0.758 0.010 2012 0.806 0.809 0.003 2013 0.842 0.846 0.004 2014 0.891 0.879 0.012 2015 0.926 0.935 0.009 2016 0.936 0.965 0.029 2017 0.966 0.957 0.009 2018 0.995 0.991 0.004 2019 1.023 2020 1.051 2021 1.079 2022 1.107 2023 1.135 2024 1.163 2025 1.191 2026 1.219 2027 1.247 2028 1.275 2029 1.303 2030 1.331 由表9的预测结果可以看出:从2018—2030年,frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度是缓慢增加的,年增长速度为2.49%。由于2019—2030年的耦合协调度大于1,不符合耦合协调度的取值范围,因此,经过归一化处理后,预测的2019—2030年frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度、协调等级和耦合协调程度如表10所示。
表 10 2019—2030年归一化处理后的frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度、协调等级和耦合协调程度Table 10. Coupling coordination degree, coordination level and coupling coordination degree of normalized frcs and forestry economic development and change from 2019 to 2030年份
Year耦合协调度
Coupling coordination
degree (D)协调等级
Coordination level耦合协调程度
Degree of coupling coordination2019 0.991 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2020 0.992 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2021 0.993 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2022 0.994 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2023 0.994 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2024 0.995 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2025 0.996 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2026 0.997 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2027 0.997 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2028 0.998 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2029 0.999 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2030 1.000 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination从表10的预测结果可以看出:按照目前森林碳储量和林业经济的发展趋势,2019—2030年,frcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度D值一直处于缓慢增加阶段,二者的协调等级也为10级,耦合协调程度也属于“优质协调”阶段。因此,维持目前良好的林业经济发展势头,提高森林资源经营管理水平和生产力,有助于促进frcs与林业经济的耦合协调发展。
同样,采用指数平滑法对2018—2030年森林碳汇与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度进行预测,再经过归一化处理后的预测结果如表11所示。从表11的预测结果也可以看出:2019—2030年,fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度D值一直处于缓慢增加阶段,二者的协调等级也为10级,耦合协调程度也属于“优质协调”阶段。fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度的变化趋势与frcs与林业经济的耦合协调度的发展变化趋势相同,进一步说明了森林碳储量、森林碳汇量是密切相关的,且提高森林资源经营管理水平和生产力,有利于提高二者的耦合协调度。frcs、fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度预测如图1所示。
表 11 2019—2030年归一化处理后的fcs与林业经济发展变化的耦合协调度、协调等级和耦合协调程度Table 11. Coupling coordination degree, coordination level and coupling coordination degree of normalized fcs and forestry economic development and change from 2019 to 2030年份
Year耦合协调度
Coupling coordination
degree (D)协调等级
Coordination level耦合协调程度
Degree of coupling coordination2019 0.997 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2020 0.997 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2021 0.997 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2022 0.998 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2023 0.998 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2024 0.998 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2025 0.998 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2026 0.999 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2027 0.999 3 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2028 0.999 5 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2029 0.999 8 10 优质协调
High quality coordination2030 1.000 0 10 优质协调
High quality coordination5. 结论与讨论
耦合度协调度反映的是系统间相互依赖、相互影响的程度。耦合度协调度也反映了系统的整体功效,是对系统发展水平的综合评价。森林固碳是减少工业温室气体排放的重要途径,也是我国发展绿色低碳经济的最佳选择。森林碳汇的大小与森林资源的面积、蓄积等密切相关,也与林业经济发展、社会发展等因素密切相关。本研究开展森林碳汇与经济发展变化的耦合研究,主要目的是寻求森林碳汇与林业经济发展的长期共生关系,提高二者生产的增值性和未来发展的共生模式,进而提高我国森林资源的配置效率、优化林业产业体系和推动林业经济发展。研究得出的主要结论为:
(1)生态建设与保护投资、林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额、GDP和林产品进口额对森林资源碳储量有显著影响,其中林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额和GDP为正向影响,生态建设与保护投资和林产品进口额为负向影响,林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额的影响作用最大。林业产业总产值、林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额、林产品出口额对森林碳汇量有显著影响,其中林业产业总产值、林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额为正向影响,林产品出口额为负向影响,且林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额的影响最大。因此,无论从碳储量还是碳汇量来看,研究发现林业重点生态工程实际完成投资额对二者都有显著的影响,且都是重要的影响因素,也充分说明了林业重点生态工程建设对我国“双碳”目标的实现有重要的作用。
(2)森林资源碳储量、森林碳汇量的作用存在一定滞后性。研究表明:无论是其他因素对森林资源碳储量、森林碳汇量的作用,还是森林资源碳储量、森林碳汇量对其他因素的影响,均存在一定的滞后性。其中森林资源碳储量的滞后期为2年,森林碳汇量的滞后期为1年。二者也均通过了AIC、BIC和ADF的检验,说明存在滞后性作用。因此,在森林碳汇投资时,应提前做好部署,并做好森林资源经营管理和时间优化。
(3)1992—2018年,我国森林资源碳储量、森林碳汇量与林业经济发展的耦合度协调度是逐步上升的。其中,森林资源碳储量与林业经济发展的耦合度协调度年均增长9.24%,虽然中间有所波动,但耦合协调度由1992年的“严重失调”,上升到2018年的“优质协调”,协调等级也由1992年的2级,上升到2018年的10级;1993—2018年,森林碳汇量与林业经济发展的耦合度协调度年均增长9.63%,增长速度稍快于森林资源碳储量与林业经济发展的耦合协调度年均增长速度。耦合协调程度也由1993年的“严重失调”,上升到2018年的“优质协调”,协调等级也由1993年的2级,上升到2018年的10级。
(4)从长期变化趋势来看,预测表明:无论是森林资源碳储量与林业经济发展的耦合协调度,还是森林碳汇量与林业经济发展的耦合度协调度,均是增加的,并长期维持在“优质协调”的水平和10级上。2019—2030年,二者的耦合协调度D值均接近于1,协调等级也长期为10,耦合协调程度也长期保持在“优质协调”水平上。因此,如何提高经营管理水平,并维持目前的森林资源增加态势,是我国实现“双碳”目标的关键,也是我国森林确保落实“双碳”战略目标承诺的基础条件。为此,应不断优化林业产业结构,提高森林生产力,确保森林资源的不断增加。
另外,耦合协调度反映的是事物的协调发展水平,也反映的是系统间的相互影响和作用[31]。森林碳汇与林业经济发展之间存在很强的相关性。相关研究表明,二者之间的相关系数高达0.99以上[32],但森林碳汇与经济增长的长期互动关系及其影响机制尚不明确[33]。因此,有必要对下列问题展开讨论:
(1)森林碳汇对林业经济有滞后性作用。森林碳汇主要通过森林植被吸收大气中的CO2,并把碳固定在有关器官中;而林业经济主要是通过对森林资源的土地、劳动力和资金等投入,以产出木材、林副产品和生态、社会效益等过程。从劳动力、资金等投入,到木材、林副产品和碳汇等产出,不是立即能产生作用的,会有一定的滞后期。只有科学评估森林碳汇对林业经济作用的滞后作用,或林业经济对碳汇的滞后影响,才能有利于优化森林碳汇生产的过程的投入,也才能优化林业经济生产的组织形式等。本研究表明:我国森林碳储量对林业经济有2年的滞后作用,林业经济对森林碳汇有1年的滞后影响。因此,在森林碳汇生产投资中,应提前布局,整合优化整个生产过程,推动森林碳汇和林业经济的优化发展。
(2)森林碳汇对林业经济有重要的溢出效应。通过逐步回归研究发现,森林碳汇对林业产值、GDP等有重要的正向影响作用,说明森林碳汇对林业经济存在重要的溢出效应。实际上,相关研究表明:森林碳汇对经济增长,尤其是GDP增长的贡献作用高达2.035 8,说明在现阶段,森林碳汇平均每提高1个百分点,将拉动经济增长2.035 8个百分点[34],也反映出森林碳汇对经济增长的溢出效应是比较大的,有利于拉动经济增长。因此,推动和提高我国森林碳汇的发展,对推动我国经济发展是有一定作用的,在国家“双碳”目标的实施过程中,应加快我国森林碳汇的发展,进一步发挥林业经济的溢出效应。
(3)经济增长有利于森林碳汇的科技创新和进步。经济增长会促进技术进步,使产业结构、需求结构和地区结构等更加合理和优化,并促进森林资源存量的增加,进而促进森林碳汇增加。另外,快速的经济发展使林产品需求结构由资源型消费转变为生态型消费,使人们对森林资源和林产品的认知也发生了变化,并影响人们的消费传统;同时,消费结构的变化促使林业产业逐步变得高级化和合理化,也进一步促进了林业科技创新和技术进步,减少森林资源消耗,增加森林面积和森林蓄积量,进而促进了森林碳汇的发展[35],促进了“双碳”目标的实现。
(4)耦合协调度的不断提高有利于促进林业产业的协同进化。林业产业的生产经营对象是森林资源,在生产中独立的经济组织是企业,不同企业间共同的生产经营对象—森林资源,不仅增加了企业的效益,又推动了产业的发展。因此,森林资源或森林碳汇与林业企业很容易形成共生体[31],也十分符合产业共生理论的特质。因此,耦合协调度的不断提高,有利于促进林业产业的协同进化,也有利于直接或间接促进森林资源配置效率的提高和产业的发展[36]。
-
表 1 传统绿道技术经济指标
Table 1 Technical and economic index of traditional greenway
项目类型
Item type子项目
Subitem工程量
Engineering quantity/m2总量
Total/m2比例
Proportion/%绿地Green space 普通绿地Common green space 273 838 273 838 59.38 水体Water space 蓄水池Cistern 7 234 55 387 12.01 行洪沟Flood ditch 48 153 建筑Structure 建筑Structure 998 998 0.22 道路广场Path and square 透水铺装Permeable pavement 97 277 130 971 28.40 不透水铺装Impermeable pavement 33 694 合计Total 461 194 461 194 100.00 表 2 海绵绿道技术经济指标
Table 2 Technical and economic index of sponge greenway
项目类型
Item type子项目
Subitem工程量
Engineering quantity/m2总量
Total/m2比例
Proportion/%绿地Green space 普通绿地Common green space 247 848 273 838 59.38 植草沟Vegetative swale 8 673 雨水湿地Stormwater wetland 3 102 下沉式绿地Concave green land 14 215 水体Water space 蓄水池Cistern 7 234 55 387 12.01 景观水体Landscape water 48 153 建筑Structure 建筑Structure 998 998 0.22 道路广场Path and square 透水铺装Permeable pavement 97 277 130 971 28.40 不透水铺装Impermeable pavement 33 694 合计Total 461 194 461 194 100.00 表 3 不同降雨强度下的出水口径流量模拟结果
Table 3 Simulated results of runoff under different rainfall intensities
模拟项目Simulation item 5年一遇1 h
Once 5-year, 1 hour10年一遇1 h
Once 10-year, 1 hour20年一遇1 h
Once 20-year, 1 hour50年一遇1 h
Once 50-year, 1 hourLID开发模式
LID development
model传统开发模式
Traditional development
mode差值
Difference
valueLID开发模式
LID development
model传统开发模式
Traditional
development
mode差值
Difference
valueLID开发模式
LID development
model传统开发模式
Traditional
development
mode差值
Difference
valueLID开发模式
LID development
model传统开发模式
Traditional development
mode差值
Difference
value径流总量Total runoff/L 0 10 170 000 10 170 000 0 26 220 000 26 220 000 0 52 690 000 52 960 000 356 000 106 525 000 106 169 000 峰值流量Peak flow/(L·s-1) 0 713.83 713.83 0 2 014.14 2 014.14 0 3 905.96 3 905.96 707.33 7 724.26 7 017.26 峰现时间Time of peak flow occurrence 消失Elimination 03:09 消失Elimination 03:34 消失Elimination 02:44 09:07 02:05 302 min -
[1] 崔广柏, 张其成, 湛忠宇, 等.海绵城市建设研究进展与若干问题探讨[J].水资源保护, 2016, 32(2): 1-4. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szybh201602001 CUI G B, ZHANG Q C, ZHAN Z Y, et al. Research progress and discussion of sponge city construction[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2016, 32(2): 1-4. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szybh201602001
[2] 张海行.海绵城市低影响开发典型山城径流效应研究[D].邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10076-1016180082.htm ZHANG H X. Low impact development of the sponge cities: the research of the typical mountain runoff effect[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10076-1016180082.htm
[3] 富可荣, 余海燕, 李文君, 等.海河流域山洪灾害成因特点分析[J].海河水利, 2012(6): 29-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hhsl201206012 FU K R, YU H Y, LI W J, et al. Analysis of the causes of mountain flood disaster in Haihe River Basin[J]. Haihe Water Resources, 2012(6): 29-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hhsl201206012
[4] 冯艺佳.风景园林视角下的北京市浅山区绿色空间理想格局构建策略研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1016139952.htm FENG Y J. Study on the ideal pattern construction strategy of green spacein shallow mountain area of Beijing through the view of landscape architecture[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1016139952.htm
[5] 林耀明.华北地区的水资源和利用[J].科学对社会的影响, 1995(1): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjjn200811017 LIN Y M. Water resources and utilization in North China[J]. Impact of Science On Society, 1995(1): 36-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjjn200811017
[6] 马晓波.华北地区水资源的气候特征[J].高原气象, 1999, 18(4): 520-524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.1999.04.006 MA X B. Climate characteristics of water resources in North China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 1999, 18(4): 520-524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.1999.04.006
[7] 吴燕娟.气候变化背景下我国极端降水的时空分布特征和未来预估[D].上海: 上海师范大学, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10270-1016126128.htm WU Y J. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and future prediction of extreme precipitation in China under the background of climate change[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10270-1016126128.htm
[8] 常汉林, 于清涛.河北省山洪灾害及防御对策[J].河北水利, 2003(7): 9-10, 3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200301518046 CHANG H L, YU Q T. Mountain torrents disaster and defensive countermeasures in Hebei[J]. Hebei Water Conservancy, 2003(7): 9-10, 3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200301518046
[9] GHIMIRE S K, HIGAKI D, BHATTARAI T P. Estimation of soil erosion rates and eroded sediment in a degraded catchment of the Siwalik Hills, Nepal[J]. Land, 2013, 2(3): 370-391. doi: 10.3390/land2030370
[10] 王强.游憩导向的秦岭北麓区西安段山麓型绿道规划设计方法研究[D].西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10703-1015036417.htm WANG Q. Recreation-oriented research of the methods of planning and fesign for piedmont area-greenway of Qinling piedmont, Xi'an section[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10703-1015036417.htm
[11] 陈婷.山地城市绿道系统规划设计研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-1012049917.htm CHEN T. The research of urban greenway system planning and design in mountain city[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-1012049917.htm
[12] 俞孔坚, 李迪华, 袁弘, 等. "海绵城市"理论与实践[J].城市规划, 2015, 39(6): 26-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/csgh201506004 YU K J, LI D H, YUAN H, et al. "Sponge City" theory and practice[J]. City Planning Review, 2015, 39(6): 26-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/csgh201506004
[13] HOUDESHEL C D, POMEROY C A, HARI L, et al. Cost-estimating tools for low-impact development best management practices: challenges, limitations, and implications[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2010, 137(3): 183-189. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=043f5e698c9cdf226598b8141b6e2891&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] BRONSON H C. Silviculture best management practices[M]. Tallahassee:Florida Department of Argiculture and Consumer Services, 2008.
[15] ROUSE D C, BUNSTER-OSSA I F. Green infrastructure: a landscape approach[M]. London:Routledge, 2013.
[16] 吴彦强, 吴正旺.基于低影响开发(LID)的城市绿道雨洪设计[J].城市建筑, 2015(36): 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0232.2015.36.020 WU Y Q, WU Z W. Urban greenway stormwater design based on low impact development (LID)[J]. Urbanism and Architecture, 2015(36): 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0232.2015.36.020
[17] 黄俊杰, 沈庆然, 李田.植草沟对道路径流的水文控制效果研究[J].中国给水排水, 2016(3): 118-122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjsps201603027 HUANG J J, SHEN Q R, LI T. Study on hydrological effect of grass swales on road runoff[J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2016(3): 118-122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjsps201603027
[18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.绿道规划设计导则[R].北京: 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 2016. Ministry of Housing and Construction Rural Development. Guidelines for greenway planning and design[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Housing and Construction Rural Development, 2016.
[19] 刘家琳, 张建林.雨水径流控制的景观设计途径及在公园绿地中的应用分析[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015(11): 183-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnnydxxb201511027 LIU J L, ZHANG J L. Landscape design approach to stormwater runoff control and a case study of urban park[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2015(11): 183-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnnydxxb201511027
[20] 王佳, 王春连, 吴珊珊.基于海绵城市理念的雨水湿地设计及应用[J].北方园艺, 2017(19): 104-111. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bfyany201719021 WANG J, WANG C L, WU S S. Design and application of stormwater wetland based the sponge city concepton[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017(19): 104-111. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bfyany201719021
[21] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.海绵城市建设技术指南: 低影响开发雨水系统构建[R].北京: 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 2014. Ministry of Housing and Construction Rural Development. Technical guideline for sponge city construction : construction of rainwater system with low impact development[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Housing and Construction Rural Development, 2014.
[22] 陈垚, 杨威, 王健斌, 等.雨水生物滞留设施中植被的设计与养护[J].中国给水排水, 2017(12): 6-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjsps201712002 CHEN Y, YANG W, WANG J B, et al. Design and maintenance of vegetation in bioretention facilities[J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2017(12): 6-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjsps201712002
[23] 李秀彬, 马志尊, 姚孝友, 等.北方土石山区水土流失现状与综合治理对策[J].中国水土保持科学, 2008, 6(1): 9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.01.002 LI X B, MA Z Z, YAO X Y, et al. Current status and comprehensive control strategies of soil erosin for rocky mountain areas the Northern China[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 6(1): 9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.01.002
[24] 王利民, 翁伯琦, 罗涛, 等.山地水土流失的影响因素及其若干机理[J].安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(19): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.19.024 WANG L M, WENG B Q, LUO T, et al. Influencing factors and mechanisms of soil erosion in mountainous areas[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(19): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.19.024
[25] 夏长华.深厚杂填土地基处理应用研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2008068354.htm XIA C H. Application research on the ground treatment of thick miscellaneous fill[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2008068354.htm
[26] 樊登星, 余新晓, 贾国栋, 等.北京山区灌草坡面水土流失特征及其影响因素[J].中国水土保持科学, 2014, 12(2): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2014.02.004 FAN D X, YU X X, JIA G D, et al. Characteristics of soil and water loss and its influencing factors on slope scale in rocky mountain area of Beijing[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 12(2): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2014.02.004
[27] 王佳, 王思思, 车伍.低影响开发与绿色雨水基础设施的植物选择与设计[J].中国给水排水, 2012, 28(21): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2012.21.013 WANG J, WANG S S, CHE W. Plant selection and design of LID and GSI[J]. China Water & Waste Water, 2012, 28(21): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2012.21.013
[28] 林辰松, 邵明, 葛韵宇, 等.基于SWMM情境模拟的外源雨水型公园绿地雨洪调控效果研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(12): 92-103. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160260 LIN C S, SHAO M, GE Y Y, et al. Research of storm flood regulation efficiency of the low impact development of exogenous-rainwater park based on the SWMM simulation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(12): 92-103. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160260
[29] 戈晓宇, 李雄.基于海绵城市建设指引的迁安市集雨型绿色基础设施体系构建策略初探[J].风景园林, 2016(3): 27-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjyl201603005 GE X Y, LI X. Research on building of rainwater-harvesting green infrastructure pattern of Qian'an based on the instruction of sponge city construction[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2016(3): 27-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fjyl201603005
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 岳庆敏,何怀江,张春雨,赵秀海,郝珉辉. 阔叶红松林林木与林分生长对采伐干扰的响应. 生态学报. 2024(05): 2019-2028 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王浩东,陈梦,袁丛军,何爽,丁访军,杨瑞. 马尾松纯林阔叶化改造对土壤碳氮固持的短期效应. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2024(10): 126-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李大勇. 采伐强度对木兰围场国有林场针阔混交林碳储量的影响. 中国林副特产. 2024(06): 15-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)











 下载:
下载: