Tomography imaging algorithm based on velocity error correction for stress wave nondestructive evaluation of wood
-
摘要:目的应力波断层成像技术已经在林木无损检测领域得到了广泛的应用, 然而木材的各向异性特征以及应力波速度反演计算的误差对断层成像的精度影响较大。因此,进一步提高断层图像的准确性非常关键。方法根据传统的应力波速度反演原理, 提出了一种基于速度误差校正的断层成像算法(ECIA)。该算法利用最小二乘QR分解法(LSQR)计算应力波在林木横截面网格单元内的速度分布, 并使用误差校正机制(ECM)优化断层图像。为了评估算法的性能, 分别选取了若干实验室内的原木试样及扬州市区古树进行无损检测实验, 利用德国PICUS应力波断层成像仪获取的应力波传播数据实现了ECIA算法, 生成了各实验样本的断层图像。结果ECIA算法较为精确地检测出了原木及活树中缺陷区域的位置及大小, 尤其在活树的健康检测中, ECIA算法对于缺陷区域尤其是轻微腐朽区域的检测精度高于PICUS检测仪。结论ECIA算法能够产生较为准确的林木断层图像,适用于林木应力波无损检测。Abstract:ObjectiveStress wave tomography imaging technology has been popularly applied in wood nondestructive evaluation for many years. However, the anisotropy property of wood and the error of stress wave velocity inversion have great impact on the accuracy of tomography imaging. Therefore, it is important to improve the accuracy of the tomography image.MethodBased on the traditional stress wave velocity inversion principle, this paper proposes a tomography imaging algorithm (ECIA) with velocity error correction mechanism. The proposed algorithm computes the wave velocity distribution of the grid cells of the wood cross-section by the least square QR decomposition (LSQR) iterative inversion, and then optimizes the tomography with a velocity error correction mechanism (ECM). To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, several healthy and defective logs and ancient live trees in Yangzhou City of Jiangsu Province, southern China were selected as experimental samples, and the nondestructive testing procedures were finished. With the stress wave velocity data sets measured by PICUS equipment, ECIA algorithm was implemented, and the tomography images of log samples and live trees were generated.ResultECIA algorithm detected the decay area accurately for log samples and live tree samples. ECIA algorithm had a higher accuracy than PICUS especially for the slight decay.ConclusionECIA algorithm can generate accurately tomography images and be used for wood nondestructive evaluation.
-
无损检测对于发现林木内部缺陷,防止腐朽扩散,提高木材利用率具有重要意义。应力波无损检测技术具有成本低,操作方便,无辐射,不受被测木材的大小形状影响等优点,已经在林木无损检测中得到了广泛的应用。应力波无损检测技术通过测量应力波在树木横截面中多个传播方向的传播时间,然后反演计算应力波在内部单元的传播速度,并生成木材的断层图像,从而准确、直观地检测到木材内部缺陷大小与位置[1]。国内外关于木材应力波无损检测技术的研究已有大量成果。Dikrallah等[2]通过实验分析了湿材的声学各向异性,研究了应力波速度与方向角之间的数学关系。梁善庆等[3]与美国农业部林产品实验室合作,将弹性波断层成像技术运用到活树的检测,结果表明该技术能够直观显示活树内部腐朽位置、大小、形状和严重程度。杨学春等[4]对林木内部的应力波传播规律进行了研究,建立了相关的波动方程及其数值求解模型。Li等[5]研究了健康树木横截面内部的应力波传播速度变化规律,建立了数学模型,利用美国黑樱桃树(Prunus serotina)的无损检测实验结果验证了该模型的有效性。Socco等[6]提出了一种较为复杂的数据处理方法用于对活树的健康监测,并在地震波图像算法的基础上研究了一种反演算法用来生成树干的应力波传播时间图像,该算法对一些小的缺陷(如小空洞)不敏感,而且没有很好地考虑木材的各向异性问题。Du等[7]在考虑木材各向异性的基础上,提出了一种改进型的椭圆空间插值方法,并利用速度补偿获得更精确的空间插值数据,该方法能够有效抵抗由于缺陷区域密度变化引起的信号干扰。目前,国际市场上已有不少林木应力波断层成像检测设备(例如,匈牙利产的FAKOPP,德国产的PiCUS Sonic Tomograph和Arbotom),均能够生成木材横截面的二维或三维断层图像,但成像效果和检测精度仍然有待改善[8]。
为了进一步提高林木应力波断层图像的准确性,提出了一种应力波速度反演的误差校正机制(ECM)。在此基础上,利用最小二乘QR分解法(LSQR)设计了一种新的林木应力波无损检测断层成像算法(ECIA),并且利用大量的真实样本实验验证了该算法的有效性。
1. 应力波速度模型及反演过程
介绍应力波在健康树木中的传播速度模型及无损检测基本思想,并描述林木无损检测断层成像的速度反演过程。
1.1 应力波在健康树木中的传播速度模型
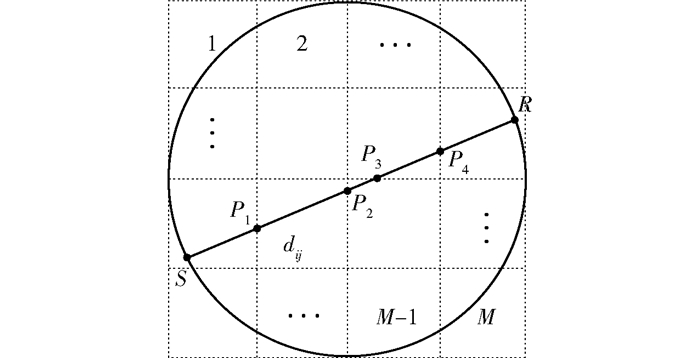
为简单起见,我们将树干视为一个圆柱体,其横截面为正圆形,如图 1所示,其中S代表应力波发射端传感器的位置,R1和R2代表应力波接收端传感器的位置。在检测过程中,通过脉冲锤敲击发射端,产生应力波,并从发射端传播到接收端。检测仪测量发射端与接收端传感器之间的应力波的传播时间。SR2代表应力波沿直径的传播路径,其传播速度称为径向传播速度,用VR表示。SR1代表应力波沿与直径成β角的弦的传播路径,其传播速度称为弦向传播速度,用VT表示[9]。通常在健康树木中,应力波的径向传播速度最快,并且随着弦向角β的增大,传播速度会变慢。Li等[5]通过研究建立了应力波在健康树木中的速度模型:
VT/VR≈1−0.2β2 (1) ![]() 图 1 树木横截面内应力波传播示意图S代表应力波发射端传感器的位置,R1和R2代表应力波接收端传感器的位置;VR、VT分别表示径向传播速度和弦向传播速度;β表示弦向角。Figure 1. Stress wave propagation in the cross-section of tree trunkS is a source sensor, and R1 and R2 are receiver sensors. VT is the tangential velocity and VR is the radial velocity. β is the angle between radial direction and tangential direction.
图 1 树木横截面内应力波传播示意图S代表应力波发射端传感器的位置,R1和R2代表应力波接收端传感器的位置;VR、VT分别表示径向传播速度和弦向传播速度;β表示弦向角。Figure 1. Stress wave propagation in the cross-section of tree trunkS is a source sensor, and R1 and R2 are receiver sensors. VT is the tangential velocity and VR is the radial velocity. β is the angle between radial direction and tangential direction.式中:VT/VR表示弦向传播速度和径向传播速度的比值,β表示弦向角。
树木产生腐朽或空洞往往从内部开始,树干外层材质相对而言更健康,所以实际检测过程中,经常使用各相邻传感器之间的应力波传播速度平均值作为健康参考值,并根据公式(1)计算横截面内任意方向的参考速度Vref[10]。对任意的传播路径,将实际测量得到的传播速度Vtest和参考传播速度Vref进行比较,可以初步判断该路径是否存在缺陷。根据国内外学者的研究经验[1],若Vtest和Vref的比值小于0.9,可以认为该路径存在缺陷。
1.2 速度反演原理及LSQR迭代算法
速度反演是指根据检测仪测量得到的不同传播路径上的应力波平均速度,反演计算应力波在横截面内不同单元的速度分布的过程[11]。目前大多数的木材断层成像反演算法都是基于地震波传播的模拟算法[12]。
如图 2所示,反演算法需将树干横截面划分为若干网格单元,且每个网格单元内需要至少有一条路径穿过。从S到R为一条应力波传播路径,该路径的传播时间t可以用慢度p(速度的倒数)从起点S到终点R的线积分表示:
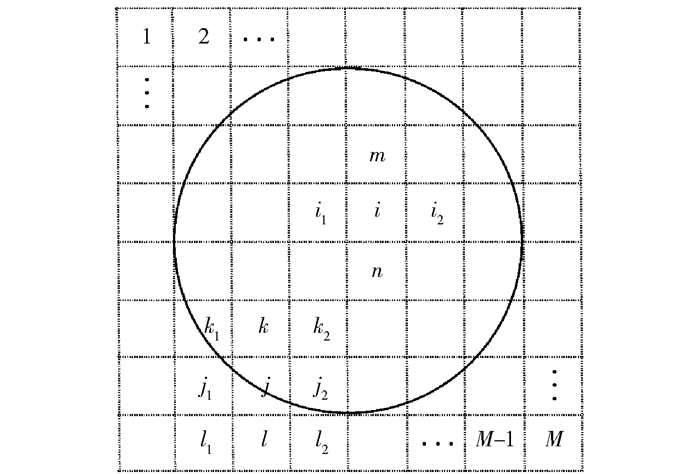
t=∫RSpdl (2) ![]() 图 2 树木横截面网格单元划分示意图S、R分别代表应力波发射端传感器和应力波接收端传感器的位置;1, 2, …, M代表网格单元编号;P1, P2, P3, P4代表传播路径与网格单元的交点;dij代表第i条路径被第j个网格单元分割的距离。Figure 2. Grid cells of a cross-section of a tree trunkS is a source sensor, and R is a receiver sensor. 1, 2, …, M represent the No. of grid cells. P1, P2, P3, P4 mean the intersections of stress wave paths and grid cells. dij is segment intercepted by the ith wave path on the jth cell.
图 2 树木横截面网格单元划分示意图S、R分别代表应力波发射端传感器和应力波接收端传感器的位置;1, 2, …, M代表网格单元编号;P1, P2, P3, P4代表传播路径与网格单元的交点;dij代表第i条路径被第j个网格单元分割的距离。Figure 2. Grid cells of a cross-section of a tree trunkS is a source sensor, and R is a receiver sensor. 1, 2, …, M represent the No. of grid cells. P1, P2, P3, P4 mean the intersections of stress wave paths and grid cells. dij is segment intercepted by the ith wave path on the jth cell.式中:dl表示路径长度的增量,p是应力波的传播慢度(速度的倒数)。
为了计算慢度分布,把图 2所示的横截面划分为M个网格单元,从左上角第一个网格单元开始,自左上至右下依次编号,将连续函数p(x, y)近似成每个网格单元内离散的慢度分布。假定每个网格单元内的慢度不变,将式(2)离散表示为[13]:
ti=M∑j=1pjdij(i=1,2,⋯,N) (3) 式中:dij表示第i条路径被第j个网格单元分割的长度,N表示总的应力波传播路径数。式(3)可用矩阵的形式表示:
\mathit{\boldsymbol{T}}{\rm{ = }}\mathit{\boldsymbol{DP}} (4) 式中:T和P分别代表N×1的传播时间列向量和M×1的传播慢度列向量,D代表传播路径被网格单元分割的长度距离矩阵,其大小为N×M。
对于给定的T和D,只需要计算出慢度列向量P后就可以生成初步的断层图像。由于一条传播路径只会被少数几个网格单元分割,所以对于任意路径i在大多数网格单元中,被分割的路径长度dij的值是0,因此式(4)中的系数矩阵D通常是一个大型稀疏矩阵。LSQR方法是一种利用Lanczos迭代法求解最小二乘问题的方法,由于其计算量小,运用矩阵的稀疏性简化计算,因此十分适合求解大型稀疏矩阵问题[14]。
由于应力波检测仪的传感器数量有限,应力波传播路径总数N通常小于网格单元总数M,故矩阵D的行数小于列数,式(4)为欠定方程组[15]。欠定方程组有多个解,为了求欠定方程组的特解,LSQR需要先将系数矩阵D对角化[14, 16]。
\left\{ \begin{array}{l} \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\mathit{\boldsymbol{D}} = \mathit{\boldsymbol{UB}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}^{\rm{T}}}}\\ {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_k} = \left[ {{u_1}, {u_2}, \cdots , {u_k}} \right]}\\ {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}_k} = \left[ {{v_1}, {v_2}, \cdots , {v_k}} \right]} \end{array}\\ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}_k} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\alpha _1}}&{}&{}&{}\\ {{\beta _2}}&{{\alpha _2}}&{}&{}\\ {}&{{\beta _3}}& \ddots &{}\\ {}&{}& \ddots &{{\alpha _k}}\\ {}&{}&{}&{{\beta _{k + 1}}} \end{array}} \right] \end{array} \right. (5) 通过逐列对比,得到迭代关系式,利用此迭代方法实现矩阵D的下双对角分解。
\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}\left( {{\beta _1}{e_1}} \right) = b}\\ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{D}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}_k} = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}_k}}\\ {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{D}}^{\rm{T}}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}} = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}_k^{\rm{T}} + {\alpha _{k + 1}}{v_{k + 1}}\mathit{\boldsymbol{e}}_{k + 1}^{\rm{T}}} \end{array}} \right. (6) 式中:ek+1T表示n阶单位矩阵的第k+1行。同理,矩阵D可以分解为上双对角矩阵。系数矩阵对角化完成后,设:
\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{r_k} = b - \mathit{\boldsymbol{D}}{x_k}}\\ {{x_k} = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}{y_k}}\\ {{t_{k + 1}} = {\beta _1}{e_1} - {\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}_k}{y_k}} \end{array}} \right. (7) 联立式(6)和式(7)可得:
\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{r_k} = b - \mathit{\boldsymbol{D}}{x_k} = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}\left( {{\beta _1}{e_1}} \right) - \mathit{\boldsymbol{D}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}{y_k} = }\\ {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}\left( {{\beta _1}{e_1}} \right) - {\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}{\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}_k}{y_k} = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{U}}_{k + 1}}{t_{k + 1}}} \end{array} (8) 由于Uk+1是正交矩阵,所以通过QR方法解yk使‖tk+1‖取极小值,求解最小二乘问题min‖β1e1- Bkyk‖,通过反复迭代,最终会收敛于极小值,从而得到式(4)的最终解。
2. 基于误差校正机制的断层成像算法
2.1 误差校正机制
经过速度反演得到每个网格单元的速度分布后,树木内部的断层成像就可以初步生成了,但是Vtest和Vref的比值的阈值0.9仅是一个经验值,可能会造成实际情况和断层图像的偏差。提出一种速度误差校正机制,用来提高成像算法的精度。
以往的断层成像算法中[13],计算每个网格单元的传播速度Vtest和参考速度Vref后,通过计算两者的比值Vtest/Vref直接决定该网格单元是否存在缺陷区域:若比值小于0.9,则该网格单元标记为缺陷区域,否则标记为健康区域。这种评判标准有时会因为速度反演的不准确导致成像误差。事实上,树木内部的缺陷通常会从一个区域向其邻近的区域扩散,所以邻居网格单元之间的健康状况是互相关联的。提出了一种基于邻居网格单元的误差校正机制ECM,对反演得到的δ分布进行校正,用来减少上述的潜在误差。ECM分析由LSQR方法求出的每个网格单元的速度分布及其相应的Vtest和Vref比值δ分布(式9),对当前网格单元的δ值进行调整,从而减少误差。
{\delta _i} = {V_{{\rm{ test }}}}/{V_{{\rm{ ref }}}} (9) 式中:δi代表第i个网格单元的Vtest和Vref比值,全部网格单元的δ值构成δ分布(用向量R表示)。
由于ECM是基于邻居网格单元的δ值进行校正的,在横截面边缘的网格单元会产生位于横截面外部的邻居网格单元(如图 3中编号为1、2、M-1、和M的网格单元),称这种网格单元为虚拟单元。因此,不同于速度反演过程,在误差校正过程中,需要将包括虚拟单元在内的所有网格单元重新编号。由于虚拟单元内没有路径穿过,故将虚拟单元内的传播速度及参考速度均设置为0,其δ值为无穷大,但为了防止计算时产生数据异常,算法将其δ值校正为0。
完全处于横截面内部的网格单元以及与横截面边缘相交的网格单元统称为横截面单元,ECM对两种横截面单元应用了不同的校正策略。如图 3所示,对于完全处于横截面内部的第i个网格单元,只需要考虑其4个紧邻的网格单元(m,n,i1,i2)的δ值大小。对于第j个网格单元,其4个紧邻的网格单元中有虚拟单元l,此时需要考察包括其对角邻居单元在内的所有8个邻居单元(k1,k,k2,j1,j2,l1,l,l2)。这8个邻居单元中,第l1、l和l2个网格单元为虚拟单元,第k1、k、k2、j1和j2个网格单元为横截面单元,故将上述5个网格单元作为第j个网格单元的新邻居网格单元。
ECM是根据当前网格单元及其邻居网格单元的δ值,对其δ值进行校正,校正方案如式(10):
{\delta _i} = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} 1, \;\;\;\;s > l/2\\ 1, \;\;\;\;s = l/2且{\delta _i} > 0.9\\ 0, \;\;\;s = l/2且{\delta _i} \le 0.9\\ 0, \;\;\;\;s < l/2 \end{array} \right. (10) 式中:δi代表第i个网格单元的δ值,s代表其邻居网格单元中δ>0.9的个数,l代表邻居网格单元的数量。该校正机制从第一个网格单元开始,逐个扫描所有网络单元,并根据公式(10)进行校正。这个过程反复进行,直到所有网格单元的δ值保持稳定为止。ECM算法的误差校正过程如下所示:
算法名:ECM误差校正机制
输入:反演生成的δ分布(用向量R表示);
输出:误差校正后的δ分布(用向量R′表示);
开始:
1:do
2:for i=1,2,…,M do
3: if第i个网格单元的四邻域均为横截面单元
4: then l=4;
5: else
6: l=第i个网格单元的八邻域中横截面单元的个数;
7: end if
8: 根据式(10)对R进行误差校正,得到R′;
9:end for
10:if R′≠R
11: then flag=1;
12:else
13: flag=0;
14: end if
15: R=R′;
16:while(flag==1)
结束
2.2 断层成像算法
基于速度反演和误差校正机制设计了断层成像算法(ECIA)。算法将树干横截面模拟成一个正圆,通过检测仪器测量应力波在树木内部的传播速度,利用LSQR方法反演计算应力波在树干横截面各个网格单元内的速度分布,并使用ECM校正速度误差,最终生成树木横截面的断层图像。
ECIA算法步骤如下:
输入.传感器个数、树木横截面周长、应力波传播时间、传感器两两间距离。
输出.树木横截面断层图像
Step1.根据输入数据建立坐标系,模拟树木横截面,划分网格单元,计算每个网格单元内的参考速度。
Step2.计算应力波传播路径被网格单元分割的距离,得到距离矩阵D。
Step3.利用LSQR反演求解速度分布,并求相应的传播速度与参考速度的比值δ分布向量R。
Step4.调用ECM算法对δ分布向量R进行误差校正。
Step5.根据各网格单元的δ值进行颜色填充。
Step6.利用区域生长算法分割缺陷区域与健康区域,对缺陷区域边缘进行曲线拟合以优化图像。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 实验材料
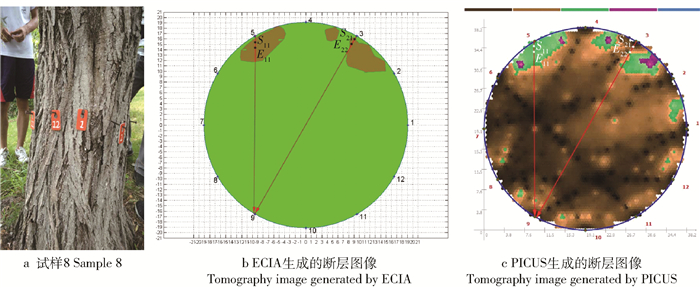
分别采用实验室原木和活树完成了两组无损检测成像实验。原木试样包括含空洞的柳杉(Cryptomeria fortunei,含水率11.5%)、含空洞的乌桕(Sapium sebiferum,含水率12.0%)和健康的柳杉(含水率12.5%)作为原木组实验对象,并分别记为试样1、2、3。此外,选取了江苏扬州市区6棵有内部缺陷的古树(香樟(Cinnamomum camphora)、枫香(Liquidambar formosana)、桑树(Morus alba)、圆柏(Sabina chinensis)、垂柳(Salix babylonica)、圆柏)作为实验对象,分别编号为试样4, 5, …, 9。实地检测的场景如图 4所示。实验过程中使用德国生产的PICUS应力波断层成像仪采集应力波传播数据,使用国产泰克曼TM410木材水分仪测量原木试样的含水率。除此之外,实验中还使用了Resistograph微钻阻力测试仪测量树木内部的阻力值,作为评估活树内部缺陷大小及位置的参考标准,从而验证成像算法的准确性。
3.2 原木的成像结果
利用PICUS对3个原木试样进行无损检测,采集应力波在试样内部的传播速度,并生成断层图像,3个原木试样所测截面周长分别为101、99和100 cm。基于相同的应力波传播速度数据,利用前文设计的ECIA算法产生断层图像,并与原木试样实际缺陷以及PICUS的断层成像进行对比。本组实验中,对于两种断层图像和实际的原木横截面照片,利用AutoCAD中不规则图形面积的计算方法得到原木横截面面积及缺陷面积[17],从而计算缺陷区域的面积与整个横截面面积之比(RS),比较断层图像与试样实际情况的RS,从而定量评估算法的准确性。
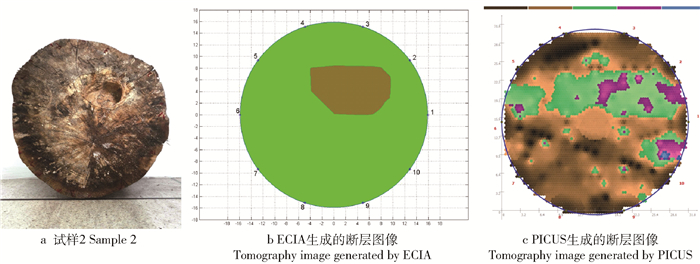
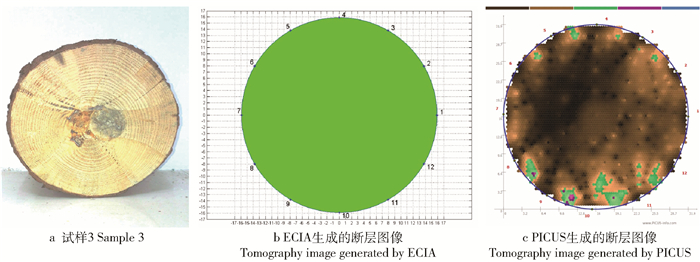
图 5~7分别展示了试样1、2、3的实际情况及两种断层成像算法所生成的图像。其中,ECIA生成的断层图像中,仅用棕色区域表示缺陷区域,PICUS生成的断层图像中,绿色、紫色和蓝色都代表不同程度的缺陷区域。因此,计算PICUS的缺陷面积时,需要计算这几部分的面积之和。
定量比较结果如表 1所示,其中,ΔRS表示断层图像的RS与真实RS的相对误差,计算方法为用它俩的差值除以真实的RS。
表 1 原木断层成像结果的定量评价Table 1. Quantitative evaluation to tomography images of logs试样编号
No. of
sample试样横截面积
Cross-sectional area
of the sample/cm2真实S
Actual S/cm2真实RS
Actual RS/%ECIA PICUS S/cm2 RS/% ΔRS/% S/cm2 RS/% ΔRS/% 1 812.593 5 297.284 1 36.584 6 324.558 8 39.941 1 -9.174 6 232.514 7 28.613 9 21.787 6 2 794.226 0 78.019 2 9.823 3 102.108 9 12.856 4 -30.876 6 285.921 4 36.000 0 -266.475 6 3 804.247 7 0 0 0 0 0 88.467 2 11.000 0 >0 注:S代表试样或断层图像中的缺陷面积;RS代表试样或断层图像中缺陷面积与横截面积的比值;ΔRS代表断层图像的RS与真实RS的相对误差。Notes:S is the defective area, RS is the ratio of the defective area to the cross-section area, and ΔRS is the relative error between the RS of ECIA or PICUS and the actual RS. 表 1中,S代表试样或断层图像中的缺陷面积,ΔRS≠0代表断层图像与试样的真实情况存在误差。从表 1可知,ECIA的断层图像比PICUS更接近于真实情况,但是其断层图像仍存在误检区域(如图 6)。较大的误检区域是由原木的低含水量造成的。国内外大量的研究与实验表明:应力波技术更适用于活树的健康检测[6]。
3.3 活树的成像结果
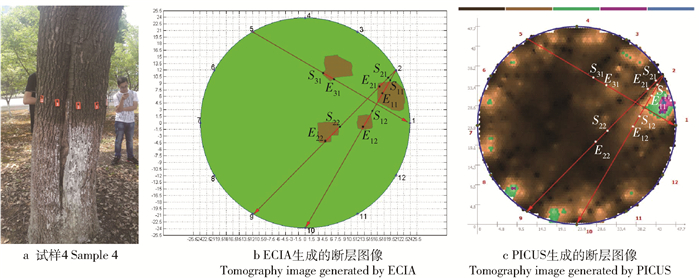
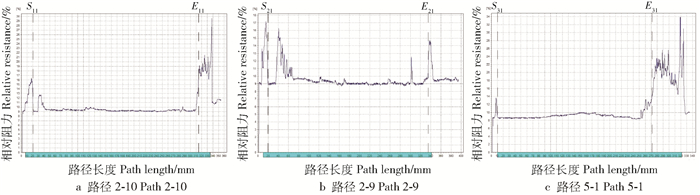
与原木实验类似,使用PICUS对6棵古树进行无损检测,采集应力波传播速度数据。由于无法砍伐树木获得真实的横截面图像,我们在同一高度的横截面上使用Resistograph进行微钻阻力测试。对于选定的应力波传播路径,Resistograph检测仪能够准确地测量该路径上缺陷区域的长度,经过多路径测量,可以确定缺陷区域的大体位置。图 8~19分别给出了6棵古树的实物图、ECIA和PICUS的断层图像,以及在同一横截面中若干路径的阻力曲线。断层图像和阻力曲线中Sij到Eij的部分代表试样在第i条阻力曲线中第j段缺陷区域,S和E分别代表该段缺陷区域的起点和终点。阻力曲线图中横坐标代表路径长度,蓝色部分为去掉树皮部分的真实长度,纵坐标代表相对阻力。在每条阻力曲线中,路径m-n表示与断层图像中第m个传感器到第n个传感器的路径相对应。
从试样4的外观可以观察出在1号和2号传感器之间有明显的缺陷区域,PICUS的检测结果也是如此。但通过Resistograph的阻力检测,发现1号和2号传感器之间仅有树皮缺陷,缺陷区域向树木内部扩散不深,反而在树木内部其他位置(如图 8中S12-E12、S22-E22、S31-E31),有若干较小的缺陷区域,ECIA通过速度反演算法检测出了这些缺陷区域,并通过ECM保证了对轻微缺陷区域的检测精度。
如图 10a所示,试样5有明显的空洞,由于这个空洞过大,使得应力波只能沿接近树皮的边缘部分传播,造成了应力波数据异常,导致PICUS生成的断层图像中缺陷区域比实际的空洞小,如路径3-8中S11-E11部分在阻力曲线图中为缺陷区域,而在图 10c中不全为缺陷。ECIA使用ECM校正了由于数据异常造成的误差,使得断层图像更精确。
由于试样6的树干胸径较大,Resistograph无法穿透树木,所以只能取得路径上的部分阻力值数据,图 12b和12c中从路径起点到L点为取得阻力值数据的部分。如图 12a,试样6外部有一处明显的缺陷区域,并且被养护人员填充了特殊的材料,这些填料造成了Resistograph测量的阻力值较高。另外,如图 13a,S11-E11部分阻力值相对较低,可视为缺陷区域。ECIA生成的断层图像准确地检测出了S11-E11段的缺陷区域,但PICUS生成的断层图像中S11-E11部分仅存在长度较小的轻微腐朽,与阻力曲线图相差较大。
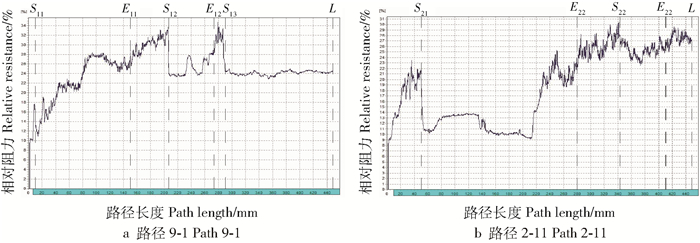
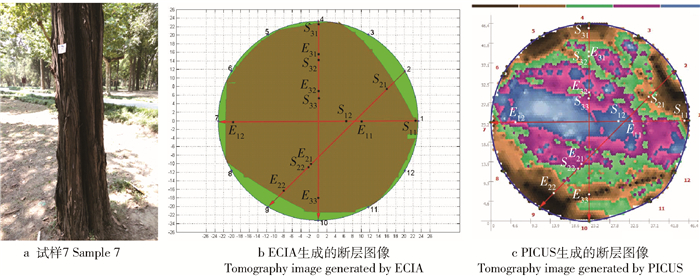
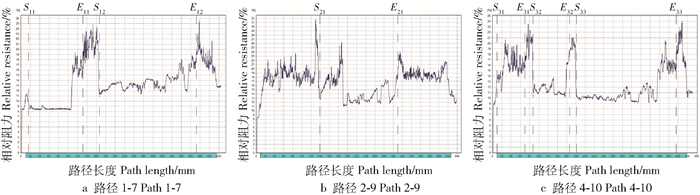
图 14和图 15分别给出了试样7的断层图像比较及3条应力波路径的阻力曲线。从图 14可以看出,ECIA和PICUS产生的断层图像对缺陷区域的位置及形状判断大致相同,但ECIA生成的断层图像中缺陷区域较大。路径1-7中两种算法都有不同程度增大了缺陷区域的长度,但ECIA生成的断层图像中路径1-7中的误检长度相对较小。路径2-9中,ECIA成功的检测到了S23-E23部分的缺陷而PICUS在该部分只检测到了较小长度的缺陷。同样在路径4-10中,PICUS生成的断层图像中S31-E31部分的缺陷长度比阻力曲线图 15中给出的该部分缺陷长度小,而ECIA生成的断层图像在该部分的缺陷长度与阻力曲线图中的缺陷长度较为符合。
对于试样8,两种算法生成的断层图像(如图 16b、c所示)十分相近,相比阻力曲线反映的实际情况,断层图像的路径3-9中,ECIA和PICUS对缺陷区域的位置长度判断都较为准确,在路径5-9中由于树木节子的存在(如图 17a,60~70 mm处阻力值突然增大的部分),导致应力波传播数据异常,使得两种算法生的断层图像在该条路径上的缺陷区域的长度都增大了。
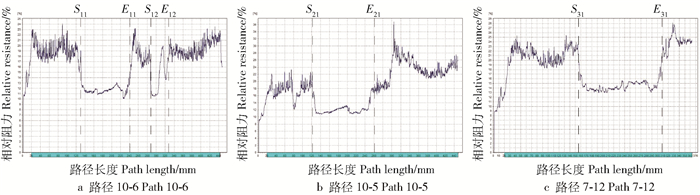
如图 18a,试样9的外部存在一个空洞,虽然空洞较小但一直扩散至树干内部,两种成像算法都成功地检测出了空洞。但在路径10-6中,S12-E12部分存在较小的缺陷区域,两种算法生成的断层图像中该部分都标记为健康区域。ECIA生成的断层图像在路径10-5中的缺陷区域与阻力曲线图 19基本一致,达到了较高的精确度,但PICUS无论在路径10-5中还是路径7-12中都存在一定程度的漏检。
活树无法像原木一样测量缺陷区域的面积,为了评估成像算法的精确度,计算了部分路径上缺陷区域的长度与路径长度的比(RL),利用Resistograph测量真实的缺陷长度,断层图像中对应路径上的缺陷长度可以通过几何计算得到。如同原木实验中的ΔRS,定义了断层图像的RL与真实RL的相对误差ΔRL。对于6棵活树试样,ECIA和PICUS生成的断层图像的实验结果如表 2所示。实验结果证明ECIA能够更准确地检测出轻微腐朽的区域。对于试样4、5、7、9,ECIA成像结果的相对误差绝对值小于8%。由于试样6的树干存在较大空洞,试样8树干中存在节子,这些特殊情况造成检测到的应力波数据异常,使得两种算法的成像结果与实际情况相比都存在较大的误差,但ECIA的相对误差值仍小于PICUS。总体来说,ECIA的精确度比PICUS高,能够较为准确地反映实际情况。但是ECIA产生的断层图像中缺陷区域的边缘真实感略显不足,需要更完善的校正机制和算法来改进断层图像的真实感。
表 2 活树断层成像结果的定量评价Table 2. Quantitative evaluation to tomography images of standing trees试样编号
Sample No.路径
Path真实RL
Actual RLECIA PICUS RL ΔRL RL ΔRL 4 2-10 17.910 4 17.254 1 3.664 4 12.537 3 29.999 9 2-9 13.432 8 12.455 2 7.277 7 0 100.000 0 5-1 5.970 1 6.275 8 -5.120 5 18.209 0 -205.003 2 5 3-8 88.549 6 87.042 3 1.702 2 67.605 6 23.652 3 4-7 83.333 3 77.500 0 7.000 0 53.928 6 35.285 7 5-10 74.626 8 76.417 9 -2.400 1 68.656 7 7.999 9 6 9-1 75.555 5 93.043 5 -23.145 9 43.478 3 42.455 1 2-11 84.444 4 88.888 9 -5.263 2 88.888 9 -5.263 2 7 1-7 89.937 1 93.548 4 -4.015 4 95.913 9 -6.645 5 2-9 75.496 7 81.073 5 -7.386 8 56.989 2 24.514 3 4-10 91.463 4 93.566 7 -2.299 6 80.444 4 12.047 4 8 5-9 3.125 0 13.437 5 -330.000 0 14.375 0 -360.000 0 3-9 3.703 7 4.521 1 -22.069 8 12.592 6 -240.000 0 9 10-6 32.558 1 31.395 3 3.571 5 27.665 6 15.027 0 10-5 27.907 0 27.702 3 0.733 5 36.511 6 -30.833 1 7-12 46.774 2 48.387 1 -3.448 3 43.037 7 7.988 4 注:RL代表试样或断层图像中路径上缺陷区域的长度与整个路径长度的比值;ΔRL代表断层图像的RL与真实RL的相对误差。Notes: RL is the ratio of the defective length to the whole length of the path under test, and ΔRL is the relative error between the RL of ECIA or PICUS and the actual RL. 4. 结论与讨论
提出了一种适用于林木应力波无损检测的断层成像算法ECIA,算法运用LSQR方法求解速度反演方程,反演计算出横截面内每个网格单元的应力波传播速度。为了减少速度反演产生的误差,提出了一种基于邻居网格单元的误差校正机制ECM,使用ECM减少了速度反演产生的误差,从而提高了断层图像的准确度。通过对9个样本的两组实验,证实了本算法的准确度高于PICUS的准确度。本算法已在扬州市区古树名木健康监测项目中得到了实际应用。今后,我们将会完善ECM及成像算法,进一步提高断层图像的真实感。
-
图 1 树木横截面内应力波传播示意图
S代表应力波发射端传感器的位置,R1和R2代表应力波接收端传感器的位置;VR、VT分别表示径向传播速度和弦向传播速度;β表示弦向角。
Figure 1. Stress wave propagation in the cross-section of tree trunk
S is a source sensor, and R1 and R2 are receiver sensors. VT is the tangential velocity and VR is the radial velocity. β is the angle between radial direction and tangential direction.
图 2 树木横截面网格单元划分示意图
S、R分别代表应力波发射端传感器和应力波接收端传感器的位置;1, 2, …, M代表网格单元编号;P1, P2, P3, P4代表传播路径与网格单元的交点;dij代表第i条路径被第j个网格单元分割的距离。
Figure 2. Grid cells of a cross-section of a tree trunk
S is a source sensor, and R is a receiver sensor. 1, 2, …, M represent the No. of grid cells. P1, P2, P3, P4 mean the intersections of stress wave paths and grid cells. dij is segment intercepted by the ith wave path on the jth cell.
表 1 原木断层成像结果的定量评价
Table 1 Quantitative evaluation to tomography images of logs
试样编号
No. of
sample试样横截面积
Cross-sectional area
of the sample/cm2真实S
Actual S/cm2真实RS
Actual RS/%ECIA PICUS S/cm2 RS/% ΔRS/% S/cm2 RS/% ΔRS/% 1 812.593 5 297.284 1 36.584 6 324.558 8 39.941 1 -9.174 6 232.514 7 28.613 9 21.787 6 2 794.226 0 78.019 2 9.823 3 102.108 9 12.856 4 -30.876 6 285.921 4 36.000 0 -266.475 6 3 804.247 7 0 0 0 0 0 88.467 2 11.000 0 >0 注:S代表试样或断层图像中的缺陷面积;RS代表试样或断层图像中缺陷面积与横截面积的比值;ΔRS代表断层图像的RS与真实RS的相对误差。Notes:S is the defective area, RS is the ratio of the defective area to the cross-section area, and ΔRS is the relative error between the RS of ECIA or PICUS and the actual RS. 表 2 活树断层成像结果的定量评价
Table 2 Quantitative evaluation to tomography images of standing trees
试样编号
Sample No.路径
Path真实RL
Actual RLECIA PICUS RL ΔRL RL ΔRL 4 2-10 17.910 4 17.254 1 3.664 4 12.537 3 29.999 9 2-9 13.432 8 12.455 2 7.277 7 0 100.000 0 5-1 5.970 1 6.275 8 -5.120 5 18.209 0 -205.003 2 5 3-8 88.549 6 87.042 3 1.702 2 67.605 6 23.652 3 4-7 83.333 3 77.500 0 7.000 0 53.928 6 35.285 7 5-10 74.626 8 76.417 9 -2.400 1 68.656 7 7.999 9 6 9-1 75.555 5 93.043 5 -23.145 9 43.478 3 42.455 1 2-11 84.444 4 88.888 9 -5.263 2 88.888 9 -5.263 2 7 1-7 89.937 1 93.548 4 -4.015 4 95.913 9 -6.645 5 2-9 75.496 7 81.073 5 -7.386 8 56.989 2 24.514 3 4-10 91.463 4 93.566 7 -2.299 6 80.444 4 12.047 4 8 5-9 3.125 0 13.437 5 -330.000 0 14.375 0 -360.000 0 3-9 3.703 7 4.521 1 -22.069 8 12.592 6 -240.000 0 9 10-6 32.558 1 31.395 3 3.571 5 27.665 6 15.027 0 10-5 27.907 0 27.702 3 0.733 5 36.511 6 -30.833 1 7-12 46.774 2 48.387 1 -3.448 3 43.037 7 7.988 4 注:RL代表试样或断层图像中路径上缺陷区域的长度与整个路径长度的比值;ΔRL代表断层图像的RL与真实RL的相对误差。Notes: RL is the ratio of the defective length to the whole length of the path under test, and ΔRL is the relative error between the RL of ECIA or PICUS and the actual RL. -
[1] Wang X P, Divos F, Pilon C, et al. Assessment of decay in standing timber using stress wave timing nondestructive evaluation tools: a guide for use and interpretation[R]. General Technical Report FPL-GTR-147. Madison, WI: United States Department of Agriculture, 2004.
[2] Dikrallah A, Hakam A, Brancheriau L, et al. Experimental analysis of acoustic anisotropy of wood by using guided waves[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Integrated Approach to Wood Structure, Behaviour and Application, Joint Meeting of ESWM and COST Action E35. Florence, Italy: Aalborg Universitet, 2006: 149-154.
[3] 梁善庆, 王喜平, 蔡智勇, 等.弹性波层析成像技术检测活立木腐朽[J].林业科学, 2008, 44(5): 109-114. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200805021 Liang S Q, Wang X P, Cai Z Y, et al. Elastic wave tomography in standing tree decay detection[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2008, 44(5): 109-114. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200805021
[4] 杨学春, 王立海.应力波在原木中传播理论的研究[J].林业科学, 2005, 41(5): 132-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200505024 Yang X C, Wang L H. Study on the propagation theories of stress wave in log[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(5): 132-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200505024
[5] Li G H, Wang X P, Feng H L, et al. Analysis of wave velocity patterns in black cherry trees and its effect on internal decay detection[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2014, 104: 32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2014.03.008
[6] Socco L V, Sambuelli L, Martinis R, et al. Feasibility of ultrasonic tomography for nondestructive testing of decay on living trees[J]. Research in Nondestructive Evaluation, 2004, 15(1): 31-54. doi: 10.1080/09349840490432678
[7] Du X C, Li S Z, Li G H, et al. Stress wave tomography of wood internal defects using ellipse-based spatial interpolation and velocity compensation[J]. BioResources, 2015, 10(3): 3948-3962.
[8] Guntekin E, Emiroglu Z G, Yilmaz T. Prediction of bending properties for Turkish red pine (Pinus brutia Ten.) lumber using stress wave method[J]. BioResources, 2013, 8(1): 231-237. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000003296196
[9] Dackermann U, Crews K, Kasal B, et al. In situ assessment of structural timber using stress-wave measurements[J]. Materials and Structures, 2014, 47(5): 787-803. doi: 10.1617/s11527-013-0095-4
[10] Divos F, Divos P. Resolution of stress wave based acoustic tomography[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Nondestructive Testing of Wood. Eberswalde: Shaker Verlag, 2005: 309-314.
[11] Maurer H R, Schubert S, Baechle F. Application of nonlinear acoustic tomography for non-destructive testing of trees[C]//Proceedings of 14th International Symposium on Nondestructive Testing of Wood. Eberswalde: Shaker Verlag, 2005: 339-349.
[12] Brancheriau L, Lasaygues P, Debieu E, et al. Ultrasonic tomography of green wood using a non-parametric imaging algorithm with reflected waves[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 2008, 65(7): 712-717. doi: 10.1051/forest:200851
[13] Jackson M J, Tweeton D R. MIGRATOM: geophysical tomography using wavefront migration and fuzzy constraints[R]//United States, report of investigation: RI 9497. Minneapolis, MN: U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, 1994.
[14] Paige C C, Saunders M A. LSQR: an algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least squares[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), 1982, 8(1): 43-71. doi: 10.1145/355984.355989
[15] 杨国铮, 禹晶, 肖创柏, 等.基于形态成分分析的复杂背景SAR图像舰船尾迹检测[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2016, 28(10): 1662-1671. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjfzsjytxxxb201610007 Yang G Z, Yu J, Xiao C B, et al. Ship wake detection in SAR images with complex backgrounds using morphological component analysis[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2016, 28(10): 1662-1671. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjfzsjytxxxb201610007
[16] 谭茂金, 邹友龙. (T2, D)二维核磁共振测井混合反演方法与参数影响分析[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(2): 683-692. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201202032 Tan M J, Zou Y L. A hybrid inversion method of (T2, D) 2D NMR logging and observation parameters effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(2): 683-692. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201202032
[17] 程绪琦, 王建华, 刘志峰, 等. AutoCAD 2014中文版标准教程[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2014: 182-184. Cheng X Q, Wang J H, Liu Z F, et al. The standard tutorial of AutoCAD 2014 in Chinese version[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014: 182-184.
-
期刊类型引用(13)
1. 夏甜甜,杜秋硕,刘鹏. 基于数字赋能的泰山古柏生态修复技术应用探究. 山东林业科技. 2024(02): 77-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶程浩,杜晓晨,鲍宇. 一种基于YOLOv5和轮廓约束的木材空洞缺陷应力波层析成像算法. 木材科学与技术. 2023(05): 61-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 侯艳芳,王鑫,侯婷婷,郭靖,张艳. 古建筑木结构损伤检测方法研究进展. 粘接. 2022(01): 123-126+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宋辉,姬晓文,高琦,缑鹏超,王志强. 基于数据驱动的不规则用电检测误差校正系统设计. 电子设计工程. 2022(06): 109-112+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨露露,董喜斌,徐华东. 电阻法和应力波法在活立木内部腐朽缺陷检测中的对比. 森林工程. 2022(04): 82-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 戴禄君,吴瑞瑞. 数据驱动的非线性光学显微成像误差校正研究. 激光杂志. 2022(07): 159-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 路程琳,何宇航,谢雨宏,刘依萍,刘嘉仪,王正. 应力波断层扫描法在立木检测方面的研究现状. 林业机械与木工设备. 2022(10): 37-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘涛,李光辉. 基于射线分割的林木应力波断层成像算法. 林业科学. 2021(09): 181-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵松,王勐. 移动AR+VR支持下全景图像拼接均匀性校正方法. 计算机仿真. 2021(11): 189-192+398 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 何宇航,陈偲,王弘历,黄席阳,王正. 断层扫描法在木材无损检测的研究进展. 木工机床. 2020(01): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张慧娟. 木材应力波检测精度的影响因素研究. 中国林副特产. 2020(01): 27-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 魏喜雯,孙丽萍,许述正,杨扬,杜春晓. 基于应力波传播速度模型的原木缺陷定量检测. 北京林业大学学报. 2020(05): 143-154 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 刘嘉新,高景泉,李超. 应用兰德韦伯算法的木材缺陷图像重建. 东北林业大学学报. 2019(12): 125-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: