Preparation and properties of mesoporous activated carbons from NaOH-pretreated corncob residues
-
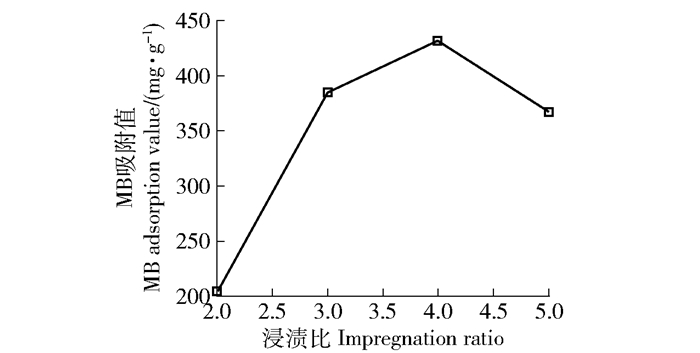
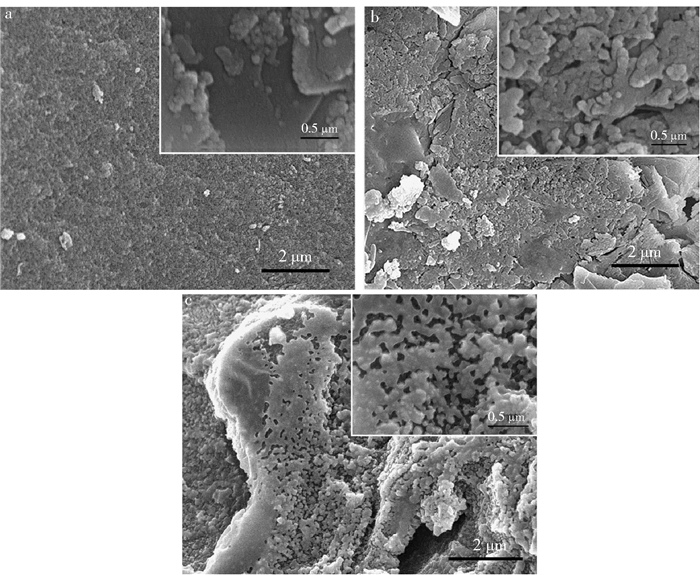
摘要:目的与普通活性炭比较,介孔活性炭具有疏水性好、孔体积大、导电性能好等优势,然而传统制备方法繁杂,原料成本较高。因此,探究新型介孔活性炭制备工艺尤为重要。方法以木糖渣为原料,采用NaOH预处理、低温硫酸辅助炭化与磷酸活化相结合的方法制备了高介孔率活性炭。通过单因素实验,分析NaOH预处理时间、浸渍比以及活化温度对活性炭的亚甲基蓝(MB)吸附性能的影响。结果研究表明:NaOH预处理脱除木质素促使原料形成孔隙通道,同时使木糖渣纤维发生润胀,有利于活化剂与原料接触,从而获得高介孔率、高比表面积活性炭。当NaOH预处理时间为4h,磷酸与原料浸渍比4:1,活化温度500℃,活化时间为1h所制备的活性炭具有较高的MB吸附值436mg/g。扫描电镜分析结果表明:样品表面含有丰富的大孔及中孔结构,整体活化充分均匀。氮气物理吸附-脱附分析结果表明:活性炭具有发达的孔隙结构,其比表面积和总孔体积分别高达2038m2/g和2.13cm3/g,其中介孔孔容1.56cm3/g,介孔率达到73.2%,平均孔径为4.18nm。结论采用适当的NaOH预处理有利于制备孔隙结构优越的活性炭,在重金属离子吸附、有机大分子废水处理以及电子元器件等领域有广泛的应用前景。本研究将为高比表面积介孔活性炭的制备奠定理论基础,并为工业木糖渣的高值化利用提供了一条新途径。Abstract:ObjectiveCompared with common activated carbon, mesoporous activated carbon has the advantages of good hydrophobic, large pore volume and high conductivity, etc. However, the traditional preparation method is complicated and has higher costs for raw materials. Therefore, it is crucial to explore new mesoporous activated carbon preparation method.MethodActivated carbon with high mesoporous rate was prepared from corncob residues by NaOH pretreatment, followed by phosphoric acid activation. The influences of NaOH-pretreated time, ratio of H3PO4/corncob residues (impregnation ratio) and activation temperature on MB adsorptive property of the activated carbon were investigated through the single factor experiments.ResultResults indicated that lignin removal from corncob residues by NaOH pretreatment may form pore gallery and swell the fibers, making it easier to contact with activator. As a consequence, activate carbon with high specific surface area and mesoporous rate was obtained. The best MB adsorption value of 436mg/g was achieved when corncob was pretreated by NaOH for 4 hours under a impregnation ratio of 4:1, activation temperature at 500℃ and activation time for 1 hour. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis showed that the surface of activated carbon was rich in mesopores and macropores. The developed pore structure and specific surface area were analyzed by N2 adsorption tests. The surface area, total pore volume and average pore size of activated carbon were 2038m2/g, 2.13cm3/g and 4.18nm, respectively. Particularly, the mesoporous volume was 1.56cm3/g and the mesoporous rate was 73.2%.ConclusionThe above mentioned results indicated that appropriate NaOH pretreatment contributes to the preparation of activated carbon with well-developed mesoporous structure, which has potential application in fields of heavy metal ion adsorption, organic macromolecular wastewater treatment and electronic components preparation, etc. Our work will provide a fundamental research for the efficient preparation of mesoporous activated carbon and promote the high-value utilization of the corncob residues.
-
Keywords:
- corncob residues /
- mesoporous /
- activated carbon /
- adsorption
-
在森林生态系统中,植物地上部分产生并归还至土壤表层的枯枝落叶,在长期积累和分解作用下,形成具有独特结构层次的凋落物层[1],影响着土壤有机质的组成和养分浓度[2],促进物质再循环和养分平衡[3-5]。多数研究基于外观轮廓特征将凋落物层分为未分解层、半分解层和完全分解层[6-9],各层所占比例不一,且养分浓度随分解程度增加呈现不同的变化趋势。如,郑路等[10]归纳得出我国森林凋落物未分解层所占比例随纬度增大而增大,随林龄增大而减小;而随分解程度增加,南方森林凋落物养分浓度呈下降趋势,北方森林呈相反的变化趋势。此外,因空间位置不同凋落物养分特征也表现出差异性和复杂性。Burghouts等[11]研究发现,马来西亚沙巴龙脑香雨林凋落物养分周转率的空间变异性较养分输入量低;乔璐等[12]发现中山湿性常绿阔叶林凋落物仅镁和钙的输入具有空间变异特征;Parsons等[13]研究表明,澳大利亚昆士兰州北部的凋落物氮和磷在更大空间尺度上具有变异性,而碳和钙因受局部因子扰动在小尺度上变异最大;Lu等[14]以台湾中部森林为研究对象,比较发现低海拔地区凋落物的碳及碳氮比明显低于高海拔地区;杨阳等[15]以西藏高原主要森林类型为研究对象,发现凋落物碳储量随着龄级的增大而增加;刘刚等[16]对东莞市不同的森林群落类型调查发现,针叶林凋落物碳储量最大,而天然林高于人工林;Kang等[17]对全球范围内凋落物养分进行了统计分析,得出凋落物氮浓度随年平均气温和年降水量呈线性增加,随纬度呈下降趋势。但这些研究多探讨不同林分类型和地形气候间以及不同空间尺度下凋落物不同养分指标和组分的异质性,目前尚无研究比较不同分解程度下凋落物养分的空间变异特征。
空间变异是森林生态系统中普遍存在且极为重要的特性,受植物、土壤、地形、气候、森林结构和干扰等多种因子的影响[18-19]。因此,探究不同分解程度下凋落物养分空间变异及其影响因素对了解凋落物养分循环利用等过程具有重要的理论和实践意义。本文选取立地条件相似的4块1 hm2温带云冷杉混交林固定样地,于凋落高峰期前(8月末)[20]收集半分解(semi-decomposed,F)层和完全分解(complete decomposed,H)层凋落物样品各400个,测定分析其有机碳(OC)、全氮(TN)及全磷(TP)含量的空间变异特征及影响因素,旨在阐明森林群落尺度上不同分解程度下凋落物养分空间格局,以期为森林的健康管理与合理经营提供理论基础。
1. 研究区概况与研究方法
1.1 研究区概况与样地设置
研究区设在吉林省汪清林业局金沟岭林场(130°05′ ~ 130°20′ E,43°17′ ~ 43°25′ N)。该区以暗棕壤为主,成土母质多为玄武岩、片麻岩和花岗岩的坡积物和残积物,平均厚度约40 cm。海拔在300 ~ 1 200 m之间,平均坡度5° ~ 25°。属温带大陆性季风气候,年均气温3.9 ℃,最高气温出现在7月份,为20.6 ℃,最低在1月份,为零下32 ℃。年降水量近600 ~ 700 mm。该区森林覆盖率高达98%,物种丰富,分布有云杉(Picea jezoensis)、冷杉(Abies nephrolepis)、红松(Pinus koraiensis)、紫椴(Tilia amurensis)和榆树(Ulmus pumila)等127科407种。
2015年,对云冷杉针阔混交中龄林中的立地条件相似的12块100 m × 100 m固定样地进行间伐处理(4种强度,3次重复)。2017年夏,随机选取其中的4块样地,涵盖4种间伐强度(表1)。
表 1 样地基本概况Table 1. Characteristics of experimental sample plots样地
Sample plot海拔
Altitude/m坡度
Slope degree/(°)坡向
Slope aspect间伐强度
Thinning intensity/%蓄积量/
(m3·hm−2)
Volume/(m3·ha−1)林分密度/(株·hm−2)
Stand density/
(stem·ha−1)平均树高
Mean tree height/m平均胸径
Mean DBH/cm树种组成
Tree
species郁闭度
Canopy densityⅠ 742 3 东北 Northeast 21.21 173.89 934 13.9 14.5 2冷2落1云1红1椴1枫1白1杂 0.74 Ⅱ 732 5 东北 Northeast 6.29 201.00 1167 11.4 12.3 2冷1红1白1云1落1椴1枫1杨1杂 0.76 Ⅲ 769 5 东北 Northeast 11.22 218.10 1301 13.6 13.7 2落2云1冷1红1白1枫1杨1椴 0.78 Ⅳ 773 3 东北 Northeast 0.00 209.10 1437 15.1 14.0 2落2水1红1冷1枫1白1云 0.81 注:云. 鱼鳞云杉;冷. 臭冷杉;落. 长白落叶松;红. 红松;椴. 紫椴 ;枫.枫桦;白. 白桦 ;杨. 大青杨;水. 水曲柳 ;杂. 杂木。Notes: 云, Picea jezoensis var. microsperma; 冷, Abies nephrolepis; 落, Larix olgensis; 红, Pinus koraiensis; 椴, Tilia amurensis; 枫, Betula costata; 白, Betula platyphylla; 杨, Populus ussuriensis; 水, Fraxinus mandschurica; 杂, others. 1.2 林分调查与凋落物采集测定
基于网格布点法将各样地按10 m × 10 m划分为100个样方,对样方内所有乔木植物(胸径 > 5 cm)进行每木检尺,并获取林分冠层图像。参考郑璐等提出的分层标准[10],采集F层和H层(50 cm ×50 cm区域)凋落物各400个,并完成称量质量。带回实验室后,对凋落物样品进行预处理,分析测定其OC、TN和TP含量[21]。
1.3 数据计算与统计分析
运用Excel 2013软件对凋落物现存量、持水率以及胸径、胸高断面积、生物多样性指数、郁闭度、株数、物种数、针叶树种和株数比例等数据进行简单运算[22-25],采用SPSS 21.0软件对4块样地进行描述性统计分析,并对F层和H层数据进行差异显著性检验(t检验);用Pearson相关分析计算相关系数;用K-S检验或Box-Cox转换数据[26]后分别在GS+ 7.0和ArcGIS 10.2软件上计算和绘制半变异函数模型拟合[27-28]和克里格空间插值图[29]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 凋落物养分的描述性统计特征
凋落物养分的描述性统计特征见图1。样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ中H层凋落物OC均值分别为354.22、368.89、321.32和358.67 g/kg,F层较H层增加14.90% ~ 20.86%,F层和H层OC变异系数(coefficient of variation,CV)介于14.51% ~ 30.18%之间,均属中等变异[30]。4块样地F层凋落物TN均值在16.45 ~ 21.77 g/kg范围内波动,变异系数介于10.94% ~ 28.63%,除样地Ⅰ外,各样地TN随分解程度增加呈下降趋势,但均表现为中等变异。样地Ⅱ中F层凋落物TP均值最大,达1.49 g/kg,样地Ⅰ次之,为1.30 g/kg,样地Ⅲ和样地Ⅳ较小,为1.12 g/kg,但TP最值均出现在样地Ⅱ,最大值为2.41 g/kg,最小值为0.53 g/kg,变异系数在16.15% ~ 26.85%,各样地H层凋落物TP均值较F层增大,变化范围在1.05 ~ 5.77 g/kg,而变异系数介于22.33% ~ 30.94%,仍属于中等变异。云冷杉针阔混交林H层凋落物的OC和TN含量均显著低于F层,而TP含量显著高于F层,且在4块样地中,样地Ⅱ的凋落物OC、TN和TP含量最低,而样地Ⅳ的凋落物TN和TP含量最高,但凋落物OC、TN和TP的空间离散程度均较小。
![]() 图 1 凋落物养分的描述性统计特征(n = 100)图中为均值(标准差)。P < 0.01表示半分解(F)层和完全分解(H)层凋落物养分含量差异极显著,P < 0.05表示F层和H层凋落物养分含量差异显著。Data in the figure are mean(standard deviation). P < 0.01 indicates extremelysignificant difference between semi-decomposed horizon (F) and complete decomposed horizon (H), while P < 0.05 indicates significant difference between F and H horizons.Figure 1. Descriptive statistical characteristics of litter nutrient concentrations (n = 100)
图 1 凋落物养分的描述性统计特征(n = 100)图中为均值(标准差)。P < 0.01表示半分解(F)层和完全分解(H)层凋落物养分含量差异极显著,P < 0.05表示F层和H层凋落物养分含量差异显著。Data in the figure are mean(standard deviation). P < 0.01 indicates extremelysignificant difference between semi-decomposed horizon (F) and complete decomposed horizon (H), while P < 0.05 indicates significant difference between F and H horizons.Figure 1. Descriptive statistical characteristics of litter nutrient concentrations (n = 100)2.2 凋落物养分的空间变异及分布
F层和H层凋落物OC半方差函数的最佳拟合模型主要为球状模型和指数模型(表2),决定系数(determination coefficients,R2)变化范围为0.173 ~ 0.967。F层和H层凋落物TN在样地Ⅱ ~ Ⅳ中的最佳拟合模型均为指数模型(R2 = 0.317 ~ 0.952),而在样地Ⅰ中为球状模型(R2分别为0.824和0.998)。在样地Ⅰ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ,指数模型对F层凋落物TP的拟合效果最佳(R2 = 0.222 ~ 0.727),而在样地Ⅱ,高斯模型拟合最佳(R2 = 0.999);H层凋落物TP在样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ的最佳拟合模型分别为球状、高斯、球状和指数模型(R2 = 0.412 ~ 0.989)。
表 2 凋落物养分空间分析的半方差函数的模型类型及参数(n = 100)Table 2. Semivariogram theoretical models and parameters for litter nutrient concentrations (n = 100)指标
Index样地
Sample
plot分层
Horizon模型
Model块金值
Nugget
(C0)基台值
Sill
(C0 + C)变程
Range
(A)/m结构比
Structural variance
ratio (C0/(C0 + C))/%决定系数
Determination
coefficients (R2)分形维数
Fractal
dimension (D)有机碳
Organic
carbonⅠ F 球状模型
Spherical model0.001 0.358 17.4 0.28 0.579 1.941 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.107 0.738 30.0 14.50 0.967 1.900 Ⅱ F* 指数模型
Exponential model0.031 0.413 10.5 7.02 0.775 1.995 H 球状模型
Spherical model0.031 0.619 18.2 5.16 0.716 1.941 Ⅲ F 球状模型
Spherical model0.005 0.605 14.2 0.83 0.173 1.964 H 球状模型
Spherical model0.001 0.574 11.9 0.17 0.560 1.996 Ⅳ F* 指数模型
Exponential model0.001 0.776 13.5 0.13 0.253 1.954 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.317 1.136 39.9 27.90 0.935 1.892 全氮
Total
nitrogenⅠ F 球状模型
Spherical model0.425 2.973 78.9 14.30 0.998 1.687 H 球状模型
Spherical model0.010 8.706 17.3 0.11 0.824 1.952 Ⅱ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.980 7.490 24.3 13.08 0.952 1.924 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.320 7.309 11.7 4.38 0.317 1.975 Ⅲ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.250 4.710 14.1 5.31 0.835 1.971 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.060 8.058 6.3 0.74 0.419 1.974 Ⅳ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.010 7.990 25.5 0.13 0.888 1.899 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.760 7.340 26.7 10.35 0.847 1.912 全磷
Total
phosphorusⅠ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.003 0.120 9.9 2.52 0.276 1.988 H* 球状模型
Spherical model0.157 0.385 71.3 40.78 0.975 1.818 Ⅱ F 高斯模型
Gauss model0.014 0.031 40.5 45.81 0.999 1.815 H 高斯模型
Gauss model0.001 0.198 14.5 0.51 0.615 1.949 Ⅲ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.005 0.151 17.1 3.45 0.727 1.952 H 球状模型
Spherical model0.375 0.786 51.4 47.71 0.989 1.855 Ⅳ F 指数模型
Exponential model0.008 0.083 11.1 0.10 0.222 1.978 H 指数模型
Exponential model0.067 0.685 11.4 9.78 0.412 1.986 注:*表示数据因不符合正态分布进行Box-Cox转换。Notes: * means that the data disobeying the normal distribution are transformed using Box-Cox. 由表2可得,各样地F层凋落物OC和TP的块金值(nugget,C0)均接近于0,表明由试验误差和取样引起的随机变异小,而TN(除样地Ⅳ外)可能由试验误差和取样引起的随机变异相对较大[31]。各样地F层凋落物OC、TN和TP的基台值(sill,C0 + C)分别为0.358 ~ 0.776、2.973 ~ 7.990和0.031 ~ 0.151,同一样地TN的变异程度较OC及TP大;各样地TN的基台值随分解程度变化趋势存在差异,而H层OC(除样地Ⅲ)和TP的基台值较F层大,表明空间变异程度随分解程度增加呈增加趋势。
各样地F层凋落物OC结构比(structural variance ratio,C0/(C0 + C))为0.13% ~ 7.02%,表明空间异质性主要由结构性因素引起,而由随机因素引起的仅占0.13% ~ 7.02%;H层凋落物OC结构比为0.17% ~ 27.90%。各样地F层和H层凋落物TN结构比介于0.11% ~ 14.30%,具有强烈的空间自相关性[32]。同样,各样地F层和H层凋落物TP具有较强的空间自相关性(结构比为0.10% ~ 47.71%)。整体来说,云冷杉针阔混交林样地F层凋落物OC和TP空间自相关性较H层强,而TN表现出相反的趋势。
云冷杉针阔混交林各样地F层凋落物OC变程(range,A)为10.5 ~ 17.4 m,TN变程为14.1 ~ 78.9 m,TP为9.9 ~ 40.5 m;H层凋落物OC、TN和TP的变程分别为11.9 ~ 39.9 m、6.3 ~ 26.7 m和11.4 ~ 71.3 m,其中,样地Ⅲ中H层凋落物TN和样地Ⅰ中F层凋落物TP变程较小,表明其空间自相关性距离和空间连续性较小[33],同一样地,H层凋落物OC和TP较F层有较大的空间自相关距离和空间连续性,说明其生态过程在较大尺度上起作用[34]。
4块样地凋落物养分的空间格局存在差异,不同分解层凋落物养分的空间分布状况也略有不同。凋落物OC和TN呈明显的斑块状分布,且F层和H层OC高值主要分布在东北及中部区域,F层TN自北向南基本表现出逐渐增加的分布特征,H层呈相反的变化趋势(除样地Ⅰ外),而F层和H层TP东西方向差异较小,自北向南基本呈明显的条带状分布,且F层和H层OC在同一样地内表现为相似的空间分布格局,而F层TN和TP高值出现的位置在H层则相对较低(图2、3)。各样地F层凋落物OC、TN和TP的分形维数(fractal dimension,D)分别为1.941 ~ 1.995、1.687 ~ 1.971和1.815 ~ 1.988;H层凋落物OC(除样地Ⅲ)和TP(除样地Ⅱ和Ⅳ)的分形维数低于F层,表明其空间分布的均一性较好,而凋落物TN的分形维数大于F层,意味着其空间分布较为复杂[35-36]。
2.3 凋落物养分空间变异的影响因素
凋落物养分与凋落物因子和林分因子的相关性(表3、4)表明,F层凋落物OC与TN/TP比(样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ)呈极显著正相关关系(P < 0.01),与TN(样地Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ)和TP(样地Ⅰ)显著正相关(P < 0.05);H层凋落物OC与持水率(样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ)、TN(样地Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ)和TN/TP比(样地Ⅱ)均表现为极显著正相关,与现存量(样地Ⅲ)、株数(样地Ⅰ)和针叶株数比例(样地Ⅲ)显著负相关。F层凋落物TN与OC/TP比(样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ)极显著正相关,与OC(样地Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ)和TP(样地Ⅲ和Ⅳ)显著正相关,与株数(样地Ⅳ)、物种数(样地Ⅲ和Ⅳ)、多样性和丰富度指数(样地Ⅲ和Ⅳ)呈显著负相关关系;H层凋落物TN与现存量(样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ)具有极显著的负相关性,与持水率(样地Ⅰ ~ Ⅳ)、OC(样地Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ)和针叶株数比例(样地Ⅳ)极显著正相关,与TP(样地Ⅰ和Ⅱ)呈显著正相关关系。F层凋落物TP与郁闭度(样地Ⅱ)极显著正相关,与4块样地的OC/TP比和TN/TP比均表现为极显著的负相关关系,与TN(样地Ⅰ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ)、物种数(样地Ⅲ)、多样性(样地Ⅲ和Ⅳ)和丰富度指数(样地Ⅲ)显著正相关,与OC/TN比(样地Ⅰ)显著负相关;H层凋落物TP仅与现存量(样地Ⅳ)和TN(样地Ⅰ和Ⅱ)显著正相关,与株数(样地Ⅰ)、郁闭度(样地Ⅱ)和针叶树种比例(样地Ⅳ)呈显著负相关关系。
表 3 凋落物养分与凋落物因子的相关系数 (n = 100)Table 3. Correlation coefficients of litter nutrient concentration with litter factors (n = 100)指标
Index样地
Sample plot分层
Horizon现存量
Standing crop持水率
Water holding rate有机碳(或全氮)
OC (TN)全氮(或全磷)
TN (TP)碳氮比
OC/TN碳磷比
OC/TP氮磷比
TN/TP有机碳
Organic carbonⅠ F 0.081 0.118 0.266* 0.205* 0.202* 0.178 0.628** H −0.143 0.324** 0.374** 0.186 0.686** 0.616** 0.031 Ⅱ F −0.008 0.080 0.200* −0.040 0.563** 0.000 0.434** H −0.188 0.654** 0.364** −0.069 0.582** 0.659** 0.281** Ⅲ F −0.041 −0.129 0.197* −0.065 0.850** 0.084 0.688** H −0.209* 0.388** 0.342** 0.078 0.747** 0.563** 0.015 Ⅳ F 0.166 −0.010 0.100 −0.370 0.699** −0.108 0.717** H −0.164 0.420** 0.008 0.025 0.885** 0.714** 0.022 全氮
Total nitrogenⅠ F −0.115 0.077 0.226* 0.091 −0.607** 0.796** 0.017 H −0.260** 0.407** 0.374** 0.223* −0.394** 0.147 0.447** Ⅱ F −0.090 0.086 0.200* 0.112 −0.616** 0.409** 0.084 H −0.428** 0.517** 0.364** 0.248* −0.494** 0.038 0.425** Ⅲ F 0.063 −0.025 0.197* 0.233* −0.322** 0.305** −0.065 H −0.290** 0.529** 0.342** 0.163 −0.334** 0.015 0.279** Ⅳ F 0.058 0.070 0.100 0.279** −0.562** 0.415** −0.244 H −0.427** 0.506** 0.008 −0.016 −0.420** −0.008 0.435** 全磷
Total phosphorusⅠ F 0.090 −0.133 0.023 0.236* −0.243* −0.725** −0.342** H −0.003 0.050 0.186 0.223* 0.036 −0.587** −0.710** Ⅱ F 0.060 0.061 0.084 0.091 −0.007 −0.758** −0.771** H −0.149 0.075 −0.069 0.248* −0.248* −0.745** −0.730** Ⅲ F −0.151 0.060 0.011 0.230* −0.131 −0.689** −0.835** H 0.000 0.089 0.078 0.163 −0.042 −0.714** −0.823** Ⅳ F −0.013 −0.078 0.046 0.271** −0.101 −0.609** −0.690** H 0.232* −0.116 0.025 −0.016 0.024 −0.598** −0.858** 注:**表示影响极显著(P < 0.01),*表示影响显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: ** means very significant influences at P< 0.01 level. * means significant influences at P< 0.05 level. The same below. 表 4 凋落物养分与林分因子的相关系数(n = 100)Table 4. Correlation coefficients of litter nutrient concentration with stand factors (n = 100)指标
Index样地
Sample plot分层
Horizon郁闭度
Canopy
density物种数
Species
number株数
Stem
number生物多样性指数
Biodiversity index针叶树种比例
Proportion of
coniferous species针叶株数比例
Proportion of
coniferous stem
DBH胸高
断面积
Basal areaD H' J 有机碳
Organic
carbonⅠ F 0.174 −0.012 0.020 −0.012 −0.044 −0.064 −0.118 −0.159 −0.088 −0.100 H 0.055 −0.114 −0.209* −0.114 −0.103 −0.067 −0.014 −0.043 0.125 0.145 Ⅱ F −0.129 0.071 0.103 0.071 0.029 −0.049 0.011 −0.113 0.121 0.097 H 0.051 0.000 −0.001 0.000 0.034 0.093 0.058 0.023 −0.024 −0.029 Ⅲ F 0.049 −0.012 −0.021 −0.012 0.026 0.070 0.110 0.074 0.159 0.138 H 0.057 0.117 0.139 0.117 0.138 0.139 −0.149 −0.208* 0.092 0.091 Ⅳ F 0.024 0.089 0.004 0.089 0.072 0.064 0.100 0.106 −0.121 −0.127 H −0.057 −0.164 −0.099 −0.164 −0.136 0.008 0.037 −0.067 −0.079 −0.099 全氮
Total
nitrogenⅠ F −0.117 −0.007 −0.061 −0.007 −0.045 −0.045 0.075 0.087 −0.022 −0.046 H −0.044 −0.175 −0.168 −0.175 −0.192 −0.114 −0.099 −0.033 0.095 0.113 Ⅱ F −0.166 −0.072 −0.121 −0.072 −0.052 0.015 −0.425** −0.438** 0.059 0.013 H −0.001 0.007 0.070 0.007 −0.040 −0.085 −0.002 −0.003 −0.073 −0.073 Ⅲ F −0.105 −0.282** −0.125 −0.282** −0.328** −0.183 0.227* 0.232* 0.078 0.064 H 0.132 0.134 0.017 0.134 0.160 0.185 −0.107 −0.114 0.166 0.146 Ⅳ F −0.146 −0.235* −0.239* −0.235* −0.208* −0.018 0.010 0.019 −0.009 −0.023 H −0.041 −0.039 0.029 −0.039 −0.101 −0.123 0.195 0.258** 0.074 0.032 全磷
Total
phosphorusⅠ F −0.106 −0.038 −0.077 −0.038 −0.066 −0.105 0.010 0.007 −0.097 −0.111 H −0.012 −0.105 −0.220* −0.105 −0.070 0.072 0.021 −0.056 0.156 0.141 Ⅱ F 0.262** 0.013 −0.109 0.013 0.043 0.058 −0.038 −0.021 0.038 0.042 H −0.218* −0.162 −0.024 −0.162 −0.186 −0.146 −0.060 −0.056 −0.026 −0.033 Ⅲ F 0.147 0.206* 0.148 0.206* 0.222* 0.123 0.023 −0.097 0.093 −0.087 H 0.114 0.076 −0.009 0.076 0.094 0.038 −0.034 −0.150 0.153 0.146 Ⅳ F 0.037 0.195 −0.030 0.195 0.212* 0.126 −0.035 −0.133 −0.057 −0.058 H 0.134 0.033 −0.052 0.033 0.065 0.132 −0.240* −0.160 −0.029 −0.017 注:D. Gleason指数;H'. Shannon-Wiener多样性指数;J. Pielou均匀度指数。Notes: D, Gleason index; H', Shannon-Wiener diversity index; J. Pielou evenness index. 3. 讨 论
凋落物层是森林生态系统中最为重要的养分库,其分解矿化与养分循环密切相关[37]。云冷杉针阔混交林作为长白山区典型的天然林分类型,其凋落物OC、TN和TP较丰富,除H层凋落物的TP含量(2.68 g/kg)外,其他均在全国森林凋落物养分浓度范围内[10],由于受地带性因子、林分类型、树种组成和凋落物生物学特性的影响,普遍高于秦岭西部山地多种针叶人工林[38]和西藏色季拉山冷杉天然林[39]凋落物各层养分浓度,低于天山西部伊犁云杉天然林[40]。本研究中各营养元素在凋落物分解过程中迁移状况有所差异,F层和H层OC、TN和TP差异显著,凋落物OC、粗蛋白、单宁等在凋落物分解过程中随有机物的分解而减少,且该区的降水集中在夏季,雨热同期,TN更易随着凋落物的分解和雨水淋溶,而云冷杉含难以分解的物质浓度较高,减慢了分解速率,从而出现了养分积累,TP相对增加的现象,这与多数研究表明从上到下随着凋落物分解程度的增加,OC浓度降低[41-42]、TN浓度降低[7, 38, 41]和TP浓度增加[43-44]的结论一致。
凋落物层是在自然条件和人为活动等的共同作用下形成的,这些要素在空间和时间上的差异性导致了凋落物养分的空间变异性。本研究中各样地间存在差异,但均表现为中等变异,H层凋落物OC和TP的变异程度较F层大,说明OC和TP的变异程度随分解程度增加,这可能与两层具有的温湿度、微生物及多种酶等影响分解过程的因子不同有关[45]。通常,根据空间自相关性的强弱将影响空间变异的因素分为结构性因素和随机性因素[46]。本研究中凋落物OC、TN和TP结构比均小于75%,变程范围为9.9 ~ 78.9 m,分形维数介于1.687 ~ 1.996之间,表明凋落物OC、TN和TP在9.9 ~ 78.9 m空间范围内自相关性较强,且随机因素引起的异质性占系统变异的1.687 ~ 1.996。因此,本研究中F层和H层凋落物OC、TN和TP空间异质性在研究尺度上主要受结构性因素影响;采用10 m × 10 m样方收集凋落物样品,基本能反映凋落物OC、TN和TP的总体变化情况;尽管分形维数差异不大,但各样地F层凋落物OC和TP的分形维数整体高于H层,表明其空间分布复杂,而凋落物TN表现出与之相反的空间结构特征。各样地凋落物OC、TN和TP克里格插值图呈明显的条带状和斑块状梯度分布,且F层和H层OC在同一样地内表现为相似的空间分布格局,而F层TN和TP浓度高值出现的位置在H层则相对较低。本研究各样地气候和地形等立地条件基本一致,F层和H层凋落物养分浓度高值区域各不相同,很可能是受天然林树种组成和郁闭度等林分因子和凋落物含水率和现存量等因子的影响。
森林生态系统林分结构决定了太阳辐射和降水的空间分配,和凋落物性质共同影响凋落物积累、分解以及养分归还利用[47-49]。采伐直接影响林分结构,主要体现在树种组成和林分密度等指标上。本研究中,在天然云冷杉针阔混交林中选取的4块样地立地条件相似,即使受到不同强度的采伐干扰后,其郁闭度也较为接近,而在相对狭窄的冠层影响范围内局部生境的小气候条件无疑是4块样地间凋落物OC、TN和TP空间分布及其与地上植被和凋落物因子的相关性存在差异的重要原因。总体上,H层凋落物OC和TN与凋落物现存量均呈显著负相关,TP与其呈显著正相关,表明凋落物现存量增高,影响H层养分变化,而对F层影响较小。H层凋落物OC和TN与持水率呈显著正相关,显然,持水率影响了微生物呼吸利用及养分固定。凋落物养分间有着密切的耦合关系,表现为随TN浓度的增加,F层和H层凋落物中OC、TP浓度及计量比显著增加[11],这与肖银龙等[50]得出氮能加速凋落物中养分的释放和循环的结论一致,而与李鑫等[51]的研究结果略有不同。本研究中,凋落物OC、TN和TP与物种数、株数和生物多样性等指标均呈一定的相关性,其中,F层凋落物TP与物种数和生物多样性指数呈显著正相关,TN与其呈显著负相关,虽然丰富的树种组成有利于F层凋落物分解和养分积累,但N较P更易淋溶损失;而H层凋落物OC和TP与针叶树种和株数比例呈显著负相关,说明H层凋落物养分的循环利用可能与针叶树种不易分解的生物学特性有关。此外,本研究中F层凋落物TP与郁闭度呈显著正相关,而H层凋落物TP与其呈显著负相关,说明随着郁闭度增大,光照和降水对凋落物影响相对减弱使其分解减慢,在未分解层凋落物较少的前提下,TP会表现在F层富集,而H层TP受表聚现象、淋溶作用和养分释放的影响呈下降趋势。
空间变异的研究结果因研究区域大小、采样间距和数量及采样方法等存在差异,其具有较强的尺度依赖性[52-53]。本研究在10 m × 10 m样方中仅取50 cm × 50 cm一份凋落物样品,仍有指标模型拟合得到的变程小于10 m,因此,为降低采样所带来的偏差,建议对1 hm2大样地内设置的100个10 m × 10 m样方中重复多次采集样品。所选样地气候条件基本一致,地势平缓,但不能排除其在凋落物养分空间格局中的微弱作用,因此,有必要进一步比较选择最优的空间插值方法。此外,本研究通过相关性定量分析了各样地中100个样方的凋落物养分与对应林分和凋落物因子的相互关系,该方法可以从数量上反映现象之间的正负效应及其密切程度,其误差随数据量的增大而减小,但是无法准确地判断现象内在联系的有无和因果关系。如本研究得出,凋落物养分的空间变异与林分因子呈显著相关关系,但未将树种分布、树木大小及落叶范围等纳入分析,同时,凋落物养分分布还可能受到物种根系或者微生物驱动,因此,除了结合专业知识和实际经验进行分析讨论外,还必须以机理性研究为指导。
4. 结 论
(1)温带天然云冷杉针阔混交林H层凋落物OC和TN含量均显著低于F层,而TP显著高于F层,但均表现为中等变异,且凋落物OC和TP的变异程度随分解程度增加基本呈增加趋势。
(2)温带天然云冷杉针阔混交林F层和H层凋落物养分的空间自相关性较强,OC空间分布格局较相似,但TN和TP极值区域不同,H层凋落物OC和TP较F层均一性好,凋落物TN呈相反的变化趋势。
(3)温带天然云冷杉针阔混交林H层凋落物养分与现存量、持水率和化学计量比相关性较F层显著,此外,F层凋落物养分特征主要受到树种丰富度和多样性指数的影响,H层则主要受针叶树种及株数比例的影响。
温带天然云冷杉针阔混交林具有复杂的局部扰动率,林下凋落物层养分格局受凋落物分解和林分结构影响较大,因此,应持续关注凋落物分解和养分格局对环境因子的响应,以充分发挥凋落物层在森林生态系统内的生态功能和实现森林的健康管理与经营。
-
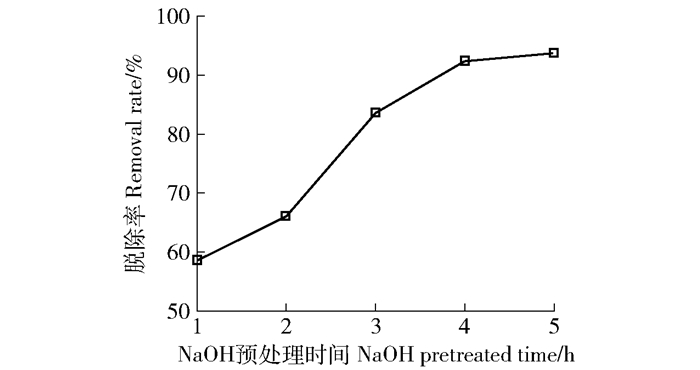
表 1 NaOH预处理时间对活性炭各参数的影响
Table 1 Effects of NaOH-pretreated time on the activated carbon parameters
NaOH预处理时间
NaOH pretreatment time/hSBET/
(m2·g-1)Vt/
(cm3·g-1)Vmic/
(cm3·g-1)Vmes/
(cm3·g-1)平均孔径
Average pore size/nm介孔率
Mesoporous rate/%0 1 325 0.79 0.67 0.12 1.78 15.2 1 1 387 0.84 0.52 0.32 2.23 38.1 2 1 416 1.04 0.49 0.65 3.36 62.5 3 1 652 1.54 0.52 0.92 3.71 59.7 4 2 038 2.13 0.57 1.56 4.18 73.2 5 1 753 1.61 0.45 1.16 4.88 72.1 注:SBET为活性炭比表面积,Vt为总孔容,Vmic为微孔孔容,Vmes为介孔孔容。Notes:SBET is the specific surface area of the activated carbon, andVt, Vmic andVmes are total pore volume, micoporous volume, and mesoporous volume, respectively. 表 2 不同活性炭样品性能指标对比
Table 2 Comparison in property index for different activated carbon
原料
RawmaterialSBET/
(m2·g-1)Vt/
(cm3·g-1)介孔率
Mesoporousrate/%MB吸附值
MBadsorptionvalue/(mg·g-1)参考文献
References木糖渣Corncobresidues 2038 2.13 73.2 436 本试验Thisexperiment 聚丙烯塑料-锯末Polypropyleneandsawdust 1462 1.04 70.0 323 [21] 锯末Sawdust 2104 1.63 71.8 387 [22] 碱木糖渣Alkalixyloseresidues 1850 1.48 360 [23] 椰壳Coconutshell 1723 0.87 375 [24] 桉木屑Eucalyptussawdust 1886 240 [25] -
[1] Chen Y, Zhai S R, Liu N, et al. Dye removal of activated carbons prepared from NaOH-pretreated rice husks by low-temperature solution-processed carbonization and H3PO4 activation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 144: 401-409. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.002
[2] 苏伟.椰壳基微孔活性炭制备与表征研究[D].天津: 天津大学, 2003. Su W. Studies on the preparation and characterization of microporous activated carbon from coconut shell[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2003.
[3] 郝一男, 王喜明.文冠果壳活性炭的结构表征及吸附Cu2+的研究[J].应用化工, 2017, 46(1): 81-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sxhg201701020 Hao Y N, Wang X M. Structure characterization and adsorption performance for Cu2+ of activated carbon derived from Xanthoceras sorbifolia bunge shell[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(1): 81-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sxhg201701020
[4] Foo K Y, Hameed B H. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from pomelo skin for the removal of anionic and cationic dyes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 173(2): 385-390. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.073
[5] Liu Q S, Zheng T, Wang P, et al. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 157(2/3): 348-356. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ace65ac4e741c5c1ce0f9874f214e15e
[6] Wu X B, Hui K N, Hui K S, et al. Adsorption of basic yellow 87 from aqueous solution onto two different mesoporous adsorbents[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 180: 91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.11.009
[7] 戴红玲, 彭小明, 胡锋平.新型有序介孔炭的制备及其对酸性黑1染料的吸附性能研究[J].环境污染与防治, 2016, 38(11): 1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwryfz201611001 Dai H L, Peng X M, Hu F P. Preparation of new ordered mesoporous carbon and its adsorption performance for acid black 1 dye[J]. Environment Pollution & Control, 2016, 38(11): 1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwryfz201611001
[8] Liu X B, Xie X X, Yan H, et al. A review of the adsorption of organic pollutants on mesoporous carbons and carbon/silica hybrids[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2013, 64: 557. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xxtcl201304001
[9] Li D W, Zhu X F. Rice husk-based activated carbon with high mesoporosity prepared by a combination of CO2 activation and boiling in alkaline solution[J]. Carbon, 2014, 67: 796. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3b5b80c19248c6b90b869af9a39efbf8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] 王力臻, 闻红丽, 孙淑敏, 等.以核桃壳为碳源微波加热制备介孔活性炭[J].功能材料, 2014, 45(18): 18144-18147, 18152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.18.031 Wang L Z, Wen H L, Sun S M, et al. The preparation of mesoporous activated carbon by microwave radiation heating walnut shell[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2014, 45(18): 18144-18147, 18152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.18.031
[11] Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, et al. Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass[R]. Golden, Colorado: National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 2008.
[12] 郝丽娜, 解强, 李兰廷, 等.金属盐催化制备煤基中孔活性炭的研究[J].炭素技术, 2008, 27(4): 26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2008.04.007 Hao L N, Xie Q, Li L T, et al. Catalytical preparation of mesoporous coal-based activated carbon by nitrate copper and nitrate manganese[J]. Carbon Techniques, 2008, 27(4): 26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3741.2008.04.007
[13] Sun Y, Webley P A. Preparation of activated carbons with large specific surface areas from biomass corncob and their adsorption equilibrium for methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and hydrogen[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(15): 9286-9294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=383d28ab9be5cdc917bcaeff6b3c9c74
[14] 王成福, 杜瑞锋, 王运刚, 等.木糖渣木质素的提取工艺研究[J].中国食品添加剂, 2015(8): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2015.08.014 Wang C F, Du R F, Wang Y G, et al. The process of separating lignin from corncob residue[J]. China Food Additives, 2015(8): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2015.08.014
[15] 朱光真, 邓先伦.磷酸法制备活性炭活化机理研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(30): 18653-18655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.30.105 Zhu G Z, Deng X L. Study on preparation mechanism of activated carbon by phosphoric acid activation[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(30): 18653-18655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.30.105
[16] 左宋林.磷酸活化法制备活性炭综述(Ⅰ)—磷酸的作用机理[J].林产化学与工业, 2017, 37(3): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2017.03.001 Zuo S L. Review on phosphoric acid activation for preparation of activated carbon (Ⅰ): roles of phosphoric acid[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2017, 37(3): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2017.03.001
[17] 黎先发, 罗学刚.磷酸活化碱木质素制备活性炭[J].中国粉体技术, 2015, 21(3): 33-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgftjs201503008 Li X F, Luo X G. Preparation of activated carbon from Kraft lignin by phosphoric acid activation[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2015, 21(3): 33-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgftjs201503008
[18] Gregg S J, Sing K S W. Adsorption, surface area and porosity[M]. London: Academic Press, 1982.
[19] 孙康.果壳活性炭孔结构定向调控及应用研究[D].北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2012. Sun K. Drective control porous structure and utilization of nutshell activated carbon[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2012.
[20] 杨娇萍.超级电容器用多孔活性炭材料的研究[D].北京: 北京化工大学, 2005. Yang J P. Study of porous active carbon materials for super-capacitors[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2005.
[21] 马培勇, 武晋州, 张贤文, 等.聚丙烯塑料-锯末干混合制备高介孔率柱状活性炭[J].环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2):484-491. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201802007 Ma P Y, Wu J Z, Zhang X W, et al. Preparation of high mesoporous granular activated carbon with polypropylene and sawdust via dry mix method[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2):484-491. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjkxxb201802007
[22] 邢献军, 孙宗康, 范方宇, 等.干法制备高中孔率生物质成型活性炭[J].化工学报, 2016, 67(6): 2638-2644. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201606059 Xing X J, Sun Z K, Fan F Y, et al. Preparation of biomass-based activated carbon with high-mesoporosity by direct zinc chloride activation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(6): 2638-2644. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hgxb201606059
[23] 侯敏, 邓先伦, 朱光真, 等.磷酸活化碱木糖渣制备高吸附性能活性炭[J].林产化学与工业, 2015, 35(5): 129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2015.05.021 Hou M, Deng X L, Zhu G Z, et al. Preparation of activated carbon from alkali xylose residue by phosphoric acid activation[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2015, 35(5): 129-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2015.05.021
[24] 刘雪梅, 蒋剑春, 孙康, 等.热解活化法制备高吸附性能椰壳活性炭[J].生物质化学工程, 2012, 46(3): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2012.03.002 Liu X M, Jiang J C, Sun K, et al. Preparation of activated carbon with high adsorption properties from coconut shell by pyrolysis and activation[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2012, 46(3): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2012.03.002
[25] 谢新苹, 孟中磊, 蒋剑春, 等.磷酸活化桉木屑制备活性炭的影响因素及表征[J].东北林业大学学报, 2013, 41(4): 116-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.04.027 Xie X P, Meng Z L, Jiang J C, et al. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from eucalyptus sawdust with phosphoric acid[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2013, 41(4): 116-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.04.027
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 闫俊霞,杨硕华,张建峰,王子帅. 景观视域下邯郸临洺关镇城镇绿地格局演变分析. 南方农业. 2024(23): 191-195 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: