Microbial and enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil of different forest stand in karst and non karst areas
-
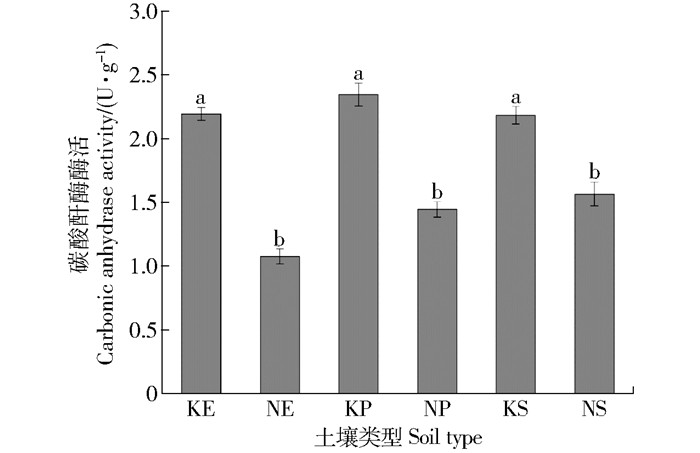
摘要:目的为明确不同地质条件下、不同林分对根际土壤微生物及土壤酶活性的影响,该研究为今后深入探究岩溶自然生态系统的恢复提供理论依据。方法本文以云南建水岩溶与非岩溶区人工桉树林、人工云南松林和天然次生林根际土壤为研究对象,通过对根际土壤微生物数量和土壤酶活性的测定,探究不同地质、不同林分对根际土壤微生物及土壤酶活性的影响,及其微生物与土壤酶间的相关性。结果本研究表明,在相同地质背景条件下,两种不同人工林土壤中桉树(阔叶林)与云南松(针叶林)放线菌的数量存在显著性差异,天然次生林微生物数量为18.2×105 cfu/g。受地质条件、植被恢复模式等影响,各样地土壤酶活性各异。相关分析表明,脲酶、过氧化氢酶活性与放线菌数量呈显著正相关,脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、碳酸酐酶、过氧化氢酶4种酶活之间存在相互联系。结论土壤微生物群落及土壤物质的转化受地质条件、林分差异和恢复模式的影响。Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to clarify the effects of different forests on soil microorganism and soil enzyme activity under different geological conditions, providing a theoretical basis for further research on restoration of natural ecological system.MethodThe soil samples were collected separately in rhizosphere of Eucalyptus robusta plantation, Pinus yunnanensis plantation and natural secondary forest growing up in karst and non-karst areas of Jianshui, Yunnan of southwestern China. The correlations between microorganisms and soil enzymes from different geological backgrounds and forests were studied by dilution coating and soil enzyme measurement.ResultThe results showed that there was a significant difference between the number of actinomycetes in the rhizosphere soil of E. robusta and P. yunnanensis forests under the same geological background. The microbial quantity of secondary forest in karst area was 18.2×105 cfu/g. Generally, influenced by the restoration patterns and geological conditions, the activities of soil enzymes were different. Correlation analysis showed that urease and catalase activity were positively correlated with the number of actinomycetes. There were interrelations between urease, acid phosphatase, carbonic anhydrase and catalase.ConclusionThe results reveal that geological backgrounds, forest stand and the restoration patterns will affect soil microbial community composition and transformation of soil substance.
-
Keywords:
- karst /
- soil enzyme /
- rhizosphere /
- soil microorganism
-
-
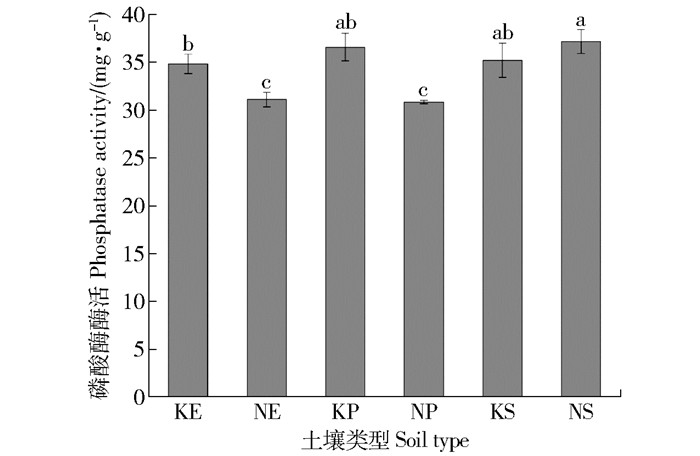
图 1 各个样地过氧化氢酶酶活
KE.岩溶桉树;NE.非岩溶桉树;KP.岩溶云南松;NP.非岩溶云南松;KS.岩溶次生林;NS.非岩溶次生林。下同。
Figure 1. Catalase activity in each sample plot
KE, eucalyptus in karst area; NE, eucalyptus in non-karst area; KP, Yunnan pine in karst area; NP, Yunnan pine in non-karst area; KS, secondary forest in karst area; NS, secondary forest in non-karst area.The same below.
表 1 各个样地土壤基本理化性质的测定
Table 1 General basic physical and chemical properties of various samples
变量Variable 林分类型Stand type 桉树Eucalyptus robusta 云南松Pinus yunnanensis 次生林Secondary forest 岩溶区Karst area 非岩溶区Non-karst area 岩溶区Karst area 非岩溶区Non-karst area 岩溶区Karst area 非岩溶区Non-karst area 速效钾Available potassium/(mg·kg-1) 124.77±2.37d 230.17±6.12c 117.5±0.35e 68.85±7.88f 335.23±1.66b 442.13±3.55a 全氮Total nitrogen/(g·kg-1) 12.94±0.06b 6.31±0.20d 9.64±0.45c 9.42±0.57c 5.74±0.22d 14.60±0.09a 全磷Total phosphorus/(g·kg-1) 2.14±0.11c 0.82±0.03e 1.20±0.05d 3.88±0.08a 0.77±0.01e 2.78±0.05b 有机质Organic matter/(g·kg-1) 123.76±0.00a 63.09±0.13ab 80.16±2.21ab 44.03±0.67c 119.85±0.00a 78.36±0.67c pH 5.59±0.03b 5.69±0.11b 5.64±0.02b 4.76±0.02c 6.59±0.11a 5.60±0.01b 电导率Electrical conductivity/(μS·cm-1) 2.29±0.16c 1.71±0.01c 1.25±0.03c 3.64±0.04a 2.87±0.13b 2.79±0.51b 表 2 各个样地的微生物数量
Table 2 Microbe number in each sample plot
cfu·g-1 土壤类型Soil type 细菌Bacteria 放线菌Actinomycetes 真菌Fungus 总计Sum 岩溶区桉树(Eucalyptus in karst areas, KE) 4.35×105±0.2a 13.67×105±1a 2.37×104±0.8b 18.2×105±1a 非岩溶区桉树(Eucalyptus in non-karst area, NE) 4.43×105±0.1a 10.30×105±1b 1.98×104±0.2b 14.9×105±1a 岩溶区云南松(Yunnan pine in karst area, KP) 4.39×105±0.2a 11.90×105±0.1ab 2.17×104±0.1b 16.5×105±1a 非岩溶区云南松(Yunnan pine in non-karst area, NP) 1.83×105±0b 4.50×105±0.3c 1.62×104±0.1b 6.5×105±0.7b 岩溶区次生林(Secondary forest in karst area, KS) 4.18×105±0ab 13.70×105±0.7a 3.58×104±0.1a 18.2×105±0a 非岩溶区次生林(Secondary forest in non-karst area, NS) 3.32×105±0ab 12.60×105±0.8ab 1.80×104±0.3b 16.1×105±0.5a 地质类型Geological type * ** NS *** 林分类型Stand type NS *** NS *** 注:***、**、*分别表示在P<0.001、P<0.01、P<0.05水平上差异显著,NS表示差异不显著。Notes:***, **, * represent significant difference at P<0.001,P<0.01,P<0.05 level, respectively. NS means difference is not significant. 表 3 土壤微生物数量与土壤酶的相关性
Table 3 Correlations between soil microbial biomass and soil enzyme
指标Index 细菌Bacteria 真菌Fungus 放线菌Actinomycetes 脲酶Urease 磷酸酶Phosphatase 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase 过氧化氢酶Catalase 细菌Bacteria 1 0.050 0.181 0.474* 0.589* 0.410 0.515* 真菌Fungus 1 0.321 0.066 -0.058 -0.058 0.000 放线菌Actinomycetes 1 0.554* 0.300 0.141 0.518* 脲酶Urease 1 0.600** 0.582* 0.930** 磷酸酶Phosphatase 1 0.564* 0.781** 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase 1 0.662** 过氧化氢酶Catalase 1 注:**、*分别表示在P<0.01,P<0.05水平上差异显著。Notes:** and * represent significant difference at P < 0.01 and P < 0.05 levels, respectively. -
[1] 邱权, 李吉跃, 王军辉, 等.西宁南山4种灌木根际和非根际土壤微生物、酶活性和养分特征[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(24): 7411-7420. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201424029 Qiu Q, Li J Y, Wang J H, et al. Microbes, enzyme activities and nutrient characteristics of rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soils under four shrubs in Xining Nanshan Prefecture, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(24): 7411-7420. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201424029
[2] 倪彬.巨桉人工林根系土壤微生物、根系土壤酶活性与根系土壤养分研究[D].雅安: 四川农业大学, 2007. Ni B. Study on rhizosphere soil microorganism and rhizosphere soil enzyme activity and rhizosphere soil nitrient in Eucalyptus grandis plantation[D].Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2007.
[3] 侯本栋, 马风云, 宋玉民, 等.不同树种对土壤养分、酶活性与微生物影响的研究[J].江西农业大学学报, 2006, 28(5): 734-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2006.05.020 Hou B D, Ma F Y, Song Y M, et al. A study on effects of different tree species on soil nutrients, enzyme activities and microorganisms[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2006, 28(5): 734-738. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2006.05.020
[4] 陈家瑞, 曹建华, 李涛, 等.西南典型岩溶区土壤微生物数量研究[J].广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 28(4): 96-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6600.2010.04.021 Chen J R, Cao J H, Li T, et al. Soil microorganisms in typical karst region of southwest China[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 28(4): 96-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6600.2010.04.021
[5] 高喜, 万珊, 曹建华, 等.岩溶区与非岩溶区土壤微生物活性的对比研究[J].地球与环境, 2012, 40(4): 499-504. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201204005 Gao X, Wan S, Cao J H, et al. Comparative investigation of soil microbial activity in the karst and non-karst areas[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(4): 499-504. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx201204005
[6] 赵维娜, 王艳霞, 陈奇伯.高山栎天然林土壤酶活性与土壤理化性质和微生物数量的关系[J].东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(9): 72-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.09.015 Zhao W N, Wang Y X, Chen Q B. Relationships between the soil enzyme activity, physical chemical properties and microorganism quantity in Quercus aquifolioides forest[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2015, 43(9): 72-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.09.015
[7] 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社, 2000. Bao S D. Soil agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005.
[8] 姚槐应.土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006. Yao H Y. Soil microbial ecology and its experimental techniques[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
[9] 李睿玉, 王煜, 王亚男, 等.土荆芥不同发育期根际土壤养分、酶活及微生物数量的变化[J].生态环境学报, 2014, 23(9): 1526-1530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.09.020 Li R Y, Wang Y, Wang Y N, et al. Changes of soil nutrient, soil enzymes activities and microbial communities in rhizosphere soil of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. at different development phases[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(9): 1526-1530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.09.020
[10] 晋曦.不同封育年限下石灰岩山地土壤微生物及酶活性研究[D].合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2014. Jin X. Dynamics of soil microbial activities following mountan closing[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2014.
[11] 涂志华.沿海防护林23个竹种根际土壤酶活性与微生物的研究[D].福州: 福建农林大学, 2012. Tu Z H. Study on rhziosphere soil enzyme activity and microorganism of 23 bamboos in costal shelter-forest[D].Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012.
[12] 李元, 牛文全, 张明智, 等.加气灌溉对大棚甜瓜土壤酶活性与微生物数量的影响[J].农业机械学报, 2015, 46(8): 121-129. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyjxxb201508018 Li Y, Niu W Q, Zhang M Z, et al. Effects of aeration on rhizosphere soil enzyme activities and soil microbes for muskmelon in plastic greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(8): 121-129. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyjxxb201508018
[13] 李国梁.柏木低效林不同改造模式土壤微生物和土壤酶活性研究[D].雅安: 四川农业大学, 2012. Li G L. Study on enzyme activity and soil microorganisms in different transformation pattern of the cypress inefficient[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2012.
[14] 吴雁, 张金池.微生物碳酸酐酶在岩溶系统碳循环中的作用与应用研究进展[J].生物学杂志, 2015, 32(3): 78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2015.03.078 Wu Y, Zhang J C. Microbial carbonic anhydrase action and application on carbon cycling in karst dynamic system: a review[J]. Journal of Biology, 2015, 32(3): 78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2015.03.078
[15] Li W, Yu L J, Yuan D X, et al. A study of the activity and ecological significance of carbonic anhydrase from soil and its microbes from different karst ecosystems of southwest China[J]. Plant & Soil, 2005, 272(1-2): 133-141.
[16] 王静, 徐广平, 曾丹娟, 等.岩溶区和非岩溶区两种优势植物凋落叶分解的比较研究[J].广西植物, 2013, 33(3): 338-345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2013.03.010 Wang J, Xu G P, Zeng D J, et al. Comparative study on decomposition of leaf litters from two dominant species under karst and non-karst terrains[J]. Guihaia, 2013, 33(3): 338-345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3142.2013.03.010
[17] 赵汝东, 樊剑波, 何园球, 等.红壤丘陵区人工林恢复措施对土壤酶活性和微生物学性质的影响[J].土壤, 2012, 44(4): 576-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.04.008 Zhao R D, Fan J B, He Y Q, et al. Effects of plantation restoration approaches on soil enzyme activities and microbial properties in hilly red soil region[J]. Soil, 2012, 44(4): 576-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.04.008
[18] 康冰, 刘世荣, 蔡道雄, 等.南亚热带不同植被恢复模式下土壤理化性质[J].应用生态学报, 2010, 21(10): 2479-2486. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201010005 Kang B, Liu S R, Cai D X, et al. Soil physical and chemical characteristics under different vegetation restoration patterns in China south subtropical area[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(10): 2479-2486. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201010005
[19] Burghelea C, Zaharescu D G, Dontsova K, et al. Mineral nutrient mobilization by plants from rock: influence of rock type and arbuscular mycorrhiza[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2015, 124(1-3): 187-203. doi: 10.1007/s10533-015-0092-5
[20] 罗达, 史作民, 唐敬超, 等.南亚热带乡土树种人工纯林及混交林土壤微生物群落结构[J].应用生态学报, 2014, 25(9): 2543-2550. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201409012 Luo D, Shi Z M, Tang J C, et al. Soil microbial community structure of monoculture and mixed plantation stands of native tree species in south subtropical China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(9): 2543-2550. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201409012
[21] 连宾, 袁道先, 刘再华.岩溶生态系统中微生物对岩溶作用影响的认识[J].科学通报, 2011, 56(26): 2158-2161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201126002 Lian B, Yuan D X, Liu Z H. Effect of microbes on karstification in karst ecosystems[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(26): 2158-2161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201126002
[22] 栾丽英, 房玉林, 宋士任, 等.不同树龄酿酒葡萄不同土壤深度根际和根区微生物数量的研究[J].西北林学院学报, 2009, 24(2): 37-41. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200902008 Luan L Y, Fang Y L, Song S R, et al. Soil microbe in vineyards with different tree ages and different soil depths[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2009, 24(2): 37-41. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200902008
[23] Yuan X F, Xu J, Chai H, et al. Differences of rhizo-bacterial diversity and the content of peimine and peiminine of Fritillaria thunbergii among different habits[J]. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 2010, 4(6): 465-470.
[24] 龙健, 李娟, 江新荣, 等.贵州茂兰喀斯特森林土壤微生物活性的研究[J].土壤学报, 2004, 41(4): 597-602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.016 Long J, Li J, Jiang X R, et al. Soil microbial activities in Maolan karst forest, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41(4): 597-602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.016
[25] 司登宇.凤阳山不同林分类型土壤生物活性研究[D].南京: 南京林业大学, 2013. Si D Y. Study on soil biological activity of different forest types in Fengyang Mountain[D]. Nanjing : Nanjing Forestry University, 2013.
[26] 陈汝, 王海宁, 姜远茂, 等.不同苹果砧木的根际土壤微生物数量及酶活性[J].中国农业科学, 2012, 45(10): 2099-2106. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.10.024 Chen R, Wang H N, Jiang Y M, et al. Rhizosphere soil microbial quantity and enzyme activity of different apple rootstocks[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(10): 2099-2106. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.10.024
[27] Colemanderr D, Desgarennes D, Fonsecagarcia C, et al. Plant compartment and biogeography affect microbiome composition in cultivated and native agave species[J]. New Phytologist, 2016, 209(2): 798-811. doi: 10.1111/nph.13697
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 苏岫,王祥,宋德瑞,李飞,杨正先,张浩. 基于改进光谱角法的红树林高分遥感分类方法研究. 海洋环境科学. 2021(04): 639-646 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈冀岱,牛树奎. 多时相高分辨率遥感影像的森林可燃物分类和变化分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2018(12): 38-48 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: