Plant diversity of different forestland in the loess region of western Shanxi Province, northern China
-
摘要:目的探索不同林地林下植物多样性特征及其与环境因子的相关性, 为黄土高原地区植被恢复与重建工作提供科学依据。方法以山西吉县蔡家川流域3种人工林(油松林、刺槐林和油松×刺槐混交林)和2种天然次生林(山杨次生林、辽东栎次生林)为研究对象, 采用标准样地调查法进行植被调查。结果结果表明:5种林地类型共出现林下植物52种(灌木植物17种, 草本植物35种), 且不同林地类型林下植物物种组成及分布差异较大, 天然次生林的灌木物种数量明显多于人工林, 而草本物种数量却要少于人工林。5种林地类型的灌木层均匀度指数无显著差异, 物种丰富度指数和多样性指数表现为天然次生林>人工林, 而草本层物种丰富度指数、均匀度指数及多样性指数均表现为人工林>天然次生林。环境因素对林下植物多样性的影响较大, 尤其是郁闭度、土壤含水量及毛管孔隙度对林下植物多样性的影响较为显著。结论不同林地林下植物多样性差异显著, 综合考虑灌木及草本层植物组成及多样性特征, 油松×刺槐混交造林方式优于纯林造林方式, 应该在该地区合理扩大油松×刺槐混交造林的面积; 郁闭度是影响林下植物多样性的主要环境因子, 因此可以通过适当开窗疏林来提高林下植物多样性。Abstract:ObjectiveThis study aims to provide scientific basis for the restoration and reconstruction of vegetation in the Loess Plateau by studying the characteristics of plant diversity and its correlations with the environmental factors in different forestland.MethodTaking 3 kinds of artificial forests (Pinus tabuliformis forest, Robinia pseudoacacia forest, mixed forest of Pinus tabuliformis and Robinia pseudoacacia)) and 2 kinds of natural secondary forests (Populus davidiana, Quercus liaotungensis) in Caijiachuan Basin of Jixian County, Shanxi Province of northern China as research objects, we carried out vegetation investigation by standard sample land survey method.ResultThe results showed that there were 52 species of undergrowth plant, including 17 shrubs and 35 herbs, and the species composition and distribution of different forest types were quite different. The number of shrub species in natural secondary forest was more than artificial forest, but the number of herb species was less than artificial forest. There was no significant difference in the evenness index of shrubs among the five forest types. Species richness index and diversity index both showed natural secondary forest > artificial forest, while the species richness index, evenness index and diversity index of the herb layer all showed as artificial forest > natural secondary forest. Environmental factors had a significant impact on plant diversity, especially canopy density, soil water content and capillary porosity.ConclusionThe characteristics of plant diversity varied significantly in different forest types. Considering the composition and diversity of shrubs and herbs, the mixed afforestation of P. tabuliformis and R. pseudoacacia was better than pure afforestation, so the area of mixed forest should be expanded reasonably. In addition, canopy density was the main environmental factors affecting plant diversity. Therefore, the appropriate intervening forest could improve the diversity of undergrowth plants.
-
作为中国西北部戈壁荒漠中独有的成林乔木,胡杨(Populus euphratica)展现出对复杂盐碱环境的强适应力,其顽强的生命力主要归功于强劲的根系。根系是植物吸收水分和营养,应对生态变化的关键器官,尤其在逆境下起着至关重要的作用[1−3]。干旱、盐碱等非生物胁迫严重影响了胡杨的生长发育,尽管已有研究[4]探讨了胡杨根系在逆境下的生理机制,但其根系耐盐性的遗传特性仍缺乏系统性探究。研究胡杨在盐胁迫下根系的遗传调控机制,可揭示其适应复杂环境的生长特性,并对农作物和林木的分子标记辅助育种具有重要意义。
研究人员对胡杨根系在盐胁迫下的生长调控机制进行了积极探索。Wang等[5]研究表明:过表达PAGERF16基因可降低胡杨的生根率,推迟生根时间,同时显著促进侧根的增殖和增厚,而主根长度未受影响。Fan等[6]研究了SPSNAC042基因在盐胁迫和干旱胁迫下的作用,发现该基因能够促进根系发育,增强胡杨对环境胁迫的耐受性。此外,Liu等[7]对WUSCHEL-related homeobox(WOX)转录因子在胡杨不定根响应逆境胁迫过程中的作用机制进行了研究,发现WOX11/12a-SMALL AUXIN UP RNA36模块通过调节生长素信号途径来促进不定根的发育,增强了对盐胁迫的适应能力。上述研究探究了特定基因在胡杨根系耐盐性中的作用,但主要集中单一表型性状的遗传机制,而对多个根系性状在盐胁迫下的综合遗传分析较为匮乏。因此,研究胡杨根系在盐胁迫下多个表型性状的遗传调控机制是十分必要的。
利用数量性状座位(quantitative trait locus,QTL)定位的方法来解析复杂性状的遗传机制是一种十分有效的手段。Ma等[8]提出了功能作图的分析方法,使用了与时间相关的生物生长函数进行分析,获得了随时间变化且与生物生长相关的QTL。研究动态性状有助于揭示基因的动态表达,为胡杨根系性状遗传调控研究提供理论依据。本研究主要选择胡杨根系在盐胁迫下的主根长、主根表面积和主根数量3个表型性状,拟采用主成分分析、方差分析和动态模型拟合等多种统计方法,分析这些性状的表型生长变化趋势,探究胡杨主根分别在正常和盐胁迫条件下的生长适应性模式。通过功能作图对正常和盐胁迫条件下的表型与基因型数据进行关联分析,有效定位影响胡杨根系表型性状的显著QTL,并进一步将遗传调控网络可视化,探究胡杨根系表型性状在盐胁迫条件下的遗传调控机制,旨在以新视角揭示胡杨根系生长发育的遗传调控机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
研究对象选用的胡杨母本Pe-1和父本0046均来自新疆库尔勒地区[9],亲本间地理距离为31 km。2014年,将父本0046的雄性花枝在北京林业大学人工气候室中进行水培,收集并保存发育完全的花粉于−20 ℃的EP管中。胡杨母本Pe-1全株移栽至北京林业大学温室种植,在雌花完全发育后,使用父本0046的花粉进行人工授粉,6月中旬获得成熟种子。种子在试管中培养4个月后,幼苗移栽至基质中,最终获得408株全同胞子代,这些子代保存于北京林业大学温室苗床中。通过这408个胡杨全同胞个体的组培无性系化和扩繁保存实验,最终获得156个能够在生根培养基上生根并正常生长发育成完整植株的系号。生根培养基配方为1/2 MS + 0.4 mg/L IBA + 25 g/L 蔗糖 + 8 g/L 琼脂。实验过程中,每个系号保持50株以上单株。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 盐胁迫浓度确定
实验设置了4个NaCl浓度梯度:0.1%(17.111 6 mmol/L)、0.3%(51.334 7 mmol/L)、0.5%(85.557 8 mmol/L)和0.7%(119.781 0 mmol/L)。为确定盐胁迫的适宜浓度,从156个胡杨无性系中随机选择20个系号进行盐胁迫浓度筛选预实验,每个系号5个重复。所有系号均选取长度约10 mm,包含4 ~ 6片叶片的顶芽进行接种,并培养45 d,期间统计生根情况(生根率和根系表型)。合适的盐胁迫浓度既能诱导轻度胁迫表型,又不完全抑制植物生根与生长。
1.2.2 表型性状测定
分别在正常条件和盐胁迫下对156个胡杨无性系进行试管接种实验。每个系号选择生长状况一致的单株,截取长度约10 mm且具4 ~ 6片叶片的顶芽,接种到长300 mm、内径45 mm的圆柱平底玻璃试管中进行培养,每个试管均加入260 mL生根培养基。每24个试管为一组,放置在3 × 8格子的试管架中。所有试管苗均在组培间统一培养条件下生长,光照强度为
1500 lx,温度为26 ℃,光照周期为16 h光照、8 h黑暗。所有系号统一在接种后第13天开始,使用Clark等[10]的方法搭建的360°拍照系统进行图像采集,每隔5 d采集一次,共进行14次采集,持续78 d。试管接种实验结果显示:在正常条件下,156个系号均能正常生根,并获得根系生长数据;在盐胁迫条件下,117个系号能够正常生根并获得根系生长数据。实验在正常和盐胁迫条件下均获得7种动态表型性状数据,包括主根长度、主根表面积、主根数量、根体积、平均根直径、平均根长度和最大根长度。每个系号进行多次接种,以确保最终每个系号在每个处理下获得较一致的3个重复的根系生长状态数据[11]。1.2.3 SNP标记开发
采集F1代每个单株的叶片,使用液氮速冻后保存于−80 ℃超低温冰箱。随后,使用TIANGEN试剂盒提取基因组DNA,并采用NanoDrop 2000(Thermo Scientific)测定DNA的浓度和纯度。将质量合格的DNA样品送至上海美吉生物公司(Majorbio,Shanghai),利用RAD技术在Illumina HiSeq2500平台上进行高通量测序。基于测序获得的SNP标记,构建了全同胞群体的胡杨连锁图谱。该图谱包含8 305个SNP位点,分布在19个连锁群中,总长度为4 574.89 cM,标记间的平均距离为0.55 cM。根据孟德尔分离原理,将标记分为测交标记和杂交标记两类,测交标记包括lm × ll和nn × np型,杂交标记记为hk × hk,测交标记有6 886个,杂交标记有1 419个。
1.2.4 表型数据的分析
针对胡杨在正常与盐胁迫条件下的7 个动态表型性状,利用14 个时间点测定的表型值分别进行相关性分析、主成分分析和方差分析。本研究采用Pearson相关性分析探究这些表型性状在不同环境下的相互关系。对数据集进行Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin(KMO)检验和巴特利特的球形检验,以确保数据满足主成分分析的条件。开展主成分分析和方差分析,利用R语言中的aov函数进行组间差异检验,并以箱线图展示,以评估不同环境条件下表型性状的差异,探究环境因素对表型性状生长的影响。针对Logistic[12]、Richards[13]、Weibull[14]、Gompertz[15]经典生长模型进行数值实验,确定拟合胡杨根系生长的最优模型。
1.2.5 功能作图
功能作图是将描绘生长表型性状的生长曲线嵌入到QTLs定位框架中的统计分析方法[8],以n(n = 156)个样本为作图群体,每个个体i在T(T = 14)个时间点测得的表型向量记为pi = pi(1),pi(2),···,pi(T),其生长曲线可用Gompertz方程拟合。
g(t)=aexp(−bexp(−ct)) (1) 式中:g(t)为时间t的表型值,a代表初始生长值,b代表生长速率,c代表最大生长天数。
在功能作图框架中,测交标记(lm × ll和nn × np)为2种基因型,杂交标记(hk × hk)为3种基因型,其中每个SNP位点第j种基因型分组下,群体的表型性状服从一个多元正态分布。
{f_j}({{\boldsymbol{p}}_i}) = \frac{1}{{(2{\text{π}} ){}^{T/2}|{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} {|^{1/2}}}}\exp \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}{{\left( {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_i} - {{\boldsymbol{m}}_j}} \right)}^\prime }{{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} ^{ - 1}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_i} - {{\boldsymbol{m}}_j}} \right)} \right] (2) 式中:mj = mj(1),mj(2),···,mj(T)是与pi对应的均值向量,可用方程(1)来拟合;{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} 代表不同组分的协方差矩阵。功能作图通过构建协方差矩阵减少需要估算的参数,提高QTLs定位的检测能力。应用Zhao等[16]推导的一阶结构前依赖(first-order structured antedependence,SAD)模型构建协方差矩阵{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} 。
{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\sigma ^2}\left( 1 \right)}& \cdots &{{\sigma ^2}\left( {1,T} \right)} \\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ {{\sigma ^2}\left( {T,1} \right)}& \cdots &{{\sigma ^2}\left( T \right)} \end{array}} \right) (3) 其中
\begin{gathered} {\sigma ^2}\left( t \right) = \frac{{1 - {\phi ^{2t}}}}{{1 - {\phi ^2}}}{\gamma ^2},{\text{ }}t = 1,2, \cdots ,T \\ {\sigma ^2}\left( {{t_1},{t_2}} \right) = {\phi ^{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\frac{{1 - {\phi ^{2{t_1}}}}}{{1 - {\phi ^2}}}{\gamma ^2},{\text{ }}{t_2} > {t_1}, \;{t_1} = 1, \cdots ,T \\ \end{gathered} (4) 式中:{\sigma ^2}(t)是表型性状在时间t的方差,{\sigma ^2}({t_1},{t_2})是表型性状在时间{t_1}和{t_2}之间的协方差,{\gamma ^2}是创新方差,\phi 是一阶时间相关参数。
结合公式1 ~ 4,针对每个SNP标记,构建如下似然函数。
L(\lambda ) = {\prod} _{j = 1}^J{\prod} _{i = 1}^{{n_j}}{f_j}({{\boldsymbol{p}}_i};{{\boldsymbol{m}}_j},{\boldsymbol{\varSigma}} ) (5) 式中:J为SNP位点基因型数,{n_j}为携带基因型j(j = 1,2,···,J)的样本数,满足\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^J {{n_j}} = n,\lambda 是包含所有未知参数的集合。
本研究用以下假设检验确定是否存在显著的QTLs影响胡杨表型性状的生长轨迹。
H0:(aj,bj,cj) ≡ (a,b,c),j = 1,2,···,J
H0:以上等式至少有一个不成立
通过极大似然估计对模型参数进行估计,通过全基因组水平上原假设{H_0}和备择假设{H_1}的计算,可以得出各标记位点上的对数似然比(log-likelihood ratio,LR)。
{{\mathrm{LR}}=-2(\log} {L} _{ {0}} {(} {\lambda } {)-\log} {L} _{ {1}} {(} {\lambda } {))} 式中:L0(λ)和L1(λ)分别是假设检验{H_0}和{H_1}下的最大似然估计[8]。使用pchisq函数将对数似然比转换计算得到所有SNPs的p值后,使用Bonferroni方法对检验结果进行校正,确定显著位点的阈值,根据阈值确定显著QTLs[17]。为了可视化不同基因组位置的显著性水平及其分布规律,本研究采用曼哈顿图对分析结果进行展示,横轴表示基因组在连锁群上的位置,纵轴表示对应的显著性统计值−lg p。以上计算均使用Rstudio软件完成。
1.2.6 遗传效应
为探究遗传因素对胡杨根系表型性状的影响,本研究使用功能作图估计每一个SNP的生长参数a、b和c,计算SNP随时间变化的遗传方差,将其作为遗传效应,对所有的QTLs遗传效应聚类。聚类可以将遗传效应相似的QTLs聚到一起,通过划分不同的模块,以分析QTLs的功能。
1.2.7 功能注释
为了解显著位点的功能和参与的生物学过程,本研究对超过阈值线的显著位点进行功能注释。利用BLAST软件将显著位点标记对应的序列与胡杨的现有基因组数据库进行比对,以识别候选基因,并进行功能注释。
1.2.8 遗传网络构建
假设检验获得的显著QTLs在调控胡杨根系表型性状的生长中发挥关键作用,构建这些QTLs的遗传网络有助于更好地理解盐胁迫下表型变异的遗传机制。通过LASSO回归模型[18]进行变量选择,分析QTLs的调控关系,使用Cytoscape软件(版本3.10.0)绘制正常与盐胁迫两种生长条件下QTLs调控网络。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 盐胁迫浓度确定
0.1%、0.3%、0.5%和0.7% NaCl下的生根率分别为100%、72%、5%和2%。与正常组相比,0.1% NaCl下胡杨各系号的主根显著变短,部分系号主根较细弱。0.1% NaCl既能保证胡杨生根率,又对胡杨根系生长产生了胁迫。因而,最终确定0.1%(17.111 6 mmol)作为盐胁迫实验的适宜NaCl浓度,以确保胡杨幼苗在盐胁迫条件下能正常生根和生长。此外,观察显示大部分组培顶芽在接种13 d后开始生根,这也为根系性状采集提供了起始时间点的依据。
2.2 相关性分析
在正常生长条件下,主根的数量、长度、表面积和体积4个表型性状间呈正相关,相关系数范围为0.23 ~ 0.91;其中主根长与主根表面积间的相关系数为0.91,显示出极强的正相关,这展现出在正常生长条件下,主根的长度与表面积在水分和养分吸收方面的密切协同作用(图1A)。平均根径与主根数量、主根长相关性较弱,但与主根体积的相关系数为0.65,显示出显著的正相关。平均根长与主根数量呈现负相关(r = −0.25),与其他表型性状呈现正相关(0.17 ~ 0.80)。最大根长与主根数量的相关性极弱,与主根长、主根表面积和平均根长呈极显著的正相关(0.75 ~ 0.80)。
在盐胁迫条件下,主根数量、主根长、主根表面积、主根体积和平均根径5个表型性状间呈正相关(0.17 ~ 0.89)(图1B)。其中主根数量、主根长和主根体积呈正相关(r > 0.36),平均根长与主根数量呈负相关(r = −0.18),但与其他表型性状呈正相关。这暗示着在盐胁迫环境中,胡杨可能倾向于减少根的数量来增加根的平均长度,并将其作为一种优化资源分配和提高吸收效率的适应性策略。
2.3 主成分分析
正常和盐胁迫条件下整体的KMO检验系数均超过0.50,巴特利特球形检验的Pb值远低于0.05,表明数据适用于主成分分析。主成分分析结果(表1)表明:在正常条件下,前两个主成分共解释了75.25%的总方差,其中第1主成分占56.09%,主要受主根长和主根表面积影响;第2主成分占19.16%,以主根数量为主导因素。在盐胁迫条件下,前两个主成分的累计方差解释率为79.35%,第1主成分占58.40%,受主根长和主根表面积影响最大;第2主成分占20.95%,主要由主根数量和平均根长决定。综合主成分分析的结果,选择主根长、主根表面积和主根数量3个性状进行下一步分析,探讨它们在正常和盐胁迫条件下的遗传调控机制。
表 1 主成分分析Table 1. Principal component analysis项目 正常条件 盐胁迫条件 主成分1 主成分2 主成分1 主成分2 特征值 3.926 1.341 4.088 1.467 贡献率/% 56.09 19.16 58.40 20.95 累计贡献率/% 56.09 75.25 58.40 79.35 主根数量 0.125 0.653 0.192 0.492 主根长 0.450 0.000 0.447 −0.126 主根表面积 0.489 0.110 0.482 0.107 主根体积 0.411 0.296 0.408 0.334 平均根径 0.198 0.380 0.283 0.409 平均根长 0.390 −0.478 0.333 −0.559 最大根长 0.428 −0.317 0.416 −0.374 2.4 方差分析
方差分析用于评估胡杨主根长、主根表面积和主根数量表型性状在不同生长条件下的生长差异。相比正常生长条件,这3种主要表型性状在盐胁迫下的表型数值有所降低,表明盐胁迫对这3种表型性状产生了抑制作用(图2)。
2.5 表型性状的动态生长拟合
本研究运用Logistic、Richards、Weibull、Gompertz 4种生长模型,分别拟合正常与盐胁迫条件下主根长、主根表面积和主根数量的平均生长轨迹。这些模型在两种条件下的拟合优度均超过0.95,有效地描述了胡杨根系的生长趋势(图3)。基于Gompertz模型适合描述生物先快后慢的不对称性生长趋势,因此本研究选择该模型进一步探究胡杨根系遗传调控机制。
正常生长条件下,胡杨的主根长在前期快速生长,第58天后生长速率下降(图3A);主根表面积则一直快速生长至第78天(图3C);主根数量在前期38 d内生长迅速,随后生长减缓(图3E)。盐胁迫条件下,胡杨主根长和主根表面积呈“S”型曲线生长,前期生长缓慢,随后生长速率上升,上升到最高值后又逐渐下降,逐渐呈现稳定(图3B,3D);主根数量呈现出前期快速生长,后期逐渐趋于稳定的生长模式(图3F)。
2.6 胡杨根系表型性状QTLs定位
通过功能作图分析,本研究定位到在不同生长条件下调控胡杨主根长、主根表面积和主根数量生长的显著SNPs,它们零散地分布在整个基因组中。我们将显著SNPs称为QTLs,以区分那些不显著的SNPs。曼哈顿图(图4)展示了显著QTLs在测交类型标记和杂交类型标记这两种SNPs类型中的分布情况。在正常生长条件下,3个性状共定位到274个显著位点,主根长共定位到100个显著SNPs位点,测交类型标记占67个,杂交类型标记33个,主要分布在1号、14号和15号连锁群(图4A)。主根表面积显示有89个显著SNPs位点,测交类型标记63个,杂交类型标记26个,其中5号连锁群的显著SNPs占16.85%(图4C)。主根数量的动态生长表型定位出85个显著SNPs位点,测交类型标记占52个,分布在1号、3号、4号、5号、8号、9号、10号、12号、13号、14号、15号和19号连锁群;杂交类型标记33个,分布在4号、5号、6号、9号、10号、11号、12号、14号、15号、18号和19号(图4E)。
盐胁迫环境下3个性状共定位到263个显著位点,胡杨主根长定位到91个显著的SNPs,包括测交类型标记68个和杂交类型标记23个,其中2号、3号、12号、13号和18号连锁群上的SNPs分别占14.29%、14.29%、12.09%、19.78%和16.48%(图4B)。主根表面积识别了85个显著的SNPs,2号、3号和13号连锁群上的SNPs分别占显著SNPs的16.47%、38.82%和16.47%,3号连锁群识别的SNPs比例最高(图4D)。主根数量识别出87个显著SNPs位点,测交类型标记占51个,杂交类型标记36个,主要分布在1号、3号和5号连锁群,其中5号连锁群拥有最集中的SNPs区域,占显著标记SNPs位点的39.08%(图4F)。
主根长、主根表面积和主根数量的生长动态表型在两种条件下的QTLs分布差异反映了胡杨根系生长与环境之间的遗传关联。盐胁迫条件下表型性状的QTLs的显著分布变化,说明这些特殊位点对胡杨基因组响应盐胁迫环境具有重要调控作用。
2.7 显著QTLs的遗传效应
为探究遗传因素对胡杨根系表型性状的影响,本研究分析了胡杨根系表型性状在正常和盐胁迫条件下显著QTLs位点的遗传效应,并绘制了随时间变化的热图,同一模块内QTLs遗传效应的变化趋势基本一致(图5)。影响主根长的显著QTLs的遗传效应在两种条件下均随时间持续上升(图5A,5B)。正常生长条件下,影响主根表面积的显著QTLs遗传效应呈现3种模式:先升后降,持续波动上升,以及先升后降再升(图5C)。在盐胁迫生长条件下,影响主根表面积的显著QTLs大多呈现持续上升的趋势(图5D)。影响主根数量的显著QTLs在两种条件下主要表现为持续上升,部分位点表现为先升后降或先降后升的趋势(图5E,5F)。不同环境条件下显著位点遗传效应的变化反映出胡杨对盐胁迫生长环境的适应性调整,这些调整可能与部分显著QTLs的基因表达调控相关。
2.8 部分显著QTLs所在候选基因的功能注释
为进一步筛选候选基因,本研究将显著位点对应的序列导入BLAST进行功能注释。在正常生长条件下,主根长相关QTLs成功注释到21个相关基因,对这些基因进行GO分析,在细胞组分、分子功能和生物学过程3个方面共富集到22个GO词条(图6A)。在细胞组分方面,富集到与叶绿体、膜复合物等相关的4个词条;在分子功能方面,富集到RNA结合、催化活性、转运活性等相关的8个词条;在生物学过程方面,主要富集到转录调控、防御反应和跨膜运输等相关的10个词条。例如:位点lm_ll_8866与GDSL脂肪酶/酯酶家族中的AT1G54790基因密切相关,此类酶对植物脂肪酸代谢和细胞膜的生物化学过程至关重要[19];位点nn_np_12107位于编码与胡杨Nudix水解酶15类似的蛋白的基因,该蛋白在细胞代谢中具有多重功能,包括水解有毒代谢产物,调节核苷酸水平和参与氧化应激反应[20]。主根表面积相关QTLs成功注释到14个候选基因,在细胞组分、分子功能和生物学过程3个方面共富集到15个GO词条(图6C)。在生物学过程中,富集到对干旱胁迫的响应、RNA加工、长链碱基生物合成等相关的7个词条;在分子功能中,富集到蛋白激酶活性、RNA结合、锌指蛋白结合等相关的5个词条;在细胞组分中,富集到细胞膜、着丝粒和膜复合物相关的3个词条。其中,显著位点nn_np_11836注释到的基因AT2G33170可编码富含亮氨酸重复的受体样蛋白激酶,可能在植物免疫应答中发挥重要角色[21];位点lm_ll_9575关联的蛋白可能与中心粒功能相关,对于细胞分裂中染色体的正确分离至关重要。主根数量相关QTLs成功注释到14个候选基因。在GO分析中,生物学过程、分子功能和细胞组分共富集到16个词条(图6E)。在生物学过程中,富集到膜运输、信号传导和染色质重塑等相关的6个词条;在分子功能中,富集到催化活性、酰基转移酶活性和DNA结合等相关的6个词条;在细胞组分中,富集到细胞核、细胞外基质和叶绿体等相关的4个词条。其中,位点lm_ll_3403与nodulation-signaling pathway 2 protein-like基因相关联,表明其可能在固氮信号传递中发挥作用,这对植物在缺氮条件下的生存至关重要[22]。上述结果表明,在正常条件下,与主根长、主根表面积和主根数量相关的候选基因主要集中在基本的代谢过程、生长素转运、染色体分离等方面,这些功能可能对维持胡杨根系的正常生长和发育起到重要作用。
在盐胁迫条件下,主根长、主根表面积和主根数量的相关QTLs分别成功注释到19、17和15个候选基因。对主根长注释到的相关基因进行GO分析(图6B),在生物学过程中,富集到转录调控、RNA加工、信号传导等相关的12个词条;在分子功能中,富集到氧化还原酶活性、转移活性、DNA结合等相关的8个词条;在细胞组分中,富集到线粒体、液泡和细胞膜等相关的5个词条。例如,在盐胁迫条件下,位点nn_np_9370与β-D-木糖苷酶基因(LOC105114908)的mRNA序列相似。β-D-木糖苷酶在植物应对生物和非生物压力时,对木质素和纤维素的分解极为重要,可影响胡杨在干旱和盐碱等逆境环境下的适应能力。对主根表面积相关基因进行GO分析(图6D),在生物学过程中,富集到RNA加工、防御反应和生长素转运等相关的10个词条;在分子功能中,富集到转运活性、催化活性和RNA结合等相关的7个词条;在细胞组分中,富集到线粒体、液泡和细胞核等相关的4个词条。例如:位点hk_hk_3008注释到的LOC105138460基因可参与胡杨的铁离子稳态调节,通过调控液泡中铁离子的存储和释放,应对环境变化引起的氧化应激。对主根数量相关候选基因进行GO分析(图6F),在生物学过程方面,富集到次生代谢、tRNA加工和防御反应等相关的9个词条;在分子功能方面,富集到DNA结合、催化活性和转运活性等相关的8个词条;在细胞组分方面,富集到线粒体相关的1个词条。如:位点lm_ll_6590注释到的LOC105132893基因可编码线粒体中的一种tRNA伪尿苷合酶A,该酶可能影响线粒体tRNA的修饰和功能[23]。综上,在盐胁迫条件下,主根长、主根表面积和主根数量相关基因主要富集于胁迫响应、氧化还原平衡、铁离子运输和tRNA修饰等方面,表明这些基因可能在适应盐胁迫引起的环境胁迫和维持根系代谢平衡方面发挥了关键作用。
2.9 遗传网络分析
在正常条件主根长遗传网络中(图7A),Q2551、Q2533和Q7998等显著QTLs产生的连接数分别占总连接数的69.9%、19.42%和7.77%,并且它们之间也存在连接,反映了主导QTLs不仅产生直接遗传效应,还间接影响其他QTLs的表达,从而影响根系的生长。在主根表面积网络中(图7C),位点Q7191、Q2241和Q7655产生的连接数分别占总网络连接的36.62%、20.66%和18.31%。在主根数量网络中(图7E),9个核心QTLs起主要调控作用,占所有节点的9.09%。
在盐胁迫主根长网络中(图7B),Q1554、Q3101和Q5128产生的连接数分别占总网络连接的55%、22%和21%。Q1554为非编码区的QTLs,未能直接定位到候选基因,不参与蛋白质编码,但其可能通过调控根生长和分化过程中基因的表达来发挥作用,从而影响根系在盐胁迫条件下的生长。Q3101表现出较高的连接数,并且其对应的位点nn_np_9370与β-D-木糖苷酶基因(LOC105114908)的mRNA序列具有相似性;主根表面积网络中的核心QTLs是Q8076和Q3053,产生的连接数分别占总连接数的74.18%和18.82%(图7D),但其核心QTLs未能直接定位到候选基因。主根数量网络包含QTLs之间的相互调控关系:Q1786促进Q2868的表达,而Q2868抑制Q1786的表达;Q2778促进Q1863的表达,而Q1863抑制Q2778的表达(图7F)。此外,连接数较高的Q1871对应的位点hk_hk_2974与ZAT10锌指蛋白(LOC105120566)的mRNA具有相似性。
3. 讨 论
植物根系能吸收水分和营养物质,提供生命所需基本元素;也可改良土壤结构,促进水土保持,对植物适应环境和维持生态系统稳定性至关重要。胡杨在沙漠生态系统中起着重要作用,是干旱和盐碱地区的重要生态屏障。盐胁迫会抑制胡杨根系生长和生物量积累,改变其分配策略,进而改变表型,从而维持胡杨在逆境环境下的生长。因此,探究并分析盐胁迫条件下胡杨的根系表型性状的变化,对于进一步解析胡杨抵御盐胁迫的内在遗传调控机制具有重要意义。
QTL定位是解析遗传机制的一种有效方法,功能作图模型是QTL定位最重要的方法之一。胡杨中已有利用QTL分析筛选耐盐候选基因的研究[24−25]。例如,王东洋等[25]通过功能作图分析,发现了一些在盐胁迫下调控胡杨愈伤组织生长的候选基因(如G6PDH2和CDC123)。其中,G6PDH2基因编码葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶,在盐胁迫条件下表达上调,参与氧化还原过程,可能缓解盐胁迫引起的氧化损伤;细胞周期蛋白 CDC123 则通过与细胞周期蛋白依赖激酶结合,调控细胞周期的进程,从而影响植物的生长发育[26]。本研究以胡杨主根性状为材料,基于正常与盐胁迫条件下的主根长、主根表面积和主根数量动态生长表型数据,采用功能作图模型进行SNP与表型性状间的关联分析,定位到调控耐盐生长的显著QTLs。相对以往利用单一时间点的QTL定位,本研究从动态角度定位盐胁迫下影响性状生长的显著QTLs,更符合生物学发育原理。
主成分分析明确了主根长、主根表面积和主根数量作为两种环境下研究的主要表型性状,扩展了以往主要集中于单一表型性状的研究。与正常生长条件相比,这3种主要表型性状在盐胁迫环境下的表型数值有所降低。已有研究表明,盐胁迫可能通过多种途径影响植物根系的生理功能,包括限制水分吸收[24],影响养分吸收和转运[27],这些生理功能的改变可能会抑制根系的生长。然而,根系形态变化也可能是植物对盐胁迫环境的一种适应性表现,例如通过减少根系生长以降低暴露于盐胁迫的面积[28]。因此,胡杨根系在盐胁迫条件下的变短可能不仅仅是生理功能受限的结果,还可能反映其适应环境的策略。在盐胁迫条件下,5号连锁群在主根数量中占据39.08%的显著SNPs,暗示了其可能包含调控根系数量动态变化的重要基因。这些基因可能涉及生长素运输、信号传导及胁迫响应通路。此外,其他连锁群中的高比例SNPs,如3号连锁群在主根表面积中的显著表现,也表明根系形态结构的遗传调控可能受多个功能基因网络的协同调控。这些发现为进一步解析胡杨根系适应盐胁迫环境的分子机制提供了新线索。QTL定位结果表明,多个基因共同影响根系的生长,关键QTLs共同调控胡杨根系表型性状,但它们在遗传网络中发挥着不同的作用。胡杨根系的生长是由这些QTLs自身的遗传效应和它们之间的上位效应共同决定的,这些作用模式反映了QTLs间的复杂性和多样性。例如,盐胁迫条件下,主根长的遗传网络中的枢纽位点Q1554产生的连接数占总网络连接的55%,但未能直接定位到编码蛋白质的基因,推测其可能通过调节与根生长和分化相关的基因表达,进而影响根系在盐胁迫下的适应性。这一发现强调了非编码区QTLs在调控植物根系发育过程中的潜在作用,尤其在环境胁迫下。因此,Q1554可能代表了一个新的潜在的调控因子,需要进一步通过功能实验来验证其作用机制。
注释结果凸显了胡杨根系在不同环境条件下的遗传调控机制差异:正常条件下注重基础代谢和生长功能,而盐胁迫条件下更多地表现为对胁迫信号的响应和代谢调控的动态调节。这种对比性研究强调了特定环境下候选基因在胁迫耐受性中的重要性,为胡杨分子育种提供了理论支持。例如,在盐胁迫条件下,nn_np_9370与β-D-木糖苷酶基因(LOC105114908)的mRNA序列表现出相似性。β-D-木糖苷酶在植物应对生物和非生物胁迫时,通过参与木质素和纤维素的分解,调节根系结构和功能,从而影响植物的适应能力[29−30];hk_hk_2974与ZAT10锌指蛋白(LOC105120566)相似,ZAT10 是植物中一种C2H2型锌指蛋白,属于转录因子,具有广泛的生物学功能,尤其在植物的逆境胁迫应答中发挥关键作用[31]。Q3103和Q1871作为2个显著核心QTL,可能分别通过调控枢纽基因LOC105114908和LOC105120566的表达,促进根系对盐胁迫的适应能力。
本研究分析了胡杨根系在盐胁迫条件下的遗传调控机制,通过QTL定位和基因功能注释,提供了对胡杨耐盐性遗传基础的理解,研究通过动态性状的分析方法提高了QTL定位的准确性和生物学意义,为胡杨耐盐性状的分子标记辅助育种提供了理论依据。但从胡杨根系相关性状基因功能注释结果发现,总体注释到的与胡杨生长发育相关的候选基因比例较少,这主要是由于胡杨研究的基础相对薄弱,特别是功能基因组学研究。随着胡杨基因组资源的完善和功能基因组学研究的深入,未来研究将解析更为精细的基因–性状关系,进一步揭示胡杨响应盐胁迫过程中的遗传调控机制。
4. 结 论
本研究基于胡杨在正常和盐胁迫条件下的表型与基因型数据,通过功能作图理论框架,正常条件下分别定位到100、89、85个调控主根长、主根表面积、主根数量的显著QTLs;在盐胁迫条件下分别定位到91、85、87个显著QTLs。正常条件下,分别注释到影响主根长、主根表面积、主根数量表型性状的21、14、14个候选基因,这些基因主要集中在基本的代谢过程、生长素转运、染色体分离等方面;盐胁迫下分别注释到19、17、15个候选基因,主要富集于胁迫响应、氧化还原平衡、铁离子运输和tRNA修饰等方面。构建遗传网络,挖掘到参与盐胁迫响应的枢纽基因LOC105114908和LOC105120566,有助于探究盐胁迫下影响胡杨根系表型性状生长的遗传机制。研究结果为进一步解析胡杨响应盐胁迫的遗传结构提供了新的方法和思路。
-
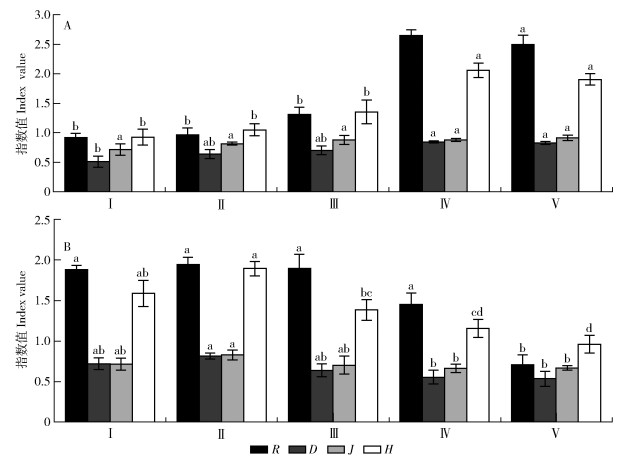
图 1 不同林地植物多样性
R. Margalef指数;D. Simpson指数;J. Pielou指数;H. Shannon-Wiener指数。A.灌木层;B.草本层。不同小写字母表示不同林地间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Figure 1. Plant diversity of different forestland
R, Margalef index; D, Simpson index; J, Pielou index; H, Shannon-Wiener index. A, shrub layer; B, herb layer. Different lowercase letters indicate that there is significant difference among different vegetation restoration types (P < 0.05).
表 1 样地基本概况
Table 1 Basic information of the sample plots
森林类型
Forest type树种组成
Species composition土壤类型
Soil type坡向
Slope aspect坡度
Slope degree林龄/a
Forest age/year海拔
Altitude/m平均树高
Average tree height/m平均胸径
Average DBH/cm郁闭度
Canopy densityⅠ 油松
Pinus tabuliformis褐土
Cinnamon soil半阴坡
Semi-shady slope25 20 1 140 6.84 12.82 0.52 Ⅱ 刺槐
Robinia pseudoacacia褐土
Cinnamon soil半阴坡
Semi-shady slope20 24 1 150 10.79 14.88 0.54 Ⅲ 油松, 刺槐
P. tabuliformis, R. pseudoacacia褐土
Cinnamon soil半阴坡
Semi-shady slope18 20 1 130 7.28 10.08 0.61 Ⅳ 山杨, 辽东栎
Populus davidiana, Quercus liaotungensis褐土
Cinnamon soil半阴坡
Semi-shady slope30 ― 1 050 9.43 10.70 0.65 Ⅴ 辽东栎
Q. liaotungensis褐土
Cinnamon soil半阴坡
Semi-shady slope33 ― 1 300 7.35 14.39 0.72 注:Ⅰ.油松人工林;Ⅱ.刺槐人工林;Ⅲ.油松刺槐人工混交林;Ⅳ.山杨次生林;Ⅴ.辽东栎次生林。下同。Notes: Ⅰ, P. tabuliformis artificial forest; Ⅱ, R. pseudoacacia artificial forest; Ⅲ, artificial mixed forests of P. tabuliformis and R. pseudoacacia; Ⅳ, P. davidiana secondary forest; Ⅴ, Q. liaotungensis secondary forest. Same as below. 表 2 不同林地灌木层物种组成及重要值
Table 2 Species composition and important values of shrub layer in different forestland
种Species 属Genus 科Family 重要值Important value Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 黄刺玫Rosa xanthina 蔷薇属Rosa 蔷薇科Rosaceae 50.28 24.27 33.33 5.78 2.49 暴马丁香Syringa reticulata var. amurensis 丁香属Syringa 木犀科Oleaceae 18.06 22.43 16.67 2.51 12.92 绣线菊Spiraea salicifolia 绣线菊属Spiraea 蔷薇科Rosaceae 11.48 14.81 10.57 6.95 金银木Lonicera maackii 忍冬属Lonicera 忍冬科Caprifoliaceae 9.26 6.66 2.49 杠柳Periploca sepium 杠柳属Periploca 萝藦科Asclepiadaceae 13.33 33.79 16.67 陕西荚蒾Viburnum schensianum 荚蒾属Viburnum 忍冬科Caprifoliaceae 12.58 18.36 胡枝子Lespedeza bicolor 胡枝子属Lespedeza 蝶形花科Leguminosae 3.43 5.56 2.01 虎榛子Ostryopsis davidiana 虎榛子属Ostryopsis 桦木科Betulaceae 3.43 15.23 12.48 山杏Armeniaca sibirica 杏属Armeniaca 蔷薇科Rosaceae 1.26 茶条槭Acer ginnala 槭属Acer 槭树科Aceraceae 3.46 7.64 2.89 4.99 黄栌Cotinus coggygria 黄栌属Cotinus 漆树科Anacardiaceae 8.44 3.70 2.50 9.98 连翘Forsythia suspensa 连翘属Forsythia 木犀科Oleaceae 18.76 12.39 胡颓子Elaeagnus pungens 胡颓子属Elaeagnus 胡颓子科Elaeagnaceae 6.54 西北栒子Cotoneaster zabelii 栒子属Cotoneaster 蔷薇科Rosaceae 7.04 9.45 沙棘Hippophae rhamnoides 沙棘属Hippophae 胡颓子科Elaeagnaceae 5.66 山茱萸Cornus officinalis 山茱萸属Cornus 山茱萸科Cornaceae 2.49 太平花Philadelphus pekinensis 山梅花属Philadelphus 虎耳草科Saxifragaceae 4.99 表 3 不同林地草本层物种组成及重要值
Table 3 Species composition and important values of herbaceous layer in different forestland
种Species 属Genus 科Family 重要值Important value Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 披针薹草Carex lancifolia 薹草属Carex 莎草科Cyperaceae 2.66 6.04 16.95 46.97 30.56 败酱Patrinia scabiosaefolia 败酱属Patrinia 败酱科Valerianaceae 21.37 12.88 23.53 9.61 铁杆蒿Artemisia sacrorum 蒿属Artemisia 菊科Compositae 27.40 16.14 15.78 狗牙根Cynodon dactylon 狗牙根属Cynodon 禾本科Gramineae 4.29 1.51 5.92 地梢瓜Cynanchum thesioides 鹅绒藤属Cynanchum 萝藦科Asclepiadaceae 4.48 4.2 委陵菜Potentilla chinensis 委陵菜属Potentilla 蔷薇科Rosaceae 8.77 1.51 紫花地丁Viola philippica 堇菜属Viola 堇菜科Violaceae 4.68 4.20 2.13 苦苣菜Sonchus oleraceus 苦苣菜属Sonchus 菊科Compositae 2.47 2.10 甘草Glycyrrhiza uralensis 甘草属Glycyrrhiza 豆科Leguminosae 5.14 茜草Rubia cordifolia 茜草属Rubia 茜草科Rubiaceae 5.52 2.70 3.82 牛筋草Eleusine indica 穇属Eleusine 禾本科Gramineae 11.22 婆婆针Bidens bipinnata 鬼针草属Bidens 菊科Compositae 2.01 艾蒿Artemisia argyi 蒿属Artemisia 菊科Compositae 11.45 4.20 葎叶蛇葡萄Ampelopsis humulifolia 蛇葡萄属Ampelopsis 葡萄科Vitaceae 4.63 蛇莓Duchesnea indica 蛇莓属Duchesnea 蔷薇科Rosaceae 6.60 4.20 乌头叶蛇葡萄Ampelopsis aconitifolia 蛇葡萄属Ampelopsis 葡萄科Vitaceae 1.35 2.10 6.79 铁线莲Clematis florida 铁线莲属Clematis 毛茛科Ranunculaceae 1.99 青杞Solanum septemlobum 茄属Solanum 茄科Solanaceae 5.57 地构叶Speranskia tuberculata 地构叶属Speranskia 大戟科Euphorbiaceae 1.51 5.49 萝藦Metaplexis japonica 萝藦属Metaplexis 萝藦科Asclepiadaceae 6.12 4.63 风毛菊Saussurea japonica 风毛菊属Saussurea 菊科Compositae 1.35 2.10 甘菊Dendranthema lavandulifolium 菊属Dendranthema 菊科Compositae 7.39 马唐Digitaria sanguinalis 马唐属Digitaria 禾本科Gramineae 13.28 3.34 狗尾草Setaria viridis 狗尾草属Setaria 禾本科Gramineae 2.62 多歧沙参Adenophora wawreana 沙参属Adenophora 桔梗科Campanulaceae 7.99 3.47 龙牙草Agrimonia pilosa 龙芽草属Agrimonia 蔷薇科Rosaceae 2.53 蛇葡萄Ampelopsis sinica 蛇葡萄属Ampelopsis 葡萄科Vitaceae 4.66 翅果菊Pterocypsela indica 翅果菊属Pterocypsela 菊科Compositae 2.13 山罗花Melampyrum roseum 山罗花属Melampyrum 玄参科Scrophulariaceae 9.61 20.83 穿山龙Dioscorea nipponica 薯蓣属Dioscorea 薯蓣科Dioscoreaceae 2.13 3.82 前胡Peucedanum praeruptorum 前胡属Peucedanum 伞形科Umbelliferae 2.13 盘叶忍冬Lonicera tragophylla 忍冬属Lonicera 忍冬科Caprifoliaceae 9.72 藜芦Veratrum nigrum 藜芦属Veratrum 百合科Liliaceae 4.86 糙苏Phlomis umbrosa 糙苏属Phlomis 唇形科Labiatae 10.07 沙参Adenophora stricta 沙参属Adenophora 桔梗科Campanulaceae 12.85 表 4 不同林地植物群落的相似性系数
Table 4 Similarity coefficient of plant communities in different forestland
森林类型
Forest typeⅠ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ Ⅰ 1 Ⅱ 0.488 1 Ⅲ 0.615 0.636 1 Ⅳ 0.364 0.367 0.340 1 Ⅴ 0.308 0.273 0.286 0.596 1 表 5 植物多样性与环境因子之间的相关性
Table 5 Correlations between plant diversity and environmental factors
环境因子Environmental factors R1 D1 J1 H1 R2 D2 J2 H2 海拔Elevation -0.204 -0.170 0.166 -0.224 -0.177 0.177 0.202 0.027 坡度Slope degree 0.433 0.429 0.232 0.458 -0.597* -0.511 -0.357 -0.545* 郁闭度Canopy density 0.361 0.420 0.540* 0.318 -0.657** -0.538* -0.428 -0.692** 土壤容重Soil bulk density 0.289 0.354 0.289 0.257 -0.643** -0.300 0.229 -0.429 土壤含水量Soil moisture content 0.500 0.550* 0.232 0.514* -0.139 -0.036 0.196 -0.046 总孔隙度Total porosity -0.389 -0.332 0.075 -0.364 0.407 0.168 0.014 0.246 毛管孔隙度Capillary porosity -0.629* -0.561* 0.000 -0.596* 0.436 0.371 0.229 0.407 非毛管孔隙度Non-capillary porosity 0.421 0.396 0.164 0.404 -0.382 -0.575* -0.450 -0.489 注:R1为灌木层Margalef指数;D1为灌木层Simpson指数;J1为灌木层Pielou指数;H1为灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数;R2为草本层Margalef指数;D2为草本层Simpson指数;J2为草本层Pielou指数;H2为草本层Shannon-Wiener指数。*表示在P<0.05水平显著;**表示在P<0.01水平显著。Notes: R1, Margalef index of shrub layer; D1, Simpson index of shrub layer; J1, Pielou index of shrub layer; H1, Shannon-Wiener index of shrub layer; R2, Margalef index of herb layer; D2, Simpson index of herb layer; J2, Pielou index of herb layer; H2, Shannon-Wiener index of herb layer. * means correlation is significant at P < 0.05 level; ** means correlation is significant at P < 0.01 level. -
[1] 陈超, 朱志红, 李英年, 等.高寒草甸种间性状差异和物种均匀度对物种多样性与功能多样性关系的影响[J].生态学报, 2016, 36(3):661-674. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201603010 Chen C, Zhu Z H, Li Y N, et al. Effects of interspecific trait dissimilarity and species evenness on the relationship between species diversity and functional diversity in an alpine meadow[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(3):661-674. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201603010
[2] Duan R Y, Wang C, Wang X A, et al. Differences in plant species diversity between conifer (Pinus tabulaeformis) plantations and natural forests in middle of the Loess plateau [J]. Russian Journal of Ecology, 2009, 40(7):501-509. doi: 10.1134/S106741360907008X
[3] Ives A R, Carpenter S R. Stability and diversity of ecosystems [J]. Science, 2007, 317:58-62. doi: 10.1126/science.1133258
[4] 彭少麟, 陆宏芳.恢复生态学焦点问题[J].生态学报, 2003, 23(7):1249-1257. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.07.001 Peng S L, Lu H F. Some key points of restoration ecology [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(7):1249-1257. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.07.001
[5] 王倩, 艾应伟, 裴娟, 等.遂渝铁路边坡草本植物多样性季节动态和空间分布特征[J].生态学报, 2010, 30(24):6892-6900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201024025 Wang Q, Ai Y W, Pei J, et al. Seasonal dynamics and spatial distribution of herbage diversity on the slopes of Suiyu Railway [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(24):6892-6900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201024025
[6] 刘平, 秦晶, 刘建昌, 等.桉树人工林物种多样性变化特征[J].生态学报, 2011, 31(8):2227-2235. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201108021 Liu P, Qin J, Liu J C, et al. Comparison of structure and species diversity of eucalyptus community [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(8):2227-2235. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201108021
[7] Gilliam F S. The ecological significance of the herbaceous layer in temperate forest ecosystems [J]. Bioscience, 2007, 57(10):845-858. doi: 10.1641/B571007
[8] 张晶晶, 赵忠, 宋西德, 等.渭北黄土高原人工刺槐林植物多样性动态[J].西北植物学报, 2010, 30(12):2490-2496. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201012021 Zhang J J, Zhao Z, Song X D, et al. Biodiversity dynamics of artificial Robinia pseudoacacia forest in Weibei Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(12):2490-2496. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201012021
[9] Mccann K S. The diversity-stability debate [J]. Nature, 2000, 405:228-233. doi: 10.1038/35012234
[10] Tilman D, Downing J A. Biodiversity and stability in grasslands [J]. Nature, 1994, 367:363-365. doi: 10.1038/367363a0
[11] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等.植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J].生物多样性, 2009, 17(6):533-548. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdyx200906002 Fang J Y, Wang X P, Shen Z H, et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory [J]. Biodiversity Science, 2009, 17(6):533-548. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdyx200906002
[12] 马克平, 刘玉明.生物群落多样性的测度方法(Ⅰ): α多样性的测度方法(下)[J].生物多样性, 1994, 2(4):231-239. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.1994.04.009 Ma K P, Liu Y M. Measure method of biological community biodiversity: measure method of (Ⅰ): α diversity (second) [J]. Biodiversity Science, 1994, 2(4):231-239. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0094.1994.04.009
[13] 田晓玲, 毕华兴, 云雷, 等.晋西黄土区林草复合系统草本植物多样性特征[J].北京林业大学学报, 2011, 33(1):64-69. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9521 Tian X L, Bi H X, Yun L, et al. Herbaceous plant diversity of silvopastoral system in the loess region of western Shanxi Province, northern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2011, 33(1):64-69. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9521
[14] 彭舜磊, 王得祥.秦岭火地塘林区华山松人工林与天然次生林群落特征比较[J].西北植物学报, 2009, 29(11):2301-2311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.11.023 Peng S L, Wang D X. Comparison of community characteristics of plantatio and secondary forest of Pinus armandii in Huoditang Forest Region of Qinling Mountain [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 29(11):2301-2311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.11.023
[15] 温远光, 雷丽群, 朱宏光, 等.广西马山岩溶植被年龄序列的群落特征[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(18):5723-5730. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201318035 Wen Y G, Lei L Q, Zhu H G, et al. Community characteristics in a chronosequence of karst vegetation in Mashan County, Guangxi [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(18):5723-5730. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201318035
[16] 陈杰, 郭屹立, 卢训令, 等.伊洛河流域草本植物群落物种多样性[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(10):3021-3030. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201210007 Chen J, Guo Y L, Lu X L, et al. Species diversity of herbaceous communities in the Yiluo River Basin [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(10):3021-3030. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201210007
[17] 王芸, 欧阳志云, 郑华, 等.南方红壤区3种典型森林恢复方式对植物群落多样性的影响[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(4):1204-1211. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201304020 Wang Y, Ouyang Z Y, Zheng H, et al. Effects of three forest restoration approaches on plant diversity in red soil region, southern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(4):1204-1211. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201304020
[18] 武文娟, 查同刚, 张志强.恢复方式和地形对晋西黄土区退耕林分物种多样性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2017, 28(4):1121-1127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201704008 Wu W J, Zha T G, Zhang Z Q. Effects of revegetation approach and terrain on plant species diversity as a result of converting croplands to forests in the loess region of western Shanxi Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(4):1121-1127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201704008
[19] 袁王俊, 卢训令, 张维瑞, 等.不同植被类型植物物种多样性[J].生态学报, 2015, 35(14):4651-4657. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201514010 Yuan W J, Lu X L, Zhang W R, et al. Plant's diversity of different vegetation types [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14):4651-4657. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201514010
[20] 王永健, 陶建平, 张炜银, 等.茂县土地岭植被恢复过程中物种多样性动态特征[J].生态学报, 2006, 26(4):1028-1036. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.04.008 Wang Y J, Tao J P, Zhang W Y, et al. Dynamics of species diversity in vegetation restoration on Tudiling of Mao County, Southwest China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(4):1028-1036. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.04.008
[21] 王健铭, 董芳宇, 巴海·那斯拉, 等.中国黑戈壁植物多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J].生态学报, 2016, 36(12):3488-3498. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201612002 Wang J M, Dong F Y, Bahai·Nasina, et al. Plant distribution patterns and the factors influencing plant diversity in the Black Gobi Desert of China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(12):3488-3498. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201612002
[22] 张继义, 赵哈林, 张铜会, 等.科尔沁沙地植被恢复系列上群落演替与物种多样性的恢复动态[J].植物生态学报, 2004, 28(1):86-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2004.01.013 Zhang J Y, Zhao H L, Zhang T H, et al. Dynamics of species diversity of communities in restoration processes in Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2004, 28(1):86-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2004.01.013
[23] Sattler T, Borcard D, Arlettaz R, et al. Spider, bee, and bird communities in cities are shaped by environmental control and high stochasticity [J]. Ecology, 2010, 91(11):3343-3353. doi: 10.1890/09-1810.1
[24] 任学敏, 杨改河, 朱雅, 等.环境因子对太白山高山植被物种组成和丰富度的影响[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(23):6993-7003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201423023 Ren X M, Yang G H, Zhu Y, et al. Effect of environmental variables on species composition and richness of alpine vegetation in Taibai Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23):6993-7003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201423023
[25] 郝文芳, 杜峰, 陈小燕, 等.黄土丘陵区天然群落的植物组成、植物多样性及其与环境因子的关系[J].生态学报, 2012, 20(4):609-615. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdxb201204002 Hao W F, Du F, Chen X Y, et al. Composition and diversity analysis of natural-community plants in the loess hilly region [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 20(4):609-615. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdxb201204002
[26] 胡相明, 程积民, 万惠娥.黄土丘陵区人工林下草本层植物的结构特征[J].水土保持通报, 2006, 26(3):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2006.03.010 Hu X M, Cheng J M, Wan H E. Structure characteristics of herbages under five types of artificial forest plantations in loess hilly region [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 26(3):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2006.03.010
[27] Liu Q F, Kang M Y, Wang H, et al. Effects of environmental factors on species richness patterns of herb layer in eastern Zhongtiao Mountain [J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2005, 16(3):175-180. doi: 10.1007/BF02856810




 下载:
下载: