Research on thermal response characteristics of domestic Quercus variabilis cork
-
摘要:目的软木是一种具有黏弹性的天然高分子材料,除天然软木塞以外,软木制品多由软木颗粒施胶后热压而成,软木材料主要化学组分的熔融温度、玻璃化转变温度等热转变温度对了解软木的黏弹性和制定热加工工艺具有重要的理论参考价值。方法首先对栓皮栎软木进行热重分析以了解其热稳定性,确定软木发生热降解的最低温度,之后又采用了DSC、DMA、TMA这3种热分析方法对国产栓皮栎软木材料在热解起始温度内的热效应温度进行分析,并相互验证。结果热重分析结果显示在219℃之前栓皮栎软木基本不发生热降解,采用DSC、DMA、TMA方法测得的软木脂微晶的熔融温度分别为66℃、78℃(1Hz)和78℃,通过DMA测得软木脂无定形区在频率为1Hz时的玻璃化转变温度在0.7℃左右,在-66℃附近有一次级松弛转变,各热效应温度与栓皮槠软木略有差异,应与两者化学组分的单体构成和分子间作用力之间的差异相关。此外,由于软木径向壁上具有褶皱,采用TMA测试时可发现在加热条件下软木径向尺寸受热膨胀程度要大于轴向。结论在栓皮栎软木发生热解前的温度范围内存在主要成分软木脂的各热效应转变温度,据此确定合适的软木热加工温度,可通过增加软木的黏性流动来促进软木材料的热成型。Abstract:ObjectiveCork is a kind of natural polymer material with viscoelasticity. Cork products are mostly formed by hot pressing of cork particles after sizing except natural cork stoppers. The melting temperature, glass transition temperature and other thermal transition temperatures of the main chemical components of cork materials have important theoretical reference value for understanding the viscoelasticity of cork and formulating thermal processing technology.MethodFirstly, the thermogravimetric analysis of the Quercus variabilis cork was carried out to determine the pyrolysis initiation temperature. Then, three thermal analysis methods, DSC, DMA and TMA, were used to analyze the thermal effect temperature of the domestic Quercus variabilis cork material within the pyrolysis initiation temperature and verify each other.ResultThermogravimetric analysis showed that the Quercus variabilis cork did not undergo thermal degradation before 219℃. The melting temperatures of suberin's microcrystalline phases measured by DSC, DMA and TMA were 66℃, 78℃ (1Hz) and 78℃, respectively. The glass transition temperature of the amorphous region of suberin measured by DMA was about 0.7℃, and there was a secondary relaxation transition near -66℃. Each thermal effect temperature was slightly different from that of Quercus suber cork, which was related to the difference in monomer composition and intermolecular force of the chemical components of the two species cork. In addition, due to the corrugations on the radial wall of the cork cell, it was found that the thermal expansion of the cork radial dimension was greater than that of the axial direction under the heating condition.ConclusionIn the temperature range before the pyrolysis of Quercus variabilis cork, suberin, the main component of the cork, will undergo different thermal effects, according to which the appropriate cork hot processing temperature can be determined, and the thermoforming of the cork material can be promoted by increasing the viscous flow of the cork.
-
Keywords:
- Quercus variabilis cork /
- thermal analysis /
- melting /
- glass transition
-
软木材料主要取自地中海沿岸的栓皮槠(Quercus suber L.)和中国的栓皮栎(Quercus variabilis)两种树种的栓皮层部分,软木细胞大致呈棱柱状,以六棱柱状居多,细胞棱柱轴向平行于软木径向排列,属于薄壁细胞且侧面壁上多具褶皱。栓皮栎软木的主要成分是软木脂,在40%左右,其次是木质素,大约为20%,而纤维素与半纤维只占了20%左右[1]。目前对于软木材料的热分析研究多是针对栓皮槠软木,对其主要化学组分的分子和超分子结构的研究还只是通过核磁共振测试以及分析解聚后单体组成、低聚物的键连接而得到的推测。Cordeiro等[2]通过DSC和偏光显微镜发现解聚得到的软木脂中存在微晶结构,熔限大约在0~50℃范围内,软木脂的无定形部分则在室温下呈黏流态。Ferreira等[3]利用己酸胆碱离子液体作为溶剂分离得到的软木脂则因条件较温和会保留部分酯键结构,对其进行DSC测试得知软木脂提取试样中微晶熔点为65.8℃,又通过DMA测试发现软木脂无定形部分的玻璃化转变温度大约为-45℃。Lagorce-Tachon等[4]通过DMA测试结果和活化能计算,推测发生在-80℃左右且活化能为72kJ/mol,以及0℃附近活化能为201kJ/mol的热效应分别为软木中某种化学成分的次级松弛和玻璃化转变,并通过DSC测试发现了在50~90℃处出现的软木脂熔融吸热峰。
我国栓皮栎软木由于质量参差不齐,一般不直接用来制作天然软木制品,常粉碎成一定粒径范围内的软木颗粒,然后施加胶黏剂后再进行成型处理。由于软木是具有黏弹性的天然高分子材料[5],在加工过程中也表现出一些高聚物所具有的特性,如软木脂存在玻璃化转变温度和熔点,木质素存在玻璃化转变温度,这对于软木材料热加工中温度、时间等参数的设定具有非常重要的意义。在软木板热压过程中,热压温度的选择不仅需要使胶黏剂充分固化,而且要在保留软木固有优良特性的前提下使软木颗粒在所设定的热压时间内产生足够的塑化,以降低热压板抬起后板材的厚度回弹,提高热压成型效率[6]。本研究则采用多种热分析方法对栓皮栎软木的热转变温度进行分析,为国内栓皮栎软木的研究提供一定基础数据参考,并为利用栓皮栎软木进行热压生产软木制品提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
所使用的软木材料为山东乐得仕软木科技有限公司提供的国产栓皮栎软木,去除了黑背皮和内层皮,平均含水率在3.7%左右,密度约为0.22g/cm3。
1.2 栓皮栎软木热稳定性分析
工业分析采用箱式马弗炉(Lindberg Blue M,Thermo Scientific)进行,具体方法参照国标《GB/T 28731—2012固体生物质燃料工业分析方法》[7],将栓皮栎软木去除夹杂、夹砂后用植物高速粉碎机粉碎,用标准筛筛取40~60目的软木粉作为工业分析试样;元素分析则采用Vario EL cube元素分析仪(德国ELEMENTAR),测试模式为CHNS模式,该模式下燃烧管温度为1150℃,还原管温度为850℃,He气流速130mL/min,氧元素质量分数(WO)计算公式[8]为:
WO=1−WM−WA−WC−WH−WN−WS 式中:WM为水分相对于气干软木的质量分数;WA为灰分相对于气干软木的质量分数;WC、WH、WN和WS分别为C、H、N和S元素相对于气干软木的质量分数。
热重分析试样为粒径小于100目的软木粉,在80℃的烘箱内烘至质量恒定后采用美国TA公司生产的TGA Discovery热重分析仪进行测试,样品用量为2~3mg左右,平铺在Pt坩埚中,吹扫气体为氮气,流速为40mL/min,以20℃/min的升温速率从室温升至600℃。
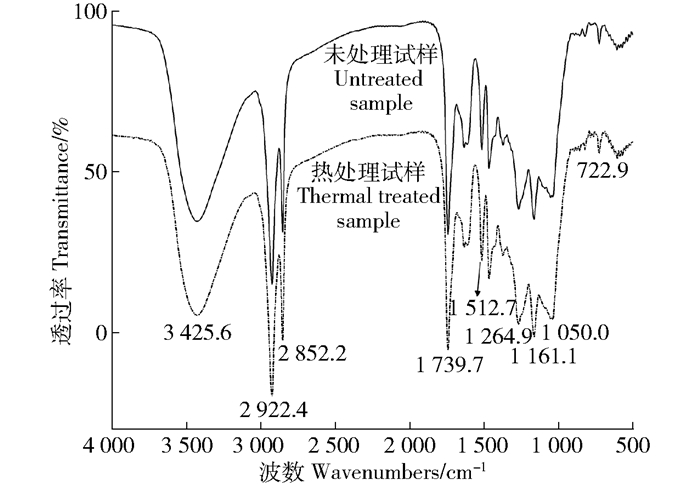
筛取粒径小于200目的软木粉末作为红外分析试样,将软木粉末在(103±2)℃的烘箱内烘至质量恒定,分为两组后取其中一组放入150℃烘箱内加热30min作为热处理试样,未热处理的为对照,将两组试样分别进行压片,先取1mg试样在红外灯箱中用玛瑙研钵进行研磨,再加入约150mg干燥的KBr粉末继续研磨均匀,取适量混合样品于洁净的压片模具中制得透明薄片试样,放入傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Nicolet 6700,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific)的样品室中进行扫描。
DSC分析采用美国TA公司生产的DSC Discovery差式扫描量热仪,试样制备同TGA,测试采用两次升温,升温速率为10℃/min,首次升温是从-90℃加热至100℃,以消除软木试样热历史和水分解吸的影响,降温后接着进行第二次升温,从-90℃升温至200℃。
1.3 栓皮栎软木的热机械性能分析
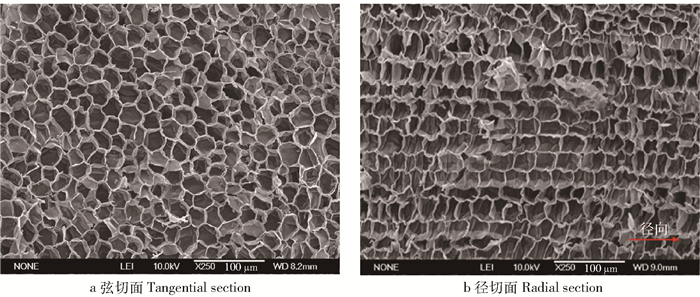
用手术刀在去除掉黑背皮的栓皮栎软木上沿径切面(或横切面)和弦切面切取尺寸约为5mm×5mm×1mm的薄片状试样,在(103±2)℃下烘至质量恒定,喷金后用导电胶黏贴在样品台上,采用JSM-6700F(日本电子)冷场发射扫描电镜对径切面(或横切面)和弦切面进行观察并获取照片。
用手术刀平行于软木三切面进行切割制得边长为5mm的立方体块状试样用于DMA和TMA测试,试样中不能含有明显的夹杂和夹砂,将压缩方向平行于径向和轴向的软木试样分别标记为R和A。
DMA测试采用美国TA公司生产的DMA Q800动态热机械分析仪,选用压缩变形模式,测试频率为1和10Hz,测试温度范围为-100~200℃,升温速率为5℃/min。
TMA测试采用美国TA公司生产的TMA Q400热机械分析仪,试样制备同DMA测试,采用膨胀测量法,在该模式下,石英制压杆以较小的压应力压在试样上,同样进行两次升温,升、降温速率为5℃/min,第一次升温为从-50℃加热至100℃以去除试样热历史,第二次升温为从-50℃加热至200℃。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 栓皮栎软木热稳定性分析
与木材相比[9],栓皮栎软木中因含有由脂肪族长链构成的软木脂而具有较高质量分数的C元素和H元素;而与栓皮槠软木[10]相比,栓皮栎软木中C、H元素质量分数稍低,O元素质量分数较高,可能因为软木脂质量分数较低,而含O元素较多的纤维素、半纤维素和木质素质量分数较高。对于工业分析,虽然软木中纤维素与半纤维素质量分数较木材少,但由于软木脂热解后残炭量与纤维素和半纤维素的相差不大,都远低于木质素热解后残重[11],而软木与木材中木质素质量分数相差不大,使得软木的挥发分和固定碳质量分数也与木材没有明显差异。
从红外光谱图(图 1)上可以看出典型的软木脂富集物特征。在2922.4和2852.2cm-1两处出现了由软木脂脂肪链上亚甲基C—H不对称和对称伸缩振动产生的强吸收峰;在1739.7、1264.9和1161.1cm-1处出现了由软木脂脂肪酸酯键中CO伸缩振动和C—O对称、不对称伸缩振动产生的强吸收峰;3425.6cm-1处出现的宽吸收峰则由软木脂中羧基上O—H键和木质素、多糖中O—H键的伸缩振动产生;1050.0cm-1处的中等强度吸收峰则由多糖和木质素中C—O键振动形成;1512.7cm-1处的中等强度吸收峰由G-型木质素的芳环振动产生;在722.9cm-1处出现了乙烯基上C—H弯曲振动吸收峰[12]。对比图 1中热处理与未处理栓皮栎软木的红外光谱图,可以发现经过热处理后软木的主要成分软木脂、木质素、纤维素与半纤维素的主要特征吸收峰强度几乎均未发生变化。
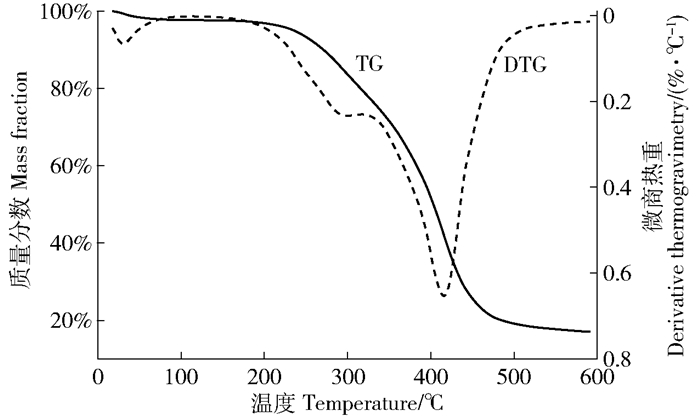
从图 2中热重(TG)曲线和微商热重(DTG)曲线可以看出栓皮栎软木试样的热解反应与栓皮槠软木的极为相近[13]。根据TG曲线可以将栓皮栎软木试样的热解失重大致分为4个阶段。第一阶段为0~100℃,由试样干燥过程残余水分的蒸发与解吸形成,质量损失为2.2%;第二阶段为100~219℃,此阶段TG和DTG曲线平稳,试样仅发生了轻微失重,包括残留水分的逐渐失去,以及少量对热敏感的抽提物的挥发,至此可得知加热温度在219℃以下时软木材料基本不会发生热降解,因此在此温度以下对软木材料进行热加工不会破坏软木细胞构造;第三阶段则为219~451℃,是软木的主要热解阶段,质量损失高达71.0%,通过微商热重曲线可发现这一区域大致可分为两个阶段,峰温为300℃的肩峰主要是由软木中半纤维素和纤维素的热解产生,峰温为416℃的最大失重峰则由软木主要成分软木脂的热解形成,软木脂因具有交联聚酯结构和交联的类木质素结构使其成为软木各组分中热稳定性最好的成分,直到300℃左右才开始有明显热失重[2, 14],这也是软木热稳定性较木材高的主要原因;第四阶段则为451~600℃,质量损失为8.5%;至终温600℃时,失重曲线趋于平稳,软木试样残余质量约为初始质量的17.0%,大致等于工业分析(表 1)中栓皮栎软木中固定碳和灰分质量分数之和。
表 1 两种软木各组分质量分数Table 1. Mass fraction of each component of the cork of two species试样
Sample工业分析Proximate analysis 元素分析Elemental analysis 水分
Moisture灰分
Ash挥发分
Volatiles固定碳
Fixed carbonC H N O S 栓皮栎软木Quercus variabilis cork 3.7% 0.6% 79.3% 16.4% 55.13% 6.67% 0.58% 33.32% 0 栓皮槠软木Quercus suber cork[10] - 0.47% - - 62.44% 7.95% 0.63% 28.51% 0 表 2 软木热解过程中各阶段特征温度和质量变化Table 2. Characteristic temperature and mass variations in various stages of cork pyrolysis阶段Stage 起始温度
Initial temperature/℃终止温度
Terminal temperature/℃峰温
Peak temperature/℃质量损失
Mass change/%第一阶段The first stage 0 100 43 2.2 第二阶段The second stage 100 219 1.3 第三阶段The third stage 219 451 415 71.0 第四阶段The fourth stage 451 600 8.5 2.2 栓皮栎软木的热转变温度分析
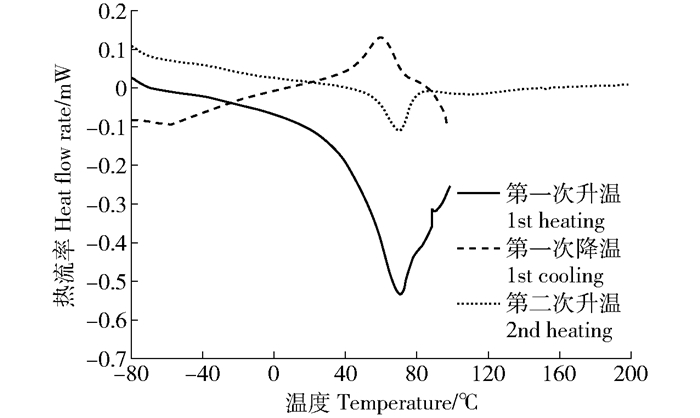
图 3为栓皮栎软木的DSC热流曲线。在第一次升温曲线上可以看见在70℃附近有一明显吸热峰,在降温曲线对应温度附近也有放热峰,并且二次升温曲线中依然在70℃处有一明显吸热峰,说明该峰的产生不是因为水分解吸或发生化学反应,而应该是由软木中化学成分结晶区的熔融和再结晶产生,由于纤维素结晶区的氢键作用使其在未熔融前已经发生热解反应[15],所以在该DSC测试温度范围内不会出现纤维素晶体产生的峰,所以该热效应应归因于软木脂微晶部分的熔融。根据去除材料热历史后得到的第二次升温热流曲线可以得到该微晶部分的熔限为49~82℃,熔点为66℃,与栓皮槠软木试样在10℃/min的升温速率下测得的71℃熔融吸热峰峰温[16]相近。
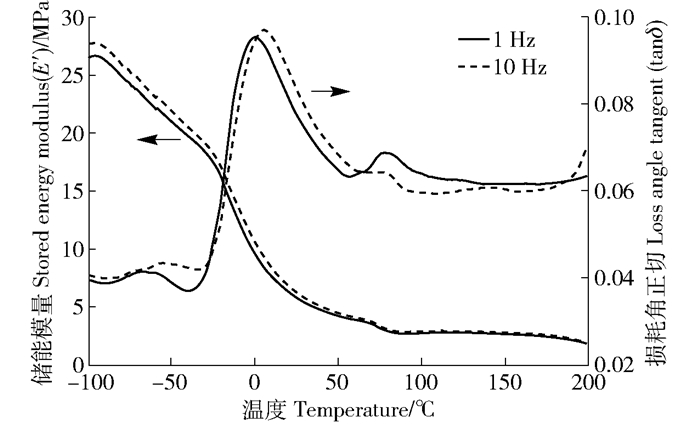
在各种热分析方法中,DMA对玻璃化转变的响应最为灵敏。由于R试样与A试样的测试结果基本一致,接下来只对R试样进行分析。图 4为1和10Hz两种频率下测得的软木R试样储能模量(E′)和损耗角正切值(tanδ)随温度的变化曲线,软木试样在温度从-100℃升至100℃的过程中储能模量发生了3次不同幅度的下降,并在相应的tanδ曲线中产生了对应的损耗峰,说明在此温度范围内发生了3次松弛转变或相转变。当频率为1Hz时,各峰值温度分别为-66、0.7、78℃;频率为10Hz时,分别为-55℃、6℃、76℃。由于松弛转变温度会随着频率的升高而升高,频率每变化10倍,玻璃化转变温度会移动5~10℃,次级转变对频率依赖性则更强,而相转变温度则不会因频率改变而改变[17],因此78℃(76℃)处的相转变损耗峰是因晶体熔融产生,而0.7℃(6℃)和-66℃(-55℃)两处峰温明显随频率变化而变化的损耗峰则是由松弛转变形成。
由于木材中木质素的玻璃化转变一般发生在100℃以后[4, 16],而软木木质素中紫丁香基苯丙烷结构单元占比较低[18],使其甲氧基含量相对较低而具有更高的玻璃化转变温度Tg[19]。此外,在Mano[5]对松木(Pinus spp.)在-25~100℃温度范围内测得的DMA结果中并未发现有松弛转变损耗峰,可以得知此温度范围内出现的松弛转变损耗峰应由软木特有的软木脂成分产生。所以推测0.7℃(6℃)附近储能模量降幅较大的松弛转变应为软木脂中无定形区的玻璃化转变,且该玻璃化转变的温度范围为-40~57℃(-33~64℃);而78℃(76℃)处的熔融损耗峰则同栓皮槠软木一样,归因于软木脂中微晶区的熔融;发生在-66℃(-55℃)附近储能模量变化较小的松弛转变则为次级转变,推测是由软木中主要成分木质素或软木脂无定形区分子链上链节、侧基等小尺寸运动单元的局部运动产生[4]。在玻璃态高聚物发生玻璃化转变后储能模量通常会发生3~4个数量级的变化,而软木试样在发生玻璃化转变后,储能模量仅下降了15MPa左右,不仅因为软木脂具有交联的三维网状分子结构,使其从玻璃态转变为高弹态后储能模量下降幅度较小[20],而且软木材料本身模量就很小[21],在发生玻璃化转变后软木脂中结晶部分仍未发生熔融,且软木细胞壁初生壁和胞间层也因其主要成分木质素未达到玻璃化转变温度而仍可为细胞壁提供支撑强度,使得模量不会有大幅大降。当温度升至150℃之后,木质素才发生玻璃化转变,使得E′又呈现下降趋势,tanδ也随之升高。
对于栓皮槠软木,以往研究者采用DMA在压缩模式下测得的玻璃化转变温度(1Hz)在10~20℃附近[4-5],明显高于栓皮栎软木的0.7℃。而本试验中采用的升温速率略高,测得的Tg理应偏高,所以推测导致测得的栓皮栎软木脂Tg较低的原因应与分子链柔性相关,由于栓皮栎软木脂构成单元中饱和单体占比多于栓皮槠软木脂[22],所以很有可能是因为链中取代基的减少使分子链间的相互作用减弱才导致栓皮栎软木脂的玻璃化转变温度降低。在玻璃化转变温度以下,软木脂无定形区虽然处于玻璃态,但仍具有比链段小的运动单元,可进行一定程度的运动,这也是软木材料在低温下柔韧性仍较好的原因之一。
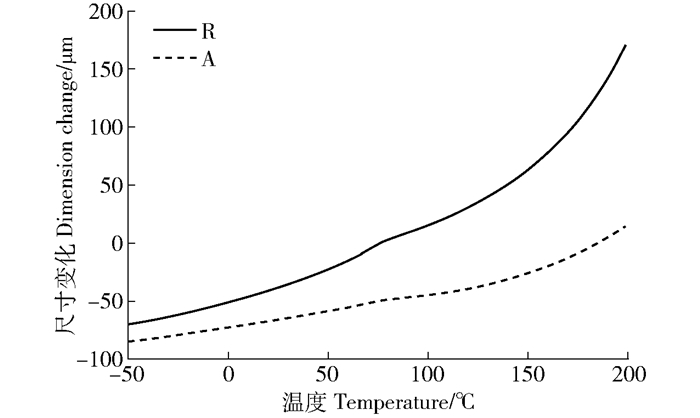
在发生玻璃化转变时,除高聚物的比热容、储能模量、自由体积以外,其热膨胀系数也会发生明显变化,TMA常用来测试材料的热膨胀系数,通过热膨胀系数发生转变处来确定材料热转变温度。图 5中两条曲线分别为以径向(R)和轴向(A)为测量方向的两试样在第二次升温过程中所得到的形变-温度曲线。
在-50~78℃温度段内两试样尺寸逐渐增加,线膨胀系数略微升高但基本保持不变,试样R和A分别为127.6和77.4μm/(m·℃);当温度达到78℃时,试样A的线膨胀系数出现暂时减小的趋势,之后又逐渐升高,且在113℃时恢复至78℃前的线膨胀系数,而试样R在78℃附近因尺寸增加减缓而出现了一个台阶,之后随温度升高尺寸快速增加;在200℃时,试样R和A的线膨胀系数分别达到了750.0和299.0μm/(m·℃)。在78℃之前,形变曲线上并未出现因玻璃化转变而形成的明显拐点,可能是由于软木脂玻璃化转变温度范围较宽,使得发生玻璃化转变而造成的曲线转折并不明显;而当温度达到78℃时,软木脂无定形区的玻璃化转变已经完成,加之在此温度附近软木脂微晶部分又发生熔融,才导致试样弹性模量有较明显的下降。压杆在试样发生膨胀的同时有压入试样的趋势,使得形变曲线斜率暂时出现减缓的趋势,但赋予软木细胞壁刚性的木质素和多糖仍未发生软化,所以随着温度的继续升高,压杆并没有继续压入试样,并且因为软木细胞壁模量减小,几乎封闭的软木细胞内气体受热膨胀效果更加明显,使得曲线在78℃以后线膨胀系数一直呈现增加的趋势。此外,在升温过程中,径向尺寸增大的幅度要明显大于轴向。从所测的电镜图(图 6b)中可以看到径向上软木细胞侧壁存在2~3个褶皱,在细胞受热发生膨胀时,首先会通过褶皱的伸展来增加细胞体积。
3. 结论
通过采用多种热分析方法对栓皮栎软木的热稳定性和各转变温度进行分析,并将不同分析方法所测得的结果进行对比和相互验证以确定各热效应的归属。结果表明:当温度低于219℃时,软木细胞仅会发生热膨胀而尺寸增大,且径向尺寸增大程度高于轴向,其细胞壁结构则不受到破坏;DSC热流曲线中66℃处放热峰、DMA中78℃(1Hz)处的tanδ峰和TMA中形变曲线在78℃左右发生的转折都是由于栓皮栎软木中软木脂微晶结构的熔融造成的,而软木脂无定形区的松弛转变仅能通过DMA测试测得,其玻璃化转变温度为0.7℃;-66℃处的次级转变则推测是由软木中主要成分木质素或软木脂无定形区上的小尺寸运动单元产生。在对软木材料进行热定形处理时,热处理温度高于78℃可一定程度上增加软木材料塑性以减少成型后的厚度回弹。
-
表 1 两种软木各组分质量分数
Table 1 Mass fraction of each component of the cork of two species
试样
Sample工业分析Proximate analysis 元素分析Elemental analysis 水分
Moisture灰分
Ash挥发分
Volatiles固定碳
Fixed carbonC H N O S 栓皮栎软木Quercus variabilis cork 3.7% 0.6% 79.3% 16.4% 55.13% 6.67% 0.58% 33.32% 0 栓皮槠软木Quercus suber cork[10] - 0.47% - - 62.44% 7.95% 0.63% 28.51% 0 表 2 软木热解过程中各阶段特征温度和质量变化
Table 2 Characteristic temperature and mass variations in various stages of cork pyrolysis
阶段Stage 起始温度
Initial temperature/℃终止温度
Terminal temperature/℃峰温
Peak temperature/℃质量损失
Mass change/%第一阶段The first stage 0 100 43 2.2 第二阶段The second stage 100 219 1.3 第三阶段The third stage 219 451 415 71.0 第四阶段The fourth stage 451 600 8.5 -
[1] 张丽丛, 雷亚芳, 常宇婷.栓皮栎软木主要化学成分的分析[J].西北林学院学报, 2009, 24(4): 163-165. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200904038 Zhang L C, Lei Y F, Chang Y T.Contents of the main chemical components of cork from Quercus variabilis[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2009, 24(4): 163-165. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200904038
[2] Cordeiro N, Belgacem N M, Gandini A, et al. Cork suberin as a new source of chemicals (2): crystallinity, thermal and rheological properties[J]. Bioresource Technology, 1998, 63(2): 153-158. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(97)00073-4
[3] Ferreira R, Garcia H, Sousa A F, et al. Suberin isolation from cork using ionic liquids: characterisation of ensuing products[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 36(10): 2014-2024. doi: 10.1039/c2nj40433h
[4] Lagorce-Tachon A, Karbowiak T, Champion D, et al. Mechanical properties of cork: effect of hydration[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 82: 148-154. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a1d6f5498c6e7b8eb18676b11370a24b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] Mano J F. The viscoelastic properties of cork[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(2): 257-263. doi: 10.1023/A:1013635809035
[6] 程捷, 闫红强.流变学特性在刨花板热压过程中的应用[J].化工时刊, 2006, 20(6): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-154X.2006.06.020 Cheng J, Yan H Q. Study on rheological characteristic applied in the process of hot-pressing for particleboard[J]. Chemical Industry Times, 2006, 20(6): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-154X.2006.06.020
[7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 28731—2012: 固体生物质燃料工业分析方法[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 28731—2012: Proximate analysis of solid biofuels[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013.
[8] 李方勇, 宋景慧.生物化学组分对生物质型煤燃烧特性影响的实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(26): 124-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201126019 Li F Y, Song J H. Experimental study about the effect of biomass chemical composition on the combustion characteristics of bio-briquette[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(26): 124-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdjgcxb201126019
[9] 潘蕊.杨木热解动力学及其固定床热解基础实验研究[D].南京: 南京林业大学, 2014. Pan R. The thermogravimetry study of pyrolysis kinetics and fixed bed experimental invesitigation of poplar wood[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2014.
[10] Pintor A M A, Silvestre-Albero A M, Ferreira C I A, et al. Textural and surface characterization of cork-based sorbents for the removal of oil from water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(46): 16427-16435. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8c6bdff7cb438126db697c4040b0a6be
[11] Shangguan W W, Chen Z J, Zhao J F, et al. Thermogravimetric analysis of cork and cork components from Quercus variabilis[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2018, 52(1): 181-192. doi: 10.1007/s00226-017-0959-9
[12] Şen A, Marques A V, Gominho J, et al. Study of thermochemical treatments of cork in the 150-400℃ range using colour analysis and FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2012, 38: 132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.01.018
[13] Atanes E, Nieto-Márquez A, Cambra A, et al. Adsorption of SO2 onto waste cork powder-derived activated carbons[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 211-212: 60-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=78602743e084b4c473dd8f7a65a21a3c
[14] Şen A, Van den Bulcke J, Defoirdt N, et al. Thermal behaviour of cork and cork components[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2014, 582: 94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.03.007
[15] 刘丽华.纤维素在离子液体中的溶解及均相热塑化改性研究[D].广州: 华南理工大学, 2014. Liu L H.Research on the dissolution and homogenous thermoplastic modification of cellulose in ionic liquid[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014.
[16] Paiva D, Magalhães F D. Dynamic mechanical analysis and creep-recovery behavior of agglomerated cork[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2018, 76(1): 133-141. doi: 10.1007/s00107-017-1158-y
[17] Wagner M.热分析应用基础[M].陆立明, 译.上海: 东华大学出版社, 2011: 154-159. Wagner M. Thermal analysis in practice[M]. Lu L M, trans. Shanghai: Donghua University Press, 2011: 154-159.
[18] Lourenço A, Rencoret J, Chemetova C, et al. Lignin composition and structure differs between xylem, phloem and phellem in Quercus suber L.[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1612. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5081372/
[19] 吕建雄, 蒋佳荔.木材动态黏弹性基础研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2015: 59. Lü J X, Jiang J L. Study on dynamic viscoelastic basics of wood[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 59.
[20] 过梅丽.高聚物与复合材料的动态力学热分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2002: 33. Guo M L. Dynamic mechanical thermal analysis of polymers and composites[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002: 33.
[21] Oliveira V, Rosa M E, Pereira H. Variability of the compression properties of cork[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2014, 48(5): 937-948. doi: 10.1007/s00226-014-0651-2
[22] Ferreira J, Pereira H, Şen U, et al. Chemical and cellular features of virgin and reproduction cork from Quercus variabilis[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2016, 94: 638-648. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.038
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 丁金华,许艳秋,钱晶. 苏南水网地区水域景观破碎化时空演变特征及驱动因子研究——以吴江区为例. 西北林学院学报. 2024(01): 247-255 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈实,陈丽捷,洪宇,刘金福,阙翔,李意敏,何东进,赵婧雯. 泉州湾湿地碳库生态安全评价及其障碍因素研究. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(05): 686-695 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨烜涵,付晖,秦煜姬,程恩起,陈圣天. 近20年来海口湿地景观格局演变及其驱动因子. 中国城市林业. 2023(03): 28-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王琦,刘子刚,周隽伊. 三江平原沼泽湿地变化的影响因素及其空间效应. 中国人口·资源与环境. 2023(07): 44-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵红梅,毛欣,刘春雷,李亚松,刘林敬. 福建泉州湾海岸带MIS 3阶段以来的海侵—海退过程. 地质力学学报. 2023(04): 569-583 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱映辰,谭芳林,阙翔,洪宇,潘爱芳,刘金福. 多时间尺度下森林公园负离子变化特征及与温湿度关系研究. 西北林学院学报. 2023(06): 211-218+227 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵红梅,刘春雷,毛欣,毕志伟,刘哲,李亚松. 泉州湾海岸带全新世地层及沉积环境演化. 地层学杂志. 2022(04): 401-410 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: