Simulation of surface fire behavior of Pinus tabuliformis forest in Ming Tombs Forest Farm in Beijing
-
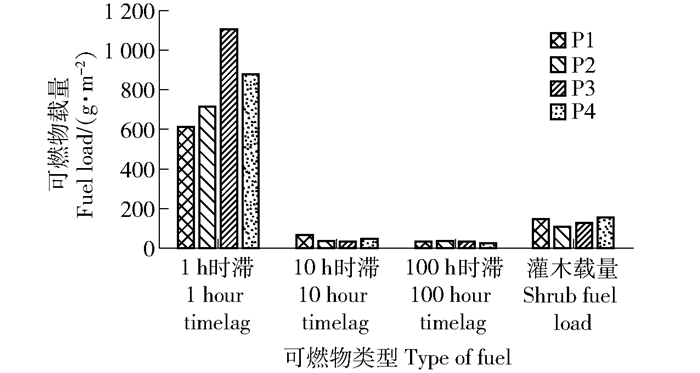
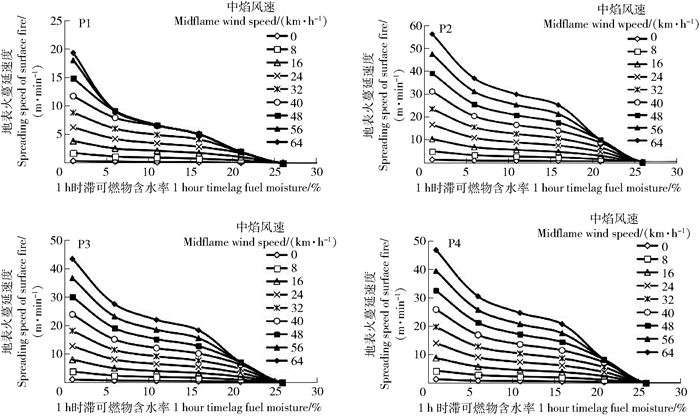
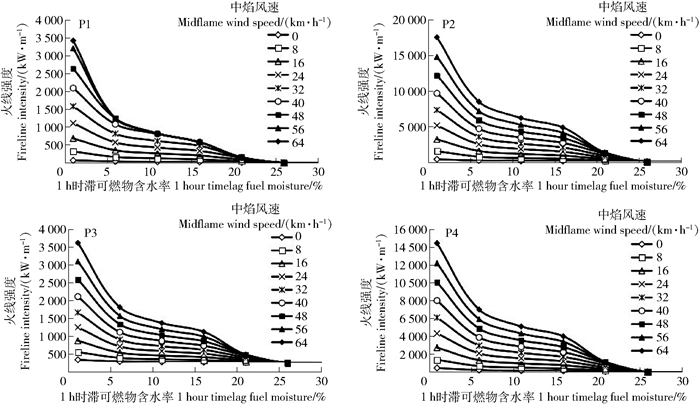
摘要:目的油松林是华北地区典型针叶林分,易发生森林火灾。通过对油松林地表火行为模拟研究可以为森林可燃物管理,林火预防及扑救提供科学依据。方法本研究以北京市十三陵林场油松林为研究对象,通过野外调查地表枯死可燃物(1、10、100 h时滞)和灌层可燃物,记录林分因子(第1枝下高、树高、林龄和胸径)和环境因子(坡度、坡向和海拔)。结合内业实验测可燃物含水率和热值,利用火行为模拟软件BehavePlus5.0,对1 h时滞可燃物设定不同含水率和风速值,模拟所研究林分地表火蔓延速度、火线强度、火焰高度以及单位面积发热量4个重要的火行为指标。结果1、10、100 h时滞和灌层可燃物占总可燃物载量比分别为78%、5%、4%和13%。基于实测可燃物载量和含水率,油松林地表火蔓延速度平均值为2.1 m/min,火线强度平均值为270 kW/m,火焰高度平均值为0.95 m单位面积发热量平均值为7 139 kJ/m2。油松林1 h时滞可燃物载量显著高于10 h时滞和灌层可燃物载量。在1 h时滞可燃物含水率为6%,风速为40 km/h的强风和干旱天气条件下,油松林地表火蔓延速度平均值为15.1 m/min,火线强度平均值为3 278.5 kW/m,火焰高度平均值为3.1 m,单位面积发热量平均值为12 337.5 kJ/m2。结论油松林内1 h时滞细小可燃物载量高于其他类型可燃物载量。地表火蔓延速度慢,火强度低,火焰高度低于第一枝下高,在正常天气条件下容易被扑灭。模拟结果表明油松林在低含水率的条件下,风速会显著增加地表火蔓延速度,难以人为扑灭,需清理地表可燃物,降低火险。
-
关键词:
- 油松林 /
- 可燃物载量 /
- BehavePlus5.0 /
- 地表可燃物 /
- 火行为
Abstract:ObjectivePinus tabuliformis is a typical coniferous forest in North China, which is prone to forest fires. By simulating the surface fire behavior of Pinus tabuliformis, it can provide a scientific basis for forest combustibles management, forest fire prevention and fire fighting.MethodTaking Pinus tabuliformis forest as the study objective, we simulated the surface fire behavior with BehavePlus5.0 software.ResultThe fuel load of 1 hour timelag, 10 hour timelag, 100 hour timelag and shrub accounted for 78%, 5%, 4% and 13%, respectively. According to the research date, the average value of the surface fire spread rate of Pinus tabuliformis forest was 2.1 m/min, the average value of the fire line intensity was 270 kW/m, the average value of the height of the flame is 0.95 m, and the average value of the heat per unit area was 7 139 kJ/m2. Under the conditions of strong wind and dry weather with 1 hour timelag fuel moisture of 6% and a wind speed of 40 km/hour, the average value of the surface fire spread rate of Pinus tabuliformis forest was 15.1 m/min. The average value of the fire line intensity was 3 278.5 kW/m, and the average flame height was 3.1 m, the average value of the heat per unit area was 12 337.5 kJ/m2. Simulation of surface fire behavior study can provide a reference for the pruning height of Pinus tabuliformis.ConclusionThe results show that 1 hour timelag fuel load was significantly higher than the other type of fuel. The surface fire spreads slowly, the fire intensity was low, the flame height was lower than the first branch, and it was easy to be extinguished under normal weather conditions. The simulation results show that under the condition of low water content, the wind speed of the Pinus tabuliformis forest will significantly increase the surface fire spread speed, which is difficult to extinguish artificially. It is necessary to clean up the surface fuel and reduce the fire risk.-
Keywords:
- Pinus tabuliformis forest /
- fuel load /
- BehavePlus5.0 /
- surface fuel /
- fire behavior
-
防浪林是种植于堤防迎水侧滩地上用于防浪护堤和抢险取材的专用林,既可以保持水土、调节气候、促进林业经济发展,又可以防浪消能、延长堤防寿命和减少堤防的维护费用,是堤防工程的重要组成部分[1-2]。目前我国各大江河堤岸的重要河段均种植了防浪林,且根据不同河段的实际情况,实施了不同的防浪林建设方案。物理模型实验是研究防浪林消浪机理的一个有效手段,对科学提出防浪林优化布局以及如何营造防浪林工程有重要理论指导意义和实用价值。目前已有很多学者进行了相关的物理实验研究。何飞等[3]在考虑植物根、茎、叶影响下设计水槽实验探究刚性植物的消浪特性,认为根、茎、叶均在不同程度上影响植物消浪特性。陈杰等[4]在研究刚性植物根、茎、叶对植物消波特性的影响中得出植物消波特性与植物淹没度有关,根、茎、叶的存在增加了植物拖曳力系数。陈杰等[5]还通过物理实验研究了规则波通过非淹没刚性植物波高的沿程变化,实验结果表明相比于矩形分布方式,三角形的分布方式消耗了更多的波能,消浪效果更明显。
以上相关的物理实验研究主要是针对植被本身的特性以及排列方式对消浪效果的影响,缺乏对林带宽度、植被密度、滩地波高等因素的考虑,以及不规则波条件下植被对消浪效果的影响。
本文以嫩江干流佰大街堤防为例,选取防浪林林带宽度、排列方式、密度、树型以及滩地波高作为影响因素,采用控制变量法,通过构建防浪林消浪物理模型研究其对消浪效果的影响,并提出合理的防浪林优化设计方案。
1. 研究区概况
嫩江干流佰大街堤防位于黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市泰来县境内,自汤池镇愚公堤经佰大街村至李地房子,堤防分为上、中、下3段,全长6.70 km。原佰大街堤上下段中间为高地相连,后因村民在高地附近修建民房,不断从高地取土,导致现有高地地面高程减少,最低处地面高程141.5 m,远低于此处河道50年一遇洪水位144 m,造成了防洪缺口。现状堤防属于扩建砂堤,筑堤土料比较松散,抗冲刷能力较弱,容易产生流土、管涌等现象。嫩江该河段高水位时,水面宽阔,堤前滩地现有防浪林1.0 km,多为5 ~ 8年生的杨树(Populus spp.)和少量柳树(Salix spp.)。预计规划新建防浪林10 km。该段堤防防洪标准目前仅为30 ~ 35年一遇。佰大街堤防如图1所示。
2. 物理模型设计
2.1 模型比尺确定
模型比尺的确定主要依据实验条件、波浪要素、造波机性能等因素,并综合考虑比尺效应带来的误差影响等。已有的物理模型实验研究中,王瑞雪[6]选择几何比尺1∶20,在长40 m× 宽0.5 m × 高0.8 m 的水槽中进行非刚性植物对波浪传播变形影响的实验研究;吉红香[7]选择几何比尺为1∶10,在长66 m × 宽1.0 m × 高1.6 m的水槽中研究滩地植物对波浪变形及消浪效果的影响。
本实验是在不规则波浪水槽中进行。为了消除比尺效应,更好的模拟嫩江干流防浪林的消浪效果,依据实际条件下防浪林的植被生长能力、波浪要素以及现有实验设备条件,结合实验方案的设计,对比造波机实际可造波周期,依照周期比例确定模型几何比尺,并根据重力相似准则确定时间比尺,最终确定本模型采用的比尺为1∶10。其中比尺确定公式[8]如(1)所示。
λ=lmlp,λt=λ−1/2,λf=λ1/2λu=λ−1/2,λF=λ−3,λQ=λ−5/2 (1) 式中:
λ 为模型长度比尺;lp 为原型长度;lm 为模型长度;λt 为时间比尺;λf 为频率比尺;λu 为速度比尺;λF 为力比尺;λQ 为流量比尺。2.2 实验方案与依据
关于植被消浪的物理模型实验设计方面,白玉川等[9]用裁减的桧柏(Sabina chinensis)枝模拟防浪林,研究了非破碎波条件下的防浪林消浪效果。胡嵋等[10]对于在堤岸上栽种植被消浪这一新的护岸工程,选取桧柏树枝作为防浪林的模型,择选出对消浪护岸具有主要影响的因素。王瑞雪[6]用PVC塑料圆管来模拟刚性植物树干进行波浪水槽物理模型实验。吴迪等[11]和曹海锦等[12]也分别利用聚乙烯仿真绿色植物模拟柔性植物进行柔性植物消浪及沿程阻流特性实验研究。通过不同的研究可以发现影响消浪效果的主要因素为防浪林林带宽度、排列方式、种植密度、林木高度等。
针对不同的实际条件,物理模型的设计方案有一定的差异,需根据实际情况和需要来设计实验方案。本实验根据嫩江干流的实际条件及水文资料,推算佰大街堤防典型断面的多年一遇水位高程及波要素极值,对比分析不同条件下波浪沿程衰减的变化。由于防浪林消浪效果的影响因素较多,因而本模型实验采用控制单因素变量法,得出各因素对消浪效果的影响。本实验中设计的主要对比方案有:不同的防浪林林带宽度、不同的防浪林排列方式、不同的防浪林密度、不同树型的防浪林、以及不同的来波波高等的消浪实验方案。分析不同实验方案条件下的消浪效果,提出该段的防浪林优化布局方案。
根据研究区实际防浪林植被的外形参数,包括树高、树干直径、树冠直径、树冠以下树干高度等,按照比尺计算模型树的外形参数,根据所需材料的尺寸对模型树进行修剪和黏合,植物树干采用圆形木棒模拟,植物树冠部分采用塑料仿真枝叶模拟,由此制作合适的模型树,如图2所示。
同时,为更好的定量分析防浪林消浪机理,定义
q 为防浪林植被消浪系数:q=(h−h′)/h (2) 式中:
h 为无防浪林的波高,h′ 为经过防浪林消波后的波高。2.3 实验断面和波要素的选取
佰大街断面50年一遇洪水条件下滩地平均水深为2.83 m,此时防浪林处于部分淹没状态。依据该断面多年一遇水位及波浪要素值的推算结果中50年一遇的波要素,得出该堤段波浪周期在2 ~ 4 s之间,平均波高在0.1 ~ 0.6 m之间。根据《海港水文规范》推算出相应的1/10大波(规则波)波高,Hs(不规则波)有效波高,分别进行了规则波和不规则波消浪效果的模拟实验,实验波要素分别为1/10波高1.16 m、有效波高0.91 m、平均波高0.57 m、平均周期3.01 m。此外,为进一步研究不同波要素条件下防浪林消浪效果的差异,选取了1.1倍和0.9倍50年一遇波高条件进行对比实验。
2.4 实验设备及布置
本实验是在河海大学海岸工程实验大厅70 m长的不规则波浪水槽中进行,水槽宽1.0 m,高1.8 m,有效实验段宽1 m。水槽一端安装了推板式不规则生波机,通过电机系统控制推波板运动行程和频率[13]。数字波高仪采用YWS200-XX型,波高采集系统采用水工试验数据采集处理系统(DJ800型),精度为0.01 cm。所有量测信号均通过计算机采集、记录和分析,能模拟最大波高0.3 m、波周期0.5 ~ 5 s的不规则波,具备研究不规则波作用下的各种动力响应机制及波浪与建筑物相互作用关键技术和理论问题的能力。水槽底部铺设灰色混凝板,在灰塑料板上打孔用以固定植物模型。水槽左侧为造波机,波高传感器两个,分别布设在防浪林模型前后,采集波高的变化。最右侧为消波层,能够有效地吸收尾波的波能,避免波浪的反射对实验造成干扰(实验布置和实验实景图分别如图3和图4所示)。
3. 防浪林消浪机理物理实验结果分析
3.1 不同防浪林林带宽度和防浪林排列方式的消浪结果
根据实验方案,进行了佰大街断面在不同排列方式(等边三角形、正方形及梅花形,如图5 ~ 7所示)条件下的消浪实验。由于模型比尺为1∶10,因此根据佰大街的种植现状,确定实验室条件下的防浪林植被密度为17株/m2,树干直径为0.7 cm,树干高度为16 cm,树冠直径为13 cm,树冠为高度8 cm。规则波和不规则波条件下的实验结果分别如图8和图9所示。
对比不同的防浪林排列方式下防浪林的消浪效果,可见在规则波条件下,当林带宽度在40 m以上时,等边三角形和梅花形排列的防浪林要明显优于正方形排列;在不规则波条件下,当林带宽度在40 m以上时,等边三角形和正方形排列的防浪林要明显优于梅花形排列。因此,等边三角形排列方式相对较优。这与陈杰等[5]通过物理实验研究规则波通过非淹没刚性植物波高的沿程变化中得出三角形分布方式消浪效果最明显的结论一致。对比相同防浪林林带宽度下的规则波和不规则的消浪效果,可以发现规则波条件下防浪林的消浪系数较大,但两者差距较小。而实际条件下的波浪为不规则波,因而不规则波的消浪系数更为接近实际条件。
同时,还可以发现,不管是规则波还是不规则波条件下,随着林带宽度增加到30 m以后,防浪林的消浪系数对于林带宽度的敏感度降低,此时消浪效果提升空间很小。
3.2 不同密度的防浪林消浪效果
根据实验方案,进行了在不同密度的防浪林(实验室条件下8株/m2,17株/m2,27株/m2)条件下的消浪实验。其中实验室条件下树型为,树干直径0.7 cm,树干高度16 cm,树冠直径13 cm,树冠高度8 m。采用不规则波,实验结果如图10所示。
对比不同密度的防浪林的消浪效果,可以发现,当防浪林林带宽度为10 m时,不同密度的防浪林消浪效果差别不大,均为8%左右;当防浪林林带宽度大于10 m时,防浪林的消浪效果随着密度的增加而增加,密度27株/m2比密度8株/m2的消浪系数大5%到10%。但过高的密度会影响防浪林树木的正常生长,而且种植成本较高。可见,当林带宽度为40 m,排列方式为等边三角形时,0.17株/m2(原型条件)是较为经济合理的植被密度方案。此时,当防浪林林带宽度进一步增大50 m时,防浪林的消浪系数仅增加3.04%。
3.3 不同树型的防浪林消浪效果
根据实地测量,选取了4种树型作为树干和树冠条件的组合,如表1所示,采用相对较优的等边三角形排列方式,实验室条件下防浪林密度为17株/m2。规则波和不规则波条件下的模型实验结果分别如图11和图12所示。
表 1 树型尺寸Table 1. Tree size项目
Item树型1
Tree type 1树型2
Tree type 2树型3
Tree type 3树型4
Tree type 4树干高度
Trunk height/m0.26 0.26 0.26 0.16 树干半径
Trunk radius/m0.025 0.015 0.015 0.007 树冠高度
Crown height/m0.35 0.35 0.35 0.08 树冠直径
Crown radius/m0.25 0.25 0.17 0.13 由以上结果可见,不同树型的消浪效果有着明显的差异。树型1(成年树)树干较粗,树冠较为茂密,茂密的根、茎、叶存在增加了植物拖曳力系数,因而消浪能力显著,规则波条件下,20 m宽的防浪林其消浪系数即达60%左右,50 m宽防浪林的消浪系数可达到80%以上。
树型2相对树型1的差别为树干半径较小,由消浪实验结果可见,树干的粗细对消浪效果的影响较小。树型3的消浪系数要小于树型2。而树型4(幼树)的消浪效果明显小于树型1、树型2和树型3。可见,不同防浪林树型对同一断面条件下的消浪效果有着重要的影响,对比其消浪系数可知,树冠的消浪作用要明显强于树干,因而在防浪林方案设计时,需考虑采用树冠消浪为主的方法。
3.4 不同来波波高影响下消浪效果
根据实验方案,进行了在不同来波波高(1.1倍50年一遇波高、50年一遇波高、0.9倍50年一遇波高)条件下的消浪实验。采用相对较优的等边三角形排列方式,实验室条件下,树干直径0.7 cm,树干高度16 cm,树冠直径13 cm,树冠高度8 cm。规则波和不规则波条件下的模型实验结果分别如图13和图14所示。
由图13和图14可见,不同波高条件下的消浪效果有所差异,但差异较小,且不规则波的消浪系数变化更为稳定。波高越大,消浪效果越好。
4. 结 论
嫩江干流佰大街堤防段,在合理的防浪林树型条件下,等边三角形排列的防浪林要优于梅花形和正方形排列方式;密度的增加对防浪林消浪效果有着一定的提高,但过高的密度会影响防浪林树木的正常生长;不同树型对不同断面条件的消浪效果有着重要的影响,且树冠的消浪作用要明显强于树干。不同波高条件下的消浪效果有所差异,但差异较小,且不规则波的消浪系数变化更为稳定。
-
表 1 外业调查基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of field investigation
样地号
Sample plot No.林龄
Stand age平均胸径
Average DBH/cm第1枝下高
Height of first lower branch/m坡度
Slope degree/(°)可燃物床厚度
Depth of fuel bed/cmP1 59 15.70 1.84 15 4.9 P2 59 13.27 2.44 18 8.6 P3 59 11.27 1.79 20 8.3 P4 59 11.85 2.30 23 8.3 表 2 不同含水率条件下油松林单位面积发热量
Table 2 Thermal value per unit area of Pinus tabuliformis forest under different moisture conditions
含水率Mositure content/% 单位面积发热量Thermal value per unit area/(kJ·m-2) P1 P2 P3 P4 1 10 580 18 754 18 789 18 571 6 8 051 13 836 13 688 13 775 11 7 327 12 473 12 309 12 446 16 6 770 11 583 11 482 11 602 21 4 622 7 942 7 907 8 085 26 0 0 0 0 表 4 不同条件下油松林地表火火焰高度
Table 4 Flame height of surface fire for Pinus tabuliformis forest under different conditions
m 项目
Item1 h时滞可燃物含水率
1 hour timelag fuel moisture/%中焰风速Mid-flame wind speed/(km·h-1) 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 均值Average 1 1.1 1.9 2.6 3.2 3.8 4.4 4.9 5.3 5.7 6 0.7 1.3 1.9 2.3 2.8 3.1 3.5 3.7 4.0 11 0.7 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.7 3.0 3.2 3.4 16 0.6 1.0 1.4 1.8 2.1 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 21 0.4 0.7 1.0 1.3 1.4 1.6 1.7 1.7 1.7 26 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 最大值Max. 1 1.3 2.2 3.2 3.9 4.6 5.3 5.9 6.4 6.9 6 0.9 1.6 2.3 2.8 3.3 3.8 4.2 4.6 5.0 11 0.8 1.4 2.0 2.4 2.9 3.3 3.6 4.0 4.3 16 0.7 1.2 1.7 2.2 2.6 2.9 3.2 3.5 3.8 21 0.5 0.8 1.2 1.5 1.7 2.0 2.1 2.1 2.1 26 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -
[1] Forrestel A B, Ramage B S, Moody T, et al. Disease, fuels and potential fire behavior: impacts of sudden oak death in two coastal California forest types[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2015, 348:23-30. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6a782045b1f1c639646d574d3840fa9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] 田晓瑞, 舒立福, 赵凤君, 等.气候变化对中国森林火险的影响[J].林业科学, 2017, 53(7):159-169. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201707016 Tian X R, Shu L F, Zhao F J, et al. Impacts of climate change on forest fire danger in China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(7):159-169. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201707016
[3] Rothermel R C. A mathematical model for predicting fire spread in wildland fuels[M]. Ogden: USDA Forest Service General Technical Report, 1972.
[4] Bilgili E, Durmaz B D, Saglam B, et al. Fire behaviour in immature calabrian pine plantations[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2006, 234:S112-S112. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=af8904844d50f9cc1a7676880df77451&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] 赵璠, 舒立福, 周汝良, 等.西南林区森林火灾火行为模拟模型评价[J].应用生态学报, 2017, 28(10):3144-3154. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201710005 Zhao P, Shu L F, Zhou R L, et al. Evaluating fire behavior simulators in southwestern China forest area[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(10):3144-3154. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201710005
[6] 陈宏伟, 常禹, 胡远满, 等.大兴安岭呼中林区森林死可燃物载量及其影响因子[J].生态学杂志, 2008, 27(1):50-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz200801009 Chen H W, Chang Y, Hu Y M, et al. Load of forest surface dead fuel in Huzhong area of Daxing' anling Mountains and relevant affecting factors[J].Journal of Ecology, 2008, 27(1):50-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz200801009
[7] 吴志伟, 贺红士, 梁宇, 等.丰林自然保护区森林可燃物模型的建立[J].应用生态学报, 2012, 23(6):1503-1510. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201206011 Wu Z W, He H S, Liang Y, et al. Establishment of standard forest fuel models for Fenglin Natural Reserve, Heilongjiang Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(6):1503-1510. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201206011
[8] 王明玉, 李涛, 任云卯, 等.森林火行为与特殊火行为研究进展[J].世界林业研究, 2009, 22(2):45-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJLY200902009.htm Wang M Y, Li T, Ren Y M, et al. Research advances in forest fire behavior and special forest fire behaviors[J].World Forestry Research, 2009, 22(2):45-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJLY200902009.htm
[9] 武军, 朱霁平, 贾敬蕊, 等.一种基于聚类分析的由林分因子估算地表可燃物载量的方法[J].火灾科学, 2011, 20(2):99-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2011.02.005 Wu J, Zhu J P, Jia J R, et al. Forest surface fuel load estimation by stand factors based on cluster analysis method[J].Fire Safety Science, 2011, 20(2):99-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2011.02.005
[10] 王刚, 金晓钟.细小可燃物易燃性的试验研究[J].森林防火, 1995(3):5-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500452011 Wang G, Jin X Z. Experimental study on flammability of fine fuel[J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 1995(3):5-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500452011
[11] Heinsch F A, Andrews P L. BehavePlus fire modeling system, version 5.0[J]. USDA Forest Service-General Technical Report RMRS-GTR, 2010, 106(213):1-110.
[12] Andrews P L. Current status and future needs of the BehavePlus Fire Modeling System[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2014, 23(1):21. doi: 10.1071/WF12167
[13] Kucuk O, Bilgili E, Fernandes P M. Fuel modelling and potential fire behavior in Turkey[J]. Sumarski List, 2015, 139(11-12):553-560. https://www.worldcat.org/title/behaveplus-fire-modeling-system-version-50-design-and-features/oclc/713836248
[14] 黄小荣, 庞世龙, 彭玉华, 等.广西苍梧马尾松林和大叶栎林的火行为比较[J].火灾科学, 2015(1):9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2015.01.02 Huang X R, Pang S L, Peng Y H, et al.Assessing fire potential of Pinus massoniana and Castanopsis fissa forests in Cangwu by fuel modelling[J]. Fire Safety Science, 2015(1):9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2015.01.02
[15] 宋洁, 朱敏, 刘晓东, 等.疏伐对北京西山油松林可燃物特征及潜在火行为影响[J].北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(5):41-47. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160353 Song J, Zhu M, Liu X D, et al. Effects of thinning on fuel characteristics and potential fire behaviors of Pinus tabuliformis forest in Beijing West Mountain[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(5):41-47. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160353
[16] 卢欣艳.北京西山森林火险影响因素时空规律研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-2010128835.htm Lu X Y. The spatial and temporal rules of forest fire factors in Beijng Xishan Centre[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-2010128835.htm
[17] 王晓丽, 牛树奎, 马钦彦, 等.以地表死可燃物评估八达岭林场森林燃烧性[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(10):5313-5319. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.10.017 Wang X L, Niu S K, Ma Q Y, et al.Forests combustibility evaluation in Badaling Forest Farm based on surface dead fuel[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(10):5313-5319. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.10.017
[18] 王凯, 牛树奎.基于Rothermel模型的北京鹫峰国家森林公园潜在火行为[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2016, 33(1):42-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjlxyxb201601006 Wang K, Niu S K. Research on the potential fire behavior in Jiufeng National Forest Park of Beijing based on the Rothermel Model [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2016, 33(1):42-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjlxyxb201601006
[19] 王晓丽.北京山区森林燃烧性研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1766516 Wang X L. Study on combustibility of forests in Beijing Mountain Area[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2010. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1766516
[20] 杨淑香, 王立明.北京十三陵林场公益林可燃物特征与经营[J].森林防火, 2007(1):14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.007 Yang S X, Wang L M.The public welfare forest combustible characteristic and management of Beijing Ming Tombs Farm[J].Forest Fire Prevention, 2007(1):14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2007.01.007
[21] Page W, Jenkins M J. Predicted fire behavior in selected mountain pine beetle-infested lodgepole pine[J]. Forest Science, 2007, 53(6):662-674. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1ca659bd12b75cd351958acbf1646a72
[22] 胡海清, 陆昕, 孙龙, 等.大兴安岭典型林分地表死可燃物含水率动态变化及预测模型[J].应用生态学报, 2016, 27(7):2212-2224. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201607021 Hu H Q, Lu X, Sun L, et al.Dynamics and prediction models of ground surface dead fuel moisture content for typical stands in Great Xing' an Mountains, Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(7):2212-2224. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201607021
[23] 张国防.杉木人工林地表易燃物含水率变化规律的研究[J].森林防火, 2000(2):19-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2000.02.013 Zhang G F.Study on the moisture change of flammable surface fuel of Chinese fir plantation[J].Forest Fire Prevention, 2000(2):19-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2511.2000.02.013
[24] Wu Z W, He H S, Chang Y, et al. Development of customized fire behavior fuel models for boreal forests of northeastern China[J]. Environmental Management, 2011, 48(6):1148-1157. doi: 10.1007/s00267-011-9707-3
[25] Fontaine J B, Westcott V C, Enright N J, et al. Fire behaviour in south-western Australian shrublands: evaluating the influence of fuel age and fire weather[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2012, 21(4):385. doi: 10.1071/WF11065
[26] Albini F A. Estimating wildfire behavior and effects[M]. Ogden: USDA Forest Service General Technical Report, 1976.
[27] Anderson W R, Cruz M G, Fernandes P M, et al. A generic, empirical-based model for predicting rate of fire spread in shrublands[J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire, 2015, 24:443-460. doi: 10.1071/WF14130
[28] 舒立福, 王明玉, 田晓瑞, 等.关于森林燃烧火行为特征参数的计算与表述[J].林业科学, 2004, 40(3):179-183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2004.03.031 Shu L F, Wang M Y, Tian X R, et al. Calculation and description of forest fire behavior characters[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2004, 40(3):179-183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2004.03.031
[29] Hunter M E. Comprehensive guide to fuels treatment practices for ponderosa pine in the Black Hills, Colorado Front Range, and Southwest[M]. Ogden: USDA Forest Service-General Technical Report RMRS-GTR, 2007.
[30] Cruz M G, Alexander M E, Sullivan A L, et al. Assessing improvements in models used to operationally predict wildland fire rate of spread[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2018, 105:54-63. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=57c53d5b64b2b66ee44745ed2b2100de




 下载:
下载: