Coupling relationship between stand structure and color patch of Platycladus orientalis plantations
-
摘要:目的色彩是森林景观中最易影响感官的信息要素,也是衡量景观质量高低的重要指标,而林分结构是影响林内景观质量的重要因子。本文旨在通过林分结构与色彩斑块的耦合关系,对北京山区侧柏人工风景林林内景观质量的影响机理进行探讨。方法采用主成分分析构建林分结构因子,通过灰色关联度分析研究林分结构与景观色彩斑块的耦合关联程度,并结合单因素方差分析和多重比较的方法研究两者间的变化规律。结果(1) 4个因子对林分结构的影响程度依次为:林内空间因子>植被生长因子>林木高度因子>林内竞争因子。(2)林分结构与景观色彩斑块的耦合关联度为0.6,属弱协调程度。其中,相关关系耦合度较大的指标包括:林内空间因子与色彩最大斑块比例(LPI)和斑块色彩多样性(SHDI)、植被生长因子与色彩斑块分离度(SPL)和色彩对比度(CPC)、林木高度因子与SHDI、SPL和CPC、林内竞争因子与色彩斑块亮度(CPB)。(3)植被生长仅在中低水平上对LPI有显著影响;林下相对高度仅在较高水平时对CPB和CPC有显著影响;而林内竞争程度在中低水平上对CPB和CPC有显著影响,在较高水平上对SPL有显著影响。结论侧柏人工风景林林内景观色彩斑块与林分结构属中等关联程度,林分结构因子对色彩斑块的影响存在差异:不同林分结构因子所影响的色彩斑块指标、同一林分结构因子在不同水平上所影响的色彩斑块指标以及对色彩斑块的影响程度不尽相同,两者间存在相对复杂的耦合关系。Abstract:ObjectiveColor is not only the most sensitive information element in forest landscape, but also an important indicator to measure the quality of landscape. And forest structure is an important factor affecting the quality of forest landscape. So this paper aims to explore the influencing mechanism of the landscape quality in Platycladus orientalis plantations in Beijing mountain area through the coupling relation of stand structure and color patch.MethodStand structure factors were constructed by principal component analysis, and the coupling correlation degree between forest structure and landscape color patches was studied by grey correlation analysis, and the change law between them was studied by univariate variance analysis and multiple comparison.Result(1) The influence degree of four factors on stand structure is, in order, forest space factor > vegetation growth factor > forest height factor > forest competition factor. (2) The coupling correlation between forest structure and landscape color patches was 0.6, which was a weak coordination degree. Among them, the indicators with high correlation coupling degree included: forest space factor with LPI and SHDI; vegetation growth factor with SPL and CPC; forest height factor with SHDI and SPL and CPC; forest competition factor with CPB. (3) Vegetation growth only had a significant impact on LPI at the medium and low levels; The relative height of forest had significant effects on CPB and CPC only at a higher level. However, the intensity of intra-forest competition had a significant impact on CPB and CPC at the medium and low levels, and on the higher level, it had a significant impact on SPL.ConclusionThe releationship between color patch and stand structure is medium correlation degree, and stand structure actors influence on color patch differences: color patch index affected by different stand structure factors, and color patch index affected by the same stand structure factor in different levels, and degree of influence on colour patch is not the same.So there is a relatively complex coupling relationship between them.
-
-
表 1 系统耦合协调度标准
Table 1 System coupling coordination standard
协调度
Coordination degree0≤C<0.4 0.4≤C<0.5 0.5≤C<0.6 0.6≤C<0.7 0.7≤C<0.8 0.8≤C<0.9 0.9≤C≤1.0 协调评价
Coordination assessment严重不协调
Serious disharmony中度不协调
Moderate disharmony轻度不协调
Mild disharmony弱协调
Weak coordination中度协调
Moderate coordination良好协调
Good coordination优质协调
Quality coordination表 2 林分结构指标间相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of stand structure indexes
指标Index X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X12 X1 1.00 X2 0.83** 1.00 X3 0.69** 0.82** 1.00 X4 -0.63** -0.78** -0.65** 1.00 X5 0.64** 0.55** 0.45** -0.41** 1.00 X6 -0.23 -0.20 -0.17 0.09 -0.10 1.00 X7 0.49** 0.55** 0.51** -0.37** 0.35* -0.10 1.00 X8 -0.18 -0.47** -0.26 0.52** -0.10 0.31* -0.13 1.00 X9 -0.02 0.00 -0.31* -0.19 -0.10 0.25 -0.04 -0.24 1.00 X10 0.19 0.22 0.14 -0.19 0.17 0.75** 0.50** 0.13 0.28 1.00 X11 0.06 0.00 0.12 0.08 0.13 -0.64** 0.07 0.00 -0.54** -0.55** 1.00 X12 -0.13 -0.19 -0.36* 0.04 -0.11 0.68** -0.12 0.07 0.57** 0.55** -0.72** 1.00 注:*表示在0.05水平上显著相关; **表示在0.01水平上极显著相关。X1代表平均树高,X2代表平均胸径,X3代表平均冠幅,X4代表林分密度,X5代表平均活枝下高,X6代表灌木盖度,X7代表草本盖度,X8代表灌木高度,X9代表草本高度,X10代表灌草盖度,X11代表透视距离,X12代表郁闭度。下同。Notes: * indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.05; ** indicates an extremely significant correlation at the level of 0.01. X1 represents average tree height, X2 represents average DBH, X3 represents average canopy width, X4 represents stand density, X5 represents average height under active branches, X6 represents shrub coverage, X7 represents herb coverage, X8 represents shrub height, X9 represents herb height, X10 represents shrub and herb coverage, X11 represents perspective distance,X12 represents canopy closure. The same below. 表 3 主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis
指标
Index主成分因子Principal component factor F1 F2 F3 F4 X1 -0.084 0.489 0.763 -0.163 X2 -0.075 0.692 0.528 -0.389 X3 -0.194 0.810 0.345 -0.087 X4 -0.024 -0.530 -0.409 0.580 X5 -0.022 0.182 0.894 0.039 X6 0.877 -0.012 -0.096 0.240 X7 0.095 0.801 0.145 -0.001 X8 0.184 -0.184 -0.003 0.855 X9 0.544 -0.279 0.020 -0.632 X10 0.842 0.447 0.083 0.118 X11 -0.801 0.010 0.142 0.066 X12 0.819 -0.332 0.068 -0.147 方差Variance 3.181 2.75 2.008 1.752 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate 26.51% 22.92% 16.73% 14.60% 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate 26.51% 49.43% 66.16% 80.76% 表 4 林分结构因子与色彩斑块因子耦合作用矩阵
Table 4 Coupling matrix of stand structure factors and color patch factors
林分结构因子
Stand structure factor因子权重
Factorweight指标构成
Index composition指标权重
Index weight综合权重
Comprehensive weight色彩斑块因子Color patch factor 均值
MeanLPI SHDI SHEI DIV SPL CPB CPC F1 0.33 X6 0.26 0.09 0.64 0.65 0.56 0.58 0.55 0.57 0.59 0.59 X10 0.25 0.08 X12 0.25 0.08 X11 0.24 0.08 F2 0.28 X3 0.35 0.10 0.56 0.57 0.60 0.60 0.65 0.55 0.64 0.60 X7 0.35 0.10 X2 0.30 0.08 F3 0.21 X5 0.54 0.11 0.60 0.61 0.59 0.57 0.61 0.57 0.67 0.60 X1 0.46 0.10 F4 0.18 X8 0.41 0.07 0.58 0.60 0.59 0.58 0.56 0.63 0.58 0.59 X9 0.31 0.06 X4 0.28 0.05 均值Mean 0.60 0.61 0.59 0.58 0.59 0.58 0.62 0.60 注:LPI为最大斑块指数; SHDI为色彩多样性指数; SHEI为色彩丰富度指数; DIV为斑块分裂指数; SPL为斑块分离度; CPB为色彩斑块亮度; CPC为色彩斑块对比度。F1代表林内空间因子; F2代表植被生长因子; F3代表林木高度因子; F4代表林内竞争因子。下同。Notes: LPI is the largest patch index; SHDI is the color diversity index; SHEI is the color richness index; DIV is the patch division index; SPL is the plaque separation degree; CPB is the brightness of color patch; CPC is the contrast of color patch. F1 represents forest space factor; F2 represents vegetation growth factor; F3 represents tree height factor; F4 represents forest competition factor. The same below. 表 5 林分结构因子聚类分级结果
Table 5 Clustering classification results of forest structure factor
因子
Factor林分结构因子
Stand structure factor等级Classification Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ F1 X6/% 70 50 20 X10/% 80 60 30 X11/m 12 17 20 X12/% 75 60 40 F2 X2/cm 10.2 11.1 14.9 X3/m 3.8 4.3 5.6 X7/% 10 20 40 F3 X1/m 6.8 7.2 8 X5/m 1.7 2.1 3.1 F4 X8/m 0.5 1.1 1.6 X9/m 0.03 0.15 0.2 X4/(株·hm-2)
X4/(tree·ha-1)1250 1500 2000 表 6 不同林分结构因子等级间景观斑块指标方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of variance of landscape patch index between different stand structure factors
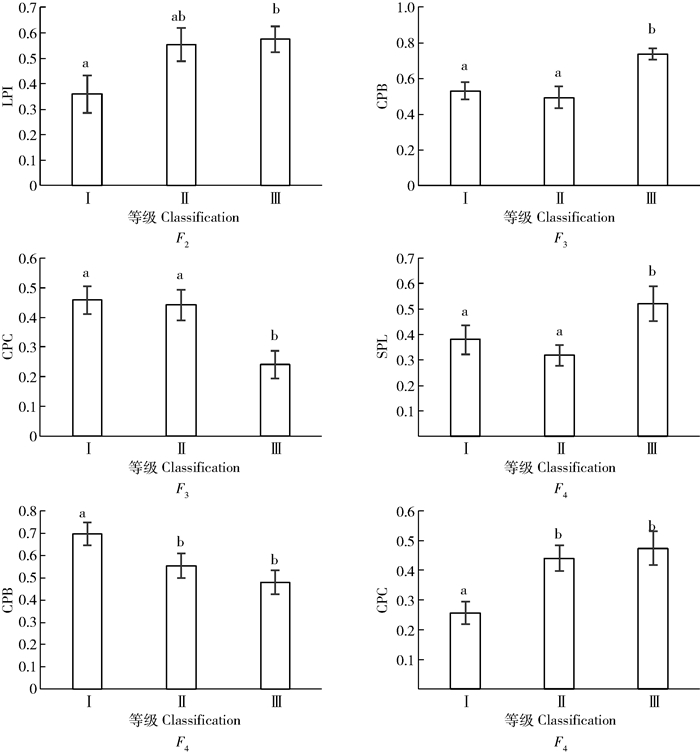
景观斑块
Landscape patch变异来源Sources of variation F1 F2 F3 F4 LPI F 2.152 3.273 0.494 2.83 P 0.128 0.047* 0.613 0.069 SHDI F 2.630 1.874 0.765 2.011 P 0.083 0.165 0.471 0.145 SHEI F 2.630 1.874 0.765 2.01 P 0.083 0.165 0.471 0.145 DIV F 1.839 2.454 0.714 2.22 P 0.170 0.097 0.495 0.12 SPL F 3.022 2.707 0.655 3.542 P 0.058 0.077 0.524 0.037* CPB F 0.200 2.503 3.812 3.345 P 0.820 0.093 0.029* 0.044* CPC F 1.200 2.596 3.758 4.217 P 0.310 0.085 0.031 0.021* 注:*表示在0.05水平上差异显著。Note:* indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.05. -
[1] 赵匡记, 汪加魏, 施侃侃, 等.北京市西山林场游憩林抚育的森林健康评价[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(10):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2014.10.012 Zhao K J, Wang J W, Shi K K, et al. Forest health evaluation for tending of recreational forest in Xishan Forest Farm in Beijing City[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2014, 34(10):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2014.10.012
[2] 毛斌.北京中幼龄人工油松、侧柏风景林抚育技术研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1015319433.htm Mao B. Studies on tending technique of scenic forest of bong and Half-Mature planted Pinus tabuliformis and Platycladus orientals in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1015319433.htm
[3] 章志都.侧柏刺槐林群落生态学特征及林内景观影响研究[D].福州: 福建农林大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10389-2007135798.htm Zhang Z D. Study on community ecology of Platycladus orientalis-Robinia pseudoacacia and the impacts on iniforest landscape in Beijing scenic-recreational forest[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10389-2007135798.htm
[4] 章志都, 徐程扬, 董建文, 等.郁闭度对风景游憩林林下植被及林内景观的影响[J].中国城市林业, 2008(2):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4925.2008.02.003 Zhang Z D, Xu C Y, Dong J W, et al.Impacts of canopy closure on undergrowth and landscape in scenic recreational forest: a case study of Platycladus orientalis-Robinia pseudoacacia forest in Beijing[J]. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2008(2): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4925.2008.02.003
[5] 章志都.京郊低山风景游憩林质量评价及调控关键技术研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10022-2010129086.htm Zhang Z D.Quality assessing and key adjusting technologies for scenic-recreational forests in the lower mountains of suburbans in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10022-2010129086.htm
[6] 毛斌, 徐程扬, 李翠翠, 等.不同修枝强度对侧柏、油松人工林林内景观美景度的影响[J].西北林学院学报, 2013, 28(3):123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2013.03.23 Mao B, Xu C Y, Li C C, et al. Effects of pruning intensity on in-forest landscape of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus tabulaeformis plantations[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2013, 28(3):123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2013.03.23
[7] 龚岚.北京城区典型城市森林结构特点分析[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1015319511.htm Gong L.Analysis of characteristics of typical urban forest structure in urbanized district of Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1015319511.htm
[8] Mohler C L, Marks P L, Sprugel D G. Stand structure and allometry of trees during self-thinning of pure stands[J]. Journal of Ecology, 1978, 66(2):599-614. doi: 10.2307/2259153
[9] 毛斌, 彭立群, 李乐, 等.侧柏风景林美景度的林内色彩斑块非线性模型研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(7):68-75. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20140481 Mao B, Peng L Q, Li L, et al. Non-linear scenic beauty model of scenic Platycladus orientalis plantations based on in-forest color patches[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(7):68-75. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20140481
[10] 刘畅, 刘亚, 刘海轩, 等.游憩型城镇景观林林内景观斑块类型特征研究[J].西北林学院学报, 2016, 31(4):305-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2016.04.51 Liu C, Liu Y, Liu H X, et al.Characteristics of in-forest landscape patch types of recreational landscape forest in urban and suburban area[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2016, 31(4):305-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2016.04.51
[11] 孟楚, 王琦, 郑小贤.北京八达岭林场水源涵养林结构与功能耦合机理研究[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(3):69-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201703011 Meng C, Wang Q, Zheng X X.Coupling mechanism between stand structure and function of water conservation forest in Badaling Forest Farm, Beijing[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2017, 37(3):69-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201703011
[12] 王威, 郑小贤, 杜丽侠.北京山区水源林林分结构与功能耦合关系[J].东北林业大学学报, 2011, 39(7):22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2011.07.007 Wang W, Zheng X X, Du L X. Coupling relationship between stand structure and function of water conservation forest in Beijing mountainous areas[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2011, 39(7):22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2011.07.007
[13] 蒋桂娟, 郑小贤, 宁杨翠.林分结构与水源涵养功能耦合关系研究——以北京八达岭林场为例[J].西北林学院学报, 2012, 27(2):175-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2012.02.35 Jiang G J, Zheng X X, Ning Y C. Relationship between forest stand structure and function of water conservation: a case study of Badaling Forest Farm[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2012, 27(2):175-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2012.02.35
[14] 于明含, 孙保平, 胡生君, 等.退耕还林地结构与生态功能的耦合关系[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(17):4991-4998. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201417022 Yu M H, Sun B P, Hu S J, et al. Modeling the degree of coupling and interaction between forest structure and ecological function in a grain for green project, Shanxi, China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(17):4991-4998. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201417022
[15] 李正明, 施诗, 潘天红, 等.基于灰色关联度和理想解法的电能质量综合评估方法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(6):14-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdq201406003 Li Z M, Shi S, Pan T H, et al.A synthetic power quality assessment based on grey correlation analysis and TOPSIS method[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(6):14-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jdq201406003
[16] 王明全, 王金达, 刘景双.吉林省西部资源环境和人口经济发展的耦合性分析[J].水土保持通报, 2008, 28(2):167-172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stbctb200802035 Wang M Q, Wang J D, Liu J S.Analysis of the coupling between resource-environment and population-economy in west Jilin Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 28(2):167-172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stbctb200802035
[17] 孙爱军, 董增川, 张小艳.中国城市经济与用水技术效率耦合协调度研究[J].资源科学, 2008, 30(3):446-453. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.03.018 Sun A J, Dong Z C, Zhang X Y.Coupling degree between urban economy and technical efficiency of water use in China[J].Resources Science, 2008, 30(3):446-453. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2008.03.018
[18] 王子, 荣媛, 李明阳, 等.森林景观色彩评价研究[J].世界林业研究, 2017, 30(3):41-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjlyyj201703008 Wang Z, Rong Y, Li M Y, et al. A review of forest landscape color evaluation[J]. World Forestry Research, 2017, 30(3):41-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjlyyj201703008
[19] 王子, 李明阳.风景林四季景观色彩规划方法研究—以紫金山为例[J].林业资源管理, 2017(增刊1):70-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lyzygl2017z1012 Wang Z, Li M Y. Methods of color plan of landscape forest at all seasons: a case study of Purple Mountain[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(Suppl.1):70-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lyzygl2017z1012
[20] Glover B J. The diversity of flower colour: how and why?[J]. International Journal of Design and Nature and Ecodynamics, 2009, 4(3):211-218.
[21] 张喆.基于公众响应评价的森林色彩特征及其影响研究[D].北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017. Zhang Z. Public response to characteristics of forest color and its influence: a case study of forest in autumn of Jiuzhai Valley, Sichuan Province[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2017.
[22] Kardan O, Demiralp E, Hout M C, et al. Is the preference of natural versus man-made scenes driven by bottom-up processing of the visual features of nature[J]. Frontier in Psychology, 2015, 6:471. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000004613992
[23] 毛斌, 徐程扬, 彭立群.基于林内色彩斑块的油松人工风景林定量分类的研究[J].西北林学院学报, 2014, 29(4):169-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2014.04.30 Mao B, Xu C Y, Peng L Q.Color patches of in-forest based study on planted Pinus tabulaeformis scenic forest quantitative classification[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2014, 29(4):169-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2014.04.30
[24] 李翠翠.京郊典型风景游憩林林内景观质量评价技术研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. Li C C.Assessment on landscape quality in stands of typical scenic and recreational forests in suburbs in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2010.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 莫崇杏,董明亮,李荣生,余纽,郑显澄,杨锦昌. 米老排杂交子代苗期生长性状遗传变异及选择. 森林与环境学报. 2023(05): 555-560 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Shuchun Li,Jiaqi Li,Yanyan Pan,Xiange Hu,Xuesong Nan,Dan Liu,Yue Li. Variation analyses of controlled pollinated families and parental combining ability of Pinus koraiensis. Journal of Forestry Research. 2021(03): 1005-1011 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 潘艳艳,许贵友,董利虎,王成录,梁德洋,赵曦阳. 日本落叶松全同胞家系苗期生长性状遗传变异. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(02): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 秦光华,宋玉民,乔玉玲,于振旭,彭琳. 旱柳苗高年生长与气象因子的灰色关联度. 东北林业大学学报. 2019(05): 42-45+51 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李峰卿,陈焕伟,周志春,楚秀丽,徐肇友,肖纪军. 红豆树优树种子和幼苗性状的变异分析及优良家系的初选. 植物资源与环境学报. 2018(02): 57-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张素芳,张磊,赵佳丽,张莉,张含国. 长白落叶松小RNA测序和其靶基因预测. 北京林业大学学报. 2016(12): 64-72 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: