Acoustic vibration properties of birch veneer/glass fiber composites
-
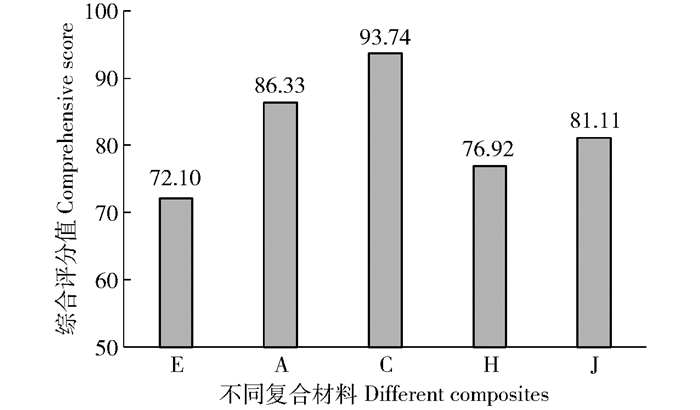
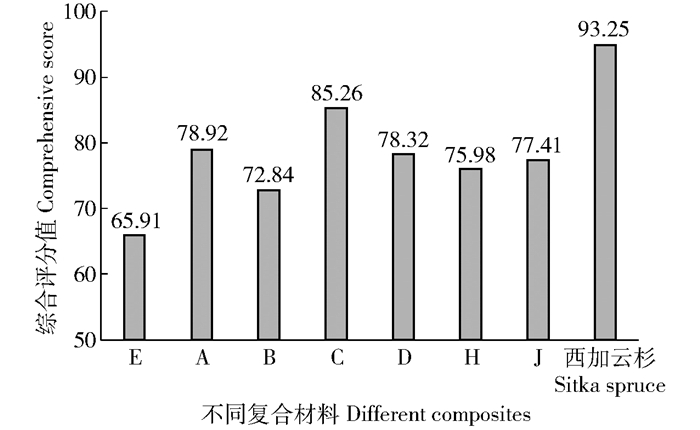
摘要:目的面对我国乐器音板用材资源的严重不足,寻找新材料替代传统乐器木质音板用材是非常有必要的。方法本试验以玻璃纤维为增强材料,桦木单板为基体,按照单板层积材结构设计制备桦木单板/玻璃纤维复合材料。通过对玻璃纤维复合材料声学振动性能检测分析,探究玻璃纤维布的不同铺放位置和铺放层数对复合材料声学振动性能的影响。结果用1层玻璃纤维布铺放在表层单板下的复合材料A的比动弹性模量和E/G值分别为22.20GPa和16.55,比用1层玻璃纤维布铺放在芯层单板单侧的复合材料B分别高了8.7%、17.8%。用2层玻璃纤维布分别铺放在上下表层单板内的复合材料C的比动弹性模量和E/G值分别为25.04GPa和17.04,比用玻璃纤维布铺放在芯层单板两侧的复合材料D高了7.5%和18.0%。纤维铺放位置对声辐射品质常数和声阻抗的影响较小。玻璃纤维布的层数与复合材料的声学振动性能不成线性关系,铺放2层玻璃纤维布的复合材料具有较高的比动弹性模量和E/G值。玻璃纤维布铺放3层和4层的复合材料的比动弹性模量和E/G比铺放2层的都小。随着玻璃纤维布层数的增加,声辐射品质常数呈减小的趋势。通过综合评分法分析发现:玻璃纤维布铺放在表层单板下的复合材料综合评分值都高于铺放在靠近芯层单板的复合材料,铺放2层玻璃纤维布的复合材料的综合评分值达到最大。结论玻璃纤维布铺放在表层单板下的复合材料声学振动性能优于纤维布铺放在靠近芯层单板的复合材料。铺放2层玻璃纤维布的复合材料C的声学振动性能达到最好。尽管复合材料C的E/G值约为西加云杉的80%,但比动弹性模量和西加云杉的相接近,说明桦木单板/玻璃纤维复合材料具有替代传统木质音板用材的可能性。Abstract:ObjectiveIt is very necessary to find new materials to replace the traditional wood materials for sound boards in China because of the serious shortage of wood materials for sound boards in our country.MethodIn this paper, birch veneer/glass fiber composites were prepared using glass fiber as reinforcement and birch veneer as matrix according to the structure design of veneer laminated building blocks. By testing and analyzing the acoustic and vibration properties of the composites, the effects of the placement position and the number of layers of glass fiber cloth on the acoustic and vibration properties of the composites were investigated.ResultThe specific dynamic elastic modulus and E/G value of composite A with one layer of glass fiber cloth under the surface layer were 22.20GPa and 16.55, respectively, which were 8.7% and 17.8% higher than those of composite material B with one layer of glass fiber cloth at the center layer. The specific dynamic elastic modulus and E/G value of composite C with two layers of glass fiber cloth in the upper and lower layers were 25.04GPa and 17.04, respectively, which were 7.5% and 18% higher than those of composite material D with glass fiber cloth in the center layer. The placement of fiber had little effect on acoustic radiation quality constant and acoustic impedance. There were no linear relationships between the layers of glass fiber cloth and the acoustic vibration properties of the composites. The composites with two layers of glass fiber cloth had better specific dynamic elastic modulus and E/G value. The specific dynamic elastic modulus of the composites with three or four layers of glass fiber cloth was lower than that of the composites with two layers of glass fiber cloth. With the increase of the number of layers, the sound radiation quality constant decreased. Through the comprehensive coordinate analysis, it was found that the composite score of glass fiber cloth on the surface was higher than the central layer, and the composite score of two layers of glass fiber cloth reached the maximum.ConclusionThe acoustic vibration properties of the composites with glass fiber cloth on the surface layer were better than those with glass fiber cloth on the center layer. The composite C with 2 layers of glass fiber cloth has the best acoustic vibration performance. Although the E/G value of composite C is about 80% of Picea sitchensis, the specific dynamic modulus of elasticity is similar to Picea sitchensis, indicating that the birch veneer/glass fiber composite has the possibility of being used as a wood substitute for musical instruments.
-
Keywords:
- glass fiber /
- composite material /
- acoustic vibration performance /
- birch veneer
-
小流域是我国水土流失综合治理的基本单元,流域短时间内地形地貌与土壤特征相对稳定,无人为影响下植被覆盖不会发生明显变化,因此短期内降雨是引起小流域土壤侵蚀的主要动力和重要因素[1-2]。降水的时程雨型是指降雨过程中雨量随历时的分配,雨型对入渗、径流和侵蚀过程有重要影响[3]。国内外学者提出了多种雨型用以描述降雨时程分配的不均匀性,Huff[4]将降雨历时等分为4个时段,根据峰值雨强出现时段划分雨型,Huff雨型没有包括均匀型降雨。邵卫云等[5]提出了双矩形雨型,用“平均降雨强度”和“峰值降雨强度”描述降雨时程分配的不均匀性。邬铃莉等[6]利用WEPP模型根据最大30分钟雨强(I30)出现的时间将不同降雨划分为递增型、峰值型、递减型和均值型。殷水清等[3]将中国的降雨过程分为降雨前期集中型(I型)、降雨中期集中型(Ⅱ型)、降雨后期集中型(Ⅲ型)和降雨均匀分布型(Ⅳ型),较好的描述了降雨时程分配的不均匀性。黄土区的雨型研究多采用王万忠等[7]的雨型分类,将降雨划分为短时局地雷暴雨(A型)、锋面性降雨夹有雷暴性质的暴雨(B型)、长历时锋面降雨(C型),但忽略了降雨时程分配的不均匀性。
黄土高原区是我国水土流失最严重的地区之一,研究黄土区的降雨−径流关系对水土流失治理具有重要意义[8-10]。许多研究者对黄土区不同小流域的降雨径流关系进行了研究,郑粉莉等[11]利用黄土区多年观测资料将侵蚀性降雨分为突发型、峰值型和均匀型3种雨型,其中突发型降雨引起的侵蚀量最大,均匀型降雨引起的侵蚀量最小。郑芳等[12]采用王万忠[7]的雨型分类研究了晋西黄土区降雨对小流域产流的影响,结果表明A型降雨条件下洪峰流量最大,C型降雨条件下径流量最大。罗娅等[13]分析了黄土区径流产沙与雨强和植被盖度变化的关系,表明植被盖度变化对产流和产沙的影响较雨强更明显。纳磊等[14]对晋西黄土区不同土地利用小流域径流关系进行了研究,得出不同降雨条件下封禁、人工林小流域场降雨地表径流系数明显小于农地和半农半牧小流域。黄明等[15]研究了晋西黄土区不同植被覆盖小流域的产流特征,结果表明自然封禁小流域对径流的拦蓄作用远大于人工梯田小流域,对于黄土高原典型暴雨的预防效果最佳。
尽管对黄土区小流域降雨−径流关系的研究很多,对降雨过程中雨量随历时的分配(雨型)对径流和侵蚀过程影响的研究相对较少。因此,本研究以晋西黄土区蔡家川流域为研究对象,利用多年实测降雨−径流资料,研究降雨过程(雨型)对小流域产流过程的影响,探明黄土区不同雨型条件径流形成过程的差异,以期为小流域尺度上产汇流分析提供依据。
1. 研究区概况
研究区位于山西省吉县蔡家川流域,为黄河的三级支流。地理坐标为110°39′45″ ~ 110°47′45″E、36°14′24″ ~ 36°18′23″N,海拔高度为900 ~ 1 513 m,呈由西向东走向,全长约12.15 km,流域面积为38 km2(图1)。属于典型的梁状丘陵沟壑区,平均降雨量为575.9 m,主要集中在7—9月,年平均气温为7 ~ 10 ℃。流域内以褐土为主,抗蚀性差,水土流失严重。流域上游主要为由辽东栎(Quercus liaotungensis)、山杨(Populus davidiana)、黑桦(Betula dahurica)、北京丁香(Syringa pekinensis)等组成的天然次生林,中游为由刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis)、侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)组成的人工林,下游为荒草地和农地。
2. 研究方法
2.1 研究流域
为了便于进行长期的水文观测,在蔡家川流域内的各小流域中安装自记雨量计实时监测降雨过程,在各小流域出口处选择控制断面,修建复合型量水堰,安装自记水位计测定径流过程。本研究选择地形地貌特征相近的农地小流域和封禁小流域为研究对象,封禁小流域的主要树种为30年的山杨、辽东栎、油松、虎榛子(Ostryopsis davidiana)等,农地小流域以水平梯田、荒草地为主,水平梯田主要种植玉米(Zea mays)、土豆(Solanum tuberosum),荒草地主要植物为虎榛子、白刺花(Sophora davidii)和蒿类。小流域基本情况见表1。
表 1 研究流域基本情况Table 1. Basic information of studied small watersheds流域类型
Watershed type流域土地利用类型
Land use of watershed森林覆盖率
Forest cover rate/%流域面积
Watershed area/km2流域长度
Watershed length/km形状系数
Shape factor河网密度
River density/
(km·km− 2)沟道比降
Channel gradient/%农地小流域
Agricultural small watershed以水平梯田为主
Based on the terraced fields15.2 0.71 1.38 2.54 1.81 8.70 封禁小流域
Closed small watershed以次生植被为主
Mainly secondary vegetation99 1.93 3.00 4.40 4.10 8.40 2.2 资料选取与数据处理
(1)降雨数据选取。本研究所用降雨数据为蔡家川流域2007—2017年5—9月(雨季)每5 min记录1次的降雨资料。侵蚀性降雨指能够引起土壤侵蚀的降雨[16-18],根据张建军等在蔡家川地区的研究结果,降雨量10 mm以上的降雨为侵蚀性降雨[19]。蔡家川流域5—9月(雨季)降水占全年降水量的78.3% ~ 83.2%,且侵蚀性降雨集中发生在雨季,所以利用5—9月降雨数据能够较好的反应蔡家川流域降雨特征。因此本文选取5—9月份74场降雨量10 mm以上的侵蚀性降雨过程作为研究对象。
(2)雨型划分。本研究采用殷水清等[3]的雨型分类办法,对降雨数据进行量纲−变换,具体步骤为:首先进行数据量纲处理,将累积降雨历时(t,t = 1,2,…,T)除以总历时(T)作为横坐标,累积降雨量(Pt)除以总降雨量(P)作为纵坐标,得到量纲−累积降雨过程曲线。再根据降雨量集中出现在降雨历时0 ~ 40%、40% ~ 60%、60% ~ 100%位置处以及均匀分布于整个降雨过程,将降雨过程分为前期型降雨(Ⅰ型)、中期型降雨(Ⅱ型)、后期型降雨(Ⅲ型)和均匀型降雨(Ⅳ型),并利用LSD多重比较对各雨型的特征值进行差异性检验。
(3)降雨侵蚀力计算。降雨侵蚀力可以反映由降雨引起土壤侵蚀的潜在能力。指标EI30是最广泛使用的降雨侵蚀力指标,但是指标EI30中动能E的整理计算繁琐复杂[20-21]。章文波[22]确定了我国降雨侵蚀力指标为降雨量和最大10 min雨强的乘积PI10,其精度与常用的侵蚀力指标EI30相当,并建立了指标PI10与EI30的转换关系:EI30 = 0.177 3·PI10。本研究以PI10表征不同雨型下降雨侵蚀力的特征。
(4)径流数据处理。选取蔡家川流域2010—2017年农地小流域和封禁小流域场降雨径流数据,其中降雨−产流事件历时指降雨起始时刻至洪水退却时刻所经历的时间。根据已标定的水位流量关系曲线计算流量。研究流域面积小,地下径流少且稳定,因此适用直线平割法分割地表径流量与地下径流量。。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 蔡家川流域的雨型特征
根据降雨量在时间轴上集中出现的位置,蔡家川流域的降雨过程(雨型)可分为前期型降雨(Ⅰ型)、中期型降雨(Ⅱ型)、后期型降雨(Ⅲ型)和均匀型降雨(Ⅳ型)。图3为不同雨型的量纲−累积降雨量历时曲线,Ⅰ型曲线呈上凸状,降雨在前期集中;Ⅱ型曲线先下凹再上凸,降雨在中期集中;Ⅲ型曲线呈下凹状,降雨在后期集中;Ⅳ型曲线平缓上升,雨量均匀分布整个降雨过程。将量纲−累积降雨历时等分为10个时段(0 ~ 1),其中Ⅰ型降雨的雨量集中在前0.4时段内,累积雨量达到次降雨量的68.4%,前0.2时段内的累积雨量占比高达40%左右,随着时间推移降雨量迅速减小并稳定在5%左右;Ⅱ型降雨的雨量主要集中在0.4 ~ 0.6时段内,累积雨量达到次降雨量的41.9%;Ⅲ型降雨的雨量主要集中在0.6至降雨结束时段内,累积雨量达到次降雨量55.9%,时段降雨量较Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型降雨更平缓;Ⅳ型降雨的时段雨量均在5% ~ 15%之间,最均衡稳定(图4)。
表2为各雨型的降雨特征值,其中不同字母表示各雨型间特征值差异性显著(P < 0.05)。4种雨型的平均雨强、I10、I30、I60差异显著(P < 0.05),降雨量和降雨历时的差异不显著(P > 0.05),Ⅰ型降雨与Ⅱ型降雨的特征值差异不显著(P > 0.05),Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型降雨的雨强特征与Ⅲ型、Ⅳ型降雨差异显著性(P < 0.05)。Ⅰ型降雨频次最高,发生33次,占比44.6%,是研究区的主要雨型,Ⅱ型降雨频次最少,仅发生10次,占比13.5%,雨型Ⅲ和雨型Ⅳ降雨频次相近,占比20.3%、21.6%。Ⅰ型降雨的平均雨量最大,为24.6 mm,平均降雨历时短,为440 min,降雨侵蚀力最强(PI10 = 1 038.86),平均雨强(7.23 mm/h)、I10(31.36 mm/h)、I30(20.16 mm/h)、I60(12.93 mm/h)均高于其他雨型;Ⅱ型降雨的平均雨量较小,为19.42 mm,平均降雨历时最短,为428 min,平均雨强较大,为6.72 mm/h,降雨侵蚀力(PI10 = 591.32)远小于Ⅰ型降雨;Ⅲ型降雨的平均雨量为22.23 mm,平均降雨历时为586 min,平均雨强为4.43 mm/h,降雨特征均衡介于Ⅰ型和Ⅳ型降雨之间。Ⅳ型降雨平均降雨历时最长,为715 min,平均降雨量最小,为17.84 mm,降雨侵蚀力最弱(PI10 = 117.83),平均雨强(1.88 mm/h)、I10(5.96 mm/h)、I30(4.59 mm/h)、I60(3.85 mm/h)远低于其他雨型。Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型降雨多为短历时强降雨,其中Ⅱ型降雨为小雨量强降雨,Ⅲ型降雨多为降雨特征均衡的降雨,Ⅳ型降雨多为长历时小雨强降雨。Ⅰ型降雨的平均雨强约为Ⅳ型降雨的3.8倍,I10约为Ⅳ型降雨的5.2倍,PI10约为Ⅳ型降雨的8.8倍。
表 2 不同雨型的降雨特征Table 2. Rainfall characteristics of different rainfall patterns雨型
Rainfall
pattern降雨量
Precipitation/mm降雨历时
Rainfall
duration/min平均雨强
Average rainfall intensity/(mm·h− 1)I10/
(mm·h− 1)I30/
(mm·h− 1)I60/
(mm·h− 1)PI10 频次
Frequency占总频次比例
Proportion in total frequency/%Ⅰ 24.60a 440.00a 7.23a 31.36a 20.16a 12.93a 1 038.86 33 44.6 Ⅱ 19.42a 428.33a 6.72a 26.13a 16.87a 10.73a 591.32 10 13.5 Ⅲ 22.23a 586.25a 4.43b 17.18b 11.54b 7.02b 470.79 15 20.3 Ⅳ 17.84a 715.94b 1.88c 5.96c 4.59c 3.85c 117.83 16 21.6 注:同一列不同字母表示特征值差异性显著(P < 0.05)。I10. 最大10 min雨强;I30. 最大30 min雨强;I60. 最大60 min雨强。下同。Notes: different small letters in the same column mean significant difference(P < 0.05). I10, maximum 10 minutes rainfall intensity; I30, maximum 30 minutes rainfall intensity; I60, maximum 60 minutes rainfall intensity. The same below. 图5为不同月份各雨型累积降雨量和降雨频次比例,由图5可知,流域内各雨型降雨集中发生在7、8月份,占雨季各雨型总降雨量的71.7%,7月份降雨量最大为88.77 mm,5月份降雨量最小仅为7.42 mm。在6—8月中Ⅰ型降雨的降雨量和降雨频次远高于其他雨型,7月份Ⅰ型降雨的降雨量占总降雨量的65%(57.7 mm),而在降水较少的5月和9月Ⅰ型降雨较少出现,表明短历时强降雨集中分布在雨水充足的6—8月;Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型降雨也多分布在6—8月,降雨量和频次分布相对均衡;Ⅳ型降雨在5月和9月出现较多,雨量和降雨频次也高于其他雨型,而在6—8月发生频次较少,表明长历时小雨强的降雨多发生在雨季的前期和后期。
3.2 雨型对小流域径流的影响
不同雨型条件下农地小流域和封禁小流域产流特征值如表3所示。不同雨型条件下农地小流域的径流深、洪峰流量的排序为:Ⅰ型降雨 > Ⅲ型降雨 > Ⅱ型降雨 > Ⅳ型降雨,其中,Ⅰ型降雨的径流深为1.87 mm,洪峰流量为3.28 L/(s.hm2),明显高于其他雨型。Ⅳ型降雨的径流深和洪峰流量最小,分别为0.076 mm、0.035 L/(s.hm2)。Ⅰ型降雨形成的径流深、洪峰流量是Ⅳ型降雨的24.6倍和93.7倍。洪峰滞后时间指洪峰出现时间滞后雨峰的时间,反映流域产流对降雨的响应情况。不同雨型条件下农地小流域的洪峰滞后时间排序为:Ⅳ型降雨(2.21 h) > Ⅱ型降雨(1.12 h) > Ⅲ型降雨(0.96 h) > Ⅰ型降雨(0.68 h)。封禁小流域在不同雨型条件下的产流规律与农地小流域相近。Ⅰ型降雨条件下的径流深、洪峰流量远高于其他雨型,洪峰对雨峰响应灵敏,形成洪峰速度快,雨型Ⅲ次之;Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨条件下的径流深均较小,但Ⅱ型降雨形成的洪峰流量较Ⅳ型降雨大,形成洪峰速度更快。
表 3 不同雨型条件下农地小流域和封禁小流域产流特征Table 3. Runoff characteristics of the agricultural small watershed and the closed small watershed under different rainfall patterns小流域
Small watershed雨型
Rainfall pattern径流量
Runoff/m3基流量
Base flow/m3径流深
Depth of runoff/mm洪峰流量/(L·s− 1·hm− 2)
Peak discharge/(L·s− 1·ha− 1)洪峰滞后时间
Peak lag time/h农地小流域
Agricultural small watershedⅠ 1 384.89 58.15 1.869 4 3.283 2 0.676 Ⅱ 88.37 30.74 0.081 2 0.074 9 1.123 Ⅲ 361.82 138.98 0.314 0 0.323 7 0.958 Ⅳ 108.03 53.76 0.076 5 0.034 8 2.211 封禁小流域
Closed small watershedⅠ 720.17 154.70 0.292 6 0.171 9 1.116 Ⅱ 229.44 42.94 0.096 5 0.033 9 1.748 Ⅲ 787.77 447.87 0.175 9 0.129 9 1.640 Ⅳ 256.02 74.52 0.093 9 0.033 1 3.243 对比农地小流域和封禁小流域的产流特征可知,在Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型降雨条件下农地小流域的径流深和洪峰流量均高于封禁小流域,尤其在Ⅰ型降雨条件下农地小流域的径流深和洪峰流量是封禁小流域的6.4倍和19.1倍;而在Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨条件下封禁小流域的径流深和洪峰流量却略高于农地小流域。各雨型条件下封禁小流域的洪峰出现时间均滞后于农地小流域,与农地小流域相比封禁小流域可推迟洪峰出现时间0.5 ~ 1 h。表明封禁小流域较农地小流域能有效拦蓄径流,削减洪峰流量,延长洪峰出现时间,尤其对大雨量强降雨的调节作用更为明显。因此,在黄土高原营造水土保持植被时应该仿拟自然开展封山育林。
不同雨型的累积降雨量和累积径流量比例如图6所示,Ⅰ型降雨的累积降雨量占总降雨量的48.2%,在Ⅰ型降雨条件下农地和封禁小流域的产流量分别占总产流量的89.7%、61.5%,远高于Ⅰ型降雨的累积降雨量占比及其他雨型的产流量。表明Ⅰ型降雨是引起小流域产流的主要雨型,封禁小流域对主要产流雨型的拦蓄能力更明显。
3.3 小流域降雨−径流相关分析
表4和表5为农地小流域和封禁小流域降雨−径流相关性统计,由表4可知,农地小流域在Ⅰ型降雨条件下的径流深、洪峰流量与降雨量、I10、I30、I60显著正相关(P < 0.01),径流深和洪峰流量与I60相关性最高,相关系数分别为0.813、0.890,洪峰滞后时间与雨强显著负相关(− 0.735),与历时显著正相关(0.681);Ⅱ型降雨条件下,洪峰滞后时间与历时相关性极显著(P < 0.01),相关系数为0.957;Ⅲ型降雨条件下,洪峰滞后时间与降雨量和历时显著负相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为− 0.683、− 0.738;Ⅳ型降雨条件下,径流深与历时和降雨量相关性极显著为0.962和0.959(P < 0.01)。对比表4和由表5可知,封禁小流域与农地小流域产流的影响因素相近,I10、I30、I60对封禁小流域产流的影响程度较农地小流域小,降雨量及历时较农地小流域影响更大。
表 4 农地小流域降雨−径流相关性统计Table 4. Rainfall-runoff correlation statistics for the agricultural small watershed项目 Item 雨型
Rainfall pattern降雨量
Precipitation平均雨强
Average rainfall intensity降雨历时
Rainfall durationI10 I30 I60 径流深
Depth of runoffⅠ 0.793** 0.176 0.090 0.686** 0.805** 0.813** Ⅱ 0.392 − 0.360 0.214 − 0.321 − 0.291 − 0.271 Ⅲ 0.146 − 0.392 0.494 − 0.198 − 0.031 0.017 Ⅳ 0.962** − 0.278 0.959** − 0.022 0.003 0.041 洪峰流量
Peak dischargeⅠ 0.768** 0.236 − 0.021 0.727** 0.863** 0.890** Ⅱ − 0.175 0.121 − 0.583 0.124 0.239 0.252 Ⅲ 0.111 − 0.399 0.451 − 0.156 − 0.034 0.002 Ⅳ 0.427 0.347 0.255 0.363 0.450 0.524 洪峰滞后时间
Peak lag timeⅠ − 0.148 − 0.735** 0.681** 0.326 0.216 0.179 Ⅱ 0.353 − 0.293 0.957** − 0.293 − 0.434 − 0.360 Ⅲ − 0.683* − 0.263 − 0.738* − 0.015 − 0.396 − 0.388 Ⅳ − 0.501 − 0.328 − 0.289 − 0.474 − 0.477 − 0.509 注:*表示在0.05水平上相关性显著;**表示在0.01水平上相关性显著。下同。Notes: * indicates significant correlation at 0.05 level; ** indicates significant correlation at 0.01 level. The same below. 表 5 封禁小流域降雨−径流相关性统计Table 5. Rainfall-runoff correlation statistics for the closed small watershed项目
Item雨型
Rainfall pattern降雨量
Precipitation平均雨强
Average rainfall intensity降雨历时
Duration of rainfallI10 I30 I60 径流深
Depth of runoffⅠ 0.734** − 0.081 0.296 0.265 0.368 0.371 Ⅱ 0.002 − 0.399 0.092 − 0.525 − 0.449 − 0.309 Ⅲ 0.571 − 0.476 0.852* − 0.556 − 0.448 − 0.274 Ⅳ 0.885** 0.009 0.842** 0.381 0.339 0.373 洪峰流量
Peak dischargeⅠ 0.673** 0.170 0.036 0.581* 0.714** 0.687** Ⅱ − 0.643 0.760 − 0.687 0.635 0.190 0.320 Ⅲ 0.480 − 0.364 0.607 − 0.184 − 0.060 0.212 Ⅳ 0.763** 0.351 0.574 0.650* 0.604* 0.602* 洪峰滞后时间
Peak lag timeⅠ − 0.251 0.295 − 0.452 − 0.578* − 0.391 − 0.389 Ⅱ − 0.943** − 0.441 0.974** − 0.728 − 0.731 − 0.811 Ⅲ − 0.824* 0.632 − 0.802* − 0.843* − 0.746 − 0.604 Ⅳ − 0.428 − 0.340 − 0.169 − 0.484 − 0.441 − 0.352 综合以上分析,在晋西黄土区降雨量和雨强在降雨过程中的分布是影响小流域产流量的主要因素,降雨历时是影响小流域洪峰出现时间的主要因素。降雨量、I30、I60是影响Ⅰ型降雨产流过程主要因素,Ⅰ型降雨条件下的产特过程与降雨要素的相关性最为显著;Ⅱ型降雨的洪峰滞后时间受降雨历时影响显著;Ⅲ型降雨的洪峰滞后时间与降雨量和降雨历时显著负相关;Ⅳ型降雨的产流量受降雨量和降雨历时影响较大。
4. 讨论与结论
4.1 讨 论
研究黄土区降雨过程(雨型)与水土流失的关系是水土保持工作中的重要内容[23]。蔡家川流域的场降雨可划分为前期型降雨(Ⅰ型)、中期型降雨(Ⅱ型)、后期型降雨(Ⅲ型)和均匀型降雨(Ⅳ型),Ⅰ型降雨在雨季出现的频次占绝对优势,为短历时强降雨。Ⅳ型降雨多为长历时低雨强的降雨,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型降雨的特征值居中,这与殷水清等[3]的雨型分类结果一致。与殷水清等的雨型分类结果相比,本研究中各雨型的降雨历时明显较小,而雨强明显较高,是因为本研究区位于晋西黄土区且主要研究雨季的侵蚀性降雨,多历时短雨强较高的降雨,导致雨型分类的特征值存在差异。
降雨过程(雨型)与小流域水土流失的程度和规律存在密切联系。雨强变化的降雨过程与雨强均匀的降雨过程相比,径流系数和洪峰流量均变化显著[24-25]。Ⅰ型降雨条件下小流域的产流量远高于其他雨型;Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨的产流量均较小。Ⅲ型降雨较Ⅱ型降雨产流量更多,洪峰出现更早,可能是因为Ⅱ型降雨属于小雨量短历时的降雨,而Ⅲ型降雨的雨量大且集中在降雨后期,前期降雨导致林冠截留达到饱和,表层土壤含水量显著提高,后期的降雨易形成地表径流,表明大雨量强降雨易造成流域的水土流失。
流域土地利用类型影响流域降雨的再分配过程以及流域下垫面性质,从而对径流过程产生影响[26]。研究不同雨型条件下各地类的产流特征,对改善晋西黄土区水土流失具有参考意义[27]。结果表明,封禁小流域较农地小流域有明显拦蓄径流、延长洪峰时间的作用,通过封禁恢复植被能有效控制水土流失,与纳磊等[14]、贺维等[27]研究结果一致。在径流深和洪峰流量方面,Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型降雨条件下农地小流域高于封禁小流域,Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨条件下封禁小流域略高于农地小流域。封禁小流域森林覆盖率高,枯枝落叶层厚,能够截持降雨、增加入渗,起到延阻、拦蓄径流泥沙的作用,所以在降雨量大的Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型降雨条件下农地小流域产流高于封禁小流域,表明封禁小流域对大雨量降雨过程的削减径流洪峰作用明显。封禁小流域基流量远高于农地小流域,其前期土壤含水量高,即使降雨量小的雨型也容易形成径流,表明封禁小流域对小雨量降雨过程的削减径流和洪峰作用不明显。农地小流域虽没有森林覆盖,但农业生产活动能够增加地表糙率,梯田等水土保持措施能够起到减缓坡度、改变地形、延阻径流的作用[28],导致雨量小的雨型不易形成径流,所以在Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨条件下封禁小流域产流略高于农地小流域,表明农业措施对小雨量的降雨过程的削减径流和洪峰作用更为显著。
研究表明,降雨量、雨强及降雨历时等降雨特征对降雨径流的形成有重要影响[29-30]。在晋西黄土区,降雨量、降雨历时和雨强在降雨过程中的分布是影响小流域产流过程的重要因素。Ⅲ型降雨的洪峰滞后时间与降雨历时呈负相关(Ⅰ、Ⅱ型呈正相关),可能是因为Ⅲ型降雨洪峰出现在降雨后期,前期降雨使表层土壤含水量饱和,导致后期的降雨易形成地表径流,降雨历时越长,洪峰滞后雨峰的时间越短。与农地小流域对比,降雨过程中的雨强分布对封禁小流域产流过程影响小,降雨量和历时对封禁小流域产流过程影响大,可能是由于封禁小流域植被覆盖率高,林冠截留使降雨无法在短时间内到达地表形成径流,导致雨强对封禁小流域的产流量影响较小;随着降雨量和降雨历时增加,林冠截留达到动态平衡,表层土壤含水量接近饱和,易形成坡面产流,所以降雨量和历时对封禁小流域产流影响较大。
4.2 结 论
(1)蔡家川流域的场降雨可分为前期型降雨(Ⅰ型)、中期型降雨(Ⅱ型)、后期型降雨(Ⅲ型)和均匀型降雨(Ⅳ型)。Ⅰ型降雨多为短历时强降雨,是主要降雨雨型,发生频次最高,降雨量最大最集中,降雨侵蚀力最强,集中分布在6—8月;Ⅳ型降雨多为长历时小雨强降雨,降雨历时最长,降雨侵蚀力最小,多发生在雨季的前期和后期;Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型降雨的特征介于Ⅰ型和Ⅳ型降雨之间。
(2)Ⅰ型降雨是引起小流域产流的主要雨型。Ⅰ型降雨条件下小流域场降雨径流深、洪峰流量远高于其他雨型,形成洪峰速度最快,Ⅲ型降雨次之,Ⅱ型和Ⅳ型降雨的径流深和洪峰流量均较小。在晋西黄土区,大雨量强降雨易造成流域的水土流失,应当作为水土流失预防的重点。
(3)封禁小流域较农地小流域有明显拦蓄径流、延长洪峰出现时间的作用,对大雨量强降雨的调节作用更明显。在水土流失严重的黄土高原地区通过封山育林恢复植被,能有效控制水土流失。
(4)在晋西黄土区,降雨量、降雨历时和雨强在降雨过程中的分布是影响小流域产流过程的重要因素。雨强在降雨过程中的分布对农地小流域产流过程影响更大,降雨量和历时对封禁小流域产流过程影响更大。
-
表 1 玻璃纤维布不同铺放位置制备的复合材料和西加云杉各项声学指标平均值
Table 1 Average values of acoustic parameters of spruce and composites prepared by different placements of glass fiber cloth
编号
No.样本数
Sample number密度
Density/(g·cm-3)比动弹性模量
Specific dynamic elastic modulus/GPaE/G值
E/G value声辐射品质常数
Acoustic radiation damping/(m·Pa-1·s-3)声阻抗
Acoustic impedance/(Pa·s·m-1)A 20 0.78 22.20 16.55 6.03 3.68 (0.01) (0.31) (0.32) (0.02) (0.02) B 20 0.79 20.42 14.05 5.75 3.55 (0.01) (0.35) (0.32) (0.02) (0.02) C 20 0.85 25.04 17.40 5.87 4.27 (0.01) (0.39) (0.19) (0.05) (0.01) D 20 0.85 23.29 14.75 5.70 4.08 (0.01) (0.35) (0.21) (0.03) (0.01) 西加云杉 20 0.43 25.32 21.14 11.37 2.39 Sitka spruce (0.01) (0.21) (0.15) (0.01) (0.01) 注:括号内为标准偏差值。Note: data in bracket is standard deviation. 表 2 不同层数玻璃纤维布复合材料的声学指标平均值
Table 2 Average acoustic index of glass fiber cloth composites with different layers
编号
No.样本数
Sample number密度
Density/(g·cm-3)比动弹性模量
Specific dynamic elastic modulus/GPaE/G值
E/G value声辐射品质常数
Acoustic radiation damping/(m·Pa-1·s-3)声阻抗
Acoustic impedance/(Pa·s·m-1)E 20 0.74 17.05 14.49 5.62 3.03 (0.01) (0.28) (0.29) (0.06) (0.01) A 20 0.78 22.20 16.55 6.03 3.68 (0.01) (0.31) (0.32) (0.02) (0.02) C 20 0.85 25.04 17.40 5.87 4.27 (0.01) (0.39) (0.19) (0.05) (0.01) H 20 0.93 22.24 15.87 5.09 4.37 (0.01) (0.36) (0.43) (0.03) (0.01) J 20 1.00 21.96 16.40 4.71 4.66 (0.01) (0.41) (0.21) (0.01) (0.05) 注:括号内为标准偏差值。Note: data in bracket is the standard deviation. 表 3 5项性能参数指标的权重
Table 3 Weight factors of five performance indicators
参数
Indicator比动弹性模量
Specific dynamic modulus of elasticity声辐射阻尼常数
Acoustic radiation damping constantE/G值
E/G value声阻抗
Acoustic impedance密度
Density权重因子Weight factor 0.40 0.20 0.20 0.07 0.13 -
[1] 刘镇波, 刘一星.乐器共鸣板用木材声学振动性能改良研究现状及趋势[J].世界林业研究, 2012, 25(1): 44-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjlyyj201201009 Liu Z B, Liu Y X. Research status and prospect of acoustic vibration properties modification of wood used for soundboard[J]. World Forestry Research, 2012, 25(1): 44-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjlyyj201201009
[2] 刁钢, 麻坤, 赵荣, 等.基于中国林业产业预警模型的木材供需仿真研究[J].林业经济, 2018, 40(4): 33-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=NSSD201808080000018241 Diao G, Ma K, Zhao R, et al. Simulation study on timber supply and demand based on forewarning model of forestry industry in China[J]. Forestry Economics, 2018, 40(4): 33-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=NSSD201808080000018241
[3] Hossen M F, Hamdan S, Rahman M R. Investigation of the acoustic properties of chemically impregnated Kayu Malam wood used for musical instrument[J/OL]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2018: 7829613[2018-10-28]. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7829613.
[4] 沙汀鸥.高温/超声波预处理对水杉振动性能影响的研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2850990 Sha T O. Effects of thermal and ultrasound pre-treatments on vibrated properties of metasequoia[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2850990
[5] Essien C, Via B K, Cheng Q Z, et al. Determining the predictive accuracy of whole tree modulus of elasticity (MOE) of 14-year-old loblolly pine using density and dynamic MOEs estimated by three different acoustic tools[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2018, 76(5): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s00107-018-1317-9
[6] 秦丽丽, 苗媛媛, 刘镇波.泡桐木材主要物理特征及化学组分对其声学振动性能的影响[J].森林工程, 2017, 33(4): 34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2017.04.007 Qin L L, Miao Y Y, Liu Z B. Influence of the main pysical characteristics and components content of P. elongata on acoustic vibration performance[J]. Forest Engineering, 2017, 33(4): 34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2017.04.007
[7] Damodaran A, Mansour H, Lessard L, et al. Application of composite materials to the chenda, an Indian percussion instrument[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 88: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.07.013
[8] Bucur V. Composite materials for musical instruments[M]//Bucur V. Handbook of materials for string musical instruments. Switzerland: Springer, 2016: 845-875.
[9] 雷福娟, 黄腾华, 陈桂丹.音板声学品质的主要影响因子及其评测方法[J].陕西林业科技, 2017(5): 85-89, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2117.2017.05.021 Lei F J, Huang T H, Chen G D. The main factors affecting acoustic quality of soundboard and the methods to evaluate the acoustic quality of soundboard[J]. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, 2017(5): 85-89, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2117.2017.05.021
[10] Newton P F. Acoustic-based non-destructive estimation of wood quality attributes within standing red pine trees[J]. Forests, 2017, 8(10): 380. doi: 10.3390/f8100380
[11] 黄英来.几种典型民族乐器木质共鸣体的声学振动性能检测与分析[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10225-1013359257.htm Huang Y L. Acoustic vibration performance detection and analysis of several typical folk instruments wooden resonators[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10225-1013359257.htm
[12] 李哲锋, 多化琼, 青龙.电声乐器中木材声学振动性能对音响特性的影响[J].林业工程学报, 2018, 3(3): 18-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201803003 Li Z F, Duo H Q, Qing L. Effects of acoustic vibration properties of wood on acoustic characteristic in electronic musical instrument[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2018, 3(3): 18-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201803003
[13] 许震宇, 于洋.复合材料古琴的动态弹性性能研究[J].玻璃钢/复合材料, 2015(8): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2015.08.002 Xu Z Y, Yu Y. The study of the specific dynamic elastic property of composite Guqin[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites, 2015(8): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2015.08.002
[14] Ono T, Miyakoshi S, Watanabe U. Acoustic characteristics of unidirectionally fiber-reinforced polyurethane foam composites for musical instrument soundboards[J]. Acoustical Science and Technology, 2002, 23(3): 135-142. doi: 10.1250/ast.23.135
[15] 李焕强.一种碳纤维吉他及碳纤维吉他的制作方法: 106328102A[P]. 2017-01-11. Li H Q. Carbon fiber guitar and making method thereof: 106328102A[P]. 2017-01-11.
[16] Phillips S, Lessard L. Application of natural fiber composites to musical instrument top plates[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2012, 46(2): 145-154. doi: 10.1177/0021998311410497
[17] Jalili M M, Mousavi S Y, Pirayeshfar A S. Investigating the acoustical properties of carbon fiber-, glass fiber-, and hemp fiber-reinforced polyester composites[J]. Polymer Composites, 2014, 35(11): 2103-2111. doi: 10.1002/pc.v35.11
[18] 吕晓东, 苗媛媛, 林斌, 等.层数与碳纤维方向对木质-碳纤维复合材料声学振动性能的影响[J].林业工程学报, 2018, 3(4): 96-101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201804016 LÜ X D, Miao Y Y, Lin B, et al. Study on acoustic vibration performance of wood-carbon fiber composite materials with different laying patterns[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2018, 3(4): 96-101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201804016
[19] Damodaran A, Lessard L, Babu A S. An overview of fibre-reinforced composites for musical instrument soundboards[J]. Acoustics Australia, 2015, 43(1): 117-122. doi: 10.1007/s40857-015-0008-5
[20] 刘镇波, 沈隽.共鸣板用材的振动特性与钢琴的声学品质[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009. Liu Z B, Shen J. Vibration characteristics of acoustics board and acoustic quality of piano[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[21] 王晓男.综合评价中若干理论方法的适用性研究[D].长沙: 湖南大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10532-1014316038.htm Wang X N. The applicability research of several theoretical methods in comprehensive evaluation[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10532-1014316038.htm
[22] 刘镇波, 沈隽, 刘一星, 等.实际尺寸乐器音板用云杉属木材的声学振动特性[J].林业科学, 2007, 43(8): 100-105. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200708017 Liu Z B, Shen J, Liu Y L, et al. Acoustic vibration property of full-size spruce wood soundboard of musical instruments[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2007, 43(8): 100-105. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx200708017
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 于宏影,闫晓娜,王晓红,王思瑶,韦睿,黄艳. 东北茶藨子果实氨基酸组成分析. 林业科技通讯. 2024(09): 72-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘哲,叶英,罗黎霞,王虹,张祎睿. 狭果茶藨子营养成分分析与氨基酸提取工艺优化及评价. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(13): 188-195 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘九庆,谢力. 植物导管中穿孔板的流体力学建模与流阻分析. 森林工程. 2022(05): 93-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 罗敏蓉. 基于不同方法的毛茛族(毛茛科)导管穿孔板比较研究. 广西植物. 2021(01): 123-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邓睿,张梅丽,周明,郑宝江. 中国茶藨子属1新记录种. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(02): 231-233 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杜习武,叶康,胡永红,邵文,陈奕飞,廖梓洋,曾丽,秦俊. 淹水胁迫对星花玉兰木质部水分运输的影响. 植物生理学报. 2021(10): 1963-1973 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张丽,乔枫. 茶藨子属植物逆境生理研究进展. 世界林业研究. 2018(01): 18-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王美娟,赵千里,李芯妍,郑宝江. 12种茶藨子属植物叶表皮微形态特征及其分类学意义. 植物研究. 2018(04): 490-496 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘虹,薛青,黄文,覃瑞. 茶藨子属ITS2序列二级结构的预测和比较分析. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版). 2018(03): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 杜婉,王丰,潘彪,陈昕. 花楸属3种1变种植物茎次生构造的比较. 安徽农业大学学报. 2017(05): 857-861 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘灵,韦睿,于宏影,王千雪,申方圆. 东北茶藨子果实性状变异研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2017(06): 23-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 韦睿,黄艳,王晓红,刘灵. 东北茶藨子研究现状及开发前景展望. 北方园艺. 2016(14): 202-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)




 下载:
下载: