QTL epistasis effect analysis of seedling growth-related traits in Populus euphratica
-
摘要:目的幼苗期是植物生长发育的重要阶段,幼苗生长相关性状的研究对改善农作物以及林木的生产以及提高抗逆性具有重要意义。目前尚无研究对胡杨幼苗生长阶段相关表型的上位互作机制进行解析。方法本研究以包含408个单株的胡杨×胡杨杂交的F1代群体为实验材料,获取茎高、主根长、总侧根长和侧根数量4种表型动态生长数据;基于该群体所构建的高密度连锁图谱,通过功能作图和2HIGWAS对基因之间的上位互作进行定位。结果共侦测出QTL-QTL互作83对,包含83个SNPs。其中主根长、茎高、侧根总长、侧根数量分别检验出24对、20对、24对、15对显著QTL互作;主根长、茎高以及侧根总长较大比例的上位互作分别集中分布于连锁群1、19和17。另外对4个表型显著上位互作的QTLs进行功能注释,19个QTLs注释到候选基因。结论影响侧根总长的显著互作具有较高的遗传力,在连锁群17集中分布,可能是重要的候选基因区域,能够为胡杨以及林木分子标记辅助育种提供重要的借鉴。Abstract:ObjectiveSeedling stage plays a vital role in plant growth and development. Up to date there are no reports about genetic mechanism of epistasis interaction during seedling growth in Populus euphratica.MethodIn this study, a full-sib F1 population including 408 individuals was derived from Populus euphratica × Populus euphratica. Dynamic growth data of four phenotypes were measured, including the taproot length, shoot length, total lateral root length, and number of lateral roots. Based on a high-density genetic linkage map, 2HIGWAS was employed to identify QTL-QTL interactions associated with four phenotypes.ResultFinally, a total of 83 pairs of QTL-QTL interactions were detected, including 83 SNPs. The taproot length, shoot length, total lateral root length and number of lateral roots found 24 pairs, 20 pairs, 24 pairs and 15 pairs epistatic interactions, respectively, and the epistatic interactions of main root length, stem height and lateral root length were distributed in linkage groups 1, 19, and 17, respectively. In addition, we conducted functional annotations for the SNPs with significant QTL-QTL epistatic interactions, and 19 QTLs were annotated with candidate genes.ConclusionInteractions associated with total lateral root length had higher heritability, and most of the SNPs were located in linkage group 17, which might be important candidate gene regions. This work may provide guidance for molecular marker-assisted breeding of Populus euphratica and other forest trees.
-
Keywords:
- QTL /
- epistasis effect /
- 2HIGWAS /
- seedling growth /
- Populus euphratica
-
植物在其生命周期中会历经多个阶段,在种子萌发后,植株进入幼苗的生长发育阶段。在幼苗生长发育期,一系列的代谢活动和形态形成的机制逐渐建立[1]。作为影响植物存活的关键性阶段,幼苗阶段通常对植物的生长发育具有决定性作用,同时也是植物适应环境的重要基础[2]。对于许多农作物来说,如果幼苗期发育良好,即便生长条件不太理想,作物仍可以达到较高的产量。植物幼苗阶段开始后,不同表型的动态变化能够反映幼苗活性和生物量的积累[3]。因此,研究幼苗生长过程中的遗传机制十分必要,对农作物以及林木分子标记育种具有重要的意义。
研究人员对影响幼苗生长的因素进行了大量的探究,并得出了若干重要理论[4-5]。Liebig[6]提出了最小因子法则,认为植物的生长是由供给量最小的资源控制的,只有增加该资源才能促进植物的生长。而多重资源限制假说则认为资源限制是一个十分复杂的过程,是多种资源互作导致的,并以此来解释资源限制对于幼苗生长的影响[7]。另外,大量研究发现激素途径在植物幼苗的生长发育中也扮演着重要角色[8-11]。随着分子生物学的发展,关于幼苗生长的分子调控机制开始被人们关注,例如,玉米的U6 biogenesis-like 1(UBL1)基因通过影响U6小核RNA的前体mRNA拼接来影响幼苗的生长发育[12]。此外,Stewart等[13]证明PIF基因家族的成员可以显著改变下胚轴每日伸长的速率,从而改变许多幼苗生长状况。Hwang等[14]研究表明,AtCYS6基因可以通过抑制储存的半胱胺酸蛋白酶活性来调控种子萌发以及幼苗的发育过程。
一般来说,反映幼苗生长的表型指标大多是数量性状,比如幼苗的茎高,主根长,侧根长以及侧根数量等。上述性状可能都是由多个基因控制的,而每个基因的效应比较微弱,因此,利用数量性状位点(Quantitative trait loci, QTL)定位的方法来解析复杂性状是一种十分有效的手段[15-17]。基于QTL定位,大量的研究对植物幼苗生长的相关复杂性状进行了解析,例如,探究了影响小麦(Triticum aestivum)、水稻(Oryza sativa)以及玉米(Zea mays)等农作物幼苗根系相关表型以及抗逆性等复杂性状的遗传机制[18-20]。然而这些研究虽然定位出大量QTLs,但大多没有获得较好的功能验证,一个重要原因是忽略了基因之间的上位互作。如果QTL定位模型中没有考虑标记之间的上位性效应很可能会导致所谓的丢失遗传力[21-22]。因此研究幼苗生长过程中基因上位互作机制是十分必要的,有助于进一步解析其内在的遗传机制。
胡杨(Populus euphratica)作为我国西北沙漠地区的重要生态树种,能够适应盐胁迫、干旱、大风以及低温等恶劣环境[23]。目前,已有大量的研究从生理生化、细胞生物学、分子生物学等角度对其抗逆机制进行了深入探索[23-24]。胡杨的繁育主要是利用种子完成,种子发育成幼苗,幼苗的生长状态对其后续发育至关重要,当前对胡杨幼苗的生长遗传机制,特别是上位性遗传机制的解析是欠缺的。为此,本研究基于胡杨F1代群体和其所构建的高密度遗传图谱,测量其幼苗生长过程中主根长、茎高、侧根长以及侧根数量的动态表型数据。利用功能作图和2HIGWAS技术进行上位效应解析,定位控制胡杨幼苗生长的关键基因互作。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
材料取自新疆库尔勒地区塔里木河沿岸,选取胡杨雌雄个体各一株,雄株的显著特征是树木较高和长势较好,雌株的显著特征是早开花,雄性亲本与雌性亲本相距31 km,在地理和生态上存在一定差异。选取生长状态良好的雄性花枝,于2014年1月置于北京林业大学人工气候室中水培,为避免花粉发育过快造成育性降低,培养温度设为20 ℃;待花粉发育完全后剪下花序,于干燥环境中低温迅速脱水,将花粉收集后密封保存于EP管中,放于4 ℃冰箱保存待用。2014年2月底将雌性单株全部移栽至北京林业大学温室中种植,待雌花发育之后,对雌花序进行人工授粉,在果实发育过程中进行疏果,避免营养竞争,保证种子发育过程中的营养供给;在培养过程中选取亲本的健康叶片放于4 ℃冰箱保存待用。
2014年6月中旬,种子发育成熟,将所有种子在无菌条件下种植于1/2MS固体培养基中,在16 h光/8 h暗条件下培养,培养温度为26 ℃。培养4个月后将所有幼苗移栽到基质中培养,温度和光照条件不变,保证水肥供给。2014年12月,待所有单株平均高度达到20 cm以上,平均叶片数达到12片以上时,采集叶片、液氮速冻后置于-80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存。最后获得F1代个体共408个。
1.2 SNP标记开发
对测序获得的原始数据进行质量检测,去除低质量序列和接头后,利用ustacks软件进行SNP标记开发,SNP分型过程中允许每个位点中存在5个碱基的错配,聚类后将重复数过多(>200)和过少(<5)的序列去除,保证后续分型的准确性,避免因拷贝数变异造成的误差[25]。次多等位基因数超过25%并小于50%时可以认为该位点为杂合,小于10%时认为该位点为纯合。完成SNP分型后,基于孟德尔遗传规律,参考双亲的基因型,去除子代之间没有变异的位点;选择杂交后出现分离的位点,最终获得的SNP标记数量为8 305个,类型分别为lm×ll,nn×np和hk×hk。基于获得的SNP构建的胡杨连锁图谱共包含19个连锁群,连锁群的总长度为4 574.89 cM,标记间的平均距离为0.55 cM[3]。
1.3 表型测定
在组培条件下,使用拍照和手眼测量获得主根长,侧根长,侧根数量以及茎高的动态变化数据。由于前期试验发现基于两种测量方式获得的表型数据进行分析之后所获得的结果差异较小[26],因此采用手眼观测的方式进行表型测量。从培养第5天开始进行数据测量,每间隔5 d测量一次,共进行15次测量。
1.4 生长曲线
目前有多种数学模型可以用来描述数量性状动态变化,包括指数型、饱和型以及S型模型[27],上述模型均通过参数变化来描述不同个体数量性状的生长模式。其中Logistic曲线是用来描述生物生长发育最常用的曲线,其数学通式如下:
g(t)=a1+be−rt (1) 式中:g(t)为时间t的表型值;t为时间点;a为t→∞时函数的极限值;b为初始生长值;r为相对生长速率。
该曲线包含指数相和渐进相两个阶段:在指数相阶段,生长曲线呈指数增长;渐进相阶段曲线增长变缓逐渐趋于极值。在某些研究中,所测量的数量性状还处于指数增长期,为此可用以下公式(2)来描述生长曲线的变化:
g(t)=a1+be−rt−ce−dt (2) 式中:a、b、r、c、d 5个参数用来描述处于指数期的个体数量性状生长发育曲线,c和d参数用于抵消logistic方程的渐进生长。
上述两个模型虽然可以用来描述胡杨幼苗的生长曲线,但是如何选取最佳模型对于后续QTL定位极为重要。本文采用AIC(Akaike's information criteria)准则来选取最佳模型[28],以提高QTL定位的精度。
1.5 功能作图
Ma等[29]提出了一种通用的理论框架,将描述生物生长的数学方程嵌入到QTL定位的框架中,该理论称之为功能作图(Functional mapping)理论。通过去除QTL条件概率,代以SNP的实际数值,对每个SNP进行假设检验,将功能作图延伸到GWAS框架中,建立了新的模型fGWAS(Functional GWAS)。本研究基于fGWAS软件包进行功能作图的分析[30]。
1.6 2HIGWAS模型
1.6.1 主效应模型构建
虽然当前的测序技术能够获得高维的SNP数据,但基于数量遗传学理论,也许只有很小比例的部分SNP影响动态复杂性状。在时间点t,决定个体i表型值的模型可表示为:
yit=ut+J∑j=1αjiξij+K∑k=1βktζik+εit i=1,2,⋯,n;t=1,2,⋯,M (3) 式中:ut为解释变量,表示平均生长量;i为个体编号;n为样本大小;M为时间点数量;J为加性SNP的数量;K为显性SNP的数量;αjt和βkt分别为在时间点t第j个SNP的加性效应和第k个SNP的显性效应;ξij和ζik为指示变量,分别表示个体i在第j个SNP的加性基因型和第k个SNP的显性基因型;εit为随机误差,其服从均值为0、方差为σt2的正态分布。
1.6.2 上位效应模型构建
基于2HIGWAS主效应模型,我们进一步扩展,以便能够估计不同SNPs之间的上位互作,扩展的模型可表示为:
yit=ut+J∑j=1αjtξij+K∑k=1βktζik+Laa∑l1<l2=1raal1l2tξil1ζil2+Lad∑l1<l2=1radl1l2tξil1ζil2+Lda∑l1<l2=1rdal1l2tξil1ζil2+Ldd∑l1<l2=1rddl1l2tξil1ζil2+εiti=1,2,⋯,n;t=1,2,⋯,M (4) 式中:Laa、Lad、Lda和Ldd分别为加性-加性、加性-显性、显性-加性和显性-显性互作的数量;rl1l2taa、rl1l2tad、rl1l2tda和rl1l2tdd分别为在时间t,SNP l1与SNP l2的加性-加性、加性-显性、显性-加性和显性-显性互作效应。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 生长曲线的拟合
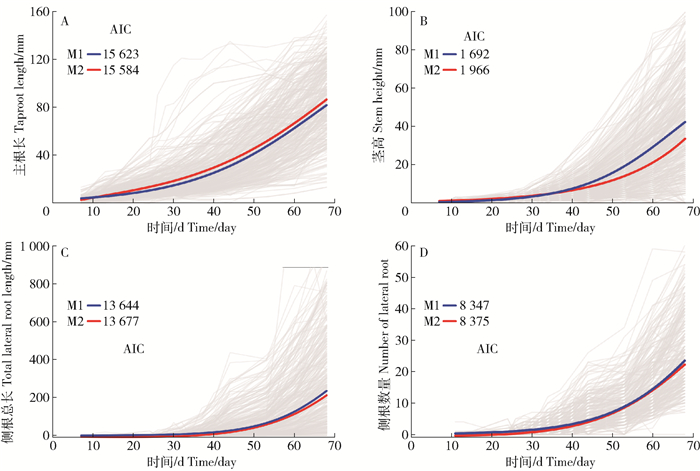
生长曲线的选取对功能作图和2HIGWAS的定位精度有较大影响。基于公式(1)和(2),分别对4种表型性状的生长曲线行进拟合,并计算AIC的值,进而为每个表型选择合适的生长曲线进行拟合。在主根长(Taproot length,TL)的拟合中(图 1A),模型1(M1)及模型2(M2)的AIC值分别为15 623和15 584;此外,由图 1A中曲线可以发现,主根生长一直处于指数期,与所选模型2所描述的曲线特征相符合,因此我们选择模型2作为主根长生长曲线的最佳拟合模型。图 1B为茎高(Shoot length,SL)的拟合情况,模型1以及模型2的AIC值分别为1 692和1 966,模型1的AIC值远小于模型2;因此在描述茎高的生长曲线时,模型1是最佳模型。同样,由茎高的生长曲线可以看出,茎高的生长已经通过拐点进入渐进生长阶段,与模型1所描述的生长曲线特征相符。在侧根总长(Total lateral root length,TLRL)(图 1C)以及侧根数量(Number of lateral roots, NLR)(图 1D)的拟合过程中,两个模型的AIC值均比较接近,因此我们均选取了AIC值较小的模型1作为最佳模型。
为检验每个性状所选取模型的拟合情况,我们对群体中每个子代进行了拟合,分别计算了每个子代的拟合优度。从4个表型的拟合来看,主根长、茎高以及总侧根长中大部分个体的拟合优度R2>0.95,侧根数量表型中大部分个体的拟合优度R2>0.90。整体来看,选取的最佳模型拟合较好,但也存在个别个体的R2<0.5,这可能是由于测量过程中误差过大所导致。为了检验模型的合理性并排除其它因素对QTL定位的影响,我们还针对每个性状所选取的最佳模型进行了残差分析。通过对描述主根长(图 2A)、茎高(图 2B)、侧根总长(图 2C)以及侧根数量(图 2D)的模型进行残差分析的结果可见,各性状所对应的残差呈随机分布,这表明对每个性状所选取的描述生长曲线的模型比较合理。
2.2 互作QTLs定位
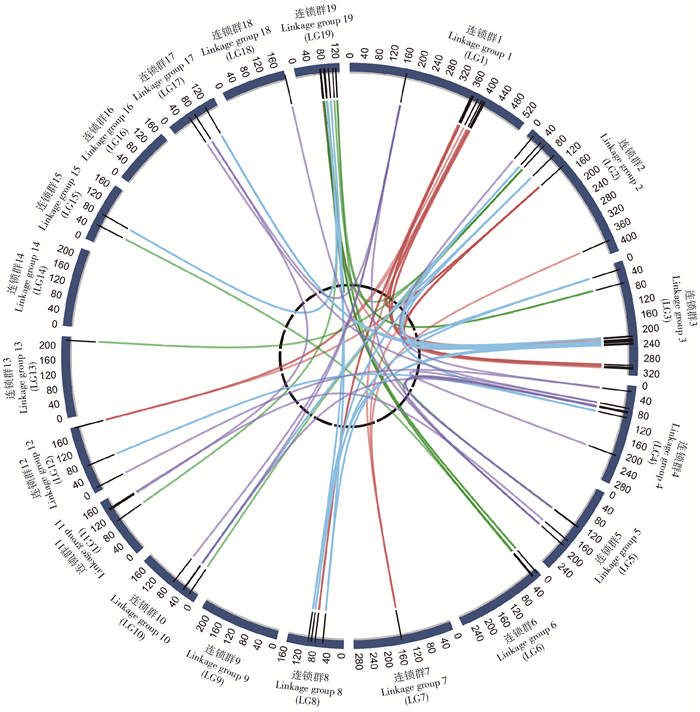
利用2HIGWAS的上位效应模型,将功能作图与2HIGWAS主效应模型筛选的SNPs进行上位互作的定位。4个表型共侦测出QTL-QTL互作83对,包含83个SNPs。QTL上位互作在大部分连锁群都有分布,但主要分布于连锁群1、2、3、4、8和19;3种QTL互作类型中,加性-加性互作、加性-显性互作和显性-显性互作的数量分别是49、22和12。加性-加性互作中,大多为测交类型互作;加性-显性互作中,测交类型互作和测交与杂交类型互作都有分布。图 3为QTL-QTL互作在胡杨19个连锁群上的分布,表 1列出了每一对互作的位置与互作类型等信息。
![]() 图 3 4个性状中显著QTL-QTL互作在胡杨连锁群的分布红色代表主根长;绿色代表茎高;蓝色代表侧根总长;紫色代表侧根数量。Figure 3. Distribution of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits along 19 linkage groups of Populus euphraticaRed represents the taproot length; green represents the stem height; blue represents total lateral root length; purple represents the number of lateral roots.表 1 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作的详细信息Table 1. Detailed information of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits
图 3 4个性状中显著QTL-QTL互作在胡杨连锁群的分布红色代表主根长;绿色代表茎高;蓝色代表侧根总长;紫色代表侧根数量。Figure 3. Distribution of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits along 19 linkage groups of Populus euphraticaRed represents the taproot length; green represents the stem height; blue represents total lateral root length; purple represents the number of lateral roots.表 1 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作的详细信息Table 1. Detailed information of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits表型
Phenotype配对数
Pair标记1 ID
SNP1标记2 ID
SNP2连锁群LG 位置Position 标记类型Marker type 互作类型
Interaction
type标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2主根长Taproot length 0 hk_hk_526 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 393.97 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 1 hk_hk_1541 lm_ll_9903 LG1 LG3 363.76 303.2 Intercross Testcross AA 2 lm_ll_11751 nn_np_10334 LG12 LG1 192.69 399.54 Testcross Testcross AA 3 lm_ll_6889 nn_np_4797 LG3 LG1 297.11 404.42 Testcross Testcross AA 4 lm_ll_9726 nn_np_10334 LG2 LG1 134.6 399.54 Testcross Testcross AA 5 hk_hk_2726 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 400.46 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 6 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_4106 LG1 LG8 366.17 82.77 Testcross Testcross AA 7 lm_ll_11751 nn_np_7270 LG12 LG1 192.69 382.18 Testcross Testcross AA 8 hk_hk_2120 hk_hk_2116 LG2 LG7 383.58 149.35 Intercross Intercross AD 9 hk_hk_526 hk_hk_2116 LG1 LG7 393.97 149.35 Intercross Intercross AD 10 nn_np_11925 lm_ll_3383 LG1 LG3 367.62 215.49 Testcross Testcross AA 11 hk_hk_1541 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 363.76 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 12 lm_ll_5873 lm_ll_9726 LG12 LG2 192.7 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 13 lm_ll_8943 nn_np_4797 LG3 LG1 297.11 404.42 Testcross Testcross AA 14 lm_ll_8943 nn_np_4582 LG3 LG19 297.11 72.68 Testcross Testcross AA 15 lm_ll_4106 nn_np_3087 LG8 LG1 82.77 361.76 Testcross Testcross AA 16 lm_ll_5853 lm_ll_9726 LG3 LG2 307.06 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 17 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_6889 LG1 LG3 366.17 297.11 Testcross Testcross AA 18 lm_ll_9726 hk_hk_2116 LG2 LG7 134.6 149.35 Testcross Intercross AD 19 lm_ll_9903 lm_ll_9726 LG3 LG2 303.2 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 20 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_3383 LG1 LG3 366.17 215.49 Testcross Testcross AA 21 nn_np_11925 lm_ll_4106 LG1 LG8 367.62 82.77 Testcross Testcross AA 22 hk_hk_2726 lm_ll_9903 LG1 LG3 400.46 303.2 Intercross Testcross AA 23 lm_ll_9726 lm_ll_9874 LG2 LG3 134.6 222 Testcross Testcross AA 茎高Stem height 24 lm_ll_3248 hk_hk_1984 LG2 LG19 55.81 75.2 Testcross Intercross AD 25 hk_hk_861 hk_hk_1984 LG19 LG19 84.22 75.2 Intercross Intercross DD 26 nn_np_8378 hk_hk_861 LG5 LG19 122.48 84.22 Testcross Intercross AD 27 hk_hk_2692 hk_hk_2705 LG19 LG3 118.55 61.26 Intercross Intercross AD 29 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 75.2 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 30 hk_hk_2765 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 75.32 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 31 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1556 LG19 LG6 75.2 18.94 Intercross Intercross DD 32 nn_np_4006 hk_hk_861 LG11 LG19 106.5 84.22 Testcross Intercross AD 33 hk_hk_2025 hk_hk_1556 LG15 LG6 49.67 18.94 Intercross Intercross DD 34 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_2234 LG19 LG19 75.2 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 35 hk_hk_1365 hk_hk_2705 LG19 LG3 109.52 61.26 Intercross Intercross AD 36 hk_hk_2155 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 74.66 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 37 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1342 LG19 LG19 75.2 75.32 Intercross Intercross DD 38 hk_hk_861 hk_hk_1342 LG19 LG19 84.22 75.32 Intercross Intercross DD 39 lm_ll_3248 nn_np_11732 LG2 LG10 55.81 23.14 Testcross Testcross AA 40 lm_ll_3248 hk_hk_2779 LG2 LG13 55.81 218.9 Testcross Intercross AD 41 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_3206 LG19 LG19 75.2 86.38 Intercross Intercross DD 42 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1206 LG19 LG6 75.2 5.36 Intercross Intercross DD 43 hk_hk_2765 hk_hk_3138 LG19 LG6 75.32 21.69 Intercross Intercross AA 44 hk_hk_1960 hk_hk_1206 LG19 LG6 118.55 5.36 Intercross Intercross AD 总侧根长Total lateral
root length45 hk_hk_3074 hk_hk_2288 LG8 LG2 102.69 95.12 Intercross Intercross DD 46 lm_ll_3911 hk_hk_3074 LG3 LG8 234.43 102.69 Testcross Intercross AD 47 lm_ll_7977 hk_hk_2288 LG2 LG2 43.08 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 48 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_3153 LG17 LG3 115.47 214.01 Testcross Testcross AA 49 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11743 LG17 LG3 115.47 236.62 Testcross Testcross AA 50 lm_ll_7977 nn_np_11395 LG2 LG10 43.08 44.49 Testcross Testcross AA 51 hk_hk_3038 lm_ll_3153 LG3 LG3 21.18 214.01 Intercross Testcross AA 52 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_8924 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 53 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11684 LG17 LG3 115.47 226.02 Testcross Testcross AA 54 hk_hk_829 hk_hk_861 LG15 LG19 82.8 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 55 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11020 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 56 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11345 LG17 LG3 115.47 236.62 Testcross Testcross AA 57 nn_np_7192 hk_hk_3074 LG19 LG8 97.44 102.69 Testcross Intercross AD 58 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11873 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.82 Testcross Testcross AA 59 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_2229 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 60 hk_hk_3038 lm_ll_11873 LG3 LG3 21.18 224.82 Intercross Testcross AA 61 lm_ll_7977 hk_hk_1848 LG2 LG4 43.08 91.98 Testcross Intercross AD 62 lm_ll_13112 hk_hk_2288 LG3 LG2 235.58 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 63 hk_hk_3038 hk_hk_2485 LG3 LG8 21.18 93.95 Intercross Intercross AD 64 hk_hk_3209 hk_hk_861 LG8 LG19 60.28 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 65 hk_hk_1848 hk_hk_1589 LG4 LG12 91.98 79.45 Intercross Intercross DD 66 lm_ll_13112 lm_ll_7977 LG3 LG2 235.58 43.08 Testcross Testcross AA 67 lm_ll_12414 hk_hk_2288 LG3 LG2 229.56 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 68 lm_ll_11873 hk_hk_3209 LG3 LG8 224.82 60.28 Testcross Intercross AD 侧根数量Number of
lateral roots69 hk_hk_3237 nn_np_6825 LG17 LG11 79.51 144.23 Intercross Testcross AA 70 lm_ll_10262 nn_np_9993 LG10 LG11 43.3 164.17 Testcross Testcross AA 71 lm_ll_10262 lm_ll_6938 LG10 LG4 43.3 78.08 Testcross Testcross AA 72 lm_ll_7471 nn_np_11905 LG4 LG17 64.6 61.54 Testcross Testcross AA 73 lm_ll_4501 nn_np_3662 LG5 LG11 170.17 148.06 Testcross Testcross AA 74 lm_ll_579 hk_hk_1675 LG4 LG12 17 12.47 Testcross Intercross AD 75 lm_ll_6938 lm_ll_10741 LG4 LG5 78.08 121.28 Testcross Testcross AA 76 nn_np_9993 lm_ll_10152 LG1 LG10 164.17 79.6 Testcross Testcross AA 77 nn_np_12080 nn_np_9993 LG5 LG1 188 164.17 Testcross Testcross AA 78 lm_ll_7471 nn_np_8146 LG4 LG4 64.6 203.23 Testcross Testcross AA 79 hk_hk_3237 nn_np_9993 LG17 LG11 79.51 164.17 Intercross Testcross AA 80 lm_ll_4374 lm_ll_10741 LG4 LG5 75.03 121.28 Testcross Testcross AA 81 nn_np_12080 lm_ll_6938 LG5 LG4 188 78.08 Testcross Testcross AA 82 lm_ll_924 lm_ll_579 LG2 LG4 15.01 17 Testcross Testcross AA 83 nn_np_12080 nn_np_2539 LG5 LG18 188 184.27 Testcross Testcross AA 注:A表示加性效应,D表示显性效应。Notes:A represents additive effect, D represents dominant effect. 对于主根长性状,共检验出24对显著QTL-QTL互作(图 3,表 1),分别分布在胡杨第1、2、3、7、8、12和19连锁群。互作类型主要为加性-加性互作,少量为加性-显性互作,没有侦测到显性-显性互作。茎高性状中具有显著互作效应的QTLs有20对,涉及连锁群6和19的分别有5和17对,另外,连锁群19内部存在8对标记互作,占总数的40%(图 3,表 1)。在这20对中,加性-加性互作、加性-显性互作和显性-显性互作的数量分别为2、10和8对。其中,连锁群19内部显性-显性互作的数量为5对,占显性-显性互作总数的60%。侧根总长性状中具有显著互作效应的QTL有24对,与主根长侦测出的QTL互作对数相同,分别分布于第2、3、4、8、10、12、15、17、19连锁群,连锁群3和17上分布较多,分别为16和8对,占总数的67%和33%,但两个性状不存在共有的QTL-QTL互作(图 3,表 1)。与连锁群3相连的主要有连锁群2,8和17,其中连锁群17与其互作数量为8对,且只与该连锁群存在互作。侧根数量所侦测的QTL互作数量为15对,是4个表型中侦测到的显著QTL-QTL互作最少的表型,且这些互作与其它表型侦测的互作没有重叠。与侧根数量变化相关的QTL-QTL互作在第1、2、4、5、10、11、12、17、18连锁群中有分布,仅存在一个加性-显性互作,其余都为加性-加性互作。
2.3 遗传力分析
数量性状受环境和遗传因素的影响很大,为探究表型变异究竟是由遗传因素还是环境因素引起,遗传力的概念被引入,用以表明某一性状受遗传因素控制的程度。为探究遗传因素对胡杨幼苗各性状的影响程度,本研究分析了4个性状中显著上位效应的遗传力,并绘制了其随时间变化的时序图(图 4)。
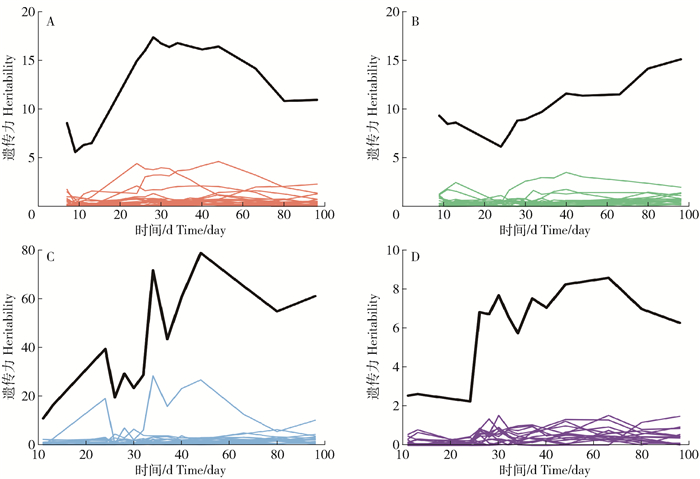
![]() 图 4 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作遗传力的时序模式A.主根长;B.茎高;C.侧根总长;D.侧根数量,黑色线条表示每个性状所有显著QTL-QTL互作的总遗传力。Figure 4. Temporal pattern of heritability of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traitsA, taproot length; B, stem height; C, total lateral root length; D, number of lateral roots, the black lines indicate the total heritability of all significant QTL-QTL interactions for each trait.
图 4 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作遗传力的时序模式A.主根长;B.茎高;C.侧根总长;D.侧根数量,黑色线条表示每个性状所有显著QTL-QTL互作的总遗传力。Figure 4. Temporal pattern of heritability of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traitsA, taproot length; B, stem height; C, total lateral root length; D, number of lateral roots, the black lines indicate the total heritability of all significant QTL-QTL interactions for each trait.从图 4A可发现,影响主根长的每个显著QTL-QTL互作的遗传力随时间呈现不同的变化趋势,但整体强度较弱,大部分组合遗传力在0~3%之间波动,有3个组合在3%~5%之间波动,包括lm_ll_11751-nn_np_10334、nn_np_11925-lm_ll_3383和lm_ll_9726-hk_hk_2116,其互作类型分别为加性-加性互作,加性-加性互作,加性-显性互作;图 4A中总的遗传力随时间在5%~17%的区间内波动。影响茎高显著上位效应的总遗传力波动范围与主根长相似,在5%~16%的区间内波动(图 4B);但大部分QTL-QTL互作组合的遗传力较弱,有3个组合的遗传力超过了3%,分别是组合hk_hk_861-hk_hk_1984、hk_hk_2765-hk_hk_861以及hk_hk_1960-hk_hk_1206,其互作类型分别是显性-显性互作,加性-显性互作,加性-显性互作。
影响侧根总长性状显著上位效应的总遗传力波动较大,波动区间为10%~80%(图 4C);从图中可发现,大部分互作组合贡献的遗传力都比较小,但组合lm_ll_13112-hk_hk_2288的贡献较大,波动范围在5%~30%。图 4D为影响胡杨幼苗侧根数量的显著上位效应的遗传力时序图,总的遗传力在2%~9%区间内波动,大部分组合在0.1%~2%区间内。从4个表型总的遗传力变化趋势图中发现,侧根总长的遗传力最大,其次为主根长和茎高,两者相接近,最小为侧根数量。随着时间变化4个性状显著上位效应的总遗传力变化趋势大概可以分为两种模式:先增加后减少和逐渐增加。其中主根长、侧根总长以及侧根数量中互作QTL的总遗传力随着时间先增加后减少,表明随着时间增加,遗传因素对上述3种表型的影响先增强之后又逐渐变弱。而茎高性状中显著上位效应的总遗传力随着时间逐渐增加,表明在胡杨幼苗的生长过程中遗传因素对茎高性状的影响逐渐增强。
2.4 功能注释
为进一步筛选候选基因,我们提取了显著互作标记对应的序列进行功能注释。首先,利用blast软件将序列与Nr数据库进行比对,然后将比对的结果导入到blast2go进行GO功能注释[31]。表 2列出了显著SNPs的主要注释结果,主根长、茎高、侧根总长和侧根数量注释的标记数量分别是5、4、5和5,整体注释比例较低;注释SNP的GO功能主要分为3类:细胞组分、分子功能以及生物学过程。其中,细胞组分涉及pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein At1g52620(GO:0043231)、cytokinin riboside 5′-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG7(GO:0005634)、ras-related protein RABA2a(GO:0005768)、transcription factor bHLH162(GO:0090575)、glutamate receptor 3.4-like(GO:0016021)、protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic(GO:0009533);分子功能主要涉及vestitone reductase(GO:0045552)、serine/arginine-rich splicing factor SC35-like isoform X1(GO:0003723)、integrase-like protein(GO:0003676)、integrase(GO:0003676)、DNA-directed DNA polymerase(GO:0003676)等;生物学过程主要涉及protein AE7-like(GO:0016226)和BTB/POZ domain-containing protein At5g41330-like(GO:0051260)。注释结果表明,侧根总长和侧根数量存在5个注释结果完全相同的显著标记:lm_ll_3153、lm_ll_11873、lm_ll_11020、lm_ll_11345、hk_hk_3209,其注释结果分别为integrase、DNA-directed DNA polymerase、Retrovirus-related Pol polyprotein from transposon 17.6、glutamate receptor 3.4-like、protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic。
表 2 2HIGWAS筛选出的上位效应位点注释信息Table 2. Annotation information of loci with epistatic effect filtered by 2HIGWAS性状
Trait标记
MarkerGO号
GO ID分类
Classification注释信息
Annotataion主根长Taproot length nn_np_3087 GO:0043231 C Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein At1g52620 nn_np_6494 GO:0016226 P protein AE7-like hk_hk_2726 GO:0051260 P BTB/POZ domain-containing protein At5g41330-like hk_hk_2120 GO:0045552 F vestitone reductase nn_np_4582 GO:0005634 C cytokinin riboside 5′-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG7 茎高Stem height hk_hk_1206 GO:0003723 F serine/arginine-rich splicing factor SC35-like isoform X1 hk_hk_1556 GO:0005768 C ras-related protein RABA2a hk_hk_2155 GO:0003676 F integrase-like protein hk_hk_3206 GO:0090575 C transcription factor bHLH162 lm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase 侧根总长Total lateral
root lengthlm_ll_11873 GO:0003676 F DNA-directed DNA polymerase lm_ll_11020 GO:0008445 F Retrovirus-related Pol polyprotein from transposon 17.6 lm_ll_11345 GO:0016021 C glutamate receptor 3.4-like hk_hk_3209 GO:0009533 C protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic lm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase 侧根数量Number of
lateral rootslm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase lm_ll_11873 GO:0003676 F DNA-directed DNA polymerase lm_ll_11020 GO:0008445 F Retrovirus-related Pol polyprotein from transposon 17.6 lm_ll_11345 GO:0016021 C glutamate receptor 3.4-like hk_hk_3209 GO:0009533 C protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic 注:P表示生物学过程、C表示细胞组分、F表示分子功能。Notes:P denotes the biological process, C denotes the cellular component, F denotes the molecular function. 3. 讨论与结论
幼苗期是植物生长发育过程中最重要的阶段之一,幼苗的生长发育及存活不仅对植物的后续生长以及种群大小有着重要影响,也在植物种群更新、扩散、群落演替及维持生物多样性中扮演重要角色。胡杨在沙漠生态系统中起着重要作用,是干旱地区的重要生态屏障。胡杨林的更新与维持主要依靠实生苗更新,但其对逆境环境的适应能力较弱,从而成为影响胡杨的更新与分布的瓶颈。干旱,盐碱等胁迫会抑制胡杨生物量的积累,导致分配策略发生变化,最终改变表型从而维持其在逆境环境下的生存[32],因此需要进一步解析胡杨生长的遗传结构,挖掘其内在的生长机制。本研究基于功能作图和2HIGWAS侦测影响胡杨幼苗生长的上位互作,解析影响胡杨幼苗生长的遗传机制。
由于标记之间的互作检测次数是单标记检测的平方,随着标记数量的增加从而导致侦测基因之间的互作无论从实验、统计还是计算的角度都是一个绝大的挑战[33]。本研究中所使用的2HIGWAS模型具有两大优势:第一,它可以完整描述表型变异中的遗传组分,并能说明这些组分如何通过作用与相互作用来影响最终的表型,弥补了单标记分析只能识别某个位点的边际效应的问题,解决了因忽略不同SNP标记间相关性造成遗传力有偏估计的问题;第二,该模型能够侦测影响表型发育的位点,进而研究关键基因如何以及何时开始影响表型发育[34]。该模型可以有效用于研究早期基因是否可以多效地影响后期表型[35],因此可作为本研究中解析胡杨幼苗生长遗传机制的良好工具。本研究基于2HIGWAS模型对胡杨幼苗生长的主根长、茎高、侧根长以及侧根数量4个表型的上位效应遗传机制进行了解析。其中,4个表型上位互作的遗传力在2%~80%之间波动,侧根总长的遗传力在某些时间点可达80%,这表明上位效应可能在其遗传调控中起重要作用。在拟南芥中,Lachowiec等[36]通过对根长的GWAS研究发现上位效应解释了大部分的表型变异,并用突变分析验证了其中的部分基因,这表明在胡杨中也可能存在类似影响胡杨幼苗根系发育的互作。
基于2HIGWAS上位效应模型,分别侦测到主根长、茎高、侧根总长和侧根数量分别有24、20、24和25对上位互作,4种表型的显著上位互作不存在重复,均为特异性互作,但上位互作中的标记存在重叠,说明部分基因可能参与多个表型的发育调控。另外,对于侧根总长和侧根数量两个涉及侧根的显著上位互作存在不同,这也说明影响总长和数量两个不同尺度表型变化的遗传调控机制不同。对于主根长、茎高以及侧根总长部分互作SNP分别在连锁群1、19和17集中分布,在这些集中分布区域可能存在与胡杨生长发育相关的候选基因。但从胡杨幼苗生长相关性状的上位显著基因注释结果发现,总体注释的基因比例较少,而且注释基因的功能与胡杨发育有直接关系的证据较少,这主要是由于胡杨研究的基础相对薄弱,特别是功能基因组学研究。本研究基于上位互作,但复杂性状是由多基因控制,是一个调控网络整体调控,因此,后续在系统水平开展对胡杨发育相关的高维QTL网络构建,挖掘关键的枢纽基因将具有更重要的价值。
与胡杨生长相关的4个性状的遗传力也展现出较大的差异,大部分QTL-QTL互作的遗传力比较小。影响主根长的遗传力随时间在5%~17%的区间内波动;影响茎高的遗传力在5%~16%的区间内波动;影响侧根总长性状显著上位效应的总遗传力波动较大,波动区间为10%~80%;由影响胡杨幼苗侧根数量的显著上位效应的遗传力时序图可知,总的遗传力在2%~9%区间内波动,这说明上位效应随时间变化对表型的贡献也发生变化,在某些时间点贡献较大。总体来看,上位效应可在一定程度上弥补缺失的遗传力,特别是本研究中对侧根总长的影响。因此,需要进一步对侧根生长的上位互作QTL区域的候选基因展开功能组学和分子生物学的研究,这有助于胡杨分子标记辅助育种的开展。
-
图 3 4个性状中显著QTL-QTL互作在胡杨连锁群的分布
红色代表主根长;绿色代表茎高;蓝色代表侧根总长;紫色代表侧根数量。
Figure 3. Distribution of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits along 19 linkage groups of Populus euphratica
Red represents the taproot length; green represents the stem height; blue represents total lateral root length; purple represents the number of lateral roots.
图 4 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作遗传力的时序模式
A.主根长;B.茎高;C.侧根总长;D.侧根数量,黑色线条表示每个性状所有显著QTL-QTL互作的总遗传力。
Figure 4. Temporal pattern of heritability of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits
A, taproot length; B, stem height; C, total lateral root length; D, number of lateral roots, the black lines indicate the total heritability of all significant QTL-QTL interactions for each trait.
表 1 4个性状显著QTL-QTL互作的详细信息
Table 1 Detailed information of significant QTL-QTL interactions for four traits
表型
Phenotype配对数
Pair标记1 ID
SNP1标记2 ID
SNP2连锁群LG 位置Position 标记类型Marker type 互作类型
Interaction
type标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2标记1
SNP1标记2
SNP2主根长Taproot length 0 hk_hk_526 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 393.97 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 1 hk_hk_1541 lm_ll_9903 LG1 LG3 363.76 303.2 Intercross Testcross AA 2 lm_ll_11751 nn_np_10334 LG12 LG1 192.69 399.54 Testcross Testcross AA 3 lm_ll_6889 nn_np_4797 LG3 LG1 297.11 404.42 Testcross Testcross AA 4 lm_ll_9726 nn_np_10334 LG2 LG1 134.6 399.54 Testcross Testcross AA 5 hk_hk_2726 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 400.46 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 6 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_4106 LG1 LG8 366.17 82.77 Testcross Testcross AA 7 lm_ll_11751 nn_np_7270 LG12 LG1 192.69 382.18 Testcross Testcross AA 8 hk_hk_2120 hk_hk_2116 LG2 LG7 383.58 149.35 Intercross Intercross AD 9 hk_hk_526 hk_hk_2116 LG1 LG7 393.97 149.35 Intercross Intercross AD 10 nn_np_11925 lm_ll_3383 LG1 LG3 367.62 215.49 Testcross Testcross AA 11 hk_hk_1541 lm_ll_9726 LG1 LG2 363.76 134.6 Intercross Testcross AA 12 lm_ll_5873 lm_ll_9726 LG12 LG2 192.7 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 13 lm_ll_8943 nn_np_4797 LG3 LG1 297.11 404.42 Testcross Testcross AA 14 lm_ll_8943 nn_np_4582 LG3 LG19 297.11 72.68 Testcross Testcross AA 15 lm_ll_4106 nn_np_3087 LG8 LG1 82.77 361.76 Testcross Testcross AA 16 lm_ll_5853 lm_ll_9726 LG3 LG2 307.06 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 17 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_6889 LG1 LG3 366.17 297.11 Testcross Testcross AA 18 lm_ll_9726 hk_hk_2116 LG2 LG7 134.6 149.35 Testcross Intercross AD 19 lm_ll_9903 lm_ll_9726 LG3 LG2 303.2 134.6 Testcross Testcross AA 20 nn_np_6494 lm_ll_3383 LG1 LG3 366.17 215.49 Testcross Testcross AA 21 nn_np_11925 lm_ll_4106 LG1 LG8 367.62 82.77 Testcross Testcross AA 22 hk_hk_2726 lm_ll_9903 LG1 LG3 400.46 303.2 Intercross Testcross AA 23 lm_ll_9726 lm_ll_9874 LG2 LG3 134.6 222 Testcross Testcross AA 茎高Stem height 24 lm_ll_3248 hk_hk_1984 LG2 LG19 55.81 75.2 Testcross Intercross AD 25 hk_hk_861 hk_hk_1984 LG19 LG19 84.22 75.2 Intercross Intercross DD 26 nn_np_8378 hk_hk_861 LG5 LG19 122.48 84.22 Testcross Intercross AD 27 hk_hk_2692 hk_hk_2705 LG19 LG3 118.55 61.26 Intercross Intercross AD 29 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 75.2 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 30 hk_hk_2765 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 75.32 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 31 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1556 LG19 LG6 75.2 18.94 Intercross Intercross DD 32 nn_np_4006 hk_hk_861 LG11 LG19 106.5 84.22 Testcross Intercross AD 33 hk_hk_2025 hk_hk_1556 LG15 LG6 49.67 18.94 Intercross Intercross DD 34 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_2234 LG19 LG19 75.2 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 35 hk_hk_1365 hk_hk_2705 LG19 LG3 109.52 61.26 Intercross Intercross AD 36 hk_hk_2155 hk_hk_861 LG19 LG19 74.66 84.22 Intercross Intercross AD 37 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1342 LG19 LG19 75.2 75.32 Intercross Intercross DD 38 hk_hk_861 hk_hk_1342 LG19 LG19 84.22 75.32 Intercross Intercross DD 39 lm_ll_3248 nn_np_11732 LG2 LG10 55.81 23.14 Testcross Testcross AA 40 lm_ll_3248 hk_hk_2779 LG2 LG13 55.81 218.9 Testcross Intercross AD 41 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_3206 LG19 LG19 75.2 86.38 Intercross Intercross DD 42 hk_hk_1984 hk_hk_1206 LG19 LG6 75.2 5.36 Intercross Intercross DD 43 hk_hk_2765 hk_hk_3138 LG19 LG6 75.32 21.69 Intercross Intercross AA 44 hk_hk_1960 hk_hk_1206 LG19 LG6 118.55 5.36 Intercross Intercross AD 总侧根长Total lateral
root length45 hk_hk_3074 hk_hk_2288 LG8 LG2 102.69 95.12 Intercross Intercross DD 46 lm_ll_3911 hk_hk_3074 LG3 LG8 234.43 102.69 Testcross Intercross AD 47 lm_ll_7977 hk_hk_2288 LG2 LG2 43.08 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 48 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_3153 LG17 LG3 115.47 214.01 Testcross Testcross AA 49 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11743 LG17 LG3 115.47 236.62 Testcross Testcross AA 50 lm_ll_7977 nn_np_11395 LG2 LG10 43.08 44.49 Testcross Testcross AA 51 hk_hk_3038 lm_ll_3153 LG3 LG3 21.18 214.01 Intercross Testcross AA 52 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_8924 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 53 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11684 LG17 LG3 115.47 226.02 Testcross Testcross AA 54 hk_hk_829 hk_hk_861 LG15 LG19 82.8 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 55 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11020 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 56 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11345 LG17 LG3 115.47 236.62 Testcross Testcross AA 57 nn_np_7192 hk_hk_3074 LG19 LG8 97.44 102.69 Testcross Intercross AD 58 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_11873 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.82 Testcross Testcross AA 59 nn_np_8297 lm_ll_2229 LG17 LG3 115.47 224.85 Testcross Testcross AA 60 hk_hk_3038 lm_ll_11873 LG3 LG3 21.18 224.82 Intercross Testcross AA 61 lm_ll_7977 hk_hk_1848 LG2 LG4 43.08 91.98 Testcross Intercross AD 62 lm_ll_13112 hk_hk_2288 LG3 LG2 235.58 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 63 hk_hk_3038 hk_hk_2485 LG3 LG8 21.18 93.95 Intercross Intercross AD 64 hk_hk_3209 hk_hk_861 LG8 LG19 60.28 84.22 Intercross Intercross DD 65 hk_hk_1848 hk_hk_1589 LG4 LG12 91.98 79.45 Intercross Intercross DD 66 lm_ll_13112 lm_ll_7977 LG3 LG2 235.58 43.08 Testcross Testcross AA 67 lm_ll_12414 hk_hk_2288 LG3 LG2 229.56 95.12 Testcross Intercross AD 68 lm_ll_11873 hk_hk_3209 LG3 LG8 224.82 60.28 Testcross Intercross AD 侧根数量Number of
lateral roots69 hk_hk_3237 nn_np_6825 LG17 LG11 79.51 144.23 Intercross Testcross AA 70 lm_ll_10262 nn_np_9993 LG10 LG11 43.3 164.17 Testcross Testcross AA 71 lm_ll_10262 lm_ll_6938 LG10 LG4 43.3 78.08 Testcross Testcross AA 72 lm_ll_7471 nn_np_11905 LG4 LG17 64.6 61.54 Testcross Testcross AA 73 lm_ll_4501 nn_np_3662 LG5 LG11 170.17 148.06 Testcross Testcross AA 74 lm_ll_579 hk_hk_1675 LG4 LG12 17 12.47 Testcross Intercross AD 75 lm_ll_6938 lm_ll_10741 LG4 LG5 78.08 121.28 Testcross Testcross AA 76 nn_np_9993 lm_ll_10152 LG1 LG10 164.17 79.6 Testcross Testcross AA 77 nn_np_12080 nn_np_9993 LG5 LG1 188 164.17 Testcross Testcross AA 78 lm_ll_7471 nn_np_8146 LG4 LG4 64.6 203.23 Testcross Testcross AA 79 hk_hk_3237 nn_np_9993 LG17 LG11 79.51 164.17 Intercross Testcross AA 80 lm_ll_4374 lm_ll_10741 LG4 LG5 75.03 121.28 Testcross Testcross AA 81 nn_np_12080 lm_ll_6938 LG5 LG4 188 78.08 Testcross Testcross AA 82 lm_ll_924 lm_ll_579 LG2 LG4 15.01 17 Testcross Testcross AA 83 nn_np_12080 nn_np_2539 LG5 LG18 188 184.27 Testcross Testcross AA 注:A表示加性效应,D表示显性效应。Notes:A represents additive effect, D represents dominant effect. 表 2 2HIGWAS筛选出的上位效应位点注释信息
Table 2 Annotation information of loci with epistatic effect filtered by 2HIGWAS
性状
Trait标记
MarkerGO号
GO ID分类
Classification注释信息
Annotataion主根长Taproot length nn_np_3087 GO:0043231 C Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein At1g52620 nn_np_6494 GO:0016226 P protein AE7-like hk_hk_2726 GO:0051260 P BTB/POZ domain-containing protein At5g41330-like hk_hk_2120 GO:0045552 F vestitone reductase nn_np_4582 GO:0005634 C cytokinin riboside 5′-monophosphate phosphoribohydrolase LOG7 茎高Stem height hk_hk_1206 GO:0003723 F serine/arginine-rich splicing factor SC35-like isoform X1 hk_hk_1556 GO:0005768 C ras-related protein RABA2a hk_hk_2155 GO:0003676 F integrase-like protein hk_hk_3206 GO:0090575 C transcription factor bHLH162 lm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase 侧根总长Total lateral
root lengthlm_ll_11873 GO:0003676 F DNA-directed DNA polymerase lm_ll_11020 GO:0008445 F Retrovirus-related Pol polyprotein from transposon 17.6 lm_ll_11345 GO:0016021 C glutamate receptor 3.4-like hk_hk_3209 GO:0009533 C protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic lm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase 侧根数量Number of
lateral rootslm_ll_3153 GO:0003676 F integrase lm_ll_11873 GO:0003676 F DNA-directed DNA polymerase lm_ll_11020 GO:0008445 F Retrovirus-related Pol polyprotein from transposon 17.6 lm_ll_11345 GO:0016021 C glutamate receptor 3.4-like hk_hk_3209 GO:0009533 C protease Do-like 2, chloroplastic 注:P表示生物学过程、C表示细胞组分、F表示分子功能。Notes:P denotes the biological process, C denotes the cellular component, F denotes the molecular function. -
[1] Silva A T, Ligterink W, Hilhorst H W M. Metabolite profiling and associated gene expression reveal two metabolic shifts during the seed-to-seedling transition in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2017, 95(4):481-496. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=349541da36d214837b0dd468180dcbb3
[2] Leishman M R, Hughes L, French K, et al. Seed and seedling biology in relation to modelling vegetation dynamics under global climate change[J]. Australian Journal of Botany, 1992, 40(5):599-613. doi: 10.1071/BT9920599
[3] Zhang M, Bo W, Xu F, et al. The genetic architecture of shoot-root covariation during seedling emergence of a desert tree, Populus euphratica[J]. The Plant Journal, 2017, 90(5): 918-928. doi: 10.1111/tpj.2017.90.issue-5
[4] Osunkjoya O O, Ash J E, Hopkins M S, et al. Factors affecting survival of tree seedlings in North Queensland rainforests[J]. Oecologia, 1992, 91(4): 569-578. doi: 10.1007/BF00650333
[5] Koger C H, Reddy K N, Poston D H. Factors affecting seed germination, seedling emergence, and survival of texasweed (Caperonia palustris)[J]. Weed Science, 2004, 52(6): 989-995. doi: 10.1614/WS-03-139R2
[6] Von Liebig J F. Die organische Chemie in ihrer Anwendung auf Agricultur und Physiologie[M]. Braunschweig:Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn Publ. Co, 1842.
[7] Kaspari M, Garcia M N, Harms K E, et al. Multiple nutrients limit litterfall and decomposition in a tropical forest[J]. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(1): 35-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01124.x
[8] Clouse S D. Integration of light and brassinosteroid signals in etiolated seedling growth[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(10): 443-445. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02102-1
[9] Nelson D C, Flematti G R, Ghisalberti E L, et al. Regulation of seed germination and seedling growth by chemical signals from burning vegetation[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63: 107-130. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105545
[10] Stanga J P, Morffy N, Nelson D C. Functional redundancy in the control of seedling growth by the karrikin signaling pathway[J]. Planta, 2016, 243(6): 1397-1406. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2458-2
[11] Hu Y, Vandenbussche F, Van Der Straeten D. Regulation of seedling growth by ethylene and the ethylene-auxin crosstalk[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(3): 467-489. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2651-6
[12] Li J, Fu J, Chen Y, et al. The U6 biogenesis-like1 plays an important role in maize kernel and seedling development by affecting the 3' end processing of U6 snRNA[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 470-482. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.10.016
[13] Stewart J L, Maloof J N, Nemhauser J L. PIF genes mediate the effect of sucrose on seedling growth dynamics[J/OL]. PLoS one, 2011, 6(5): e19894[2018-09-27]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019894
[14] Hwang J E, Hong J K, Je J H, et al. Regulation of seed germination and seedling growth by an Arabidopsis phytocystatin isoform, AtCYS6[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2009, 28(11): 1623-1632. doi: 10.1007/s00299-009-0762-7
[15] Liang H, Yu Y, Yang H, et al. Inheritance and QTL mapping of related root traits in soybean at the seedling stage[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2014, 127(10): 2127-2137. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2366-z
[16] Li P, Chen F, Cai H, et al. A genetic relationship between nitrogen use efficiency and seedling root traits in maize as revealed by QTL analysis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(11): 3175-3188. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv127
[17] Li G, Xu X, Bai G, et al. Genome-wide association mapping reveals novel QTL for seedling leaf rust resistance in a worldwide collection of winter wheat[J]. The Plant Genome, 2016, 9(3): 1-12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27902805
[18] Genc Y, Oldach K, Verbyla A P, et al. Sodium exclusion QTL associated with improved seedling growth in bread wheat under salinity stress[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2010, 121(5): 877-894. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1357-y
[19] Bai C, Liang Y, Hawkesford M J. Identification of QTLs associated with seedling root traits and their correlation with plant height in wheat[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(6): 1745-1753. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert041
[20] Takagi H, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, et al. MutMap-Gap: whole-genome resequencing of mutant F 2 progeny bulk combined with de novo assembly of gap regions identifies the rice blast resistance gene Pii[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 200(1): 276-283. doi: 10.1111/nph.12369
[21] Eichler E E, Flint J, Gibson G, et al. Missing heritability and strategies for finding the underlying causes of complex disease[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2010, 11(6): 446-450. doi: 10.1038/nrg2809
[22] Bloom J S, Ehrenreich I M, Loo W T, et al. Finding the sources of missing heritability in a yeast cross[J]. Nature, 2013, 494: 234. doi: 10.1038/nature11867
[23] Ma T, Wang J, Zhou G, et al. Genomic insights into salt adaptation in a desert poplar[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2797. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3797
[24] Janz D, Lautner S, Wildhagen H, et al. Salt stress induces the formation of a novel type of 'pressure wood'in two Populus species[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 194(1): 129-141. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03975.x
[25] Hohenlohe P A, Bassham S, Etter P D, et al. Population genomics of parallel adaptation in threespine stickleback using sequenced RAD tags[J/OL]. PLoS Genetics, 2010, 6(2): e1000862[2018-09-24]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000862.
[26] Topp C N, Iyer-Pascuzzi A S, Anderson J T, et al. 3D phenotyping and quantitative trait locus mapping identify core regions of the rice genome controlling root architecture[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(18): E1695-E1704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304354110
[27] West G B, Brown J H, Enquist B J. A general model for ontogenetic growth[J]. Nature, 2001, 413: 628. doi: 10.1038/35098076
[28] Bozdogan H. Model selection and Akaike's information criterion (AIC): the general theory and its analytical extensions[J]. Psychometrika, 1987, 52(3): 345-370. doi: 10.1007/BF02294361
[29] Ma C X, Casella G, Wu R. Functional mapping of quantitative trait loci underlying the character process: a theoretical framework[J]. Genetics, 2002, 161(4): 1751-1762. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_1462199
[30] Wang Z, Wang N, Wu R, et al. fGWAS: an R package for genome-wide association analysis with longitudinal phenotypes[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2018, 45(7): 411. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2018.06.006
[31] Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez J M, et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(18): 3674-3676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
[32] Wang L, Zhao C, Li J, et al. Root plasticity of Populus euphratica seedlings in response to different water table depths and contrasting sediment types[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0118691[2018-09-27]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118691.
[33] Mackay T F C. Epistasis and quantitative traits: using model organisms to study gene-gene interactions[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2014, 15(1): 22. doi: 10.1038/nrg3627
[34] Jiang L, Liu J, Zhu X, et al. 2HiGWAS: a unifying high-dimensional platform to infer the global genetic architecture of trait development[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2015, 16(6): 905-911. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv002
[35] Donohue K. The epigenetics of adaptation: focusing on epigenetic stability as an evolving trait[J]. Evolution, 2014, 68(3): 617-619. doi: 10.1111/evo.12347
[36] Lachowiec J, Shen X, Queitsch C, et al. A genome-wide association analysis reveals epistatic cancellation of additive genetic variance for root length in Arabidopsis thaliana[J/OL]. PLoS Genetics, 2015, 11(9): e1005541[2018-09-27]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005541.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: