Effects of transgenic sense and antisense of BpCCR1 on 7-year-old potted birch and selection of excellent lines
-
摘要:目的肉桂酰辅酶还原酶(Cinnamoyl-CoA Reductase,CCR)是催化木质素合成特异途径中的第一个限速酶。通过测定转基因株系和野生型株系(WT)的木质素和单体含量,探究转BpCCR1基因正义链和反义链对白桦木质素含量的影响,进而筛选出转基因优良株系。方法以获得的7年生白桦转BpCCR1正、反义链株系为试验材料,采用PCR及qRT-PCR技术分别对目标基因的稳定性及表达量进行检测,采用改进的Klason法及液相色谱法分别对木质素含量及单体含量进行测定,采用硝酸-氯酸钾法和排水法分别对木纤维长和宽及基本密度进行测定,并调查树高及胸径,以此来分析转BpCCR1正、反义链对白桦上述性状的影响。结果PCR检测表明,5个转正义链株系及14个转反义链株系的目标基因均为阳性;qRT-PCR分析显示,BpCCR1基因不但在转正义链株系中上调表达,而且在转反义链株系中也呈上调表达。转正、反义链白桦株系木质素含量均增加,其中10个转反义链株系的Klason木质素和总木质素含量均值较野生型株系(WT)分别提高了7.46%和7.05%,木质素含量最高的FCR11株系较WT株系分别提高了12.26%和11.81%;转基因株系基本密度虽然有一定的变化,但无明显规律。转正义链株系的木纤维宽明显变小,5个株系均值较WT减少8.82%;而转反义链株系的木纤维长受到明显抑制,有11个株系与WT的差异达到了显著性水平(P < 0.05),其均值较WT减少12.12%。转基因株系与WT的材积差异也达到显著性水平,有11个转反义链株系的材积大于WT,7个株系达到显著性水平(P < 0.05),其平均材积生长量较WT提高77.1%。采用主成分分析法选择FCR2、FCR27和FCR33株系为优良株系。结论转BpCCR1正义链及反义链均提高白桦木质素含量,综合树高、胸径等6个性状筛选出3个优良转基因株系。Abstract:ObjectiveCinnamoyl-CoA Reductase (CCR) is the first rate-limiting enzyme in the specific pathway for the synthesis of lignin and plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of lignin. Measuring the lignin and monomer content of transgenic lines and wild lines (WT) aims to explore the effects of BpCCR1-sense and BpCCR1-antisense on the lignin of Betula platyphylla.Method7-year-old BpCCR1-sense and BpCCR1-antisense transgenic lines were selected as experimental materials. The expression of BpCCR1 in transgenic lines was determined using PCR and qRT-PCR, respectively. The lignin content and monomer content were determined by the modified Klason method and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), respectively. The length and width of the wood fiber and basic density were measured by the method of nitric acid-potassium chlorate and drainage, and the height (H) and diameter at breast height (DBH) of the trees were investigated to investigate the effects of BpCCR1 sense and antisense lines in B. platyphylla.ResultPCR analysis showed that the BpCCR1 was successfully integrated into the birch genome in 5 BpCCR1-sense transgenic lines and 14 BpCCR1-antisense transgenic lines. QRT-PCR analysis revealed that the expression of BpCCR1 was up-regulated in transgenic lines compared with wild type (WT). Lignin content of the transgenic lines was increased. There into, the average Klason lignin and total lignin content of 10 transgenic lines were respectively 7.46% and 7.05% higher than wild type. Compared with WT, FCR11 line had the highest content of average Klason lignin and total lignin, which was respectively increased by 12.26% and 11.81%. Although the wood basic density of transgenic lines had changed, while there was no obvious law. The wood fiber width of BpCCR1-sense transgenic lines was significantly smaller than WT, the average value of which decreased by 8.82% in five transgenic lines. Whereas, the wood fiber length of BpCCR1-antisense transgenic lines was restrained, and the difference between 11 lines and WT reached a significant level (P < 0.05), and the average value was 12.12% shorter than WT. The difference in volume between transgenic lines and WT also reached a significant level. The volume of 11 transgenic lines was larger than WT, and 7 lines reached a significant level, and the average volume growth was 77.1% higher than WT. FCR2, FCR27 and FCR32 lines were selected as excellent lines using principal component analysis.ConclusionBoth the sense and antisense of BpCCR1 can increase the lignin content of B. platyphylla, three excellent transgenic lines were selected by six characters including height and DBH.
-
Keywords:
- Betula platyphylla /
- CCR /
- lignin /
- fiber /
- excellent line
-
-
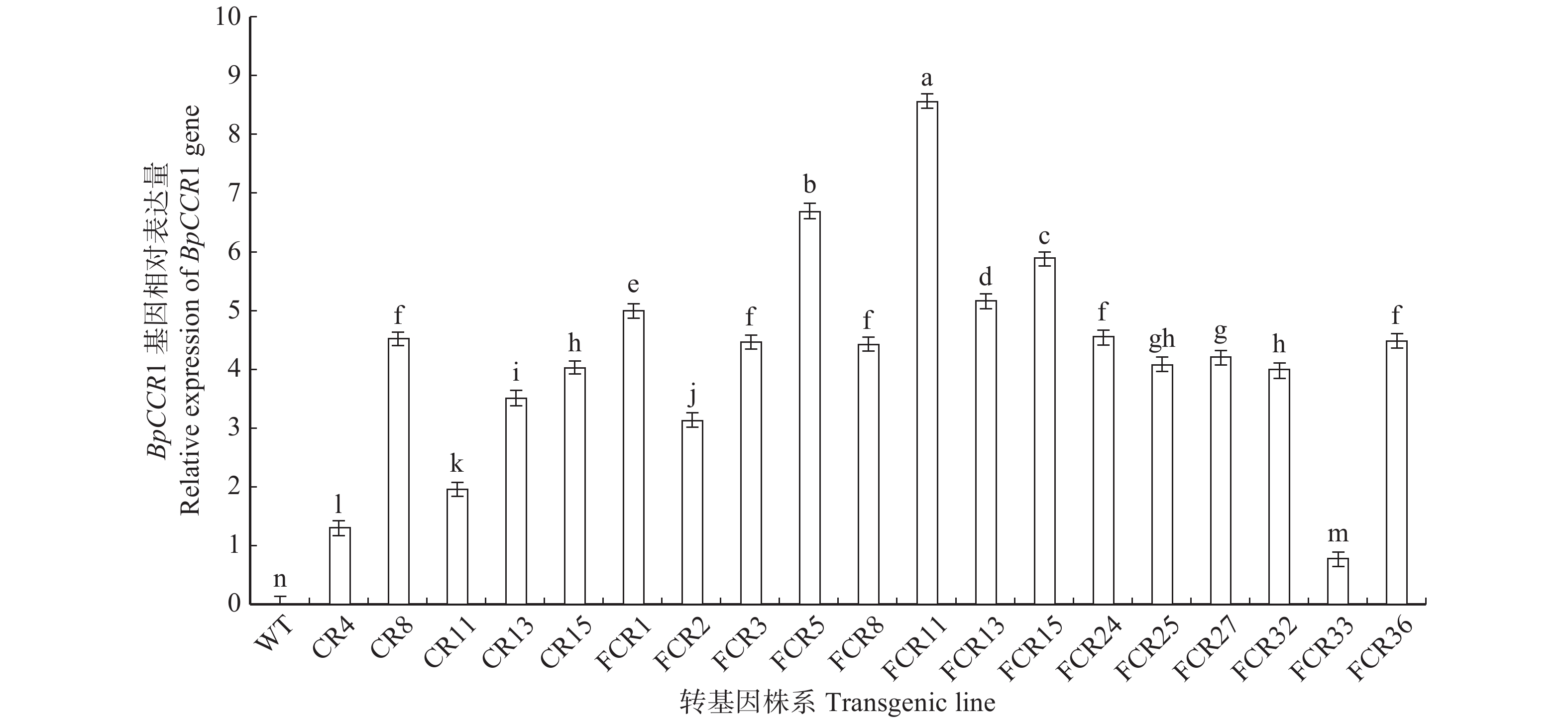
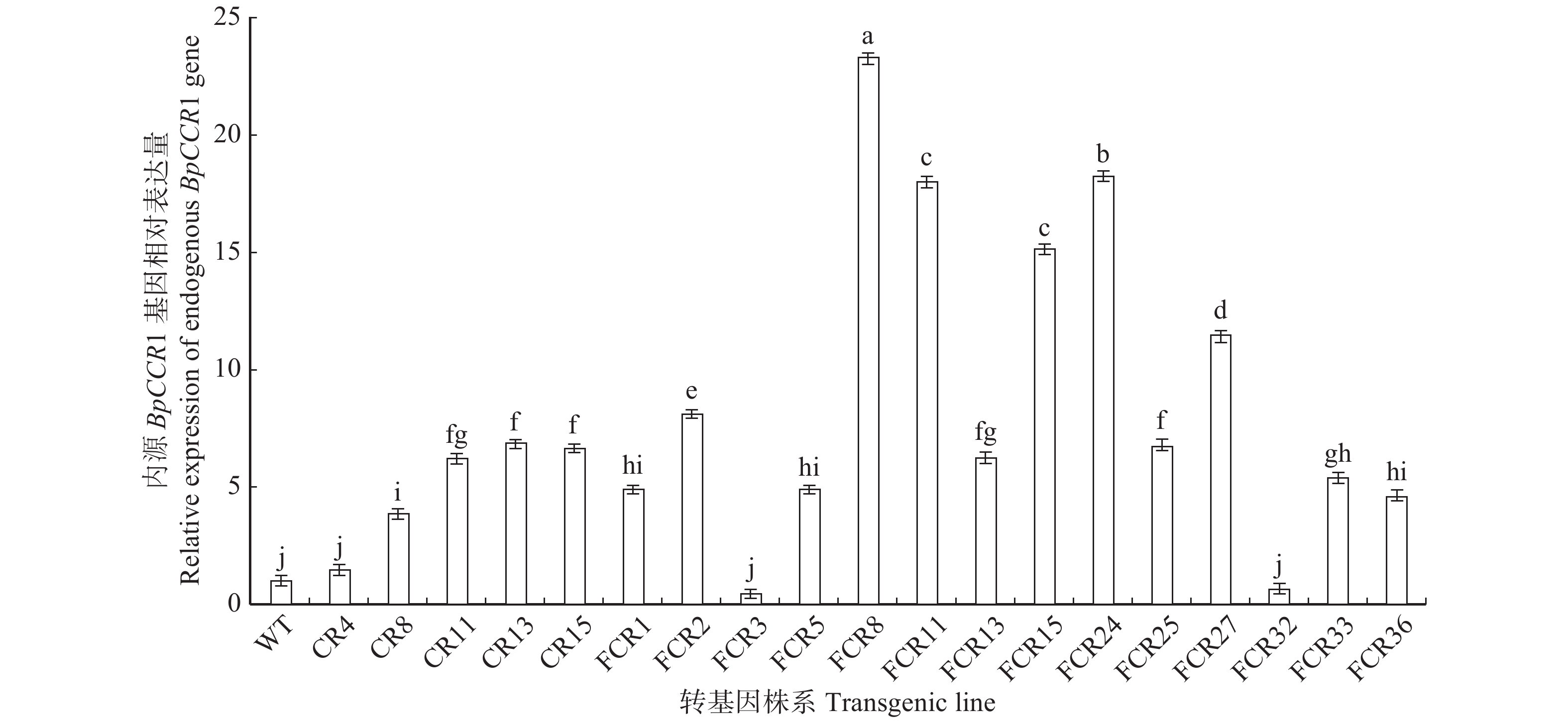
图 2 转BpCCR1基因株系qRT-PCR检测
WT. 野生型;CR. 转BpCCR1正义链株系;FCR. 转BpCCR1反义链株系;不同小写字母代表差异显著,P < 0.05。下同。WT, wild type; CR, sense BpCCR1 transgenic lines; FCR, antisense BpCCR1 transgenic lines; different lowercase letters represent significant differences at P < 0.05 level. The same below.
Figure 2. Detection of BpCCR1 transgenic lines by qRT-PCR
表 1 BpCCR1基因及内源BpCCR1基因qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequence for BpCCR1 gene and endogenous BpCCR1 gene
基因名称 Gene name 正向引物(5′→3′) Forward primer (5′→3′) 反向引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer (5′→3′) 18S rRNA GAGGTAGCTTCGGGCGCAACT GCAGGTTAGCGAAATGCGATAC BpCCR1 AGCATGTGCGAGAACACCATC ACTCATCACTCCAGCAGCCA 内源BpCCR1 Endogenous BpCCR1 CAAGAATGCAGCAGGCAGATAC GAGAGAGGTGACATAAACGGCC 表 2 转BpCCR1株系木质素含量多重比较
Table 2 Multiple comparisons of lignin content of BpCCR1 transgenic lines
基因
Gene株系
Line木质素含量 Lignin content/% 木质素单体类型 Type of lignin monomer Klason木质素
Klason lignin酸溶性木质素
Acid-soluble lignin总木质素
Total ligninG S S/G H 正义链
SenseCR15 23.098 ± 0.206a 0.744 ± 0.015a 23.841 ± 0.192a 0.261 ± 0.002cd 0.726 ± 0.002c 2.779 ± 0.035cd 0.012 8 CR13 22.827 ± 0.287ab 0.867 ± 0.158a 23.694 ± 0.160ab 0.280 ± 0.006a 0.715 ± 0.006d 2.552 ± 0.070e 0.004 6 CR4 22.683 ± 0.392ab 0.776 ± 0.012a 23.459 ± 0.399abc — — — — CR11 22.472 ± 0.497ab 0.566 ± 0.035b 23.038 ± 0.506bc — — — — WT 22.042 ± 0.337b 0.845 ± 0.046a 22.887 ± 0.331c 0.259 ± 0.002cd 0.736 ± 0.002b 2.841 ± 0.024bc 0.004 3 CR8 21.284 ± 0.648c 0.879 ± 0.025a 22.163 ± 0.626d 0.243 ± 0.002e 0.752 ± 0.002a 3.101 ± 0.026a 0.005 0 反义链
AntisenseFCR11 24.745 ± 0.065a 0.844 ± 0.061abcd 25.589 ± 0.091a 0.257 ± 0.001d 0.738 ± 0.001b 2.873 ± 0.011b 0.005 0 FCR8 24.338 ± 0.109ab 0.816 ± 0.111bcd 25.154 ± 0.190ab — — — — FCR36 24.323 ± 0.116ab 0.799 ± 0.061cde 25.122 ± 0.128ab — — — — FCR25 23.896 ± 0.500bc 0.933 ± 0.026ab 24.829 ± 0.526b — — — — FCR5 23.617 ± 0.164cd 0.960 ± 0.041a 24.578 ± 0.204bc — — — — FCR13 23.411 ± 0.145cd 0.763 ± 0.043de 24.174 ± 0.139cd 0.267 ± 0.003b 0.729 ± 0.003c 2.725 ± 0.048d 0.003 7 FCR15 23.370 ± 0.049cd 0.738 ± 0.096def 24.108 ± 0.145cd — — — — FCR24 23.248 ± 0.022de 0.666 ± 0.143ef 23.914 ± 0.124d — — — — FCR1 23.206 ± 0.432de 0.733 ± 0.089def 23.938 ± 0.371cd — — — — FCR3 22.708 ± 0.566ef 0.898 ± 0.029abc 23.606 ± 0.541de — — — — FCR32 22.385 ± 0.426fg 0.752 ± 0.048de 23.137 ± 0.395ef — — — — WT 22.042 ± 0.337g 0.845 ± 0.046abcd 22.887 ± 0.331fg 0.259 ± 0.002cd 0.736 ± 0.002b 2.841 ± 0.024bc 0.004 3 FCR2 22.016 ± 0.356g 0.669 ± 0.058ef 22.685 ± 0.380fg 0.262 ± 0.001c 0.734 ± 0.001b 2.796 ± 0.017c 0.004 4 FCR33 22.010 ± 0.497g 0.674 ± 0.037ef 22.683 ± 0.534fg — — — — FCR27 21.772 ± 0.579g 0.611 ± 0.055f 22.383 ± 0.571g — — — — 注:“—” 代表未测定的数据;表中不同字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著;表中数据表示形式为均值 ± 标准差。下同。Notes: “—” stands for unmeasured values. Different letters mean significant difference at P < 0.05 level; data in the table are mean ± standard deviation. The same below. 表 3 转BpCCR1株系纤维长、宽及基本密度多重比较
Table 3 Multiple comparisons of fiber length, width and basic density of BpCCR1 transgenic lines
基因
Gene株系
Line木纤维 Wood fiber 基本密度
Basic density/(g·cm− 3)长 Length/μm 宽 Width/μm 长/宽 Length/width 正义链 Sense CR15 661.2 ± 55.5b 14.4 ± 2.2b 46.7 ± 3.8b 0.365 5 ± 0.001 1d CR13 657.5 ± 42.4bc 14.9 ± 2.3b 45.0 ± 3.8b 0.392 2 ± 0.001 5b CR4 637.0 ± 52.4c 14.2 ± 2.1b 45.7 ± 3.9b 0.382 0 ± 0.003 9c CR11 652.4 ± 37.9bc 14.7 ± 2.5b 45.4 ± 4.7b 0.382 9 ± 0.008 9c WT 650.4 ± 38.8bc 16.1 ± 1.8a 40.8 ± 2.3c 0.381 0 ± 0.001 3c CR8 798.3 ± 48.2a 15.2 ± 1.9b 53.4 ± 3.9a 0.423 5 ± 0.006 7a 反义链 Antisense FCR11 619.6 ± 38.8cd 15.3 ± 1.9def 41.2 ± 5.4a 0.387 7 ± 0.004 5bcd FCR8 622.2 ± 37.1cd 15.4 ± 1.9def 41.0 ± 5.3a 0.371 9 ± 0.001 3g FCR36 605.9 ± 43.9de 16.7 ± 2.1bc 36.5 ± 3.6b 0.382 1 ± 0.007 9def FCR25 562.3 ± 29.9f 15.1 ± 1.5ef 37.5 ± 3.9b 0.376 4 ± 0.005 2fg FCR5 587.1 ± 37.0e 16.3 ± 2.8bcde 37.0 ± 5.9b 0.387 4 ± 0.002 1bcd FCR13 469.6 ± 30.9h 13.5 ± 1.9g 35.3 ± 4.8bc 0.411 0 ± 0.002 6a FCR15 638.1 ± 31.9bc 17.4 ± 2.7b 37.3 ± 4.9b 0.381 6 ± 0.005 3def FCR24 610.4 ± 58.4d 15.1 ± 2.2f 41.1 ± 5.3a 0.378 0 ± 0.000 4efg FCR1 708.6 ± 55.4a 17.3 ± 2.6b 42.3 ± 4.8a 0.373 3 ± 0.003 0fg FCR3 559.2 ± 51.5f 16.0 ± 2.9cdef 35.9 ± 6.0bc 0.379 1 ± 0.001 9defg FCR32 544.7 ± 37.6f 16.3 ± 2.1bcd 33.7 ± 4.4c 0.386 0 ± 0.007 9cde WT 650.4 ± 38.8b 16.1 ± 1.9cdef 40.8 ± 4.3a 0.381 0 ± 0.001 3def FCR2 640.1 ± 43.9bc 15.6 ± 2.9cdef 42.6 ± 4.8a 0.395 6 ± 0.008 0b FCR33 609.3 ± 40.5d 16.6 ± 2.0bc 37.2 ± 4.5b 0.385 7 ± 0.000 3cde FCR27 496.8 ± 37.9g 18.5 ± 2.2a 27.2 ± 3.6d 0.394 0 ± 0.005 7bc 表 4 转BpCCR1基因株系树高、地径、胸径及材积多重比较
Table 4 Multiple comparisons of tree height, ground diameter, DBH and volume of BpCCR1 transgenic lines
基因 Gene 株系 Line 树高 Tree height/m 地径 Ground diameter/mm 胸径 DBH/mm 材积 Volume/cm3 正义链 Sense CR13 421.5 ± 21.5a 32.4 ± 1.2ab 16.3 ± 1.2b 400.0 ± 32.2a CR4 402.0 ± 11.5ab 33.2 ± 1.3a 17.7 ± 0.8ab 447.3 ± 30.5a CR15 388.3 ± 26.4abc 30.3 ± 0.9ab 18.0 ± 0.9ab 446.0 ± 39.5a WT 368.8 ± 24.8bc 28.1 ± 1.6b 16.7 ± 0.8b 374.0 ± 20.8a CR11 352.0 ± 10.2cd 30.1 ± 0.2ab 19.6 ± 1.0a 473.3 ± 26.8a CR8 310.5 ± 13.5d 28.3 ± 0.9b 13.8 ± 0.8c 217.6 ± 31.8b 反义链 Antisense FCR2 467.5 ± 14.5a 39.1 ± 1.7a 25.1 ± 1.4a 993.4 ± 41.4a FCR11 460.7 ± 16.2ab 36.1 ± 2.9abc 23.8 ± 0.6a 889.3 ± 33.8b FCR8 440.5 ± 12.5abc 38.4 ± 2.5a 20.0 ± 1.2b 612.6 ± 28.9c FCR36 432.5 ± 16.5bc 31.7 ± 1.7cde 17.7 ± 1.0cd 483.5 ± 40.8de FCR33 420.3 ± 6.7cd 33.4 ± 0.5bcd 19.7 ± 0.5b 571.3 ± 20.4cd FCR27 410.0 ± 10.0cd 37.5 ± 2.2ab 20.5 ± 1.3b 597.4 ± 47.8c FCR32 396.0 ± 6.0de 37.1 ± 0.6ab 18.8 ± 0.0bc 489.6 ± 4.9de FCR5 390.7 ± 17.8def 29.6 ± 2.5de 16.9 ± 0.7cde 398.3 ± 27.4ef FCR1 390.5 ± 12.5def 30.2 ± 0.8de 16.7 ± 0.6de 391.6 ± 21.4ef FCR15 389.0 ± 0.0def 30.5 ± 0.0de 17.0 ± 0.0cde 400.9 ± 0.0ef FCR24 373.0 ± 7.0ef 34.3 ± 1.0abcd 17.8 ± 1.3cd 421.6 ± 38.1ef WT 368.8 ± 24.8ef 28.1 ± 1.6ef 16.7 ± 0.8de 374.0 ± 40.8f FCR3 356.7 ± 10.8f 23.9 ± 1.7f 11.9 ± 0.6g 191.1 ± 8.6g FCR25 310.0 ± 5.0g 30.4 ± 2.1de 15.5 ± 0.5ef 268.5 ± 11.8g FCR13 306.0 ± 36.1g 31.5 ± 1.3cde 14.3 ± 1.6f 233.9 ± 43.2g 表 5 特征根及标准化特征向量
Table 5 Characteristic roots and standardized eigenvectors
主成分
Main component特征根
Characteristic root方差贡献率
Variance contribution rate/%累积贡献率
Cumulative contribution rate/%性状
Trait因子载荷1
Factor loading 1特征向量1
Standardized eigenvector 1因子载荷2
Factor loading 2特征向量2
Standardized eigenvector 2Y1 2.852 47.526 47.526 树高
Tree height (X1)0.928 0.549 5 − 0.003 − 0.002 5 Y2 1.402 23.373 70.900 胸径
DBH (X2)0.927 0.548 9 0.278 0.234 8 Y3 0.929 15.482 86.382 材积
Volume (X3)0.949 0.561 9 0.275 0.232 3 Y4 0.602 10.038 96.420 总木质素含量
Total lignin content (X4)0.237 0.140 3 − 0.766 − 0.646 9 Y5 0.203 3.391 99.811 纤维长/宽
Fiber length/
width (X5)− 0.155 − 0.091 8 0.404 0.341 2 Y6 0.011 0.189 100.000 密度
Density (X6)− 0.386 − 0.228 6 0.706 0.596 3 表 6 参试株系综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive evaluation of each tested lines
株系
Line标准分 Standardized value Y1 排名
RankY2 排名
RankX1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 WT − 0.442 3 − 0.375 1 − 0.453 0 − 0.889 7 0.123 7 − 0.369 8 − 0.755 1 16 0.205 0 8 CR4 0.273 2 − 0.064 3 − 0.088 2 − 0.298 7 0.982 9 − 0.288 1 − 0.001 0 9 0.320 5 7 CR8 − 1.698 6 − 1.323 3 − 1.230 8 − 1.636 2 2.334 0 2.859 3 − 3.448 8 20 2.967 4 1 CR11 − 0.804 3 0.553 2 0.040 8 − 0.733 7 0.933 9 − 0.223 6 − 0.253 0 14 0.801 3 4 CR13 0.693 4 − 0.520 5 − 0.323 7 − 0.056 6 0.854 6 0.482 0 − 0.283 1 15 0.416 5 6 CR15 − 0.021 3 0.037 8 − 0.094 8 0.095 1 1.150 5 − 1.545 1 0.216 7 8 − 0.603 4 13 FCR1 0.025 4 − 0.372 2 − 0.365 3 0.195 1 0.381 9 − 0.951 9 − 0.185 7 13 − 0.735 9 14 FCR2 1.684 7 2.323 2 2.627 7 − 1.097 7 0.432 9 0.735 1 3.315 7 1 2.447 9 2 FCR3 − 0.703 7 − 1.912 8 − 1.362 6 − 0.147 3 − 0.748 8 − 0.510 7 − 2.037 5 18 − 1.228 6 18 FCR5 0.029 0 − 0.326 5 − 0.332 0 0.854 3 − 0.559 7 − 0.719 1 − 0.014 3 10 − 1.326 2 20 FCR8 1.102 8 0.672 5 0.734 0 1.449 5 0.154 5 − 1.054 0 1.817 7 3 − 1.187 8 16 FCR11 1.537 4 1.911 1 2.109 8 1.897 7 0.189 5 0.142 9 3.295 5 2 − 0.142 8 11 FCR13 − 1.795 6 − 1.153 0 − 1.149 7 0.438 4 − 0.861 9 1.909 3 − 2.561 4 19 0.027 6 10 FCR15 − 0.007 0 − 0.286 7 − 0.319 3 0.370 0 − 0.497 0 − 0.321 9 − 0.169 5 11 − 0.742 4 15 FCR24 − 0.351 8 − 0.020 7 − 0.216 0 0.170 4 0.163 6 − 0.596 3 − 0.180 8 12 − 0.464 2 12 FCR25 − 1.709 4 − 0.776 8 − 0.977 4 1.113 5 − 0.469 8 0.119 4 − 1.742 8 17 − 1.214 6 17 FCR27 0.445 6 0.822 4 0.658 3 − 1.409 0 − 2.277 5 0.615 7 0.936 8 4 0.846 5 3 FCR32 0.143 9 0.277 5 0.122 0 − 0.631 6 − 1.131 0 0.010 7 0.312 7 7 0.122 2 9 FCR33 0.668 3 0.590 3 0.528 3 − 1.099 3 − 0.523 0 − 0.009 8 0.884 1 5 0.786 5 5 FCR36 0.930 4 − 0.056 2 0.091 9 1.415 8 − 0.633 3 − 0.284 0 0.853 8 6 − 1.295 5 19 -
[1] 路瑶, 魏贤勇, 宗志敏, 等. 木质素的结构研究与应用[J]. 化学进展, 2013, 25(5):838−858. Lu Y, Wei X Y, Zong Z M, et al. Structural investigation and application of lignins[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2013, 25(5): 838−858.
[2] 胡可, 严雪锋, 栗丹, 等. 沉默CCR和CAD基因培育低木质素含量转基因多年生黑麦草[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5):72−83. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130509 Hu K, Yan X F, Li D, et al. Genetic improvement of perennial ryegrass with low lignin content by silencing genes of CCR and CAD[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(5): 72−83. doi: 10.11686/cyxb20130509
[3] Chen H C, Song J, Wang J P, et al. Systems biology of lignin biosynthesis in Populus trichocarpa: heteromeric 4-coumaric acid: coenzyme A ligase protein complex formation, regulation, and numerical modeling[J]. Plant Cell, 2014, 26(3): 876−893. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.119685
[4] 高原, 陈信波, 张志扬. 木质素生物合成途径及其基因调控的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2007(2):47−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5464.2007.02.011 Gao Y, Chen X B, Zhang Z Y. Advances in research on lignin biosynthesis and its molecular regulation[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2007(2): 47−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5464.2007.02.011
[5] 国增超, 侯静, 郭炜, 等. 簸箕柳材性性状株内纵向变异的趋势分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(5):149−152. Guo Z C, Hou J, Guo W, et al. Variation trends of wood property along stem in Salix suchowensis[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2014, 38(5): 149−152.
[6] Lacombe E, Hawkins S, Van D J, et al. Cinnamoyl CoA reductase, the first committed enzyme of the lignin branch biosynthetic pathway: cloning, expression and phylogenetic relationships[J]. The Plant Journal, 1997, 11(3): 429−441. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11030429.x
[7] 李波, 梁颖, 柴友荣. 植物肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶(CCR)基因的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2006, 4(增刊1):55−65. Li B, Liang Y, Chai Y R. Achievements in research on plant cinnamoyl-CoA reductase(CCR) genes[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2006, 4(Suppl.1): 55−65.
[8] 李魏, 谭晓风, 陈鸿鹏. 植物肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶基因的结构功能及应用潜力[J]. 经济林研究, 2009, 27(1):7−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2009.01.002 Li W, Tan X F, Chen H P. Structure, function and application potential of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR) gene in plant[J]. Nonwood Forest Research, 2009, 27(1): 7−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2009.01.002
[9] Wadenback J, Arnold S V, Egertsdotter U, et al. Lignin biosynthesis in transgenic Norway spruce plants harboring an antisense construct for cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR)[J]. Transgenic Research, 2008, 17(3): 379−392. doi: 10.1007/s11248-007-9113-z
[10] Rest V D B. Down-regulation of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) induces dramatic changes in soluble phenolic pools[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(6): 1399−1411. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erj120
[11] 秋增昌, 王海毅. 木质素的应用研究现状与进展[J]. 西南造纸, 2004, 33(3):29−33. Qiu Z C, Wang H Y. Current status and progress of application research of lignin[J]. Southwest Pulp and Paper, 2004, 33(3): 29−33.
[12] 刘宇, 徐焕文, 尚福强, 等. 16年生白桦种源变异及区划[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(9):48−56. Liu Y, Xu H W, Shang F Q, et al. Variation and zoning of 16-year-old Betula platyphylla provenance[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2016, 52(9): 48−56.
[13] 韦睿. 白桦木质素BpCCR1基因的克隆及遗传转化[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2012. Wei R. Gene clone and genetic transformation of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase gene 1 in Betula platyphylla[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2012.
[14] 王朔, 黄海娇, 杨光, 等. 转基因白桦杂种T1代的生长发育及AP1基因的遗传分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(9):1−7. Wang S, Huang H J, Yang G, et al. Growth and developmental analysis of T1 generation from BpAP1 transgenic birch[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(9): 1−7.
[15] 黄海娇, 李慧玉, 姜静. BpAP1转基因白桦中开花相关基因的时序表达[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(1):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.001 Huang H J, Li H Y, Jiang J. Quantitative expression analysis of several flowering-related genes in BpAP1 transgenic birch (Betula platyphylla × Betula pendula)[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2017, 45(1): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2017.01.001
[16] Lu S, Li Q, Wei H, et al. Ptr-miR397a is a negative regulator of laccase genes affecting lignin content in Populus trichocarpa[J]. PNAS, 2013, 110(26): 10848−10853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308936110
[17] Yeh T F, Yamada T, Capanema E, et al. Rapid screening of wood chemical component variations using transmittance near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(9): 3328−3332. doi: 10.1021/jf0480647
[18] 刘超逸, 刘桂丰, 方功桂, 等. 四倍体白桦木材纤维性状比较及优良母树选择[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(2):9−15. Liu C Y, Liu G F, Fang G G, et al. Comparison of tetraploid Betula platyphylla wood fiber traits and selection of superior seed trees[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(2): 9−15.
[19] 穆怀志, 刘桂丰, 姜静, 等. 白桦半同胞子代生长及木材纤维性状变异分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2009, 37(3):1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2009.03.001 Mu H Z, Liu G F, Jiang J, et al. Variations of growth and fiber properties of half-sib family progeny of Betula platyphylla[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2009, 37(3): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2009.03.001
[20] 冯德君, 张文辉, 赵泾峰, 等. 陕西不同天然类型栓皮栎木材的构造与性质[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(8):93−98. Feng D J, Zhang W H, Zhao J F, et al. Structures and properties of different natural Quercus variabilis woods in Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(8): 93−98.
[21] 宁坤, 刘笑平, 林永红, 等. 白桦子代遗传变异与纸浆材优良种质选择[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(1):39−46. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2015.01.008 Ning K, Liu X P, Lin Y H, et al. Germplasm selection of the progeny genetic variation and superior pulpwood of Betula platyphylla[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(1): 39−46. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2015.01.008
[22] 刘宇, 徐焕文, 尚福强, 等. 3个地点白桦种源试验生长稳定性分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(5):50−57. Liu Y, Xu H W, Shang F Q, et al. Growth stability of Betula platyphylla provenances from three sites[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(5): 50−57.
[23] 蔺占兵. 小麦肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶(CCR)基因的分离和功能分析[D]. 北京: 中国科学院植物研究所, 2003. Lin Z B. Cloning and functonal analysis of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase(CCR) gene from Triticum aesticum L. cv. H4564[D]. Beijing: Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003.
[24] Xu W, Xu H, Li K, et al. The R-loop is a common chromatin feature of the Arabidopsis genome[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(9): 704−714. doi: 10.1038/s41477-017-0004-x
[25] 谢兆辉. 天然反义转录物及其调控基因的表达机制[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(2):122−128. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4386.2010.02.014 Xie Z H. Natural antisense transcript and its mechanism of gene regulation[J]. Hereditas, 2010, 32(2): 122−128. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4386.2010.02.014
[26] Katayama S, Tomaru Y, Kasukawa T, et al. Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome[J]. Science, 2005, 309: 1564−1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1112009
[27] 毕延震, 黄捷, 姜黎. 天然反义RNA (NATs): 基因表达的重要调控分子[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2010, 26(9):788−795. Bi Y Z, Huang J, Jiang L. Natural antisense transcripts (NATs): important regulatory molecules upon gene expression[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 26(9): 788−795.
[28] Leple J, Dauwe R, Morreel K, et al. Down regulation of cinnamoyl-coenzyme a reductase in poplar: multiple-level phenotyping reveals effects on cell wall polymer metabolism and structure[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(11): 3669−3691. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054148
[29] Prashant S, Sunita M S, Pramod S, et al. Down-regulation of Leucaena leucocephala cinnamoyl CoA reductase (LlCCR) gene induces significant changes in phenotype, soluble phenolic pools and lignin in transgenic tobacco[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2011, 30(12): 2215−2231. doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1127-6
[30] 安培钧, 邱荣, 刘丽萍. 尤金杨等九种杨树木材纤维形态值及对制浆造纸适宜性的研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 1985, 3(2):14−31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.1985.02.002 An P J, Qiu R, Liu L P. Research on wood-fibre morphological value of nine kinds of populars-Populus × euramericana (Dode) Guinier cv " Eugenei” etc. and their suitability of paper-pulp for paper-making[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 1985, 3(2): 14−31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.1985.02.002
[31] 任建中, 刘长青, 汪清锐, 等. 杨树纸浆材优良无性系选择方法的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(4):25−29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2003.04.006 Ren J Z, Liu C Q, Wang Q R, et al. Methods to select superior clones of poplar pulpwood[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2003, 25(4): 25−29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2003.04.006
[32] 刘宇, 徐焕文, 姜静, 等. 基于种子活力及苗期生长性状的白桦四倍体半同胞家系初选[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(2):74−80. Liu Y, Xu H W, Jiang J, et al. Family selection of birch tetraploid half-sibling based on seed vigor and seedling growth traits[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(2): 74−80.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 莫崇杏,董明亮,李荣生,余纽,郑显澄,杨锦昌. 米老排杂交子代苗期生长性状遗传变异及选择. 森林与环境学报. 2023(05): 555-560 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Shuchun Li,Jiaqi Li,Yanyan Pan,Xiange Hu,Xuesong Nan,Dan Liu,Yue Li. Variation analyses of controlled pollinated families and parental combining ability of Pinus koraiensis. Journal of Forestry Research. 2021(03): 1005-1011 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 潘艳艳,许贵友,董利虎,王成录,梁德洋,赵曦阳. 日本落叶松全同胞家系苗期生长性状遗传变异. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(02): 14-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 秦光华,宋玉民,乔玉玲,于振旭,彭琳. 旱柳苗高年生长与气象因子的灰色关联度. 东北林业大学学报. 2019(05): 42-45+51 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李峰卿,陈焕伟,周志春,楚秀丽,徐肇友,肖纪军. 红豆树优树种子和幼苗性状的变异分析及优良家系的初选. 植物资源与环境学报. 2018(02): 57-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张素芳,张磊,赵佳丽,张莉,张含国. 长白落叶松小RNA测序和其靶基因预测. 北京林业大学学报. 2016(12): 64-72 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: