Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance of clones of Fraxinusin spp. seedling stage under salt stress
-
摘要:目的本研究通过对9个白蜡无性系的耐盐性进行综合评价,为探究白蜡无性系的耐盐能力,选育优良耐盐林木品种,利用生物措施提高土地生产力提供理论依据。方法以1年生白蜡无性系扦插盆栽苗为试验材料,对9个无性系在不同盐胁迫条件下(0、2、4、6、8 g/L)的生长与生理指标的变化进行研究。结果在盐胁迫下,各无性系的生长受到明显抑制,并且随着NaCl质量浓度增大,无性系的生长指标(苗高增量、地径增量、生物量累积)都呈现下降的趋势,无性系YL的下降幅度最为平缓;9个无性系中的叶绿素含量也随着盐质量浓度升高而下降,YL与其他无性系存在显著性差异(P < 0.05)。盐胁迫导致无性系体内细胞膜透性与MDA含量增大,但在同一盐质量浓度时,无性系YL与Y3低于其他无性系;当盐胁迫逐步增大时,脯氨酸、可溶性糖含量因无性系品种不同而呈现不同的趋势,其中在YL、L5、QB、L2、Y3无性系中一直处于增长状态,在其余4种无性系中呈现单峰曲线,最高值出现在盐质量浓度为6 g/L的处理中;SOD酶活性呈现先升高后下降的趋势,无性系YL酶活性最高,与其他无性系有显著性差异(P < 0.05)。结论本试验采用主成分分析法对9个白蜡无性系的耐盐性进行综合评价,耐盐能力大小依次为YL、Y3、L5、QB、JJ、JN11、HX、L2、J10,试验结果为白蜡耐盐无性系的选育提供理论基础和育种材料。Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to explore the salt tolerance of ash tree clones, breed excellent salt tolerant of clones, and improve land productivity through biological measures.MethodCutting potted seedlings of 1-year-old ash clones were taken as materials, and their growth and physiological index of 9 clones under different salt stress conditions (0, 2, 4, 6, 8 g/L) were studied.ResultUnder salt stress, the growth of clones was significantly inhibited, and with the increase of NaCl concentration, the growth indicators (seedling height increment, ground diameter increment, biomass accumulation) of clones showed a decreasing trend, and the decline of ‘YL’ of clones was the slowest; the chlorophyll content of nine clones also decreased with the increase of salt concentration, and there was significant difference between saline wax and other clones (P < 0.05). Under salt stress, the cell membrane permeability and MDA content of clones increased, but at the same salt concentration, ‘YL’ and ‘Y3’ of clones were lower than those of other clones; when salt stress increased gradually, the contents of proline and soluble sugar showed different trends according to different varieties. Among them, osmotic regulators in ‘YL’,‘L5’, ‘QB’, ‘L2’ and ‘Y3’ had been increasing, the content of the other four clones showed a single peak curve, and the highest value reached 6 g/L. SOD activity increased first and then decreased. Its value of ‘YL’ was the highest, which was significantly different from that of other clones (P < 0.05).ConclusionPrincipal component analysis was used to evaluate the salt tolerance of nine ash tree clones. The salt tolerance of nine ash tree clones was ordered as follows: ‘YL’, ‘Y3’, L5’, QB, JJ, JN11, HX, ‘L2’ and‘J10’. The results provided are not only theoretical basis but also breeding materials for the breeding of ash tree salt tolerant clones.
-
Keywords:
- ash tree /
- clone /
- salt stress /
- salt tolerance
-
我国已有盐碱土面积为3.4 × 107 hm2,不包括潜在盐碱土面积1 700万hm2[1-2],而且在山东、河北、东北、江苏等地广泛分布。盐渍土中有较高的含盐量,不仅严重制约农作物生产,更直接影响植被生长以及整体生态环境质量。尤其随着经济迅速发展,土地资源减少、耕地面积减小问题日益增长,盐渍化土地的开发利用可有效增加农林业用地,同时改善生态环境[3-4]。由于适宜生活在盐渍土的植物非常有限,因此,选育优良耐盐林草品种,对通过生物措施提高土地生产力具有战略意义。
白蜡树为木犀科(Oleaceae)白蜡属(Fraxinus)的总称,20世纪前期由美国向济南引进,后期在天津等地大规模推广,是北方常用的造林树种,在防护林与城市绿化中都有广泛应用,具有较高的生态和经济价值。白蜡有适应高Na+浓度的能力,在盐胁迫下可以吸收Na+[5],且研究发现其体内含有泌盐腺体,叶片内栅栏组织发达[6],这些性状可能与耐盐性有关。植物耐盐性与植物体内独特的组织结构有关,且更大可能是与复杂的生理调节机制相关,如矿物质的吸收、有机物的积累、蛋白质的合成等,而脯氨酸、可溶性糖、无机离子、甜菜碱等作为渗透调节物质均参与了植物体的生理调节机制,研究这些渗透调节物质在盐胁迫条件下的变化规律,有助于揭示植物的耐盐机理,为选择较强耐盐能力的植物新品种提供依据。
近年对白蜡的研究较多也备受重视的方向由以往的选择育种、栽培技术改良向生物技术与抗逆性方向发展,但对于白蜡无性系的耐盐机理研究较少,报道不多。因此,本试验以9个白蜡无性系为材料,研究其在盐胁迫环境下的生长指标变化规律与生理特性,探讨9个白蜡无性系抗盐能力与耐盐机理,为选择较为抗盐的白蜡无性系提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验材料为9个无性系白蜡的一年生扦插苗,分别为京10(Fraxinus velutina ‘Jing10’,J10)、鲁蜡2号(Fraxinus velutina ‘Lula2’,L2)、鲁蜡5号(Fraxinus pennsylvanica ‘Lula5’,L5)、盐蜡(Fraxinus velutina ‘Yanla’,YL)、盐3(Fraxinus velutina‘Yan3’,Y3)、胶南11(Fraxinus velutina ‘Jiaonan11’,JN11)、金箭(Fraxinus velutina ‘Jinjian’,JJ)、华雄(Fraxinus velutina ‘Huaxiong’,HX)、青碧(Fraxinus velutina ‘Qinbi’,QB)。幼苗来源于山东省林业科学研究院饮马泉苗圃基地,该基地处于半湿润温带大陆性季风气候区,季风明显,四季分明,雨热同期,年平均气温13.8 ℃,7月平均气温最高为27.2 ℃,年平均降水量685 mm,年日照时数1 870.9 h。
于2018年3月将扦插苗种植于塑料盆中,每盆定植1株,花盆规格是30 cm × 25 cm(高 × 口径)。盆栽内基质是由大地土壤和育苗基质1∶1(体积比)混合均匀,每盆土壤质量约为10 kg。植株选择生长健壮,根系完整的1年生扦插苗,地径约在4.5 ~ 7.6 cm内,无失水损伤等问题。于2018年7月选取长势基本一致的苗木,每个无性系25株,置于苗圃基地的遮雨棚下进行试验。
1.2 试验方法
试验采用随机区组设计,设置5个盐分(NaCl)质量浓度梯度进行处理,NaCl质量浓度分别为0(对照)、2、4、6、8 g/L,每个质量浓度梯度设5个重复。试验设置对照组作为处理组数据的参考,指标增长率为实验组与对照组的比值。试验开始前对每株无性系做控水处理(苗木浇透后自然落干),自7月23日起每隔10 d在各处理组盆栽中浇1.5 L对应浓度的NaCl溶液(2、4、6、8 g/L),对照盆栽中施相等体积的纯净水,盘底收集渗出液再次浇灌,期间所有盆栽浇纯净水直至略有水分渗出托盘,以防止水分流失。胁迫进行60 d后取样,观察植株形态,每个处理随机选取相同部位的功能叶,样品分别放入自封袋置于冰壶中带回实验室,剪碎样品进行生长与生理指标测定。
1.3 指标测定
1.3.1 生长指标
分别测定盐胁迫处理前的无性系苗高(H0)、地径(B0),NaCl胁迫后的苗高(H)、地径(B),(H − H0)与(B − B0)即为植株生长指标苗高和地径的增长量。胁迫前每种无性系选取长势相同的参照株用去离子水将整个植株表面清洗干净,迅速用吸水纸擦干后放于105 ℃烘箱中,待无性系植株烘干至恒重时取出称其质量,试验结束后测定参加试验无性系的质量(不含落叶),试验末质量减去试验始质量为胁迫间生物累积量。
1.3.2 生理指标
叶绿素采用乙醇萃取法测定[7];细胞膜透性用DDS-12A型电导率仪测定;采用氮蓝四唑(NBT)还原法测定超氧化物歧化酶活性(SOD)[8];测丙二醛(MDA)含量采用硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)法;并分别采用茚三酮法与蒽酮法测定脯氨酸含量和可溶性糖含量[9]。
1.4 数据处理
试验数据运用Excel进行整理计算以及图表绘制,用SPSS 21.0软件单因素方差分析、多重比较(Duncan’s法)检验差异显著性。采用数据间相关性以及主成分分析的方法,最后得到各无性系主成分值(Zi):
Zi=Lij×Xn (1) 式中:Lij为主成分荷载,i表示数据特征,j表示数据中样本的个数;Xn为每一水平下的试验指标,其中n表示因子数目。最后运用主成分值评价9个无性系在盐胁迫下生理响应差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系苗高增长量的影响
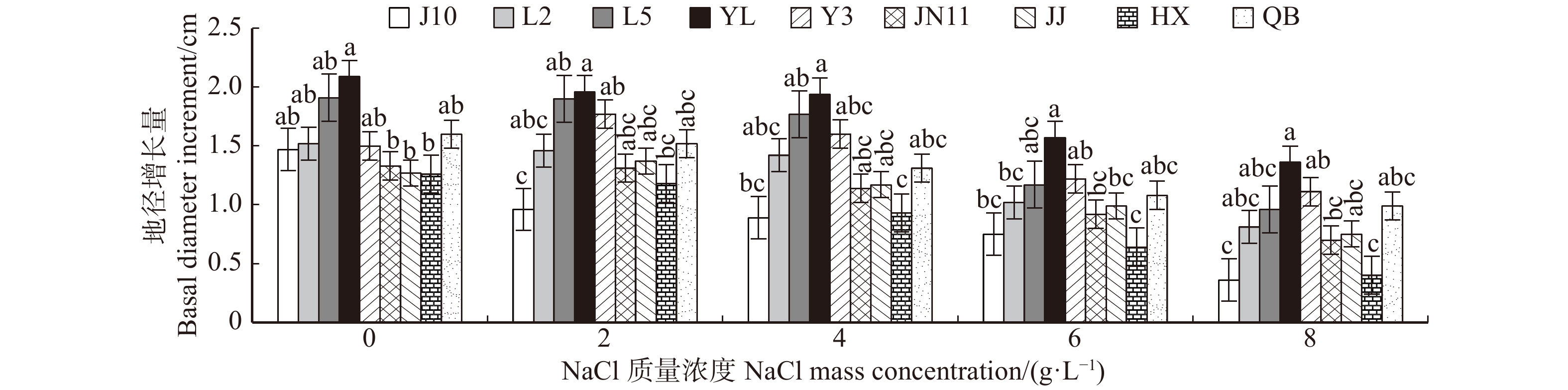
盐胁迫直接影响植株生长。由图1可以发现随着NaCl质量浓度的升高,各无性系苗高增量表现出下降趋势,并且随着质量浓度升高对幼苗的生长抑制越明显。不同无性系苗高增长量在下降程度上有较大差异,在最高盐质量浓度处理下,无性系J10与HX苗高增长量下降明显,与对照相比分别下降了66.8%和55.9%;6 g/L盐质量浓度下,HX、JJ、JN11、J10 4个无性系下降幅度较为明显;低盐质量浓度(2 g/L)时,各无性系增长量与对照相差不大。无性系YL在各盐质量浓度处理下苗高增长量一直保持最高水平,受盐胁迫影响小,总降幅为20.67%。
![]() 图 1 NaCl胁迫对苗高增长量的影响J10、L2、L5、YL、Y3、JN11、JJ、HX、QB分别代表京10、鲁蜡2号、鲁蜡5号、盐蜡、盐3、胶南11、金箭、华雄、青碧。不同小写字母表示同一处理不同无性系间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。J10, L2, L5, Y3, JN11, YL, JJ, HX, QB represent Fraxinus velutina ‘Jing10’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Lula2’、Fraxinus pennsylvanica ‘Lula5’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yanla’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yan3’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jiaonan11’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jinjian’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Huaxiong’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Qinbi’. Different letters within the same column indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below.Figure 1. Effects of NaCl stress on seedling height growth
图 1 NaCl胁迫对苗高增长量的影响J10、L2、L5、YL、Y3、JN11、JJ、HX、QB分别代表京10、鲁蜡2号、鲁蜡5号、盐蜡、盐3、胶南11、金箭、华雄、青碧。不同小写字母表示同一处理不同无性系间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。J10, L2, L5, Y3, JN11, YL, JJ, HX, QB represent Fraxinus velutina ‘Jing10’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Lula2’、Fraxinus pennsylvanica ‘Lula5’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yanla’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yan3’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jiaonan11’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jinjian’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Huaxiong’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Qinbi’. Different letters within the same column indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below.Figure 1. Effects of NaCl stress on seedling height growth2.2 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系地径增长量的影响
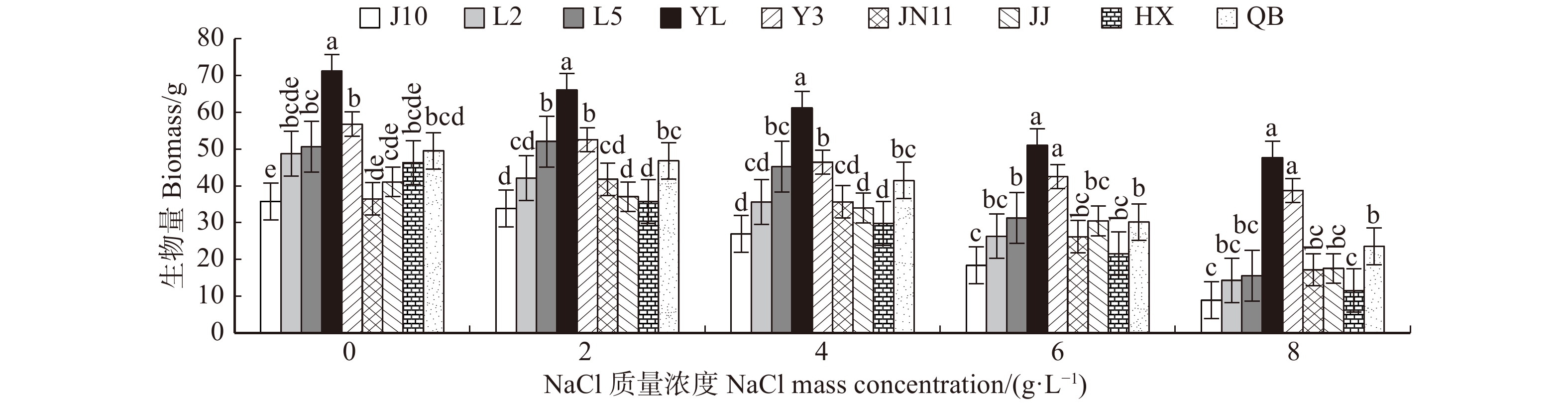
9个无性系的地径增长量随着NaCl质量浓度增加总体呈现下降趋势(图2)。各胁迫处理下无性系YL的地径增长量最大。在最高NaCl质量浓度胁迫下J10与HX的地径增长量分别为对照组的24.4%与31.7%,与YL存在显著性差异(P < 0.05),其他无性系差异不明显。
2.3 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系生物量的影响
生物量是盐胁迫下植株最直接的反映结果。如图3所示,各无性系在低盐(2 g/L)处理下与对照组相比,生物量累积值变化不明显,在6 g/L盐质量浓度处理下无性系植株总体生物累积量有明显的下降。在最高盐质量浓度(8 g/L)处理下,无性系J10的生物量累积值只有对照组的24.7%,而无性系YL与Y3累积量与对照组的比值分别为66.9%、68.1%,表现出显著性差异(P < 0.05)。在整个试验中,YL生物量累积值一直处于最高水平,Y3次之,两者之间无显著性差异,都表现出耐盐性。
2.4 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系细胞膜透性的影响
细胞膜透性增大表明质膜受到伤害的程度较高,如表1所示,各无性系随着盐质量浓度增大电导率均呈上升趋势。在对照组中,各无性系相对电导率差异性不显著;在低质量浓度(2 g/L)下总体平缓增长,QB、J10、HX 3个无性系较其他无性系而言增长幅度较大;在6 g/L质量浓度处理下总体增幅变大,最高质量浓度处理下无性系J10与HX的增幅较高,分别为134%与108%,无性系Y3增幅小,膜透性较低,与以上2个无性系有显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
表 1 NaCl胁迫下各无性系细胞膜透性Table 1. Effects of NaCl stress on membrane permeability of clones无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 34.25 ± 7.23abc 39.62 ± 1.28b 44.49 ± 3.11bc 49.22 ± 3.3b 53.21 ± 5.38cde YL 33.52 ± 1.07bc 36.52 ± 1.08b 38.30 ± 1.35d 40.63 ± 1.87bc 42.89 ± 2.61e L5 35.00 ± 0.55ab 47.34 ± 0.83a 51.33 ± 1.78ab 56.00 ± 2.72a 60.25 ± 4.42bcd J10 30.41 ± 7.72c 45.92 ± 9.68a 54.07 ± 12.23a 61.87 ± 15.01a 71.36 ± 19.94a QB 36.69 ± 1.12a 49.63 ± 1.96a 53.88 ± 3.13a 58.92 ± 4.59a 64.00 ± 7.08abc JN11 27.46 ± 0.79c 30.80 ± 0.88c 35.00 ± 3.08d 39.55 ± 3.26c 44.21 ± 4.75e JJ 33.60 ± 0.82bc 46.56 ± 2.93a 51.18 ± 3.38abc 54.23 ± 3.73a 57.97 ± 5.10bcd HX 32.19 ± 1.19bc 49.38 ± 4.34a 55.38 ± 6.84a 61.47 ± 9.84a 67.18 ± 10.92ab Y3 27.66 ± 1.22c 40.52 ± 2.97b 43.87 ± 2.46cd 46.67 ± 3.80b 49.85 ± 2.24de 注:同列中字母不同表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: different letters within the same column indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below. 2.5 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系MDA含量的影响
细胞膜受破坏程度同样可以用MDA含量表示,从表2中可以看出其增长趋势与细胞膜透性大体一致。与对照相比,在最高盐质量浓度处理下所有无性系的MDA含量均增加,J10叶片中含量最高,多重比较分析发现与其他无性系有显著性差异(P < 0.05),膜脂过氧化程度高。在8 g/L质量浓度处理下,JJ无性系MDA含量最低,且QB、JJ、Y3无性系含量出现不同程度的上升,与6 g/L质量浓度下相比分别上升了23.81%、21.39%、3.96%,可能是无性系体内酶活性升高减轻了细胞膜的氧化程度。
表 2 NaCl胁迫下各无性系MDA含量Table 2. MDA content of clones under NaCl stress无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 1.84 ± 0.26abc 1.9 ± 0.24ab 2.21 ± 0.49ab 2.42 ± 0.23ab 2.75 ± 0.18bc YL 1.43 ± 0.19bc 1.57 ± 0.4b 1.8 ± 0.36b 2.01 ± 0.19b 2.19 ± 0.49cd L5 1.8 ± 0.18abc 2.21 ± 0.1ab 2.41 ± 0.28ab 2.51 ± 0.43ab 2.91 ± 0.71bc J10 2.32 ± 0.32a 2.38 ± 0.41a 2.71 ± 0.6a 3.11 ± 0.51a 3.69 ± 0.33a QB 1.39 ± 0.26c 1.81 ± 0.44ab 2.21 ± 0.49ab 2.52 ± 0.46ab 1.92 ± 0.4d JN11 1.61 ± 0.21bc 2.05 ± 0.42ab 2.13 ± 0.46ab 2.42 ± 0.51ab 2.49 ± 0.81bcd JJ 1.67 ± 0.41bc 2.05 ± 0.42ab 2.23 ± 0.45ab 2.29 ± 0.63b 1.8 ± 0.53d HX 2.02 ± 0.51ab 2.16 ± 0.81ab 2.37 ± 0.81ab 2.75 ± 0.66ab 3.11 ± 0.47ab Y3 1.64 ± 0.84bc 1.88 ± 0.37ab 2.29 ± 0.64ab 2.02 ± 0.76b 1.94 ± 0.68d 2.6 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系叶绿素含量的影响
NaCl胁迫会造成白蜡无性系叶片中叶绿素含量的下降,不同无性系下降程度不同(表3)。盐胁迫影响叶细胞超微结构中的细胞膜系统与叶细胞器,其中叶绿体最敏感。以无性系YL为例,在不同盐质量浓度处理下叶绿素含量均显著高于其他无性系,但与对照相比分别下降19%、26%、30%、37%。无性系J10,在不同盐质量浓度处理下叶绿素含量较低,与对照相比分别下降了8%、23%、35%、51%,在盐质量浓度达到较高水平时,下降幅度增大。
表 3 NaCl胁迫下各无性系叶绿素含量Table 3. Chlorophyll content of clones under NaCl stress无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 8.35 ± 1.17def 7.03 ± 1.28cde 6.48 ± 0.94bcd 5.64 ± 2.53b 4.93 ± 2.77bc YL 12.02 ± 1.45a 9.68 ± 0.56a 8.82 ± 1.00a 8.33 ± 1.22a 7.51 ± 1.64a L5 9.41 ± 0.13bc 9.01 ± 1.12ab 7.69 ± 0.62ab 6.53 ± 0.87ab 5.65 ± 0.72abc J10 7.59 ± 0.50f 6.91 ± 0.88cde 5.78 ± 0.68cd 4.92 ± 2.16b 3.69 ± 1.6c QB 8.85 ± 0.34cd 8.46 ± 1.75abc 7.65 ± 1.91ab 6.69 ± 1.63ab 5.58 ± 1.8abc JN11 7.73 ± 0.61ef 6.46 ± 1.48de 6.18 ± 1.87bcd 5.39 ± 1.18b 4.08 ± 0.97bc JJ 8.65 ± 0.65cde 7.9 ± 1.49bcd 6.66 ± 1.56bcd 5.92 ± 2.68b 5.55 ± 2.33abc HX 8.12 ± 0.33def 6.22 ± 1.3e 5.34 ± 0.47d 5.1 ± 1.63b 4.44 ± 1.12bc Y3 10.22 ± 0.52b 8.02 ± 0.9bcd 7.31 ± 1.16abc 6.62 ± 0.98ab 6.05 ± 1ab 2.7 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量的影响
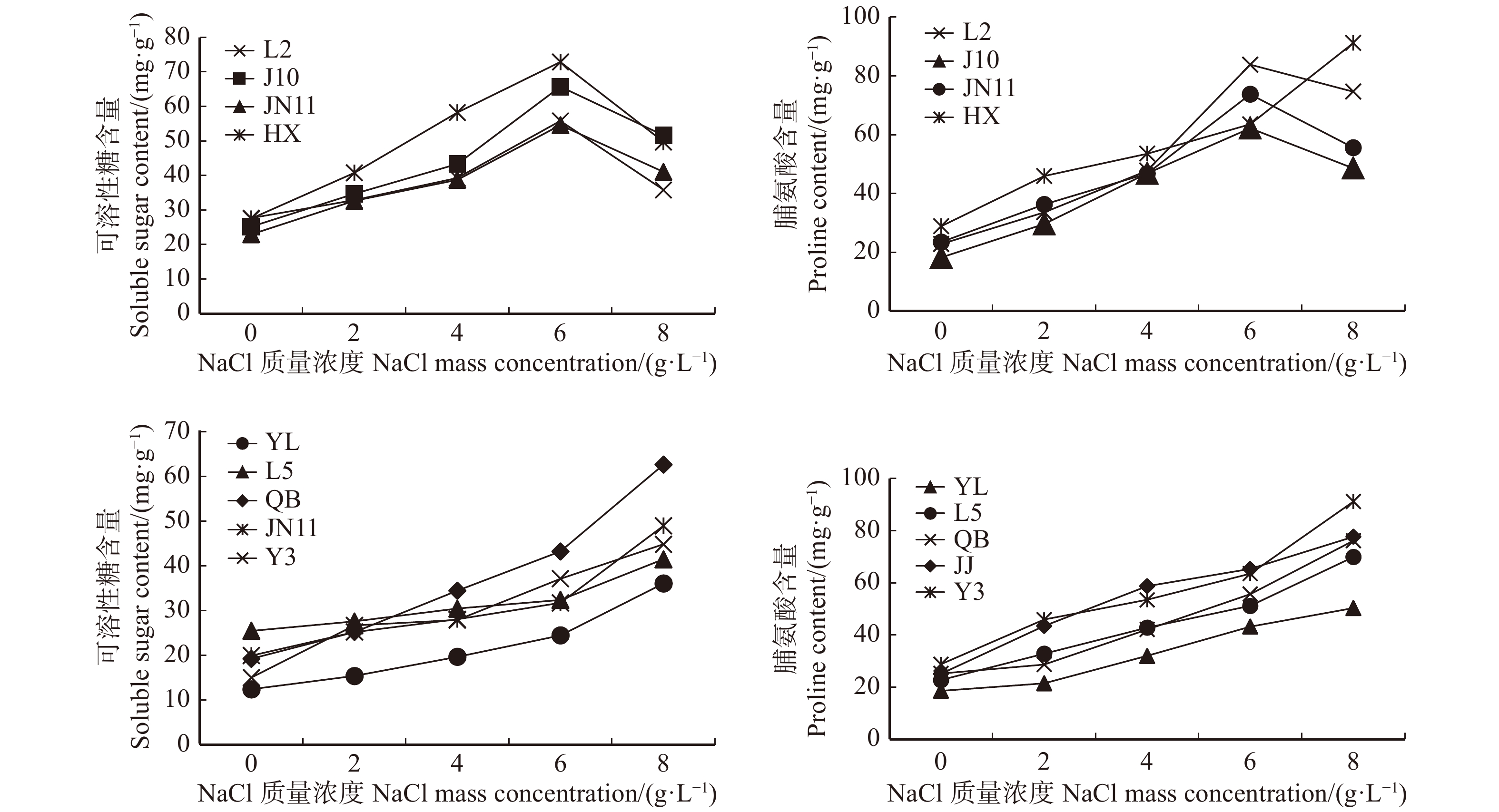
试验显示对照中各无性系脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量变化比较平缓,并无显著差异,当NaCl质量浓度升高时调节物质在植株体内的含量呈正相关增加,在达到一定质量浓度(8 g/L)时,不同白蜡无性系品种有不同的趋势,如图4所示。无性系JJ、J10、JN11、HX在盐质量浓度为6 g/L时,脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量达到最大值,盐质量浓度再升高时含量便出现下降趋势,这可能是由于盐质量浓度过高导致渗透调节物质合成受阻。可溶性糖与脯氨酸在植物体内发挥相同的作用,其变化趋势大体一致,其余5个无性系随NaCl质量浓度升高均呈现上升趋势,YL中与可溶性糖含量均最低,分别是对照的2.9倍与2.7倍。
2.8 NaCl胁迫对白蜡无性系过氧化物酶的影响
9个白蜡无性系中的SOD活性均随盐胁迫增大呈现先增大后减小的趋势(表4),增幅因无性系而异。各无性系在无盐处理时酶活性低,在盐质量浓度为6 g/L时活性最高,增幅最高的是无性系J10(114.5%)与JJ(99.1%),增幅较小的无性系是YL(29.3%),但无性系YL在各盐质量浓度下酶活性均较高,与其他无性系表现出显著差异(P < 0.05)。当盐质量浓度增大到8 g/L时,各无性系SOD酶活性均出现下降趋势,表明6 ~ 8 g/L的盐质量浓度可能是白蜡无性系最高耐盐范围,当超过该范围时,植物通过自身调节不能维持体内机制的平衡。
表 4 NaCl胁迫下各无性系SOD活性Table 4. SOD Activity of clones under NaCl stress无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 83.99 ± 24.68cd 121.06 ± 19.89cd 140.23 ± 7.37cd 167.16 ± 28.4cd 83.45 ± 17.44c YL 234.03 ± 26.86a 244.35 ± 22.03a 292.56 ± 19.37a 304.28 ± 21.34a 241.9 ± 12.16a L5 126.71 ± 24.6bc 185.51 ± 25.11b 170.24 ± 21.33bcd 211.15 ± 7.25bc 115.48 ± 17.42bc J10J 67.72 ± 18.02d 103.07 ± 16.84d 127.32 ± 14.95d 145.27 ± 20.24cd 74.6 ± 22.91c QB 130.01 ± 28.94bc 159.21 ± 29.53bcd 199.07 ± 25.05bc 214.86 ± 36.12bc 158.42 ± 23.05b JN11 118.63 ± 18.99bcd 149.76 ± 12.91bcd 168.7 ± 33.15bcd 182.17 ± 21.41bcd 111.09 ± 18.25bc JJ 110.05 ± 12.18cd 120.79 ± 11.73cd 149.78 ± 26.15cd 162.21 ± 11.65cd 107.76 ± 19.77bc HX 72.43 ± 11.81d 103.17 ± 11.91d 133.1 ± 18.72cd 128.57 ± 17.43d 66.17 ± 27.41c Y3 104.26 ± 5.23b 136.92 ± 15.26bc 158.03 ± 16.65b 174.04 ± 12.59ab 105.59 ± 18.07b 2.9 相关性分析
将9个白蜡无性系在所有盐胁迫处理下的各项指标进行相关性分析,结果如表5。SOD与地径增量、生物量、叶绿素、脯氨酸、可溶性糖、细胞膜透性均呈极显著相关,其中与细胞膜透性和MDA活性呈极显著正相关,其余各指标均为极显著负相关。叶绿素与生长指标呈极显著正相关,并分别与细胞膜透性、MDA与SOD呈极显著负相关;MDA是膜脂过氧化的产物,由表5可以看出,细胞膜透性与MDA之间呈极显著正相关;脯氨酸与可溶性糖是植物中重要的渗透调节物质,两者呈极显著正相关。总体而言,生长指标与生理指标变化紧密联系,受到盐胁迫时,植物不仅表现在生长量下降,还通过调节自身体内各种物质含量以维持机体正常运行。因此,不能将某一指标作为衡量植物耐盐的依据,应将生长指标与生理指标结合分析,对无性系耐盐性进行综合评价。
表 5 NaCl胁迫下白蜡无性系各指标间相关性分析Table 5. Correlation analysis of various indicators of clones to NaCl stress指标 Index X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X1 1 X2 0.883** 1 X3 0.661** 0.644** 1 X4 0.551** 0.552** 0.493** 1 X5 − 0.086 − 0.129 − 0.189* − 0.605** 1 X6 − 0.315* − 0.272 − 0.168 − 0.873** 0.607** 1 X7 − 0.292** − 0.238 − 0.288* − 0.845* − 0.759** 0.873** 1 X8 − 0.538** − 0.459** 0.530** 0.266* − 0.125 0.191 0.349 1 X9 − 0.485* − 0.445** − 0.392** − 0.745** 0.618** − 0.646** − 0.689** 0.867** 1 注:X1. 苗高增量;X2. 地径增量;X3. 生物量;X4. 叶绿素;X5. 细胞膜透性. X6. 丙二醛;X7. 脯氨酸;X8. 可溶性糖;X9. 超氧化物歧化酶活性(SOD)。下同。**表示在P < 0.01水平上差异极显著,*表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著。Notes: X1, height increment; X2, basal diameter increment; X3, biomass; X4, chlorophyll; X5, membrane permeability; X6, MDA; X7, proline; X8, soluble sugar; X9, SOD. The same below. ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01 level, * indicates significant difference at P < 0.05 level. 2.10 主成分分析
在盐胁迫条件下,植物生长与生理指标均有所差异,利用单个指标对植物耐盐性进行评价会产生较大偏差,本研究对各白蜡无性系的9个指标进行主成分分析,结果表明(表6),成分值越大,该指标在评价植物耐盐性方面的可信度更高。在盐质量浓度为6 g/L时,第一主成分与第二主成分累积贡献率为83.822%,可知在此质量浓度下,第一主成分包含的指标为苗高增量、地径增量、生物量、MDA含量、SOD活性、叶绿素含量等,并且这6个指标各成分值均在0.8以上,;第二主成分包含的指标主要是细胞膜透性、可溶性糖等。最高盐胁迫(8 g/L)处理下,第一主成分贡献率为63.318%,前3主成分累计贡献率达到87.371%,大于80%,其中第一主成分的各指标与6 g/L质量浓度下的指标相一致,而第二主成分包含的指标主要有细胞膜透性、脯氨酸、可溶性糖等。综合以上各指标与所对应成分值分析白蜡无性系耐盐强弱的结果通过数值表示(表7)。结果显示,耐盐性强弱依次为YL、Y3、L5、QB、JJ、JN11、HX、L2、J10。
表 6 NaCl胁迫下无性系各指标主成分分析Table 6. Principal component analysis of clones under salt stress测定指标 Measured index 主成分 Principal components 6 g/L 8 g/L Prin1 Prin2 Prin1 Prin2 Prin3 特征值 Characteristic value 6.313 1.231 5.789 1.131 0.764 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 70.142 83.822 64.318 78.884 87.371 苗高增量 Height increment 0.860 0.202 0.902 0.285 0.246 地径增量 Basal diameter increment 0.917 0.157 0.902 0.285 0.246 生物量 biomass 0.885 0.017 0.971 − 0.021 0.125 叶绿素 Chlorophyll 0.973 0.166 0.917 0.126 − 0.028 细胞膜透性 Membrane permeability − 0.629 0.752 − 0.770 0.314 0.261 脯氨酸 Proline − 0.704 − 0.617 − 0.669 0.526 0.213 2 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar − 0.775 0.246 − 0.452 0.753 0.207 超氧化物岐化酶 SOD 0.915 0.032 0.867 0.068 − 0.045 丙二醛 MDA 0.819 − 0.360 0.618 − 0.430 − 0.622 表 7 主成分值Table 7. Principal component value项目 Item L2 YL L5 J10 QB JN11 JJ HX Y3 6 g/L 主成分值 6 g/L Principal component value − 6.711 32.625 11.186 − 3.325 10.766 − 1.189 1.674 − 2.495 11.259 8 g/L 主成分值 8 g/L Principal component value 6.325 35.632 11.980 − 1.233 10.054 9.738 7.510 2.499 12.459 平均值 Average value − 0.193 34.128 11.583 − 2.279 10.410 4.275 4.592 0.002 11.859 排序 Sort 8 1 3 9 4 6 5 7 2 3. 讨 论
植物生长对盐胁迫较为敏感,它直接影响植物的生长发育[10]。胁迫试验后发现,J10、HX无性系出现3 ~ 4片落叶,JN11与JJ无性系叶片出现盐害现象,叶缘发黄扭曲,其他无性系盐害现象不明显。
植株生长指标在盐胁迫时会有显著变化,因此植物的生长量是评价耐盐性最直接的指标[10]。本试验以苗高、地径增长量为生长指标,发现随着NaCl浓度升高,9个白蜡无性系增长量均下降,在低盐质量浓度(2 、4 g/L)下,下降幅度较小;NaCl质量浓度达到6 g/L时,降幅有所增加;在质量浓度为8 g/L时降幅最大,分别达到47.3%、47.5%,与对照组存在明显差异。此结果说明低盐质量浓度对白蜡无性系影响较小,对植株造成的伤害不明显,这与刘海曼等[11]对苗高地径增长量与盐质量浓度关系的研究结果基本一致,即白蜡无性系在2 g/L质量浓度下,与对照相比苗高地径增长量会有一定的下降,但随盐质量浓度增大,下降幅度变化不明显,在8 g/L盐胁迫处理下叶片出现毒害症状。生物量累积量同样作为测定植物生长的指标,反应植株生长变化,并且随盐质量浓度增大,生物量的积累与苗高增长量变化一致。说明高质量浓度盐分直接影响植株生长,无性系Y3在测定的所有生长指标中降幅相对较小,受盐胁迫伤害程度低。
植物生长变化特征还可从叶绿素含量指标中反映,盐胁迫会抑制植物生长过程中的光合作用,从而影响叶绿素含量,造成植物体内叶绿素含量下降[12-13]。本试验中所有无性系植株的叶绿素含量均随盐质量浓度增大而降低,但降幅不一。无性系YL在高盐质量浓度时下降幅度无明显变化,无性系J10随着NaCl质量浓度升高,增幅明显升高,最高盐处理下达到51%,这可能是无性系植株受到盐胁迫,色素系统被破坏导致叶绿素含量急剧减少[14],该结果与李淑娟[15]在研究混合胁迫对白蜡的影响中得到的结果大体一致。
植物细胞膜系统受到盐胁迫时通过影响膜脂与膜蛋白引起膜脂过氧化,使细胞膜透性增大,破坏膜结构从而影响细胞膜正常的功能,使正常接触的细胞壁与质膜变形,造成细胞内电解质外渗,导致电导率的增大[16]。并且随着盐胁迫增加,细胞膜相对透性呈上升趋势[17]。研究表明,NaCl质量浓度越高,相对电导率值增加幅度越大,在8 g/L质量浓度下,细胞膜透性较其他盐质量浓度有显著增大。MDA含量与膜透性显著相关[18],作为受到盐害时细胞膜的氧化产物,其含量与细胞膜透性变化趋势一致。试验研究表明,丙二醛含量也随着盐质量浓度上升而增高,且增长幅度跟盐浓度呈正比,即高盐质量浓度下涨幅大。植物细胞膜在盐胁迫处理下的受损程度可以用相对细胞膜透性表示,相对电导率小反映该品种受到伤害的程度低[19]。本研究中,在高盐胁迫下,无性系YL与Y3相对膜透性低,耐盐能力强于其他无性系。
在盐胁迫处理时,植物体内抗氧化平衡机制被打破,自身会产生清除氧自由基的物质[20]。超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)与过氧化物酶(POD)作为细胞膜系统内抗氧化酶,其活性增加能够降低膜脂过氧化水平,清除体内过多活性氧[21]。本试验显示,盐胁迫后对照组SOD活性与处理组的差异显著, 对照组SOD活性低,变化不明显,其余4个处理组的SOD活性有明显提高并且各无性系增幅不同。POD活性变化趋势与SOD相同,SOD活性总体呈现先升高再降低的趋势,研究结果与刘翠兰等[14]的研究结果一致,随着盐质量浓度增大,SOD活性增强,减轻细胞膜系统氧化损伤,当NaCl质量浓度达到8 g/L时,SOD活性下降,表明植物体内酶合生受到抑制,酶合成机制无法达到平衡[22]。
渗透调节是植物对抗逆境最基础的方式,而可溶性糖与脯氨酸又是最基础的渗透调节物质,不仅维持渗透压平衡改善植物体内微环境,还可以作为评价植物耐盐性差异的指标[23-24]。本试验中,9个无性系的脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量随盐质量浓度增高表现出不同的趋势,4个无性系(L2、J10、JN11与HX)渗透物质含量先增高后降低,其余无性系呈现一致上升的趋势。表明植物受到盐胁迫时,体内会合成大量脯氨酸与可溶性糖等渗透调节物质来减轻逆境造成的伤害[25]。但当盐质量浓度达到最高(8 g/L)时,脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量有下降趋势,表明这些无性系品种无法承受高盐胁迫而使自身调解能力遭到破坏[26]。
耐盐性是植物为了适应环境而引起自身生长生理指标变化从而形成的对抗逆境的机制[27]。本试验是以一年生盆栽自根苗为试材,无性系扦插苗保留原有的生理生长状态,与嫁接苗相比,可以更好地反应该无性系的抗逆能力,一年生苗木抗性差,说明该无性系的耐盐特性较差。分析上述9个白蜡无性系的耐盐性,考虑生长与生理两方面的指标,植物生长受多方面影响,是多种因子共同作用的结果,采用主成分分析的方法,在综合评价函数中,消除评价指标之间的相关影响,各主成分的贡献率反映了该主成分包含原始数据比重,客观的、合理的克服了某些评价方法中确定权数的缺陷,通过各无性系平均成分值综合评价得出耐盐性结果。
本试验可以在一定程度上反映出幼苗期不同白蜡无性系耐盐能力,全面总结白蜡无性系植株不同生长时期的耐盐性还需进一步验证。
-
图 1 NaCl胁迫对苗高增长量的影响
J10、L2、L5、YL、Y3、JN11、JJ、HX、QB分别代表京10、鲁蜡2号、鲁蜡5号、盐蜡、盐3、胶南11、金箭、华雄、青碧。不同小写字母表示同一处理不同无性系间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。J10, L2, L5, Y3, JN11, YL, JJ, HX, QB represent Fraxinus velutina ‘Jing10’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Lula2’、Fraxinus pennsylvanica ‘Lula5’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yanla’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Yan3’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jiaonan11’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Jinjian’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Huaxiong’, Fraxinus velutina ‘Qinbi’. Different letters within the same column indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below.
Figure 1. Effects of NaCl stress on seedling height growth
表 1 NaCl胁迫下各无性系细胞膜透性
Table 1 Effects of NaCl stress on membrane permeability of clones
无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 34.25 ± 7.23abc 39.62 ± 1.28b 44.49 ± 3.11bc 49.22 ± 3.3b 53.21 ± 5.38cde YL 33.52 ± 1.07bc 36.52 ± 1.08b 38.30 ± 1.35d 40.63 ± 1.87bc 42.89 ± 2.61e L5 35.00 ± 0.55ab 47.34 ± 0.83a 51.33 ± 1.78ab 56.00 ± 2.72a 60.25 ± 4.42bcd J10 30.41 ± 7.72c 45.92 ± 9.68a 54.07 ± 12.23a 61.87 ± 15.01a 71.36 ± 19.94a QB 36.69 ± 1.12a 49.63 ± 1.96a 53.88 ± 3.13a 58.92 ± 4.59a 64.00 ± 7.08abc JN11 27.46 ± 0.79c 30.80 ± 0.88c 35.00 ± 3.08d 39.55 ± 3.26c 44.21 ± 4.75e JJ 33.60 ± 0.82bc 46.56 ± 2.93a 51.18 ± 3.38abc 54.23 ± 3.73a 57.97 ± 5.10bcd HX 32.19 ± 1.19bc 49.38 ± 4.34a 55.38 ± 6.84a 61.47 ± 9.84a 67.18 ± 10.92ab Y3 27.66 ± 1.22c 40.52 ± 2.97b 43.87 ± 2.46cd 46.67 ± 3.80b 49.85 ± 2.24de 注:同列中字母不同表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes: different letters within the same column indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below. 表 2 NaCl胁迫下各无性系MDA含量
Table 2 MDA content of clones under NaCl stress
无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 1.84 ± 0.26abc 1.9 ± 0.24ab 2.21 ± 0.49ab 2.42 ± 0.23ab 2.75 ± 0.18bc YL 1.43 ± 0.19bc 1.57 ± 0.4b 1.8 ± 0.36b 2.01 ± 0.19b 2.19 ± 0.49cd L5 1.8 ± 0.18abc 2.21 ± 0.1ab 2.41 ± 0.28ab 2.51 ± 0.43ab 2.91 ± 0.71bc J10 2.32 ± 0.32a 2.38 ± 0.41a 2.71 ± 0.6a 3.11 ± 0.51a 3.69 ± 0.33a QB 1.39 ± 0.26c 1.81 ± 0.44ab 2.21 ± 0.49ab 2.52 ± 0.46ab 1.92 ± 0.4d JN11 1.61 ± 0.21bc 2.05 ± 0.42ab 2.13 ± 0.46ab 2.42 ± 0.51ab 2.49 ± 0.81bcd JJ 1.67 ± 0.41bc 2.05 ± 0.42ab 2.23 ± 0.45ab 2.29 ± 0.63b 1.8 ± 0.53d HX 2.02 ± 0.51ab 2.16 ± 0.81ab 2.37 ± 0.81ab 2.75 ± 0.66ab 3.11 ± 0.47ab Y3 1.64 ± 0.84bc 1.88 ± 0.37ab 2.29 ± 0.64ab 2.02 ± 0.76b 1.94 ± 0.68d 表 3 NaCl胁迫下各无性系叶绿素含量
Table 3 Chlorophyll content of clones under NaCl stress
无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 8.35 ± 1.17def 7.03 ± 1.28cde 6.48 ± 0.94bcd 5.64 ± 2.53b 4.93 ± 2.77bc YL 12.02 ± 1.45a 9.68 ± 0.56a 8.82 ± 1.00a 8.33 ± 1.22a 7.51 ± 1.64a L5 9.41 ± 0.13bc 9.01 ± 1.12ab 7.69 ± 0.62ab 6.53 ± 0.87ab 5.65 ± 0.72abc J10 7.59 ± 0.50f 6.91 ± 0.88cde 5.78 ± 0.68cd 4.92 ± 2.16b 3.69 ± 1.6c QB 8.85 ± 0.34cd 8.46 ± 1.75abc 7.65 ± 1.91ab 6.69 ± 1.63ab 5.58 ± 1.8abc JN11 7.73 ± 0.61ef 6.46 ± 1.48de 6.18 ± 1.87bcd 5.39 ± 1.18b 4.08 ± 0.97bc JJ 8.65 ± 0.65cde 7.9 ± 1.49bcd 6.66 ± 1.56bcd 5.92 ± 2.68b 5.55 ± 2.33abc HX 8.12 ± 0.33def 6.22 ± 1.3e 5.34 ± 0.47d 5.1 ± 1.63b 4.44 ± 1.12bc Y3 10.22 ± 0.52b 8.02 ± 0.9bcd 7.31 ± 1.16abc 6.62 ± 0.98ab 6.05 ± 1ab 表 4 NaCl胁迫下各无性系SOD活性
Table 4 SOD Activity of clones under NaCl stress
无性系 Clone NaCl 质量浓度 NaCl mass concentration 0 g/L 2 g/L 4 g/L 6 g/L 8 g/L L2 83.99 ± 24.68cd 121.06 ± 19.89cd 140.23 ± 7.37cd 167.16 ± 28.4cd 83.45 ± 17.44c YL 234.03 ± 26.86a 244.35 ± 22.03a 292.56 ± 19.37a 304.28 ± 21.34a 241.9 ± 12.16a L5 126.71 ± 24.6bc 185.51 ± 25.11b 170.24 ± 21.33bcd 211.15 ± 7.25bc 115.48 ± 17.42bc J10J 67.72 ± 18.02d 103.07 ± 16.84d 127.32 ± 14.95d 145.27 ± 20.24cd 74.6 ± 22.91c QB 130.01 ± 28.94bc 159.21 ± 29.53bcd 199.07 ± 25.05bc 214.86 ± 36.12bc 158.42 ± 23.05b JN11 118.63 ± 18.99bcd 149.76 ± 12.91bcd 168.7 ± 33.15bcd 182.17 ± 21.41bcd 111.09 ± 18.25bc JJ 110.05 ± 12.18cd 120.79 ± 11.73cd 149.78 ± 26.15cd 162.21 ± 11.65cd 107.76 ± 19.77bc HX 72.43 ± 11.81d 103.17 ± 11.91d 133.1 ± 18.72cd 128.57 ± 17.43d 66.17 ± 27.41c Y3 104.26 ± 5.23b 136.92 ± 15.26bc 158.03 ± 16.65b 174.04 ± 12.59ab 105.59 ± 18.07b 表 5 NaCl胁迫下白蜡无性系各指标间相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis of various indicators of clones to NaCl stress
指标 Index X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X1 1 X2 0.883** 1 X3 0.661** 0.644** 1 X4 0.551** 0.552** 0.493** 1 X5 − 0.086 − 0.129 − 0.189* − 0.605** 1 X6 − 0.315* − 0.272 − 0.168 − 0.873** 0.607** 1 X7 − 0.292** − 0.238 − 0.288* − 0.845* − 0.759** 0.873** 1 X8 − 0.538** − 0.459** 0.530** 0.266* − 0.125 0.191 0.349 1 X9 − 0.485* − 0.445** − 0.392** − 0.745** 0.618** − 0.646** − 0.689** 0.867** 1 注:X1. 苗高增量;X2. 地径增量;X3. 生物量;X4. 叶绿素;X5. 细胞膜透性. X6. 丙二醛;X7. 脯氨酸;X8. 可溶性糖;X9. 超氧化物歧化酶活性(SOD)。下同。**表示在P < 0.01水平上差异极显著,*表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著。Notes: X1, height increment; X2, basal diameter increment; X3, biomass; X4, chlorophyll; X5, membrane permeability; X6, MDA; X7, proline; X8, soluble sugar; X9, SOD. The same below. ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01 level, * indicates significant difference at P < 0.05 level. 表 6 NaCl胁迫下无性系各指标主成分分析
Table 6 Principal component analysis of clones under salt stress
测定指标 Measured index 主成分 Principal components 6 g/L 8 g/L Prin1 Prin2 Prin1 Prin2 Prin3 特征值 Characteristic value 6.313 1.231 5.789 1.131 0.764 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 70.142 83.822 64.318 78.884 87.371 苗高增量 Height increment 0.860 0.202 0.902 0.285 0.246 地径增量 Basal diameter increment 0.917 0.157 0.902 0.285 0.246 生物量 biomass 0.885 0.017 0.971 − 0.021 0.125 叶绿素 Chlorophyll 0.973 0.166 0.917 0.126 − 0.028 细胞膜透性 Membrane permeability − 0.629 0.752 − 0.770 0.314 0.261 脯氨酸 Proline − 0.704 − 0.617 − 0.669 0.526 0.213 2 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar − 0.775 0.246 − 0.452 0.753 0.207 超氧化物岐化酶 SOD 0.915 0.032 0.867 0.068 − 0.045 丙二醛 MDA 0.819 − 0.360 0.618 − 0.430 − 0.622 表 7 主成分值
Table 7 Principal component value
项目 Item L2 YL L5 J10 QB JN11 JJ HX Y3 6 g/L 主成分值 6 g/L Principal component value − 6.711 32.625 11.186 − 3.325 10.766 − 1.189 1.674 − 2.495 11.259 8 g/L 主成分值 8 g/L Principal component value 6.325 35.632 11.980 − 1.233 10.054 9.738 7.510 2.499 12.459 平均值 Average value − 0.193 34.128 11.583 − 2.279 10.410 4.275 4.592 0.002 11.859 排序 Sort 8 1 3 9 4 6 5 7 2 -
[1] 张建锋. 盐碱地生态修复原理与技术[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2008: 36. Zhang J F. Principle and technology of ecological restoration of saline-alkali land[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2008: 36.
[2] 孙广玉. 盐碱土上马蔺的渗透调节和光合适应性研究[D].北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. Sun G Y. Studies on osmotic adjustment and photosynthetic adaptability of Iris lactea on saline-alkali soil[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005.
[3] 赵可夫, 范海, 王宝增, 等. 改良和利用盐渍化土壤的研究进展[J]. 园林科技信息, 2004(1):32−35. Zhao K F, Fan H, Wang B Z, et al. Advances in the improvement and utilization of saline soil[J]. Landscape Science and Technology Information, 2004(1): 32−35.
[4] 张华新, 宋丹, 刘正祥. 盐胁迫下11个树种生理特性及其耐盐性研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2008, 21(2):168−175. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2008.02.007 Zhang H X, Song D, Liu Z X. Study on physiological characteristics and salt tolerance for seeding of 11 tree species[J]. Forestry Science Research, 2008, 21(2): 168−175. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2008.02.007
[5] 刘桂民, 尹国良, 王振猛, 等. 白蜡优良无性系的抗逆性能评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(28):34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.28.006 Liu G M, Yin G L, Wang Z M, et al. Stress tolerance evaluation of suprerior clones of Fraxinus chinensis[J]. Chinese Agricalture Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(28): 34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.28.006
[6] 孟康敏. 绒毛白蜡等树种耐盐力研究[J]. 辽宁林业科技, 1999(3):43−45, 47. Meng K M. Study on the salt tolerance of Fraxinus velutina et al[J]. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology, 1999(3): 43−45, 47.
[7] 赵世杰, 刘华山, 董新纯. 植物生理实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1997: 152−154. Zhao S J, Liu H S, Dong X C. Guide to plant physiology experiment[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 1997: 152−154.
[8] 郝建军, 康宗利, 于洋. 植物生理学实验技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 45−48. Hao J J, Kang Z L, Yu Y. Plant physiology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Publishing House, 2007: 45−48.
[9] 李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 134−137. Li H S, Sun Q, Zhao S J. Experimental principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 134−137.
[10] 孙海菁, 王树凤, 陈益泰. 盐胁迫对6个树种的生长及生理指标的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2009, 22(3):315−324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2009.03.002 Sun H J, Wang S F, Chen Y T. Effects of salt stress on growth and physiological indexes of 6 tree species[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2009, 22(3): 315−324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2009.03.002
[11] 刘海曼, 封晓辉, 刘毅, 等. 绒毛白蜡对NaCl胁迫的生理响应[J]. 北方园艺, 2016(10):70−75. Liu H M, Feng X H, Liu Y, et al. Physiological response of Fraxinus to NaCl stress[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2016(10): 70−75.
[12] 王振猛, 李永涛, 杨庆山, 等. 绒毛白蜡不同无性系光合特性的研究[J]. 农业与技术, 2015, 35(1):1−3, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-962X.2015.01.001 Wang Z M, Li Y T, Yang Q S, et al. Studies on photosynthetic characteristics of different Fraxinus clones[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2015, 35(1): 1−3, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-962X.2015.01.001
[13] 吴永波, 薛建辉. 盐胁迫对3种白蜡树幼苗生长与光合作用的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 26(3):19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2002.03.006 Wu Y B, Xue J H. Impacts of stress on the growth and photosynthesis of three Fraxinus species[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 26(3): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2002.03.006
[14] 刘翠兰, 吴德军, 王开芳, 等. NaCl胁迫下白蜡杂交苗的生长与生理响应[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(28):16−21. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16010152 Liu C L, Wu D J, Wang K F, et al. Growth and physiological responses of hybrid seedlings of Fraxinusto NaCl stress[J]. Chinese Agricalture Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(28): 16−21. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16010152
[15] 李淑娟, 詹亚光, 杨传平, 等. 混合盐胁迫对引种绒毛白蜡生长及相关生理指标的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2010, 38(1):15−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2010.01.005 Li S J, Zhan Y G, Yang C P, et al. Effect on growth and physiological indices of introduced species of Fraxinus velutina under mixed salt stress[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2010, 38(1): 15−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2010.01.005
[16] 于金平, 俞珊, 梁有旺, 等. NaCl胁迫对美国白蜡幼苗部分生理指标的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(1):110−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.01.18 Yu J P, Yu S, Liang Y W, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on some physiological indexes of Fraxinusamericana seedlings[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(1): 110−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.01.18
[17] Mckay H M, Mason W L. Physiological in dicators of tolerance to cold storage in SiTka spruce and Douglas-fir seedlings[J]. Canadian Journal Forest Research, 1991, 21(6): 890−901. doi: 10.1139/x91-124
[18] 陈少裕. 膜脂过氧化与植物逆境胁迫[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1989, 6(4):211−217. Chen S Y. Membrane lipid peroxidation and plant stress[J]. Plant Physiology Communication, 1989, 6(4): 211−217.
[19] 陶晶. 东北主要杨树抗盐机理及抗性品种选育的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2002. Tao J. Main research on salt-resistant mechanism and selection of salt-resistant varieties of poplar[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2002.
[20] 李敏, 张健, 李玉娟, 等. 植物耐盐生理及耐盐基因的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2012, 40(10):45−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2012.10.013 Li M, Zhang J, Li Y J, et al. Advances in plant salt-tolerant physiology and salt-tolerant genes[J]. Agricultural Sciences in Jiangsu, 2012, 40(10): 45−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2012.10.013
[21] Dionisio S, Tobita M L. Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress[J]. Plant Science, 1998, 135(1): 1−9. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00025-9
[22] 杨升, 刘正祥, 张华新, 等. 3个树种苗期耐盐性综合评价及指标筛选[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(1):91−98. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130114 Yang S, Liu Z X, Zhang H X, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance and screening identification index for three tree species[J]. Forestry Science, 2013, 49(1): 91−98. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130114
[23] Anamul H M, Eiji O, Mst N A B, et al. Exogenous proline mitigates the detrimental effects of salt stress more than exogenous bentaine by increasing antioxidant enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2007, 164(5): 553−561. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.03.010
[24] Wided M, Nader B A, Ahmed D, et al. Salt tolerance of the annual halophyte Cakite maritima as affected by the provenance and the developmentat stage[J]. Acta Physiol Plant, 2007, 29(4): 375−384. doi: 10.1007/s11738-007-0047-0
[25] 林栖凤, 李冠一. 植物耐盐性研究进展[J]. 生物工程进展, 2000, 20(2):20−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8135.2000.02.005 Lin Q F, Li G Y. Research progress in salt tolerance of plants[J]. Advances in Bioengineering, 2000, 20(2): 20−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8135.2000.02.005
[26] 汤章城. 逆境条件下植物脯氨酸的累积及其可能意义[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1984(1):15−21. Tang Z C. Accumulation and possible significance of plant proline under stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 1984(1): 15−21.
[27] 杨传宝, 倪惠箐, 李善文, 等. 白杨派无性系苗期对 NaHCO3 胁迫的生长生理响应及耐盐渍性综合评价[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(10):1555−1564. Yang C B, Ni H Q, Li S W, et al. Growth and physiological response to NaHCO3 stress, salt tolerance and comprehensive evaluation of Populus clones at seedling stage[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 52(10): 1555−1564.
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 姬新颖,唐佳莉,李敖,郑旭,王红霞,张俊佩. 盐胁迫下不同基因型核桃实生幼苗生长及生理响应. 林业科学. 2024(02): 65-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙叶烁,田海英,姚玉涛,丁守鹏,张国新,韩民利. 咸水胁迫对草莓生长·品质的影响及耐盐综合评价. 安徽农业科学. 2023(02): 47-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 纪发达. 一种抗逆型复合调节剂的制备及其应用. 化肥设计. 2023(02): 8-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高铖铖,燕丽萍,吴德军,王因花. 基于SSR标记的白蜡群体遗传多样性和群体结构分析. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(06): 69-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王介华,睢金凯,崔令军,石开明. AMF对盐胁迫下桢楠生长和生理特性的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(06): 51-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 程俊森,王溢,李永泉,魏尚霖,李超楠,姜维,黄润生. 基于Label-free技术的高州油茶铝胁迫蛋白质组学研究. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(08): 169-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘京,马洁怡,张金池,马仕林,王宇浩,聂晖,曹鹏翔. 不同土壤改良措施对苏北盐碱地薄壳山核桃生长的影响. 东北林业大学学报. 2022(07): 11-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘翠兰,王开芳,吴德军,燕丽萍,李善文,王芳,任飞,王因花. 滨海盐碱胁迫下白蜡无性系生长及生理特性的响应. 中国农学通报. 2022(35): 7-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李寿冰,赵钰琪,曹帮华,袁洪振,耿颖,陈炳卓,张家昌. 盐碱胁迫对2种地被竹叶绿素含量的影响. 世界竹藤通讯. 2022(S1): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 崔令军,刘瑜霞,林健,石开明. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下桢楠光合生理的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(01): 101-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 巩志勇,辛建华,商小雨,郭晓明,王延平. 盐碱胁迫下香椿幼苗光合及抗逆生理特性. 西北植物学报. 2021(07): 1199-1209 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 范馨月,张华,赵继业,杜子沫,丛日晨. 绒毛白蜡耐盐碱响应机制的研究进展. 中国农学通报. 2021(28): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 缪李飞,于晓晶,张秋悦,封超年. 4个杜梨半同胞家系苗期耐盐性分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(05): 157-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 赵宝泉,邢锦城,温祝桂,徐海东,王进左,李玉明,董静,洪立洲. 林木盐胁迫响应机制研究进展. 现代农业科技. 2020(21): 159-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)



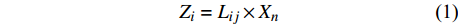

 下载:
下载: