Isolation and identification of the allelochemicals in Artemisia ordosica aqueous extracts
-
摘要:目的研究沙蒿根、茎、叶和种子水浸提液的化感物质,探究其对沙米种子发芽的影响,为沙蒿在群落演替过程中化感作用的研究提供理论依据。方法用超纯水室温浸提沙蒿根、茎、叶和种子48 h,离心,上清液经萃取后得到酸性、中性和碱性浸提液。将3种浸提液分为两部分,一部分用气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS)对其组分含量进行分析,另一部分用于沙米种子发芽实验。结果沙蒿水浸提液酸性组分共检测到35种化合物,根的酸性组分主要为丁二酸(22.42%)和3,4-二羟基苯甲酸(13.13%);茎的酸性组分主要为丁二酸(25.81%)、咖啡酸(13.53%)、3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸(12.12%)和2-羟基丙酸(11.13%);叶的酸性组分主要为3,4-二羟基苯甲酸(23.15%)、苯甲酸(16.62%)和3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸(15.68%);种子的酸性组分主要为2-羟基丙酸(47.64%)和丁二酸(32.28%)。中性组分共检测到20种化合物,根、茎、叶和种子的主要成分均为2-呋喃丙醇,分别占检测到物质的62.28%、33.10%、47.42%、85.13%。碱性组分共检测到6种化合物,根中主要成分为乙胺(43.80%),茎、叶和种子中主要成分为2-羟基乙胺,分别占检测到物质的53.95%、42.45%、56.29%。沙蒿水浸提液酸性、中性和碱性组分对沙米种子发芽均有抑制作用,其中酸性组分的抑制作用最强,其次为碱性组分,影响最弱的为中性组分。结论沙蒿化感物质主要是酸性物质,在沙蒿与其他植物竞争中具有重要作用。不同部位水浸提液所表现出来的化感效应强度不同,表明化感作用与其含有的化感物质的种类与含量有关。
-
关键词:
- 气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS) /
- 沙蒿 /
- 水浸提液 /
- 化感物质
Abstract:ObjectiveThe allelochemicals of aqueous extracts from roots, stems, leaves, and seeds of Artemisia ordosica were investigated, and their effects on germination of Agriophyllum squarrosum seeds were also studied, which provided a theoretical basis for better understanding allelopathy in the process of A. ordosica community succession.MethodThe roots, stems, leaves and seeds of A. ordosica were extracted with ultrapure water for 48 hours at room temperature, centrifugated, and the supernatants were separated into acidic, neutral and alkaline extracts by re-extraction. These extracts were respectively divided into two parts (1/40 for the GC-MS analysis, 39/40 for A. squarrosum seed germination experiment).ResultThirty-five compounds were identified in the acidic extracts of A. ordosica. Succinic acid (22.42%) and 3,4- dihydroxybenzoic acid (13.13%) were main compounds in roots. Succinic acid (25.81%), caffeic acid (13.53%), 3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid (12.12%), and 2-hydroxypropionic acid (11.13%) were main compounds in stems. 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (23.15%), benzoic acid (16.62%), and 3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid (15.68%) were main compounds in leaves. 2-hydroxypropionic acid (47.64%) and succinic acid (32.28%) were main compounds in seeds. Twenty compounds were identified in the neutral extracts of A. ordosica. 2-furan propanol was main compound in roots, stems, leaves and seeds, accounting for 62.28%, 33.10%, 47.42%, 85.13% of the detected substances, respectively. Six compounds were identified in the alkaline extracts of A. ordosica. Ethylamine (43.80%) was main compound in roots. 2-hydroxyethylamine was main compound in stems, leaves and seeds, and its relative content was 53.95%, 42.45%, 56.29%, respectively. Acidic, neutral and alkaline extracts of A. ordosica all inhibited the germination of A. squarrosum seeds. Among them, the strongest inhibitory effect was observed for the acidic extract, followed by alkaline extract, and the weakest was neutral extract.ConclusionThe allelochemicals of A. ordosica are mainly acidic substances, which play an important role in the competition between A. ordosica and other plants. The aqueous extracts of different parts of A. ordosica exhibited different intensity of allelopathic effects, indicating that the allelopathic effect is related to the type and content of allelochemicals.-
Keywords:
- GC-MS /
- Artemisia ordosica /
- aqueous extract /
- allelochemical
-
化感作用使植物能够增加自身对环境的适应能力和竞争能力,普遍存在于生态系统中[1-2],植物常常释放化学物质与其他共生植物争夺有限的自然资源,以利于自身的生长[3]。几乎所有植物器官中均存在化感物质[4],并通过挥发和淋溶等途径释放到环境中,影响其他植物种子发芽和幼苗的生长发育[5],从而改变群落中的物种组成与分布格局[6],因此对化感物质的研究是植物化感作用中的主要部分。植物的化感物质是生长过程中通过次生代谢而产生和释放的次生物质[7],而且长期生长在极端恶劣条件下的植物,常常会增加次生代谢物质的释放[8]。
在我国西北地区的流动沙地,沙米(Agriophyllum squarrosum)是最早出现的植物,随着流动沙地的固定,沙米迅速退出植物群落。沙蒿(Artemisia ordosica)种群不断扩大,最终形成单优势种群落[9],占据了大部分沙丘和沙梁地,成为最发达的沙生植被群落类型,并逐渐进化为最具适应性的沙生植物,是广泛存在的固沙植物种[10]。
沙蒿是菊科(Compositae)蒿属多年生半灌木状植物,在西北地区生态修复过程中,具有耐旱、耐沙埋、耐土壤贫瘠等特征[11-12]。其固沙能力非常强,在农牧业生产和生态环境保护方面,沙蒿具有极其重要的作用[13-14]。研究表明,在相同的环境条件下,沙蒿群落的生物多样性较低,可能与沙蒿含有大量的化感物质有关[15]。为此采用气相色谱−质谱联用技术(GC-MS)分析了沙蒿根、茎、叶和种子水浸提液的化学成分,并通过沙米种子发芽实验来初步探讨沙蒿不同部位和不同极性浸提液的化感作用,为阐明其化感作用机理提供帮助。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材 料
供体材料:沙蒿根、茎、叶、种子;受体材料:沙米种子。均采自宁夏盐池县荒漠生态系统定位研究站沙蒿标准样地,选取生长状况良好的沙蒿植株5株,挖取并选择完好的根系以及地上部的茎叶,剪碎后立即置于液氮罐中,携回实验室− 80 ℃低温冰箱保存,沙蒿和沙米种子4 ℃冰箱中储藏备用。
1.2 仪 器
美国PE Clarus 600气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS),Beckman Avanti J-26 XP 高速离心机(美国),Lab Tech EV311旋转浓缩仪,RGX-150光照培养箱。
1.3 试 剂
实验用水为美国Milli-Q plus超纯水机生产的超纯水,硅烷化试剂(BSTFA)购自Sigma公司,盐酸、乙酸乙酯、碳酸氢钠、氢氧化钠为分析纯(北京化工厂生产)。
1.4 方 法
1.4.1 浸提液的制备
分别称取20 g沙蒿根、茎、叶、种子,放入三角瓶中,加入400 mL超纯水室温浸提48 h(每隔12 h摇动5 min),粗提液10 000 r/min离心10 min,上清液用2 mol/L HCl调节pH至2.5后,用等体积的乙酸乙酯萃取3次,合并乙酸乙酯相,用pH 10的8%的碳酸氢钠溶液等体积萃取3次,乙酸乙酯相为中性组分。碳酸氢钠溶液再用2 mol/L HCl调节pH为2.5,乙酸乙酯等体积萃取3次,得到含有酸性组分的乙酸乙酯相。第1次乙酸乙酯萃取后剩下的水相用2 mol/L NaOH溶液调节pH为10后,再用等体积的乙酸乙酯萃取3次,得到含有碱性组分的乙酸乙酯相,分别将酸性、碱性和中性乙酸乙酯萃取液各分为两部分(1/40用于GC/MS分析,39/40用于种子发芽实验),旋转蒸发仪40 ℃以下蒸发至干,用于GC/MS分析的样品分别用100、50、50 µL的乙酸乙酯分3次把样品转移至玻璃毛细管中,真空干燥器抽干,中性组分加入10 µL乙酸乙酯溶解后,GC/MS分析其组分。酸性和碱性组分各加入10 µL BSTFA衍生化(105 ℃,1 h)后,GC/MS分析。用于种子发芽实验的乙酸乙酯相旋转蒸发至干,加入390 mL超纯水,使浸提液浓度为0.05 g/mL。
1.4.2 GC-MS分离与鉴定
GC条件:色谱柱DB-5,30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm,载气为氦气(99.999%),流速1 mL/min。色谱柱采用程序升温,起始温度50 ℃,以10 ℃/min 升至290 ℃,保持8 min,进样口温度250 ℃,传输线温度280 ℃,分流比10:1,进样量1 μL。
MS条件:EI源,离子源温度190 ℃,倍增电压350 V,全扫描,扫描范围29 ~ 540,扫描时间0.2 s。利用NIST谱图库对采集到的质谱图进行检索,相对含量采用面积归一化法计算。
1.4.3 化感活性测定
选取籽粒饱满、大小基本一致的沙米种子,均匀播于垫有2层滤纸的直径9 cm的玻璃培养皿中,每皿50粒,加入0.05 g/mL的沙蒿水浸提液5 mL,以蒸馏水培养做对照,5次重复。于白天25 ℃、湿度70%、光照3 000 lx(12 h),夜晚15 ℃、湿度80%、黑暗(12 h)的光照培养箱中培养,每天补充1 mL浸提液和蒸馏水以保持滤纸湿润,并定时观察记录发芽种子数(以胚根突破种皮并达种子长度的1/2为发芽标准)。连续2天没有新增加的发芽种子数,记为发芽结束。发芽数据采用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 沙蒿浸提液的酸性成分
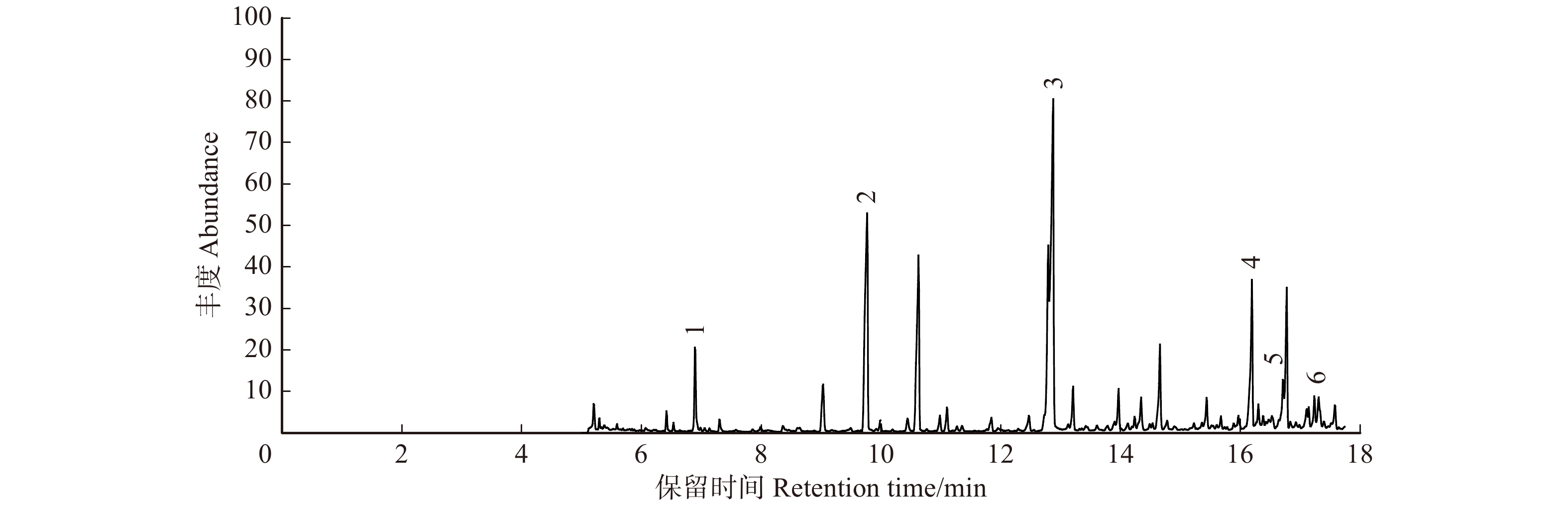
对沙蒿水浸提液酸性组分进行GC/MS分析,检测出35种化合物(图1),共3类物质,包括酚酸、小分子有机酸和脂肪酸(表1)。根、茎、叶、种子中检测到的酚酸类物质分别占检测到的总物质的43.76%、44.34%、81.06%、9.49%,小分子有机酸分别为47.79%、54.10%、15.13%、84.70%,脂肪酸分别为8.45%、1.56%、3.81%、5.81%。检测到的物质种类最多的是叶浸提液,共检测到34种酸性物质;其次是茎浸提液,检测到33种物质;根和种子浸提液检测到的物质种类相同,共检测到31种物质。根中主要成分为丁二酸和3,4-二羟基苯甲酸,分别占检测到物质的22.42%和13.13%;茎中主要成分为丁二酸、咖啡酸、3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸和2-羟基丙酸,占检测到物质的25.81%、13.53%、12.12%和11.13%;叶中主要成分为3,4-二羟基苯甲酸、苯甲酸和3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸,占检测到物质的23.15%、16.62%和15.68%,4-羟基苯丙酸为叶中特异性组分,占检测到物质的1.44%;种子中主要成分为2-羟基丙酸和丁二酸,占检测到物质的47.64%和32.28%。
表 1 酸性物质GC-MS分析结果Table 1. GC-MS results of acidic compounds% 序号 No. 化合物名称
Compound name分子式 Formula 峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 乙醇酸 Glycolic acid C2H4O3 0.49 0.11 0.18 0.44 2 2-羟基丙酸 2-Hydroxypropionic acid C3H6O3 8.12 11.13 1.72 47.64 3 2-甲基丁二酸 2-Methylsuccinic acid C5H8O4 0.91 0.27 0.25 0.61 4 2-己烯酸 2-Hexenoic acid C6H9O2 0.30 — 0.77 0.40 5 3-甲基己二酸 3-Methyldipic acid C7H12O4 0.79 0.36 0.13 0.49 6 2-羟基-4-甲基戊酸 2-Hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid C6H12O3 0.40 0.38 — 0.37 7 3-羟基丁酸 3-Hydroxybutyric acid C4H7O3 3.20 0.34 0.12 0.14 8 2-乙基己酸 2-Ethylhexanoic acid C8H16O2 2.50 0.50 0.17 0.48 9 乙二酸 Oxalic acid C2H2O4 0.36 5.21 5.64 0.27 10 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid C7H6O2 3.62 1.53 16.62 0.16 11 丙酮酸 Pyruvic acid C3H4O3 0.65 0.14 0.11 0.29 12 苯乙酸 Phenylacetic acid C8H8O2 0.58 0.19 2.55 0.14 13 丁二酸 Succinic acid C4H6O4 22.42 25.81 2.56 32.28 14 丁烯二酸 Butenedioic acid C4H4O4 0.49 6.65 1.59 0.32 15 戊二酸 Glutaric acid C5H8O4 1.58 0.43 0.10 0.66 16 2-羟基丁二酸 2-Hydroxysuccinic acid C4H6O5 0.75 1.29 0.26 0.12 17 2-羟基苯甲酸 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O3 3.25 3.57 1.17 0.33 18 4-甲氧基苯甲酸 4-Methoxybenzoic acid C8H8O3 — 0.20 0.49 — 19 2,3-二甲基丁二酸 2,3-Dimethylsuccinic acid C6H10O4 3.51 0.69 0.36 — 20 3-甲氧基苯丙烯酸 4-Methoxy phenylacrylic acid C9H12O 0.46 0.29 0.12 0.44 21 庚二酸 Pimelic acid C7H10O4 1.32 0.79 1.17 0.19 22 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O3 1.03 1.76 2.78 1.09 23 4-羟基苯乙酸 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid C8H7O3 2.20 0.22 0.35 0.75 24 1,2-苯二甲酸 1,2-Phthalic acid C8H6O4 7.14 0.93 0.66 3.34 25 十四烷酸 Myristic acid C14H28O2 1.08 0.25 0.21 0.64 26 4-羟基苯丙酸 Hydroxyphenyl propionic acid C9H9O3 — — 1.44 — 27 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid C8H7O4 4.17 12.12 15.68 0.55 28 香豆酸 Coumalic acid C6H4O4 1.07 0.23 0.51 0.03 29 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O4 13.13 2.81 23.15 1.47 30 3,5-二甲氧基-4-羟基苯甲酸 3,5-Dimethoxyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid C9H10O5 3.48 4.52 0.21 — 31 肉桂酸 Cinnamic acid C9H8O2 — 0.60 0.61 0.16 32 十六烷酸 Hexadecanoic acid C16H32O2 7.37 1.09 3.36 3.84 33 阿魏酸 Ferulic acid C10H10O4 2.07 1.84 8.03 0.28 34 咖啡酸 Caffeic acid C9H8O4 1.56 13.53 6.69 0.75 35 9,12,15-十八碳三烯酸 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid C18H30O2 — 0.22 0.24 1.33 2.2 沙蒿浸提液的中性成分
对沙蒿水浸提液中性组分进行GC/MS分析,检测出20种化合物(图2),共5类物质,包括醇、醛、酮、烯和酯类(表2)。根、茎、叶、种子浸提液检测到的醇类物质分别占检测到物质的83.01%、46.45%、56.66%、93.36%,醛酮类物质占检测到物质的4.86%、3.27%、6.40%、0.73%,烯类物质占检测到物质的3.37%、0.98%、1.10%、0.78%,酯类物质占检测到物质的8.76%、49.30%、35.84%、5.13%。叶浸提液检测出全部20种物质,其次是茎和根浸提液,分别检测出18种和16种化合物,种子浸提液检测到的物质种类最少,只检测到11种中性物质。根、茎、叶、种子的主要成分均为2-呋喃丙醇,分别占检测到物质的62.28%、33.10%、47.42%和85.13%。
表 2 中性物质GC-MS分析结果Table 2. GC-MS results of neutral compounds% 序号 No. 化合物名称
Compound name分子式 Formula 峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 2,5-二甲基-3-己炔-2,5-二醇 2,5-Dimethyl-3-hexyne-2,5-diol C8H14O2 0.21 0.10 0.10 — 2 1,3,3-三甲基-2-乙烯基环己烯 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-Vinylcyclohexene C11H18 — 0.10 0.11 — 3 紫丁香醇 Lilac alcohol C8H10O3 0.55 0.28 0.34 — 4 2,3-蒎烷二醇 2,3-Pinanediol C10H18O2 0.20 0.09 0.32 — 5 4,4,6-三甲基-2-环己烯-1-醇 4,4,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1-alcohol C9H16O — 0.05 0.03 — 6 4-异丙烯基-1-甲基-1,2-环己烷二醇 4-Isopropenyl-1-methyl-1,2-cyclohexane diol C10H18O2 1.40 0.28 0.40 — 7 8-羟基芳樟醇 8-Hydroxyl linalool C10H19O2 0.41 0.09 0.23 0.03 8 2-羟基苯乙酮 2-Hydroxyacetophenone C8H8O2 0.98 1.78 3.62 0.28 9 1,4-二乙酰基苯 1,4-Diacetylbenzene C10H10O2 0.34 — 1.01 0.45 10 斯巴醇 Spathulenol C15H24O — 0.65 0.73 0.59 11 3,7,11-三甲基-1,3,6,10-十二碳四烯 3,7,11-Trimethyl-1,3,6,10- dodecatetraene C15H24 3.37 0.88 0.99 0.78 12 柠檬酸三乙酯 Triethyl citrate C12H20O7 2.57 31.83 31.71 1.45 13 2-呋喃丙醇 2-Furan propanol C7H10O2 62.28 33.10 47.42 85.13 14 红没药醇 Dragosantol C15H26O 1.66 — 1.04 0.45 15 6,10-二甲基-5,9-十一碳二烯-2-酮 6,10-Dimethyl-5,9- undecadiene-2-ketone C13H22O 1.84 0.83 1.11 — 16 红没药醇氧化物A Bisabolol oxide A C15H26O2 16.30 11.81 6.05 7.16 17 8-羟基喹啉-2-甲醛 8-Hydroxyquinoline-2-formaldehyde C10H7NO2 1.70 0.66 0.66 — 18 9,12-亚油酸甲酯 Methyl linoleate C19H33O2 — 0.47 0.32 — 19 柠檬酸三丁酯 Tributyl citrate C18H32O7 1.01 1.09 0.86 0.25 20 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基)己酯 Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate C24H38O4 5.18 15.91 2.95 3.43 2.3 沙蒿浸提液的碱性成分
对沙蒿水浸提液碱性组分进行GC/MS分析,检测出6种化合物(图3),共3类物质,包括杂环化合物吗啉、胺和嘧啶(表3)。根、茎、叶、种子浸提液检测到的主要物质均为胺类,分别占检测到物质的67.27%、95.55%、95.96%、79.33%。其次为嘧啶类物质,分别占检测到物质的11.62%、4.45%、4.04%、20.67%。根中检测到全部6种化合物,特异性组分为吗啉,占检测到物质的21.11%。根中主要成分为乙胺,占检测到物质的43.80%,与茎、叶中的乙胺相比,具有差异显著性。种子中未检测到乙胺。茎、叶、种子浸提液中各检测到4种物质,且茎和叶浸提液检测到的物质种类相同,在茎、叶和种子浸提液中,检测到的主要成分均为2-羟基乙胺,分别占检测到物质的53.95%、42.45%、56.29%。其次为尿素,分别占检测到物质的31.37%、29.43%、23.04%。
表 3 碱性物质GC-MS分析结果Table 3. GC-MS results of alkaline compounds% 序号
No.化合物名称
Compound name分子式
Formula峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 尿素 Carbamide CH4N2O 6.54 31.37 29.43 23.04 2 吗啉 Morpholine C4H9NO 21.11 — — — 3 乙胺 Ethylamine C2H7N 43.80 10.23 24.08 — 4 2-羟基乙胺 2-Hydroxyethylamine C2H7NO 16.93 53.95 42.45 56.29 5 2,4-二羟基嘧啶 2,4-Dihydroxypyrimidine C4H4N2O2 8.98 4.45 4.04 9.90 6 2,4,6-三甲氧基嘧啶 2,4,6-Trimethoxypyrimidine C7H10N2O3 2.64 — — 10.77 2.4 沙蒿浸提液对沙米种子发芽的影响
沙蒿根、茎、叶、种子水浸提液酸性、中性和碱性组分对沙米种子发芽均有抑制作用(表4)。酸性组分对沙米种子发芽抑制效果最为明显,抑制作用由大到小依次为叶浸提液、茎浸提液、根浸提液和种子浸提液,抑制率分别为58.21%、55.72%、54.23%和46.77%;其次为碱性组分,抑制作用由大到小依次为根浸提液、叶浸提液、茎浸提液和种子浸提液,抑制率分别为23.88%、18.91%、16.42%和14.43%;最后为中性组分,抑制作用由大到小依次为叶浸提液、根浸提液、茎浸提液和种子浸提液,抑制率分别为15.92%、14.93%、13.43%和5.97%。水浸提液不同部位和不同组分对沙米种子发芽所表现出来的化感效应强度不同,表明化感作用与化感物质的种类与含量有关。沙蒿化感物质主要是酸性物质。
表 4 沙蒿水浸提液不同组分对沙米种子发芽率的影响Table 4. Influences of different components of aqueous extracts of A. ordosica on seed germination rates of A. squarrosum% 处理 Treatment 发芽率 Germination rate 酸性组分 Acidic component 中性组分 Neutral component 碱性组分 Alkaline component 对照 Control 80.40 ± 5.90a 80.40 ± 5.90a 80.40 ± 5.90a 根浸提液 Root extract 36.80 ± 3.63b 68.40 ± 4.34c 61.20 ± 5.02d 茎浸提液 Stem extract 35.60 ± 3.29b 69.60 ± 5.18c 67.20 ± 4.82c 叶浸提液 Leaf extract 33.60 ± 2.61b 67.60 ± 4.56c 65.20 ± 3.63c 种子浸提液 Seed extract 42.80 ± 4.15b 75.60 ± 5.55a 68.80 ± 5.22c 注:同行中不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different letters in same row indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). 3. 结论与讨论
由GC/MS分析可知,沙蒿叶浸提液检测到的化合物种类(56种)最多,其次是根和茎浸提液(53种),种子浸提液(45种)最少。在检测到的物质中,酸性共有物27种,所占比例分别为根92.31%、茎93.39%、叶95.88%、种子97.74%;碱性共有物3种,所占比例分别为根32.45%,茎89.77%,叶75.92%,种子89.23%;中性共有物8种,所占比例分别为根92.10%,茎96.49%,叶93.83%,种子98.51%。
根和茎中酸性组分以小分子有机酸和酚酸为主,分别占检测到物质的91.55%和98.44%,所占比例最高的均为丁二酸,分别占22.42%和25.81%;叶中以酚酸为主,占检测到物质的81.06%,所占比例最高的为3,4-二羟基苯甲酸,占23.15%,4-羟基苯丙酸为叶中特异性组分,占1.44%;种子中以小分子有机酸为主,占检测到物质的84.70%,所占比例最高的为2-羟基丙酸,占47.64%。
根和种子中中性组分以醇类物质为主,分别占检测到物质的83.01%和93.36%;茎和叶中以醇和酯类物质为主,分别占检测到物质的95.75%和92.50%;根、茎、叶、种子中所占比例最高的均为2-呋喃丙醇,分别占62.28%、33.10%、47.42%和85.13%。
根、茎、叶、种子中碱性组分以胺类为主,分别占检测到物质的67.27%、95.55%、95.96%、79.33%。根中所占比例最高的为乙胺,占43.80%,吗啉为根中特异性组分,占21.11%;茎、叶和种子中,所占比例最高的均为2-羟基乙胺,分别占53.95%、42.45%和56.29%。
沙蒿水浸提液酸性、中性和碱性组分对沙米种子发芽均有抑制作用。其中酸性组分的抑制效果最为明显,抑制作用由大到小依次为叶浸提液、茎浸提液、根浸提液和种子浸提液,其次为碱性组分,影响最弱的为中性组分。说明沙蒿化感物质主要是酸性物质,根主要化感物质为丁二酸和3,4-二羟基苯甲酸;茎主要化感物质为丁二酸、咖啡酸、3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸和2-羟基丙酸;叶主要化感物质为3,4-二羟基苯甲酸、苯甲酸和3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸;种子主要化感物质为2-羟基丙酸和丁二酸。由此可知,酚酸和小分子有机酸在沙蒿与其他植物竞争中具有重要作用。不同部位、不同极性水浸提液所表现出来的化感效应强度不同,表明化感作用与其含有的化感物质的种类与含量有关,这与前人的研究结果一致[16] 。一些水溶性有机酸、酚酸、脂肪酸、醇、烯、醛、酮、酯、胺等小分子有机化合物,均具有化感作用,被认为是化感物质[17-18]。如烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)根系分泌物中的苯甲酸和3,4-二羟基苯甲酸等酚酸类物质被认为是造成连作障碍的重要原因[19],梭鱼草(Pontederia cordata)释放的丁二酸可抑制铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)和斜生栅藻(Scenedesmus obliquus)的生长[20],咖啡酸能够诱导莴苣(Lactuca sativa)体内活性氧的产生和积累,降低幼苗根尖细胞活力,从而影响莴苣幼苗的生长发育[21],美人蕉(Canna indica)释放出的2-羟基丙酸等化感物质对铜绿微囊藻的生长具有明显的抑制作用[22],水溶性有机酸和苯甲酸类物质能显著抑制黄瓜(Cucumis sativus)幼苗的生长[23]。化感物质在增强沙蒿生存竞争能力与扩大繁衍中起着重要作用,可能是其形成单优群落的关键因素之一。
-
表 1 酸性物质GC-MS分析结果
Table 1 GC-MS results of acidic compounds
% 序号 No. 化合物名称
Compound name分子式 Formula 峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 乙醇酸 Glycolic acid C2H4O3 0.49 0.11 0.18 0.44 2 2-羟基丙酸 2-Hydroxypropionic acid C3H6O3 8.12 11.13 1.72 47.64 3 2-甲基丁二酸 2-Methylsuccinic acid C5H8O4 0.91 0.27 0.25 0.61 4 2-己烯酸 2-Hexenoic acid C6H9O2 0.30 — 0.77 0.40 5 3-甲基己二酸 3-Methyldipic acid C7H12O4 0.79 0.36 0.13 0.49 6 2-羟基-4-甲基戊酸 2-Hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid C6H12O3 0.40 0.38 — 0.37 7 3-羟基丁酸 3-Hydroxybutyric acid C4H7O3 3.20 0.34 0.12 0.14 8 2-乙基己酸 2-Ethylhexanoic acid C8H16O2 2.50 0.50 0.17 0.48 9 乙二酸 Oxalic acid C2H2O4 0.36 5.21 5.64 0.27 10 苯甲酸 Benzoic acid C7H6O2 3.62 1.53 16.62 0.16 11 丙酮酸 Pyruvic acid C3H4O3 0.65 0.14 0.11 0.29 12 苯乙酸 Phenylacetic acid C8H8O2 0.58 0.19 2.55 0.14 13 丁二酸 Succinic acid C4H6O4 22.42 25.81 2.56 32.28 14 丁烯二酸 Butenedioic acid C4H4O4 0.49 6.65 1.59 0.32 15 戊二酸 Glutaric acid C5H8O4 1.58 0.43 0.10 0.66 16 2-羟基丁二酸 2-Hydroxysuccinic acid C4H6O5 0.75 1.29 0.26 0.12 17 2-羟基苯甲酸 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O3 3.25 3.57 1.17 0.33 18 4-甲氧基苯甲酸 4-Methoxybenzoic acid C8H8O3 — 0.20 0.49 — 19 2,3-二甲基丁二酸 2,3-Dimethylsuccinic acid C6H10O4 3.51 0.69 0.36 — 20 3-甲氧基苯丙烯酸 4-Methoxy phenylacrylic acid C9H12O 0.46 0.29 0.12 0.44 21 庚二酸 Pimelic acid C7H10O4 1.32 0.79 1.17 0.19 22 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O3 1.03 1.76 2.78 1.09 23 4-羟基苯乙酸 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid C8H7O3 2.20 0.22 0.35 0.75 24 1,2-苯二甲酸 1,2-Phthalic acid C8H6O4 7.14 0.93 0.66 3.34 25 十四烷酸 Myristic acid C14H28O2 1.08 0.25 0.21 0.64 26 4-羟基苯丙酸 Hydroxyphenyl propionic acid C9H9O3 — — 1.44 — 27 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid C8H7O4 4.17 12.12 15.68 0.55 28 香豆酸 Coumalic acid C6H4O4 1.07 0.23 0.51 0.03 29 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid C7H6O4 13.13 2.81 23.15 1.47 30 3,5-二甲氧基-4-羟基苯甲酸 3,5-Dimethoxyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid C9H10O5 3.48 4.52 0.21 — 31 肉桂酸 Cinnamic acid C9H8O2 — 0.60 0.61 0.16 32 十六烷酸 Hexadecanoic acid C16H32O2 7.37 1.09 3.36 3.84 33 阿魏酸 Ferulic acid C10H10O4 2.07 1.84 8.03 0.28 34 咖啡酸 Caffeic acid C9H8O4 1.56 13.53 6.69 0.75 35 9,12,15-十八碳三烯酸 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid C18H30O2 — 0.22 0.24 1.33 表 2 中性物质GC-MS分析结果
Table 2 GC-MS results of neutral compounds
% 序号 No. 化合物名称
Compound name分子式 Formula 峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 2,5-二甲基-3-己炔-2,5-二醇 2,5-Dimethyl-3-hexyne-2,5-diol C8H14O2 0.21 0.10 0.10 — 2 1,3,3-三甲基-2-乙烯基环己烯 1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-Vinylcyclohexene C11H18 — 0.10 0.11 — 3 紫丁香醇 Lilac alcohol C8H10O3 0.55 0.28 0.34 — 4 2,3-蒎烷二醇 2,3-Pinanediol C10H18O2 0.20 0.09 0.32 — 5 4,4,6-三甲基-2-环己烯-1-醇 4,4,6-Trimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1-alcohol C9H16O — 0.05 0.03 — 6 4-异丙烯基-1-甲基-1,2-环己烷二醇 4-Isopropenyl-1-methyl-1,2-cyclohexane diol C10H18O2 1.40 0.28 0.40 — 7 8-羟基芳樟醇 8-Hydroxyl linalool C10H19O2 0.41 0.09 0.23 0.03 8 2-羟基苯乙酮 2-Hydroxyacetophenone C8H8O2 0.98 1.78 3.62 0.28 9 1,4-二乙酰基苯 1,4-Diacetylbenzene C10H10O2 0.34 — 1.01 0.45 10 斯巴醇 Spathulenol C15H24O — 0.65 0.73 0.59 11 3,7,11-三甲基-1,3,6,10-十二碳四烯 3,7,11-Trimethyl-1,3,6,10- dodecatetraene C15H24 3.37 0.88 0.99 0.78 12 柠檬酸三乙酯 Triethyl citrate C12H20O7 2.57 31.83 31.71 1.45 13 2-呋喃丙醇 2-Furan propanol C7H10O2 62.28 33.10 47.42 85.13 14 红没药醇 Dragosantol C15H26O 1.66 — 1.04 0.45 15 6,10-二甲基-5,9-十一碳二烯-2-酮 6,10-Dimethyl-5,9- undecadiene-2-ketone C13H22O 1.84 0.83 1.11 — 16 红没药醇氧化物A Bisabolol oxide A C15H26O2 16.30 11.81 6.05 7.16 17 8-羟基喹啉-2-甲醛 8-Hydroxyquinoline-2-formaldehyde C10H7NO2 1.70 0.66 0.66 — 18 9,12-亚油酸甲酯 Methyl linoleate C19H33O2 — 0.47 0.32 — 19 柠檬酸三丁酯 Tributyl citrate C18H32O7 1.01 1.09 0.86 0.25 20 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基)己酯 Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate C24H38O4 5.18 15.91 2.95 3.43 表 3 碱性物质GC-MS分析结果
Table 3 GC-MS results of alkaline compounds
% 序号
No.化合物名称
Compound name分子式
Formula峰面积 Peak area 根 Root 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 种子 Seed 1 尿素 Carbamide CH4N2O 6.54 31.37 29.43 23.04 2 吗啉 Morpholine C4H9NO 21.11 — — — 3 乙胺 Ethylamine C2H7N 43.80 10.23 24.08 — 4 2-羟基乙胺 2-Hydroxyethylamine C2H7NO 16.93 53.95 42.45 56.29 5 2,4-二羟基嘧啶 2,4-Dihydroxypyrimidine C4H4N2O2 8.98 4.45 4.04 9.90 6 2,4,6-三甲氧基嘧啶 2,4,6-Trimethoxypyrimidine C7H10N2O3 2.64 — — 10.77 表 4 沙蒿水浸提液不同组分对沙米种子发芽率的影响
Table 4 Influences of different components of aqueous extracts of A. ordosica on seed germination rates of A. squarrosum
% 处理 Treatment 发芽率 Germination rate 酸性组分 Acidic component 中性组分 Neutral component 碱性组分 Alkaline component 对照 Control 80.40 ± 5.90a 80.40 ± 5.90a 80.40 ± 5.90a 根浸提液 Root extract 36.80 ± 3.63b 68.40 ± 4.34c 61.20 ± 5.02d 茎浸提液 Stem extract 35.60 ± 3.29b 69.60 ± 5.18c 67.20 ± 4.82c 叶浸提液 Leaf extract 33.60 ± 2.61b 67.60 ± 4.56c 65.20 ± 3.63c 种子浸提液 Seed extract 42.80 ± 4.15b 75.60 ± 5.55a 68.80 ± 5.22c 注:同行中不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。Note: different letters in same row indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). -
[1] Gruntman M, Pehl A K, Joshi S, et al. Competitive dominance of the invasive plant Impatiens glandulifera: using competitive effect and response with a vigorous neighbour[J]. Biological Invasions, 2014, 16(1): 141−151. doi: 10.1007/s10530-013-0509-9
[2] Sieg R D, Kubanek J. Chemical ecology of marine angiosperms:opportunities at the interface of marine and terrestrial systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2013, 39(6): 687−711. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0297-9
[3] Kueh B W B, Yusup S, Osman N, et al. Analysis of Melaleuca cajuputi extract as the potential herbicides for paddy weeds[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2019, 11: 36−40. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2018.12.004
[4] Gatti A B, Ferreira A G, Arduin M, et al. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts of Artistolochia esperanzae O.Kuntze on development of Sesamum indicum L. seedlings[J]. Acta Botanica Brasilica, 2010, 24(2): 454−461. doi: 10.1590/S0102-33062010000200016
[5] Thiébaut G, Thouvenot L, Rodríguez-Pérez H. Allelopathic effect of the invasive Ludwigia hexapetala on growth of three macrophyte species[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9(12): 1−10.
[6] Madrigal-González J, Cea A P, Sánchez-Fernández L A, et al. Facilitation of the non-native annual plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum(Aizoaceae) by the endemic cactus Eulychnia acida(Cactaceae) in the Atacama Desert[J]. Biological Invasions, 2013, 15(7): 1439−1447. doi: 10.1007/s10530-012-0382-y
[7] 杜明利, 高群英, 高岩, 等. 外来物种大花金鸡菊不同器官成分的气质联用(GC-MS)分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(2):313−318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2012.02.024 Du M L, Gao Q Y, Gao Y, et al. Organic compounds in exotic Coreopsis grandiflora using GC-MS[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2012, 29(2): 313−318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2012.02.024
[8] 孔垂华, 胡飞. 植物化感(相生相克)作用及其应用[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001. Kong C H, Hu F. Plant allelopathy and its application[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2001.
[9] Li X R, Xiao H L, Zhang J G, et al. Long-term ecosystem effects of sand-binding vegetation in the Tengger Desert, northern China[J]. Restoration Ecology, 2004, 12(3): 376−390. doi: 10.1111/rec.2004.12.issue-3
[10] Zhang J H, Wu B, Li Y H, et al. Biological soil crust distribution in Artemisia ordosica communities along a grazing pressure gradient in Mu Us Sandy Land, northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2013, 5(2): 172−179. doi: 10.1007/s40333-013-0148-0
[11] Li S L, Werger M J A, Zuidema P A, et al. Seedlings of the semi-shrub Artemisia ordosica are resistant to moderate wind denudation and sand burial in Mu Us sandland, China[J]. Trees, 2010, 24(3): 515−521. doi: 10.1007/s00468-010-0422-0
[12] 张财, 查天山, 贾昕, 等. 毛乌素沙地油蒿群落叶面积指数动态及模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(3):75−83. Zhang C, Zha T S, Jia X, et al. Dynamics and simulation of leaf area index for Artemisia ordosica community in the Mu Us Desert of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(3): 75−83.
[13] Khurelbat D, Densmaa D, Sanjjav T, et al. Artemisioside, a new monoterpene glucoside from the aerial parts of Artemisia ordosica (Asteraceae)[J]. Journal of Natural Medicines, 2010, 64(2): 203−205. doi: 10.1007/s11418-009-0385-x
[14] Fan D Q, Zhang Y Q, Qin S G, et al. Relationships between Artemisia ordosica communities and environmental factors following sand-dune stabilization in the Mu Us desert, northwest China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2017, 28(1): 115−124. doi: 10.1007/s11676-016-0289-z
[15] 周凯, 郭维明, 徐迎春. 菊科植物化感作用研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(8):1780−1788. Zhou K, Guo W M, Xu Y C. Advances of research on allelopathic potential in compositae[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(8): 1780−1788.
[16] Inderjit D S O. Ecophysiological aspects of allelopathy[J]. Planta, 2003, 217(4): 529−539. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1054-z
[17] 李朝婵, 乙引, 全文选, 等. 野生高山杜鹃群落林内自然挥发的化感成分[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(12):35−44. Li C C, Yi Y, Quan W X, et al. The natural volatile components of allelochemicals in the wild alpine Rhododendron community[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(12): 35−44.
[18] 崔翠, 蔡靖, 张硕新. 核桃根系分泌物化感物质的分离与鉴定[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(2):54−60. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130209 Cui C, Cai J, Zhang S X. Isolation and identification of the allelochemicals in walnut (Juglans regia) root exudates[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2013, 49(2): 54−60. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20130209
[19] 于会泳, 申国明, 高欣欣. 连作烟田土壤根系分泌物的变化和分解[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2014, 35(1):43−47. Yu H Y, Shen G M, Gao X X. The changes and degradation of tobacco root exudates in tobacco field with continuous cropping[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2014, 35(1): 43−47.
[20] 许蓝心, 田如男. 梭鱼草化感物质丁二酸对微囊藻和栅藻生长及竞争的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(3):770−777. Xu L X, Tian R N. Effects of succinic acid, an allelopathic substance of Pontederi cordata, on the growth and competition of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus obliquus[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(3): 770−777.
[21] 郭凯, 燕志强, 金辉, 等. 肉桂酸和咖啡酸对莴苣生长的化感作用及其机理研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(1):93−99. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2016.01.0093 Guo K, Yan Z Q, Jin H, et al. Allelopathic effect and mechanism of cinnamic acid and caffeic acid on the growth of lettuce[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(1): 93−99. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2016.01.0093
[22] 潘琦, 邹国燕, 宋祥甫, 等. 美人蕉根系对铜绿微囊藻的化感作用[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(10):1193−1198. Pan Q, Zou G Y, Song X F, et al. Inhibitory effects of the roots of floating bed plants of Canna indica on[J]. Research of Enviromental Sciences, 2014, 27(10): 1193−1198.
[23] 周志红, 骆世明, 牟子平. 番茄(Lycopersicon)的化感作用研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1997, 8(4):445−449. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1997.04.023 Zhou Z H, Luo S M, Mou Z P. Allelopathic effect of tomato[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1997, 8(4): 445−449. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1997.04.023
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 冯林艳,周火艳,赵晓迪. 乌兰布和沙漠两种植物的分布格局及其变化. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(01): 155-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾红,徐永艳,邵琳亚,闻永慧,夏小丽,汪琼. 4种植物叶片浸提液成分分析及其对珊瑚樱种子萌发的影响. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(04): 39-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马光宗,徐高峰,杨韶松,杨云海,张付斗,温丽娜,陶琼,申时才,叶敏. 甘薯提取物对3种杂草种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用. 西南农业学报. 2022(06): 1295-1302 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 路文杰,佛芒芒,肖毅,王永新,杜利霞,钟华,赵祥,董宽虎. 草地植物凋落物浸提液对根际微生物碳源利用的影响. 中国草地学报. 2021(06): 35-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张林媚,刘姝玲,郭彩云. 立地条件对榆林沙区樟子松嫁接红松生长的影响. 林业科技通讯. 2021(11): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王方琳,尉秋实,柴成武,王理德,张德魁,王昱淇,王飞,胡小柯. 沙蒿(Artemisia desertorum)浸提液对自身种子萌发与幼苗生长的化感作用. 中国沙漠. 2021(06): 21-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: