Effects of applying mixed composting of municipal sludge and garden waste on growth of Amorpha fruticosa and soil environment
-
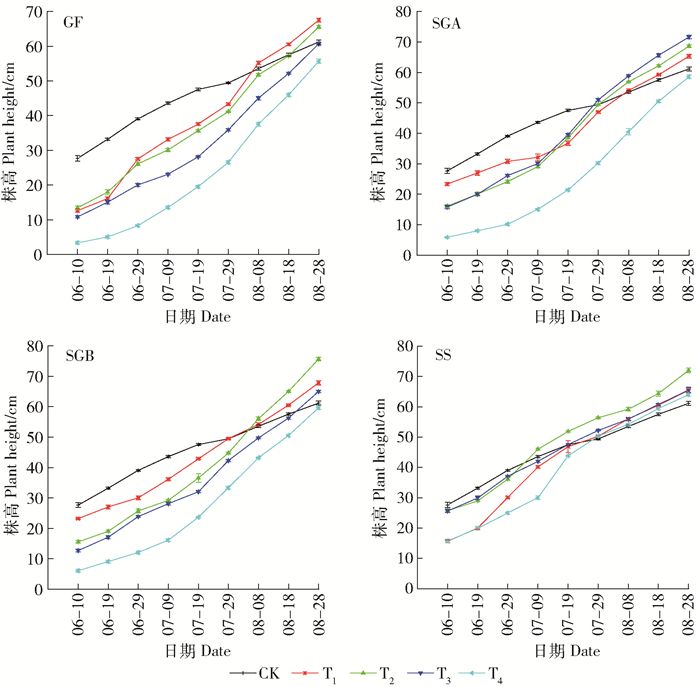
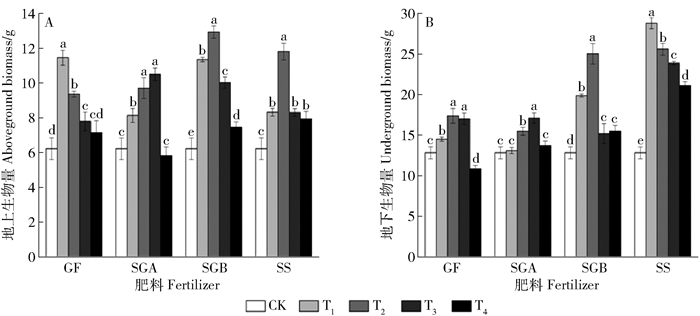
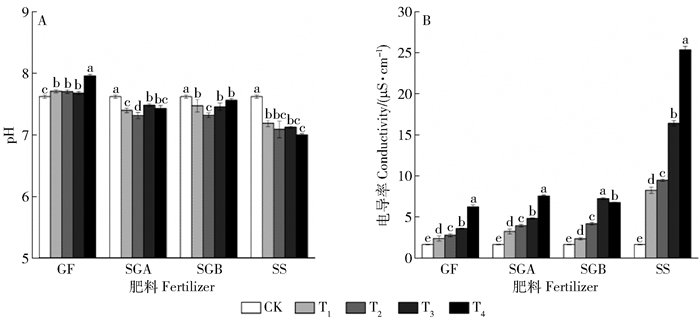
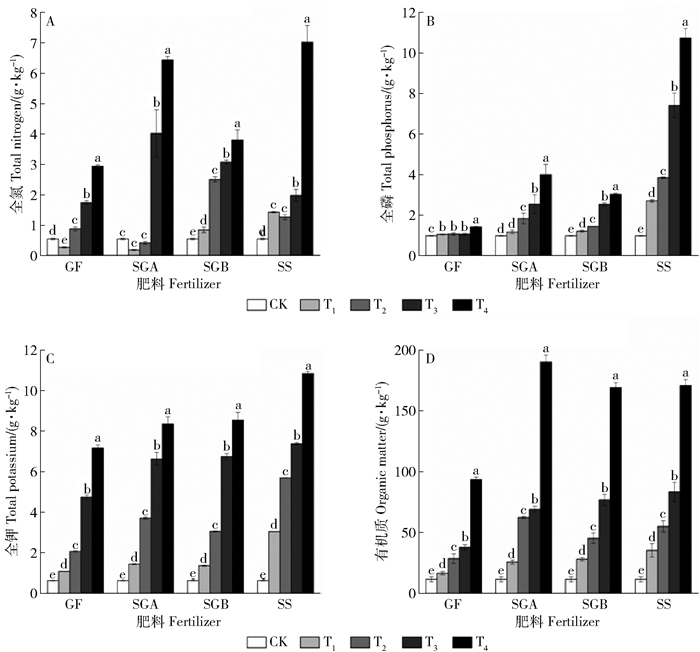
摘要:目的通过观察城市污泥与园林废弃物不同配比的堆肥产品及不同施用量对紫穗槐生长及土壤环境的影响,探究何种配比与施用量的组合下最有利于紫穗槐的生长,以期同时实现城市污泥与园林废弃物的最大化处理,为今后城市污泥和园林废弃物的循环利用提供科学依据。方法本文通过盆栽实验,研究了4种不同堆肥产品(GF、SGA、SGB、SS,即污泥与园林废弃物混合比分别为0:1、1:3、1:1、1:0)和不同施用量(0、25%、50%、75%、100%分别记作CK、T1、T2、T3、T4)对紫穗槐生长及其土壤环境的影响。结果4种堆肥产品在施用量达100%时,对紫穗槐种子萌发表现出一定的抑制作用,SS在各个施用量处理中均表现出较高的抑制作用;在紫穗槐生长初期,与对照相比,4种堆肥产品不同施用量处理均生长较缓慢,但实验中后期,施用堆肥产品的处理组植物生长速度加快,超过对照组植株的生长速度,逐渐表现出堆肥产品的肥效营养作用;施用上述堆肥产品后累积地上生物量和地下生物量均显著提高,最大值分别出现在SGB的T2处理和SS的T1处理;施用堆肥产品能够提高土壤全氮、全磷、全钾、有机质的含量和土壤电导率,且随施用量的增加而显著增加,并不同程度提高了土壤脲酶、碱性磷酸酶、脱氢酶活性,改善土壤环境。结论综合分析,施用50%的SGB时,有利于紫穗槐生长,确定其为较为适宜的施用比例。Abstract:ObjectiveThe optimal conditions for the growth of Amorpha fruticosa were determined by observing the effects of different ratio of mixed composting of municipal sludge and garden waste and different application amount on its growth and soil environment, in order to maximize the processing of municipal sludge and garden waste, and provide the scientific basis for the circulation of garden waste and municipal sludge.MethodA pot-based experiment was designed with four different compost products and different dosages in Beijing. Two kinds of materials were mixed at four volume ratios (0:1, 1:3, 1:1, 1:0, marking as GF, SGA, SGB, SS), and each compost was put together with soil at different volume ratios (0, 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%, marking as CK, T1, T2, T3, T4).ResultThe results showed that seed germination of A. fruticosa was inhibited when the application of four kinds of compost products was 100%. SS showed a high inhibitory effect on each application. Compared with the control, the growth of A. fruticosa was slower in the early stage of fertilization, but accelerated at later phase. The growth rate of A. fruticosa treated with the compost products exceeded than treated without compost product, and its growth gradually showed the nutrition effect of organic fertilizer. The biomass of above ground and underground were significantly increased after composting, and the maximum values appeared in T2 and T1 of the treatment of SGB and SS, respectively. The application of composting products can improve soil physical and chemical properties. Soil total nitrogen, total phosphorus, total potassium, organic matter content and soil electrical conductivity increased significantly with the increase of the amount of fertilizer, and the activities of soil urease, alkaline phosphatase and dehydrogenase were improved after applying composting products. Soil environment was improved at the same time.ConclusionThe application of 50% SGB is most beneficial to the growth of A. fruticosa. In summary, 50% SGB is the optimal application proportion.
-
Keywords:
- municipal sludge /
- garden waste /
- mixed compost /
- Amorpha fruticosa /
- plant growth /
- soil environment
-
-
图 1 城市污泥与园林废弃物混合堆肥施用对紫穗槐种子相对发芽率的影响
GF、SGA、SGB、SS表示污泥与园林废弃物混合物比分别为0:1、1:3、1:1、1:0。T1、T2、T3、T4表示不同施用量(25%、50%、75%、100%)。下同。
Figure 1. Effects of applying mixed composting of municipal sludge and garden waste on relative germination rate of Amorpha fruticosa seeds
GF, SGA, SGB, SS represent the mixture ratio of municipal sludge and garden waste is 0:1, 1:3, 1:1 and 1:0, respective. T1, T2, T3, T4 represent the application amount is 25%, 50%, 75% and 100%, respectively. The same below.
表 1 供试土壤和堆肥产品的基本理化性质
Table 1 General physical and chemical properties of compost products and soil
供试材料
Experimental materialpH 电导率
Conductivity/
(μS·cm-1)有机质
Organic matter
(OM)/(g·kg-1)全氮
Total nitrogen
(TN)/(g·kg-1)全磷
Total phosphorus
(TP)/(g·kg-1)全钾
Total potassium
(TK)/(g·kg-1)土壤Soil 8.65 139.6 28.16 1.53 2.19 0.93 GF 8.80 775.5 186.82 10.17 2.79 3.65 SGA 8.06 1 239.6 293.35 12.37 7.89 9.56 SGB 8.23 1 352.2 235.89 13.56 6.65 5.23 SS 7.70 1 775.6 259.97 16.86 15.53 12.72 注:GF为纯园林废弃物堆肥产品;SGA为污泥、园林废弃物按1:3体积比混合堆肥产品;SGB为污泥、园林废弃物按1:1体积比混合堆肥产品;SS为纯污泥堆肥产品。下同。Notes: GF, 100% garden waste; SGA, 25% sludge and 75% garden waste on the volume; SGB, 50% sludge and 50% garden waste on the volume; SS, 100% municipal sludge. The same below. 表 2 城市污泥与园林废弃物混合堆肥施用对土壤酶活性的影响
Table 2 Effects of applying mixed composting of municipal sludge and garden waste on soil enzyme activities
堆肥产品
Compost product处理
TreatmentUr/
(mg·g-1)Pho/
(mg·g-1)DHA/
(ug·g-1)CK 18.86±0.91b 24.07±0.96a 12.12±0.24e T1 17.69±0.86b 21.95±0.39a 28.42±0.22d GF T2 18.76±0.30b 23.38±1.01a 41.42±0.13c T3 19.59±0.85b 23.26±1.23a 84.02±1.23b T4 25.70±1.60a 21.49±2.62a 379.58±3.11a CK 18.86±0.91c 24.07±0.96a 12.12±0.24e T1 18.33±0.89c 23.52±0.19a 89.24±0.17c SGA T2 18.28±0.61c 23.60±1.23a 95.41±0.51b T3 23.16±0.56b 22.71±0.10a 103.20±2.35a T4 29.56±0.62a 22.42±0.38a 58.49±0.96d CK 18.86±0.91e 24.07±0.96a 12.12±0.24e T1 20.17±0.27d 24.82±1.27a 37.75±0.30d SGB T2 22.16±0.42c 24.91±2.86a 54.99±0.64c T3 26.72±0.91b 24.93±0.64a 73.45±1.91b T4 33.32±0.53a 24.71±0.76a 158.80±0.76a CK 18.86±0.91e 24.07±0.96a 12.12±0.24e T1 30.12±1.39d 23.81±0.53a 51.99±0.90c SS T2 36.91±0.54c 23.97±0.83a 160.46±3.46a T3 43.15±1.42a 24.17±0.41a 140.28±5.98b T4 39.59±1.26b 24.09±0.45a 41.49±2.83d 注:Ur为脲酶;Pho为碱性磷酸酶;DHA为脱氢酶。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P < .05)。Notes: Ur, urease; Pho, alkali phosphatease; DHA, dehydrogenase. Different lowercase letters in a column within a crop mean significant difference at P < .05 level. -
[1] 张璐, 孙向阳, 田赟.园林废弃物堆肥用于青苹果竹芋栽培研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2011, 33(5):109-114. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9657 Zhang L, Sun X Y, Tian Y. Application of green waste compost for Calathca rotundifola cv. Fasciata cultivation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2011, 33(5):109-114. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9657
[2] 谭国栋, 李文忠, 何春利.北京市城市污水处理厂污泥处理处置技术研究探讨[J].南水北调与水利科技, 2011, 9(2): 105-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nsbdyslkj201102027 Tan G D, Li W Z, He C L. Preliminary discussions on the sludge treatment and disposal technology in urban municipal sewage treatment plants in Beijing[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology, 2011, 9(2): 105-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nsbdyslkj201102027
[3] 李萍萍, 薛彬, 孙德智.施用城市污泥堆肥对土壤理化性质及白三叶生长的影响[J].北京林业大学学报, 2013, 35(1):127-131. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9866 Li P P, Xue B, Sun D Z. Effects of applying sewage sludge compost on the physicochemical properties of soil and growth of Trifolium repens[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2013, 35(1):127-131. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9866
[4] 梁晶, 吕子文, 方海兰.园林绿色废弃物堆肥处理的国外现状与我国的出路[J].中国园林, 2009, 25(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2009.04.002 Liang J, Lü Z W, Fang H L. Status of composting treatment of garden waste abroad and application in China[J]. Chinese Landscape Science, 2009, 25(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2009.04.002
[5] 杨桐桐, 封莉, 张立秋.城市污泥堆肥产品施用对沙荒地土壤理化性质及高羊茅生长的影响[J].环境工程学报, 2017, 11(4): 2462-2468. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201704073 Yang T T, Feng L, Zhang L Q. Effects of application of composted municipal sludge on physicochemical properties of desert land soil and growth of tall fescue[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(4): 2462-2468. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjwrzljsysb201704073
[6] Zorpas A A, Loizidou M. Sawdust and natural zeolite as a bulking agent for improving quality of a composting product from anaerobically stabilized sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(16): 7545-7552. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.02.014
[7] Chen H, Yan S H, Ye Z L, et al. Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2012, 19(5): 1454-1463. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-0760-0
[8] 田赟.园林废弃物堆肥化处理及其产品的应用研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1012348940.htm Tian Y. Green waste composting and the products as the peat substitutes in growth media[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1012348940.htm
[9] Antolin M C, Pascual I, Garcia C, et al. Growth, yield and solute content of barley in soils treated with sewage sludge under semiarid Mediterranean conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2005, 94(2): 224-237. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378429005000080
[10] 李贵宝, 尹澄清, 单保庆.我国森林与园林绿地污泥的利用及其展望[J].北京林业大学学报, 2001, 23(4):71-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2001.04.015 Li G B, Yin C Q, Shan B Q. Land use and prospect of sewage sludge in forestland and green areas[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2001, 23(4):71-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2001.04.015
[11] 莫测辉, 吴启堂, 蔡全英, 等.论城市污泥农用资源化与可持续发展[J].应用生态学报, 2000, 11(1): 157-160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2000.01.040 Mo C H, Wu Q T, Cai Q Y, et al. Utilization of municipal sludge in agriculture and sustainable development[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2000, 11 (1): 157-160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2000.01.040
[12] Lakhdar A, Hafsi C, Rabhi M, et al. Application of municipal solid waste compost reduces the negative effects of saline water in Hordeum maritimum L[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(15): 7160-7167. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.071
[13] Kulikowska D, Klimiuk E. Organic matter transformations and kinetics during sewage sludge composting in a two-stage system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(23): 10951-10958. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.009
[14] 陈耀宁.堆肥化中协同降解木质纤维素的混合菌筛选及其培养[D].长沙: 湖南大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2007159592.htm Chen Y N. Sereening and co-eulture of mixed strains for synergistie decomposing of lignocellulose from compost[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2007159592.htm
[15] 司莉青, 陈利民, 郑景明, 等.城市污泥与园林废弃物堆肥的混合施用对高羊茅萌发与生长的影响[J].生态学杂志, 2016, 35(10): 2643-2650. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201610011 Si L Q, Chen L M, Zheng J M, et al. Effects of mixed sewage sludge and garden waste compost on germination and growth of Festuca arundinacea L.[J]. Chinese Journal Ecology, 2016, 35 (10): 2643-2650. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201610011
[16] Moretti S M L, Bertoncini E I, Abreujunior C H, et al. Composting sewage sludge with green waste from tree pruning[J]. Scientia Agricola, 2015, 72(5): 432-439. doi: 10.1590/0103-9016-2014-0341
[17] 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M]. 3版.北京:中国农业出版社, 2000: 30-42, 71-99. Bao S D. Analysis of soil agriculture[M]. 3 edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 30-42, 71-99.
[18] 姚槐应.土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006: 187-190. Yao H Y. Soil microbial ecology and its experimental techniques[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 187-190.
[19] 顾兵.绿色植物废弃物在城市绿地土壤上的应用[D].南京: 南京农业大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10307-2010173745.htm Gu B. Application of green plant waste on urban green soil[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10307-2010173745.htm
[20] 尹守东, 王凤友, 李玉文.城市污泥堆肥林地应用研究进展[J].东北林业大学学报, 2004, 32(5): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2004.05.021 Yin S D, Wang F Y, Li Y W. Advances inapplication of urban sludge compost forest[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2004, 32 (5): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2004.05.021
[21] Amir S, Hafidi M, Merlina G, et al. Sequential extraction of heavy metals during composting of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59(6): 801-810. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.016
[22] 李梦红, 黄现民, 诸葛玉平.污泥农用对土壤理化性质及作物产量的影响[J].水土保持通报, 2009, 29(6): 95-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbctb200906020 Li M H, Huang X M, Zhuge Y P. Effects of agricultural utilization of sewage sludge on soil physical and chemical properties and crop output[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 29(6): 95-98. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbctb200906020
[23] 李艳霞, 陈同斌, 罗维, 等.中国城市污泥有机质及养分含量与土地利用[J].生态学报, 2003, 23(11): 2464-2474. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.11.031 Li Y X, Chen T B, Luo W, et al. Contents of organic matter and major nutrients and the ecological effect related to land application of sewage sludge in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23 (11): 2464-2474. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.11.031
[24] Horswell J, Speir T W, Schaik A P V. Bio-indicators to assess impacts of heavy metals in land-applied sewage sludge[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2003, 35(11): 1501-1505. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038071703002475
[25] 杨志新, 刘树庆.重金属Cd、Zn、Pb复合污染对土壤酶活性的影响[J].环境科学学报, 2001, 21(1): 60-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2001.01.012 Yang Z X, Liu S Q. Effect of compound pollution of heavy metals on soil enzymic activities[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2001, 21 (1): 60-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2001.01.012
[26] 滕应, 黄昌勇, 龙健, 等.铅锌银尾矿污染区土壤酶活性研究[J].中国环境科学, 2002, 22(6): 551-555. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2002.06.016 Teng Y, Huang C Y, Long J, et al. Studies on soil enzymatic activities in areas contaminated by tailings from Pb, Zn, Ag mine[J]. China Environmental Science, 2002, 22 (6): 551-555. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2002.06.016
[27] 滕应, 黄昌勇, 姚槐应, 等.不同相伴阴离子对镉污染红壤的微生物活性影响[J].土壤学报, 2003, 40(5): 738-744. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2003.05.015 Teng Y, Huang C Y, Yao H Y, et al. Effects of different concomitant anions on microbial activities in red soil contaminated by cadmium[J]. Acta Soils Sinica, 2003, 40(5): 738-744. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2003.05.015
[28] 段劼, 马履一, 贾忠奎, 等.抚育强度对侧柏人工林林下植物生长的影响[J].西北林学院学报, 2010, 25(5): 128-135. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb201005028 Duan J, Ma L Y, Jia Z K, et al.Effects of thinning intensity on the undergrowth vegetations under Platycladus orientalis young plantation[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2010, 25(5): 128-135. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb201005028
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李玲琴,吕银华,刘江燕. 超临界CO_2脱除构皮木质素的研究. 仲恺农业工程学院学报. 2020(01): 28-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李萌,李鑫,童延斌,李婷婷,马玉萍,王婷. 甘草渣中木质素的超临界CO_2脱除工艺研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医. 2019(01): 113-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴燕,韩岩,黄楠,吴佳敏,唐彩云,周季纯,黄琼涛. 脱木素工艺对透明木材性能的影响. 林业工程学报. 2019(06): 98-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李新鑫,余学军,俞暾,蒋玉俭. 竹林环境中木质素降解菌株的分离鉴定. 竹子学报. 2016(02): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 左林,程皓,刘江燕. 超临界CO_2萃取脱除甘蔗渣木质素的研究. 生物质化学工程. 2014(06): 44-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: