Population structure and spatial distribution point patterns of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in Wuyishan Mountain, Jiangxi of eastern China
-
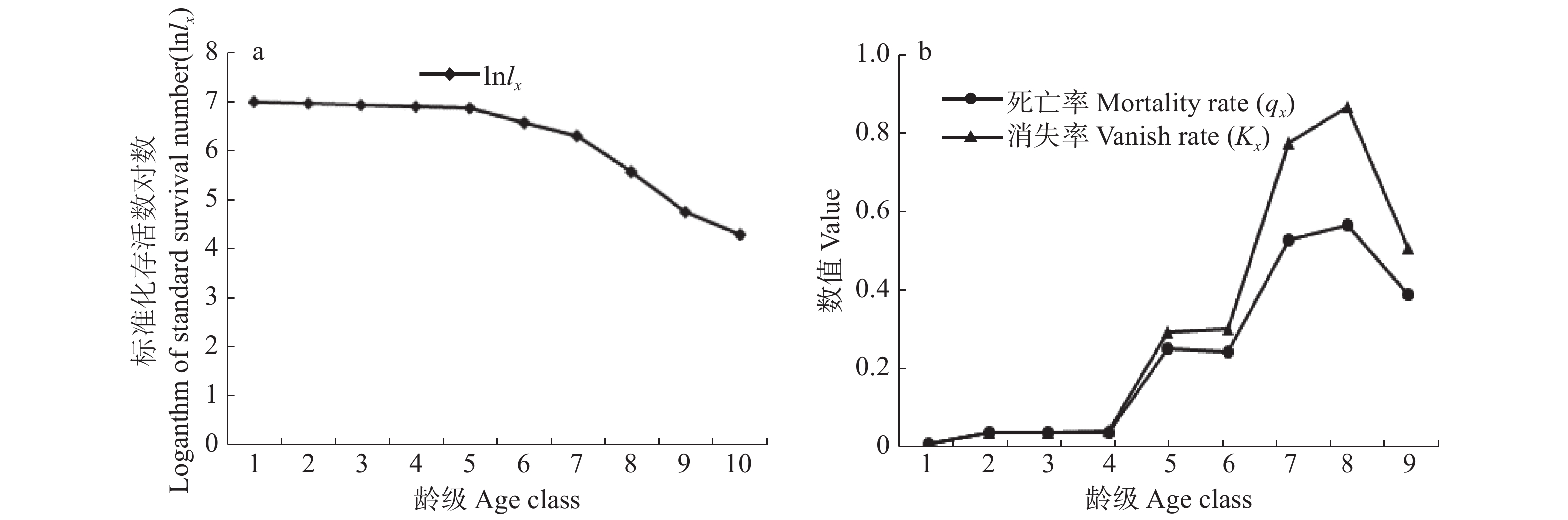
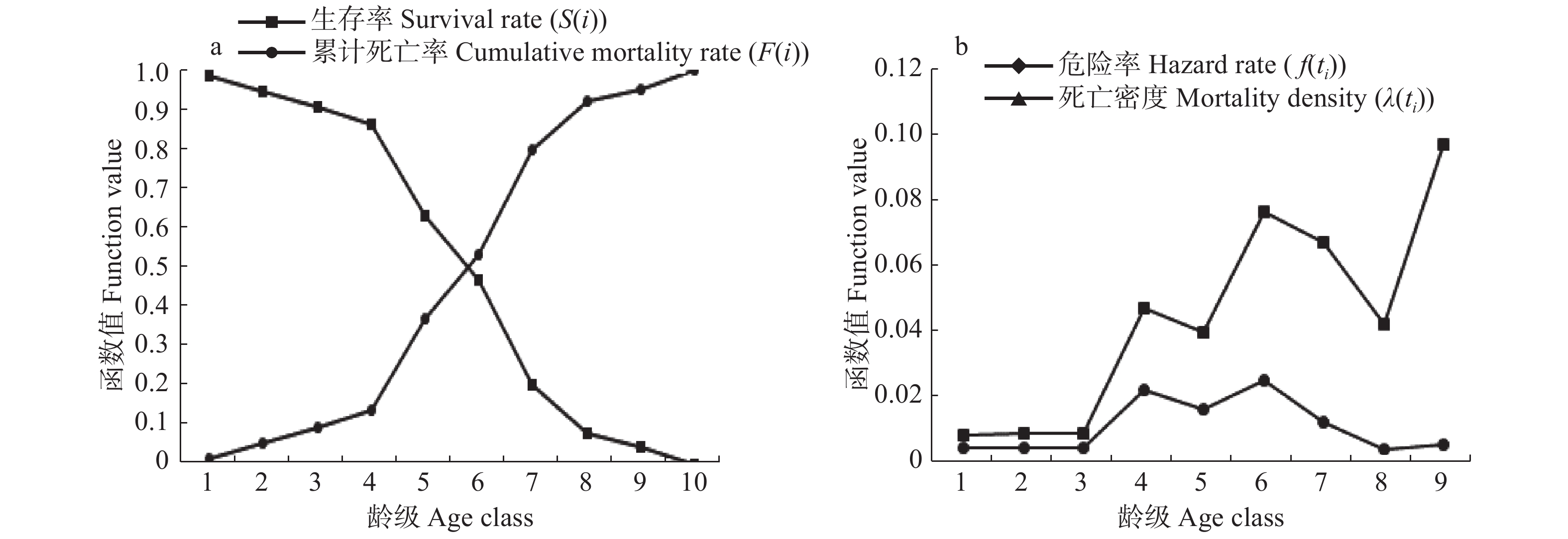
摘要:目的 了解武夷山自然保护区内南方铁杉的种群结构及空间分布情况,对揭示南方铁杉的演替更新具有重要意义。方法 对南方铁杉种群进行样地调查,通过种群年龄结构分析、静态生命表编制、生存分析、时间序列模型预测和点格局分析探索了南方铁杉种群结构和空间分布格局。结果 (1)南方铁杉种群年龄结构呈“金字塔”型,属增长型种群,存活曲线趋于Deevey-Ⅰ型,存活曲线、死亡率和消失率曲线以及生存函数分析表明种群具有前期稳定、中期减少和后期衰退的特点。(2)时间序列预测未来3、6和9个龄级时间后南方铁杉种群各龄级个体数均逐渐增加,南方铁杉幼年个体数相对丰富,老龄级树有较充足的后备资源得以补充,种群能自然更新。(3)南方铁杉种群整体在小尺度(r < 20 m)呈聚集分布,随尺度的增加呈随机分布或均匀分布;种群不同发育阶段的空间分布格局与研究尺度紧密相关,幼树明显呈聚集分布,中树随研究尺度增大由聚集分布向随机分布转变,老树基本呈随机分布。结论 南方铁杉种群天然更新能力较强,保护区维持现有的生境条件,南方铁杉种群将继续呈增长状态。Abstract:Objective Understanding the population structure and spatial distribution pattern of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in Wuyishan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi of eastern China, is of great significance to reveal the succession and regeneration of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis.Method Based on plot investigation of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis population, we analyzed the population structure and spatial distribution point pattern of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis by studying many parameters, such as age structure, static life table, survival curves, time sequence model and point pattern analysis.Result (1) The population presented an increasing population with an age structure of ‘pyramid’ type, and the survival curves suggested that population of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis tended to be the type of Deevey-Ⅰ. The survival curve, mortality curve and vanish curve and survival function analysis of population showed that the characteristics of the population were stable in early age stage, decreased in middle age period, then declined in old age period. (2) Time sequence model predicted that the number of each age class individuals of the Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis population would increase in the age classes of 3, 6 and 9 in the future. The number of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis was relatively abundant at a young stage, so that sufficient reserve resources can replenish the old trees, and the population can naturally renewed. (3) Point pattern analysis indicated that the individuals were significantly clustered at the small scale (r < 20 m), and the distribution became more random and regular at larger scales. The spatial distribution pattern of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis population at different developmental periods was closely related to the study scale. The spatial distribution point pattern of young individuals was of obviously aggregated distribution. The spatial distribution point pattern of middle individuals was aggregated to random as the study scale increased, and the old individuals showed randomly distribution.Conclusion The population can regenerate naturally and the population will tend to increase under the maintaining of the current habitat.
-
-
表 1 南方铁杉种群静态生命表
Table 1 Static life table of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis population
龄级
Age classDBH/cm 组中值
Group median/cmax lx lnlx dx qx Lx Tx ex Kx Sx 1 0 ~ 10 5 146 1 000 6.908 14 0.014 0 993 5 629 5.629 0.014 0.986 2 10 ~ 20 15 144 986 6.894 41 0.041 6 965.5 4 636 4.702 0.043 0.958 3 20 ~ 30 25 138 945 6.851 41 0.043 4 924.5 3 670.5 3.884 0.045 0.957 4 30 ~ 40 35 132 904 6.806 41 0.045 4 883.5 2 746 3.038 0.046 0.955 5 40 ~ 50 45 126 863 6.760 233 0.270 0 746.5 1 862.5 2.158 0.314 0.730 6 50 ~ 60 55 92 630 6.446 164 0.260 3 548 1 116 1.771 0.322 0.740 7 60 ~ 70 65 68 466 6.144 261 0.560 1 335.5 568 1.219 0.821 0.440 8 70 ~ 80 75 30 205 5.323 123 0.600 0 143.5 232.5 1.134 0.916 0.400 9 80 ~ 90 85 12 82 4.407 34 0.414 6 65 89 1.085 0.536 0.585 10 90 ~ 100 95 7 48 3.871 − − 24 24 0.5 − − 注:ax存活数;lx存活量;dx死亡数;qx死亡率;Lx区间寿命;Tx总寿命;ex期望寿命;Kx消失率;Sx存活率。Notes: ax means survival; lx means survival quantity; dx means death number; qx means mortality rate; Lx means span life; Tx means total life; ex means life expectancy; Kx means vanish rate; Sx means survival rate. 表 2 南方铁杉种群龄级结构的时间预测
Table 2 Time sequence prediction in the quantitative dynamics of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis population
龄级
Age class原始数据
Primary dataM3(1) M6(1) M9(1) 1 146 − − − 2 144 − − − 3 138 143 − − 4 132 138 − − 5 126 132 − − 6 92 117 130 − 7 68 95 117 − 8 30 63 98 − 9 12 35 77 99 10 7 16 56 83 -
[1] 张志祥. 珍稀濒危植物南方铁杉研究进展[J]. 生物学教学, 2011, 36(6):3−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7549.2011.06.002 Zhang Z X. Research advance of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis[J]. Biological Teaching, 2011, 36(6): 3−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7549.2011.06.002
[2] 杨清培, 钟安建, 金志农, 等. 江西武夷山南方铁杉群落分类及更新能力评价[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2014, 36(6):1275−1283. Yang Q P, Zhong A J, Jin Z N, et al. A community classification of natural forest of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis and its regeneration capacity[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2014, 36(6): 1275−1283.
[3] 陈林, 龚粤宁, 谢国光, 等. 广东南岭国家级自然保护区珍稀濒危植物及其保护[J]. 植物科学学报, 2012, 30(3):277−284. Chen L, Gong Y N, Xie G G, et al. Rare and endangered plants and conservation in Guangdong Nanling National Nature Reserve[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2012, 30(3): 277−284.
[4] 李林, 魏识广, 黄忠良, 等. 猫儿山两种孑遗植物的更新状况和空间分布格局分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(2):144−150. Li L, Wei S G, Huang Z L, et al. Regenerative condition and analysis of spatial distribution pattern of two relic plants in Maoershan Mountain, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(2): 144−150.
[5] 冯祥麟, 胡刚, 刘正华. 贵阳高坡南方铁杉群落特征及种群结构调查研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2011, 39(2):26−29. Feng X L, Hu G, Liu Z H. Research on the community characteristics and population dynamics of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis on Gaopo in Guiyang City[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 2011, 39(2): 26−29.
[6] 丁巧玲, 刘忠成, 王蕾, 等. 湖南桃源洞国家级自然保护区南方铁杉种群结构与生存分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(6):1233−1244. Ding Q L, Liu Z C, Wang L, et al. Structure and survival analysis of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis populations in Taoyuandong National Nature Reserve, Hunan Province[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(6): 1233−1244.
[7] 杨清培, 金志农, 裘利洪, 等. 江西武夷山南方铁杉更新格局及代际关联性分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(4):939−945. Yang Q P, Jin Z N, Qiu L H, et al. Regeneration pattern and intergeneration association of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(4): 939−945.
[8] 祁红艳, 金志农, 杨清培, 等. 江西武夷山南方铁杉生长规律及更新困难的原因解释[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2014, 36(1):137−143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2014.01.021 Qi H Y, Jin Z N, Yang Q P, et al. Growing law and cause of poor regeneration of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2014, 36(1): 137−143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2014.01.021
[9] 何建源, 卞羽, 吴焰玉, 等. 不同坡向濒危植物南方铁杉的分布格局[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(13):122−125. He J Y, Bian Y, Wu Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution pattern of the endangered plant Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in different aspect[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(13): 122−125.
[10] 罗金旺. 福建光泽天然林中南方铁杉的种内与种间竞争[J]. 林业科技开发, 2011, 25(4):71−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8101.2011.04.018 Luo J W. Intra and interspecific competition in Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in a natural forest in Guangze, Fujian, China[J]. China Forestry Science & Technology, 2011, 25(4): 71−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8101.2011.04.018
[11] 赵峰. 莽山南方铁杉群落种间关系研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(31):68−72. Zhao F. The relationship of species in Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis community in Mangshan Mountain Natural Reserve[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(31): 68−72.
[12] 何建源, 荣海, 吴焰玉, 等. 武夷山南方铁杉群落乔木层种间联结研究[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2010, 30(2):169−173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2010.02.018 He J Y, Rong H, Wu Y Y, et al. Study on interspecific association of main populations in arborous layer of a Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis community in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2010, 30(2): 169−173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2010.02.018
[13] 罗金旺. 福建光泽南方铁杉天然林的生长规律与生物量[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2011, 31(2):156−160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2011.02.013 Luo J W. Growth and biomass of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in a natural forest in Guangze, Fujian, China[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2011, 31(2): 156−160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2011.02.013
[14] 张强, 郭传友, 张兴旺, 等. 基于光合作用和抗氧化机制的南方铁杉和褐叶青冈越冬策略研究[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(2):200−207. Zhang Q, Guo C Y, Zhang X W, et al. Photosynthesis and antioxidant defense strategies in overwintering plants of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis and Cyclobalanopsis stewardiana[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(2): 200−207.
[15] 张志祥, 刘鹏, 徐根娣, 等. 不同群落类型下南方铁杉金属元素含量差异及其与土壤养分因子的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(5):505−516. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.05.004 Zhang Z X, Liu P, Xu G D, et al. Metal element contents of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in different community types and its relationship with soil nutrient factors in eastern China[J]. Chinese Journal of plant Ecology, 2010, 34(5): 505−516. doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.05.004
[16] 谢琼中. 南方铁杉群落物种多样性及乔木优势种生态位初步研究[J]. 天津农业科学, 2011, 17(2):133−136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2011.02.039 Xie Q Z. Primary study on species diversity and niche characteristics of dominant tree species in Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis community[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Science, 2011, 17(2): 133−136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2011.02.039
[17] 吴九玲, 钱晓鸣, 刘燕. 南方铁杉外生菌根的扫描电镜观察[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然版), 2001, 40(6):1337−1341. Wu J L, Qian X M, Liu Y. SEM-observation of ectomycorrhizal outer surface of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis (Flous) Cheng[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science Edition), 2001, 40(6): 1337−1341.
[18] 钱晓鸣, 黄耀坚, 张艳辉, 等. 武夷山自然保护区南方铁杉外生菌根生物多样性[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然版), 2007, 36(2):180−185. Qian X M, Huang Y J, Zhang Y H, et al. Biodiversity of the ectomycorrhizal on the rare and endangered tree species Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis (Flous) Cheng in Wuyishan Nature ReServe[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 36(2): 180−185.
[19] 何建源, 卞羽, 吴焰玉, 等. 南方铁杉林林隙自然干扰规律[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2009, 29(6):7−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1914.2009.06.002 He J Y, Bian Y, Wu Y Y, et al. Study on the law of natural disturbance in the gaps of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis fores[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2009, 29(6): 7−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1914.2009.06.002
[20] 李晓铁, 玉伟朝, 罗远周, 等. 南方铁杉扦插繁殖技术[J]. 林业实用技术, 2008(6):21−22. Li X T, Yu W C, Luo Y Z, et al. Cutting propagation techniques of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis[J]. Practical Forestry Technology, 2008(6): 21−22.
[21] 袁荣斌, 邹思成, 兰文军, 等. 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区南方铁杉资源调查初报[J]. 南方林业科学, 2012(4):37−39. Yuan R B, Zou S C, Lan W J, et al. Report of resources investigation of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve[J]. South China Forestry Science, 2012(4): 37−39.
[22] 王大来. 莽山南方铁杉种群格局分布格局研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(1):74−77. Wang D L. Distribution pattern of Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis populations in Mang Mountain[J]. Chinses Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(1): 74−77.
[23] 郑万钧. 中国树种分类分布的研究[J]. 林业科学, 1981, 17(4):453−455. Zheng W J. Note on the scientific names and geographical distribution of some Chinese trees[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1981, 17(4): 453−455.
[24] 陈易之. 武夷山自然保护区动、植物资源[J]. 资源科学, 1994, 16(3):65−67. Chen Y Z. Plant and animal resources in natural reserve of Wuyishan Mountain[J]. Resources Science, 1994, 16(3): 65−67.
[25] 袁在翔, 金雪梅, 马婷瑶, 等. 南京灵谷寺栓皮栎种群结构与动态[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(6):1488−1494. Yuan Z X, Jin X M, Ma T Y, et al. The population structure and dynamics of Quercus variadilis in Nanjing Spirit Valley[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(6): 1488−1494.
[26] 杨凤翔, 王顺庆, 徐海根, 等. 生存分析理论及其在研究生命表中的应用[J]. 生态学报, 1991, 11(2):153−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1991.02.013 Yang F X, Wang S Q, Xu H G, et al. The theory of survival analysis and its application to life table[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1991, 11(2): 153−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.1991.02.013
[27] 李妍, 李登武, 韩东辰. 贺兰山东坡青海云杉种群结构[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(1):50−56. Li Y, Li D W, Han D C. Population dynamics of Picea crassifolia on the eastern slope of Helan Mountain[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2014, 31(1): 50−56.
[28] 刘丹, 刘士玲, 郭忠玲, 等. 水冬瓜赤杨种群生命表与时间序列分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(10):62−69. Liu D, Liu S L, Guo Z L, et al. Population life table and time sequence prediction of Alnus sibirica[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(10): 62−69.
[29] Wiegand T, Moloney K A. Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology[J]. Oikos, 2004, 104(2): 209−229. doi: 10.1111/oik.2004.104.issue-2
[30] 王鑫厅, 张维华, 姜超, 等. 重复取样条件下的点格局分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(5):577−584. Wang X T, Zhang W H, Jiang C, et al. Point pattern analysis under conditions of replicated sampling[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(5): 577−584.
[31] 张金屯. 植被数量生态学方法[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1995: 79−86. Zhang J T. Methods of exposure vegetation ecology [M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 1995: 79−86.
[32] He F, Legendre P, Lafrankie J V. Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2010, 8(1): 105−114.
[33] Ripley B D. Modelling spatial patterns[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1977, 39(2): 172−212.
[34] 宗国, 白雪娇, 张淑媛, 等. 辽东山区次生林乔木幼苗分布格局与种间空间关联性[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(1):18−24. Zong G, Bai X J, Zhang S Y, et al. Spatial pattern and interspecific spatial association of tree seedlings in a secondary forest in montane region of eastern Liaoning Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(1): 18−24.
[35] 樊登星, 余新晓. 北京山区栓皮栎林优势种群点格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(2):318−325. Fan D X, Yu X X. Spatial point pattern analysis of Quercus variabilis and Pinus tabulaeformis populations in a mountainous area of Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(2): 318−325.




 下载:
下载: