Runoff collection and irrigation utilization cost of park green space in semi humid area: a case study of the green space of East Binhu Road in Qian’an City, Hebei Province of northern China
-
摘要:目的 为探索半湿润地区城市公园绿地海绵城市建设的可行性和经济性,为设计师和决策者提供经济层面的决策参考,本文以雨水径流收集灌溉利用的成本效益为研究内容,以河北省迁安市滨湖东路已建成集雨型绿地为研究对象,研究半湿润地区公园绿地径流收集灌溉利用成本。方法 根据场地径流量确定雨水调蓄池容积,基于2014—2021年逐日实测降雨数据和2022—2024年预测降雨数据,利用容积法测算年收集径流量,对比绿地完全用自来水灌溉成本和用收集径流与自来水共同灌溉成本,得到节约成本,并对比建设成本和维护成本得出建设效益。结果 基于2014—2021年的实际降雨数据和2022—2024年的预测降雨数据与建设成本测算,在汇水面积为155.37 hm2、灌溉面积为151.410 hm2时,以解决径流为目的,从长期效益出发,调蓄池规模最佳选择方案为3 000 m3,年平均节约灌溉费用101 114.15元,年平均效益65 424.15元。结论 半湿润地区径流收集灌溉利用具有一定效益,基于某个时间段内植物的灌溉需求量作为径流收集的标准,可明显减少建设成本,增加径流利用效率。Abstract:Objective In order to explore the feasibility and economy of urban park green space sponge city construction in semi humid area and provide economic decision-making reference for designers and decision makers, this paper takes the cost-effectiveness of rainwater runoff collection and irrigation as the research content, and takes the built rainwater collection green space on Binhu East Road, Qian’an City, Hebei Province of northern China as the research object to study the cost of rainwater collection and irrigation of park green space in semi humid area.Method The volume of rainwater storage tank was determined according to the site runoff. Based on the daily measured rainfall data from 2014 to 2021 and the predicted rainfall data from 2022 to 2024, the volume method was used to calculate the annual collected runoff. The cost savings were obtained by comparing the cost of green land irrigation with tap water and the cost of irrigation with collected runoff and tap water, and the construction benefits were obtained by comparing the construction cost and maintenance cost.Result Based on the actual rainfall data from 2014 to 2021, the predicted rainfall data from 2022 to 2024 and the calculation of construction cost, when the catchment area was 155.37 ha and the irrigation area was 151.410 ha, for the purpose of solving runoff and from the perspective of long-term benefits, the best scheme for the scale of regulating and storage tank was 3 000 m3, and the average annual irrigation cost was 101114.15 CNY, the average annual benefit was 65 424.15 CNY.Conclusion Runoff collection and irrigation utilization in semi humid areas has certain benefits. Taking the irrigation demand of plants in a certain period of time as the standard of runoff collection can significantly reduce the construction cost and increase the runoff utilization efficiency.
-
-
表 1 滨湖东路东侧绿地雨水径流控制量
Table 1 Amount of rainwater runoff control on the east side of Binhu East Road
设计降雨量
Design rainfall/mm汇水区域名称
Name of catchment area汇水面积/hm2
Catchment area/ha综合雨量径流系数Comprehensive rainfall
runoff coefficient设计调蓄容积
Design storage capacity/m3总计
Total/m342.6 外部汇水面(汇流入东侧场地)External catchment surface (flow into the east site) 地块1 Plot 1 15.30 0.15 ~ 0.80 4 330.93 40 361.71 地块2 Plot 2 60.42 0.15 ~ 0.80 18 118.41 地块3 Plot 3 35.10 0.15 ~ 0.80 10 660.65 滨湖东路
Binhu East Road10.00 0.80 3 408.00 阜安大街
Fu’an Street3.40 0.80 1 158.72 惠兴大街
Huixing Street4.40 0.80 1499.52 29.6 内部汇水面
Internal catchment surface滨湖东路绿地(东侧)
Binhu East Road greenland (east side)26.75 0.15 1 185.48 表 2 各类园林植物系数相关指标
Table 2 Indexes related to the coefficients of various garden plants
植被类型
Vegetation type种类因子
Type factor(Ks)密度因子
Density factor(Kd)小气候因子Microclimate factor(Kmc) 长势好
Good growth长势一般
Average growth长势差
Bad growth长势好
Good growth长势一般
Average growth长势差
Bad growth长势好
Good growth长势一般
Average growth长势差
Bad growth乔木 Tree 0.90 0.50 0.20 1.30 1.00 0.50 1.40 1.00 0.50 灌木 Shrub 0.70 0.50 0.20 1.10 1.00 0.50 1.30 1.00 0.50 地被植物
Ground-cover plant0.90 0.50 0.20 1.10 1.00 0.50 1.20 1.00 0.50 乔−灌−草
Tree-shrub-grass0.90 0.50 0.20 1.30 1.00 0.60 1.40 1.00 0.50 冷季型草
Cool season grass0.80 1.00 1.00 0.60 1.20 1.00 0.80 注:表2来源于参考文献[25]。Note: Tab. 2 is cited from reference [25]. 表 3 各园林植物的园林系数
Table 3 Landscape coefficients of each garden plant
植被类型
Vegetation type种类因子
Type factor (Ks)密度因子
Density factor(Kd)小气候因子Microclimate factor(Kmc) 园林系数
Garden coefficient(KL)乔木 Tree 0.90 1.30 1.40 1.64 灌木 Shrub 0.70 1.10 1.30 1.00 地被植物
Ground-cover plant0.90 1.10 1.20 1.19 乔−灌−草
Tree-shrub-grass0.90 1.30 1.40 1.64 冷季型草
Cool season grass0.80 1.00 1.20 0.96 注:表3来源于参考文献[25]。Note: Tab. 3 is cited from reference [25]. 表 4 LID设施及其配件造价维护表
Table 4 Cost maintenance table of lid facilities and their accessories
名称
Name建设单价/元
Construction unit price/CNY维护单价/(元·a−1)
Maintenance unit price/(CNY·year−1)雨水调蓄池 Rainwater storage tank 388 690.70 16 575.00 自控自吸泵 Self-control self-priming pump 6 750.00 1 270.00 表 5 2014—2024年年平均调蓄池收集量与节约成本
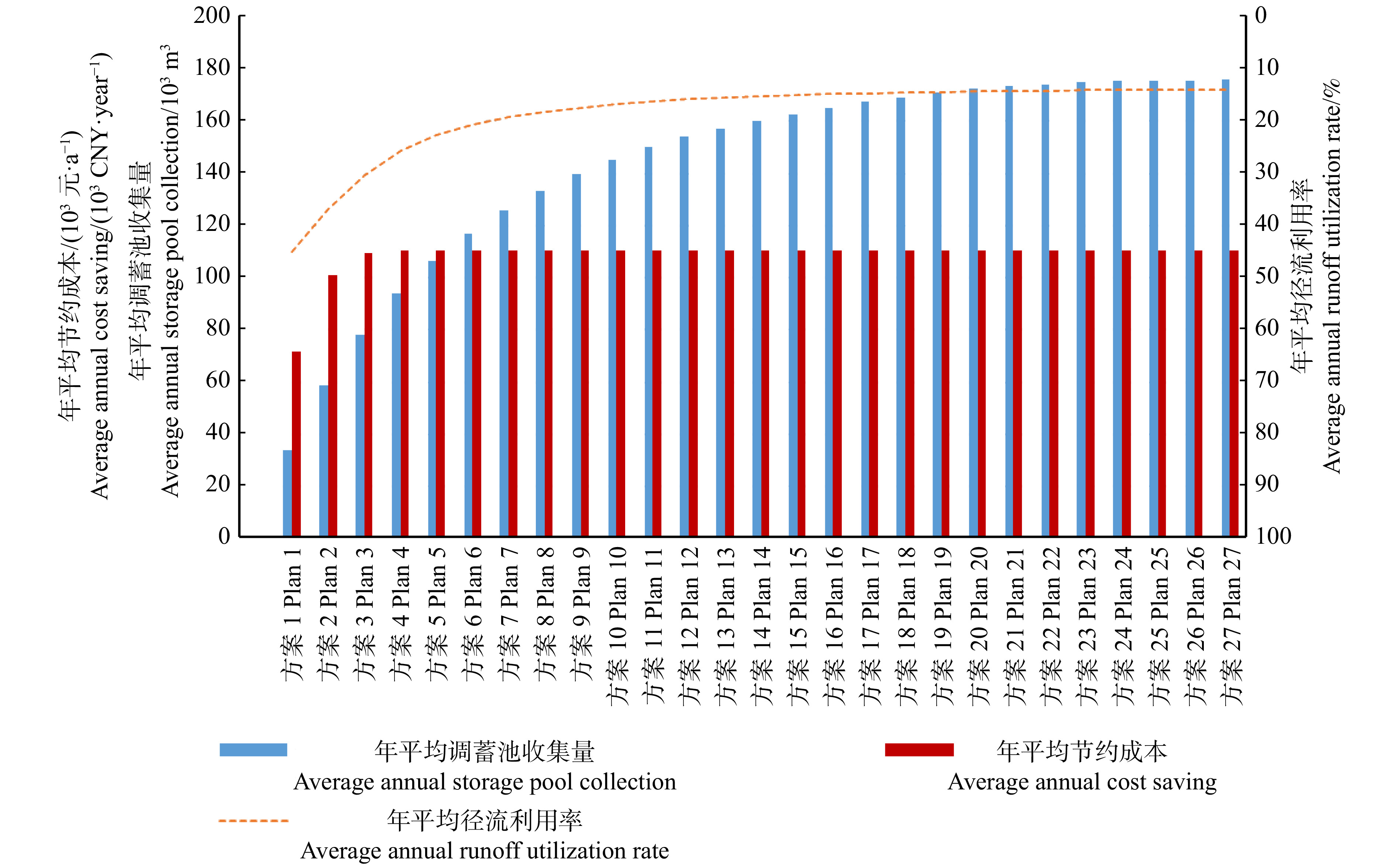
Table 5 Annual average collection volume of regulation and storage tank and cost savings from 2014 to 2024
方案
Plan年平均调蓄池收集量Average annual storage pool collection/m3 年平均径流利用率
Average annual runoff utilization rate/%年平均节约成本/(元·a−1)
Average annual cost saving/(CNY·year−1)方案1 Plan 1 34 123.38 44.95 71 908.34 方案2 Plan 2 58 951.48 36.84 101 114.15 方案3 Plan 3 78 271.25 30.35 109 667.28 方案4 Plan 4 93 944.53 25.63 110 661.16 方案5 Plan 5 106 598.61 22.66 110 661.16 方案6 Plan 6 116 944.00 20.69 110 661.16 方案7 Plan 7 125 803.95 19.24 110 661.16 方案8 Plan 8 133 404.79 18.14 110 661.16 方案9 Plan 9 139 876.88 17.31 110 661.16 方案10 Plan 10 145 352.78 16.66 110 661.16 方案11 Plan 11 150 115.53 16.14 110 661.16 方案12 Plan 12 154 119.79 15.72 110 661.16 方案13 Plan 13 157 221.16 15.42 110 661.16 方案14 Plan 14 160 084.80 15.18 110 661.16 方案15 Plan 15 162 763.84 14.96 110 661.16 方案16 Plan 16 165 218.39 14.76 110 661.16 方案17 Plan 17 167 532.34 14.58 110 661.16 方案18 Plan 18 169 215.16 14.47 110 661.16 方案19 Plan 19 170 851.52 14.35 110 661.16 方案20 Plan 20 172 450.50 14.25 110 661.16 方案21 Plan 21 173 464.57 14.17 110 661.16 方案22 Plan 22 174 277.92 14.12 110 661.16 方案23 Plan 23 174 893.48 14.07 110 661.16 方案24 Plan 24 175 358.54 14.04 110 661.16 方案25 Plan 25 175 629.89 14.02 110 661.16 方案26 Plan 26 175 766.26 14.01 110 661.16 方案27 Plan 27 175 902.62 14.00 110 661.16 -
[1] 张伟, 车伍. 海绵城市建设内涵与多视角解析[J]. 水资源保护, 2016, 32(6): 19−26. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2016.06.003 Zhang W, Che W. Connotation and multi-angle analysis of sponge city construction[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2016, 32(6): 19−26. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2016.06.003
[2] 张盼盼. 基于CNKI的我国海绵城市研究文献计量分析[J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(增刊1): 16−19. Zhang P P. Bibliometric analysis on sponge city in China based on CNKI[J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(Suppl.1): 16−19.
[3] 王俊岭, 聂练桃, 张雅君, 等. 低影响开发雨洪管理技术费效分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2018, 44(4): 99−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.04.025 Wang J L, Nie L T, Zhang Y J, et al. Analysis on cost and benefit of low impact development in storm-water management[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 44(4): 99−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.04.025
[4] USEPA. Reducing stormwater costs through low impact development (LID) strategies and practices[Z/OL]. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency Nonpoint Source Control Branch, 2007[2020−08−18]. http://sarasota.wateratlas.usf.edu/upload/documents/Reducing-Stormwater-Costs-through-LID.pdf.
[5] 李大龙, 贾绍凤, 吕爱锋, 等. 中国城市LID技术设施的成本效益区域差异[J]. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(11): 1402−1412. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.009 Li D L, Jia S F, Lü A F, et al. Regional difference of cost effectiveness of low impact development (LID) technical facilities in Chinese cities[J]. Progress in Geography, 2017, 36(11): 1402−1412. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.009
[6] 黄初冬, 彭祖平, 邹澄昊, 等. 基于SWMM模型与成本效益的LID布局优化方法研究: 以嘉兴某住宅小区为例[J]. 建筑与文化, 2019(10): 62−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4909.2019.10.023 Huang C D, Peng Z P, Zou C H, et al. A study on an optimization method of LID distribution based on SWMM and cost-effectiveness: a case study in Jiaxing residence community[J]. Architecture & Culture, 2019(10): 62−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4909.2019.10.023
[7] 陈韬, 李业伟, 张雅君. 典型城市雨水低影响开发(LID)措施的成本−效益分析[J]. 西南给排水, 2014, 36(2): 41−46. Chen T, Li Y W, Zhang Y J. Cost-benefit analysis of typical urban rainwater low-impact development (LID) measures[J]. Southwest China Water Supply and Drainage, 2014, 36(2): 41−46.
[8] 樊超, 孙学良. 建筑小区的海绵化改造效益核算: 以固原市玫瑰苑小区为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(2): 316−322. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190019 Fan C, Sun X L. Benefit accounting analysis of sponge transformation in building and communities: taking Rose Communities in Guyuan City as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2020, 10(2): 316−322. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190019
[9] Icekson-Tal N, Avraham O, Sack J, et al. Water reuse in Israel: the Dan Region Project: evaluation of water quality and reliability of plant’s operation[J]. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 2003, 3(4): 231−237. doi: 10.2166/ws.2003.0067
[10] Roseen R M, Janeski T V, Simpson M, et al. Economic and adaptation benefits of low impact development[C]//Proceedings of low impact development technology: implementation and economics. Reston: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2015: 74−92.
[11] 林辰松. 半湿润地区集雨型绿地设计研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2017. Lin C S. The research on rainwater harvesting green space design in semi-humid region[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2017.
[12] 戈晓宇, 李雄. 基于海绵城市建设指引的迁安市集雨型绿色基础设施体系构建策略初探[J]. 风景园林, 2016, 23(3): 27−34. Ge X Y, Li X. Research on building of rainwater-harvesting green infrastructure pattern of Qian’an based on the instruction of sponge city construction[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2016, 23(3): 27−34.
[13] 康嘉奇, 戈晓宇. 半湿润地区外源径流型海绵绿地设计方法研究: 以迁安市滨湖东路绿地为例[J]. 风景园林, 2019, 26(8): 77−82. Kang J Q, Ge X Y. Method for designing exogenous runoff sponge green space in semi-humid region: a case study of the green space of East Binhu Road in Qian’an City[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2019, 26(8): 77−82.
[14] 阳烨, 何俊超, 朱江, 等. 西北半干旱河谷型城市海绵城市专项规划方法研究: 以青海省西宁市为例[J]. 风景园林, 2021, 28(3): 56−61. Yang Y, He J C, Zhu J, et al. Research on sponge city special planning method in semi-arid valley cities in Northwest China: a case study of Xining City, Qinghai Province[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2021, 28(3): 56−61.
[15] 王立鹏, 王颖, 刘晓红. 浅谈迁安市园林绿化树种的选择[J]. 太原科技, 2007(7): 47−48. Wang L P, Wang Y, Liu X H. Talk about the choice of garden afforestation seeds in Qian’an City[J]. Taiyuan Science and Technology, 2007(7): 47−48.
[16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 海绵城市建设技术指南: 低影响开发雨水系统构建(试行)[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. Technical guide for sponge city construction: construction of low-impact development rainwater system (trial)[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2014.
[17] 上海市建设和交通委员会. 室外排水设计标准: GB 50014—2021[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2021. Shanghai Construction and Transportation Commission. Design standard for outdoor drainage: GB 50014−2021[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2021.
[18] 北京清华同衡规划设计研究院有限公司. 迁安市海绵城市专项规划(2015—2030)(修编稿)[Z]. 北京: 北京清华同衡规划设计研究院有限公司, 2016. Beijing Tsinghua Tongheng Planning and Design Institute Co., Ltd. Qian’an City: an sponge city special planning (2015−2030) (revised draft)[Z]. Beijing: Beijing Tsinghua Tongheng Planning and Design Institute Co., 2016.
[19] 河北省城乡规划设计研究院. 迁安市城市排水(雨水)防涝综合规划说明书[Z]. 石家庄: 河北省城乡规划设计研究院, 2014. Hebei Urban and Rural Planning and Design Institute. Qian’an City urban drainage (rainwater) waterlogging prevention comprehensive planning manual[Z]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Urban and Rural Planning and Design Institute, 2014.
[20] 上海同济城市规划研究院. 迁安市中心城区雨水工程规划图[Z]. 上海: 上海同济城市规划研究院, 2013. Shanghai Tongji Urban Planning and Research Institute. Planning map of rainwater engineering in Qian ’an City Center[Z]. Shanghai: Shanghai Tongji Urban Planning and Research Institute, 2013.
[21] 中国建筑标准设计院. 国家建筑标准设计图集10SS705: 雨水综合利用: GJBT—1147[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2010. China Building Standard Design Institute. Comprehensive utilization of rainwater 10SS705: GJBT−1147[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2010.
[22] 中国建筑标准设计院. 国家建筑标准设计图集05S804: 矩形钢筋混凝土蓄水池: GJBT—873[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2007. China Building Standard Design Institute. Rectangular reinforced concrete reservoir 05S804: GJBT−873[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2007.
[23] 于淼, 戈晓宇. 基于SWMM模拟的首钢西十地块低影响开发系统雨洪调控效果研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(12): 97−109. Yu M, Ge X Y. Effects of rain flood control about low impact development system in west 10 plot of Shougang based on the SWMM simulation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(12): 97−109.
[24] 林辰松, 邵明, 葛韵宇, 等. 基于SWMM情境模拟的外源雨水型公园绿地雨洪调控效果研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(12): 92−103. Lin C S, Shao M, Ge Y Y, et al. Research of storm flood regulation efficiency of the low impact development of exogenous-rainwater park based on the SWMM simulation[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(12): 92−103.
[25] 邱振存, 管健. 园林绿化植物灌溉需水量估算[J]. 节水灌溉, 2011(4): 48−50, 54. Qiu Z C, Guan J. Estimation of irrigation water demand for landscaping plants[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2011(4): 48−50, 54.
[26] 陈泓宇, 董宇翔, 林辰松. 集雨节水型绿地设计研究[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 46(12): 56−59. Chen H Y, Dong Y X, Lin C S. Study on design of rainwater harvesting and water-saving green space[J]. Water Supply and Drainage, 2020, 46(12): 56−59.
[27] 霍治澎, 吴小强. 下沉式绿地和雨水回收中水利用相结合绿色建筑技术在延安地区的具体应用[J]. 建筑节能, 2017, 45(12): 70−72. Huo Z P, Wu X Q. Green building techniques applied in Yan’an: sunken green land and rainwater as reclaimed water[J]. Building Energy Efficiency, 2017, 45(12): 70−72.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李玲琴,吕银华,刘江燕. 超临界CO_2脱除构皮木质素的研究. 仲恺农业工程学院学报. 2020(01): 28-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李萌,李鑫,童延斌,李婷婷,马玉萍,王婷. 甘草渣中木质素的超临界CO_2脱除工艺研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医. 2019(01): 113-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴燕,韩岩,黄楠,吴佳敏,唐彩云,周季纯,黄琼涛. 脱木素工艺对透明木材性能的影响. 林业工程学报. 2019(06): 98-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李新鑫,余学军,俞暾,蒋玉俭. 竹林环境中木质素降解菌株的分离鉴定. 竹子学报. 2016(02): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 左林,程皓,刘江燕. 超临界CO_2萃取脱除甘蔗渣木质素的研究. 生物质化学工程. 2014(06): 44-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: