Analysis on spatial distribution pattern and overlapping status of natural protected area in Liaoning Province of northeastern China
-
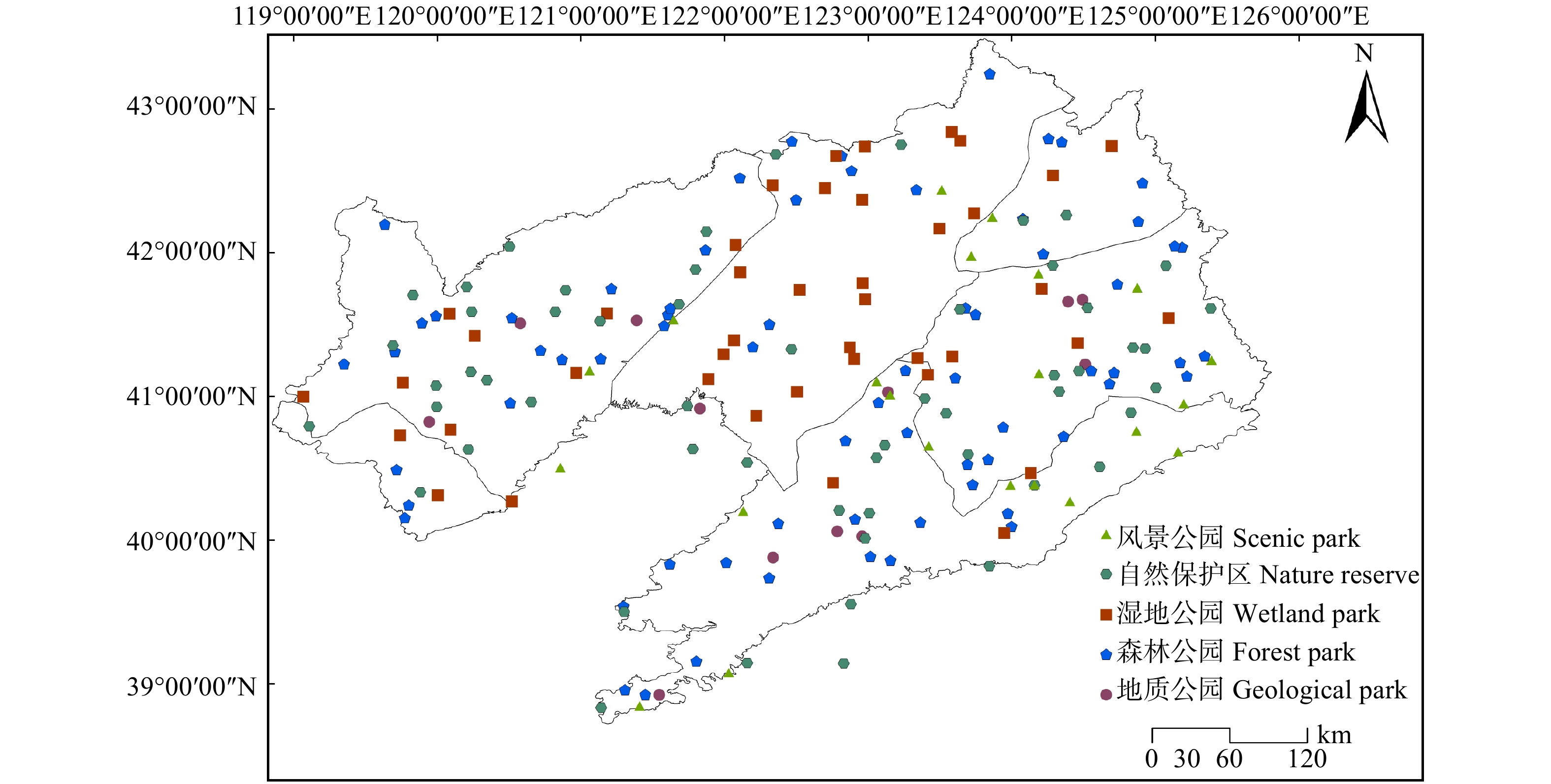
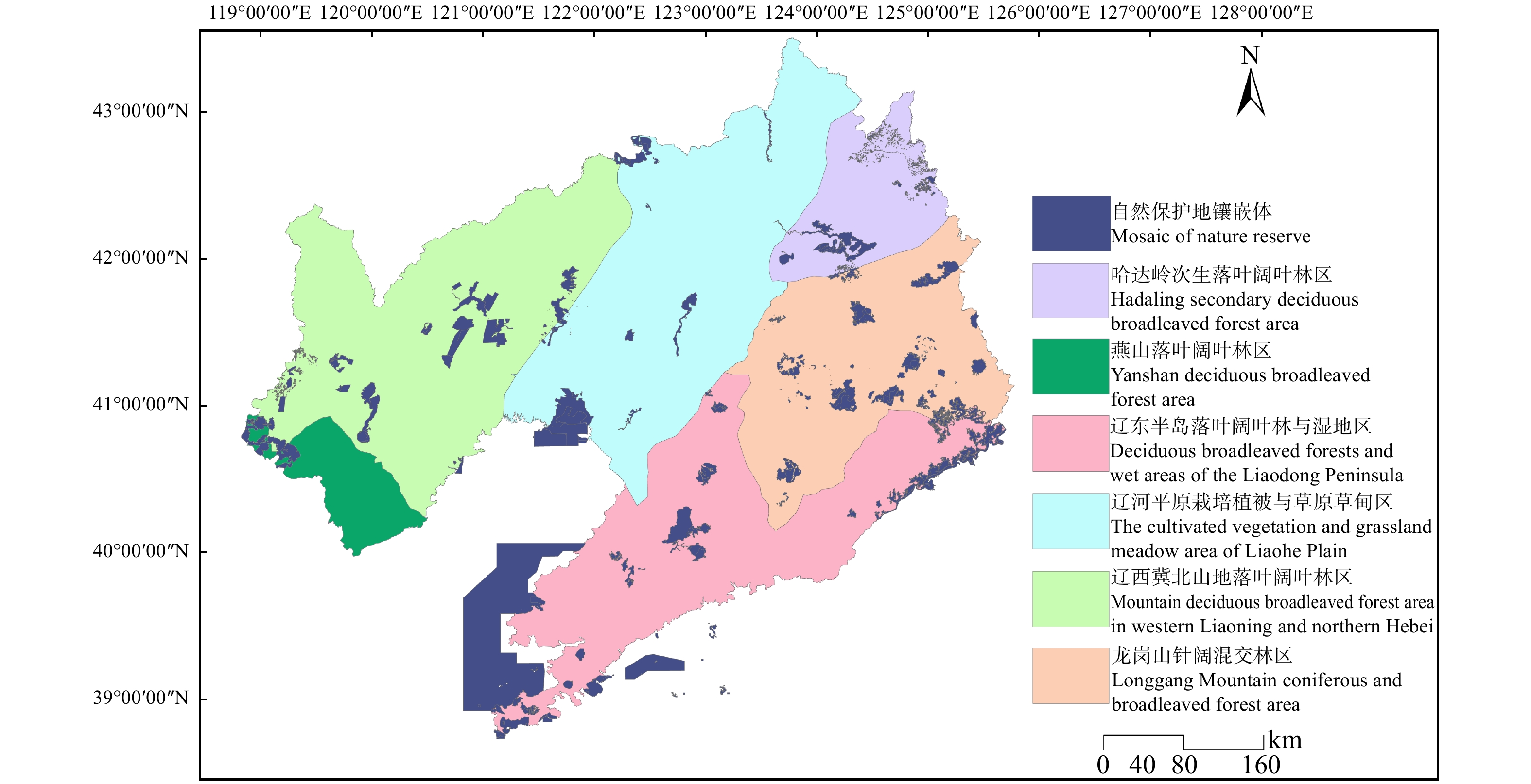
摘要:目的 通过对辽宁省自然保护地重叠现状进行定性与定量的分析,描述辽宁省6类235处自然保护地空间分布情况与重叠现状及特征,由此对辽宁省自然保护地空间分布格局现状进行评价,为辽宁省自然保护地的整合优化提供科学参考与理论依据。方法 利用最邻近指数分析与核密度分析,评价辽宁省自然保护地空间分布现状,同时提出了自然保护地镶嵌体的概念,通过分析镶嵌体内部的重叠板块占比情况,对辽宁省自然保护地重叠现状进行定性与定量的分析,相较于传统重叠率分析方法,为分析一个区域内多层重叠的情况我们提出了自然保护地多元重叠率计算方法。结果 (1)辽宁省自然保护地的最邻近比率为0.904,表明辽宁省自然保护地分布属聚集型分布;(2)结合自然保护综合地理区划,辽宁省自然保护地主要形成4个聚集区域;(3)辽宁省自然保护地存在重叠情况的自然保护地数量占自然保护地总数的50.43%,重叠面积占辽宁省自然保护地的8.63%。重叠情况主要发生在自然保护区与自然公园之间,数量共107处,面积达134 421.1 hm2;(4)辽宁省存在重叠的斑块中两层重叠82处、三层重叠13处、四层重叠1处;(5)辽宁省可划分为36个自然保护地镶嵌体,其中内部重叠率高于50%的保护地镶嵌体有8处,最高为81.34%;低于10%的保护地镶嵌体有6个,最低为1.82%。结论 将重叠保护地进行整合优化时,镶嵌体重叠率过高代表保护服务功能与划定保护范围过剩,整合时对于这种情况所涉及的保护地建议以合并为主。下一步对于计划新建自然保护地应将现有保护服务力度较低或中等区域进行补充完善,将如辽东半岛阔叶落叶林与湿地区南部的沿海陆域利用起来。在解决重叠与地质遗迹等情况后确保保护等级不下降,保证保护力度与保护效率。Abstract:Objective In order to provide scientific proposals and theoretical basis for the integration and optimization of protected areas (PAs) in Liaoning Province of northeastern China, we analyzed the spatial distribution pattern and overlapping status of 235 PAs of six categories in Liaoning Province qualitatively and quantitatively.Method The nearest neighbor index analysis and kernel density analysis were used to evaluate the spatial distribution of the PAs. By calculating the proportion of overlap in each protected area mosaic, the overlap status of PAs in Liaoning Province was analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. We also proposed a new method to calculate the overlap rate of multiple layers.Result (1) The nearest neighbor ratio of PAs in Liaoning Province was 0.904, indicating the aggregation distribution pattern of PAs in Liaoning Province. (2) The PA in Liaoning Province mainly formed four aggregation regions: deciduous broadleaved forest in western Liaoning Province and northern Hebei Province, mixed coniferous and broadleaved forest in Longgang Mountains, grassland and cultivated vegetation in Liaohe Plain, northern part of wetland and deciduous broadleaved forest in Liaodong Peninsula. (3) The PAs with overlap accounted for 50.43% (by amount) and 8.63% (by area) of the total PAs in Liaoning Province. The overlaps mainly occurred between nature reserves and natural parks, with a total area of 134, 421 ha occurred in 107 PAs. (4) There were 82, 13, and one overlapped patche (s) with two, three and four overlapped layers, respectively in Liaoning Province. (5) Based on the concept of PAM, a total of 36 PAMs were recognized in Liaoning Province, of which eight had an overlap rate more than 50%, maximum of 81.34%; 6 less than 10%, minimum of 1.82%.Conclusion The high overlap rate of PAMs indicated over evaluation of the area and conservation service function of the PAs. In this case, we suggested that the PA overlaps should be merged, and appropriate reduction of the total area should be permitted during the integration and optimization of the PA system in Liaoning Province. Furthermore, given the low protection effectiveness of some regions worthy of conservation, e. g., the coastal areas at the southern part of the deciduous broadleaved forest and wetland in Liaodong Peninsula, we suggested new PAs be established or expansion of the existing PAs to ensure the protection intensity and effectiveness of the PA system of Liaoning Province of northeastern China.
-
-
表 1 各类型自然保护地最邻近值及分布模式
Table 1 The nearest neighbor values and distribution patterns of different types of natural protected area
类型
Type平均观测距离
Average observation
distance (r1)/km预期平均距离
Expected average
distance (rE)/km最邻近比率
Nearest neighbor
ratio (R)分布模式
Distribution mode自然保护地 Natural protected area 15.548 17.188 0.904 聚类型 Polytype 自然保护区 Nature reserve 33.316 29.862 1.115 均匀型 Uniform 湿地公园 Wetland park 29.521 30.146 0.979 聚类型 Polytype 森林公园 Forest park 23.238 26.927 0.863 聚类型 Polytype 地质公园 Geological park 29.521 30.146 0.979 聚类型 Polytype 表 2 各自然保护综合地理单元上的自然保护地面积及占比表
Table 2 Area and proportion of natural protected area on natural conservation geographical regionalization
自然保护综合地理单元
Natural conservation
geographical regionalization各地理单元在辽宁省面积/hm2
Area of each geographical
unit in Liaoning Province/ha自然保护地数量
Number of natural
protected area自然保护地面积/hm2
Area of natural
protected area/ha自然保护地面积占比
Proportion of natural
protected area/%燕山落叶阔叶林区
Yanshan deciduous and broadleaved forest area596 049 16 81 365 13.65 龙岗山针阔混交林区
Longgang Mountain coniferous and broadleaved
mixed forest area2 562 604 63 490 272 19.13 辽西冀北山地落叶阔叶林区
Mountain deciduous broadleaved forest area
in western Liaoning and northern Hebei3 543 917 62 383 625 10.82 辽河平原栽培植被与草原草甸区
Cultivated vegetation and grassland
meadow area of Liaohe Plain3 566 904 51 195 066 5.47 辽东半岛落叶阔叶林与湿地区
Deciduous broadleaved forests and wet
areas of the Liaodong Peninsula3 253 033 71 630 623 19.38 哈达岭次生落叶阔叶林区
Hadaling secondary deciduous
broadleaved forest area1 018 263 19 96 894 9.52 表 3 自然保护地之间重叠情况
Table 3 Overlap condition between natural protected areas
涉及重叠保护地情况 Involving overlapping protected areas 数量 Number 重叠面积/hm2 Overlapping area/ha 自然保护区之间重叠 Overlap between nature reserves 27 14 511.49 自然保护区与自然公园重叠 Overlap between nature reserves and nature parks 107 134 421.10 自然公园之间重叠 Overlap between nature parks 51 42 903.16 表 4 辽宁省自然保护地镶嵌体情况及内部重叠率
Table 4 Mosaic situation and internal overlap rate of natural protected area in Liaoning Province
镶嵌体编号
Inlay No.镶嵌体名称
Name of inlay自然保护地数量
Number of natural
protected area类型
Type级别 Level 内部重叠率
Internal
overlap
rate/%国家级
National level省级
Provincial level市级
Municipal level县级
County level1 老秃顶子
Laotudingzi7 NR 1 2 19.48 FP 3 GP 1 2 章古台
Zhanggutai4 NR 1 1 39.44 FP 1 DP 1 3 长山群岛
Changshan Archipelago4 NR 1 1 10.94 FP 1 MP 1 4 仙人洞
Xianrendong3 NR 1 65.02 FP 1 GP 1 5 三块石
Sankuaishi3 NR 1 81.34 FP 1 GP 1 6 凤凰山
Phoenix Mountain2 NR 1 22.36 FP 1 7 大伙房
Dahuofang2 FP 1 15.74 WP 1 8 大连西郊
Dalian West Suburb2 FP 2 25.14 9 陨石山
Aerolite Hill2 NR 1 20.54 FP 1 10 辽河湿地
Liaohe Wetland2 WP 2 4.77 11 首山
Shoushan Mountain2 FP 1 2.35 WP 1 12 千山
Qianshan Mountain2 FP 1 54.94 GP 1 13 楼子山
Louzishan Mountain2 NR 1 28.80 FP 1 14 海棠山
Haitangshan Mountain2 NR 1 21.65 FP 1 15 普兰店
Pulandian2 FP 1 19.52 GP 1 16 辽河口
Liaohe Estuary7 NR 1 1 22.21 FP 1 WP 1 MP 2 GP 1 17 朝阳鸟化石
Chaoyang Bird Fossil10 NR 1 2 3 1 13.01 FP 2 GP 1 18 猴石
Houshi4 NR 2 37.63 FP 1 GP 2 19 医巫闾山
Yiwulü Mountain6 NR 1 1 29.34 FP 1 1 WP 1 GP 1 20 营口
Yingkou4 NR 1 20.68 FP 2 1 21 白狼山
Bailang Mountain7 NR 1 1 2 69.22 FP 2 GP 1 22 龙潭湾
Longtan Bay2 NR 1 8.24 FP 1 23 老虎山
Laohu Mountain2 NR 1 49.37 FP 1 24 大辽河
Daliao River2 NR 1 1.98 WP 1 25 浑河源
Hunheyuan River2 NR 1 34.82 FP 1 26 白云山
Baiyun Mountain2 NR 1 22.57 FP 1 27 大连沿海
Dalian Coast11 NR 3 1 5.24 FP 2 1 MP 3 GP 1 28 沈阳
Shenyang2 NR 1 19.48 FP 1 29 五龙山
Wulong Mountain2 NR 1 31.70 FP 1 30 海王九岛
Haiwang Jiudao2 NR 2 16.53 31 蒲石河
Pushi River2 NR 1 60.42 FP 1 32 西平
Xiping2 NR 1 73.07 FP 2 33 辽中蒲河
Puhe River in Liaozhong2 NR 1 17.45 WP 1 34 冰砬山
Binglashan Mountain3 NR 1 53.51 FP 1 1 35 高山台
Gaoshantai2 NR 1 66.72 FP 1 36 寇河
Kou River2 NR 1 1.82 WP 1 注:NR. 自然保护区;FP. 森林公园;GP. 地质公园;DP. 沙漠公园;MP. 海洋公园;WP. 湿地公园。Notes: NR, nature reserve; FP, forest park; GP, geological park; DP, desert park; MP, marine park; WP, wetland park. -
[1] 姜超, 马社刚, 王琦淞, 等. 中国5种主要保护地类型的空间分布格局[J]. 野生动物学报, 2016, 37(1):61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0127.2016.01.011 Jiang C, Ma S G, Wang Q S, et al. Spatial distribution pattern of five major categories of protected area in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 2016, 37(1): 61−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0127.2016.01.011
[2] 喻泓, 肖曙光, 杨晓晖, 等. 我国部分自然保护区建设管理现状分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(9):1061−1067. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.09.011 Yu H, Xiao S G, Yang X H, et al. Current status of nature reserves management in parts of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(9): 1061−1067. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.09.011
[3] 沈员萍, 黄萌, 罗毅, 等. 国家公园体制背景下的自然保护地体系管理分类研究[J]. 规划师, 2019, 35(17):11−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2019.17.002 Shen Y P, Huang M, Luo Y, et al. Management categorization of nature reserves with national park system background[J]. Planners, 2019, 35(17): 11−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2019.17.002
[4] 李涛, 陶卓民, 李在军, 等. 基于GIS技术的江苏省乡村旅游景点类型与时空特征研究[J]. 经济地理, 2014, 34(11):179−184. Li T, Tao Z M, Li Z J, et al. The research on types and times-spatial structure of rural tourism attractions in Jiangsu Province based on GIS[J]. Economis Geography, 2014, 34(11): 179−184.
[5] 欧阳志云, 杜傲, 徐卫华. 中国自然保护地体系分类研究[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(20):7207−7215. Ouyang Z Y, Du A, Xu W H. Research on China’s protected area system classification[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(20): 7207−7215.
[6] 彭杨靖, 樊简, 邢韶华, 等. 中国大陆自然保护地概况及分类体系构想[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3):315−325. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017235 Peng Y J, Fan J, Xing S H, et al. Overview and classification outlook of natural protected areas in mainland China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(3): 315−325. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017235
[7] 高昌源. 基于地理信息系统的辽宁省生物多样性保护优先区的识别与评估[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2020. Gao C Y. Recognition and evaluation of priority areas of biodiversity conservation based on geographic information system[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2020.
[8] 韦贵红. 重构自然保护地新体系[J]. 小康, 2018(16):26−27. Wei G H. Reconstructing the new system of nature reserves[J]. Macro, 2018(16): 26−27.
[9] 张芳玲, 蒲真, 梁晓玉, 等. 中国东北地区自然保护地数量特征分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(2):61−67. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190139 Zhang F L, Pu Z, Liang X Y, et al. The quantitative characteristics of natural protected areas in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(2): 61−67. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190139
[10] 唐芳林, 吕雪蕾, 蔡芳, 等. 自然保护地整合优化方案思考[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(3):8−13. Tang F L, Lü X L, Cai F, et al. Reflections on integrated optimization schemes of protected areas[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(3): 8−13.
[11] 黄宝荣, 马永欢, 黄凯, 等. 推动以国家公园为主体的自然保护地体系改革的思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(12):1342−1351. Huang B R, Ma Y H, Huang K, et al. Strategic approach on promoting reform of China’s natural protected areas system with national parks as backbone[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(12): 1342−1351.
[12] 唐芳林. 国家公园体制下的自然公园保护管理[J]. 林业建设, 2018(4):1−6. Tang F L. Protection and management of nature park under the national park system[J]. Forestry Construction, 2018(4): 1−6.
[13] 靳川平, 刘晓曼, 王雪峰, 等. 长江经济带自然保护地边界重叠关系及整合对策分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(20):7323−7334. Jin C P, Liu X M, Wang X F, et al. Overlapping relationship of the protected area boundary in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and its integration countermeasures[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(20): 7323−7334.
[14] 唐小平, 蒋亚芳, 刘增力, 等. 中国自然保护地体系的顶层设计[J]. 林业资源管理, 2019(3):1−7. Tang X P, Jiang Y F, Liu Z L, et al. Top-level design of the natural protected area system in China[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2019(3): 1−7.
[15] 虞虎, 钟林生, 曾瑜皙. 中国国家公园建设潜在区域识别研究[J]. 浙江国土资源, 2018(11):33. Yu H, Zhong L S, Zeng Y X. Study on the identification of potential areas of national park construction in China[J]. Zhejiang Land & Resources, 2018(11): 33.
[16] 郭子良. 中国自然保护综合地理区划与自然保护区体系有效性分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. Guo Z L. Analysis on the effectiveness of nature reserve network and natural conservation geographical regionalization of China[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016.
[17] 刘国明, 杨效忠, 张琳伟. 中国国家级水利风景区的旅游空间结构分析[J]. 河海大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2011, 13(1):49−53, 91. Liu G M, Yang X Z, Zhang L W. Analysis on tourism spatial structure of national water conservancy scenic spots in China[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2011, 13(1): 49−53, 91.
[18] 马童慧, 吕偲, 张呈祥, 等. 中国5种类型湿地保护地空间重叠特征[J]. 湿地科学, 2019, 17(5):536−543. Ma T H, Lü C, Zhang C X, et al. Spatial overlapping characteristics of 5 types of protected areas for wetlands in China[J]. Wetland Science, 2019, 17(5): 536−543.
[19] 冯达, 胡理乐, 陈建成. 北京市自然保护地空间分布格局与交叉重叠特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(10):3421−3429. Feng D, Hu L L, Chen J C. Spatial distribution and the overlapping feature of Beijing protected areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(10): 3421−3429.
[20] 马童慧, 吕偲, 雷光春. 中国自然保护地空间重叠分析与保护地体系优化整合对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(7):758−771. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019087 Ma T H, Lü C, Lei G C. The spatial overlapping analysis for China’s natural protected area and countermeasures for the optimization and integration of protected area system[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2019, 27(7): 758−771. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019087
[21] 高吉喜, 徐梦佳, 邹长新. 中国自然保护地70年发展历程与成效[J]. 中国环境管理, 2019, 11(4):25−29. Gao J X, Xu M J, Zou C X. Development achievement of natural conservation in 70 years of new China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 11(4): 25−29.
[22] 周刚. 自然保护地整合优化建议方案问题与对策思考: 以凉山州木里县为例[J]. 绿色科技, 2020(14):65−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2020.14.021 Zhou G. Problems and countermeasures of the suggestion scheme for the integration and optimization of nature reserves: take Muli County of Liangshan Prefecture as an example[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2020(14): 65−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2020.14.021
[23] 唐小平, 张云毅, 梁兵宽, 等. 中国国家公园规划体系构建研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 18(1):5−12. Tang X P, Zhang Y Y, Liang B K, et al. Construction of the planning system of China’s national parks[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 2019, 18(1): 5−12.
[24] 何雪婷. 厦门本岛应急避难场所空间布局合理性评价: 基于GIS网络分析[J]. 福建建筑, 2016(1):20−24. He X T. Reasonability of spatial distribution for urban emergency shelter in Xiamen Island: based on GIS network analysis[J]. Fujian Architecture & Construction, 2016(1): 20−24.
[25] 潘竟虎, 徐柏翠. 中国国家级自然保护地的空间分布特征与可达性[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(2):353−362. Pan J H, Xu B C. Spatial distribution characteristics and accessibility of protected areas in China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(2): 353−362.
[26] 杨振, 程鲲, 付励强, 等. 东北林业系统自然保护区、森林公园和湿地公园的空间重叠分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(11):3305−3310. Yang Z, Cheng K, Fu L Q, et al. Spatial overlapping analysis for nature reserves, forest parks and wetland parks in forestry management system of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(11): 3305−3310.
[27] 张卓然, 唐晓岚, 贾艳艳. 保护地空间分布特征与影响因素分析: 以长江中下游为例[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2017, 44(3):439−447. Zhang Z R, Tang X L, Jia Y Y. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of protected areas: a case of middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2017, 44(3): 439−447.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 赵熙来,周正,葛锐,罗伟豪,马旭彤,蒋慧,苏华维. 残次香梨与乳酸菌组合对四翅滨藜青贮的影响. 中国饲料. 2024(17): 155-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张衡锋,杨绮,韦庆翠,张焕朝. 盐胁迫对10个品种紫薇的影响及其耐盐性综合评价. 东北林业大学学报. 2023(09): 34-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李雨欣,罗秀丽,张婷婷,康宇乾,王鹏,江行玉,周扬. 盐胁迫下海马齿生理指标变化及相关基因表达分析. 农业生物技术学报. 2022(07): 1279-1289 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘鹤莹,张嫚,翟中葳,杨鹏,支苏丽,沈仕洲,张克强. 大薸对奶厅废水主要污染物的去除效果研究. 农业环境科学学报. 2022(11): 2525-2538 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王涛,蒙仲举,张佳鹏,雷虹娟,张格. NaCl胁迫对紫穗槐幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 西北林学院学报. 2021(01): 25-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘学良,姚俊修,刘翠兰,李善文,任飞,李庆华,吴海涛,翟红莲,吴德军,邢世岩,高红萍. 7个接骨木无性系苗木对盐胁迫的生理响应与评价. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2021(01): 37-44+79 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 鲁俊倩,武舒,钟姗辰,张伟溪,苏晓华,张冰玉. ‘84K’杨组氨酸激酶基因PaHK3a的表达及功能分析. 北京林业大学学报. 2021(02): 46-53 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 丁丁,王红宝,郑伶杰,左永梅,韩民利,吴新海,郭艳超. 不同品种茶菊对NaCl胁迫的生理响应及耐盐性评价. 植物生理学报. 2021(03): 692-702 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵佳伟,李清亚,路斌,李艳,朱玉菲,栗浩,路丙社. 不同品种北美豆梨对NaCl胁迫的生理响应及耐盐性评价. 植物生理学报. 2019(01): 23-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 邹晓君,列志旸,薛立. NaCl胁迫对4种园林植物养分含量和贮量的影响. 华南农业大学学报. 2018(06): 77-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨传宝,孙超,李善文,姚俊修,刘敬国,矫兴杰. 白杨派无性系苗期耐盐性综合评价及筛选. 北京林业大学学报. 2017(10): 24-32 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: