Tensile creep characteristics of compression wood and normal wood under different temperatures and loads
-
摘要:目的
探究马尾松应压木和正常木的拉伸蠕变特性对温度和载荷的响应规律,旨在为马尾松木材的高附加值利用提供数据参考和基础理论依据。
方法以应压木和正常木早材组织切片为研究对象,分别采用X射线衍射仪和动态力学分析仪测定试材的微纤丝角和拉伸应力–应变曲线;在50 ~ 170 ℃范围内,利用动态力学分析仪分别获得3个应力水平和不同恒定温度水平下应压木和正常木的拉伸蠕变曲线。
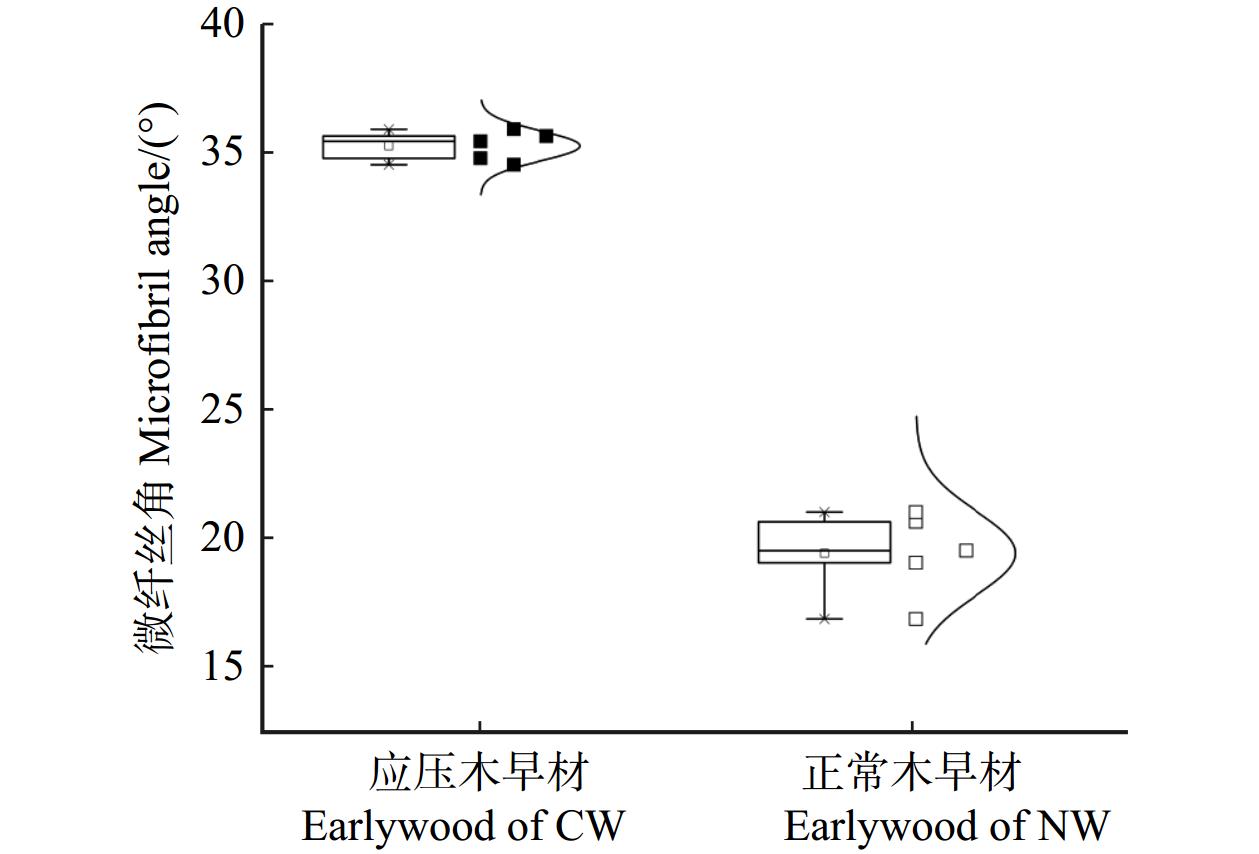
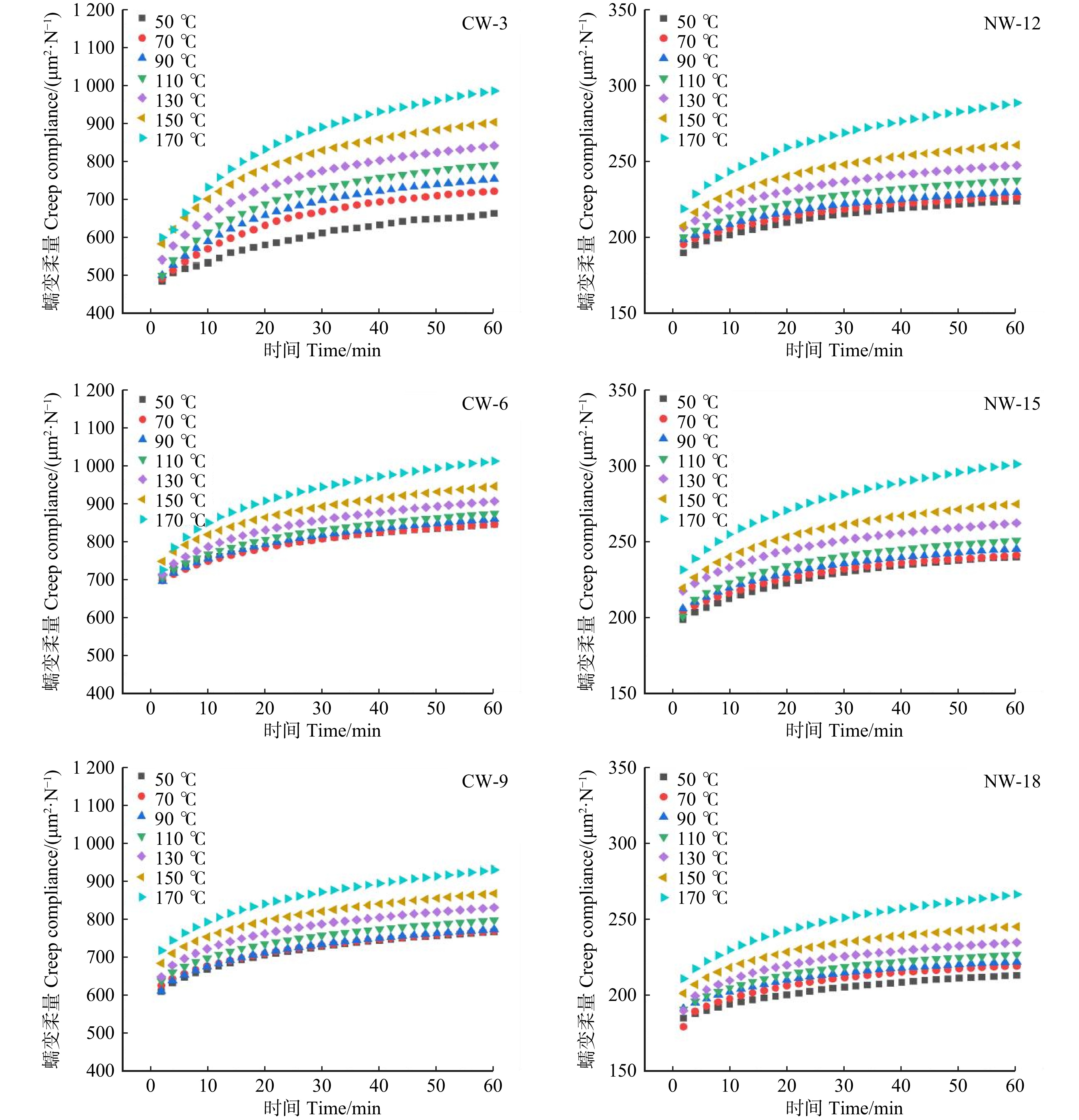
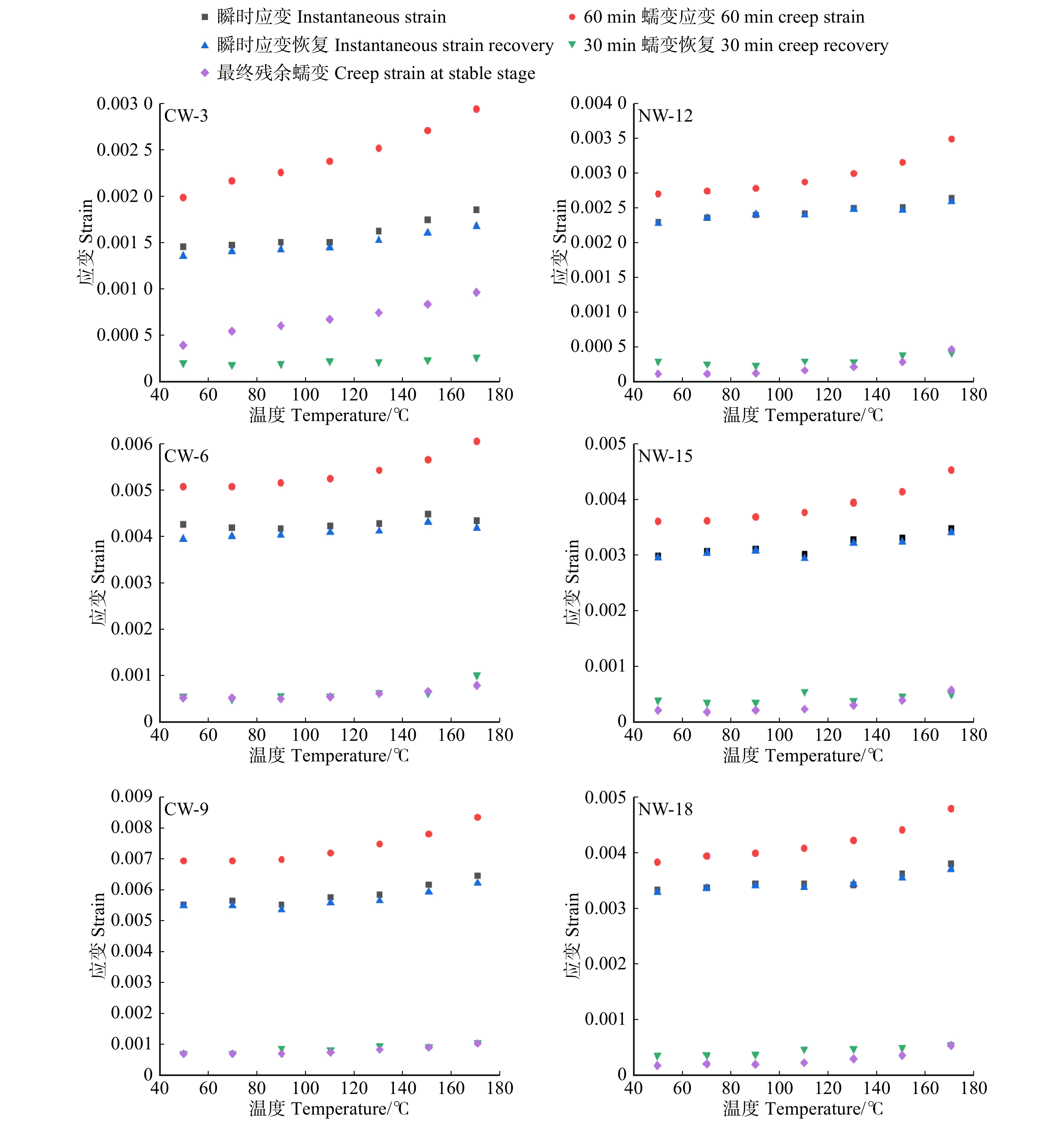
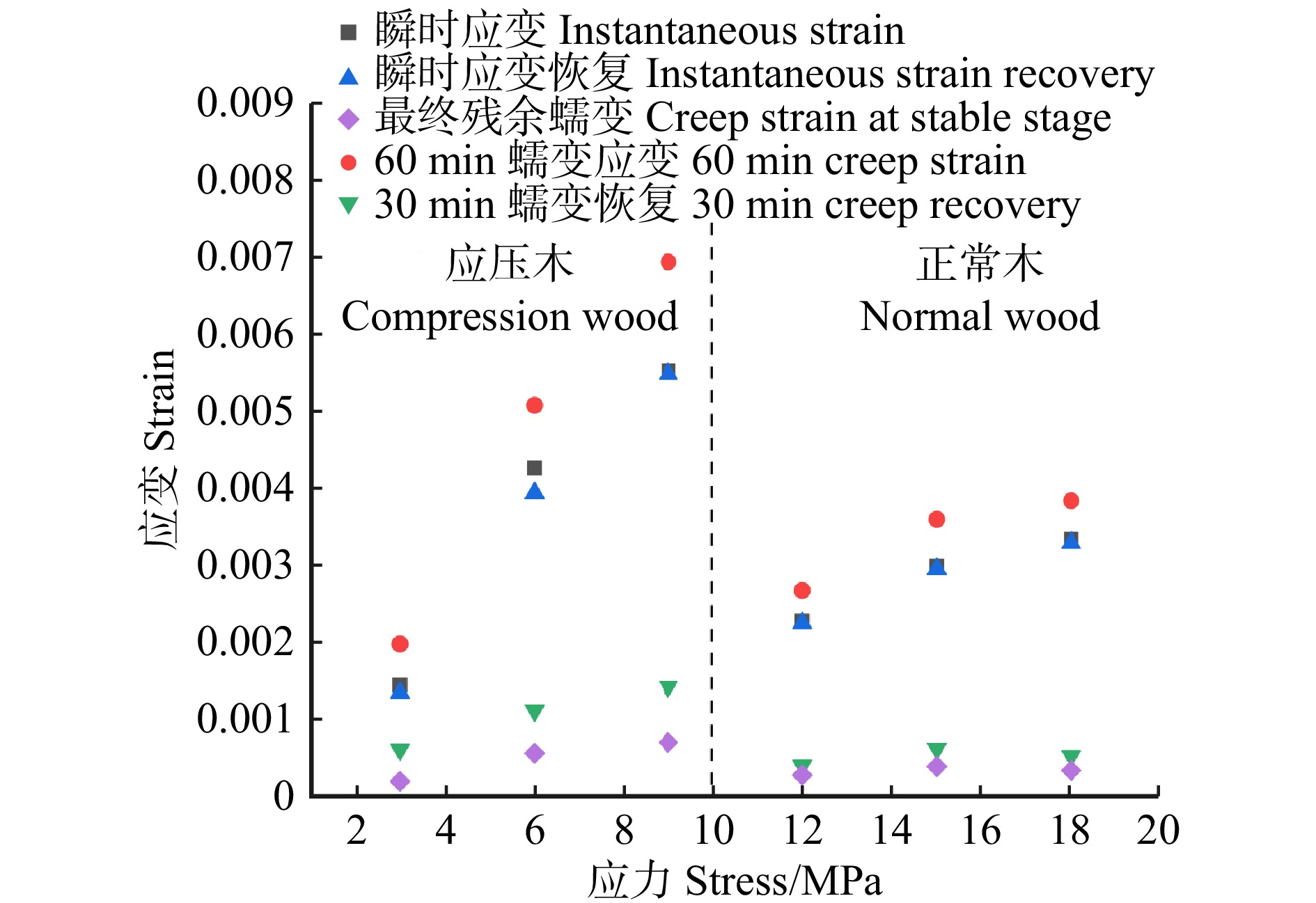
结果与正常木相比,应压木的基本密度、微纤丝角、拉伸应变、拉伸蠕变柔量和最终残余应变均较大,而拉伸应力和弹性模量较小。应压木或正常木的瞬时应变均略大于瞬时应变恢复应变量。应压木与正常木试样的瞬时应变、瞬时应变恢复量、60 min蠕变应变量和30 min蠕变恢复量均分别随温度、施加载荷的增大而增加;最终残余应变随温度升高而增加,而对施加载荷的响应无明显规律。在50 ~ 170 ℃范围内,单位应力增加引起应压木与正常木试样的瞬时应变增加量分别为0.063% ~ 0.076%和0.016% ~ 0.020%,拉伸黏弹变形增加量分别为0.078% ~ 0.095%和0.019% ~ 0.028%。
结论与正常木相比,单位应力对应压木的拉伸瞬时应变和黏弹变形增加量影响更为明显,应压木中较大的微纤丝角导致其抵抗外力变形的能力较弱。升高温度加剧了单位应力对应压木与正常木瞬时应变和拉伸黏弹变形的影响。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis research was carried to explore the difference in tensile creep behavior between compression wood (CW) and normal wood (NW) from masson pine (Pinus massoniana) under different temperature and load levels, aiming to provide the data reference and theoretical basis for high value-added utilization of plantation wood.
MethodThe tissue sections of earlywood (EW) between CW and NW were used as research objects, and the microfiber angle (MFA) and tensile stress-strain curve were characterized by X-ray diffraction and dynamic mechanical analyzer, respectively. Dynamic mechanical analyzer was also used to determine tensile creep for CW and NW specimens in the temperature range of 50 to 170 ℃ and at three stress levels.
ResultCompared with NW, the basic density, MFA, tensile strain, creep compliance and creep strain at stable stage of CW were larger, while the tensile stress and modulus of elasticity were smaller. The instantaneous strain of CW or NW specimens was slightly higher than instantaneous recovery strain. The instantaneous strain, instantaneous recovery strain, 60 min creep strain, and 30 min creep recovery of CW and NW specimens increased with increasing temperature and stress level, respectively. Furthermore, the creep strain at stable stage increased with increasing temperature, while its response to load level was not obvious. In the temperature range from 50 to 170 ℃, the increase of instantaneous strain caused by per unit stress for CW and NW was 0.063%−0.076% and 0.016%−0.020%, respectively. And the increase of creep strain in 60 min caused by per unit stress for CW and NW was 0.078%−0.095% and 0.019%−0.028%, respectively.
ConclusionCompared with NW, per unit stress shows obvious influence on the increase of tensile instantaneous strain and viscoelastic deformation, and CW with larger MFA has less ability to resist external deformation. The increasing temperature intensifies the effect of per unit stress on instantaneous strain and tensile viscoelastic deformation for NW and CW specimens.
-
Keywords:
- tensile strain /
- creep /
- loads /
- stresses /
- viscoelasticity /
- masson pine /
- compression wood
-
现如今城市居住空间紧张,小户型的比例在逐渐加大。中国政府出台规定建筑面积90平方米以下户型占比必须达到70%以上[1],这预示着更多的家庭面临功能空间不足的情况,就有大量家庭有一房两用的需求,即一个房间除了卧室的主要功能外,还可通过功能家具实现客厅或书房等功能,而其中翻转床则是实现睡眠–休闲、学习空间转换的功能家具的典型代表产品。
虽然翻转床有着可观的市场需求,但对于其力学性能的检测还是依赖整体破坏性试验为主要手段,目前其设计和分析尚缺乏科学的理论指导[2]。20世纪90年代气弹簧作为新型支撑出现,张琦等[3]对气弹簧的力学性能进行了计算分析;王殿武[4]研究了气弹簧力学特性并将其运用到汽车尾盖上;刘迎林等[5]对全塑车身后备箱气撑杆进行运动仿真并验证其安装位置;王定虎[6]运用力矩平衡原理和理想气体方程对汽车背门撑杆的选择及布置进行校核。截止目前,气弹簧的研究主要集中在汽车领域,而鲜有在家具领域内的研究,为了弥补翻转床气弹簧机构设计和性能分析的理论欠缺,本文从实际应用需求出发,运用静力学和力矩平衡原理对气弹簧机构进行结构分析计算和选型。
1. 研究方法
1.1 翻转床气弹簧机构概况
翻转床床体翻转的目的是实现床体的收纳,以便满足房间睡眠–休闲、学习空间转换的用户功能需求。根据使用场景分析,翻转床运动功能示意图如图1所示。因为翻转床的床体框架、床板、床垫和床上用品等零部件加起来质量较大,如仅凭借人手部力量支撑则翻转困难,且在操作过程中存在砸到人的风险,所以实际翻转床产品均需要借助辅助结构实现翻转和随停的功能。由于气弹簧具有支撑、缓冲的作用,因此恰好适用于翻转床的运动功能需求。
壁柜式翻转床的翻转功能主要由气弹簧机构实现,分析翻转床的运动本质就是分析气弹簧机构。壁柜式翻转床结构和气弹簧机构简图如图2所示,翻转床左右两侧具有相同连杆结构,其中A点为翻转床的翻转中心,由螺栓将床体翻转框架和固定柜体铰接;BC为气弹簧,气弹簧两端分别和固定柜体及床体翻转框架铰接;床体翻转存在两个极限状态,即收纳状态(图2a)和使用状态(图2b),处于收纳状态时气弹簧处在伸展状态,即B1C,处于使用状态时气弹簧处在压缩状态,即BC。
![]() 图 2 翻转床结构和气弹簧机构简图1. 固定柜体;2. 气弹簧;3. 床体翻转框架;A. 翻转中心;B. 气弹簧压缩末端;B1. 气弹簧伸展末端;C. 气弹簧固定端; l. A点到床头距离。 1, fixed cabinet; 2, gas spring; 3, rotate frame; A, rotation center; B, compression end of gas spring; B1, stretching end of gas spring; C, fixed end of gas spring; l, the distance from A point to the head of the bed.Figure 2. Diagram of foldable bed structure and gas spring mechanism
图 2 翻转床结构和气弹簧机构简图1. 固定柜体;2. 气弹簧;3. 床体翻转框架;A. 翻转中心;B. 气弹簧压缩末端;B1. 气弹簧伸展末端;C. 气弹簧固定端; l. A点到床头距离。 1, fixed cabinet; 2, gas spring; 3, rotate frame; A, rotation center; B, compression end of gas spring; B1, stretching end of gas spring; C, fixed end of gas spring; l, the distance from A point to the head of the bed.Figure 2. Diagram of foldable bed structure and gas spring mechanism1.2 气弹簧计算方法
根据国家标准GB 25751—2010压缩气弹簧技术条件、GB/T 1805—2001弹簧术语和JB/T 10418—2004气弹簧设计计算为依据,对气弹簧特性进行研究。对极限位置的床体进行平面力系的简化,并结合力矩平衡原理对床体和气弹簧机构进行受力分析。运用有限元的优化思路对气弹簧安装位置进行列表格寻最优解。运用静力学知识分析床体运动规律。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 气弹簧机构分析计算和选型
如图2所示,翻转床在收纳时气弹簧处于伸展过程,气弹簧的伸展力辅助床体的上翻过程。床体完全收纳进柜体时,此时床体重力矢量经过翻转中心A,在无外力情况下床体静止不动。翻转床展开过程中气弹簧处于压缩过程,气弹簧的压缩力为床体下翻过程提供缓冲力。
图3为气弹簧展开长度与压缩、伸展过程曲线示意图,其中F1为最小伸展力,F2为最大伸展力,F3为最小压缩力,F4为最大压缩力,S为气弹簧的行程,t为端头长度,结合图2气弹簧初始长度BC = S + t,展开长度L = B1C = S + t + S = 2S + t,t的取值一般为10 mm。
![]() 图 3 气弹簧展开长度与压缩、伸展过程曲线示意图d. 活塞杆直径;D1. 缸筒内径;D2. 缸筒外径;S. 行程;L. 伸展长度;t. 端头长度;F0. 启动力;F1. 最小伸展力;F2. 最大伸展力;F3. 最小压缩力;F4. 最大压缩力;Fa. 公称力a;Fb. 公称力b;C. 采力点。图引自文献[7]。d, piston rod diameter; D1, cylinder inner diameter; D2, cylinder outer diameter; S, stroke; L, extended length; t, end length; F0, star-up force; F1, minimum extension force; F2, maximum extension force; F3, minimum compress force; F4, maximum compress force; Fa, nominal force a; Fb, nominal force b; C, measuring point. Diagram is cited from reference [7].Figure 3. Diagram of expansion length of gas spring and curve of compression and stretching process
图 3 气弹簧展开长度与压缩、伸展过程曲线示意图d. 活塞杆直径;D1. 缸筒内径;D2. 缸筒外径;S. 行程;L. 伸展长度;t. 端头长度;F0. 启动力;F1. 最小伸展力;F2. 最大伸展力;F3. 最小压缩力;F4. 最大压缩力;Fa. 公称力a;Fb. 公称力b;C. 采力点。图引自文献[7]。d, piston rod diameter; D1, cylinder inner diameter; D2, cylinder outer diameter; S, stroke; L, extended length; t, end length; F0, star-up force; F1, minimum extension force; F2, maximum extension force; F3, minimum compress force; F4, maximum compress force; Fa, nominal force a; Fb, nominal force b; C, measuring point. Diagram is cited from reference [7].Figure 3. Diagram of expansion length of gas spring and curve of compression and stretching process气弹簧的选型需要的参数为气弹簧的伸展长度L和行程S以及气弹簧最小伸展力F1[8]。现以翻转床两个极限位置进行受力分析。使用状态下,当人手抬起床的边沿时以A点为旋转中心,能够将床体抬起。此时受力分析如图4所示。
![]() 图 4 使用状态手抬床体时床体受力分析简图A. 翻转中心;B. 气弹簧压缩末端;C. 气弹簧固定端;F2. 气弹簧最大伸展力;G1. A点左侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;G2. A点右侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;FAx. A点沿x轴方向分力;FAy. A点沿y轴方向分力;l. A点到床头距离;FL. 手对床体的抬力;A, rotation center;B, compression end of gas spring;C, fixed end of gas spring;F2, maximum extension force;G1, bed weight on the left side of point A;G2, bed weight on the right side of point A;FAx, x component of point A;FAy, y component of point A;l, A point to the head of the bed;FL, hand lift on the bed.Figure 4. Diagram of foldable bed force analysis when hand up the bed in using state
图 4 使用状态手抬床体时床体受力分析简图A. 翻转中心;B. 气弹簧压缩末端;C. 气弹簧固定端;F2. 气弹簧最大伸展力;G1. A点左侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;G2. A点右侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;FAx. A点沿x轴方向分力;FAy. A点沿y轴方向分力;l. A点到床头距离;FL. 手对床体的抬力;A, rotation center;B, compression end of gas spring;C, fixed end of gas spring;F2, maximum extension force;G1, bed weight on the left side of point A;G2, bed weight on the right side of point A;FAx, x component of point A;FAy, y component of point A;l, A point to the head of the bed;FL, hand lift on the bed.Figure 4. Diagram of foldable bed force analysis when hand up the bed in using state由力矩平衡可得:
xF2l+G1l2−G2LB−l2+FL(LB−l)=0 (1) 式中:F2为气弹簧最大伸展力,单位N;x为气弹簧个数;FL为手对床体的抬力,单位N;LB为床体总长,单位mm;G1为A点左侧床体质量与重力加速度之积,单位N;G2为A点右侧床体质量与重力加速度之积,单位N;l为A点到床头距离,单位mm。
设床体和床垫总质量为m,
G1=lLBmg ,G2= LB−lLBmg ,则可将式(1)简化得:xF2l−(LB2−l)mg+FL(LB−l)=0 (2) 式中:F2为气弹簧最大伸展力,单位N;x为气弹簧个数;FL为手对床体的抬力,单位N;LB为床体总长,单位mm;l为A点到床头距离,单位mm;m为床体和床垫总质量,单位kg;g为重力加速度,单位N/kg。
收纳状态下,拉手与A、B1点视作在同一竖直线上。拉动床体时,人手拉动拉手的力矩能够平衡气弹簧对A点的弹力矩,此时受力分析简图如图5所示。
![]() 图 5 收纳状态手拉床体时床体受力分析简图A. 翻转中心;B1. 气弹簧伸展末端;C. 气弹簧固定端;FAx. A点沿x轴方向分力;FAy. A点沿y轴方向分力;F0. 启动力;F0x. F0沿x轴方向分力;F0y. F0沿y轴方向分力;l. A点到床头距离;θ. F0与垂直方向夹角;FP. 手对拉手拉力。A, rotation center;B1, stretching end of gas spring;C, fixed end of gas spring;FAx, x component of point A;FAy, y component of point A; F0, star-up force; F0x, x component of F0; F0y. y component of F0; l, A point to the head of the bed; θ, angle of F0 with vertical direction; FP, hand pull on the handle.Figure 5. Diagram of foldable bed force analysis when hand drag the bed in storage state
图 5 收纳状态手拉床体时床体受力分析简图A. 翻转中心;B1. 气弹簧伸展末端;C. 气弹簧固定端;FAx. A点沿x轴方向分力;FAy. A点沿y轴方向分力;F0. 启动力;F0x. F0沿x轴方向分力;F0y. F0沿y轴方向分力;l. A点到床头距离;θ. F0与垂直方向夹角;FP. 手对拉手拉力。A, rotation center;B1, stretching end of gas spring;C, fixed end of gas spring;FAx, x component of point A;FAy, y component of point A; F0, star-up force; F0x, x component of F0; F0y. y component of F0; l, A point to the head of the bed; θ, angle of F0 with vertical direction; FP, hand pull on the handle.Figure 5. Diagram of foldable bed force analysis when hand drag the bed in storage state因为F0y与A点在水平方向上没有距离,所以F0在y轴方向上的力矩为0。由力矩平衡可得:
x(F0xl+F0y⋅0)−FP(lP−l)=0 (3) 式中:F0为气弹簧启动力,单位N;lP为拉手高度,单位mm;FP为手对拉手拉力,单位N;l为A点到床头距离,单位mm;x为气弹簧个数;F0x为F0沿x轴方向分力,单位N;F0y为F0沿y轴方向分力,单位N。
图5中,依据压缩气弹簧技术条件,气弹簧启动力F0略大于气弹簧最小压缩力F3,取F3值近似为F0值,由三角函数可知:
F0=F0xsinθ=F3 (4) 式中:θ为F0与垂直方向夹角,单位°;F0为气弹簧启动力,单位N;F0x为F0沿x轴方向分力,单位N;F3为气弹簧最小压缩力,单位N。
在符合人机工程的情况下,使lP尽量大可以加大手拉开床体的力矩,减小手部力量,取lP = 1 750 mm。依据人机工程学,为使得操作力比较恰当,收纳床体时推荐的操作力范围为50 ~ 80 N[9],此处取手对床体的抬力FL = 80 N,手拉拉手的力FP = 80 N。
F1与F3之间有一段由于摩擦力产生的差值,依据GB25751—2010其计算公式为Fr =(F3 − F1)/2,即动态摩擦力Fr是最小压缩力和最小伸展力之差的平均值[10]。气弹簧摩擦力所产生的阻力与杆的运动方向相反,其与标称力值(图样及产品上标注的力,包括F1、Fa、
F3⋯⋯ )极限偏差应符合下表1的规定。表 1 标称力值极限偏差与动态摩擦力Table 1. Nominal force limit deviation and dynamic friction标称力值 Nominal force 标称力值的极限偏差 Nominal force limit deviation 最大动态摩擦力 Maximum dynamic friction ≤ 100 + 15 − 5 25 101 ~ 200 + 20 − 10 30 201 ~ 400 + 30 − 15 40 401 ~ 600 + 40 − 20 60 601 ~ 800 + 50 − 25 80 801 ~ 1 000 + 60 − 30 100 1 001 ~ 1 200 + 70 − 35 130 > 1 200 + 80 − 40 150 注:表1引自文献[7]。Note: Tab.1 is cited from reference [7]. F1与F2的关系可由弹性系数求得。弹性系数k表示的是单位压缩力变化的弹簧常数[10],单位为N/mm,行程S的单位是mm。伸展阶段气弹簧弹性系数公式[11]为:
k=(F2−F1)/S (5) 其中,k的大小可由厂家进行调节,其具体值可通过实验得出。一般商家提供的气弹簧的弹性系数k介于1.05和1.8之间,弹性系数越小意味着制造难度越高。
以市场常见的床体规格为准,此处选取宽900 mm、长1 900 mm、质量为25 kg的床垫。选取匹配的床体框架结构的材质为钢,其质量约为25 kg。刨花板密度为650 kg/m3,则18 mm(厚) × 900 mm(宽) × 1 900 mm(长)的床板质量为20 kg。则床体总重力为:(25 + 25 + 20) × 9.8 = 686 N。如固定柜体目标深度为300 mm,为了保证A、C两点安装位置距离柜体板前后两边有足够的距离保证强度,则取l = 160 mm。
依据式(2),xF2 = 2 517.1 N,选取气弹簧个数x = 4,则F2 = 629.3 N。
由图4、图5可知:取l为160 mm时,以B、B1为圆心,以(S + 10)、(2S + 10)为半径作圆,作交点可得C点安装位置。并结合式(3)、式(4)、表1以及k的计算方程,可将相关参数整理成表2。
表 2 气弹簧相关参数及安装位置与行程S的关系Table 2. Relationship between gas spring stroke and relevant parameters and installation positionS/mm θ/° F3/N Fr/N F1/N k 170 18 643.2 180 20 581.1 60 461.1 0.934 190 23 508.0 40 428.0 1.059 200 26 453.4 40 373.4 1.280 注:S为行程;θ为F0与垂直方向夹角;F3为最小压缩力;Fr为最大动态摩擦力;F1为最小伸展力;k为气弹簧弹性系数。表3同此。Notes:S, stroke; θ, angle of F0 with vertical direction; F3, minimum compress force; Fr, maximum dynamic friction; F1, minimum extension force; k, gas spring modulus coefficient. Same as Tab.3. 由表2可知:θ角越大,k则越大,气弹簧的制作难度越小。为减小安装宽度,选择S为190 mm,F1 = 428 N作为最小伸展力的气弹簧,则要求厂家提供的气弹簧弹性系数k为1.06。参考表3可知F1和S的参数符合设计要求。
表 3 气弹簧活塞杆直径与最小伸展力大小选择范围推荐表Table 3. Recommended table of minimum extension force range and stroke range of gas spring序号
No.活塞杆
直径 Diameter of piston rod/mm最小伸展力
Minimum extension force (F1)/N行程范围
Stroke range/mm推荐范围
Recommended
range可选范围
Optional
range1 6 50 ~ 250 50 ~ 350 50 ~ 400 2 8 200 ~ 450 100 ~ 700 100 ~ 700 3 10 300 ~ 700 100 ~ 1 200 150 ~ 1 100 4 12 450 ~ 1 000 150 ~ 1 500 150 ~ 1 600 5 14 600 ~ 1 400 200 ~ 2 500 1 600 ~ 2 200 6 20 1 250 ~ 3 100 1 000 ~ 5 200 2 200 ~ 4 500 注:表3引自文献[12]。Note: Tab.3 is cited from reference [12]. 此时C点的安装位置如图6所示,BC = S + 10 = 200 mm,B1C = 2S + 10 = 390 mm。如果床体总质量加大,可以适当改变固定柜体深度以加大l的取值,使气弹簧机构获得更大的力臂。
2.2 翻转床运动规律分析
翻转床旋转到任意角度时的受力图如图7所示。取气弹簧对床体弹力FB与矩心A点的力臂为a,G1与矩心A点的力臂为b,G2与矩心A点的力臂为c。矩心A点右侧力矩减去左侧合力矩可列式:
![]() 图 7 任意位置下床架受力图A. 翻转中心;B′. 在β旋转角度下的床尾位置;C. 气弹簧固定端;β. 床体翻转框架翻转角度;G1. A点左侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;G2. A点右侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;a. FB对矩心A点的力臂;b. G1对矩心A点的力臂;c. G2对矩心A点的力臂。A, rotation center; B′, bed tail position at β rotation angle; C, fixed end of gas spring; β, flip angle of rotate frame; G1, bed mass on the left side of point A multiply gravity acceleration; G2, bed mass on the right side of point A multiply gravity acceleration; a, FB force arm to point A; b, G1 force arm to point A; c, G2 force arm to point A.Figure 7. Diagram of foldable bed force at arbitrary degree
图 7 任意位置下床架受力图A. 翻转中心;B′. 在β旋转角度下的床尾位置;C. 气弹簧固定端;β. 床体翻转框架翻转角度;G1. A点左侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;G2. A点右侧床体质量与重力加速度之积;a. FB对矩心A点的力臂;b. G1对矩心A点的力臂;c. G2对矩心A点的力臂。A, rotation center; B′, bed tail position at β rotation angle; C, fixed end of gas spring; β, flip angle of rotate frame; G1, bed mass on the left side of point A multiply gravity acceleration; G2, bed mass on the right side of point A multiply gravity acceleration; a, FB force arm to point A; b, G1 force arm to point A; c, G2 force arm to point A.Figure 7. Diagram of foldable bed force at arbitrary degreeMA=MA(xFB)+MA(G1)−MA(G2)=xFBa+G1b−G2c (6) 式中:MA为合力对A点的力矩,单位N;x为气弹簧个数;FB为气弹簧对床体弹力,单位N;G1为A点左侧床体重力,单位N;G2为A点右侧床体重力,单位N;a为FB对矩心A点的力臂,单位mm;b为G1对矩心A点的力臂,单位mm;c为G2对矩心A点的力臂,单位mm;MA(xFB)为单边气弹簧对A点力矩,单位N·mm;MA(G1)为G1对A点力矩,单位N·mm;MA(G2)为G2对A点力矩,单位N·mm。
气弹簧压缩和伸展两个过程曲线中任意点的值可以用伸展长度和k值求出,在不同旋转角度β下分别量取a、b、c的值代入式(6),并作出β与MA的关系曲线如图8所示。图8两条曲线为分别代入了弹簧伸展过程力值和压缩过程力值后的曲线。由图 8可知:床体在打开18°以内会弹回收纳状态;18° ~ 24°之间床体可悬停;大于24°以后,A点右侧力矩大于A点左侧合力矩。
3. 结 论
基于静力学和力矩平衡原理完成了翻转床两个极限位置的受力分析,构建了翻转床气弹簧分析计算理论,运用该理论能够通过翻转床的床身质量和尺寸得到气弹簧的最小伸展力、行程和弹性系数,从而完成气弹簧选型;运用CAD工具做两圆相交的几何法得出气弹簧安装位置的确立方法;基于力矩平衡原理构建合力矩和翻转角度β的关系式,得出翻转床悬停范围。设定床体尺寸宽900 mm、长1 900 m、固定柜体目标深度300 mm,则可得气弹簧最小伸展力为428 N,行程为190 mm,弹性系数为1.06,悬停角度范围为18° ~ 24°,翻转角大于24°后则为自由下翻。本文构建的分析方法和结果可为家具行业的壁柜式翻转床设计、选型和性能分析提供理论支撑和实践指导。
-
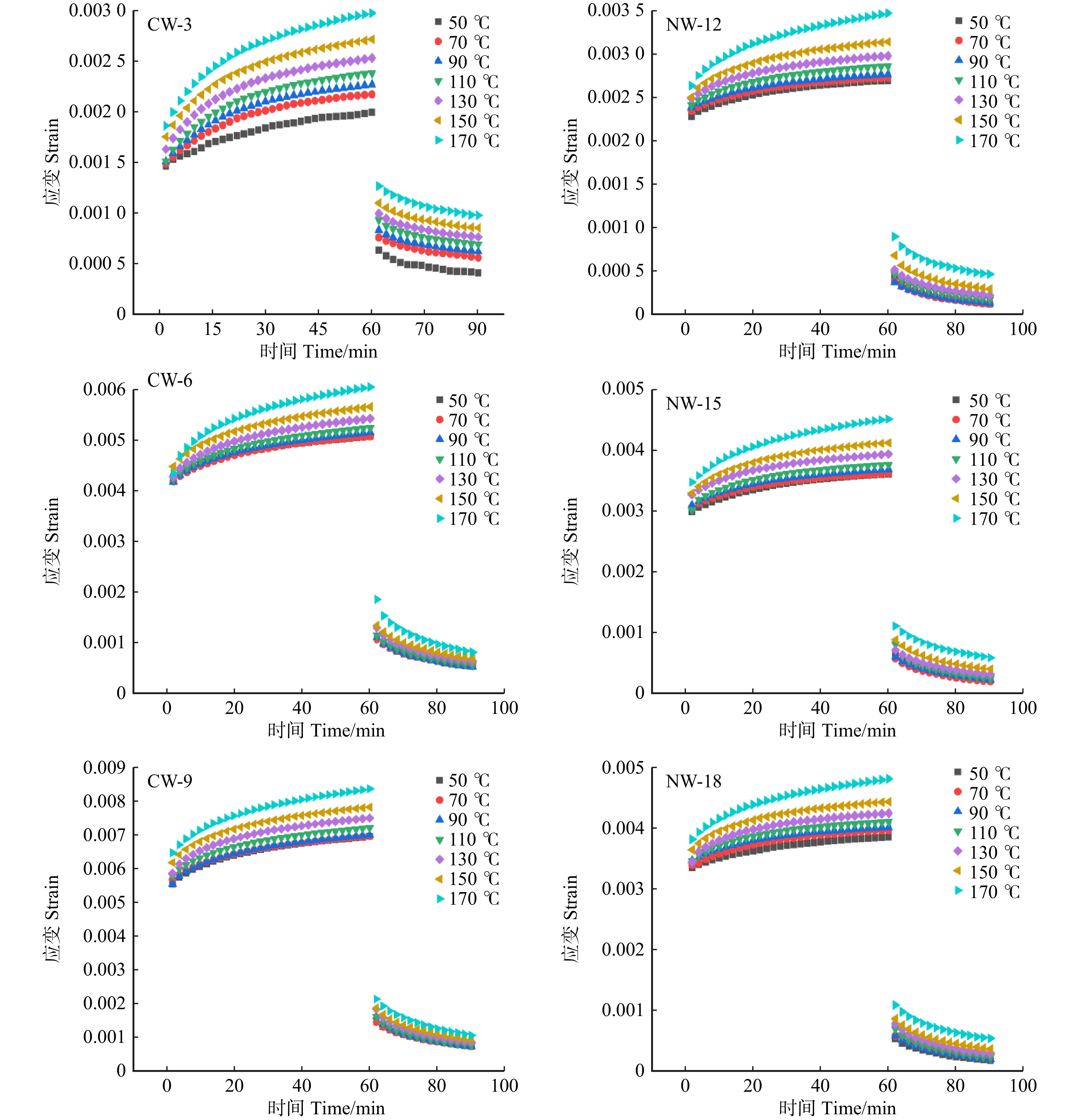
图 2 不同温度水平下应压木和正常木早材试样拉伸蠕变曲线
CW-3、CW-6和CW-9分别代表蠕变应力值3、6和9 MPa的应压木。NW-12、NW-15和NW-18分别代表蠕变应力值12、15和18 MPa的正常木。下同!CW-3, CW-6, and CW-9 represent compressive wood with creep stress values of 3, 6, and 9 MPa, respectively. NW-12, NW-15, and NW-18 represent normal wood with creep stress values of 12, 15, and 18 MPa, respectively. The same below!
Figure 2. Tensile creep curves of earlywood between CW and NW at different temperature levels
表 1 马尾松应压木和正常木早材试样拉伸力学参数
Table 1 Tensile mechanical parameters of earlywood between CW and NW from masson pine
试样
Specimen拉伸弹性模量 Tensile elastic modulus 应力 Stress 应变 Strain 均值
Mean value/MPaCV/% 均值
Mean value/MPaCV/% 均值
Mean value/%CV/% 应压木早材 Earlywood of CW 1 164 10.98 15.97 0.30 1.47 14.65 正常木早材 Earlywood of NW 2 680 5.06 19.38 1.66 0.65 7.53 -
[1] Stevanic J S, Salmén L. Molecular origin of mechano-sorptive creep in cellulosic fibres[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 230: 115615. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115615
[2] Salmén L, Stevanic J S, Olsson A M. Contribution of lignin to the strength properties in wood fibres studied by dynamic FTIR spectroscopy and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA)[J]. Holzforschung, 2016, 70(12): 1155−1163. doi: 10.1515/hf-2016-0050
[3] Peng H, Salmén L, Stevanic J S, et al. Structural organization of the cell wall polymers in compression wood as revealed by FTIR microspectroscopy[J]. Planta, 2019, 250(1): 163−171. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03158-7
[4] Salmén L, Bergström E. Cellulose structural arrangement in relation to spectral changes in tensile loading FTIR[J]. Cellulose, 2009, 16: 975−982. doi: 10.1007/s10570-009-9331-z
[5] Roszyk E, Mania P, Moliński W. The influence of microfibril angle on creep of Scotch pine wood under tensile stress along the grains[J]. Wood Research, 2012, 57(3): 347−358.
[6] 王东, 林兰英, 傅峰, 等. 傅里叶变换红外光谱研究拉伸过程中应压木主要化学组分的响应规律[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(11): 3585−3589. Wang D, Lin L Y, Fu F, et al. Chemical construction changes of compression wood main components in longitudinal tension by the FTIR analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(11): 3585−3589.
[7] Peng H, Salmén L, Jiang J L, et al. Creep properties of compression wood fiber[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2020, 54: 1497−1510. doi: 10.1007/s00226-020-01221-1
[8] Purusatama B D, Choi J K, Lee S H, et al. Microfibril angle, crystalline characteristics, and chemical compounds of reaction wood in stem wood of Pinus densiflora[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2020, 54(1): 123−137. doi: 10.1007/s00226-019-01140-w
[9] 李珠, 殷方宇, 蒋佳荔, 等. 杉木应压木和对应木的水分吸附特性比较研究[J]. 木材科学与技术, 2022, 36(5): 37−42. doi: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2022018 Li Z, Yin F Y, Jiang J L, et al. Comparative studies on water vapor sorption characteristics between compression wood and opposite wood of Chinese fir[J]. Chinese Journal of Wood Science and Technology, 2022, 36(5): 37−42. doi: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2022018
[10] Engelund E T, Salmén L. Tensile creep and recovery of Norway spruce influenced by temperature and moisture[J]. Holzforschung, 2012, 66(8): 959−965. doi: 10.1515/hf-2011-0172
[11] 邓彪, 罗迎社, 李贤军, 等. 荷载、含水率及温度对桉树木材抗弯蠕变性能的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(5): 142−131. Deng B, Luo Y S, Li X J, et al. Effects of load, moisture content and temperature on flexural creep behavior of Eucalyptus[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2013, 33(5): 142−131.
[12] 林金星, 李正理. 马尾松正常木与应压木的比较解剖[J]. 植物学报, 1993, 35(3): 201−205. Lin J X, Li Z L. Comparative anatomy of normal wood and compression wood of masson pine (Pinus massoniana)[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1993, 35(3): 201−205.
[13] Wang J F, Wang X, He Q, et al. Time-temperature-stress equivalence in compressive creep response of Chinese fir at high-temperature range[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 235: 117809. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117809
[14] Li Z, Zhan T Y, Eder M, et al. Comparative studies on wood structure and microtensile properties between compression and opposite wood fibers of Chinese fir plantation[J]. Journal of Wood Science, 2021, 64(1): 12.
[15] Hou J F, Jiang Y Q, Yin Y Q, et al. Experimental study and comparative numerical modeling of creep behavior of white oak wood with various distributions of earlywood vessel belt[J]. Journal of Wood Science, 2021, 67(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s10086-021-01989-1
[16] 尹业桥, 侯俊峰, 姜志宏, 等. 早材管孔分布对环孔材栎木蠕变特性的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2021, 6(3): 54−60. Yin Y Q, Hou J F, Jiang Z H, et al. Effect of earlywood vessel distribution on creep characteristics of ring-porous oak wood[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2021, 6(3): 54−60.
[17] 王聪, 吴强, 林鹏, 等. 不同纹理方向栎木微小无疵试样板材蠕变特性[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(4): 76−83. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180409 Wang C, Wu Q, Lin P, et al. Orthotropic creep performance of small flawless oak board[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2018, 54(4): 76−83. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20180409
[18] Peng H, Zhan T Y, Jiang J L, et al. Comparison of the time-moisture and time-temperature equivalences in the creep properties of Chinese fir[J]. Wood Material Science & Engineering, 2022, 17(6): 911−917.
[19] 蔡绍祥, 李延军, 王思群, 等. 马尾松木材轴向管胞细胞壁黏弹性变异研究[J]. 林产工业, 2021, 58(11): 1−7. Cai S X, Li Y J, Wang S Q, et al. Study on the variation of viscoelasticity of cell wall of masson pine tracheid at axial direction[J]. China Forest Products Industry, 2021, 58(11): 1−7.
[20] Keckes J, Burgert I, Klaus F, et al. Cell-wall recovery after irreversible deformation of wood[J]. Nature Materials, 2003, 2(12): 810−814. doi: 10.1038/nmat1019




 下载:
下载: