Study on spatial-temporal variability of volatile components inLagerstroemia indica 'Xiang Xue Yun'
-
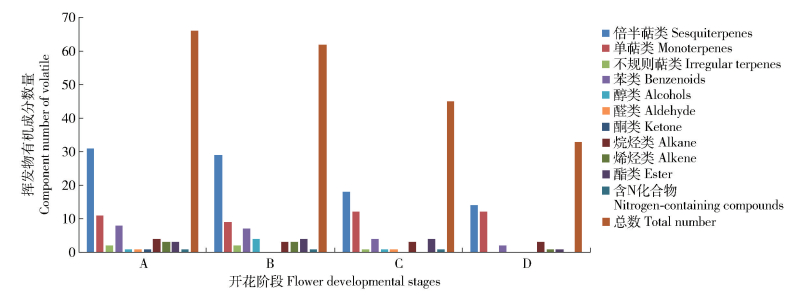
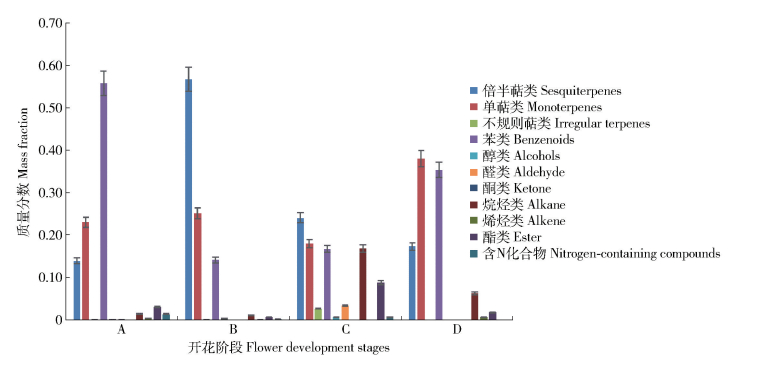
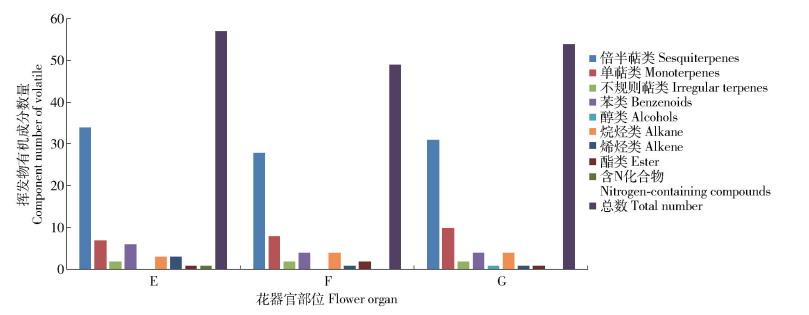
摘要: 为了研究紫薇‘香雪云’香气成分的时空动态变化,本文利用顶空-固相微萃取结合气相色谱-质谱(HS-SPME-GC-MS)联用技术,分析‘香雪云’花朵挥发性成分在4个开花时期(半开期、盛开期、盛开末期、衰败期)和盛开期花朵的3个花器官部位(花瓣、雄蕊、雌蕊)中的释放规律。结果表明:1)从紫薇‘香雪云’花朵的4个开花时期中,共检测出80种挥发性成分,分别属于11个类别;倍半萜类、单萜类和苯类化合物是其中具有较高质量分数的化合物类别;α-法尼烯、松香芹酮和苯乙醇等是盛开期中具有较高质量分数的挥发性成分。2)在紫薇‘香雪云’的不同开花阶段,各挥发性成分的释放规律不同;共呈现出6种主要的挥发模式,即持续下降模式、先下降后上升模式、先下降后上升再下降模式、持续上升模式、先上升后下降模式和先上升后下降再上升模式。3)就花器官而言,花瓣中的苯类化合物和萜类化合物的质量分数均较高;雌蕊和雄蕊中则均以萜类化合物为主,但化合物种类及其质量分数也存在较大差异。研究结果为了解紫薇属植物的香气成分奠定了基础,为紫薇香花定向育种提供了依据。Abstract: This study aims to determine the spatial-temporal variability of volatile components ofLagerstroemia indica 'Xiang Xue Yun' by headspace solid micro-extraction (HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The aroma compounds of flowers at four different developmental periods(middle-opening period, full-opening period, late-blooming period, bloom-declining period) and three floral organs(petal, stamen, pistil) in full-opening period were studied. The results showed that: 1) eighty volatile compounds belonging to 11 categories were identified from flowers during the whole flowering process ofL.indica'Xiang Xue Yun', of which, sesquiterpenes, monoterpenes and benzenoids were the main categories with high mass fraction and α-farnesene, pinocarvone and phenylethyl alcohol were the major volatile components emitted with high mass fraction. 2) Volatile compounds emitted fromL.indica 'Xiang Xue Yun' flower during flowering showed six different modes: the continuely-declining pattern; declining first and then rising pattern; the pattern of declining first, rising later and then declining again; continuely-rising pattern; rising first and then declining pattern; the pattern of rising first, later declining and then rising again. 3) In petals, the mass fraction of benzenoids and terpene compounds was high, while in pistil and stamen, the relative content of terpene compounds was high. But the volatile compounds and their mass fraction were distinctly different at different floral organs ofL.indica 'Xiang Xue Yun'. This study lays a good foundation to understand the volatile organic compounds ofLagerstroemia plants and to provide the basis for fragrant breeding of crape myrtle.
-
-
表 1 ‘香雪云’不同开花时期及花器官部位释放的挥发性有机成分及质量分数
Table 1 Components and mass fraction of volatile organic compounds(VOCs) at different developmental stages and floral organs ofLagerstroemia indica ‘Xiang Xue Yun’
% 保留时间
Retention time
(Rt)/min保留指数
Retention index
(RI)化合物
Compound质量分数Mass fraction/% A B C D E F G 5.60 761(762) 甲苯Toluene 0.06 — — — — Tr 0.20 9.86 866(868) 反-4-己烯醇Trans-4-hexenol 0.12 0.09 — — — — — 10.03 869(857) 叶醇Leaf alcohol — 0.07 — — — — — 10.11 871(869) E-3-己烯醇E-3-hexenol — 0.16 — — — — — 10.76 883(874) 5-甲基-3-亚甲基-5-己烯-2-酮
5-methyl-3-methylene-5-hexen-2-one0.03 — — — — — — 11.12 890(892) 苯乙烯Styrene 0.04 — — — — — 0.29 12.46 917(915) 茴香醚Anisole — 0.02 — — — 0.22 — 13.23 933(930) α-侧柏烯α-thujene — — — — — — 0.08 14.09 950(946) 莰烯Camphene — — — — — — 0.09 14.96 966(962) 安息香醛Benzaldehyde 1.84 — — — — — — 17.30 1 006(992) (4E)-4-已烯基乙酯(4E)-4-hexenyl acetate 0.2 0.03 2.44 — — — — 17.72 1 015(1 011) 乙酸己酯Hexyl acetate — — 1.33 — — — — 18.01 1 021(1 018) 对-甲基茴香醚p-methylanisole — 0.08 1.12 — 0.31 — — 18.12 1 023(1 019) o-伞花烃o-cymene — — 0.57 0.91 — — — 18.36 1 028(1 028) D-柠檬烯D-limonene 0.03 0.03 1.32 3.32 — — 0.20 18.80 1 037(1 037) 顺-α-罗勒烯cis-α-ocimene 0.02 0.06 0.75 1.45 — — 0.12 19.00 1 041(1 043) 2-乙基己酸甲酯Methyl2-ethylhexanoate 0.76 0.28 1.99 1.81 0.02 0.28 Tr 19.33 1 047(1 045) α-甲苯甲醛α-tolualdehyde 16.57 1.83 11.63 33.00 0.22 0.32 1.54 19.40 1 048(1 046) β-反-罗勒烯β-trans-ocimene 14.32 0.58 Tr — — — — 19.99 1 060(1 066) 2-异丙基-5-甲基-1-己醇
2-isopropyl-5-methyl-1-hexanol— — — — — — 0.17 20.30 1 065(1 051) 苯甲醇Benzyl alcohol — 0.07 — — — — — 21.16 1 080(1 068) β-苯乙基甲酯β-phenylethyl methyl ether — — — — 0.05 — — 21.32 1 083(1 083) 萜品油烯Terpinolene — — 0.24 0.77 — — — 21.72 1 090(1 119) 顺-马鞭草烯酮cis-verbenone Tr 0.55 0.61 2.38 0.31 2.31 0.55 22.03 1 095(1 099) 紫苏烯Perillen — — Tr 0.57 0.03 0.70 0.45 22.61 1 106(1 111) 玫瑰醚Rose oxide 0.03 0.04 1.55 1.37 0.01 0.80 — 22.76 1 110(1 114) 松香芹酮Pinocarvone 0.88 21.66 11.26 24.80 16.31 13.60 14.82 23.00 1 115(1 116) 苯乙醇Phenylethyl alcohol 33.54 11.85 — — 36.71 — — 23.45 1 125(1 127) 反-玫瑰醚trans-rose oxide — — 0.32 1.85 — — — 24.20 1 141(1 142) 苯乙腈Benzyl nitrile 1.42 0.27 0.70 — 1.46 — — 24.80 1 154(1 151) β-香茅醛β-citronellal 0.55 — — — 0.08 0.18 0.04 26.01 1 178(1 177) 苯乙酸甲酯Methyl phenylacetate 0.15 0.10 0.14 — 0.02 — — 26.64 1 190(1 191) 1-十二烯1-dodecene Tr 0.03 — 0.70 0.02 Tr 0.23 27.04 1 197(1 195) 龙蒿脑Estragole 0.38 0.15 1.14 Tr 4.55 0.11 0.43 27.47 1 205(1 213) 2-甲基-3-十一醇2-methyl-3-decanol — 0.04 0.72 — — — — 27.49 1 206(1 207) 癸醛Decanal 0.16 — 3.49 — — — — 28.55 1 230(1 226) 顺-3-己烯基-α-丁酸甲酯
cis-3-hexenyl-α-methylbutyrate— 0.30 3.14 — — — — 29.02 1 240(1 240) β-柠檬醛β-citral 1.03 — — — — — — 29.81 1 257(1 260) 3, 7-二甲基-6-辛烯酸甲酯Methyl citronellate 2.26 0.16 — — — 4.82 — 29.90 1 259(1 252) p-茴香醛p-anisaldehyde 2.88 — — — — — — 30.44 1 270(1 268) 柠檬醛Citral 1.10 0.02 0.29 Tr 0.01 0.17 0.48 32.59 1 316 2, 6-二甲基-2, 6-十二二烯
2, 6-dimethyl-2, 6-dodecadiene0.17 0.06 — — 0.19 — — 32.73 1 319(1 322) 甲酸香叶酯Methyl geranate 4.71 2.09 — 0.61 — 46.1 — 33.63 1 340(1 350) (5Z)-2, 6, 10-三甲-1, 5, 9-十一三烯
(5Z)-2, 6, 10-trimethyl-1, 5, 9-undecatriene0.22 0.07 — — 0.03 — — 33.81 1 344 异喇叭烯Isoledene — — — — 0.02 — — 33.86 1 345(1 367) 2, 5-二甲基-2, 5双(过氧化氢)己烷
2, 5-dimethylhexane-2, 5-dihydroperoxide1.22 1.05 12.06 5.17 0.03 0.11 8.39 34.15 1 352(1 387) 长叶烯-(V4)Longifolene-(V4) — — — — 0.03 — — 35.06 1 372(1 375) α-古巴烯α-copaene 0.16 0.38 0.78 0.87 0.36 0.44 0.91 36.09 1 395(1 400) 十四烷Tetradecane 0.08 0.05 1.10 0.53 0.02 0.17 1.45 36.30 1 399(1 394) β-榄香烯β-elemene Tr Tr — — 0.01 0.04 0.32 36.41 1 401(1 403) α-古芸烯α-gurjunene 0.08 0.64 0.39 Tr 0.56 0.58 0.31 36.52 1 404(1 404) 长叶烯Longifolene 0.10 0.02 0.83 0.31 Tr 0.19 1.19 36.80 1 411(1 415) α-雪松烯α-cedrene 0.11 0.02 0.70 0.40 0.04 0.08 0.38 36.94 1 414(1 418) β-石竹烯β-caryophyllene 3.17 4.99 5.34 9.82 3.23 4.33 16.33 37.13 1 419(1 421) β-雪松烯β-cedrene 0.02 Tr — — Tr Tr 0.06 37.29 1 423(1 428) 罗汉柏烯Thujopsene Tr 0.06 Tr Tr 0.03 0.07 0.31 37.37 1 426(1 423) β-荜澄茄油烯β-cubebene 0.10 0.05 — — 0.04 0.07 0.25 37.57 1 430(1 433) 二氢-β-紫罗兰酮Dihydro-β-ionone 0.02 0.02 — — 0.01 Tr 0.17 37.76 1 435(1 439) (+)-香橙烯(+)-aromadendrene — — — — — — 0.34 38.06 1 443(1 431) β-刺柏烯β-gurjunene — — — — 0.10 0.11 0.24 38.21 1 446(1 453) 香叶基丙酮Geranyl acetone 0.09 0.07 2.73 — 0.06 Tr 0.30 38.31 1 448(1 447) (Z)-β-金合欢烯(Z)-β-farnesene 0.12 0.34 — — 0.25 0.12 0.59 38.44 1452(1 455) α-律草烯α-humulene 0.26 0.86 0.64 0.80 0.65 0.87 2.17 38.61 1456(1 457) 香树烯Allo-aromadendrene 0.30 0.75 — — 0.79 0.91 1.46 39.12 1468(1 473) τ-古芸烯τ-gurjunene 0.03 0.11 — — 0.11 0.16 0.18 39.28 1471(1 473) τ-衣兰油烯τ-muurolene 0.08 0.19 Tr — 0.15 0.17 0.72 39.49 1477(1 475) α-紫穗槐烯α-amorphene 0.07 0.33 — — 0.36 0.16 0.05 39.87 1485(1 496) (Z,E)-α-法尼烯(Z,E)-α-farnesene 0.30 1.96 1.22 Tr 1.12 0.70 1.74 40.13 1 491(1 499) 瓦伦烯Valencene 0.13 0.45 0.82 — 0.73 0.8 1.00 40.24 1 494(1 495) α-衣兰油烯α-muurolene 0.37 0.46 — — 0.44 0.65 3.28 40.42 1 498(1 503) α-法尼烯α-farnesene 2.50 33.72 6.99 1.98 19.40 5.30 7.54 40.60 1 503(1 494) α-桉叶烯α-selinene Tr 0.07 — — 0.01 — 0.18 40.82 1 508(1 510) τ-杜松烯τ-cadinene 1.13 3.95 2.15 0.40 4.13 6.44 2.66 41.02 1 514(1 520) δ-杜松烯δ-cadinene 0.66 2.53 1.06 2.27 2.66 3.96 12.12 41.20 1 518(1 520) (+)-喇叭烯(+)-ledene 0.11 0.84 0.62 — 0.47 0.16 0.62 41.76 1 533(1 536) α-杜松烯α-cadinene 0.12 0.36 0.19 — 0.37 0.48 0.48 42.71 1 559(1 559) ±-反-橙花叔醇±-trans-nerolidol 0.33 0.31 — — 0.46 0.04 7.30 42.90 1 562(1 564) 橙花叔醇Nerolidol — 0.27 — — 0.15 — — 43.14 1 568(1 560) 榧素Dendrolasin — 0.54 0.84 0.56 0.67 1.00 0.24 43.67 1 583(1 591) 异丁酸酯Txib 0.73 0.24 3.90 2.40 0.04 0.13 1.29 44.15 1 594(1 600) 十六烷Hexadecane 0.10 — — — — 0.10 0.40 44.64 1 606(1 604) 雪松醇Cedrol 0.28 — — — 0.01 — 0.20 44.75 1 609(1 594) 胡萝卜醇Carotol 0.95 — — — 0.03 — — 44.90 1 613(1 614) 异愈创木醇Bulnesol 0.18 1.70 0.56 Tr 0.61 0.28 0.43 45.86 1 639(1 638) 杜松醇Cadinol 0.32 0.83 0.99 Tr 1.03 1.45 3.71 47.87 1 691(1 700) 正十七烷n-heptadecane 0.08 0.04 3.73 0.64 0.01 0.11 0.40 48.40 1 705(1 714) E,E-金合欢醛E,E-farnesal 0.49 — — — — — — 49.35 1 732(1 730) 反-金合欢醇trans-farnesol 1.50 — — — — — — 注:A,半开期;B,盛开期;C,盛开末期;D,衰败期;E,花瓣;F,雄蕊;G,雌蕊;Tr,质量分数<0.01%;—,不含该化合物。保留指数列中括号内数值为文献值。Notes: A, middle-opening period; B, full-opening period; C, late-blooming period; D, bloom-declining period; E, petal; F, stamen; G, pistil; Tr, mass fraction is<0.01%; —, not contained this kind of compound. Bracketed value in retention index column is literature value. -
[1] MUHLEMANN J K, KLEMPIEN A, DUDAREVA N. Floral volatiles: from biosynthesis to function[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2014, 37(8): 1936-1949. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_153728
[2] SIDERHURST M S, JANG E B. Cucumber volatile blend attractive to female melon fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett)[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2010, 36(7): 699-708. doi: 10.1007/s10886-010-9804-4
[3] CHANDLER S, TANAKA Y. Genetic modification in floriculture[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2007, 26(4): 169-197. doi: 10.1080/07352680701429381
[4] 傅若农.固相微萃取(SPME)近几年的发展[J].分析试验室, 2015, 34(5): 602-620. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sp201612007 FU R N. Development of solidphase microextraction (SPME) in recent years[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2015, 34(5):602-620. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sp201612007
[5] 戚军超, 周海梅.固相微萃取-气质联用技术在天然产物挥发性成分分析中的应用[J].信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2005, 18(4): 471-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0972.2005.04.033 QI J C, ZHOU H M. Applications of solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technique on analysis of volatile components in natural products[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 18(4): 471-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0972.2005.04.033
[6] 杨通在, 罗顺忠.固相微萃取技术的现状与进展[J].环境研究与监测, 2006, 19(1): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gshjyjyjc200601001 YANG T Z, LUO S Z. Status and progress of solid phase micro extraction technology[J]. Environmental Study and Monitoring, 2006, 19(1): 1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gshjyjyjc200601001
[7] 蒋生祥, 冯娟娟.固相微萃取研究进展[J].色谱, 2012, 30(3): 219-221. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxkxxb200205024 JIANG S X, FENG J J. Advances in solid phase micro extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2012, 30(3): 219-221. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxkxxb200205024
[8] SUN H, ZHANG T, FAN Q, et al. Identification of floral scent in Chrysanthemum cultivars and wild relatives by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20(4): 5346-5359. doi: 10.3390/molecules20045346
[9] IWABUCHI H, IMAYOSHI Y, YOSHIDA Y, et al. Gas chromatography-olfactometry (the state of the art)[M]. Washington D C: ACS Symposium, 2001:11-22.
[10] DUDAREVA N, KLEMPIEN A, MUHLEMANN J K, et al. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 198(1): 16-32. doi: 10.1111/nph.12145
[11] 孔滢.百合花香组成成分及时空释放规律研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2012. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0305197816302575 KONG Y. Floral scent compositions and space-time emission patterns ofLilium flowers[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0305197816302575
[12] 孔滢, 孙明, 潘会堂, 等.花香代谢与调控研究进展[J].北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(2): 146-154. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9745 KONG Y, SUN M, PAN H T, et al. Advances in metabolism and regulation of floral scent[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(2): 146-154. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9745
[13] 赵印泉, 潘会堂, 张启翔, 等.梅花花朵香气成分时空动态变化的研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(4): 201-206. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9556 ZHAO Y Q, PAN H T, ZHANG Q X, et al. Dynamics of fragrant compounds from Prunus mume flowers[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2010, 32(4): 201-206. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9556
[14] DUDAREVA N. Molecular control of floral fragrance[M]//VAINSTEIN A. Breeding for ornamentals: classical and molecular approaches. Berlin: Springer, 2002: 295-309.
[15] PICHERSKY E, LEWINSOHN E, CROTEAU R. Purification and characterization of S-linalool synthase, an enzyme involved in the production of floral scent in Clarkia breweri[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1995, 316(2): 803-807. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1107
[16] 向林, 陈龙清.花香的基因工程研究进展[J].中国农业科学, 2009, 42(6): 2076-2084. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.06.025 XIANG L, CHEN L Q. Advances in genetic engineering of floral scent[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(6): 2076-2084. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.06.025
[17] 张启翔.紫薇品种分类及其在园林中的应用[J].北京林业大学学报, 1991, 13(4): 57-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BJLY199104008.htm ZHANG Q X.Studies on cultivars of crape-myrtle (Lagerstroemia indica) and their uses in urban greening[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 1991, 13(4): 57-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BJLY199104008.htm
[18] 王献, 张启翔, 杨秋生, 等. 2004中国观赏园艺研究进展[C]//中国园艺学会观赏园艺专业委员会, 2004年学术年会论文集.北京: 中国林业出版社, 2004: 5-9. WANG X, ZHANG Q X, YANG Q S, et al. 2004 Advances in ornamental horticulture in China[C]//Chinese Horticultural Society Ornamental Horticulture Specialized Committee, Proceedings of the 2004 Academic Annual Conference. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2004: 5-9.
[19] 张洁, 王亮生, 张晶晶, 等.紫薇属植物研究进展[J].园艺学报, 2007, 34(1): 251-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2007.01.052 ZHANG J, WANG L S, ZHANG J J, et al. Advances in studies on genusLagerstroemia[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2007, 34(1): 251-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2007.01.052
[20] 王晓玉.尾叶紫薇与紫薇种间杂交育种研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1012350642.htm WANG X Y. Interspecific hybridizing betweenLagerstroemia indica andL. caudata[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1012350642.htm
[21] 蔡明.紫薇种质资源评价和香花种质利用[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2010. CAI M. Evaluation ofLagerstroemia germplasm resources and utilization of germplasms with fragrant flowers[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2010.
[22] 蔡明, 王晓玉, 张启翔, 等.紫薇品种与尾叶紫薇种间杂交亲和性研究[J].西北植物学报, 2010, 30(4): 697-701. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201004009 CAI M, WANG X Y, ZHANG Q X, et al. Compatibility of interspecific crosses betweenLagerstroemiaindica cultivars andLagerstroemia caudata[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(4): 697-701. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201004009
[23] 王金凤, 刘新红, 陈卓梅.紫薇属植物育种研究进展[J].园艺学报, 2013, 40(9): 1795-1804. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/huah201718003 WANG J F, LIU X H, CHEN Z M. Research progress in breeding ofLagerstroemia plant[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2013, 40(9): 1795-1804. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/huah201718003
[24] EGOLF D R. 'Biloxi', 'Miaxni' and 'Wichita'Lagerstroemia[J]. HortScience, 1987, 22(2): 336-338.
[25] POUNDERS C, RINEHART T, SAKHANOKHO H. Evaluation of interspecific hybrids betweenLagerstroemia indica andL. speciosa[J]. HortScience, 2007, 42(6): 1317-1322. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.42.6.1317
[26] 徐婉.紫薇的香花育种和性状遗传改良研究[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2014. XU W. Breeding in fragrance and improvement of significant ornamental traits ofLagerstroemia[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2014.
[27] ZHANG J J, KANG W Y. Volatiles from flowers ofLagerstroemia caudata by HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2014, 50(5): 933-934. doi: 10.1007/s10600-014-1123-5
[28] 王晓玉, 徐婉, 胡杏, 等.尾叶紫薇开花及花粉萌发研究[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(6): 966-970. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjlxyxb201206024 WANG X Y, XU W, HU X, et al. Florescence and pollen germination inLagerstroemia caudata[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2012, 29(6): 966-970. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjlxyxb201206024
[29] 周继荣, 倪德江.蜡梅不同品种和花期香气变化及其花茶适制性[J].园艺学报, 2010, 37(10): 1621-1628. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201010010 ZHOU J R, NI D J. Changes in flower aroma compounds of cultivars ofChimonanthus praecox (L.) Link and at different stages relative toChimonanthus tea quality[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2010, 37(10): 1621-1628. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yyxb201010010
[30] 谭谊谈, 薛山, 唐会周.不同花期栀子花的香气成分分析[J].食品科学, 2012, 33(12): 223-227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPKX201212046.htm TAN Y T, XUE S, TANG H Z. Analysis of aroma constituents inGardenia jasminoides at different flowering stages[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(12): 223-227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPKX201212046.htm
[31] 李祖光, 李新华, 高建荣, 等.白丁香鲜花在不同开花期的香气化学成分研究[J].林产化学与工业, 2005, 25(4): 63-66. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2417.2005.04.015 LI Z G, LI X H, GAO J R, et al. Study on chemical constituents of fragrance released from fresh flowers of Syringa oblata var.affinis during different florescences[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2005, 25(4): 63-66. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2417.2005.04.015
[32] 李祖光, 曹慧, 朱国华, 等.三种桂花在不同开花期头香成分的研究[J].林产化学与工业, 2008, 28(3): 75-80. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2417.2008.03.015 LI Z G, CAO H, ZHU G H, et al. Study on chemical constituents of fragrance released from fresh flowers of three differentOsmanthus franrans Lour. during different florescences[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2008, 28(3): 75-80. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2417.2008.03.015
[33] 陈家华, 林祖铭, 金声, 等.动态法研究啤酒花头香成分变化[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1991, 27(4): 406-413. doi: 10.1016-j.suc.2009.06.008/ CHEN J H, LIN Z M, JIN S, et al. The kinetic study of volatile components in hop[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinensis, 1991, 27(4): 406-413. doi: 10.1016-j.suc.2009.06.008/
[34] DUDAREVA N, PICHERSKY E. Biochemical and molecular genetic aspects of floral scents[J]. Plant Physiology, 2000, 122 (3): 627-633. doi: 10.1104/pp.122.3.627
[35] 杜明利, 高群英, 高岩, 等.外来物种大花金鸡菊不同器官成分的气质联用(GC-MS)分析[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(2): 313-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2012.02.024 DU M L, GAO Q Y, GAO Y, et al. Organic compounds in exoticCoreopsis grandiflora using GC-MS[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2012, 29(2): 313-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0756.2012.02.024
[36] 付庆霞.忍冬不同器官化学成分分析比较[D].济南: 山东中医药大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10441-2009176544.htm FU Q X. Comparison analysis of chemical constituents in different organs ofLonicera japonica[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10441-2009176544.htm
[37] LI Z G, LEE M R, SHEN D L. Analysis of volatile compounds emitted from freshSyringa oblata flowers in different florescence by headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2006, 576(1): 43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2006.01.074
[38] 范正琪, 李纪元, 李辛雷, 等.基于HS-SPME/GC-MS分析山茶品种'克瑞墨大牡丹'花器官香气成分[J].植物研究, 2014, 34(1): 136-142. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-MBZW201401019.htm FAN Z Q, LI J Y, LI X L, et al. Analysis on the aroma components of different floral organs of aromaticCamellia 'Kramer's supreme' based on HS-SPME/GC-MS[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 136-142. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-MBZW201401019.htm
[39] 杨慧君.中国兰花挥发性成分分析[D].呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10129-1011178750.htm YANG H J. Analysis on the volatile components of Chinese orchids[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10129-1011178750.htm
[40] WANG C, YOON S H, JANG H J, et al. Metabolic engineering ofEscherichia coli for α-farnesene production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13(6): 648-655. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2011.08.001
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张苗苗,罗于洋,王树森,张丽娜,马成功,于胜利,王景圆. 内蒙古旺业甸华北落叶松人工林空间结构分析及其优化. 西北林学院学报. 2024(01): 81-87+107 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 荆媛,魏爽,史文辉,马梓贺,王德宇,戎可. 天然次生林中小斑啄木鸟的取食偏好. 野生动物学报. 2024(01): 84-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙宇,刘盛,田佳歆,程福山,赵士博,王诗俊. 基于空间结构优化的长白落叶松人工林分间伐模型构建. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(01): 72-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘鑫,黄浪,卿东升,李建军. 基于Voronoi空间单元的林分空间结构智能优化研究. 林业资源管理. 2023(04): 27-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: