Construction of SSR fingerprint and research of genetic structure in relative Quercus species
-
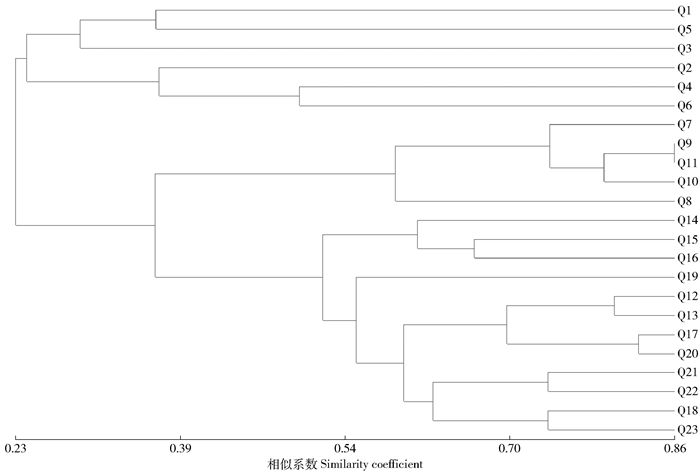
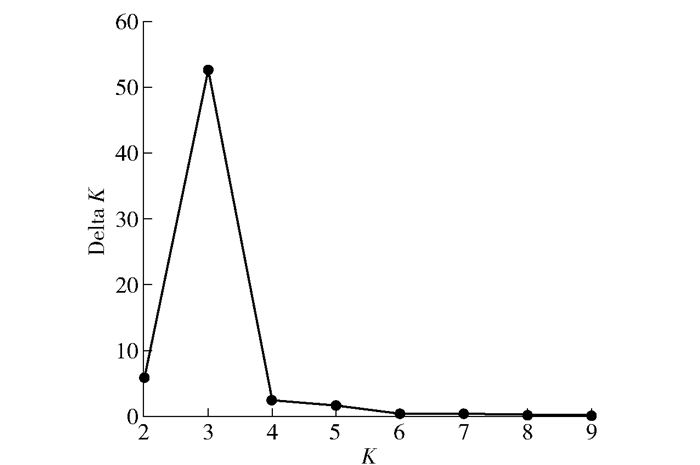
摘要:目的对栎属近缘种质进行指纹图谱构建,并分析其遗传结构,为栎属近缘种鉴定及分类提供了重要工具。方法以23份栎属近缘种质为研究对象,利用遗传背景差异大的4份种质进行SSR引物筛选,选出9对扩增条带清晰、具有多态性且重复性好的引物对其进行扩增,利用毛细管电泳技术对PCR荧光产物进行检测,采用引物-分子量组合法构建23份种质的指纹图谱,利用NTsys和STRUCTURE软件进行聚类分析和群体遗传结构分析。结果9对SSR引物共扩增出78个条带,每个位点的等位标记数4~14个,平均每对引物为8.67个,多态信息含量变幅为0.58~0.82,平均为0.73。聚类分析显示辽东栎、蒙古栎分别聚为两个类群,猩红栎和北美红栎聚为一个类群,群体遗传结构分析显示23份种质为3个亚群体,遗传结构分析与聚类分析结果一致。结论23份栎属近缘种质可以划分为辽东栎组、蒙古栎组、猩红栎-北美红栎混合组,辽东栎与蒙古栎是两个独立的分类单位,上述结果为栎属分类、品种鉴定和知识产权保护提供了理论依据。Abstract:ObjectiveThe fingerprint of the relative Quercus species was constructed and the genetic structure was analyzed, it provides an important tool for the identification and classification in relative Quercus species in order to classify and identify the relative Quercus species.Method23 germplasms of relative Quercus were used as the materials in this study, SSR primers were selected by 4 accessions of genetically distant germplasms, 9 pairs of primers with clear amplification bands, high polymorphism and stable repeatability were selected and used for PCR amplification of the 23 germplasms, PCR products labeled fluorescent were detected using capillary electrophoresis technology, a strategy of combining primer pair with molecular weight for fingerprint construction was developed and applied to the 23 germplasms, the software of NTsys and STRUCTURE were used in clustering analysis and population genetic structure analysis.ResultThe 78 fragments were amplified by 9 pairs of SSR primers, the number of alleles at each locus was between 4 and 14, with an average of 8.67 alleles for each pair of primers, polymorphism information content values for the primer pairs ranged from 0.58 to 0.82, with an average of 0.73. Clustering analysis showed that Quercus liaotungensis and Quercus monglica were respectively divided into two groups, Quercus coccinea and Quercus rubra were clustered into a group, population genetic structure analysis showed that 23 germplasms for the three groups, genetic structure analysis and clustering analysis results were consistent.ConclusionThe 23 germplasms are divided into Quercus liaotungensis group, Quercus monglica group, Quercus coccinea-Quercus rubra mixed group, Quercus liaotungensis and Quercus monglica are two separate taxonomies, the results provide a theoretical basis for Quercus classification, variety identification and protection of intellectual property centers.
-
Keywords:
- Quercus liaotungensis /
- Quercus monglica /
- fingerprint /
- genetic structure
-
-
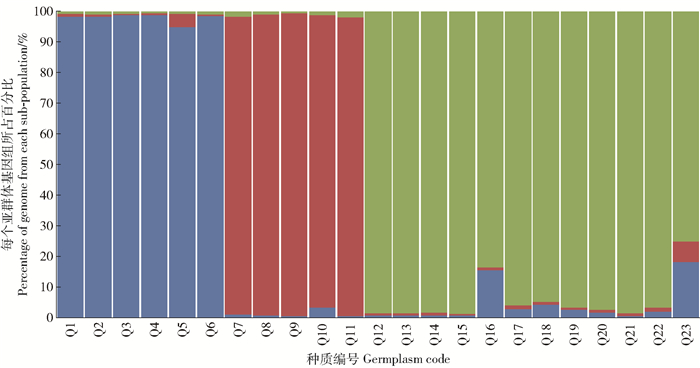
图 4 23份种质的群体结构(K=3)
23份栎属近缘种质被划分为3个亚群体,每一个颜色代表一个亚群体,蓝色为辽东栎亚群;红色为蒙古栎亚群;绿色为猩红栎-北美红栎亚群。
Figure 4. Population structure for 23 germplasms(K=3)
The 23 germplasms were clustered into 3 sub-population, each color represents a sub-population, blue color represents Quercus liaotungensis sub-population, red color represents Q. monglica sub-population, green color represents Q. coccinea-Q. rubra sub-population.
表 1 试验材料
Table 1 Experimental materials
编号Code 种质Germplasm 种源Provenance Q1 晋辽东栎1号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong1’ 山西省中条山国有林管理局横河林场,良种编号:晋R-SC-QL-001-2016
Shanxi Province Zhongtiao Mountain State Forest Administration, Henghe Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin R-SC-QL-001-2016Q2 晋辽东栎2号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong2’ 山西省太岳山国有林管理局灵空山林场,良种编号:晋R-SC-QL-002-2016
Shanxi Province Taiyue Mountain State Forest Administration, Lingkongshan Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin R-SC-QL-002-2016Q3 晋辽东栎3号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong3’ 山西省吕梁山国有林管理局康城林场,良种编号:晋R-SC-QL-003-2016
Shanxi Province Lüliang Mountain State Forest Administration, Kangcheng Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin R-SC-QL-003-2016Q4 晋辽东栎4号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong4’ 山西省吕梁山国有林管理局东山林场,良种编号:晋R-SC-QL-004-2016
Shanxi Province Lüliang Mountain State Forest Administration, Dongshan Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin R-SC-QL-004-2016Q5 晋辽东栎5号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong5’ 山西省太行山国有林管理局坪松林场,良种编号:晋S-SS-QL-005-2014
Shanxi Province Taihang Mountain State Forest Administration, Pinsong Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin S-SS-QL-005-2014Q6 晋辽东栎6号Querecus liaotungensis ‘Jinliaodong6’ 山西省关帝山国有林管理局真武山林场,良种编号:晋S-SS-QL-006-2014
Shanxi Province Guandi Mountain State Forest Administration, Pinsong Forest Farm, the code of improved variety: Jin S-SS-QL-006-2014Q7 蒙古栎1号Quercus monglica 1 吉林省引种种质The introduction of germplasm in Jilin Province Q8 蒙古栎2号Quercus monglica 2 吉林省引种种质The introduction of germplasm in Jilin Province Q9 蒙古栎3号Quercus monglica 3 吉林省引种种质The introduction of germplasm in Jilin Province Q10 蒙古栎4号Quercus monglica 4 吉林省引种种质The introduction of germplasm in Jilin Province Q11 蒙古栎5号Quercus monglica 5 吉林省引种种质The introduction of germplasm in Jilin Province Q12 猩红栎1号Quercus coccinea 1 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q13 猩红栎2号Quercus coccinea 2 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q14 猩红栎3号Quercus coccinea 3 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q15 猩红栎4号Quercus coccinea 4 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q16 猩红栎5号Quercus coccinea 5 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q17 猩红栎6号Quercus coccinea 6 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q18 北美红栎1号Quercus rubra 1 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q19 北美红栎2号Quercus rubra 2 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q20 北美红栎3号Quercus rubra 3 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q21 北美红栎4号Quercus rubra 4 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q22 北美红栎5号Quercus rubra 5 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina Q23 北美红栎6号Quercus rubra 6 美国北卡罗来纳州引种种质The introduction of germplasm in the United States North Carolina 表 2 SSR引物信息表
Table 2 Table of SSR primer information
引物名称
Primer name正向引物
Forward primer (5′→3′)反向引物
Reverse primer(5′→3′)ssrQrZAG 96 CCCAGTCACATCCACTACTGTCC GGTTGGGAAAAGGAGATCAGA ssrQrZAG 102 GCCTACACTCTTCAATCTACATGA GACTTGTAACACCTTAAGCATTATCT ssrQrZAG 112 TTCTTGCTTTGGTGCGCG GTGGTCAGAGACTCGGTAAGTATTC ssrQrZAG 7 CAACTTGGTGTTCGGATCAA GTGCATTTCTTTTATAGCATTCAC Qden 03011 AACCC AACCTTCCCTTCATC GCAGTGGTGCCTAATGTAGAC Qden 03021 ACAGCAAACCAGACTCCAC CCCCAAAGTTTCGGCTAATAC Qden 03032 AGTTGTGGTCCTGCTCGC GAAAAGTGCGATGACGGTTG Qden 05011 CCCACTCCCTGTCCATTGT CACTGTGTGCTGCGACTTG Qden 05031 CCCCGATTCGCCATCATTGT GTAACGCCGTTTTTCTCCACC 表 3 9对SSR引物的多态检测
Table 3 Polymorphism detection of 9 pairs of SSR primer
引物名称
Primer name等位标记数
Allele number多态信息含量
PICssrQrZAG 96 8 0.76 ssrQrZAG 102 14 0.82 ssrQrZAG 112 8 0.77 ssrQrZAG 7 10 0.71 Qden 03011 7 0.65 Qden 03021 4 0.58 Qden 03032 7 0.78 Qden 05011 12 0.79 Qden 05031 8 0.72 总计Total 78 平均Mean 8.67 0.73 表 4 23份种质的指纹图谱
Table 4 Fingerprint of 23 germplasms based on SSR markers
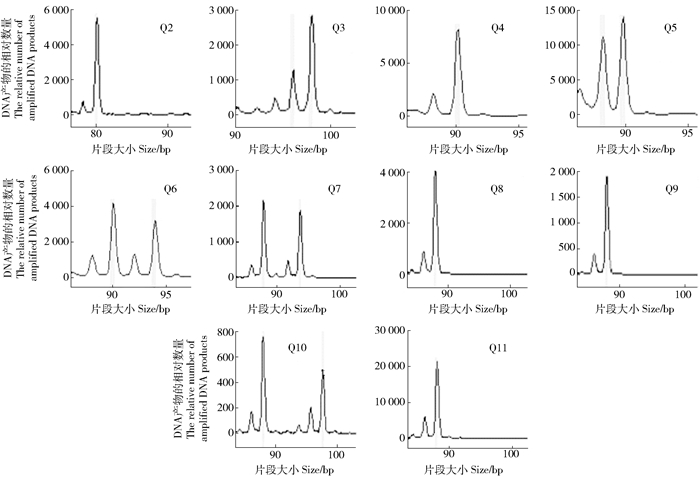
编号Code 指纹图谱Fingerprint Q1 ssrQrZAG96, 152, 152 ssrQrZAG112, 78, 90 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 140 Qden03011, 142, 144 Qden03021, 252, 254 Qden 05011, 174, 180 Q2 ssrQrZAG96, 154, 166 ssrQrZAG112, 81, 81 ssrQrZAG7, 134, 140 Qden03011, 140, 150 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 180, 188 Q3 ssrQrZAG96, 145, 150 ssrQrZAG112, 96, 98 ssrQrZAG7, 128, 138 Qden03011, 140, 140 Qden03021, 252, 256 Qden 05011, 176, 178 Q4 ssrQrZAG96, 150, 168 ssrQrZAG112, 90, 90 ssrQrZAG7, 126, 128 Qden03011, 140, 140 Qden03021, 252, 260 Qden 05011, 172, 180 Q5 ssrQrZAG96, 160, 186 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 90 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 124 Qden03011, 140, 142 Qden03021, 254, 256 Qden 05011, 176, 192 Q6 ssrQrZAG96, 154, 166 ssrQrZAG112, 90, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 126, 126 Qden03011, 138, 140 Qden03021, 252, 260 Qden 05011, 180, 186 Q7 ssrQrZAG96, 147, 149 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 134 Qden03011, 137, 137 Qden03021, 254, 254 Qden 05011, 175, 183 Q8 ssrQrZAG96, 147, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 88 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 124 Qden03011, 137, 137 Qden03021, 254, 254 Qden 05011, 175, 183 Q9 ssrQrZAG96, 147, 149 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 88 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 134 Qden03011, 137, 139 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 175, 175 Q10 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 149 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 98 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 134 Qden03011, 137, 139 Qden03021, 252, 254 Qden 05011, 177, 183 Q11 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 88, 88 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 134 Qden03011, 137, 139 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 175, 183 Q12 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 134, 146 Qden03011, 138, 140 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 183, 185 Q13 ssrQrZAG96, 151, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 134, 146 Qden03011, 140, 142 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 183, 185 Q14 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 149 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 130, 134 Qden03011, 138, 142 Qden03021, 252, 254 Qden 05011, 183, 185 Q15 ssrQrZAG96, 151, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 130, 130 Qden03011, 138, 140 Qden03021, 254, 254 Qden 05011, 185, 185 Q16 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 130, 138 Qden03011, 140, 155 Qden03021, 256, 256 Qden 05011, 183, 185 Q17 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 96 ssrQrZAG7, 134, 138 Qden03011, 138, 138 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 183, 183 Q18 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 94 ssrQrZAG7, 129, 131 Qden03011, 140, 142 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 183, 183 Q19 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 127, 129 Qden03011, 136, 140 Qden03021, 252, 254 Qden 05011, 185, 185 Q20 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 134, 144 Qden03011, 138, 140 Qden03021, 252, 252 Qden 05011, 183, 183 Q21 ssrQrZAG96, 151, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 130, 134 Qden03011, 136, 136 Qden03021, 252, 254 Qden 05011, 183, 183 Q22 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 130, 134 Qden03011, 138, 142 Qden03021, 254, 254 Qden 05011, 174, 183 Q23 ssrQrZAG96, 149, 151 ssrQrZAG112, 92, 92 ssrQrZAG7, 124, 130 Qden03011, 142, 151 Qden03021, 254, 254 Qden 05011, 180, 183 -
[1] 傅立国, 陈谭清, 郎楷永, 等.中国高等植物[M].青岛:青岛出版社, 2001:240-254. Fu L G, Chen T Q, Lang K Y, et al. Higher plants of China[M].Qingdao: Qingdao Publishing House, 2001:240-254.
[2] Alexis R, Sullivan, Sandra A, et al. Hybridization and divergence in multi-species oak(Quercus) communities[J].Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 2016, 181:99-114. doi: 10.1111/boj.2016.181.issue-1
[3] Aldrich P R, Michler C H, Sun W, et al. Microsatellite markers for northern red oak (Fagaceae: Quercus rubra)[J].Molecular Ecology Notes, 2002, 2(4):472-474. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00282.x
[4] 张嘉, 刘爱青, 张淑玲, 等.利用荧光标记SSR绘制中国芍药品种分子身份证[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(6):101-109. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150349 Zhang J, Liu A Q, Zhang S L, et al. Using the SSR with fluorescent labeling to establish SSR molecular ID code for cultivars of the Chinese herbaceous peony[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(6):101-109. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150349
[5] Wei L, Li Y F, Zhang H, et al. Variation in morphological traits in a recent hybrid zone between closely related Quercus liaotungensis and Q. mongolica (Fagaceae)[J].Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 8(2):224-229. https://academic.oup.com/jpe/article/8/2/224/886517
[6] Zeng Y F, Wang W T, Liao W J, et al. Multiple glacial refugia for cool-temperate deciduous trees in northern East Asia:the Mongolian oak as a case study[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2015, 24(22):5676-5691. doi: 10.1111/mec.13408
[7] 秦英英, 韩海荣, 康峰峰, 等.基于SSR标记的山西省辽东栎自然居群遗传多样性分析[J].北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(2):61-65. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9730 Qin Y Y, Han H R, Kang F F, et al. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Quercus liaotungensis in Shanxi Province based on nucelar SSR markers[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(2):61-65. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9730
[8] 刘牧.蒙古栎和辽东栎的遗传转化关系研究[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10225-1012446109.htm Liu M. The research on genetic evolution relationship of Quercus mongolica and Quercus wutaishanlica[D].Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10225-1012446109.htm
[9] Zeng Y F, Liao W J, Petit R J, et al. Exploring species limits in two closely related Chinese oaks[J/OL]. PloS One, 2010, 5(11): el5529[2017-10-12]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015529.
[10] Yang J, Di X Y, Meng X, et al. Phylogeography and evolution of two closely related oak species(Quercus) from north and northeast China[J].Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2016, 12(5):89. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d468996dd61ea064f2fae0f2153918ea&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[11] Moran E V, Willis J, Clark J S, et al. Genetic evidence for hybridization in red oaks(Quercus sect. Lobatae, Fagaceae)[J].American Journal of Botany, 2012, 99(1):92-100. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1100023
[12] Collins E, Sullivan A R, Gailing O, et al. Limited effective gene flow between two interfertile red oak species[J]. Trees, 2015, 29(4):1135-1148. doi: 10.1007/s00468-015-1194-3
[13] Lind J F, Gailing O. Genetic structure of Quercus rubra L. and Quercus ellipsoidalis E. J. Hill populations at gene-based EST-SSR and nuclear SSR markers[J].Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2013, 9(3):707-722. doi: 10.1007%2Fs11295-012-0586-4
[14] Ramos-Ortiz S, Oyama K, Rodgíguez-Correa H, et al. Geographic structure of genetic and phenotypicvariation in the hybrid zone between Quercus affinis and Q.laurina in Mexico[J]. Plant Species Biology, 2016, 31(3):219-232. doi: 10.1111/psbi.2016.31.issue-3
[15] Cavender-Bares J, González-Rodríguez A, Eaton D A R, et al. Phylogeny and biogeography of the American live oaks (Quercus subsection Virentes): a genomic and population genetics approach[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2015, 24(14):3668-3687. doi: 10.1111/mec.13269
[16] Lind-Riehl J, Gailing O. Fine-scale spatial genetic structure of two red oak species, Quercus rubra and Quercus ellipsoidalis[J]. Plant Systematics & Evolution, 2015, 301(6):1601-1612.
[17] Aldrich P R, Parker G R, Michler C H, et al. Whole-tree silvic identifications and the microsatellite gentic structure of a red oak species complex in Indiana old-growth forest[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2003, 33(11):2228-2237. doi: 10.1139/x03-160
[18] Allen G C, Floresvergara M A, Krasynanski S, et al. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrime thylammonium bromide[J].Nature Protocals, 2006, 1(5):2320-2325. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.384
[19] Sullivan A R, Lind J F, Mccleary T S, et al. Development and characterization of genomic and gene-based microsatellite markers in north American red oak species[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2013, 31(1):231-239. doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0495-6
[20] 王越.基于SSR标记的槲树、蒙古-辽东栎种间杂交研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10422-1012463338.htm Wang Y. Natural hybridization between Quercus denata and Q.mongolica-liaotungensis revealed by microsatellite markers[D].Jinan: Shandong University, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10422-1012463338.htm
[21] Mishima K, Watanabe A, Isoda K, et al. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci from Quercus mongolica var.crispula[J].Molecular Ecology Notes, 2006, 6(3):695-697. doi: 10.1111/men.2006.6.issue-3
[22] Kampfer S, Lexer C, Glossl J, et al. Characterization of (GA)n microsatellite loci from Quercus robur[J]. Hereditas, 1998, 129(2):183-186. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1998.00183.x
[23] Rohlf F J. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 1.80[CP/OL]. Setauket, New York: Distribution by Exeter SoftWare, NTSYS-pc, 1993[2017-05-11]. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10011286550/.
[24] Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, et al. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism[J].American Journal of Human Genetics, 1980, 32(3):314-331. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f7598618a9ca10600a92934a0b0a94e9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] Pritchard J K, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data[J].Genetics, 2000, 155:2945-2959. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=551c3f92ac318765221dc2240f3a75fa&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] 杜庆章.利用连锁与连锁不平衡联合作图解析毛白杨重要性状的等位遗传变异[D].北京: 北京林业大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1014319154.htm Du Q Z. Dissection of allelic variation underlying important traits in Populus tomentosa Carr.by using joint linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping[D].Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10022-1014319154.htm
[27] Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J, et al. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2005, 14(8):2611-2620. doi: 10.1111/mec.2005.14.issue-8
[28] Coutinho J P, Carvalho A, Limo-Brito J, et al. Fingerprinting of Fagaceae individuals using intermicrosatellite markers[J].Journal of Genetics, 2015, 94(Suppl.1):132-140. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a2b94a34d36c65b7f996d96a80a6b35d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] 曹明, 周浙昆.中国栎属植物花粉形态及其系统学意义[J].广西植物, 2002, 22(1):14-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxzw200201005 Cao M, Zhou Z K. Pollen morphology and its systematic significance of the Quercus from China[J]. Guihaia, 2002, 22(1):14-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxzw200201005
[30] Rushton B S. Natural hybridization within the genus Quercus L.[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 1993, 50:73-90. doi: 10.1051/forest:19930707
[31] Coutinho J P, Carvalho A, Martin A, et al. Oak ribosomal DNA: characterization by FISH and polymorphism assessed by IGS PCR-RFLP[J].Plant Systematics & Evolution, 2016, 302(5):527-544. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f99e26fee853f4bc8b00dd2135b14d8a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] Alexander L W, Woeste K E. Pyrosequencing of the northern red oak (Quercus rubra L.) chloroplast genome reveals high quality polymorphisms for population management[J].Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2014, 10(4):803-812. doi: 10.1007/s11295-013-0681-1
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 李健康,李云,孙宇涵. 中国蒙古栎遗传育种及繁育研究进展. 分子植物育种. 2024(10): 3398-3404 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张旻桓,姚奕平,黄宇,金晓玲,叶烨,邢文,雍玉冰,张雨朦,黄承前. 基于SSR标记的江南牡丹品种群遗传多样性及亲缘关系. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(01): 164-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 廖科,刘振华,童方平,陈瑞,吴敏,蒋龙,龚发武,李贵. 不同混交比例对栎类混交林生长和土壤养分的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(09): 80-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 何旭东,郑纪伟,田雪瑶,教忠意,窦全琴. 薄壳山核桃品种亲缘关系分析与指纹图谱构建. 林业科学研究. 2021(04): 95-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 关媛,吕秀立,于泽群,李秀芬,李水根,刘群录,朱建军. 基于SSR分子标记的栎属植物资源的亲缘关系分析. 上海农业学报. 2021(05): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 娄明华,张会儒,雷相东,白超,杨同辉. 天然栎类阔叶混交林林分平均高与平均胸径关系模型. 北京林业大学学报. 2020(09): 37-50 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 禹靓倩,吴毅,彭继庆,李娇婕,谭志超,曹基武. 基于ISSR分子标记的27种栎属树种亲缘关系研究. 湖南林业科技. 2020(05): 7-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: