Modeling method for compressive elastic modulus of softwood based on fiber angle prediction
-
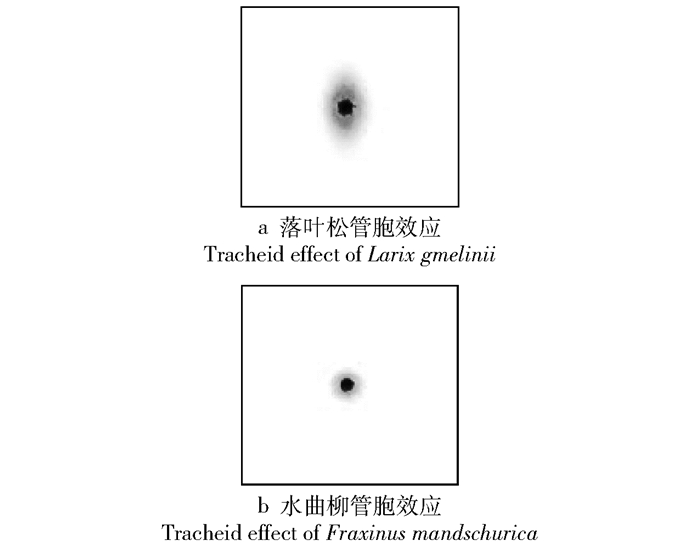
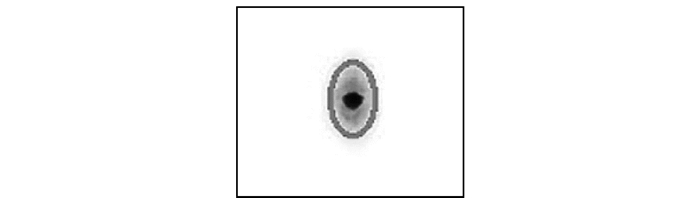
摘要:目的针叶材的管胞不仅具有输导养分的作用,而且具有较强的支撑能力,其管胞分布状态影响着木材力学特性。探究管胞分布状态与木材力学特征的内部关系对实现木材抗压弹性模量的预测有重要意义。方法本研究从针叶材管胞效应入手,设计了一套集光源发射、光斑采集与分析、木材遍历为一体的纤维角检测平台,构建了木材纤维角分布与其抗压弹性模量的数值关系模型。首先,利用最小二乘法拟合投射在木材表面激光光斑的椭圆轮廓,完成纤维角测量;然后,通过分析纤维角测量误差,选用系数为20的均值滤波方法以提高纤维角测量精度;通过对木材遍历采样,完成纤维角分布的采集;最后,以木材两个面上纤维角分布的均值、潜入系数与标准差为输入,以试样的抗压弹性模量为输出,构建了6输入1输出的4层神经网络,完成抗压弹性模量的预测。按照GB/T 15777—1995《木材顺纹抗压弹性模量测定方法》加工了落叶松试样100个,应用检测平台采集了相应试件的纤维角分布后,采用力学试验机得到对应力学真值,按照3:1的比例划分训练样本与测试样本。结果平均滤波次数选取20时,该设备纤维角采集测量误差达到0.65°以下;分别构建了以双面纤维角分布特征、单面纤维角分布特征以及双面纤维角分布特征均值为输入,抗压弹性模量为输出的网络预测模型。实验比较发现:以双面纤维角分布特征为变量的网络模型预测精度上优于其他两组,此时网络预测的抗压弹性模量准确率达到90.80%。结论应用纤维角分布特征可以实现针叶材抗压弹性模量的有效预测。最小二乘拟合与均值滤波法的结合可以有效、准确地表达纤维角的特征信息。纤维角的均值、潜入系数与标准差可以有效描述纤维角的分布特征。在构建木材抗压弹性模量时,木材双面的纤维角分布特征对其抗压弹性模量预测精度最高。Abstract:ObjectiveThe tracheid of softwood not only has the function as a medium of nutrient transportation, but also is a strong support to the trees, and its state has close relationship to the mechanical properties of timber. The investigation of internal relationship between the distribution of tracheid and the mechanical properties of wood is of great significance for the prediction of compressive elastic modulus of wood.MethodThis paper starts with the tracheid effect of coniferous timber and introduces a set of detection platform covering the functions of light source, spot collection, spot analyses and plate traversal to build the numeric relationship between fiber angle distribution and compressive elastic modulus. First, least square method was used to fit the ellipse contour of the spots to measure the fiber angle; second, by analyzing the measurement error of fiber angle, a filtering method with mean value of 20 was selected to improve the accuracy of fiber angle measurement, and then the collection of fiber angle was completed after a traversal sampling. Finally, taking the mean value, diving coefficient and standard deviation of fiber angle distribution on the two surfaces of the plate as input, and the compressive modulus of the sample as output, a four-layer neural network with 6 inputs and 1 output was constructed to predict the compressive elastic modulus. To testify the effect of the study, 100 samples of Larix gmelini were processed in accordance with the requirement of GB/T 15777—1995, the National Standard of Compressive Modulus of Elasticity, and divided into training and testing samples with proportion of 3:1 after collecting their fiber angle and mechanic truth value with the detection platform and testing machines.ResultThe results of the experiment revealed that when the average frequency of filtering was 20, the measurement error of the fiber angle acquisition was less than 0.65 degrees and the same time, the precision of compression modulus of the network prediction could reach 90.80%.ConclusionThe compressive elastic modulus of the softwood can be predicted by collecting the fiber angle distribution. The combination of the least squares and filtering method can effectively express the characteristic information and ensure the measurement precision of the fiber angle. The mean value, diving coefficient and standard deviation can effectively describe the distribution characteristics of the fiber angle. By selecting different features as input, the elastic modulus prediction accuracy is directly affected. In the experiment of this paper, with the double-sided feature as input, the elastic modulus prediction accuracy is the highest.
-
正常的花器分化发育与果实形成密切相关,围绕植物开花机理国内外均开展了广泛而深入的研究工作。目前,花器分化发育ABCDE模型和四因子模型被人们所熟知并广泛接受[1-3]。花器中的萼片、花瓣、雄蕊、心皮和胚珠由花器官特异性的MIKC型MADS转录因子四聚体复合物所决定,这些转录因子四聚体复合物与相邻的两个DNA顺式元件(CArG盒)相结合,使DNA顺式元件中间的DNA折叠成环[1]。2个A类蛋白APETALA1(AP1)与2个E类蛋白SEPALLATA(SEP)形成的四聚体复合物决定萼片发育;AP1、SEP、B类蛋白APETALA3(AP3)和PISTILLATA(PI)组成的四聚体复合物决定花瓣的发育;SEP、AP3、PI和C类蛋白AGAMOUS(AG)组成的四聚体复合物决定雄蕊的发育;2个SEP与2个AG蛋白组成的四聚体复合物决定心皮的发育;SEP、AG和D类蛋白SHATTERPROOF(SHP)和/或SEEDSTICK(STK)决定胚珠的发育[1]。可见,SEP可能是决定植物胚珠发育的一类重要蛋白。
榛子(Corylus spp.)是桦木科(Betulaceae)榛属(Corylus)植物,由于良好的环境适应性和较高的栽培效益,近年来,榛子成为东北退耕还林后广阔还林地的首选替代树种[4]。正常的胚珠充实是榛子种仁形成的前提与基础,胚珠充实不足可频繁导致瘪仁、空壳果实的形成[5]。清朝梁章钜撰的《巧对录》用“十榛九空”贴切的描述了榛子胚珠充实障碍的频繁程度;实际生产中,东北榛子产区仍采用传统的水选法来筛除空壳、瘪仁果实,通过水选的饱满果实俗称“水漏”。可见,榛子胚珠(种仁)充实障碍是一个历史久远且相当普遍的问题。目前SEP参与榛子胚珠发育的证据还不多。在此前的研究中,已经构建了榛子胚珠不同发育阶段的转录谱[6];新近,利用PacBio单分子实时测序和Hi-C辅助组装策略,获得并发布了榛子高质量的基因组,并构建了平榛(Corylus heterophylla)基因组数据库HazelOmics,该数据库集成了组装基因组、基因编码序列、蛋白序列和各种注释信息[7]。这些研究为深入研究榛子SEP(ChSEP)基因的功能提供了良好的工作基础。本研究在此基础上,拟鉴定参与榛子胚珠发育的重要作用ChSEP基因,并制备ChSEP的多克隆抗体,开展正常发育与败育胚珠中ChSEP的免疫组织化学分析,以期为深入解析榛子胚珠发育机制提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究材料
平欧杂交榛(C. heterophylla × C. avellana)植株种植于吉林省四平市伊通满族自治县榛园,品种为“达维”,树龄12年,株高3.0 ~ 3.5 m。榛子果实有胚珠2枚,未受精时,这2枚胚珠大小相同。受精以后,胚珠大小出现差异,在绝大多数情况下,仅大胚珠发育充实并形成单仁果实,而小胚珠发育停滞,成为败育胚珠。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 ChSEP基因家族鉴定及系统发育分析
在榛子基因组数据库HazelOmics(http://122.9.151.76/)中下载蛋白序列,构建本地BioEdit[8]数据库。另外,下载拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliala)、葡萄(Vitis vinifera)与毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)的SEP与AGL6(作为外群)蛋白序列。以收集的拟南芥、葡萄与毛果杨的蛋白序列作为查询序列,在自建BioEdit数据库中检索榛子的SEP与AGL6同源蛋白,选择BLASTP程序,参数为E < e−20。同时,使用关键词“SEPALLATA”及“AGL6”在HazelOmics数据库进行序列检索。将检索得到的序列汇总去冗余,于Pfam和CDD[9]在线数据库进行蛋白结构域验证,删除不含SRF-TF结构域和K-box结构域的序列。使用MEGA软件[10]Muscle程序对上述序列进行比对,并用邻接法(Neighbor-joining,NJ)构建进化树,主要参数设置如下:统计方法为最大似然法,重复次数为1 000次,替换类型为氨基酸,模型为泊松模型。
1.2.2 SEP蛋白特性分析与基因表达热图汇制
此前,以平欧杂交榛(C. heterophylla × C. avellana)‘达维’ 4个发育时期的胚珠为材料,建立了榛子胚珠的基因表达谱[6],原始测序数据保存于SRA数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/?term=PRJNA591492)。这4个时期包括:胚珠形成期(Ov1),胚珠早期生长期(Ov2)、胚珠快速生长期(Ov3)和胚珠成熟期(Ov4)。使用EvolView[11]绘制ChSEP家族的基因表达热图,基因表达水平根据FPKM(fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments)值确定。采用MEME软件[12]对ChSEP进行蛋白保守结构域预测,motif数量设置为15,长度设置为10 ~ 300 aa。
1.2.3 原核表达载体构建及诱导表达
构建目的基因和载体pMD18-T的重组质粒,进行ChSEP多克隆抗体的制备。以重组质粒为模板,对目的基因N端特异性片段进行PCR扩增,纯化PCR产物,再克隆至pGEX-4T-AB1载体(含His标签)。对克隆后的产物进行PCR检测和测序鉴定,提取阳性质粒并转化至Escherichia coli Rosetta菌株,使用氨苄青霉素选择培养基进行筛选及培养。检菌后,挑取单克隆阳性菌株于液体培养基中培养至菌液OD600达到0.6 ~ 1.0。实验组加入异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷至终浓度为0.8 mmol/L,37 ℃摇床培养4 h;空白对照组加入等量无菌水。收集少量菌体进行菌落聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE),检测目的蛋白是否表达。若目的蛋白表达,再将剩余全部菌液离心、收集菌体、重悬、超声波破碎至菌液清澈,离心分离上清和沉淀,通过SDS-PAGE判断蛋白的表达形式,用8 mol/L尿素溶解包涵体蛋白,用His标签蛋白纯化试剂盒(碧云天生物技术有限公司,上海)纯化后,SDS-PAGE鉴定蛋白浓度。
1.2.4 抗体制备和纯化及Western Blot检测
将纯化后的蛋白作为抗原分4次对2只实验级雄性日本大耳白兔进行酶联免疫吸附效价检测,免疫流程见表1。取免疫前兔的耳缘静脉血清作阴性对照,59 d后取等量兔的耳缘静脉抗血清为阳性实验组。在聚苯乙烯板中加入200 ng稀释后的抗原,37 ℃孵育6 h。弃孔内液体,加封闭液,37 ℃湿盒孵育6 h,弃反应液,洗涤液洗涤。将抗血清按不同梯度稀释(1∶1 000 ~ 1∶512 000)后加至反应孔,37 ℃水浴45 min,洗涤。加稀释后的二抗(1∶8 000)进行显色反应,酶标仪测定OD450吸光值并进行效价分析[13]。用pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP蛋白作抗原对抗血清亲和纯化后,得到浓缩后的抗体。抗体浓度用Nanodrop 2000/2000 C超微量分光光度计进行检测,纯度用SDS-PAGE进行检测。以ChSEP(N-64-216)蛋白作为抗原,取梯度为10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg的抗原进行SDS-PAGE分析,抗体(1∶1 000)稀释后进行Western Blot(WB)检测[14],以确定抗体检测下限。
表 1 免疫流程Table 1. Immunization process过程
Process周期
Cycle剂量
Dose/mg弗氏佐剂
Freund’s adjuvant动物状态
Animal state第1次免疫 1st immunization 第1天 1st day 0.30 完全 Completely 良好 Good 第2 ~ 4免疫 2nd to 4th immunization 第12、26、40天 12th, 26th, 40th day 0.15 不完全 Incompletely 良好 Good 免疫动物采血
Blood collection from immunized animal第59天 59th day 采血正常
Blood collection is normal1.2.5 样品采集与免疫组织化学检测
在6月20日—7月20日取榛子完整果实,解剖获得受精后的发育胚珠与败育胚珠,并置于4%多聚甲醛溶液中固定。将胚珠取出,进行石蜡包埋。将包埋好的组织置于切片机上,切出厚度7 ~ 9 μm的切片,于36 ℃摊片机摊平,并于25 ℃电热板上烤干。选择包含完整组织的切片进行免疫组织化学染色,处理流程如下:二甲苯浸泡30 min脱蜡,体积分数为100%、95%、80%、70%的酒精梯度水化处理玻片,蒸馏水洗净;随后用柠檬酸缓冲液(pH = 6.0)浸泡材料,微波炉加热3 min,冷却后,蒸馏水冲洗;PBS缓冲液处理2次,每次5 min,滴加封闭液封闭,37 ℃恒温箱孵育30 min;吸水纸吸干封闭液,处理组与实验组均加制备获得的一抗(1∶100),40 ℃恒温箱保存过夜;将玻片取出,PBS处理,晾干后,实验组加辣根过氧化物酶标记二抗(1∶100),对照组加蒸馏水,37 ℃孵育30 min;PBS洗净,加DAB(3, 3-N-Diaminobenzidine Tertrahydrochloride)显色剂显色。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ChSEP基因家族鉴定与进化分析
本研究共鉴定到3条榛子的ChSEP蛋白序列(Cor0142960.1、Cor0054610.1、Cor0008190.1),为了研究ChSEP家族成员之间的系统发育关系,与源自拟南芥、葡萄、毛果杨的17条蛋白序列及榛子的2条AGL6蛋白序列(Cor0152110.1、Cor0119400.1)进行序列比对后构建NJ树。全部22条蛋白序列聚类为2组,包括:AGL2-like和AGL6-like(图1)。其中,ChSEP蛋白序列Cor0054610.1与拟南芥的AtSEP1和AtSEP2聚在同一进化分枝中;ChSEP蛋白序列Cor0142960.1和拟南芥的AtSEP4聚在同一进化分枝中;ChSEP蛋白序列Cor0008190.1和拟南芥的AtSEP3聚在同一进化分枝中;AGL6蛋白序列Cor0152110.1、Cor0119400.1与AtAGL6及AtAGL13等聚在同一进化分枝中(图1)。鉴定到的ChSEP与拟南芥、葡萄、毛果杨的SEP序列的平均相似性分别为67.71%、78.72%、77.07%,其中榛子与葡萄的平均相似性最高。
2.2 SEP蛋白特性分析与胚珠发育过程中的基因表达变化
从序列相似性来看,Cor0054610.1与Cor0142960.1序列相似性较高,Cor0008190.1与上述2个ChSEP家族成员序列相似性相对较低(图2A)。保守结构域分析结果表明:鉴定到的3条榛子所有的ChSEP蛋白序列均含有SRF-TF与K-box结构域,具有SEP蛋白的典型特征,而且,在3条鉴定到的SEP蛋白中SRF-TF与K-box出现的位置相对接近,这表明SRF-TF与K-box结构域在不同的ChSEP蛋白中高度保守(图2B)。在榛子的胚珠形成期(Ov1)、胚珠早期生长期(Ov2)、胚珠快速生长期(Ov3)和胚珠成熟期(Ov4)进行了连续采样与RNA-seq分析,比较了3个ChSEP基因在4个发育时期基因表达丰度的变化(图2C)。其中,胚珠形成期(Ov1)时榛子还没有完成受精,胚珠早期生长期(Ov2)时榛子完成了受精,胚珠尺寸显著增加[6]。如果某个ChSEP基因参与胚珠发育调控,认为该基因表达丰度不应太低,而且在Ov2期的基因表达丰度可能会显著高于Ov1期。按以上标准进行筛选,认为Cor0054610.1和Cor0008190.1的FPKM值较高,而且Ov2期的基因表达丰度远高于Ov1期,推测这2个基因可能参与榛子胚珠发育调控。进一步考虑到K-box结构域是SEP的重要结构域,而Cor0008190.1的K-box结构域短于Cor0054610.1,关键结构域序列的缩短可能影响蛋白的调控功能,推测Cor0054610.1可能对胚珠发育调控起重要调控作用,但不排除Cor0008190.1及Cor0142960.1可能也具有调控胚珠发育的功能。
2.3 原核表达载体的构建及表达
选择Cor0054610.1(ChSEP)的N-64-216作为抗原的特异性片段,N-64-216区段涵盖K-box保守区,也包含抗原的特异性片段(图2B)。以测序正确的pMD18-T-ChSEP质粒为模板DNA,对目的片段进行PCR扩增,获得的PCR扩增产物长度为459 bp,符合预期(图3A)。将该PCR扩增产物克隆到pGEX-4T-AB1表达载体上,构建pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP(N-64-216)重组载体,测序鉴定正确,重组载体构建成功。将阳性pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP(N-64-216)重组质粒转化至E. coli Rosetta菌株中进行表达,重组蛋白融合了分子量约33 kDa的组氨酸标签。SDS-PAGE分析结果表明:实验组相比于对照组多1条分子量为45 kDa的特异性条带(图3B),和预期大小相符,表明ChSEP(N-64-216)在E. coli Rosetta菌株中获得成功表达。
![]() 图 3 ChSEP(Cor0054610.1)PCR扩增结果与蛋白表达纯化检测A. PCR扩增结果:1. Marker;2. ChSEP(N-64-216)。B. 蛋白表达及可溶性检测:1. pGEX-4T-AB1空载诱导表达;2. 0.4 mg/mL BSA;3. Marker;4. 上清;5. 上清2;6. 包涵体2倍稀释(8 mol/L尿素溶解);7. 包涵体10倍稀释(8 mol/L尿素溶解)。C. 纯化检测:1. Marker;2. 0.4 mg/mL 牛血清白蛋白; 3. 包涵体10倍稀释液(8 mol/L尿素溶解);4. 包涵体5倍稀释液(8mol/L尿素溶解)。A, PCR amplification results: 1, marker; 2, ChSEP (N-64-216). B, protein expression and solubility detection: 1, pGEX-4T-AB1 empty-load-induced expression; 2, 0.4 mg/mL BSA; 3, marker; 4, supernatant; 5, supernatant 2; 6, two times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea); 7, ten times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea). C, purification detection:1, marker; 2, 0.4 mg/mL bovine serum albumin; 3, ten times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea); 4, five times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea).Figure 3. ChSEP (Cor0054610.1) PCR amplification results and detection of protein expression and purification
图 3 ChSEP(Cor0054610.1)PCR扩增结果与蛋白表达纯化检测A. PCR扩增结果:1. Marker;2. ChSEP(N-64-216)。B. 蛋白表达及可溶性检测:1. pGEX-4T-AB1空载诱导表达;2. 0.4 mg/mL BSA;3. Marker;4. 上清;5. 上清2;6. 包涵体2倍稀释(8 mol/L尿素溶解);7. 包涵体10倍稀释(8 mol/L尿素溶解)。C. 纯化检测:1. Marker;2. 0.4 mg/mL 牛血清白蛋白; 3. 包涵体10倍稀释液(8 mol/L尿素溶解);4. 包涵体5倍稀释液(8mol/L尿素溶解)。A, PCR amplification results: 1, marker; 2, ChSEP (N-64-216). B, protein expression and solubility detection: 1, pGEX-4T-AB1 empty-load-induced expression; 2, 0.4 mg/mL BSA; 3, marker; 4, supernatant; 5, supernatant 2; 6, two times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea); 7, ten times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea). C, purification detection:1, marker; 2, 0.4 mg/mL bovine serum albumin; 3, ten times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea); 4, five times dilution of inclusion bodies (dissolved in 8 mol/L urea).Figure 3. ChSEP (Cor0054610.1) PCR amplification results and detection of protein expression and purification2.4 抗原蛋白的可溶性检测及纯化
菌液经过超声波破碎离心后,分别取上清和沉淀进行ChSEP(N-64-216)抗原蛋白的可溶性检测。SDS-PAGE分析结果显示:在分子量45 kDa处,上清和上清2两条带不清晰,而沉淀中的包涵体经过8 mol/L尿素溶解后,2倍稀释和10倍稀释条件下条带都很清晰。可见,pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP(N-64-216)蛋白在包涵体中进行了表达。由于pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP(N-64-216)蛋白具有组氨酸标签,所以选择组氨酸蛋白纯化试剂盒对抗原蛋白进行纯化。纯化前,ChSEP(N-64-216)蛋白非特异性条带较多,经过纯化后,非特异性条带基本消失,分子量45 kDa处的特异性条带清晰(图3B和C),包涵体蛋白质量浓度为5 mg/mL时,纯度达到免疫要求,可用于后续免疫实验。
2.5 多克隆抗体的制备及效价分析
2只日本雄性大耳兔注射纯化的ChSEP抗原后,获得ChSEP多克隆抗血清E18305和E18306。将多克隆抗血清按一定浓度梯度稀释后进行酶联免疫吸附检测(表2)。在不同稀释倍数下,抗血清均能与抗原蛋白进行特异性结合并出现显色反应,这表明抗血清均具有较好的免疫原性,根据(OD阳性–OD空白)/(OD阴性–OD空白) > 2.1标准,E18305和E18306抗血清效价均已达到1∶512 000。
表 2 ChSEP(Cor0054610.1)抗血清ELISA效价检测Table 2. ELISA titer detection of ChSEP (Cor0054610.1) antiserum分组 Group 稀释比例 Dilution ratio OD450 (OD阳性−OD空白)/(OD阴性−OD空白)
(ODpositive−ODblank)/(ODnegative−ODblank)E18305 E18306 E18305 E18306 阳性对照 Positive control 1∶1 000 1.365 0 1.448 3 103.48 882.00 1∶4 000 1.230 8 1.384 7 92.25 842.25 1∶8 000 1.082 8 1.247 0 81.43 756.19 1∶16 000 0.902 9 1.142 2 67.38 690.06 1∶32 000 0.720 9 0.968 1 53.16 581.88 1∶64 000 0.533 9 0.767 2 704.86 33.19 1∶128 000 0.352 3 0.548 4 445.43 23.24 1∶256 000 0.2338 0.369 2 276.14 15.10 1∶512000 0.152 3 0.237 2 159.71 9.09 阴性对照 Negative control 1∶1 000 0.053 3 0.038 7 1∶64 000 0.041 2 0.059 1 空白对照 Blank control 0.040 5 0.037 1 2.6 多克隆抗体的纯化及WB检测
亲和纯化用pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP蛋白质量浓度为4 mg/mL,与破菌纯化后质量浓度和纯度差异不大,可进行抗原亲和纯化。抗血清用pGEX-4T-AB1-ChSEP蛋白作抗原进行亲和纯化后,得到浓缩后的抗体。多克隆抗血清E18305质量浓度为2.05 mg/mL,E18306质量浓度为2.64 mg/mL,SDS-PAGE电泳后无杂带,纯度高。将抗体按1∶1 000稀释后,加到含10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg ChSEP抗原的泳道中,进行WB检测(图4)。结果显示:多克隆抗血清E18305和E18306抗体抗原条带分子量在45 kDa左右,与预期相符。多克隆抗血清E18305和E18306抗体经1∶1 000 稀释后,前者在1 ng ChSEP抗原泳道产生清晰条带,在500 pg ChSEP抗原泳道产生模糊条带,认为E18305的检测下限为1 ng ChSEP抗原;E18306抗体在1 ng ChSEP抗原泳道产生的条带较模糊,在5 ng ChSEP抗原泳道产生的条带粗且清晰,认为其检测下限为2 ng左右 ChSEP抗原。
![]() 图 4 ChSEP E18305(A)和E18306(B)抗体的Western Blot检测泳道上方10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg分别表示该泳道中加有10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg ChSEP抗原。10 ng, 5 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg above the lane respectively indicate that 10 ng, 5 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg ChSEP antigen have been added to the lane.Figure 4. Western blot detection of ChSEP E18305 (A) and E18306 (B) antibody
图 4 ChSEP E18305(A)和E18306(B)抗体的Western Blot检测泳道上方10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg分别表示该泳道中加有10 ng、5 ng、1 ng、500 pg ChSEP抗原。10 ng, 5 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg above the lane respectively indicate that 10 ng, 5 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg ChSEP antigen have been added to the lane.Figure 4. Western blot detection of ChSEP E18305 (A) and E18306 (B) antibody2.7 正常发育与败育胚珠的免疫组织化学分析
在本研究中,在二抗辣根过氧化物酶的催化下,DAB会产生棕色沉淀,从而显示ChSEP在组织中的表达情况。此前,我们报道了正常发育与败育胚珠的受精过程[5],认为榛子含2枚胚珠,多数情况下会形成单仁果实。2枚胚珠均会受精,并发育形成幼胚。但败育胚珠生长停滞,无法完成充实[5]。图A1与A2中同时含有败育胚珠与正常发育胚珠,败育胚珠(左)尺寸小,正常发育胚珠(右)尺寸明显较大。与对照A1相比较,A2中发育胚珠ChSEP主要分布于珠被,也分布于幼胚子叶,但子叶中的ChSEP浓度小于珠被(图5A1和A2,B1和B2);败育胚珠ChSEP主要分布于珠被,珠被内的幼胚有少量ChSEP分布(图5A1和A2,C1和C2)。因此,正常发育胚珠与败育胚珠ChSEP分布特征差异不明显。
![]() 图 5 榛子正常发育与败育胚珠的免疫组织化学分析A1与A2含正常发育与败育2个胚珠,A1为对照,一抗为清水,A2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。B1与B2为正常发育胚珠,B1为对照,一抗为清水,B2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。C1与C2为败育胚珠,C1为对照,一抗为清水,C2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。ov. 败育胚珠;OV. 正常发育胚珠;Int. 珠被;F. 珠柄。A1 and A2 contain two ovules: normal development and abortive ovules. A1 is the control, the first antibody is distilled water, A2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody; B1 and B2 are normal ovules, B1 is control, the first antibody is distilled water, B2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody; C1 and C2 are aborted ovules, C1 is the control, the first antibody is distilled water, C2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody. ov, abortive ovule; OV, normal development ovule. Int, integument; F, funicle.Figure 5. Immunohistochemical analysis of normal development and abortive ovules of hazelnut
图 5 榛子正常发育与败育胚珠的免疫组织化学分析A1与A2含正常发育与败育2个胚珠,A1为对照,一抗为清水,A2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。B1与B2为正常发育胚珠,B1为对照,一抗为清水,B2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。C1与C2为败育胚珠,C1为对照,一抗为清水,C2为处理,一抗为ChSEP抗体。ov. 败育胚珠;OV. 正常发育胚珠;Int. 珠被;F. 珠柄。A1 and A2 contain two ovules: normal development and abortive ovules. A1 is the control, the first antibody is distilled water, A2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody; B1 and B2 are normal ovules, B1 is control, the first antibody is distilled water, B2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody; C1 and C2 are aborted ovules, C1 is the control, the first antibody is distilled water, C2 is treatment, and the first antibody is ChSEP antibody. ov, abortive ovule; OV, normal development ovule. Int, integument; F, funicle.Figure 5. Immunohistochemical analysis of normal development and abortive ovules of hazelnut3. 讨 论
SEPALLATA是一类MADS转录因子,属同源异型蛋白亚家族,参与花发育过程的调节,决定花器与胚珠发育[15]。拟南芥基因组有4个SEP基因,包括:SEP1、SEP2、SEP3和SEP4[16-17]。在sep1 sep2 sep3三重突变体中,原本会发育为花瓣、雄蕊和心皮的原基结果发育成萼片状器官[16]。此外,在sep1 sep2 sep3三重突变体中,花器官生长受到干扰,花器官在第4个轮花中连续产生[16]。由于在单基因突变中很少观察到这种剧烈变异的表型,因此,一般认为SEP存在基因功能冗余[17-18]。本研究在榛子基因组中鉴定到3个ChSEP基因,所有的ChSEP蛋白序列均含有SRF-TF与K-box结构域,且SRF-TF与K-box出现的位置相对接近,认为这些ChSEP基因应当存在基因冗余。在转录水平上,这3个基因在榛子胚珠发育的不同时期均有表达,推测这些ChSEP基因均有可能参与了榛子胚珠的发育调控;其中,Cor0054610.1和Cor0008190.1的表达丰度相对较高,认为这2个基因可能在榛子胚珠发育中起到更重要的调控作用。进一步,在胚珠形成期(Ov1)、胚珠早期生长期(Ov2)、胚珠快速生长期(Ov3)和胚珠成熟期(Ov4)等4个发育期中,Cor0008190.1仅在Ov2期大量表达,表达量远高于其他3个时期,而Ov1、Ov3和Ov4等3个发育时期表达量相比无显著差异,认为该基因可能对受精后胚珠的早期生长有重要调控作用。Cor0054610.1在Ov1 vs Ov2、Ov1 vs Ov3、Ov1 vs Ov4、Ov2 vs Ov3、Ov2 vs Ov4这5种比较中均存在明显差异,推测Cor0054610.1可能广泛参与胚珠形成、早期生长、快速生长等生物学过程的调控。Cor0054610.1与拟南芥的SEP1与SEP2序列相似性高,成功制备了Cor0054610.1的多克隆抗体,开展了SEP的免疫组化定位分析,结果表明,ChSEP在胚珠的珠被及子叶等部位表达。因此,本研究在转录与蛋白水平上提供了ChSEP参与榛子胚珠发育调控的证据。
榛子是壳斗目(Fagales)植物,果实发育经历特殊的延迟受精过程[19-20]。在雌花开放时,榛子的子房还没有形成,需要等到花粉管进入柱头基部以后,子房原基才逐步发育,开始形成子房。随后,胚珠逐步发育,胚囊成熟,此时,在柱头基部长期驻留的花柱管恢复生长,进入胚囊完成受精作用。因此,榛子花粉管呈间歇性生长特征,受精时间耗时约2个月左右,远长于多数被子开花植物[19]。榛子含有2枚胚珠,可能存在3种情况。(1)1枚胚珠发育充实,1枚胚珠发生败育,形成单仁果实,在多数情况下榛子果实的确只含有1枚可食用的种子。(2)2枚胚珠同时发育充实,形成双仁果实,这种情况偶尔发生。(3)2枚胚珠均不发育充实,形成空壳果实[5],果园中如果空壳果实大量形成,会导致严重的产量损失。单仁果实中存在1枚败育胚珠,而空壳果实中存在2枚败育胚珠,败育胚珠中均可观察到明显的胚结构,表明它们已经完成了受精,但营养物质运输受阻导致胚珠发育停滞[5, 21]。可见,胚珠败育在榛子果实生长过程中普遍发生。E 类SEP基因可与B、C和D类MADS-box基因进行协作并共同参与植物花果发育的调控[22]。在苹果(Malus pumila)中,SEP1/2的基因敲除导致花瓣变为萼片,果实尺寸变小[23];枣(Ziziphus jujuba)和桃(Amygdalus persica)的基因组中各有3个SEP基因,实时荧光定量分析表明其在花和果实中表达[22, 24]。因此,目前SEP参与植物育性的证据多来自假果,如苹果、枣和桃等,其表达部位的证据一般来自实时定量分析或遗传转化后花果形态变化,少有SEP蛋白的免疫组织化学证据。榛子果实是真果,由子房发育而来。为确定ChSEP在胚珠败育过程中的调控作用,排除免疫组织化学分析中染色时间差异对研究结果的影响,特别选用同时含有败育胚珠(小胚珠)和正常发育胚珠(大胚珠)榛子幼果为材料,对比研究ChSEP分布特征的差异。结果表明,ChSEP在珠被中的表达量相对较高,而子叶表达量相对较低,认为ChSEP参与榛子珠被、子叶的发育调控,对榛子果实发育有重要影响,这与前人关于SEP基因参与植物花果发育调控的研究结果相一致。SEP参与番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)育性的调控[25]。番茄的TM29与拟南芥的SEP1/2/3高度同源,在所有四轮花器官的原基中均有mRNA积累。通过共抑制或反义RNA干扰技术抑制了TM29的基因表达,转基因植株的内三轮花器官发生变化,且转基因番茄出现雄蕊和子房不育,还出现单性结实现象[25]。类似的,TM5 RNA表达受干扰后也会导致单性结实现象的发生[26]。综上,认为番茄SEP的直系同源基因通常都会限制单性结实果实的发育[25]。在本研究中,榛子发育胚珠与败育胚珠的ChSEP分布特征类似,意味着ChSEP似乎没有参与胚败育调控,这与番茄中SEP基因敲除导致单性结实(种子不可育)的结论并不一致,这应该与两者在果实结构及果实发育过程的差异有关。本研究完成了Cor0054610.1的抗体制备与免疫组织化学分析,另一个重要的SEP基因(Cor0008190.1)是否参与榛子胚败育调控还需进一步的研究。
-
表 1 样本的纤维角特征与抗压弹性模量分布
Table 1 Fiber angle characteristics of sample and distribution of compressive elastic modulus
测量值Measured value 最大值Max. 最小值Min. 平均值Average 纤维角均值Mean value of fiber angle (μ)/(°) 8.76 1.38 4.54 纤维角标准差Standard deviation of fiber angle (σ) 9.86 0.69 1.40 潜入系数均值Mean value of latent coefficient (d) 0.75 0.68 0.70 抗压弹性模量Compressive elastic modulus (E)/MPa 4 103.51 2 764.48 3 475.49 表 2 部分样本的力学真值与模型预测值
Table 2 Mechanical values and predictive values of partial samples
样本序号
Sample No.抗压弹性模量Compressive
elastic modulus/MPa预测值
Predicted value/MPa误差
Error/MPa准确率
Accuracy rate/%1 4045.40 4011.24 -34.15 99.16 2 3683.00 3771.25 88.25 97.60 3 3448.46 3647.42 198.95 94.23 4 3477.47 3438.81 -37.66 98.89 5 2974.65 2951.13 -23.52 99.21 6 3346.48 3285.21 -61.27 98.17 7 3434.86 3487.14 52.28 98.48 8 3320.31 3297.48 -22.83 99.31 9 2972.30 3018.53 46.23 98.45 10 2967.62 2694.60 -273.02 90.80 表 3 参数选择对比实验
Table 3 Comparison results in parameter selecting
输入参数
Input parameter最大绝对误差
Maximum absolute error/MPa平均绝对误差
Mean absolute error/MPa最大相对误差
Maximum relative error/%平均相对误差
Mean relative error/%相关系数
Correlation coefficient双面特征Double-sided feature
(μ1,μ2,σ1,σ2,d1,d2)273.02 76.13 9.20 2.17 0.921 单面特征One side feature (μ, σ, d) 798.56 217.51 28.56 6.35 0.514 双面特征均值
Mean value of double-sided feature (μ, σ, d)773.29 178.66 19.42 5.18 0.713 注:μ1为正面纤维角分布均值;μ2为反面纤维角分布均值;σ1为正面纤维角分布标准差;σ2为反面纤维角分布标准差;d1为正面潜入系数分布均值;d2为反面潜入系数分布均值;μ为单面纤维角分布均值;σ为单面纤维角分布标准差;d为单面潜入系数分布均值;μ为正反两面纤维角分布均值;σ为正反两面纤维角分布标准差;d为正反两面潜入系数分布均值。Notes:μ1 is the average of fiber angle distribution on one side, μ2 is the average of fiber angle distribution on the other side, σ1 the standard deviation of fiber angle on one side, σ2 is the standard deviation of fiber angle on the other side, d1 is the average of diving coefficient distribution on one side, d2 is the average of diving coefficient distribution on the other side, μ is the average of fiber angle distribution on the one side, σ is the standard deviation of fiber angle on the one side, d is the average of diving coefficient distribution on the one side, μ is the average value of fiber angle distribution on both sides, σ is the standard deviation of fiber angle distribution on both sides, and d is the average of diving coefficient distribution on both sides. -
[1] 张怡卓, 苏耀文, 李超, 等.蒙古栎抗弯弹性模量多模型共识的近红外检测方法[J].林业工程学报, 2016, 1(6): 17-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201606003 Zhang Y Z, Su Y W, Li C, et al. Determination of modulus of elasticity for Quercus mongolica using near-infrared spectroscopy based on consensus model[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2016, 1(6): 17-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykjkf201606003
[2] 赵荣军, 霍小梅, 张黎.利用近红外光谱技术预测粗皮桉木材弹性模量[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2009, 29(9): 2392-2395. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200909021 Zhao R J, Huo X M, Zhang L. Estimation of modulus of elasticity of Eucalyptus pellita wood by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2009, 29(9): 2392-2395. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200909021
[3] 张怡卓, 苏耀文, 李超, 等.蒙古栎木材MOR与MOE的近红外光谱预测模型分析[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(8): 99-105. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150505 Zhang Y Z, Su Y W, Li C, et al.Analysis of MOR and MOE prediction model of Quercus mongolica wood by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(8): 99-105. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20150505
[4] 王德仁.近红外技术在木材科学中的应用综述[J].科技创新与应用, 2014(11): 255. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qgsj201411243 Wang D R.A review of the application of near infrared technology in wood science[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2014(11): 255. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qgsj201411243
[5] 田昭鹏, 王朝晖, 王金林, 等.漠河产兴安落叶松弹性模量分级与力学性能[J].西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(3): 211-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.03.39 Tian Z P, Wang Z H, Wang J L, et al. Classification in modulus of elasticity and mechanical properties of larch lumber in Mohe[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2017, 32(3): 211-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2017.03.39
[6] 郭继龙, 南生春, 杨全文.木质材料无损检测和评价方法[J].木材加工机械, 2012, 23(6): 51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-036X.2012.06.015 Guo J L, Nan S C, Yang Q W. The methods for wood non-destructive testing technology[J]. Wood Processing Machinery, 2012, 23(6): 51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-036X.2012.06.015
[7] 孙燕良, 张厚江, 朱磊, 等.木材弹性模量无损检测方法及其研究现状[J].林业机械与木工设备, 2011, 39(7): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2953.2011.07.003 Sun Y L, Zhang H J, Zhu L, et al.Non-destructive inspection methods for elastic modulus of wood and relevant research status[J]. Forestry Machinery & Woodworking Equipment, 2011, 39(7): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2953.2011.07.003
[8] 张厚江, 申世杰, 崔英颖, 等.振动方式测定木材弹性模量[J].北京林业大学学报, 2005, 27(6): 91-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2005.06.017 Zhang H J, Shen S J, Cui Y Y, et al. Measuring elastic modulus of wood using vibration method[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2005, 27(6): 91-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2005.06.017
[9] 周志茹, 赵茂程, 王正.意杨木材弹性模量3种方法检测的比较[J].福建林学院学报, 2014, 34(4): 368-373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2014.04.014 Zhou Z R, Zhao M C, Wang Z.Comparative study of modulus of elasticity of Populus euramericana lumber with three nondestructive methods[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2014, 34(4): 368-373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2014.04.014
[10] 林兰英, 傅峰.三种无损检测方法预测四种桉树木材弹性模量的对比研究[J].木材加工机械, 2007(3): 24-29, 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-036X.2007.03.007 Lin L Y, Fu F.Comparative study of MOE on three methods of nondestructive test forecasting four kinds of lumber[J]. Wood Processing Machinery, 2007(3): 24-29, 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-036X.2007.03.007
[11] Nyström J. Automatic measurement of fiber orientation in softwoods by using the tracheid effect[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2003, 41(1/3): 91-99. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=179823931d64d29436409df934dda08f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] Simonaho S P, Palviainen J, Tolonen Y, et al. Determination of wood grain direction from laser light scattering pattern[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2004, 41(1): 95-103. doi: 10.1016/S0143-8166(02)00144-6
[13] 闫蓓, 王斌, 李媛.基于最小二乘法的椭圆拟合改进算法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2008, 34(3): 295-298. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjhkhtdxxb200803010 Yan B, Wang B, Li Y. Optimal ellipse fitting method based on least-square principle[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008, 34(3): 295-298. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjhkhtdxxb200803010
[14] Viguier J, Jehl A, Collet R, et al. Improving strength grading of timber by grain angle measurement and mechanical modeling[J]. Wood Material Science & Engineering, 2015, 10(1): 145-156. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01063383
-
期刊类型引用(20)
1. 吕佩芟,蒋涵,周敏,刘一念,邓宇晴,刘雄琴,王业社,王灯. 不同海拔梯度对亮叶水青冈叶形态与光合色素的影响. 现代园艺. 2025(05): 34-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周航宇,付琪瑶,梁婉婷,宋沼鹏,侯继华. 天然油松叶-枝-根氮磷含量随降水和温度的变化规律. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(01): 44-54 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 郭文芳,陈艳梅,高飞,王佳乐. 太行山7种药用植物性状特征及其对土壤因子的响应. 环境工程技术学报. 2024(02): 612-621 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张月萍,张梦婷,李敏瑄,代鹏跃,李润泽,王妍方. 不同生境下木棉幼苗叶性状和光合特性研究. 西部林业科学. 2024(02): 64-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵秋玲,郭小龙,张晶,张彦仲. 水曲柳叶片功能性状及C、N、P化学计量对海拔的响应. 西北植物学报. 2024(05): 792-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 邹旭阁,王寅,王健铭,曲梦君,朱威霖,赵航,司建华,李景文. 胡杨叶功能性状的协同与权衡及对树龄、土壤因子的响应. 北京林业大学学报. 2024(05): 82-92 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 毛开泽,高漫娟,吴睿,张月萍,程希平. 木棉树形结构和叶性状对生境要素的响应研究. 广西植物. 2024(05): 863-872 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李永宁,宗鹏. 植物功能性状对环境的响应及在森林经营中的应用. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2024(06): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李娜娜,黄健,吴镜辉,张婷,侯晓龙,吴鹏飞. 马尾松林下套种阔叶树的叶功能性状和化学计量特征季节动态研究. 西北林学院学报. 2024(06): 87-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 郭美灵,赵伊玲,殷宝,宁春如,杜维波,王旭虎,周晓雷,张晓玮. 野外同质园内油松叶功能性状的种内变异研究. 西北林学院学报. 2024(06): 95-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 俞群,高伟,施家意,傅成杰,林国江,康天琪,邱敏. 珍稀植物银粉蔷薇叶功能性状对环境变化的响应. 热带亚热带植物学报. 2024(06): 705-714 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 周靖 ,杨邵 ,华绍贵 ,吴甘霖 . 大别山五针松针叶功能性状及其与土壤养分关系的研究. 安庆师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 96-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 王洁茹,石文凯,吴会峰,胡保安,程小琴,韩海荣. 晋北典型针叶人工林叶功能性状特征及其与土壤因子的关系. 西北植物学报. 2023(05): 835-845 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 曹向文,张淼淼,陈健,史作民. 川滇高山栎叶片氮磷含量的海拔变化. 陆地生态系统与保护学报. 2023(05): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 吴天彧,杨依康,周帅,张清舒,罗建. 色季拉山不同海拔梯度下三花杜鹃叶表型性状变异研究. 高原农业. 2022(01): 41-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 王超,卢杰,姚慧芳,于德水,段斐,周晨霓. 急尖长苞冷杉叶功能性状特征及其环境响应. 森林与环境学报. 2022(02): 123-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 何雅琴,史晓洁,陈国杰,赖敏英,曾纪毅,魏凯,邓传远. 滨柃叶功能性状对环境因子的响应. 生态学报. 2022(06): 2418-2429 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 杨巧,朱润军,杨畅宇,李仕杰,程希平. 基于树形结构的木棉叶功能性状差异性研究. 生态学报. 2022(07): 2834-2842 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 黄郑雯,杨霖,王玉洁,毛开泽,高漫娟,程希平. 不同生境下木棉树形结构特征及其影响因子. 生态学杂志. 2022(08): 1552-1559 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 黄汐月,陈卓,黄梦月,杨文静,石松林,李景吉,彭培好,王国严. 藏东木本植物群落功能性状分布与环境的关系. 生态学报. 2022(22): 8964-8976 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(20)



 下载:
下载: