Response of plant functional traits and leaf economics spectrum to urban thermal environment
-
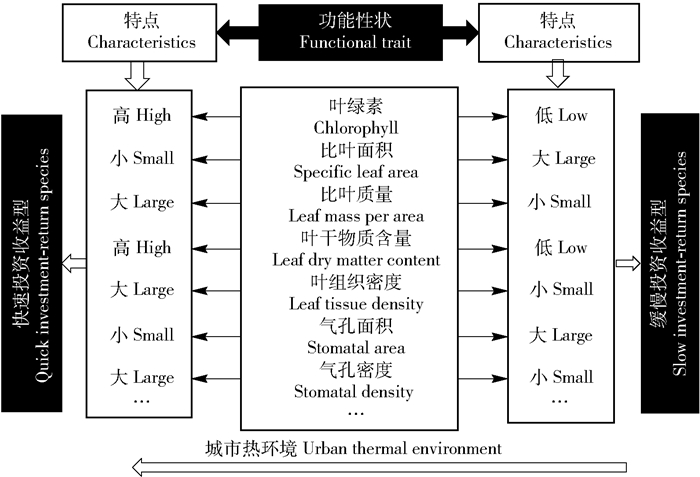
摘要:目的了解植物功能性状及叶经济谱对城市热环境的响应,有助于从功能生态学角度理解植物对城市环境的适应机制。方法以北京热环境高温点和低温点常见绿化树种国槐、栾树和洋白蜡为研究对象,测定地表温度、土壤含水量及叶功能性状指标。结果(1) 城市热环境地表温度表现为高温点(HTR)显著高于低温点(CTR)(P < 0.05);土壤含水量则表现为CTR相对大于HTR,但未达到显著水平。(2)城市热环境对不同树种影响存在一定差异,其中对国槐、栾树的影响主要源于高温胁迫,对洋白蜡的影响主要源于干旱胁迫。(3)在城市热环境中,叶性状关系与全球尺度基本一致,比叶面积(SLA)与叶绿素含量(CHL)、叶干物质含量(LDMC)、叶组织密度(LTD)呈极显著的负相关关系(P < 0.01);CHL与LDMC、LTD间存在极显著的正相关关系(P < 0.01);LDMC与LTD间呈现显著的正相关关系(P < 0.05)。气孔密度(SD)与气孔面积(SS)、气孔开度(SA)、SLA之间分别呈负相关关系,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。(4) RDA结果显示,植物功能性状指标中SLA主要受地表温度的正向影响(R2=0.97,P < 0.05),但土壤水分含量对它们具有负向影响(R2=0.75,P < 0.05);地表温度对LDMC、LTD、CHL有正向作用,但土壤含水量对它们有负向作用。结论全球叶经济谱在城市热环境中也同样存在,总体上向“快速投资-收益”型一端偏移,在HTR植物具有低的SLA,小的SS和SA,高的CHL、LDMC、LTD和SD,以适应高温、干旱的特殊生境。因此,在城市绿化植物配置时,在热环境高值区应选择耐高温、耐旱的树种,同时采取降温、灌溉等措施来降低高温的影响。Abstract:ObjectiveExploring variations of plant functional traits and leaf economics spectrum along urban thermal environment provides a chemical basis for examining species strategies as shaped by their local habitat.MethodIn this study, we quantified the land surface temperature, soil moisture content and leaf functional traits of Sophora japonica, Koelreuteria paniculate and Fraxinus pennsylvanica, which were grown in urban thermal environment in Beijing.Result(1) The urban thermal environment significantly increased the land surface temperature (P < 0.05), and showed high temperature region(HTR)>low temperature region(CTR); the soil moisture content was CTR>HTR, but the difference was not significant(P>0.05). (2) There were some differences in the effects of urban thermal environment on different tree species. The effects of urban thermal environment on Sophora japonica and Koelreuteria paniculate were mainly originated from high temperature stress, and its effects on Fraxinus pennsylvanica were mainly originated from drought stress, especially in high temperature environments. (3) The relationships between leaf traits under the urban thermal environment were similar to those on the global scale. Specific leaf area (SLA) presented significant negative correlation with chlorophyll content (CHL), leaf dry matter content (LDMC) and leaf tissue density(LTD) (P < 0.01). CHL presented significant positive correlation with LDMC and LTD (P < 0.01), and there was a positive correlation between LDMC and LTD (P < 0.05). Stomatal density(SD) showed a negative correlation with stomatal size(SS), stomatal aperture(SA) and SLA, but they did not reach a significant level (P>0.05). (4) RDA results showed that SLA was mainly affected by land surface temperature (R2=0.97, P < 0.05), but soil moisture content had negative effects on plant functional traits (R2=0.75, P < 0.05). Land surface temperature had positive effects on LDMC, LTD, and CHL, but soil moisture content had negative effects on them.ConclusionThe results of this study indicated that a leaf economics spectrum also existed in plant species in the urban thermal environment with a quick investment-return on the leaf economics spectrum. The species in HTR had lower SLA, SS and SA, higher CHL, LDMC, LTD and SD, which may be involved in the adaptation of plants to high-temperature and arid conditions. Therefore, when planting plants in urban areas, heat-resistant and drought-tolerant tree species should be selected in HTR. At the same time, the effects of high temperature should be reduced by increasing cooling and irrigation in the growing season.
-
扦插繁殖是一种简便高效的林木种质资源保存方法。其操作简便、周期短、繁殖效率高,能够在林木繁殖过程中高度遗传并保持母株的优良特性,因此被广泛用于优质林木遗传资源(如珍稀长寿基因和抗逆基因)的保存[1−2]。目前,林木扦插生根机理的研究侧重于生理、生化等方面,揭示了插穗的营养水平、酶活性、内源激素变化等与生根的关系[3−4]。然而,对于抑制林木扦插生根的物质研究还鲜有报道。
扦插生根抑制物是指在植物扦插繁殖过程中,阻碍或抑制插穗根系形成和生长的化学物质,如激素(脱落酸、乙烯等)、代谢物(酚酸、类黄酮和生长抑制剂等)[5]。林木插穗中的抑制物含量受树种和树龄的影响[6],如樱桃(Prunus spp.)插穗中的酚类物质(芦丁、香草酸、表儿茶素、咖啡酸和芥子酸)含量较高,导致扦插生根率低[7]。在巨桉(Eucalyptus grandis)插穗中发现了3种与单元酚相近的生根抑制物[8]。在落叶松(Larix kaempferi)扦插过程中,邻苯二酚、对羟基苯甲酸、儿茶酸、阿魏酸和没食子酸含量在难生根的无性系中均高于易生根无性系,且在扦插过程中逐渐减少,表明这些物质在生根过程中具有抑制作用[9]。
树龄的增长会导致抑制物含量的增加,这也是影响林木扦插生根能力的重要因素之一。如苯酚类和类黄酮含量随马尾松(Pinus massoniana)、紫杉(Taxus cuspidata)、核桃楸(Juglans mandshuric)树龄增长而逐渐积累,从而对扦插生根产生抑制作用[10−12]。有研究表明,通过使用酒精、高锰酸钾、硝酸银和抗酚剂等溶液处理,以及机械处理,可以去除插穗中的部分抑制物,从而提高其生根率[13−15]。
古树具有较强的气候和土壤适应能力,是林木用材、困难立地造林和园林美化等方面的优良种质资源[1−2]。侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)是我国重要的长寿命树种之一,在陕西、河南和山西等地分布着寿命长达数百年甚至数千年的侧柏古树[16−17]。然而,侧柏古树扦插繁殖中存在生根时间长、生根率低的问题[4],这严重限制了古树的繁殖效率和数量,不利于古树优良基因保存和生态功能的发挥。目前,针对侧柏古树扦插过程中类黄酮和酚酸物质含量及其影响的研究仍较少。本文在3月份和6月份选取树龄为5、100、300和700 年生的侧柏母树的插穗进行扦插,研究不同树龄、不同扦插季节以及扦插过程中类黄酮和酚酸物质对侧柏生根的影响,为提高林木扦插生根率和保留古树优良种质资源提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
选取中国林业科学研究院和北京植物园内树龄约为5、100、300和700年生(根据古树树龄记载)的侧柏母树,其中以5 年生侧柏作为对照试验材料。在3月份、6月份分别采集各林龄生长健壮、无病虫害的新梢。不同部位插穗试验采取5、100、300和700 年生侧柏古树的东、南、西、北的上和下8个方位的枝条,截成10 ~ 15 cm长的插穗,在离芽1.0 ~ 1.5 cm处的基部斜切。每个处理25个插穗,3次重复。插穗用质量浓度为1 000 mg/L的溶液(mNAA∶mIBA = 1∶1)浸泡处理1 min。使用轻基质网袋容器,基质选用体积比为2∶8的泥炭和珍珠岩的混合物。扦插试验在中国林业科学研究院内的全光照喷雾插床中进行,管理参照杜常健等[18]研究。
根据前期实验观察到的扦插过程中插穗基部的形态变化,本文将5、100、300和700年生侧柏母树的插穗中的3个不定根形成过程进行设定,扦插试验当天设为第0 天(S1)、愈伤组织形成期设为第45天(S2)和不定根形成期设为第90天(S3)。对每个重复随机选取插穗进行样本取材。拔出插穗后,用蒸馏水冲洗干净,滤纸擦干,迅速剥取插穗基部0.5 cm(除去木质部),剪碎混匀后保存。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 不同季节的不同树龄侧柏插穗的浸提液对白菜籽发芽的影响
在3月份、6月份分别取5、100、300和700年生侧柏的插穗。在S1阶段时采取除木质部外的组织0.2 g,液氮研磨成粉末,放入6 mL的80%甲醇提取液中,用超声波浸提2 h。将所得浸提液定容至3 mL,然后稀释至浸提液原浓度的0%(CK)、25%、50%、100%,分别导入培养皿,待溶液蒸干后加入2 mL蒸馏水,每个处理重复3次。在每个培养皿中放置50粒白菜种子,置于25 ℃光照培养箱中进行培养和观察,3 d后统计发芽率。
1.2.2 树龄对侧柏扦插生根的影响
在6月份分别开展5、100、300和700年生侧柏母树扦插试验,3个月后统计生根率和生根数,分别取平均值。
1.2.3 内源生根抑制物的测定
采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)(Agilent 1100,美国Agilent公司)测定内源生根抑制物,包括类黄酮(芦丁和槲皮素)和酚酸物质(水杨酸、香豆酸、苯酚、阿魏酸、没食子酸、邻苯二酚)。
1.2.4 不同种类酚酸、类黄酮物质含量在不同季节的变化
在3月份和6月份,以母树树龄为5、100、300和700年生侧柏在S1阶段时插穗为试验材料,测定类黄酮(芦丁和槲皮素)和酚酸物质(水杨酸、香豆酸、苯酚、阿魏酸、没食子酸、邻苯二酚)的含量。
1.2.5 扦插过程中不同种类酚酸、类黄酮的含量的变化
在6月份进行扦插后,以母树树龄为5、100、300和700年生侧柏在S1、S2和S3阶段时插穗为试验材料,测定类黄酮(芦丁和槲皮素)和酚酸物质(水杨酸、香豆酸、苯酚、阿魏酸、没食子酸、邻苯二酚)的含量。
1.2.6 清除内源生根抑制物对扦插生根的影响
在6月份,选取100年生的侧柏插穗为试验材料,分别用0.1%硝酸银、0.1%醋酸、2%乙醇溶液进行20 h处理,分别用温水、洗洁精溶液处理3 h,用0.05%高锰酸钾溶液处理15 min。每个处理设25个插穗、3次重复。其他步骤同扦插试验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 树龄对侧柏扦插生根的影响
本文研究了树龄对侧柏扦插生根率和生根数的影响。结果表明在6月份的扦插试验中,5年生侧柏扦插的生根率和生根数分别为83.5%和6.12;100、300和700年生侧柏扦插生根率分别为19.31%、13.54%和7.78%,生根数分别为3.21、2.84和2.24(图1)。5年生侧柏扦插的生根率和生根数显著高于100、300和700年生(P < 0.05)。随着树龄增加,生根能力显著下降,而100、300和700年生的扦插生根率和生根数没有显著差异(P > 0.05)。
2.2 不同季节和不同树龄侧柏插穗的浸提液对白菜籽发芽的影响
进一步探讨不同树龄和季节侧柏插穗浸提物对扦插生根的影响,研究结果表明除了CK外,3月份和6月份的侧柏插穗浸提液随着浓度的增加,白菜种子的发芽率均呈下降趋势。同时,随树龄增长,发芽率总体上呈现降低的趋势。尤其是浸提液占比为25%和50%时,来自300和700年生侧柏插穗的浸提液处理过的白菜籽的发芽率显著低于5年生侧柏插穗的浸提液处理过的白菜籽(P < 0.05)(表1,2)。总体来看,6月份的白菜籽的发芽率高于3月份,因此在6月份对侧柏古树进行扦插能够取得较好的效果。
表 1 3月份不同树龄侧柏不同插穗浸提液占比对白菜籽发芽率的影响Table 1. Effects of extraction solution with different proportions from Platycladus orientalis cuttings of different ages on germination rates of cabbage seeds in March% 树龄/a
Tree age/year0(CK) 25% 50% 100% 5 96.67 ± 1.33a 86.63 ± 7.05a 82.69 ± 6.37a 76.67 ± 6.66a 100 96.67 ± 1.35a 71.33 ± 7.23ab 70.00 ± 7.34ab 61.00 ± 7.22b 300 96.67 ± 1.38a 70.67 ± 6.87b 61.33 ± 6.59b 60.67 ± 6.13b 700 96.67 ± 1.33a 66.67 ± 7.15b 62.67 ± 6.78b 58.67 ± 5.93b 注:不同小写字母表示同一浸提液占比不同年龄间发芽率存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。下同。Notes:different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level between cuttings of different ages under the same proportion of extraction solution. The same below. 表 2 6月份不同树龄侧柏不同插穗浸提液占比对白菜籽发芽率的影响Table 2. Effects of cabbage seeds treated with different proportion extraction solutions from cuttings propagated from P. orientalis at different ages on germination rates in June% 树龄/a
Tree age/year0(CK) 25% 50% 100% 5 96.60 ± 1.81a 88.15 ± 8.62a 83.47 ± 6.94a 78.67 ± 5.97a 100 96.60 ± 1.81a 73.33 ± 7.16b 72.00 ± 7.25ab 65.00 ± 6.26b 300 96.60 ± 1.81a 73.67 ± 7.10b 68.33 ± 5.92b 65.67 ± 6.29b 700 96.60 ± 1.81a 72.67 ± 7.13b 65.67 ± 6.97b 63.67 ± 6.16b 2.3 不同季节侧柏插穗类黄酮物质含量的变化
季节对林木酚酸含量有显著影响,本研究用HPLC对各类插穗内源抑制物进行分离,最终只检测出2种类黄酮物质:芦丁和槲皮素。3月份5、100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的芦丁含量显著高于6月份(P < 0.05),而6月份的槲皮素含量则显著低于3月份(P < 0.05),这表明季节对各树龄侧柏插穗的类黄酮含量影响显著(图2)。侧柏100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的芦丁含量在3月份和6月份都显著高于5年生侧柏(P < 0.05),5年生侧柏插穗槲皮素含量则显著高于100、300、700年生侧柏(P < 0.05),而100、300、700年生侧柏插穗之间的芦丁含量差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
![]() 图 2 不同树龄侧柏在不同季节类黄酮含量变化不同大写字母表示不同生根阶段在同一树龄的差异显著(P < 0.05);不同小写字母表示不同树龄在同一生根阶段间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Different capital letters indicate significant differences among varied rooting stages in same tree age (P < 0.05); different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among varied tree ages in same stage (P < 0.05). Same as below.Figure 2. Changes of flavonoids contents of P. orientalis at different ages in varied seasons
图 2 不同树龄侧柏在不同季节类黄酮含量变化不同大写字母表示不同生根阶段在同一树龄的差异显著(P < 0.05);不同小写字母表示不同树龄在同一生根阶段间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Different capital letters indicate significant differences among varied rooting stages in same tree age (P < 0.05); different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among varied tree ages in same stage (P < 0.05). Same as below.Figure 2. Changes of flavonoids contents of P. orientalis at different ages in varied seasons2.4 不同季节侧柏插穗酚酸物质含量的变化
本研究检测出的酚酸物质包括香豆酸、阿魏酸、苯酚、水杨酸、没食子酸和邻苯二酚。结果发现3月份5、100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的香豆酸、水杨酸含量均高于6月份,特别是3月份700年生侧柏插穗的水杨酸、香豆酸含量较高,分别为40.47 和111.05 mg/g(图3)。3月份5、100、700年生侧柏插穗的阿魏酸、没食子酸、邻苯二酚含量均显著高于6月份(P < 0.05)。以上数据表明,3月份侧柏插穗的酚酸含量大多高于6月份,生长旺盛期的各种酚酸和类黄酮物质含量减少,说明6月份的枝条更适合侧柏古树扦插。5、100、300、700年生侧柏插穗香豆酸、水杨酸和邻苯二酚在3月份和6月份总体上呈现升高的趋势,这说明古树插穗的木质化程度较高,在不同季节中均具有较强的酚酸合成能力,可能与古树抗氧化和防御机制更强相关。
2.5 扦插过程中不同种类酚酸、类黄酮的含量的变化
林木插穗中含有过量的酚酸和类黄酮对不定根形成具有抑制作用[19]。结果表明100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的芦丁含量在S1、S2和S3都显著高于5年生(P < 0.05),5、100、300、700年生侧柏扦插过程中芦丁含量随着生根阶段总体上呈上升趋势(图4),且在S3阶段达到峰值,分别为0.20、0.60、0.88 和0.90 mg/g,这表明芦丁对侧柏古树的生根具有抑制作用。而5年生侧柏插穗的槲皮素含量在S3时显著高于100、300 、700年生侧柏(P < 0.05),为1.49 mg/g。
![]() 图 4 不同树龄侧柏扦插过程中类黄酮含量变化S1为扦插试验当天,S2为愈伤组织形成期(第45天),S3为不定根形成期(第90天)。下同。S1 refers to the day of cutting experiment, S2 refers to callus formation period (the 45th day), and S3 refers to the adventitious root formation period (the 90th day). The same below.Figure 4. Changes of flavonoid content during rooting process of cuttings propagated from P. orientalis at different ages
图 4 不同树龄侧柏扦插过程中类黄酮含量变化S1为扦插试验当天,S2为愈伤组织形成期(第45天),S3为不定根形成期(第90天)。下同。S1 refers to the day of cutting experiment, S2 refers to callus formation period (the 45th day), and S3 refers to the adventitious root formation period (the 90th day). The same below.Figure 4. Changes of flavonoid content during rooting process of cuttings propagated from P. orientalis at different ages2.6 扦插过程中不同种类酚酸、类黄酮的含量的变化
不同树龄的酚酸含量在侧柏扦插生根过程的影响研究表明,300、700年生侧柏扦插过程中S2和S3的香豆酸含量显著高于5 年生侧柏插穗(图5)。100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的水杨酸、邻苯二酚含量随生根进程显著上升,并且在S1、S2和S3显著高于5 年生侧柏插穗(P < 0.05)。没食子酸的含量随树龄升高总体上呈现升高的趋势。除此之外,5 年生侧柏插穗的苯酚、阿魏酸含量在S1时显著高于100、300、700年生侧柏古树插穗。结果说明香豆酸、水杨酸、没食子酸和邻苯二酚)的含量随年龄增加总体上呈现增加趋势。
不同生根阶段的酚酸含量对侧柏扦插的影响研究结果表明,5、100、700年生侧柏插穗的香豆酸含量随生根进程(S1 ~ S3)显著上升(P < 0.05)。100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的阿魏酸、苯酚含量在S3显著高于S1和S2,而5年生侧柏插穗的苯酚含量在3个生根时期没有显著变化。S2和S3时5、100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的没食子酸含量显著高于S1时的含量;S3时5、100、300、700年生侧柏插穗的邻苯二酚含量显著高于S1、S3时的含量。结果表明酚酸物质含量随生根阶段(S1 ~ S3)的进展显著增加,尤其是在700年生插穗中的S3阶段,表明年龄较大的插穗在生根过程中会积累更多的酚类化合物。
2.7 清除内源生根抑制物对扦插生根的影响
清除100年生侧柏插穗的内源生根抑制物的试验结果显示,不同清除抑制物方式对扦插生根结果存在显著差异(P < 0.05)(表3)。使用0.1%硝酸银、清水、0.05%高锰酸钾处理100年生侧柏插穗能显著提高扦插生根率,生根率分别为26.55%、22.97%、23.63%,高于用0.1% 醋酸、2%乙醇、洗洁精处理后的生根率。此外,0.1%硝酸银和0.05%高锰酸钾处理100年生侧柏插穗能提高扦插生根数,生根数分别为5.13和5.44,高于其他方法处理后的生根率。0.1%硝酸银和0.05%高锰酸钾处理插穗后扦插生根效果较好,说明适合的方法能清除侧柏古树的内源抑制物,提高扦插生根率。
表 3 清除抑制物对100年生侧柏古树扦插生根的影响Table 3. Effects of removing inhibitors on rooting rates of cuttings of 100 years old ancient P. orientalis清除方式
Clear method处理时间
Treating time/h生根率
Rooting rate/%生根数
Rooting number最长根长
Max. root length/cm0.1% AgNO3 20 26.55 ± 2.66a 5.13 ± 0.48a 1.68 ± 0.22a 0.1% CH3COOH 20 19.25 ± 2.28b 2.52 ± 0.23c 1.24 ± 0.29b 2% EtOH 20 21.14 ± 3.24b 3.78 ± 0.39b 1.57 ± 0.19ab 水Water 3 22.97 ± 2.98ab 3.16 ± 0.46bc 1.52 ± 0.21ab 洗洁精Abluent 3 18.52 ± 2.72b 3.59 ± 0.77b 1.17 ± 0.26b 0.05% KMnO4 0.25 23.63 ± 2.91ab 5.44 ± 0.69a 1.95 ± 0.23a 注:不同小写字母表示不同清除方法之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。Note: different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level between removal methods. 3. 讨 论
林木的树龄和季节是影响扦插生根的重要因素[4]。本研究发现随树龄的增加,侧柏扦插生根率降低,这与马尾松、桉树等林木扦插生根的结果一致[10,20]。同时,插穗的浸提液抑制白菜种子发芽的作用增强,与沉水樟和核桃楸等林木的研究结果相似[5,12]。而侧柏插穗的水杨酸、香豆酸等酚酸物质在3月份的含量普遍高于6月份。因此,6月份较适合侧柏古树扦插,这与荷花玉兰(Magnolia grandiflora)扦插的最佳时间同期[6]。这主要是因为6月份插穗生长旺盛,营养物质(可溶性和淀粉)含量高,次生物质(酚酸和类黄酮)含量少,木质化程度低[9]。本研究根据树龄和季节对林木扦插生根的重要性,选择适宜的季节进行插穗扦插有助于提高生根率。
当插穗中的酚酸化合物含量较高时,扦插不定根的形成受阻[21]。随着树龄增长,侧柏古树(100、300、700年生)插穗的芦丁和水杨酸等酚酸和类黄酮物质含量升高,这表明古树扦插生根率低可能与侧柏古树插穗木质化程度高导致的酚酸和类黄酮物质积累有关[9]。牛樟(Cinnamomum kanehirae)插穗在木质素含量高时,不定根形成困难[22]。樱桃(Prunus spp.)插穗木质化程度高时,酚酸物质(芦丁、香草酸、表儿茶素、咖啡酸和芥子酸)含量也高,而扦插生根率却比较低,与本文的研究结果相似[7]。这些抑制物在树龄较大的侧柏插穗中的含量普遍较高,进一步说明了抑制物(酚酸和类黄酮)是导致古树难生根的关键因素之一。
酚酸类物质的积累与植物抵御胁迫有关,但也对扦插生根具有抑制作用。在生根的不同阶段(S1 ~ S3),各种酚类化合物(如水杨酸、没食子酸和邻苯二酚)的含量随生根的进程显著增加,700年生侧柏的插穗在S3阶段的酚酸含量显著高于其他年龄组。水杨酸作为逆境内源信号参与植物的抗性,是侧柏插穗在扦插过程中受到病菌侵染产生的应激反应物质。侧柏古树(100、300、700年生)的插穗在S3阶段水杨酸含量较高,使愈伤组织趋于成熟生长,再分化能力降低[23]。如巴拉圭冬青(Ilex paraguariensis)插穗在高光照胁迫下总酚含量升高,但是生根率却降低[24]。这主要是因为在胁迫条件下,插穗中的酚酸和类黄酮物质积累增加,这些物质不仅具有增加细胞壁厚度、提高细胞刚性的作用,还会抑制扦插不定根形成。因此,未来的研究可以重点关注通过调控类黄酮和酚酸物质的含量来提高林木插穗的生根能力。
有些酚酸和类黄酮物质可能对林木扦插生根起到促进作用。本研究显示,6月份5年生侧柏插穗中槲皮素和阿魏酸含量高,说明在幼嫩的植物组织中有些种类的酚酸含量高,这与苦丁茶(IIex kudingcha)嫩叶比老叶中的槲皮素含量高的结果相似[25]。5年生侧柏插穗在生根阶段槲皮素和邻苯二酚的含量增加,这可能是由于槲皮素可保护吲哚乙酸(IAA)免受羧化作用的伤害,从而促进生根。在Rosa bourboniana嫩枝扦插过程中,高浓度的酚类促进不定根发生[26],这主要是因为酚酸在不定根形成过程中能提高插穗抗逆能力。蛇足石杉(Huperzia serrata)插穗中IAA、儿茶酚、绿原酸、阿魏酸的含量与PPO、POD的活性正比时促进扦插生根[27]。这些不同种类的酚酸和类黄酮物质对扦插生根的影响还需要进一步研究。
通过清除插穗中抑制物(如酚酸和类黄酮),能够提高侧柏扦插的生根率[28]。本研究发现,使用0.1%的硝酸银或0.05%的高锰酸钾溶液处理侧柏插穗,能有效促进不定根的形成。这与使用0.2%硝酸银溶液处理弗吉尼亚栎(Quercus vinginiana)插穗、3%乙醇与0.5%高锰酸钾的组合处理马尾松插穗能获得良好的生根效果相似[29]。因此,需要进一步筛选和优化清除插穗抑制物的对比试验,以获得较好的生根效果。
4. 结 论
综上所述,随着树龄的增长,5、100、300、700年生侧柏扦插生根的能力下降,表明树龄与扦插生根能力呈负相关关系。同时,侧柏插穗的浸提液抑制白菜种子发芽的作用增强。除了槲皮素和苯酚外,100、300、700年生侧柏的酚酸和类黄酮物质含量大都高于5年生侧柏。除了槲皮素和阿魏酸外,3月份的酚酸和类黄酮物质含量普遍高于6月份。随着生根阶段(S1 ~ S3)的推进,酚酸含量显著增加,尤其在700年树龄插穗的S3阶段,年龄较大的母树插穗在生根过程中会积累更多的酚类化合物。使用0.1%的硝酸银处理侧柏插穗后生根率和生根数量较高,而0.05%的高锰酸钾处理后插穗不定根的长度增长。本文通过研究不同树龄侧柏插穗的酚酸和类黄酮物质的作用以及清除方法,为提高林木的扦插生根率提供了理论依据。
-
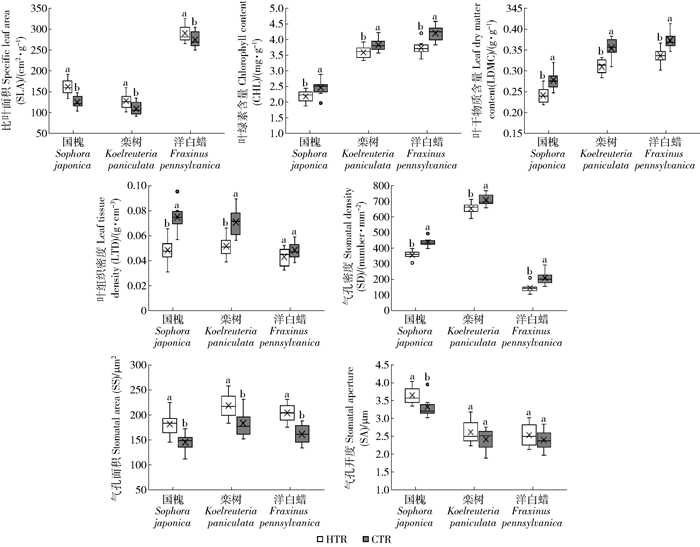
图 2 城市热环境对植物叶功能性状的影响
不同字母表示同一树种的性状指标在高温点与低温点的差异达到显著水平(P < 0.05)。
Figure 2. Effects of urban thermal environment on plant leaf functional traits
Different letters indicate that the traits of the same tree species have a significant difference between the high temperature region(HTR) and the low temperature region(CTR) at P < 0.05 level.
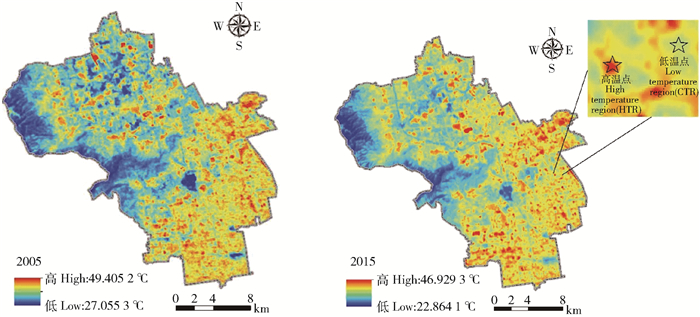
表 1 高温点与低温点的地表温度和土壤含水量均值样本T检验
Table 1 Paired T test of mean value sample for land surface temperature and soil moisture content between HTR and CTR
指标Index 树种Tree species HTR-CTR均值差
Mean value difference for HTR and CTR白天Day 夜间Night 地表温度Land surface temperature/℃ 国槐Sophora japonica 4.65±2.62 * 2.01±1.67 * 栾树Koelreuteria paniculata 4.27±2.37 * 1.96±1.43 * 洋白蜡Fraxinus pennsylvanica 3.25±1.56 * 1.90±1.17 * 土壤含水量Soil moisture content/% 国槐Sophora japonica -1.31±0.83 -0.63±0.23 栾树Koelreuteria paniculata -1.18±0.92 -0.59±0.35 洋白蜡Fraxinus pennsylvanica -1.93±1.05 -0.88±0.54 注:**表示在P < 0.01水平上差异显著, *表示在P < 0.05水下上差异显著,下同。Notes: ** means extremely significant difference at P < 0.01 level, * means significant difference at P < 0.05 level. The same as below. 表 2 7—10月份地表温度日最高值大于40℃和土壤含水量日均值小于15%的天数
Table 2 Total days for land surface temperature more than 40℃ and daily mean value of soil moisture content less than 15% in July to October
d 指标Index 树种Tree species HTR CTR 地表温度 > 40℃ Land surface temperature > 40℃ 国槐Sophora japonica 73 29 栾树Koelreuteria paniculata 66 23 洋白蜡Fraxinus pennsylvanica 40 5 土壤含水量 < 15% Soil moisture content < 15% 国槐Sophora japonica 11 0 栾树Koelreuteria paniculata 30 0 洋白蜡Fraxinus pennsylvanica 49 8 表 3 植物功能性状指标显著性差异分析
Table 3 Analysis on significance difference among plant functional traits
变异来源
Source of variation环境间Inter-environment 种间Interspecies 种内Intraspecies F P F P F P CHL 14.469 0.0029 18.092 0.0410 18.092 0.3410 SLA 26.581 0.0032 25.667 0.0430 25.667 0.275 2 LDMC 14.184 0.0075 32.131 0.0046 32.131 0.0874 LST 12.012 0.0085 18.098 0.3423 18.098 0.5121 SD 24.932 0.0001 45.321 0.0133 45.321 0.0523 SS 45.093 0.0027 7.834 0.0721 7.834 0.0932 SA 21.214 0.0013 45.321 0.0033 45.321 0.1433 表 4 植物功能性状之间的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analyses on plant functional traits
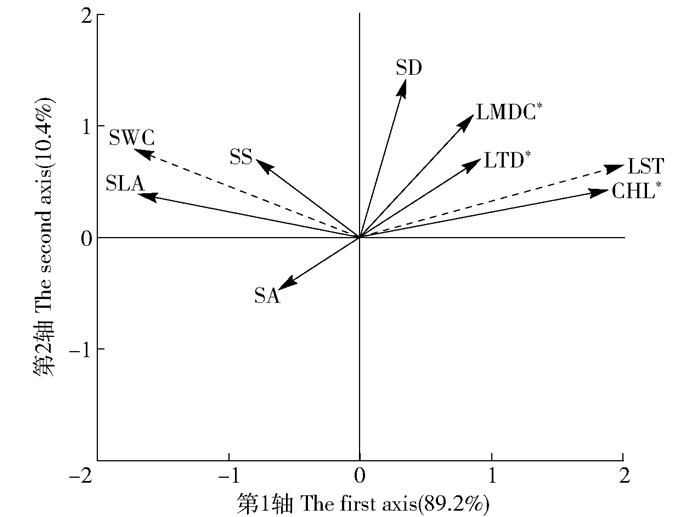
叶性状Leaf trait CHL SLA LDMC LTD SD SS SA CHL 1 SLA -0.522 ** 1 LDMC 0.561 ** -0.632 ** 1 LTD 0.616 ** -0.814 ** 0.457 * 1 SD 0.012 0.203 0.102 -0.016 1 SS 0.201 0.193 0.093 0.028 -0.321 1 SA 0.215 0.325 0.032 0.021 -0.193 -0.108 1 表 5 植物功能性状前2轴的RDA分析
Table 5 RDA analyses on plant functional traits in the first two axes
变量Variable 第1轴
The first axis第2轴
The second axisLST -0.972 ** 0.374 SWC 0.751 ** -0.105 相关性Relativity 0.892 0.104 -
[1] Pitman S D, Daniels C B, Ely M E. Green infrastructure as life support: urban nature and climate change[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Australia, 2015, 139(1): 97-112. doi: 10.1080/03721426.2015.1035219
[2] Priyadarsini R, Hien W N, David C K W. Microclimatic modeling of the urban thermal environment of Singapore to mitigate urban heat island[J]. Solar Energy, 2008, 82(8):727-745. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2008.02.008
[3] Nowak D J, Hoehn R E, Bodine A R, et al. Urban forest structure, ecosystem services and change in Syracuse, NY[J]. Urban Ecosystems, 2016, 19(4): 1455-1477. doi: 10.1007/s11252-013-0326-z
[4] Duan J L, Song X, Zhang X L. Spatiotemporal variation of urban heat island in Zhengzhou City based on RS DUAN[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011(1): 165-170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201101025
[5] 侯鹏, 蒋卫国, 曹广真.城市湿地热环境调节功能的定量研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(3): 191-196. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9401 Hou P, Jiang W G, Cao G Z. Quantitative analyses of thermal regulation function of urban wetland[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2010, 32(3): 191-196. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9401
[6] Lun I, Mochida A, Ooka R. Progress in numerical modelling for urban thermal environment studies[J]. Advances in Building Energy Research, 2009, 3(1):147-188. doi: 10.3763/aber.2009.0306
[7] Fernández F J, Alvarez-Vázquez L J, García-Chan N, et al. Optimal location of green zones in metropolitan areas to control the urban heat island[J]. Journal of Computational & Applied Mathematics, 2015, 289(C): 412-425. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=535aeb0174944032dec2f1cd450cc68b
[8] 冯悦怡, 胡潭高, 张力小.城市公园景观空间结构对其热环境效应的影响[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(12) : 3179-3187. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201412006 Feng Y Y, Hu T G, Zhang L X. Impacts of structure characteristics on the thermal environment effect of city parks[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(12):3179-3187. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201412006
[9] 武鹏飞, 王茂军, 张学霞.北京市植被绿度与城市热岛关系研究[J].北京林业大学学报, 2009, 31(5): 54-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2009.05.010 Wu P F, Wang M J, Zhang X X. Relationship between vegetation greenness and urban heat island effect in Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2009, 31(5): 54-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2009.05.010
[10] Priyadarsini R, Hien W N, David C K W. Microclimatic modelingof the urban thermal environment of Singapore to mitigate urban heat island[J]. Solar Energy, 2008, 82(8): 727-745. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2008.02.008
[11] 王亚婷, 范连连.城市热岛对植物生长的影响以及叶片形态构成的适应性[J].生态学报, 2011, 30(20): 5992-5998. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_stxb201120015 Wang Y T, Fan L L. Effect of urban heat island on plant growth and adaptability of leaf morphology constitute[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 30(20): 5992-5998. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_stxb201120015
[12] Shipley B, Lechowicz M J, Wright I, et al. Fundamental trade-offs generating the worldwide leaf economics spectrum[J]. Ecology, 2006, 87(3): 535-541. doi: 10.1890/05-1051
[13] Royer D L, Miller I M, Peppe D J, et al. Leaf economic traits from fossils support a weedy habit for early angiosperms[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2010, 97(3): 438-445. doi: 10.3732/ajb.0900290
[14] Wright I J, Reich P B, Westoby M, et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum[J]. Nature, 2004, 428: 821. doi: 10.1038/nature02403
[15] 陈莹婷, 许振柱.植物叶经济谱的研究进展[J].植物生态学报, 2014, 38(10): 1135-1153. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201410012 Chen Y T, Xu Z Z. Review on research of leaf economics spectrum[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(10): 1135-1153. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201410012
[16] 张耘, 于强, 李梦莹, 等.基于EnKF-3DVar模型的海淀区地表温度模拟[J].农业机械学报, 2017, 48(9): 166-172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyjxxb201709021 Zhang Y, Yu Q, Li M Y, et al. Simulation of land surface temperature in Haidian District based on EnKF-3DVar model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(9): 166-172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nyjxxb201709021
[17] 江樟焰, 陈云浩, 李京.基于Landsat TM数据的北京城市热岛研究[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2006, 31(2):120-123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whchkjdxxb200602007 Jiang Z Y, Chen Y H, Li J. Heat island effect of Beijng based on Landsat TM data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2006, 31(2): 120-123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whchkjdxxb200602007
[18] 朱济友, 徐程扬, 吴鞠.基于eCognition植物叶片气孔密度及气孔面积快速测算方法[J].北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(5): 37-45. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170412 Zhu J Y, Xu C Y, Wu J. Fast estimation of stomatal density and stomatal area of plant leaves based on eCognition[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(5): 37-45. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170412
[19] 张立荣, 牛海山, 汪诗平, 等.增温与放牧对矮嵩草草甸4种植物气孔密度和气孔长度的影响[J].生态学报, 2010, 30(24): 6961-6969. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201024033 Zhang L R, Niu H S, Wang S P, et al. Effects of temperature increase and grazing on stomatal density and length of four alpine Kobresia meadow species, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(24): 6961-6969. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201024033
[20] 陈媛媛, 江波, 王效科, 等.元宝枫幼苗生长和光合特性对硬化地表的响应[J].生态学杂志, 2016, 35(12): 3258-3265. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201612015 Chen Y Y, Jiang B, Wang X K, et al. Responses of growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Acer truncatum seedlings to hardening pavements[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(12): 3258-3265. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz201612015
[21] 叶子奇, 邓如军, 王雨辰, 等.胡杨繁殖根系分枝特征及其与土壤因子的关联性[J].北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(2): 31-39. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170426 Ye Z Q, Deng R J, Wang Y C, et al. Branching patterns of clonal root of Populus euphratica and its associations with soil factors[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2018, 40(2): 31-39. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170426
[22] 陈媛媛, 江波, 王效科, 等.北京典型绿化树种幼苗光合特性对硬化地表的响应[J].生态学报, 2017, 37(11): 3673-3682. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201711009 Chen Y Y, Jiang B, Wang X K, et al. Effect of pavement on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics of saplings of three common tree species (Pinus tabulaeformis, Fraxinus chinensis, and Acer truncatum) in Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 3673-3682. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201711009
[23] 杨锐, 张博睿, 王玲玲, 等.元谋干热河谷植物功能性状组合的海拔梯度响应[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1): 49-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj2015010009 Yang R, Zhang B R, Wang L L, et al. The response of plant functional traits' group to gradients of altitude in dry-hot valley of Yuan-Mou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(1): 49-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj2015010009
[24] 韩威, 刘超, 樊艳文, 等.长白山阔叶木本植物叶片形态性状沿海拔梯度的响应特征[J].北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(4): 47-53. doi: 10.13332/j.cnki.jbfu.2014.04.012 Han W, Liu C, Fan Y W, et al. Responses of leaf morphological traits for broadleaved woody plants along the altitudinal gradient of Changbai Mountain, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(4): 47-53. doi: 10.13332/j.cnki.jbfu.2014.04.012
[25] Garnier E, Cortez J, Billès G, et al. Plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during secondary succession[J]. Ecology, 2004, 85(9): 2630-2637. doi: 10.1890/03-0799
[26] Lavorel S, Grigulis K, Lamarque P, et al. Using plant functional traits to understand the landscape distribution of multiple ecosystem services[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2011, 99(1): 135-147. doi: 10.1111/jec.2010.99.issue-1
[27] Chave J, Coomes D, Jansen S, et al. Towards a worldwide wood economics spectrum[J]. Ecology Letters, 2010, 12(4): 351-366. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0216596116/
[28] Murru V, Marignani M, Acosta A T R, et al. Bryophytes in Mediterranean coastal dunes: ecological strategies and distribution along the vegetation zonation[J]. Plant Biosystems, 2018(1): 1-8. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b917109773ae5a77e7b0710f54f52e5d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] Huang H, Ooka R, Kato S. Urban thermal environment measurements and numerical simulation for an actual complex urban area covering a large district heating and cooling system in summer[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(34): 6362-6375. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.07.018
[30] 黄群芳, 陆玉麒.短期大规模人口流动对上海市城市热岛的影响[J].气候与环境研究, 2017, 22(6): 708-716. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhyhjyj201706006 Huang Q F, Lu Y Q. Effects of short-term massive human migration during the Chinese new year on the urban heat island effect in Shanghai[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2017, 22(6): 708-716. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhyhjyj201706006
[31] Freschet G T, Cornelissen J H C, Logtestijn R S P, et al. Evidence of the 'plant economics spectrum' in a subarctic flora[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2010, 98(2): 362-373. doi: 10.1111/jec.2010.98.issue-2
[32] Mason C M, Donovan L A. Does investment in leaf defenses drive changes in leaf economic strategy? A focus on whole-plant ontogeny[J]. Oecologia, 2015, 177(4): 1053-1066. doi: 10.1007/s00442-014-3177-2
[33] Cornelissen J H C, Lavorel S, Garnier E, et al. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide[J]. Australian Journal Botany, 2003, 51(4): 335-380. doi: 10.1071/BT02124
[34] Wang H, Chen H. Plant functional groups based on vegetative and reproductive traits in a subtropical forest community[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 2013, 18(6): 482-490. doi: 10.1007/s10310-012-0376-8
[35] Swenson N G. The functional ecology and diversity of tropical tree assemblages through space and time: from local to regional and from traits to transcriptomes[J]. Isrn Forestry, 2013, 2012(2): 133-140. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_42c46ee37d9ba9663a3dcdbf9129987b
[36] 赵新风, 徐海量, 张鹏, 等.养分与水分添加对荒漠草地植物群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J].植物生态学报, 2014, 38(2): 167-177. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201402008 Zhao X F, Xu H L, Zhang P, et al. Effects of nutrient and water additions on plant community structure and species diversity in desert grasslands[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(2): 167-177. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201402008
[37] 王均伟, 侯嫚嫚, 黄利亚, 等.长白山阔叶红松林系统发育和功能性状beta多样性[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(10): 21-27. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160062 Wang J W, Hou M M, Huang L Y, et al. Phylogenetic and functional beta diversity in a broadleaved Korean pine mixed forest in Changbai Mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(10): 21-27. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160062
[38] 任昱, 卢琦, 吴波, 等.不同模拟增雨下白刺比叶面积和叶干物质含量的比较[J].生态学报, 2015, 35(14): 4707-4715. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201514016 Ren Y, Lu Q, Wu B, et al. Specific leaf area and leaf dry matter content of Nitraria tangutorum in the artificially simulated precipitation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(14): 4707-4715. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201514016
[39] 张林, 罗天祥, 邓坤枚, 等.云南松比叶面积和叶干物质含量随冠层高度的垂直变化规律[J].北京林业大学学报, 2008, 30(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2008.01.007 Zhang L, Luo T X, Deng K M, et al. Vertical variations in specific leaf area and leaf dry matter content with canopy height in Pinus yunnanensis[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2008, 30(1): 40-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.2008.01.007
[40] 张桐, 洪秀玲, 孙立炜, 等. 6种植物叶片的滞尘能力与其叶面结构的关系[J].北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(6): 70-77. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170012 Zhang T, Hong X L, Sun L W, et al. Particle-retaining characteristics of six tree species and their relations with micro-configurations of leaf epidermis[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(6): 70-77. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20170012
[41] 徐振锋, 胡庭兴, 张力, 等.模拟增温对川西亚高山林线交错带绵穗柳生长、叶物候和叶性状的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2009, 20(1): 7-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb200901002 Xu Z F, Hu T X, Zhang L, et al. Effects of simulated warming on the growth, leaf phenology, and leaf traits of Salix eriostachya in subalpine timberline ecotone of western Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(1): 7-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb200901002
[42] 赵文霞, 邹斌, 郑景明, 等.常绿阔叶林常见树种根茎叶功能性状的相关性[J].北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(6): 35-41. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160087 Zhao W X, Zou B, Zheng J M, et al. Correlations between leaf, stem and root functional traits of common tree species in an evergreen broad-leaved forest[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2016, 38(6): 35-41. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160087
[43] 杨士梭, 温仲明, 苗连朋, 等.黄土丘陵区植物功能性状对微地形变化的响应[J].应用生态学报, 2014, 25(12): 3413-3419. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201412005 Yang S S, Wen Z M, Miao L P, et al. Responses of plant functional traits to micro-topographical changes in hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(12): 3413-3419. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yystxb201412005
[44] Marteinsdóttir B, Eriksson O. Plant community assembly in seminatural grasslands and eaarable fields: a trait-based approach[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2013, 25(1): 77-87. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8fe18906bc882def9011dfce9c0fe6b5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 姬新颖,唐佳莉,李敖,郑旭,王红霞,张俊佩. 盐胁迫下不同基因型核桃实生幼苗生长及生理响应. 林业科学. 2024(02): 65-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙叶烁,田海英,姚玉涛,丁守鹏,张国新,韩民利. 咸水胁迫对草莓生长·品质的影响及耐盐综合评价. 安徽农业科学. 2023(02): 47-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 纪发达. 一种抗逆型复合调节剂的制备及其应用. 化肥设计. 2023(02): 8-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高铖铖,燕丽萍,吴德军,王因花. 基于SSR标记的白蜡群体遗传多样性和群体结构分析. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(06): 69-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王介华,睢金凯,崔令军,石开明. AMF对盐胁迫下桢楠生长和生理特性的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(06): 51-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 程俊森,王溢,李永泉,魏尚霖,李超楠,姜维,黄润生. 基于Label-free技术的高州油茶铝胁迫蛋白质组学研究. 中南林业科技大学学报. 2023(08): 169-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘京,马洁怡,张金池,马仕林,王宇浩,聂晖,曹鹏翔. 不同土壤改良措施对苏北盐碱地薄壳山核桃生长的影响. 东北林业大学学报. 2022(07): 11-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘翠兰,王开芳,吴德军,燕丽萍,李善文,王芳,任飞,王因花. 滨海盐碱胁迫下白蜡无性系生长及生理特性的响应. 中国农学通报. 2022(35): 7-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李寿冰,赵钰琪,曹帮华,袁洪振,耿颖,陈炳卓,张家昌. 盐碱胁迫对2种地被竹叶绿素含量的影响. 世界竹藤通讯. 2022(S1): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 崔令军,刘瑜霞,林健,石开明. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下桢楠光合生理的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(01): 101-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 巩志勇,辛建华,商小雨,郭晓明,王延平. 盐碱胁迫下香椿幼苗光合及抗逆生理特性. 西北植物学报. 2021(07): 1199-1209 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 范馨月,张华,赵继业,杜子沫,丛日晨. 绒毛白蜡耐盐碱响应机制的研究进展. 中国农学通报. 2021(28): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 缪李飞,于晓晶,张秋悦,封超年. 4个杜梨半同胞家系苗期耐盐性分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(05): 157-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 赵宝泉,邢锦城,温祝桂,徐海东,王进左,李玉明,董静,洪立洲. 林木盐胁迫响应机制研究进展. 现代农业科技. 2020(21): 159-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)




 下载:
下载: