Grain size characteristics of core sedimentation from the Gaoqiao mangrove area in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province of southern China
-
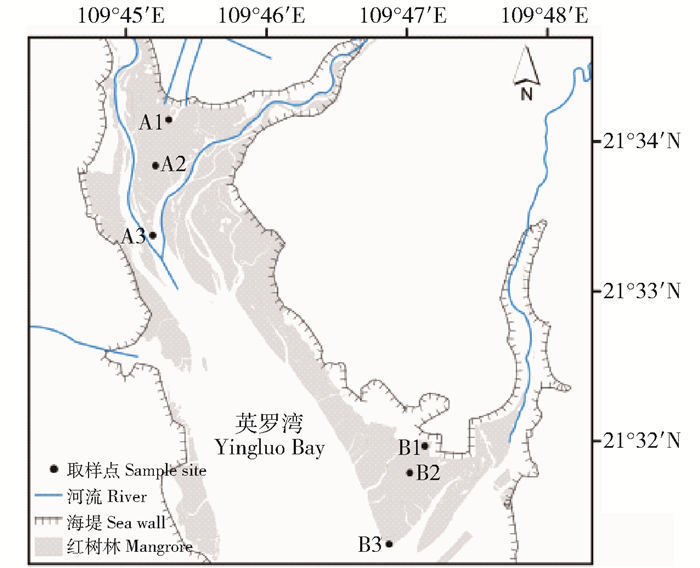
摘要: 红树林是一种特殊的生物海岸类型,具有多种生态系统服务功能。以广东湛江高桥红树林湿地为研究区,在英罗湾的湾内和湾口的两片红树林集中分布区,沿水动力梯度,垂直于海岸布设两条样线进行柱状取样,并采用矩值法计算平均粒径、分选系数、偏度和峰度等粒度参数,分析了沉积物在水平和垂直方向上的粒度特征,旨在了解研究区红树林湿地生境演变过程。结果表明:1)沉积物以粉粒和砂粒组分为主,随着红树林发育成熟度和沉积过程,红树林内带和表层样点均呈细化趋势。2)粒度分布曲线可以看出,红树林外带更多受水动力条件的影响,样点沉积过程相似,内带的沉积因水动力条件和生物过程的影响而复杂,但白骨壤纯林的沉积环境相对稳定。3)粒度参数受水动力条件和生物地貌过程影响,空间异质性显著。水平方向上,湾内样线自内带向外表现为平均粒径变小(质地粗化)趋势,湾外样线平均粒径变化趋势性不明显,但有红海榄群落分布的中间带样点的粒度更细;沉积物分选性属于较差到差,频率曲线呈负偏到很正偏,峰度呈平坦到尖锐的分布。垂直方向上,自表层向下平均粒径减小、分选性变差、偏态值增加、峰态增加,反映出林下环境的沉积过程。4)相关性分析表明,粒度参数与不同粒级体积含量相关,平均粒径和峰度参数与黏粒、粉粒含量正相关而与砂粒含量负相关,分选系数和偏度与细颗粒物含量显著负相关。粒度参数之间的相关性表现为平均粒径与峰度正相关,而与分选系数和偏度负相关,分选系数与峰度负相关,偏度与峰度负相关。研究区沉积物的形成过程有多种作用共同参与,红树林的存在改变了海岸的水动力条件而影响沉积过程,研究结果对于了解百年尺度上红树林湿地的生物地貌形成过程具有一定意义。Abstract: Mangrove coast is a special type of biological coast and it provides a variety of ecosystem services. To understand the evolution of the habitat of mangrove wetland, sediment cores along a hydrodynamic gradient in the inner and outer gulf of Yingluo Bay, the grain size characteristics (average grain size, sorting coefficient, skewness and kurtosis) of the sediments in the horizontal and vertical directions were analyzed using the moment method. The results showed that the sediments were mainly composed of silt and sand components, the surface samples of mangrove zone showed a trend of refinement with the maturation and deposition process of mangrove forests. The grain size distribution curve showed that the outer mangrove was more affected by hydrodynamic conditions than inner mangrove. The deposition processes of inner zone and outer zone were similar. The inner deposition was complicated by the influence of hydrodynamic conditions and biological processes. However, the sedimentary environment of the pure stand of Avicennia marina was relatively stable.Grain size parameters were affected by the hydrodynamic conditions and biogeography processes, and spatial heterogeneity was significant. In horizontal direction, the average particle size of the inner sample line of the bay turned to be small (texture coarsening) from inside to outside. The average particle size of the outer samples showed no obvious trends but become finer in intermediate zone distributed with Rhizophora stylosa trees. The sediment segregation was poor to worse, the frequency curve was negative biased to positive bias, and the peak presented from flat to sharp distribution. In vertical direction, the average particle size decreased from the surface to deeper layer, the separation became worse, the skewness increased, and the peak state increased too, reflecting the deposition process of the forest understory environment.The correlation analysis showed that the grain size parameters of the sediments were related to different volume levels, the average grain size and kurtosis parameters were positively correlated with the content of clay and grains, and negatively correlated with the sand content, the separation coefficient and skewness were negatively correlated with the fine particulate matter content. The average grain size was positively correlated with the kurtosis, but negatively correlated with the sorting coefficient and the skewness. The separation coefficient was negatively correlated with the kurtosis, and the skewness was negatively correlated with the kurtosis. A variety of roles were involved in the formation of sediment, and mangrove forests changed the hydrodynamic conditions of the coast, which affected the deposition process in turn. The results are significant to understand the biomechanical processes of mangrove wetlands on a century scale.
-
Keywords:
- mangrove /
- wetland /
- sediment /
- grain size
-
-
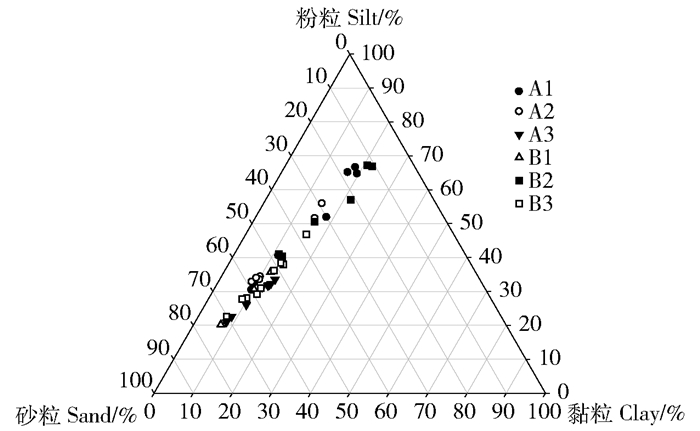
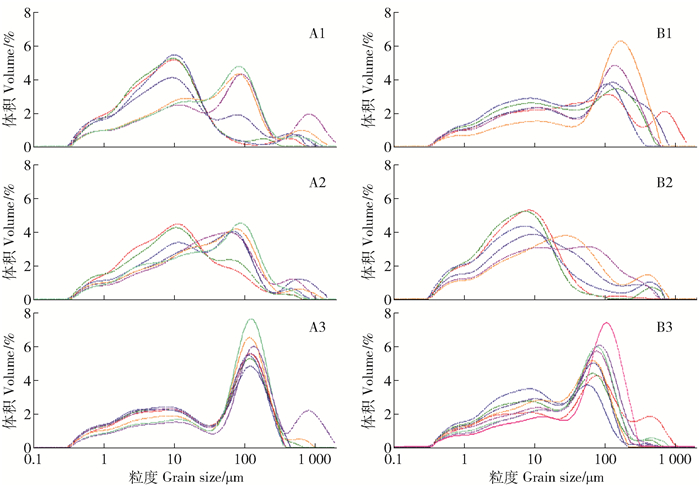
图 3 沉积柱粒径组成累积面积图
CS为粗砂,MS为中砂,FS为细砂,VFS为极细砂,VCS为极粗粉,CSI为粗粉,MSI为中粉,FSI为细粉,C为黏粒。下同。
Figure 3. Cumulative area ratio of grain size composition in core sediments
CS refers to coarse sand, MS refers to medium sand, FS refers to fine sand, VFS refers to very fine sand, VCS refers to very coarse silt, CSI refers to coarse silt, MSI refers to medium silt, FSI refers to fine silt, C refers to clay. The same as below.
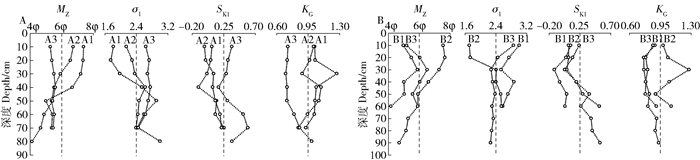
表 1 样柱粒度参数均值(标准差)
Table 1 Average(SE) of grain size parameters in the core sediments
样点
Sample
point粒度频率曲线形态
Curve form of grain size distribution平均粒径
Average grain size
(MZ)分选系数
Sorting
coefficient(σ1)偏度
Skewness
(SK1)峰度
Kurtosis
(KG)A1 单峰、双峰Single peak, double peak
多峰Multiple peak6.34φ(1.05φ)ab 2.29(0.44) b 0.08(0.11)cd 1.05(0.10) a A2 单峰、双峰Single peak, double peak
多峰Multiple peak5.86φ(0.56φ)b 2.39(0.15) b 0.10(0.09)cd 0.97(0.09) a A3 双峰Double peak 5.11φ(0.51φ) c 2.70(0.15) a 0.37(0.14)a 0.78(0.10) b B1 双峰Double peak 5.10φ(0.58φ) bc 2.74(0.18) a 0.21(0.18)bc 0.81(0.07) b B2 双峰、多峰Double peak, multiple peak 6.83φ(0.79φ) a 2.22(0.39) b 0.01(0.08)d 1.05(0.13) a B3 双峰Double peak 5.60φ(0.57φ) bc 2.38(0.19) b 0.29(0.16)ab 0.85(0.06) b 注:不同字母间表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。φ为尤登-温德华氏等比例粒级。下同。Notes: different letters indicate significant difference from each other at P < 0.05 level. φ is Udden-Wentworth (U-W) equal proportional size fraction. The same as below. 表 2 沉积物各粒径含量与粒度参数相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between grain size parameters and the volume content of different grain size sediment
项目
ItemFSI MSI CSI VCS VFS FS MS CS MZ σ1 SK1 KG C 0.965** 0.869** 0.310* -0.542** -0.846** -0.652** -0.389* -0.336* 0.948** -0.655** -0.665** 0.353* FSI 0.961** 0.466** -0.506** -0.910** -0.732** -0.393** -0.292 0.971** -0.742** -0.711** 0.489** MSI 0.648** -0.368* -0.902** -0.812** -0.433** -0.251 0.951** -0.770** -0.744** 0.598** CSI 0.353* -0.555** -0.824** -0.359* -0.108 0.569** -0.452** -0.702** 0.530** VCS 0.505** -0.17 -0.22 0.004 -0.320* 0.184 0.117 -0.18 VFS 0.700** 0.088 0.058 -0.850** 0.528** 0.822** -0.597** FS 0.539** 0.095 -0.822** 0.601** 0.786** -0.554** MS 0.256 -0.518** 0.555** 0.215 -0.09 CS -0.386* 0.514** -0.02 0.29 MZ -0.768** -0.736** 0.460** σ1 0.238 -0.388* SK1 -0.491** 注:**表示在0.01水平上显著相关, *表示在0.05水平上显著相关。Notes:** means correlation is significant at P < 0.01 level, * means correlation is significant at P < 0.05 level. -
[1] COSTANZA R R, D'ARGE R, GROOT R D, et al. The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital 1[J]. Nature, 1997, 387:253-260. doi: 10.1038/387253a0
[2] CHMURA G L, ANISFELD S C, CAHOON D R, et al. Global carbon sequestration in tidal, saline wetland soil[J/OL]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2003, 17(4): 1111[2017-05-11].https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228736624. doi: 10.1029/2002GB001917
[3] DUKE N C, MEYNECKE J O, DITTMANN S, et al. A world without mangrove[J]. Nature, 2007, 317: 41-42. doi: 10.1126-science.317.5834.41b/
[4] 但新球, 廖宝文, 吴照柏, 等.中国红树林湿地资源、保护现状和主要威胁[J].生态环境学报, 2016, 25(7): 1237-1243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201607021 DAN X Q, LIAO B W, WU Z B, et al. Resources, conservation status and main threats of mangrove wetlands in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(7): 1237-1243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201607021
[5] 王文卿, 王瑁.中国红树林[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007: 67. WANG W Q, WANG M. The mangroves of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007:67.
[6] 张乔民, 施祺, 余克服, 等.华南热带海岸生物地貌过程[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3): 449-455. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.018 ZHANG Q M, SHI Q, YU K F, et al. Biogeomorphologic process of tropical biological coasts of south China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(3): 449-455. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.03.018
[7] 周蒂.利用沉积物粒度数据反演沉积水动力参数[J].地质科学, 1999, 34(1): 49-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1999.01.006 ZHOU D. The estimation of sedimentary hydrodynamic parameters from sediment grain-size data[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1999, 34(1):49-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1999.01.006
[8] 金秉福, 林振宏, 季福武.海洋沉积环境和物源的元素地球化学记录释读[J].海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1): 99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.013 JIN B F, LIN Z H, JI F W. Interpretation of element geochemical records of marine sedimentary environment and provenance[J]. Advance in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1) : 99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.013
[9] 陈木宏, 郑范, 陆均, 等.南海西南陆坡区沉积物粒级指标的物源特征及古环境意义[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(7): 684-690. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.07.012 CHEN M H, ZHENG F, LU J, et al. The source characteristics and pale environmental significance of sediment gradient index in southwestern South China Sea slope region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50 (7) : 684-690. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.07.012
[10] LIM D I, JUNG H S, CHOI J Y, et al. Geochemical compositions of river and shelf sediments in the Yellow Sea: Grain-size normalization and sediment provenance[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2006, 26(1):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.10.001
[11] 王恒波, 许江.北仑河口柱状沉积物粒度特征[J].台湾海峡, 2010, 29(4): 555-565. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twhx201004017 WANG H B, XU J. Characteristics of grain size of core sediment in Beilun Estuary[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2010, 29(4):555-565. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twhx201004017
[12] ANTHONY E J, HÉQUETTE A. The grain size characterization of coastal sand from the Somme Estuary to Belgium: sediment sorting processes and mixing in a tidal and storm dominated setting[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 202(3): 369-382 doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.03.022
[13] 杨世伦.长江口沉积物粒度参数的统计规律及其沉积动力学解释[J].泥沙研究, 1994(3): 23-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400357227 YANG S L. Statistic features for grain size parameters of the Yangtze River Estuary and their hydrodynamic explanation[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1994(3): 23-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400357227
[14] 王敏京, 徐军, 冉娟, 等.海南岛西南部砂质岸滩沉积特征[J].海洋通报, 2011, 30(1): 60-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hytb201101010 WANG M J, XU J, RAN J, et al. Sediment characteristics of southwest beach of Hainan Island[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(1): 60-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hytb201101010
[15] FLEMMING B W, ZIEGLER K. High-resolution grain size distribution patterns and textural trends in the backbarrier tidal flats of Spiekeroog Island (southern North Sea)[J]. Senckenbergiana Maritima, 1995, 26(1):1-24.
[16] ROUX J P L, ROJAS E M. Sediment transport patterns determined from grain size parameters: overview and state of the art[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 202(3):473-488. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.03.014
[17] 廖宝文, 郑松发, 陈玉军, 等.红树林湿地恢复技术的研究进展[J].生态科学, 2005, 24(1): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2005.01.018 LIAO B W, ZHENG S F, CHEN Y J, et al. Advance in researches on rehabilitation technique of mangrove wetlands[J]. Ecologic Science, 2005, 24(1): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2005.01.018
[18] 彭逸生, 周炎武, 陈桂珠.红树林湿地恢复研究进展[J].生态学报, 2008, 28(2): 786-797. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.02.041 PENG Y S, ZHOU Y W, CHEN G Z.The restoration of mangrove wetland: a review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 786-797. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.02.041
[19] 隋淑珍, 张乔民.华南沿海红树林海岸沉积物特征分析[J].热带海洋学报, 1999, 18(4): 17-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY199904002.htm SUI S Z, ZHANG Q M. Characteristics of sediments along mangrove coast of South China[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1999, 18(4): 17-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY199904002.htm
[20] 刘金铃, 李柳强, 林慧娜, 等.中国主要红树林区沉积物粒度分布特征[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 47(6): 891-893. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2008.06.026 LIU J L, LI L Q, LIN H N, et al. Characters of gain size of sediments from mangrove wetlands of China[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2008, 47(6): 891-893. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2008.06.026
[21] 邢永泽, 周浩郎, 阎冰, 等.广西沿海不同演替阶段红树群落沉积物粒度分布特征[J].海洋科学, 2014, 38(9): 53-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX201409009.htm XING Y Z, ZHOU H L, YAN B, et al. Characteristics of sediment grain size distribution of mangrove communities at different successional stages along the coast of Guangxi[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(9): 53-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX201409009.htm
[22] 朱耀军, 郭菊兰, 武高洁, 等.湛江高桥红树林沉积物理化性质与金属元素的空间分布[J].北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(2):1-9. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9975 ZHU Y J, GUO J L, WU G J, et al. Spatial distribution of physicochemical properties and metal concentration in mangrove sediments from Gaoqiao in Zhanjiang, Guangdong of southern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(2):1-9. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9975
[23] 梁士楚.广西英罗湾红树植物群落的研究[J].植物生态学报, 1996, 20(4): 310-321. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWSB604.002.htm LIANG S C. Studies on the mangrove communities in Yingluo Bay of Guangxi[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 1996, 20(4): 310-321. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWSB604.002.htm
[24] 刘美龄, 叶勇, 曹长青, 等.海南东寨港红树林土壤粒径分布的分形特征及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志, 2008, 27(9): 1557-1561. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz200809018 LIU M L, YE Y, CAO C Q, et al. Fractal characteristics and related affecting factors of particle size distribution in mangrove soil in Dongzhai Harbor of Hainan[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2008, 27 (9): 1557-1561. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxzz200809018
[25] 梁文, 李智, 范航清, 等.防城港湾红树林表层沉积物粒度分形特征及与环境因子的相关性[J].应用海洋学学报, 2013, 32(2): 184-192. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.006 LIANG W, LI Z, FAN H Q, et al. Fractal characteristics and correlation with environmental factor on the surface sediments in mangrove areas of Fangchenggang Bay[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2013, 32(2): 184-192. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.006
[26] 黄财宾, 陈建宁, 王爱军.福建洛阳江河口湿地沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境意义[J].台湾海峡, 2009, 28(3): 410-416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2009.03.017 HUANG C B, CHEN J N, WANG A J. Grain size characteristics and the significance of sedimentary environments of the sediments on Luoyangjiang Estuary wetlands, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2009, 28(3): 410-416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2009.03.017
[27] 许艳, 王拓夫.湛江红树林保护区现代沉积物粒度特征及其对风暴事件的响应[J].台湾海峡, 2011, 30(2): 269-274. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-8160.2011.02.018 XU Y, WANG T F. Characteristics of sediment particle size and their response to storm surge in the Zhanjiang Mangrove Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2011, 30(2): 269-274. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-8160.2011.02.018
[28] TU Q, YANG S, ZHOU Q, et al. Sediment transport and carbon sequestration characteristics along mangrove fringed coasts[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(2):21-26. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0614-y
[29] 朱耀军, 郭菊兰, 武高洁, 等.近20年来英罗湾红树林景观过程及周边土地利用/覆盖变化[J].北京林业大学学报, 2013, 35(2): 22-29. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9871 ZHU Y J, GUO J L, WU G J, et al. Mangrove landscape changing process and land use coverage change of its surrounding areas in Yingluo Bay, southern China during the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2013, 35(2): 22-29. http://j.bjfu.edu.cn/article/id/9871
[30] FOLK R L, WARD W C. Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1):3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[31] 李志亮, 杜小如.沉积物粒度参数求解方法的对比[J].长江科学院院报, 2008, 25(4): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2008.04.005 LI Z L, DU X R. Comparison of methods solving sediment particle size paramters[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2008, 25(4): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2008.04.005
[32] SWANSON F J. Landform effects on ecosystem patterns and processes[J]. BioScience, 1988, 38(2):92-98. doi: 10.2307/1310614
[33] URBAN M A. Conceptualizing anthropogenic change in fluvial systems: drainage development on the upper Embarras River, Illinois[J]. Professional Geographer, 2000, 54(2): 204-217. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b3a3d7f170571955790fd0dbe4c771d1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[34] FUMKAWA Y, WO1ANSKI E, MUEUER H.Currents and sediment transport in mangrove forests[J].Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1997, 44(3): 301-310. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1996.0120
[35] ALONGI D M. The energetics of mangrove forests[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 60-61.
[36] 张乔民, 张叶春.华南红树林海岸生物地貌过程研究[J].第四纪研究, 1997, 17(4): 344-353. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.04.008 ZHANG Q M, ZHANG Y C. Study on biogeomorphologic process of mangrove coasts in south China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1997, 17(4): 344-353. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.04.008
[37] 范航清, 尹毅, 黄向东, 等.广西沙生红树植物-土壤互作用及群落演替的研究[J].广西科学院学报, 1993, 9(2): 2-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXKX199302000.htm FAN H Q, YIN Y, HUANG X D, et al. Interaction of sandy mangrove plant soil and sucession of community in Guangxi[J]. Journal of the Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 1993, 9(2): 2-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXKX199302000.htm
[38] YANG J, GAO J, CHEUNG A, et al. Vegetation and sediment characteristics in expanding mangrove forest in New Zealand[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2013, 134(12):11-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=46527bf3ecefbd5e3e4b14c48ec56282
[39] 朱耀军, 赵峰, 郭菊兰, 等.湛江高桥红树林湿地有机碳分布及埋藏特征[J].生态学报, 2016, 36(23):7841-7849. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201623032 ZHU Y J, ZHAO F, GUO J L, et al.Below ground organic carbon distribution and burial characteristics of the Gaoqiao mangrove area in Zhanjiang, Guangdong, Southern china[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(23):7841-7849. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201623032
[40] 陈沈良, 杨世伦, 吴瑞明.杭州湾北岸潮滩沉积物粒度的时间变化及其沉积动力学意义[J].海洋科学进展, 2004, 22(3): 299-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.03.006 CHEN S L, YANG S L, WU R M. Temporal changes in tidal flat sediment grain size along the north bank of the Hangzhou Bay and their implication of sedimentation dynamics[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2004, 22(3): 299-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.03.006
[41] 陈波.北部湾台风暴潮研究现状与展望[J].广西科学, 2014, 21(4): 325-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.002 CHEN B. Research status and prospect of storm surge in Beibu Gulf[J].Guangxi Science, 2014, 21(4): 325-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.002
[42] 彭晓彤, 周怀阳, 叶瑛, 等.珠江河口沉积物粒度特征及其对底层水动力环境的指示[J].沉积学报, 2004, 22(3): 487-493. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.016 PENG X T, ZHOU H Y, YE Y, et al. Characteristics of sediment grain size and their implications for bottom hydrodynamic environment in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(3): 487-493. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.03.016
[43] PÜ N, MEHLIG U, NORDHAUS I, et al. Mangrove crab Ucides cordatus removal does not affect sediment parameters and stipule production in a one year experiment in Northern Brazil[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(12): e0167375[2017-02-11].doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167375.
[44] KUMAR G, RAMANATHAN A L. Assessment of marine environment by study of textural characteristics of the surface sediments of a tropical mangrove ecosystem Gulf of Kachchh, Gujarat, India: a GIS approach[J]. Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences, 2016, 45(11):1593-1597.



 下载:
下载: